#AC-DC Switching Converter
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--Led-lighting-components--led-driver-modules-rev--constant-current-acdc-led-drivers/ess030w-0500-42-erp-power-3120461
LED driver converts, DC-to-DC converter, power supply switching, high power led
100 - 277Vac, 21W, 500mA, 24-42V, [0-10V, TRI...], IP64 LED Driver
#Constant Current AC/DC LED Drivers#ESS030W-0500-42#ERP Power#converts#DC-to-DC converter#power supply switching#high power led#engine#replacement#circuit#Modules#LED Lighting Components#switch mode power supplies
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--Led-lighting-components--led-driver-modules-rev--constant-current-acdc-led-drivers/xi040c110v050vwt1-signify-north-america-8116785
Constant current led driver circuit, DC to DC Power Supplies, high power led
100 - 277Vac, 40W, 100 - 1100mA, 16-50V, [DALI 2], IP20 LED Driver
#Signify North America#XI040C110V050VWT1#Constant Current AC/DC LED Drivers#circuit#DC to DC Power Supplies#high power led#Module#led light engine#DC-to-DC converter#switching#LED Lighting Components#switch mode power supplies
1 note
·
View note
Text
Terms and definitions that you can maybe apply to your fan works
I don't know anything about computer or mechanical engineering (it's very funny to me that I am in the Transformers fandom and I don't even care about cars), but I do care about improving my writing. I have gathered a list of terms that sound very sciencey and applicable to mechs, some from Martha Wells's "Murderbot Diaries," some from fanfiction/fandom (shout-out to the Crime in Crystals series by Aard_Rinn and Baebeyza, they wrote Transformers better than any Transformers comic/TV show did), and a lot from just surfing through Google and going, "well, what the hell is this? Okay, but what the hell is THAT?".
Also, as I was writing this post, I ended up getting sucked into this article:
And this really bloated my already long list of terms. Very easy to read if you want to glance it over yourself.
It's not an exhaustive list and who knows if it will be useful to you - but maybe you can reblog with your own add-ons of terms and definitions you think make a Transformers fan work just that much better.
The list is below the cut:
100% CPU Load - CPU is fully occupied with too many processors/applications/drivers/operations - not necessarily synonymous with an overload.
Actuators* - A device that causes a machine or other device to operate (Ex: a computerized unit instructs the actuator how to move the tires on a vehicle); create linear and rotary movement (Ex: A hydraulic actuator on a valve will move that valve in response to a sensor/signal); Linear actuators "move a piston back and forth inside a cylinder to build pressure and 'actuate', or complete an action".
* Think of actuators as devices that help produce linear motion and motors as devices that help produce rotational movement. Hence, some consider actuators as a type of motor. But a motor is not a type of actuator (jhfoster.com).
Alternator - Converts mechanical energy to electrical energy with an alternating current. The stator and rotor inside the alternator work as magnets and rotate to generate the alternating current. Then the alternating current (AC) is transformed into a direct current (DC) that charges the battery.
Archive (Archive files) - used to collect multiple data files together into a single file for easier portability and storage, or simply to compress files to use less storage space.
Arithmetic Log Unit (ALU) - the part of a central processing unit that carries out arithmetic and logic operations on the operands in computer instruction words. In some processors, the ALU is divided into two units: an arithmetic unit (AU) and a logic unit (LU).
Augment - Make something greater; increase.
Auxiliary Battery - Designed to run as a backup to the starting battery and provide power to some essential equipment like engine start/stop and other systems that require power while the engine is off to put less strain on the main battery and alternator.
Bandwidth - A measurement indicating the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to transmit data over a network connection in a given amount of time.
Behavioral Coding - A term used in Martha Wells' Murderbot Diaries; essential, code for behaviors.
Branch Instructions - Use programming elements like if-statements, for-loops, and return-statements; used to interrupt the program execution and switch to a different part of the code.
Branch Predictors - Track the status of previous branches to learn whether or not an upcoming branch is likely to be taken or not.
Buffer - A region of memory used to store data temporarily while it is being moved from one place to another.
Cathodes vs Anodes - Cathodes are the positive electrode while the anode is the negative electrode; electrons flow from the anode to the cathode and this creates the flow of electric charge in a battery or electrochemical cell.
Catastrophic Failure - Complete, sudden and unexpected breakdown in a machine, indicating improper maintenance.
Central Processing Unit (CPU) - Primary component of a computer that acts as its "control center"; complex set of circuitry that runs the machine's operating systems and apps; the brains of the computer. * Components: Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), Control Unit (CU), Datapath, Instruction Cycle, Registers, Combinational Logic, the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), etc...
Clock - Determines how many instructions a CPU can process per second; increasing its frequency through overclocking will make instructions run faster, but will increase power consumption and heat output.
Combustion Chambers - An enclosed space in which combustion takes place, such as an engine; jet engines also have combustion chambers.
Condition Codes - Extra bits kept by a processor that summarize the results of an operation and that affect the execution of later instructions.
Control Bus - Manages the communication between the computer's CPU and its other components.
Control Unit (CU) - Manages the execution of instructions and coordinates data flow within the CPU and between other computer components.
Cybermetal - Element native to Cybertron and Cybertron alone.
Datapath - The path where data flows as it is processed; receives input, processes it, and sends it out to the right place when done processing; datapaths are told how to operate by the CU; depending on instructions, a datapath can route signals to different components, turn on and off different parts of itself, and monitor the state of the CPU.
Diagnostic and Data Repair Sequence - Term used in Martha Wells' Murderbot Diaries; exactly what it sounds like.
Diode - A semiconductor device with two terminals (a cathode and an anode), typically allowing the flow of current in one direction only.
Discrete Circuit vs Integrated Circuit- Single device with a single function (ex: Transistor, diode) vs Devices with multiple functional elements on one chip (ex: Memories, microprocessor IC and Logic IC).
Drivers - A set of files that help software (digital components, such as Microsoft Office) interface/work with hardware (physical components, such as a keyboard); allows an operating system and a device to communicate.
Electromagnetic (EM) Field - A combination of invisible electric and magnetic fields of force; used in fandom by mechs to broadcast emotions to others.
