#Are there C. difficile infection studies?
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
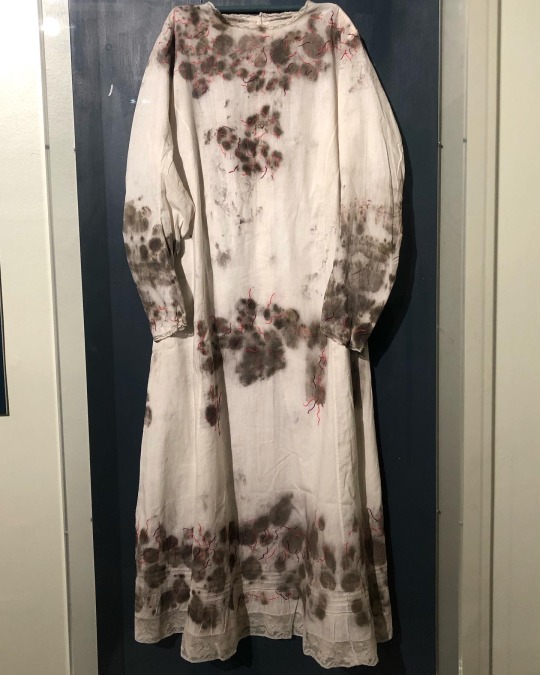
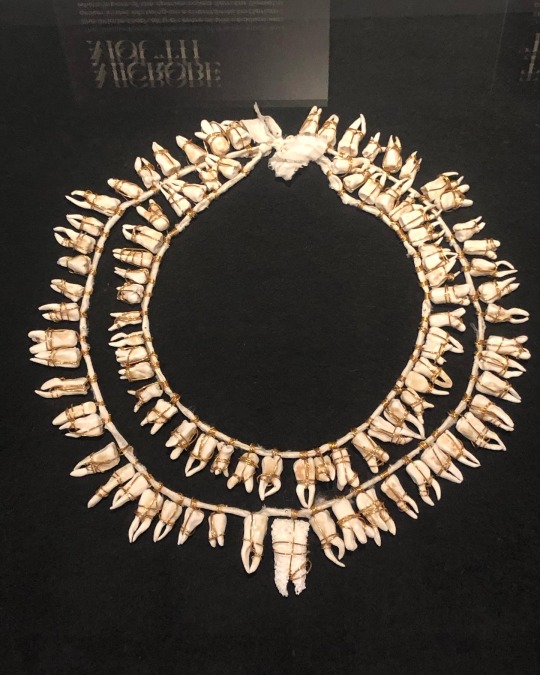
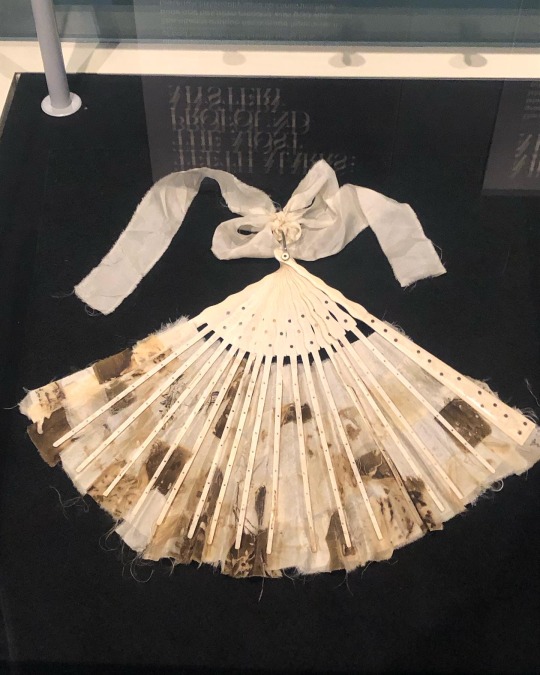
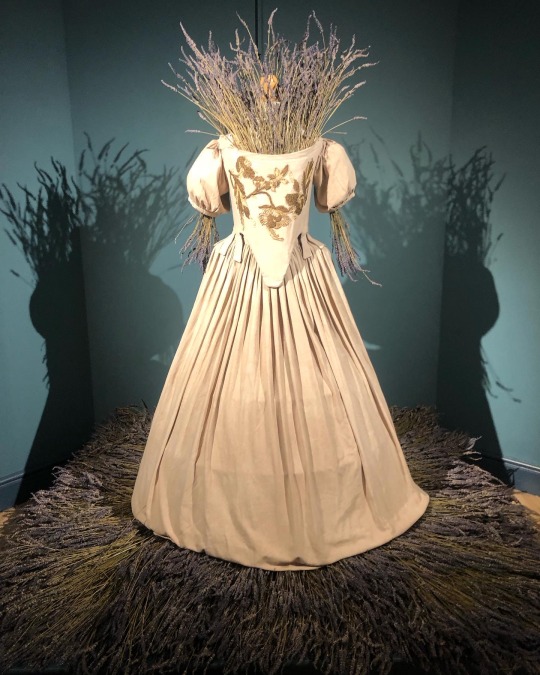
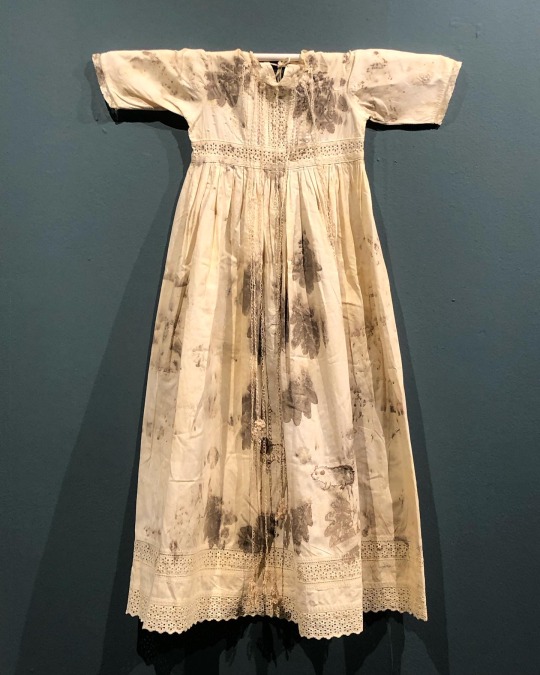
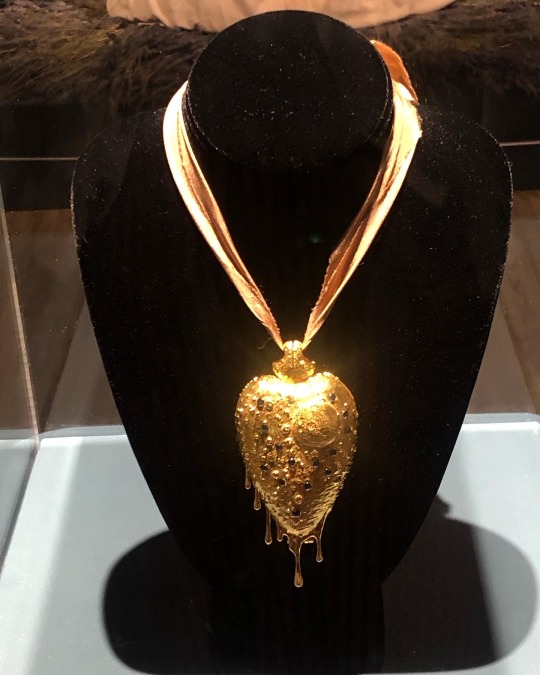






‘Fragile Microbiomes’ by bio-artist Anna Dumitriu
1. SYPHILIS DRESS- This dress is embroidered with images of the corkscrew-shaped bacterium which causes the sexually transmitted disease syphilis. These embroideries are impregnated with the sterilised DNA of the Nichols strain of the bacterium - Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum - which Dumitriu extracted with her collaborators.
2. MICROBE MOUTH- The tooth at the centre of this necklace was grown in the lab using an extremophile bacterium which is part of the species called Serratia (Serratia N14) that can produce hydroxyapatite, the same substance that tooth enamel is made from.
The handmade porcelain teeth that make up this necklace have been coated with glazes derived from various bacterial species that live in our mouths and cause tooth decay and gum disease, including Porphyromonas gingivalis, which can introduce an iron-containing light brown stain to the glaze.
3. TEETH MARKS: THE MOST PROFOUND MYSTERY- In his 1845 essay “On Artificial Teeth”, W.H. Mortimer described false teeth as “the most profound mystery” because they were never discussed. Instead, people would hide the stigma of bad teeth and foul breath using fans.
This altered antique fan is made from animal bone and has been mended with gold wire, both materials historically used to construct false teeth (which would also sometimes incorporate human teeth). The silk of the fan and ribbon has been grown and patterned with two species of oral pathogens: Prevotella intermedia and Porphyromonas gingivalis. These bacteria cause gum disease and bad breath, and the latter has also recently been linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
4. PLAGUE DRESS- This 1665-style 'Plague Dress' is made from raw silk, hand-dyed with walnut husks in reference to the famous herbalist of the era Nicholas Culpeper, who recommended walnuts as a treatment for plague. It has been appliquéd with original 17th-century embroideries, impregnated with the DNA of Yersinia pestis bacteria (plague). The artist extracted this from killed bacteria in the laboratory of the National Collection of Type Cultures at the UK Health Security Agency.
The dress is stuffed and surrounded by lavender, which people carried during the Great Plague of London to cover the stench of infection and to prevent the disease, which was believed to be caused by 'bad air' or 'miasmas'. The silk of the dress references the Silk Road, a key vector for the spread of plague.
5. BACTERIAL BAPTISM- based on a vintage christening gown which has been altered by the artist to tell the story of research into how the microbiomes of babies develop, with a focus on the bacterium Clostridioides difficile, originally discovered by Hall and O’Toole in 1935 and presented in their paper “Intestinal flora in new-born infants”. It was named Bacillus difficilis because it was difficult to grow, and in the 1970s it was recognised as causing conditions from mild antibiotic-associated diarrhoea to life-threatening intestinal inflammation. The embroidery silk is dyed using stains used in the study of the gut microbiome and the gown is decorated with hand-crocheted linen lace grown in lab with (sterilised) C. difficile biofilms. The piece also considers how new-borns become colonised by bacteria during birth in what has been described as ‘bacterial baptism’.
6. ZENEXTON- Around 1570, Swiss physician and alchemist Theophrastus Paracelsus coined the term ‘Zenexton’, meaning an amulet worn around the neck to protect from the plague. Until then, amulets had a more general purpose of warding off (unspecified) disease, rather like the difference today between ‘broad spectrum’ antibiotics and antibiotics informed by genomics approaches which target a specific organism.
Over the next century, several ideas were put forward as to what this amulet might contain: a paste made of powdered toads, sapphires that would turn black when they leeched the pestilence from the body, or menstrual blood. Bizarre improvements were later made: “of course, the toad should be finely powdered”; “the menstrual blood from a virgin”; “collected on a full moon”.
This very modern Zenexton has been 3D printed and offers the wearer something that genuinely protects: the recently developed vaccine against Yersinia pestis, the bacterium that causes plague.
#my favourite pieces from this exhibition that I visited last month at the Thackray medical museum in Leeds#absolutely fascinating reading about the process and meanings behind these works#mine#anna dumitriu#works
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
A new study has shown that an mRNA vaccine protected mice against deadly intestinal C. difficile

- By Nuadox Crew -
Researchers have developed an mRNA vaccine targeting Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile), a severe intestinal pathogen responsible for about 30,000 deaths annually in the U.S.
This new vaccine showed promising results in mice, offering protection from severe illness and death after exposure to lethal doses of the bacteria.
Unlike conventional vaccines, the mRNA version triggered a broad immune response, including antibodies and T cells. Vaccinated mice survived, experiencing only mild symptoms, and maintained immunity for six months.
While the vaccine has yet to be tested on humans, early studies in rhesus macaques suggest it might also elicit an immune response in primates.
However, more research, including testing on "dirty mice" with more naturalistic immune systems, is needed before moving to human trials.
Header image: Clostridioides difficile pathogen. Credit: National Foundation for Infectious Diseases (NFID).
Read more at Science News
Scientific paper: Alameh, M., Semon, A., Bayard, N. U., Pan, Y., Dwivedi, G., Knox, J., Glover, R. C., Rangel, P. C., Tanes, C., Bittinger, K., She, Q., Hu, H., Bonam, S. R., Maslanka, J. R., Planet, P. J., Moustafa, A. M., Davis, B., Chevrier, A., Beattie, M., . . . Zackular, J. P. (2024). A multivalent mRNA-LNP vaccine protects against Clostridioides difficile infection. Science, 386(6717), 69–75. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adn4955
Other recent news
Israel at COP29: Israel will showcase 20 climate-tech firms at the COP29 Climate Conference in Baku,Azerbaijan. These companies offer solutions in fields such as emissions, pollution, and carbon capture.
Revolutionary Super Polymer: Researchers at Osaka University have developed a new type of polymer that is unbelievably tough and endlessly recyclable.