Flags - A value that acts as a signal for a function or process. The value of the flag is used to determine the next step of a program; flags are often binary flags which contain a boolean value (true or false).
Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) - Consists of an electronic control unit (ECU) and related accessors that control aircraft engine performances.
Gestation Tank - Used in mech pregnancies, you can pry it from my cold, dead hands.
Heads Up Display (HUD) - A part of the user interface that visually conveys information to the player during gameplay.
Heat Spreader - Often used in computer processors to prevent them from overheating during operation; transfers energy as heat from a hotter source to a colder heat sink or heat exchanger.
HUB - A device that connects multiple computers and devices to a local area network (LAN).
Inductive Charging - How I imagine berths work; wireless power transfer (ex: Wireless charger or charging pad used for phones).
Instruction Cycle - Also known as fetch-decode-execute cycle; basic operation performed by a CPU to execute an instruction; consists of several steps, each of which performs a specific function in the execution of the instruction.
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) - The figurative blueprint for how the CPU operates and how all the internal systems interact with each other (I think of it like a blueprint for the brain).
Irising - Term used in fanfiction (specifically the Crime in Crystals series) to describe the action of the of the spark chamber opening ("The Talk", chapter 6, my absolute favorite chapter out of the entire series). I just really liked how the word sounded in that context.
Life Codes - "For those of us who were forged, Primus, through Vector Sigma, generated a pulse wave. Each one a data-saturated life code faster than thought, brighter than light, racing across Cybertron, sowing sparks..." (~Tyrest/Solomus, Volume 5 of More Than Meets the Eye)
Memory Hierarchy - Represents the relationship between caches, RAM, and main storage; when a CPU receives a memory instruction for a piece of data that it doesn't yet have locally in its registers, it will go down the memory hierarchy until it finds it.
Levels: L1 cache (usually smallest and fastest), L2 cache, L3 cache, RAM, and then main storage (usually biggest and slowest); available space and latency (delay) increase from one level to the next
Depending on the multi-core (a core is usually synonymous with a CPU) system, each core will have its own private L1 cache, share an L2 with one other core, and share an L3 with more or more cores.
Motors* - Any power unit that generates motion; electric motors work by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy... when this happens within a magnetic field, a force is generated which causes shaft rotation.
Multitasking Operating System - Allows users to run multiple programs and tasks almost simultaneously without losing data; manage system resources (such as computer memory and input/output devices), allocate resources, enable multiple users, and eliminate long wait times for program execution.
Network - A set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other.
Network Feed - The continuously updating stream of content that users encounter on networking platforms.
Neural Network - A type of machine learning process that uses interconnected nodes (like neurons) to teach computers to process data in a way similar to the human brain; a form of deep learning that can help computers learn from their mistakes and improve their time.
Nimbus - A luminous cloud or a halo surrounding a supernatural being or a saint; has been used in fanfiction synonymously or in junction with the corona of the spark.
Nodes - A connection point between devices that allows data to be sent and received between them.
Oil Sump/Oil Pan - Don't forget to change your mech's oil.
Out-Of-Order Execution - A paradigm used to minimize downtime while waiting for other instructions to finish; allows a CPU to choose the most timely instructions to execute out of an instruction queue.
Overload - Orgasm; an electrical overload occurs when too much electricity passes through a circuit, exceeding its capacity; an information overload is when a system receives more input than it can process, or a state of being overwhelmed by the amount of data presented for processing.
Pedes - Feet
Pipelining - A technique used in computer architecture that allows a processor to execute multiple instructions simultaneously, improving overall performance.
Processing Capacity - The ability and speed of a processor, and how many operations it can carry out in a given amount of time.
Program Counter - A special register in a computer processor that contains the memory address (location) of the next program instruction to be executed.
Programmable Nanobots/Nanites - Cybertronian microbots programmed to do work at the molecular level; used popularly for surface healing and pigment in mechs.
Protected Storage - Provides applications with an interface to store user data that must be kept secure or free from modification; a storage method; a function in mainframe hardware.
Protoform - Formed of an ultra-dense liquid metal and are extremely hard to damage; the most basic Cybertronian form of raw, free-flowing living metal; first stage of Cybertronian life cycle
To create a Cybertronian, you need the protoform, the life-giving spark, and alt-form information.
Register - A type of computer memory built directly into the processor or CPU that is used to store and manipulate data during the execution of instructions.
Ex: "When you run a .exe on Windows... the code for that program is moved into memory and the CPU is told what address the first instruction starts at. The CPU always maintains an internal register that holds the memory location of the next instruction to be executed [the Program Counter]"...
Resource Allocations - The process of identifying and assigning available resources to a task or project to support objectives.
Risk Assessment - Focus on identifying the threats facing your information systems, networks, and data and assessing the potential consequences should these adverse events occur.
Routine - A component of a software application that performs a specific task (ex: Saving a file).
Servomechanism - A powered mechanism producing motion or force at a higher level of energy than the input level (ex: In the brakes and steering of large motor vehicles) especially where feedback is employed to make the control automatic.
Servos - Hands
Shellcode - A small piece of executable code used as a payload, built to exploit vulnerabilities in a system or carry out malicious commands. The name comes from the fact that the shellcode usually starts a command shell which allows the attacker to control the compromised machine.
Semiconductor - A material used in electrical circuits and components that partially conduct electricity.
Semiconductor materials include silicon, germanium, and selenium.
Struts - Bones; A rod or bar forming part of a framework and designed to resist compression.
System/System Unit (in computers) - A setup that consists of both hardware and software components organized to perform complex operations/The core of your computer where all the processing happens.
Task Specific Accelerator - Circuits designed to perform one small task as fast as possible (ex: Encription, media encoding & machine learning).
Teek - Used in Transformers fandom in conjunction with EM Fields; when a mech "teeks" another mech's field, they are feeling the emotions that mech is broadcasting.
Transistor - Enables a computer to follow instructions to calculate, compare and copy data.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) - A standard plug-and-play interface that allows computers and peripheral devices to connect with each other, transfer data, and share a power source; allows data exchange and delivery of power between many types of electronics; plug-and-play interface is also a type of sexual activity used in fandom.
Warren - Used to refer to a group of minibots with their own social hierarchy and culture (Seriously, read the Crime in Crystals series, it's better than canon).