Hubble's Galactic Masterpiece: The Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled a stunning image of NGC 5248, a spiral galaxy located 42 million light-years away.
Brain-Controlled Bionic Limbs: Advances in brain-controlled bionic limbs are inching closer to reality, offering new possibilities for individuals with mobility impairments.
#c difficile#pathogen#mrna#vaccine#israel#cop29#startups#innovation#climate change#emvironment#polymer#materials#space#astronomy#imaging#Prosthesis#robotics#health#medicine
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, but Im not sure the connection between "too many enemas" and "condition which qualifies you for an FMT" is there.
Like, there was really only one thing I know of in the US which qualified you for an FMT, which was recurrent C. difficile infection. As in you had to get it at least twice. Depsite FMTs have an over 90% cure rate in RCTs (and this being an independent cure rate, so if you failed one, all you had to do was try another.) Some of this is because C. dificile fucks you up so badly that I could show you a picture of a C. diff microbiome and a health microbiome and you, lay person who does not study microbiomes could play the "one of these things are not like the other" game and win.
We know the things that put you at elevated risk of C. diff. Things like antibiotics use (especially specific classes), PPI use, a diet low in vegetables and having endogenous C. diff.
Id love to see evidence that douching or being a receptive partner for anal sex also increase these risks. We know anal sex leads to changes in the microbiome, but Im not sure there's evidence that they're detrimental enough to cause a specific condition like C. diff for an FMT
40K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hospital Sanitation: The Foundation of Infection Prevention and Patient Trust
When patients enter a hospital, they place their health—and their lives—in the hands of healthcare professionals. But beyond medical expertise, one silent but equally critical factor influences their safety: hospital sanitation. A meticulously cleaned environment can mean the difference between recovery and relapse.
The High Stakes of Hospital Cleanliness
Hospitals are high-traffic zones where pathogens can spread rapidly. Patients with weakened immune systems, open wounds, or surgical sites are especially vulnerable. In this setting, even one missed spot can lead to a serious healthcare-associated infection (HAI).
Key pathogens of concern include:
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
Clostridium difficile (C. diff)
Norovirus
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE)
Preventing these infections starts with rigorous sanitation standards that leave no surface unchecked—from floors and instruments to soft furnishings like curtains.
Key Areas of Focus in Hospital Sanitation
Floor and Surface Disinfection Hospital floors and touchpoints like railings, switches, and counters must be disinfected with EPA-approved agents. Using single-use microfiber mop pads prevents the unintentional transfer of microbes from one area to another.
Sanitizing Equipment and Patient Areas Medical tools, IV stands, patient monitors, and mobile carts should undergo scheduled disinfection cycles to limit germ exposure.
Curtain and Linen Hygiene Often, hospital sanitation efforts focus on hard surfaces, overlooking textiles. Privacy curtains, which are touched frequently by multiple people throughout the day, can harbor harmful bacteria for long periods. That’s why it’s crucial to understand how often hospital curtains should be cleaned as part of a facility's infection control plan.
Hand Hygiene Support Ensuring hand sanitizer stations are well-stocked and placed at every room entrance encourages better compliance among staff and visitors.
Challenges in Maintaining Consistent Sanitation
Hospitals face challenges such as:
High patient turnover
Limited housekeeping staff during night shifts
Time constraints during emergency patient transfers
Miscommunication between departments about cleaning responsibilities
Overcoming these challenges requires structured cleaning schedules, checklists, and strong collaboration between environmental services and medical teams.
Elevating Sanitation with Smart Solutions
Healthcare environments are embracing innovation to improve cleaning outcomes:
UV-C disinfection systems for rooms and high-risk equipment
Antimicrobial wall coatings and fabrics to reduce contamination between cleanings
Disposable privacy curtains, especially in isolation units or post-operative recovery wards
Digital cleaning logs and audit systems to track and improve sanitation practices
Combining manual cleaning with technology ensures no detail is overlooked.
Curtain Cleaning: A Non-Negotiable Priority
Despite their importance, privacy curtains are rarely cleaned as often as needed. Yet studies have shown they become contaminated with dangerous microbes within just a few days of installation.
It’s time for hospitals to follow structured guidelines on how often hospital curtains should be cleaned—with many now opting for scheduled laundering or disposable options to stay compliant and protect patients.
Final Thoughts: Sanitation Is a Shared Responsibility
Ultimately, hospital sanitation isn’t just the job of the cleaning staff—it’s a shared responsibility that involves every department and individual. When everyone—from doctors and nurses to visitors and facility managers—plays their part, hospitals become truly safe spaces for healing.
From patient satisfaction to infection prevention, sanitation is the silent force that supports every successful recovery story.
0 notes
Text
When to take Saccharomyces Boulardii
When to Take Saccharomyces boulardii – A Guide Without the Brand Hype
Probiotics are everywhere today, but one name that consistently stands out in both research and clinical use is Saccharomyces boulardii. Unlike most probiotics, this one isn’t a bacterium — it’s a yeast. And while that might sound strange, this unique microorganism has been extensively studied and proven to offer several gut-health benefits.
But with all the noise from supplement companies pushing their own branded versions, it’s easy to lose sight of a basic question: When should you actually take Saccharomyces boulardii?

What Is Saccharomyces boulardii?
Saccharomyces boulardii is a tropical yeast strain first isolated from lychee and mangosteen fruit in the 1920s. It's now recognized for its ability to support gut health by:
Helping restore the natural balance of intestinal flora
Supporting digestion during and after antibiotic use
Reducing the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea
Supporting the management of certain gastrointestinal infections
It’s classified as a probiotic, even though it’s a yeast — which makes it especially interesting, because it won’t be killed off by antibiotics (unlike bacterial probiotics).
When Should You Take Saccharomyces boulardii?
1. During Antibiotic Use
One of the most evidence-backed uses of S. boulardii is to prevent antibiotic-associated diarrhea, including Clostridium difficile (C. diff) infection. Because it's a yeast, it survives antibiotic exposure.
When to take: Alongside your antibiotic — ideally a few hours apart (e.g., take the antibiotic in the morning, and the probiotic at lunch or evening).
Why: It helps maintain gut flora stability while antibiotics wipe out bacteria.
2. For Traveler’s Diarrhea
Studies show that S. boulardii can reduce the risk and duration of traveler’s diarrhea — a common issue when visiting countries with different microbial environments.
When to take: Start 5–7 days before travel, and continue throughout your trip.
Why: It preps your gut and provides a barrier against potentially harmful pathogens.
3. During or After Gastrointestinal Infections
For conditions like acute diarrhea caused by viruses or bacteria (e.g., rotavirus in children or food poisoning), Saccharomyces boulardii can shorten symptom duration and promote recovery.
When to take: At the onset of symptoms or immediately after; continue for several days after recovery.
Why: It competes with pathogens and helps restore intestinal lining integrity.
4. With Inflammatory Bowel Conditions
Some evidence supports its use in managing inflammation and symptoms in IBD (like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis), though results can vary between individuals.
When to take: As advised by a healthcare provider — often during flare-ups or after antibiotic courses.
Why: It may help modulate immune responses and improve gut barrier function.
5. Post-Antibiotic Recovery
Even after you finish antibiotics, your gut flora may need time to rebalance. S. boulardii can support this transition phase.
When to take: For 1–2 weeks post-antibiotic treatment.
Why: It supports the regrowth of healthy microbes and helps reduce post-antibiotic bloating or irregularity.
Tips for Taking Saccharomyces boulardii
Consistency matters: Take it daily during the needed period.
Timing: Can be taken with or without food, but spacing it from antibiotics helps maximize its effect.
Hydration: Especially important during diarrhea; combine with oral rehydration solutions if needed.
Form: Available in capsules, powders, or sachets — choose based on preference, not brand.
Who Should Be Cautious?
While S. boulardii is generally well-tolerated, it’s not recommended for:
Severely immunocompromised individuals
Patients with central venous catheters (risk of fungemia, although rare)
Those with known yeast allergies
Always consult your healthcare provider if you’re managing a chronic illness or are unsure about introducing any supplement.
Final Thoughts
Saccharomyces boulardii is a unique and effective probiotic with broad applications — from antibiotic support to travel protection and digestive health recovery. The key to its effectiveness lies not just in taking it, but in taking it at the right time and for the right reason.
Whether you're looking to prevent digestive issues or recover faster from them, Saccharomyces boulardii can be a smart, science-backed ally for your gut.
URL: For more information, visit Vakya Lifescience : When to take Saccharomyces Boulardii
0 notes
Text
Smart Vinyl Flooring Solutions Transforming Modern Interiors
Introduction: The Quiet Revolution in Vinyl Flooring
Request Report Sample: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-548
The vinyl flooring market has experienced rapid expansion, with projections indicating a valuation of over USD 63.8 Billion by 2035, driven by increasing demand for luxury vinyl tiles (LVT), resilient flooring, and PVC-based planks. While much attention has been given to aesthetic appeal, cost-efficiency, and durability, a lesser-known but game-changing trend is the integration of antimicrobial technologies into vinyl flooring—particularly in healthcare and elder care environments.
This niche but crucial development is reshaping how institutions design their interiors, blending infection control with design flexibility.
Antimicrobial Vinyl Flooring: The Unseen Line of Defense
In high-risk environments such as hospitals, clinics, and long-term care homes, flooring plays a more vital role than most realize. These spaces are prone to the spread of pathogens, including MRSA, C. difficile, and norovirus. Traditional cleaning methods, though important, cannot offer 24/7 protection. This is where antimicrobial vinyl flooring steps in.
These flooring products are treated with built-in antimicrobial agents—such as silver ion technology or zinc-based additives—which actively inhibit bacterial growth on the surface. Unlike coatings that can wear off, these technologies are embedded during manufacturing, ensuring long-term effectiveness.
Key Takeaways from the Vinyl Flooring Market Study
South Korea market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 6.5% over the forecast period, reflecting rapid infrastructure development and urban housing expansion.
The USA commanded approximately 6.8% CAGR of the global vinyl flooring market in 2035, driven by strong demand for luxury vinyl tile (LVT) and renovation activities.
Printed vinyl flooring segment is forecast to expand at a CAGR close to 7%, thanks to increasing adoption in residential and commercial interiors for design flexibility.
Why It Matters for Senior Care Facilities
While hospitals are an obvious application, elder care homes and assisted living centers are rapidly adopting antimicrobial vinyl flooring as part of infection control strategies. Seniors often have compromised immune systems, making them more vulnerable to infections.
Vinyl’s slip resistance, ease of wheelchair movement, and comfort underfoot already make it a popular choice, but adding pathogen resistance further elevates its value. For example, in Japan—where the aging population drives innovation in eldercare infrastructure—vinyl flooring products with antimicrobial and odor-neutralizing features are now standard in new facility construction.
Browse the Complete Report: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/vinyl-flooring-market
Product Innovation & Market Impact
This trend has triggered innovation from key players in the resilient flooring industry. Companies like Tarkett, Armstrong Flooring, and Gerflor have introduced LVT collections specifically targeting healthcare environments. These include advanced features like seamless installation, heat-welded joints, and UV-cured finishes, which enhance both hygiene and longevity.
Moreover, the Asia-Pacific region, with its growing medical tourism and hospital infrastructure boom, is emerging as a hotbed for antimicrobial vinyl flooring demand. By 2030, India and Southeast Asia are expected to account for over 25% of global demand for healthcare-grade LVT flooring.
From a regulatory perspective, antimicrobial flooring solutions are also aligning with hospital accreditation standards and infection control guidelines, which further fuels market demand.
Looking Ahead: A Market Shift Driven by Health and Safety
As healthcare and senior care continue to evolve, the role of surfaces—including floors—is becoming central to infection prevention design. Beyond visual appeal or durability, the market is seeing growing investment in function-first vinyl flooring, driven by health considerations.
In the near future, we may see antimicrobial vinyl flooring expand into schools, public transportation hubs, gyms, and restaurants, where hygiene is equally critical.