#transformers#macaddam#world building#Terms and Definitions#Transformers Terms#Computer Terms#Please Add Your Own Terms and Definitions as you see fit
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of the downsides with old AT standard power supplies is that, in lacking a "soft", mainboard-controlled power switch, they tend to need a rather beefy DPST (Double Pole, Single Throw) mechanical power switch through which all current going into the PC needs to pass through. You basically need something that can take a good 10 Amps at 250 Volts AC at minimum if you don't want to risk that thing potentially melting and possibly even burning your house down.
this is basically me complaining I can't just use one of these cute round little light up single pole switches that I kind of want to use and instead will need something bigger and chomkier for an on/off button.
technically I could just use a smaller switch coupled with a smaller AC to DC power converter and a sufficiently chomky relay, but that feels kind of overkill.
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
You underestimate my desire for knowledge. Do it. Talk about refrigeration compressor motors.
Hello hi, sorry for the delay. I had to wait for the brain power to return to me.
So, an electric motor's job is to convert electrostatic potential energy into magnetic potential energy in order to rotate a shaft, thus making one final energy conversion from magnetic PE to kinetic energy. There is a secret fourth energy conversion, though, and that is another form of kinetic energy: heat. The heat is waste, though.
Anyways, the power available in your home is not the power generated at the source powerplant; it is just a single phase of alternating current (AC), instead of three. Electric motors running on single-phase encounter an interesting problem: they need a special winding, called a start winding, to get the motor going. It is phase shifted from the run winding (which keeps the motor running after startup). The easiest way to explain phase shift, in this context, is to think of it like the pedals on a bicycle: if the pedals weren't opposite each other (offset from each other 180 degrees), it would be very difficult to pedal. Unlike a bicycle, the phase shift in the motor isn't 180 degrees. It's less than that. About 45 degrees.
Both the start and run windings are coils of wire. The more times the wire is wound, the stronger the magnetic field it generates. The start coil has more windings than the run coil.
To help smooth power delivery and introduce the aforementioned phase shift, we need capacitors. Capacitors are just small batteries. They can hold a charge and be discharged. They also block direct current (DC), but allow AC to pass through it. It's really neat. On startup, a single-phase motor using capacitors only needs the start coil and the start capacitor briefly. If they remain in the circuit afterwards, they risk overheating and destroying themselves. So how do we automatically take the start coil and capacitor out of the circuit after startup?
One way is to use a centrifugal mechanical switch that will disconnect the start components from the circuit once the motor reaches 75% of its maximum RPM. This switch must be in the motor, though, and will create a spark when it breaks contact. This is okay for motors that are in the air, but what about the motors in a hermetically sealed refrigerant compressor? That spark would degrade the refrigerant, and that's a non-starter.
We need an RPM sensitive switch outside the compressor motor, and one way to do this is with a potential relay.

This is a diagram of a potential relay circuit with a capacitor-start, capacitor-run compressor motor.
On startup, the relay contacts, 2 and 1, are closed. Power can flow through the start winding and through both the run and start capacitors. This gives the motor a good grunt to get it going, with the start winding slightly out of phase with the run winding. Once the motor reaches 75% of its max. RPM, though, the magnets on the rotor/shaft of the motor induce a back electromotive force, or BEMF, in the start winding. The start winding becomes a voltage source in tandem with the incoming power from the outlet.
The induced AC voltage is stronger than the incoming power, and is also out of phase with it. This is demonstrated in the diagram with voltmeters 1 and 2. The induced voltage flows through the coil of the potential relay at terminals 2 and 5, and the coil generates a magnetic field which pulls the relay contacts open, breaking the connection to the start capacitor and preventing the start winding from connecting with the other side of our power supply. So long as the motor is running, the BEMF is present and keeps the relay open.
This is what the voltage looks like on an oscilloscope. CH1 is the smaller wave and it's on the common run terminal. CH2 is the larger wave and is at terminal 2 of the relay.

As we can see, the induced voltage on the start winding lags behind the line voltage by about 45 degrees and it is much stronger.
When the motor shuts off and slows down, the induced voltage disappears and the relay contacts close again. The relay sits outside the motor where sparks are acceptable.
As a cherry on top, I've drawn the current paths through the circuit to help illustrate what's happening:

^ Start condition (red). Current flow through the start winding and start + run capacitors
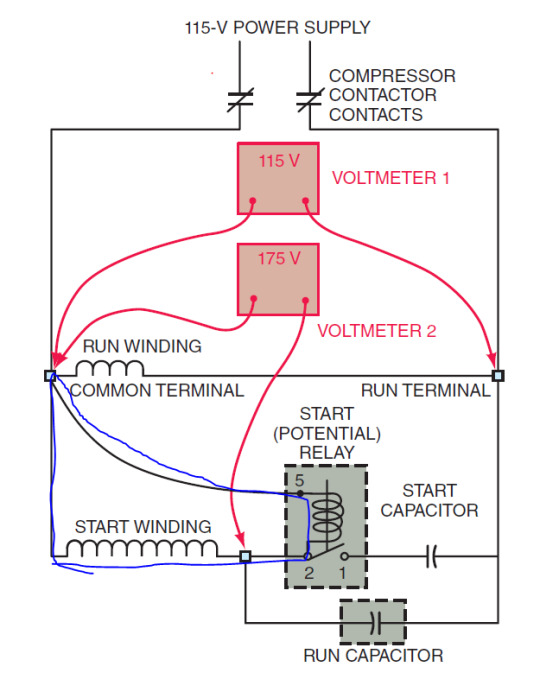
^ Run condition (blue). BEMF across the start winding powers the relay coil and opens the contacts.