General & Advanced Materials Industry Analysis: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/industry-analysis/general-and-advanced-materials
0 notes
Photo


ialling 'poo pills' to flush out dangerous superbugsUK doctors are attempting to clear dangerous superbug infections using "poo pills" containing freeze-dried faeces.The stool samples come from healthy donors and are packed with good bacteria.Early data suggests superbugs can be flushed out of the dark murky depths of the bowel and replaced with a mix of healthy gut bacteria.It is a new approach to tackling infections that resist antibiotics, which are thought to kill a million people each year.The focus is on the bowels which are "the biggest reservoir of antibiotic resistance in humans" says Dr Blair Merrick, who has been testing the pills at Guys and St Thomas' hospitals.Drug-resistant superbugs can escape their intestinal home and cause trouble elsewhere in the body – such as urinary tract or bloodstream infections."So there's a lot of interest in 'can you get rid of them from the gut?'," says Dr Merrick.The idea of poo-pills isn't as far-fetched as it might seem. Faecal transplants – also known as a trans-poo-tion - are already approved for treating severe diarrhoea caused by Clostridium difficile bacteria.But scientists noticed hints that faecal transplants for C. difficile also seemed to get rid of superbugs.New research has focused on patients who had an infection caused by drug-resistant bacteria in the past six months.They were given pills made from faeces which people had donated to a stool bank.Each stool sample is tested to ensure it does not contain any harmful bugs, undigested food is removed and then it is freeze dried into a powder.This is stored inside a pill that can pass through the stomach unscathed and reach the intestines where it dissolves to release its poopy powdery payload.The stool samples were tested to ensure they did not contain anything dangerousThe trial has taken place on 41 patients at Guy's and St Thomas' hospitals in London to lay the groundwork for a large-scale study. It showed patients were up for taking a poo pill and the donated bacteria were still being detected in the bowels at least a month later.Dr Merrick says there are "really promising signals" that poo pills could help tackle the rising scourge of superbugs and that donor bacteria could be going to microbial war with the superbugs as they compete over food and space on the lining of the gut and either rid the body of them completely or "reduce them down to a level that doesn't cause problems".The study also suggests the array of gut bacteria becomes more varied after the therapy. This is a sign of good health and "may well be promoting colonisation resistance" so it is harder for new infectious bugs to get in."It's very exciting. There's a real shift from 20 years ago where all bacteria and viruses were assumed to do you harm; to now where we realise they are completely necessary to our overall health," says Dr Merrick.Earlier this week scientists showed the good bacteria our bodies meet – in the hours after we are born – seem to halve the risk of young children being admitted to hospital with lung infections.Our body's own human cells are outnumbered by the bacteria, fungi and others that live inside us - known as the microbiome.This has led to research implicating the microbiome in everything from Crohn's disease to cancer to mental health. If poo pills are proven to work against superbugs in larger studies then the researchers think they could be used for both treatment and prevention in people at risk. Medical procedures that suppress the immune system - including cancer therapies and organ transplants - can make the body more vulnerable."A lot of these individuals come to a lot of harm from drug resistant organisms," Dr Merrick.The UK's drugs regulator – the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) – said there were more than 450 microbiome medicines currently in development."Some of them will succeed, so I do think we will see them coming through quite soon," said Dr Chrysi Sergaki, the head of microbiome researc
0 notes
Text
North America Microbiome Therapeutics Market Size, Revenue, End Users And Forecast Till 2030
The North America microbiome therapeutics market was valued at US$ 161.64 million in 2022 and is expected to reach US$ 342.99 million by 2030; it is estimated to record a CAGR of 9.9% from 2022 to 2030.
Inflow of Funds to Ameliorate Microbiome Discovery Pipeline Drives North America Microbiome Therapeutics Market
Research has shown that imbalances or disruptions in the microbiome can contribute to various conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease and obesity, as well as mental health disorders. The recognition of the microbiome's role in overall health has generated significant interest in developing therapeutics to target and modulate the microbiome. Additionally, advancements in technology and research tools have made it easier to study and manipulate the microbiome. Next-generation sequencing and metagenomic analysis have allowed for a deeper understanding of microbial communities and their functions. The increased knowledge has opened up new possibilities for developing targeted therapies. Regulatory agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have also shown a willingness to support the development of microbiome therapeutics. The FDA has established guidelines for FMT and has expressed interest in advancing the field through regulatory pathways that ensure safety and efficacy. All these factors combined have created a favorable investment climate for companies working in the field of microbiome therapeutics.
Grab PDF To Know More @ https://www.businessmarketinsights.com/sample/BMIRE00029954
North America Microbiome Therapeutics Market Overview
The increasing understanding of the importance of the human microbiome in maintaining health and preventing diseases has led researchers in the US to explore microbiome-based interventions as a promising approach to treating various conditions. Additionally, the dominance of this country in the North America microbiome therapeutics market is mainly attributed to its well-developed research infrastructure that favors the development of innovative treatments Further, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as obesity and inflammatory bowel disease has created a demand for innovative treatments, spurring the development of microbiome therapeutics. Technological advancements in gene sequencing and bioinformatics enable the study and alteration of the microbiome, facilitating the development of personalized microbiome-based interventions. The trend toward personalized medicine aligns well with tailormade microbiome therapeutics.
Market Segmentation
The North America microbiome therapeutics market is segmented based on type, application, end user, and country.
Based on type, the North America microbiome therapeutics market is bifurcated into therapeutics and procedure. The procedure segment held a larger share in 2022. The therapeutics segment is further subsegmented into fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), prebiotics & probiotics, and others.
By application, the North America microbiome therapeutics market is segmented into metabolic disorder and obesity, C. difficile infection, inflammatory bowel disease, and others. The C. difficile infection segment held the largest share in 2022.
By end user, the North America microbiome therapeutics market is hospitals and clinics, ambulatory surgical centers, homecare, and others. The hospitals and clinics segment held the largest share in 2022.
Market leaders and key company profiles
AOBiome Therapeutics Inc
Ferring Holdings SA
Finch Therapeutics Group Inc
Pendulum Therapeutics Inc
Seres Therapeutics Inc
About Us:
Business Market Insights is a market research platform that provides subscription service for industry and company reports. Our research team has extensive professional expertise in domains such as Electronics & Semiconductor; Aerospace & Defence; Automotive & Transportation; Energy & Power; Healthcare; Manufacturing & Construction; Food & Beverages; Chemicals & Materials; and Technology, Media, & Telecommunications.
0 notes
Text
Practicum Project According to Ho et al. (2015), statistics indicate that approximately 20% to 40% of health care associated infections have been linked to cross-infection through the hands of health care workers. Efficacious hand hygiene is imperative to prevent communication of healthcare associated pathogens. A great deal of hand hygiene programs in healthcare settings lay emphasis on compliance of healthcare personnel, for the reason that transitory contamination of their hands is deemed to be the key basis for transmission of pathogens (Kundrapu et al., 2014). The use of alcohol-founded hand sanitizers in health units has become prevalent since their recommendation by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during 2002. This was acclaimed due to patient interaction especially in case hands are soiled, physically. However, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are not efficacious against some classifications of pathogens (Carter, 2013). The problem identified is in healthcare settings; are the use of alcohol base hand rubs more effective or less effective in reducing hospital rate infection statistics (HRIS) in comparison to water and soap techniques? Problem My mentored practicum experience took place in an Acute Rehabilitation/ Brain Center. Nursing care can be undertaken via a mixture of organizational approaches. The model of nursing care utilized differs largely from one healthcare facility to another and from one set of patient situations to another. The model of care delivery applied in my practicum experience is progressive patient care. This is a system of nursing care in which the patients are set in units based on their necessities for healthcare as ascertained by magnitude of illness (Current Nursing, 2012). Our unit was made up of 10 nurse assistants and 8 registered nurses. The main way in which my nurse manager proposes to solve this problem is the use of alcohol-based hand sanitizers five times before washing hands with soap and water. With the manager employing a dictatorial style of leadership, the decision-making process employed is one that fails to take into consideration the thoughts and ideas of external sources or internal sources such as employees. This particular problem has an adverse impact on patient outcome. Taking into account the fact that alcohol-based hand sanitizers are not fully effective in eradicating bacteria, particularly C. difficile bacteria, this solution leads to poor patient health care (Carter, 2013). In the end, this can give rise to patient dissatisfaction. In addition, it can lead to lack of employee motivation as they have no sense of input in activity and their opinions are not taken into account. Intervention I believe that this problem could be resolved in a different way from the manager's proposal. In particular, my proposal entails employing soap and water in washing hands. Moreover, if there is a low level of hospital rate infection statistics for a period of 6 months, the personnel ought to receive financial bonuses and also have a written note in their personal file. Kundrapu et al. (2014) ascertained that the hand of patients with Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and asymptomatic carriers were repeatedly contaminated with C. difficile bacteria. This sort of contamination could prospectively lead to transmission or recurrence of CDI when bacteria on hands are consumed. The research indicated that soap and water washing was efficacious for diminishing the rate of recurrence of constructive cultures and the problem of bacteria on hands, while alcohol hand rub was not. Results of the study recommend that patient hand washing could be a beneficial and simple way to execute aide to standard control measures for C. Difficile. Carter (2013) assesses the ideal balance between hand washing and hand sanitizers. The articles consider the question whether over dependency on alcohol-based hand sanitizers has played a part in causing disease outbreaks or generating more infectious strains of pathogens. The author obtains insight from experts such as Aron Hall, who happens to be an epidemiologist and an expert at the CDC's Viral Diseases Division, along with Clifford Mcdonald, who is an authority of C. difficile as well as high-ranking adviser intended for science and integrity at the CDC's Health Quality Promotion Division. It is noted that overreliance was not a case as noroviruses mutate quite repeatedly. Both experts agree that there is no evidence that alcohol-based hand sanitizers played a part in strain or outbreaks selection. The recommendation is going against additional modifications in CDC guiding principles so that the substantial advancement in ABHS use, leading to decreasing health-linked infections, will not be misplaced. In overall, the proper equilibrium for hygiene of hand encompasses increased devotion to appropriate hygiene of hands via education and constantly prompting staff to at least scrub all hand surfaces for at least forty to sixty seconds with water and soap or twenty to thirty seconds with 3 to 5 mL involving alcohol. The research study by Edmonds et al. (2013) sought to determine whether surrogate organisms are able to envisage activity against C. Difficile bacteria and made the comparison of the effectiveness of hygiene processes against C. difficile. The outcomes of the study delineate that C. difficile bacteria were much harder to remove through hand washing in comparison to bacteria of surrogate species. These outcomes are in line with preceding research studies and point out that surrogate organisms ought not to be employed to predict effectiveness of hand hygiene against C. difficile bacteria. Moreover, the results of the study show that prevailing hand hygiene interventions have restricted effectiveness against C. difficile spores. As a result, healthcare workers ought to continue adhering to the recommendations for hand washing with soap and water and lay emphasis on contact safety measures for providing healthcare to patients with CDI. According to Ho et al. (2015), the use of alcohol hand rub is acknowledged as the gold standard for hand hygiene of non-soiled hands and is deemed to decrease the time needed for hand hygiene. On one hand, recommendation from the World Health Organization (WHO) is to employ alcohol hand rub adhering to the similar 7-step procedure as for handwashing with antimicrobial soap and water. On the other hand, the recommendation from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the application of alcohol for covering all surfaces of both hands and fingers to the point when hands are dry. The authors attempt to assess the efficacy of 3 hand hygiene procedures in decreasing hand carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) amongst health care workers. The research study demonstrates that use of alcohol hand rub, either covering all hand surfaces in no precise directive or by means of the 7-step procedure, and chlorhexidine handwashing, were similarly efficacious for the elimination of hand carriage of MRSA and MSSA. According to Tuladhar et al. (2015), human norovirus is the principal origin of acute gastroenteritis, which affects individuals of all age brackets. The spread of the virus takes place either directly through person-to-person contact or indirectly through soiled food, water, and environmental fomites. A great deal of norovirus epidemics are linked to person-to- person spread and hands are considered to be a primary means for spreading viruses, directly or indirectly. In addition, human norovirus, and other pathogenic infections can continue being communicable on human hands for hours. The research study by Tuladhar et al. (2015) tested the effectiveness of alcohol hand antiseptic against human enteric and respiratory infections. It also compared the effectiveness of an alcohol-based hand antiseptic and handwashing with soap and water against norovirus. Therefore, the authors concluded that washing hands with soap and water is more effective compared to using alcohol-based hand antiseptics in eradicating noroviruses from hands. For this reason, it is the favored intervention method to preclude communication through hands in healthcare environments and food preparation amenities. Other facilities deal with this problem differently. A different approach utilized is that of smearing alcohol to cover all surfaces of both hands and fingers until the hands are dry. I believe the good solution to this problem is utilizing the 7-step technique as for handwashing with antimicrobial soap and water. In addition, I also consider staff education and training to be a longstanding solution to this particular problem. Personnel enlightenment enables them to have a better understanding as to why using soap and water in hand washing is the most efficacious approach for eradicating bacteria and precluding hospital infections (Ho et al., 2015). Comparison In the contemporary, the manner in which the issue, whether alcohol-based hand rub is more effective or less effective in reducing HRIS than soap and water techniques, is taken care of subsequent to using alcohol-based hand sanitizers five times, is washing hands with soap