There is a lot more going on I could talk about, but that's just the part I wanted to be autistic about. There is actually a better way to draw out this circuit that looks like this:
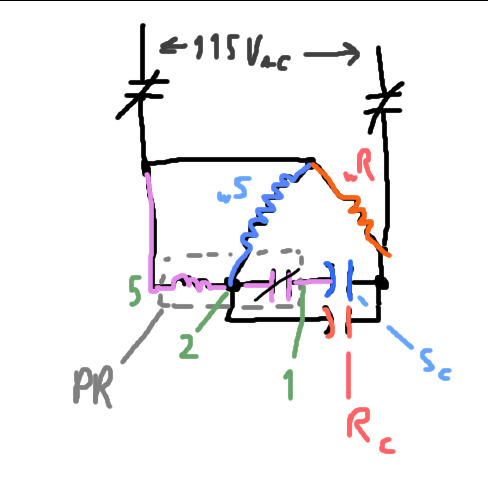
Sw = Start winding
Rw = Rung winding
PR = Potential relay
Sc = Start Capacitor
Rc = Run capacitor
And isn't that fascinating?
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is UPS?
What is UPS?
In this block we see following points
What is UPS?
UPS block diagram
How UPS works?
UPS power range and backup time
Now we will discuss
What is UPS and its functionality?
UPS stands for Uninterruptable Power Supply. It is an electronic power supply which leads for enable some load for short period of time when electricity goes off.
There are Two Types of UPS system
Offline UPS
Online UPS
How UPS Works?

Simply UPS means provides uninterrupted power to the AC load. This AC load converts into DC power. It is also known as standby or emergency power supply and standby generator. After light shut down it switch into the battery bank power and provides 10-15 minutes standard backup time at full load.
In operating conditions, the current is drawn from the main AC power supply or power grid, while Online UPS provides load current in case of a power failure. Here the battery is used as the backup source to transfer power to the load in case of power break.
UPS power range and backup time
Each UPS have different output power, which is designed and calculated according to the connected load. Usually, the output power is shown in the volt-ampere (VA) unit. The common online or offline UPS output power in the market are 600VA, 1kVA, 1.5kVA, 2kVA, 6kVA, 10kVA, 15kVA, and 20kVA and also available in higher kva e.g30Ka, 100Kva etc. Backup time is the time that UPS can provide the connected load/loads and depends on how many batteries UPS has.
Advantages of UPS
Here are some advantages of Uninterruptable Power Supply
Highly reliable
Better protection
Noise free
Offers continuous power
In case of main power failure, no need to change the operation mode.
Negligible transfer time.
Wide Input voltage range
Disadvantages of UPS
Every machine has own drawbacks.
It generates more heat because of continuous power on
Complex design
High Power Loss
We Sycom Power Protection Pvt. Ltd provides all range of online and line interactive UPS. We provide Pan India service of batteries, UPS, Inverters and stabilizer. For more details please contact us www.sycompower.com
#online ups#UPS#Uninterruptable Power Supply#sales#Sycom Power Protection#line interactive UPS#batteries#battery#voltage stabilizer#offline UPS
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is the Difference Between Solar Inverter And Energy Storage Inverter?

Solar power generation and energy storage systems have gradually been integrated into daily life. When we don't know how to choose the right inverter when buying, solar inverter and energy storage inverter are often confused. Below, Xindun will take you to re-understand the difference between solar inverter and energy storage inverter.
Solar inverter
The solar inverter is the core component of the solar system. It mainly converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) to meet the electricity needs of households and enterprises, or transmit electricity to the power grid. Its efficiency and performance are directly related to the power generation efficiency and economic returns of the entire solar system.
Solar inverter can be mainly divided into off grid inverter, grid connected inverter and hybrid inverter.
Off grid inverters are not connected to the public power grid and are mainly used in remote areas without power grid coverage, such as mountainous areas and pastoral areas. It can convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for local loads. At the same time, it needs to work with batteries to ensure that the load can still be powered normally in the case of insufficient light at night or on rainy days. Off grid inverters need to have stable output voltage and frequency to ensure the normal operation of load equipment. They usually have battery charging management functions, which can effectively extend the service life of batteries.
Grid connected inverters are inverters connected to the public power grid. Their main task is to convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) with the same frequency and phase as the power grid, and then transmit the power to the grid. They are widely used in urban residential areas, industrial and commercial plants and other areas covered by the power grid.
Hybrid inverters are inverter that combines off grid and grid connected operating modes, which is more flexible. It can be connected to the grid to transmit excess power to the grid, or it can automatically switch to off grid mode when the grid is out of power, relying on batteries to power the load. Hybrid inverters are very suitable for scenarios that require high stability of power supply, such as hospitals, data centers, etc. They can make full use of solar power generation and ensure the normal operation of key equipment when there is a problem with the grid.
Energy storage inverter
Energy storage inverter, also known as energy storage converter (PCS), is a key device in the energy storage system. It is mainly responsible for controlling the charging and discharging process of the battery and realizing the bidirectional conversion of electric energy. In the power system, it can improve energy utilization efficiency, balance power supply and demand, and enhance the stability of the power grid.
In the energy storage integrated system, the energy storage inverter obtains battery status information through real time interaction with the battery management system (BMS), and then controls the charging and discharging of the energy storage battery. It can convert the DC power output by the battery into AC power that can be transmitted to the power grid or other loads, and can also convert the AC power of the power grid into DC power to charge the battery. At the same time, it accepts the control instructions of the energy management system (EMS) to accurately control the charging and discharging voltage and current, etc., and improve the power transmission efficiency and power quality while ensuring the safety of the battery.
According to different application scenarios, energy storage inverters can be divided into four categories: household, industrial and commercial, centralized and energy storage power stations, corresponding to different power ranges: low power (<10KW), medium power (10KW-250KW), high power (250KW-1MW), ultra-high power (>1MW).
Differences between solar inverter and energy storage inverter
Control strategy
The power control of photovoltaic inverters is mainly unidirectional conversion. Off grid inverter mainly supply power to local loads and rely on batteries to maintain stability; grid connected inverters transmit power to the grid in one direction, which is greatly affected by light and has unstable power generation, but has functions such as max power tracking control; although hybrid inverters can switch in both directions, the core is still around the conversion and utilization of solar energy.
The power control of energy storage inverters is more complicated and is a process of bidirectional conversion. It can obtain power from the grid or solar system to charge the battery, and can also release the power stored in the battery to the grid or load, and the operating time is not too restricted. It stores electric energy when the load is low, releases electric energy when the load is high, and can switch to off grid mode to supply power when the grid fails, so as to achieve stable control of energy.
Application scenarios
The application scenarios of solar inverter mainly revolve around solar systems. Off grid inverters are used for independent solar systems in areas without grids; grid connected inverters are used for solar systems connected to the grid, such as urban residential, industrial and commercial rooftop solar, etc.; hybrid inverters are used for solar systems with high requirements for power stability.
Energy storage inverters are mainly used between energy storage systems and grids, such as industrial and commercial energy storage power stations, household solar storage systems, etc., through the charge and discharge management of energy storage batteries, to meet the power demand in different periods and ensure the stability and reliability of power supply.
Technical requirements
solar inverters pay more attention to DC-AC conversion efficiency, power density, and protection levels to adapt to different environments.
Energy storage inverters focus more on charge and discharge efficiency, grid connected and off grid switching speed, synergy with battery management systems, and storage energy density, so as to ensure efficient and safe operation during the two-way conversion of electric energy.
The above is an analysis of solar inverter and energy storage inverter. If you want to know more details, please feel free to contact Xindun.
0 notes
Text
How Solar Pump Inverters Reduce Electricity Costs Long-Term?
In light of increasing energy prices and environmental concerns, more people are investing in sustainable solutions. One such solution is the solar pump inverter. Solar pump inverters are intelligent devices that not only harness green energy but also reduce the long-term costs of electricity. If you're operating a farm, factory, or water supply at a more remote location, investing in solar pump systems can greatly benefit you. Let's get into how solar inverter systems save you money on electricity and why you should consider investing in one.
What Is a Solar Pump Inverter?
A solar pump inverter converts the direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC) to power water pumps. But it doesn’t just convert energy—it also manages the system’s performance efficiently. The inverter adjusts the motor speed based on sunlight availability and water demand. This smart control reduces energy waste and boosts operational efficiency.
Key Benefits That Lead to Cost Savings
1. No Electricity Bills
This is the most significant benefit. Traditional electric pumps use grid resources and incur a monthly energy charge. Conversely, a solar pump inverter uses the sun as energy. There is no cost of electricity after it is installed. Eventually, these savings provide a substantial benefit— especially when utilized in high-use applications like agriculture or rural water systems.
2. Efficient Motor Control
Several solar pump inverter manufacturers now use variable frequency drive (VFD) technology in their products. It adjusts the speed of the pump motor in response to demand, which stops wasted energy. This way you can save power. Smart motor management is a major contributor to bill savings.
3. Low Maintenance and Long Life
Solar pump inverters have fewer moving parts than generators and traditional pump equipment. This means experiencing lower maintenance costs. In addition, high-end variable frequency drive (VFD) manufacturers, design VFD systems to last longer, which means less downtime for repair and maintenance. The cumulative cost savings of less maintenance add up over the life of a system.
4. Grid Independence and Incentives
Solar systems lessen dependence on the local power grid. This is particularly useful in remote or difficult-to-access areas. Many governments and local municipality bodies also have incentives, rebates, or tax credits in place for solar-based systems. With incentives, the initial costs decrease, increasing return on investment (ROI).
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
To get the most out of your system, choose experienced and reliable solar pump inverter manufacturers. And it would be wise to work with someone who specializes as variable frequency drive manufacturers, as they often offer better integration, advanced features, and robust after-sales support.
In The End
A solar pump inverter is not just a great choice for the environment, but it is a smart financial option. The systems lower current and future electricity costs and are easier to maintain, along with ensuring reliable water supply in off-the-grid areas. Also, with advanced technology, costs are decreasing, which makes it a perfect time to make a solar switch.
When you partner with reputable solar pump inverter manufacturers and select systems with VFD integration, you will enjoy sustainable savings for years to come.
0 notes
Text
Bright Savings Ahead Why Solar Energy Systems for Homes Are the Future of Power
In today's world, where electricity prices are constantly rising and the effects of climate change are becoming more visible, many homeowners are turning to a cleaner and smarter solution Solar Energy Systems for Homes. Not only do these systems help reduce your monthly energy bills, but they also contribute to a greener and more sustainable planet. If you're wondering whether solar power is right for your home, read on to understand how it works, why it’s worth the investment, and what benefits it brings.
What Are Solar Energy Systems for Homes
Simply put, a solar energy system for homes converts sunlight into electricity using solar panels installed on your rooftop. These panels capture solar radiation and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then converted into alternating current (AC) using an inverter making it suitable to power your lights, fans, appliances, and more.
The great thing is that this system works silently in the background while cutting down your power bills and reducing your carbon footprint.
Why More Homeowners Are Choosing Solar
Installing a solar energy system is more affordable and efficient than ever before. With technological advancements, solar panels are now more durable, lightweight, and capable of generating more energy from limited sunlight. Governments in many countries also offer incentives, tax credits, and rebates that significantly reduce the installation cost.
Once installed, solar systems require very little maintenance and can last for 25 years or more, making them a one-time investment for long-term savings.

Key Benefits of Solar Energy Systems for Homes
1. Lower Electricity Bills: The most obvious advantage is a significant drop in your electricity expenses. You’ll start noticing the savings from the very first month.
2. Increased Property Value: Homes with solar systems are more attractive to buyers and often sell faster at higher prices.
3. Energy Independence: Say goodbye to power cuts and grid dependency. With solar, especially when combined with battery storage, you can run your home efficiently even during outages.
4. Eco-Friendly Lifestyle: Solar energy is clean, renewable, and emission-free. By going solar, you’re doing your part to reduce harmful carbon emissions and protect the planet.
Things to Consider Before Installation
Before you install a solar energy system for your home, consider your rooftop size, direction of sunlight, local weather conditions, and electricity usage patterns. It’s also important to choose a trusted solar installer who can offer you quality equipment, warranties, and expert advice tailored to your needs.
Final Thoughts
Making the switch to Solar Energy Systems for Homes is a smart and responsible decision. It’s an investment in your financial future and in a healthier planet. With the right system in place, you can enjoy clean, reliable, and affordable power for decades. So why wait? Let the sun power your home and brighten your future.