and water. However, this particular approach is ineffective. This is due to increase in hospital rate infection statistics. There is a great need for more education of employees. It is imperative to note that personnel are adherent to the commands and directions given. A great deal of employees are uninformed that alcohol is ineffectual in killing pathogens, and this suggests the great need for education of employees in dealing with infections and the significance of hand washing (Kundrapu et al., 2014). The manager within the unit employs a dictatorial style of leadership. In essence, being an autocratic leader, the manager tells the employees what she wants them to do. In a dictatorial leadership style, the individual giving the orders has complete authority and control over decision-making. By virtue of their position and job duties, they not only control the determinations of the team, but also constantly observe them under close examination to ensure they accomplish their duties. The decision-making process encompasses handing down instructions to the members within the unit devoid of any discussion or vote. The leader does not enquire for any recommendations or thoughts from external sources and chooses from his or her own inherent information and discernment of the state of affairs (Leadership Management Development Center, 1997). For instance, in this case, the manager of the unit hands out instructions for the employees to wash their hands using soap and water subsequent to using alcohol-based hand sanitizers five times, without taking into account the thoughts, perspectives and experiences of personnel working under her. This problem does have an impact on patient outcome. In particular, owing to the decision made and the issue at hand, staff within the unit still walk around with dirty gloves outside patients' room. In turn, this has had an adverse impact on patient case as it recently gave rise to two patients developing Clostridium difficile infection (CDI). As initially pointed out, alcohol hand rub is not efficacious in diminishing the rate of recurrence of constructive cultures and the problem of bacteria on hands (Kundrapu et al., 2014; Tuladhar et al., 2015). Therefore, in general, this gives rise to lack of patient satisfaction, which is the core of the healthcare unit. In addition, this has an impact on staff. One of the immediate effects is that personnel are obligated to adhere to the autocratic decisions made by the manager devoid of any of their input taken into consideration for improving team effort. In this case, regardless of whether the staff consider the need to undertake hand washing with soap and water as more effective, they still have to adhere to the rule of using alcohol-based sanitizers five times first. A key adverse impact is on the morale of the personnel. According to Leadership Management Development Center (1997), it is quite challenging to obtain a balance between the use of authority and the morale of personnel. A great deal of direct scrutiny through the dictatorial leadership style causes the subordinates to be unhappy, and being too heavy handed ends up crushing all group participation. Motivation is an intricate element that is influenced by acuities and reinforced by manifold factors. A largely autocratic style of leadership ends up demotivating the staff, which as a result leads to poor delivery of health care to patients. The lack of employee input in the decision-making process gives a sense of lack of ownership, which in turn, gives rise to employee dissatisfaction (Bhatti et al., 2012). Outcome The outcome of my PICOT question that I hope to achieve through the new intervention I am proposing is lower infection rate. Taking into account that the proposal will address the main issue that alcohol-based hand sanitizers are not completely effective in eradicating the transmission of hand bacteria, the result ought to be decreased rate of infection. In particular, this will enable the capacity to ensure that C. difficile infections are not prevalent in the healthcare setting. Improved staff morale and higher patient satisfaction are other expected outcomes. Time Frame The timeframe for measuring outcomes of this PICOT question will be 6 to 12 months. References Bhatti, N., Maitlo, G. M., Shaikh, N., Hashmi, M. A., & Shaikh, F. M. (2012). The impact of autocratic and democratic leadership style on job satisfaction. International Business Research, 5(2), 192. Carter, D. (2013). The Right Balance Between Hand Sanitizers and Handwashing. AJN The American Journal of Nursing, 113(7), 13. Current Nursing. (2012). Models of Nursing Care Delivery. Retrieved from: http://currentnursing.com/nursing_theory/models_of_nursing_care_delivery.html Edmonds, S. L., Zapka, C., Kasper, D., Gerber, R., Mccormack, R., Macinga, D.,...& Gerding, D. N. (2013). Effectiveness of hand hygiene for removal of Clostridium difficile spores from hands. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 34(03), 302-305. Ho, H. J., Poh, B. F., Choudhury, S., Krishnan, P., Ang, B., & Chow, A. (2015). Alcohol hand rubbing and chlorhexidine handwashing are equally effective in removing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from health care workers' hands: A randomized controlled trial. American journal of infection control, 43(11), 1246-1248. Kundrapu, S., Sunkesula, V., Jury, I., Deshpande, A., & Donskey, C. J. (2014). A randomized trial of soap and water hand wash versus alcohol hand rub for removal of Clostridium difficile spores from hands of patients. Infection control and hospital epidemiology, 35(2), 204-206. Leadership Management Development Center. (1997). Decision-Making Styles. Retrieved from: http://www.leadershipmanagement.com/html-files/decision.htm Tuladhar, E., Hazeleger, W. C., Koopmans, M., Zwietering, M. H., Duizer, E., & Beumer, R. R. (2015). Reducing viral contamination from finger pads: handwashing is more effective than alcohol-based hand disinfectants. Journal of Hospital Infection, 90(3), 226-234. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Inibitori della pompa protonica ed infezioni da C. difficile nei pazienti ospedalizzati

Secondo uno studio pubblicato sul Journal of Hospital Infection, il rischio di insorgenza di infezioni da Clostridioides difficile è più elevato nei pazienti ricoverati in ospedale che per trattare l’ulcera da stress utilizzano inibitori della pompa protonica rispetto a quello degli individui che assumono antagonisti del recettore H2 dell’istamina. “Studi precedenti sull’infezione…
View On WordPress
#antagonisti del recettore H2 dell’istamina (H2RA)#Clostridium difficile#infezione da C. Difficile#inibitori di pompa protonica#ulcera da stress
0 notes
Text

Heartburn and acid reflux can be uncomfortable and disruptive, preventing people from enjoying their meals and sleeping well. A lot of people seek relief from Dexilant, a commonly utilized medicine. Although Dexilant works well, the cost may be a concern for people suffering from chronic problems. Fortunately, there are inexpensive choices that provide good heartburn relief. This article will define acid reflux and heartburn, explain how Dexilant works, and discuss cost-effective symptom control options.
Understanding Acid Reflux and Heartburn
What Are Acid Reflux and Heartburn?
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat and stomach. This reverse movement can cause discomfort, resulting in a burning sensation in the chest, which is commonly referred to as heartburn.
Causes of Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to properly close. Some of the most common triggers include:
Eating large meals or lying down right after eating
Consuming acidic, spicy, or fatty foods
Drinking beverages like coffee, soda, or alcohol
Smoking
Stress or anxiety
Risk Factors
Obesity, pregnancy, and certain medical problems, such as hiatal hernia, can all increase the risk of developing acid reflux.
Emerging Insights on Acid Reflux
According to recent study, various hereditary variables, such as LES muscle tone and esophageal sensitivity, may increase the likelihood of acid reflux. Gut microbiota has also been shown to play an important role in acid reflux. Disruptions in the gut microbiome can cause increased inflammation and acid production, resulting in the development of symptoms. This research could lead to novel treatments for gut health, such as probiotics and individualized dietary adjustments to maintain a healthy microbiome.
Impact on Long-Term Health
Untreated persistent acid reflux can lead to esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, and even esophageal cancer. Recent research emphasizes the need of quick intervention in minimizing these risks. Avoiding long-term harm requires regular monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and the use of appropriate drugs. This emphasizes the growing necessity of discovering cost-effective and easily accessible medicines for general health and well-being.
Dexilant: A Closer Look
Dexilant (dexlansoprazole) is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that reduces acid production in the stomach. Dexilant lowers acid levels, protecting the esophagus and relieving heartburn symptoms.