#SolarEnergyForHomes#HomeSolarInstallation#RenewableEnergySolutions#ResidentialSolarSystems#GoSolarSaveMoney
1 note
·
View note
Text
12v 5 amp smps
A 12V 5 Amp SMPS (Switched-mode power supply) is a type of power supply that converts AC (alternating current) voltage to a stable, regulated DC (direct current) voltage using switching regulators. It is commonly used to power electronic devices that require 12V DC power with a current rating of up to 5 Amps.

0 notes
Text
Silent Powerhouses: How igbt rectifiers Are Redefining Industrial Energy Conversion
Picture a bustling manufacturing floor at dawn. Conveyor belts glide, robotic arms pivot with precision, and high-power motors hum in perfect synchrony. All of this choreographed action relies on stable direct current—even though the utility grid delivers alternating current. Converting AC to DC might sound mundane, yet it’s the unglamorous heartbeat of virtually every modern factory, data center, and electric-rail system. Tucked inside control cabinets and power bays, igbt rectifiers are the silent powerhouses making this conversion cleaner, smarter, and dramatically more efficient.
From Diodes to Digital Brains
For decades, silicon diodes and thyristors dominated rectification. They were sturdy, inexpensive, and—let’s be honest—fairly dumb. They could only switch on and off in crude, bulk fashion, producing DC that was rife with voltage ripple and harmonic distortion. That was acceptable in an analog world, but today’s precision-driven operations need better. Enter the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT): a semiconductor that marries the high-current capability of a bipolar transistor with the fast switching of a MOSFET.
When engineers embed IGBTs in rectifier topologies, the result is a new class of high-frequency converters capable of pulse-width modulation (PWM), soft-start functions, and active power-factor correction. Suddenly, rectification isn’t just about flipping waveform polarity—it’s about sculpting perfect current for sensitive loads, saving megawatts in the process.
A Day in the Life: Humanizing High Tech
Let’s walk in the shoes of Ananya, maintenance lead at a sprawling metro-rail depot in Bengaluru. She remembers the era when traction substations ran on mercury-arc or SCR rectifiers. “It was like taming a dragon,” she jokes. Voltage spikes chewed through bearings, transformers overheated, and harmonics crept back onto the grid. Then came the retrofit: a modular cabinet stuffed with igbt rectifiers. Overnight, the depot saw a 6 % drop in energy losses and, more surprisingly, quieter lines. “Passengers didn’t notice the upgrade,” Ananya says, “but my team sleeps better knowing the system’s self-diagnostics flag issues before they escalate.”
That’s the hidden human upside—less emergency call-outs, more predictive maintenance, and a work culture that shifts from crisis mode to optimization mode.
Under the Hood: Why IGBT Architecture Shines
High-Frequency Switching IGBTs can switch tens of kilohertz, shrinking bulky transformers and filters. Smaller magnetics mean lighter enclosures and better thermal management.
Low Conduction Losses Compared to MOSFETs at high voltage, IGBTs maintain lower on-state resistance, translating into cooler operation and longer component life.
Built-In Protection Advanced gate-driver ICs monitor temperature, current, and voltage in real time, shutting down the device within microseconds if thresholds are breached.
Bidirectional Capability Paired with appropriate circuitry, they enable regenerative braking in electric locomotives, feeding energy back to the grid instead of dumping it as heat.
Sustainability by Design
Energy efficiency isn’t just a line on a spec sheet—it’s a planetary necessity. Traditional 12-pulse SCR rectifiers often hover near 90 % efficiency under ideal loads. Modern PWM-controlled igbt rectifiers push beyond 97 %, slicing gigawatt-hours off cumulative utility bills over their service life. Multiply that by thousands of installations and you have a tangible dent in global CO₂ emissions.
Moreover, precise DC output means motors run cooler, electrolytic capacitors last longer, and upstream generators experience smoother load profiles. Less wear equals fewer raw materials mined, shipped, and processed for replacements—a virtuous cycle of resource conservation.
Beyond the Factory: Emerging Frontiers
Data Centers – Hyperscale operators love IGBT rectifiers for redundant, hot-swappable power shelves that squeeze more watts per rack while meeting stringent harmonic limits (IEEE 519).
Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen – Stable, low-ripple DC is crucial for membrane longevity. As electrolyzer farms scale into the gigawatt realm, PWM rectifiers slash idle losses and enable dynamic ramp-up tied to renewable generation.
EV Hyper-Chargers – Ultra-fast DC stations (350 kW and higher) rely on modular IGBT blocks to convert grid AC into tightly regulated DC that won’t fry delicate vehicle battery chemistries.
Challenges on the Road Ahead
No technology is perfect. IGBT modules are sensitive to over-voltage transients and require sophisticated snubber networks. Their thermal cycling limits call for meticulous heatsink design and, in harsh climates, liquid cooling. Meanwhile, wide-bandgap semiconductors—silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN)—are nipping at IGBT heels, promising even faster switching and lower losses.
Yet cost remains king. For high-power (≥ 1 MW) applications, mature supply chains and proven robustness keep igbt rectifiers solidly in the lead. Hybrid topologies that mix SiC diodes with IGBT switches already deliver incremental gains without breaking budgets.
Skills and Workforce Implications
Technicians who once wielded soldering irons on analog boards now brandish oscilloscopes with gigahertz bandwidth to capture nanosecond edge transitions. Training programs are evolving: power-electronics courses in Indian ITIs and polytechnics now include gate-drive design, thermal simulation, and module-level repair practices.
For young engineers, this field offers a blend of hands-on tinkering and digital analytics. Predictive-maintenance dashboards stream real-time data—junction temperatures, switching losses, harmonic spectra—turning power rooms into high-tech command centers.
Final Reflections: Small Silicon, Massive Impact
It’s easy to overlook the humble converter tucked behind a metal door. But in the grand choreography of electrification, igbt rectifiers are the quiet conductors, synchronizing renewable surges, feeding smart grids, and keeping industry humming. They exemplify how incremental innovations—faster switches, smarter firmware, better cooling—compound into game-changing efficiency.
Next time you glide on an electric train, boot up a cloud server, or see a wind farm blinking on the horizon, remember: somewhere underneath, tiny gates are opening and closing thousands of times a second, silently shaping the clean-energy era. And that is technology worth celebrating, even if it never seeks the spotlight.
0 notes
Text
Your Complete Guide to Solar Panel Installation in Dindigul
As more residents across Tamil Nadu look for reliable, eco-friendly power solutions, solar panel installation in Dindigul has emerged as a top choice. With high sunlight availability, supportive government policies, and trusted local installers, it’s never been easier to switch to solar.
In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about going solar in Dindigul—cost, process, benefits, and top providers.
☀️ Dindigul + Solar = A Perfect Match
Why is Dindigul ideal for solar panel installations?
📍 Location Advantage – Over 280 sunny days per year means higher energy generation
⚡ High Grid Dependency – Rising TNEB charges make solar a cost-saving choice
🌱 Green Energy Push – Solar is clean, silent, and sustainable
Whether you’re in Palani, Nilakottai, Batlagundu, or Dindigul town, solar works efficiently for homes, businesses, and farms.
💡 How Does Solar Work?
A typical solar setup includes:
Solar Panels (monocrystalline/polycrystalline)
Inverter (converts DC to usable AC)
Net Meter (records how much power you send to the grid)
Optional Battery (for backup, in hybrid/off-grid setups)
You generate electricity during the day, use what you need, and export the rest to the grid—earning credits!
💰 Cost of Solar Panel Installation in Dindigul
System SizeApprox. Cost (Before Subsidy)Subsidy AvailableNet Cost1 kW₹70,000–₹80,000~₹28,000₹42,000–₹52,0003 kW₹2,10,000–₹2,40,000~₹78,000₹1,30,000–₹1,60,0005 kW₹3,40,000–₹4,00,000~₹1,00,000₹2,40,000–₹3,00,000
🟢 Farmers can get up to 70% subsidy on solar water pumps through agricultural schemes.
🛠 Trusted Solar Installers in Dindigul
Here are some top-rated service providers offering solar panel installation in Dindigul:
Smart Solar Dindigul – Known for smart metering and post-installation support
Naviksun Solar – TEDA-approved, subsidy experts, and agricultural solar specialists
Synergy Solar – Provides on-grid and hybrid solar systems with net metering setup
Kay Tech Solar – End-to-end solution provider, including panels, inverters, and permits
These companies handle everything—design, installation, TNEB approvals, and maintenance.
📋 What to Ask Before You Install
🔹 What brands of panels and inverters are used?
🔹 How long is the warranty?
🔹 Will you handle subsidy and net metering?
🔹 Do you offer EMI or maintenance plans?
A reliable installer will walk you through each step clearly.
🗣️ Local Impact Stories
“We went solar in 2023. Our 4 kW setup produces enough to cover our full usage—and we still get credit!” — Revathi M., Dindigul Town
“We installed solar for our poultry farm in Vadamadurai. It paid for itself in just 3 years.” — Arunraj, Farm Owner
✅ Summary: Why You Should Act Now
☀️ Use Dindigul’s sunlight to your advantage
💸 Save on your monthly electricity bill
📉 Get high government subsidies
🔧 Enjoy reliable installation and service from local experts
📞 Ready to Get Started?
If you're searching for solar panel installation in Dindigul, contact a local provider today. Book a site visit, get a quote, and start powering your life with sunshine.
0 notes
Text
Power Up with a 2000-Watt Inverter for Reliable Off-Grid Energy
Choosing a high-quality inverter is very important when you set up an off-grid power system. A 2000-watt inverter is a good way to turn the DC power from your solar battery into AC power that can be used by appliances, tools, and electronics in your home. This capacity is the perfect balance between efficiency and capability, whether you're powering necessities during a power outage or running equipment off the grid.

Benefits of a 2000-Watt Inverter Charger
A 2000-watt inverter charger does more than just convert energy. You can use it as an inverter, a battery charger, and an AC auto-transfer switch all in one. This all-in-one solution makes your setup easier and gives you more options for how to use it. The LFP series from SunGoldPower has extra features like adjustable charging current, AC/Battery priority settings, and even an Auto Generator Start function. This means that the inverter can turn on your generator when the battery voltage is low and turn it off when the battery is fully charged. This keeps the energy flow going.
Consistent Output with a 2000-Watt Pure Sine Wave Inverter Waveform quality is important for sensitive electronics and household appliances. A 2000-watt pure sine wave inverter makes sure that the energy output is clean and stable, just like grid power. This lowers the chance of breaking your devices and makes all of your connected appliances work better. The SW4 control switch on SunGoldPower's inverter lets it work with both 50Hz and 60Hz frequencies and always outputs 120VAC.

Designed for effectiveness and flexibility
Using low-frequency technology and low idle current helps save energy. There is also a BTS (Battery Temperature Sensor) cable and a remote control that comes with the system to make it easier to use. With the SW5 setting, you can easily switch between AC and battery priority, which gives you control over how you use your energy.
Why You Should Get This 2000-Watt Inverter Setup
A 2000-watt inverter is a smart buy for people who need reliable off-grid energy solutions. This is especially true if it has built-in charging and transfer capabilities. SunGoldPower has a solution that works for both home and mobile energy needs. It has advanced features and works well.
0 notes
Text
Global SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market : Regional Analysis & Forecast to 2032

Global SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market was valued at USD 3.86 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 12.74 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 16.10% during the forecast period (2025-2032).
SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market Overview
The SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market includes devices and systems that utilize silicon carbide semiconductors in power electronic applications. Silicon carbide offers superior characteristics compared to traditional silicon, such as higher breakdown voltage, thermal conductivity, and switching efficiency.
Power electronics involve the control and conversion of electrical power using semiconductor devices, while inverters are used to convert DC power into AC power. SiC technology is revolutionizing these fields by enabling faster switching, greater efficiency, and reduced size and weight of electronic systems.
This report provides a deep insight into the global SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market, covering all its essential aspects. This ranges from a macro-overview of the market to micro details of the market size, competitive landscape, development trend, niche market, key market drivers and challenges, SWOT analysis, value chain analysis, etc.
The analysis helps the reader to shape the competition within the industries and strategies for the competitive environment to enhance the potential profit. Furthermore, it provides a simple framework for evaluating and assessing the position of the business organization. The report structure also focuses on the competitive landscape of the Global SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market. This report introduces in detail the market share, market performance, product situation, operation situation, etc., of the main players, which helps the readers in the industry to identify the main competitors and deeply understand the competition pattern of the market.
In a word, this report is a must-read for industry players, investors, researchers, consultants, business strategists, and all those who have any kind of stake or are planning to foray into the SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market in any manner.
Get Full Report : https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/global-sic-based-power-electronics-and-inverter-market/
SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Key Market Trends :
Rapid Growth in EV Adoption – Automakers increasingly use SiC inverters to improve vehicle performance and range.
Expansion in Renewable Energy Applications – Solar and wind energy systems demand higher-efficiency inverters, driving SiC market growth.
Miniaturization and Efficiency – SiC allows for smaller, lighter, and more energy-efficient power electronic systems.
Increased Investments in Semiconductor R&D – Governments and companies are funding SiC technology to gain a competitive edge.
Emergence of Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Market – SiC is becoming a preferred material over silicon due to better thermal and electrical properties.
SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market Regional Analysis :
North America:Strong demand driven by EVs, 5G infrastructure, and renewable energy, with the U.S. leading the market.
Europe:Growth fueled by automotive electrification, renewable energy, and strong regulatory support, with Germany as a key player.
Asia-Pacific:Dominates the market due to large-scale manufacturing in China and Japan, with growing demand from EVs, 5G, and semiconductors.
South America:Emerging market, driven by renewable energy and EV adoption, with Brazil leading growth.
Middle East & Africa:Gradual growth, mainly due to investments in renewable energy and EV infrastructure, with Saudi Arabia and UAE as key contributors.
SiC Based Power Electronics and Inverter Market Segmentation :
The research report includes specific segments by region (country), manufacturers, Type, and Application. Market segmentation creates subsets of a market based on product type, end-user or application, Geographic, and other factors. By understanding the market segments, the decision-maker can leverage this targeting in the product, sales, and marketing strategies. Market segments can power your product development cycles by informing how you create product offerings for different segments.
Market Segmentation (by Application)
Automotive
Consumer Electronics
Aerospace
Information Technology (IT)
Others
Market Segmentation (by Type)
Power Electronics
Inverter
Key Company
STMicroelectronics
Wolfspeed
ON Semiconductor
ROHM CO., LTD.
Infineon Technologies AG
NXP Semiconductor N.V.
ABB Group
Renesas Electronics Corporation
Fuji Electric Co, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Electric Corp
Get A Detailed Sample Report : https://semiconductorinsight.com/download-sample-report/?product_id=96351
Drivers
Surging EV Demand SiC components are widely adopted in EVs due to their superior power efficiency and thermal properties.
Energy Efficiency Regulations Government policies promoting clean energy and emission reductions are boosting SiC-based technologies.
Renewable Energy Integration SiC inverters offer high conversion efficiency, making them ideal for solar and wind applications.
Restraints
High Manufacturing Costs SiC devices are more expensive than traditional silicon, limiting their use in cost-sensitive sectors.
Limited Supply Chain Few manufacturers currently produce high-quality SiC wafers, affecting supply consistency.
Technological Barriers Integrating SiC in legacy systems requires new designs, which can be technically challenging.
Opportunities
Expansion into Emerging Markets Countries in Latin America and Southeast Asia are starting to adopt SiC for infrastructure and energy needs.
Smart Grid Developments Growing demand for grid modernization is boosting the deployment of SiC inverters in smart grid systems.
R&D and Innovation Support Continued investments in materials science and semiconductor engineering offer pathways for cost reduction and performance improvement.
Challenges
Slow Adoption in Traditional Industries Conservative industries are hesitant to switch from proven silicon systems to newer SiC technologies.
Technical Expertise Requirements Designing and integrating SiC devices requires specialized knowledge, limiting its uptake among smaller firms.
Economic Uncertainty Global economic slowdowns can delay investments in new semiconductor infrastructure.
Customization of the Report
In case of any queries or customisation requirements, please connect with our sales team, who will ensure that your requirements are met.
Related Reports :
Contact us:
+91 8087992013
0 notes
Text
Basically, the UPS battery system is the electric device which has rectifier for providing the backup power to the system whereas the inverter converts the AC into DC. … During the power outages, the digital online UPS immediately switch over from the main supply to the ups battery whereas the inverter has a time delay. While purchasing ups battery system customer having several questions in their mind and so as Costa power is leading ups dealers, ups distributors in India giving some basic idea in the form of question and answer. While checking right ups battery system in Mumbai for your project kindly refer: What are main type of ups?
UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY, ups battery systems Mains voltage variations occur more often than expected. This results in crashes, data losses and cost intensive downtimes. The solution Costa Power provides as online ups distributors in India which offers various levels of protection for different applications.
CPIPL offers solutions based on thyristorized chargers, Online UPS / Online UPS battery, alkaline and lead-acid industrial battery, online ups in Mumbai, switching sources, grid-connected Online ups, embedded and stationary electrical converters for the rail world, and in general solutions. In high quality power electronics and reliability Costa Power offers solutions based through the organization engage in UPS PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE and with its own personnel the following ups AMC services in IndiaUPS AMC, Corrective Maintenance, UPS battery Installation in India.
Mumbai's monsoon brings a welcome respite from the heat, but also frequent power cuts. Rains disrupt your work life! Invest in a reliable online UPS in Mumbai to ensure your devices stay powered during outages. Costa Power is the Online UPS dealers in Mumbai who offer a wide variety of options, from global brand ups manufacturers to extended backup times. Your search for online ups in Mumbai to find the perfect fit for your needs is over, with a Online UPS, you can enjoy the rainy season knowing your electronics are protected.
#Upsbattery#Upsbatterydealers#Upsbatterydistributor#Upsbatterysuppliers#Upsamc#Upsapc#Microtekinverter#Quatabattery#Luminousups#Emersonups#Onlineups#Digitalups#Offlineups#Bestups#Bestbattery#Servostabilizer#Vertivups#Exidebattery#Luminousinverter#Upsdealers#Upssuppliers#Upsdistributors
0 notes
Text
24v smps power supply
A 24V SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) is an efficient and reliable power solution that provides a regulated 24-volt output. This power supply is designed to convert alternating current (AC) input voltage into a precise and stable direct current (DC) output for a wide range of electronic devices.

0 notes