Benefits of Dexilant
Dual delayed-release technology gives longer relief, which can last up to 24 hours.
Effective for treating GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) and repairing esophageal damage.
Potential Side Effects
Dexilant is effective, however it may cause headaches, nausea, diarrhea, or constipation. Prolonged use may lead to issues such as low magnesium levels or brittle bones.
The Cost Factor
Dexilant’s high cost is justified by its efficacy. Those without insurance or limited coverage may find the monthly expense prohibitively expensive. This is when budget-friendly options become critical.
New Research on PPIs Like Dexilant
Recent study has looked into the long-term health repercussions of using PPIs, including suspected links to kidney difficulties and an increased risk of certain infections such Clostridioides difficile (C. diff). These findings have generated discussions about being more cautious with the use of PPIs and ensuring they are only administered when necessary. This emphasizes the importance of considering cost-effective alternatives to avoid becoming overly reliant on a single medicine.
Emerging Benefits of Dexilant’s Mechanism
Beyond symptom relief, research suggests that Dexilant’s dual delayed-release mechanism may offer other benefits. Its ability to regulate stomach acid levels over lengthy periods of time may be especially advantageous for people who suffer from severe nocturnal reflux or require esophageal repair. However, cheaper comparable medications with the same functionalities are already appearing, offering patients with cost-effective options for managing their money.
Affordable Alternatives to Dexilant
Over-the-Counter Medications
Antacids
Antacids neutralize stomach acid, offering immediate, temporary relief.
How They Work:These medications act by neutralizing stomach acid, reducing esophageal irritation.
Popular Brands:Tums, Rolaids, and Maalox can be purchased for between $5 and $10 per bottle.
Limitations:Antacids are most effective when used sparingly and do not address the underlying causes of acid reflux. Excessive use might have negative consequences like constipation or diarrhea.
H2-Receptor Blockers
H2-receptor blockers lower stomach acid production.
How They Work:These medications suppress histamine, a chemical that causes the stomach to produce acid.
Popular Brands:Famotidine products like Pepcid and Zantac 360 are popular, with prices ranging from $10 to $15 for a modest container.
Effectiveness and Side Effects:They have a delayed onset than antacids but provide longer-lasting comfort. Possible adverse effects include dizziness or fatigue.
Prescription Medications
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs are one of the most effective therapy options for heartburn and acid reflux.
How They Work:They inhibit the acid pumps in the stomach, causing a significant decrease in acid output.
Popular Brands: Nexium (esomeprazole), Prilosec (omeprazole), and Prevacid (lansoprazole) are well-known and cost between $30 and $50 a month.
Generic Options: Non-branded proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole, cost $10-$15 a month and provide the same level of efficacy as their branded counterparts.
Side Effects: As with Dexilant, prolonged use may result in nutritional shortages or bone issues.
Other Prescription Options
Other drugs that may help those who do not respond well to PPIs include:
Sucralfate:Creates a protective layer on the stomach lining to defend against acid, with a monthly cost of around $20-$30.
Baclofen: Reduces relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, which prevents acid reflux. Monthly costs range from $15 to $40.
New Non-PPI Options
Emerging alternatives to standard PPIs, such as potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCABs), offer potential. Medications like vonoprazan act faster and may have fewer long-term negative effects than PPIs. Though not yet widely available, preliminary research suggests they could provide effective relief for chronic heartburn at a cost comparable to present treatments.
Combination Therapies
Recent research suggests that combining drugs, such as sucralfate and a PPI, can improve the efficacy of treatment for severe reflux. These mixes protect the esophagus by reducing acid production, providing total comfort. They also underline the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional to tailor medicines to individual needs, hence improving efficacy and cost-effectiveness.
Lifestyle Modifications for Heartburn Relief
Aside from medicine, lifestyle changes can considerably reduce heartburn symptoms.
Dietary Changes
Certain foods and drinks can trigger acid reflux.
Foods to Avoid: Avoid eating citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, coffee, and spicy or fatty foods.
Better Choices: Choose bananas, oats, lean meats, and non-citrus veggies.
Tip: Eating smaller, more frequent meals may help reduce symptoms.
Recent studies also show that limiting late-night eating and finishing meals at least three hours before bedtime can significantly reduce nocturnal heartburn. Choosing herbal teas like chamomile or ginger tea over caffeine-containing beverages might help relax the digestive tract and prevent reflux symptoms.
Weight Management
Carrying extra pounds can put stress on your stomach, leading to an exacerbation of acid reflux.
Why It Matters: Losing 5-10% of your body weight can help improve your symptoms.
How to Start: To achieve long-term weight loss, combine consistent physical exercise with a well-balanced diet.
According to new research, prioritizing core-strengthening activities such as yoga or Pilates not only helps with weight management but also improves digestive health by improving posture and relieving stomach pressure. Including these workouts in your weekly routine may also help reduce episodes of reflux.
Lifestyle Habits
Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
Sleeping Posture: Prop your head up with a wedge cushion and avoid eating within 2-3 hours of going to bed.
Avoid Tight Clothing: Loose clothing can help relieve abdominal pressure.
Choosing the Right Alternative
Personalized Approach
Everybody has various symptoms and needs. Take into account Remember:
Severity of your symptoms
Medical history
Budget and insurance coverage
Recent advances in pharmacogenomics suggest that genetic testing may soon be used to assist choose the best medicine for treating acid reflux. These tests may be able to predict how well your body will process particular medications, resulting in more targeted and effective therapies. Despite being in development, this strategy has the potential to reduce the guesswork associated in medicine selection.
Consult a Healthcare Provider
A physician can recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on your specific needs. Other solutions or alternative therapies may be equally effective as Dexilant but significantly less expensive.
Pharmacists can also help you identify more affordable solutions. Numerous pharmacies now provide consultation services to assist patients in understanding pharmaceutical options and potential savings schemes. These services may also include offering discount cards or access to manufacturer coupons, which can help make treatment more inexpensive.
Why Choose Our Online Pharmacy Referral Service?
If you require low-cost heartburn medicine, our online pharmacy referral service can help. Here’s the reason:
Affordable Options: We connect you with pharmacies that offer the most affordable prices for both prescription and non-prescription medications.
Convenience: Make purchases from the comfort of your own home and have medications delivered to your door.
Quality Assurance: Working with accredited pharmacies ensures the availability of safe and effective pharmaceuticals.
Support: Our team can assist you in finding the best treatment that fits your budget and matches your needs.
Conclusion
Heartburn can be properly treated without the high cost of Dexilant. Over-the-counter drugs including antacids and H2-receptor blockers, as well as prescription PPIs and generic versions, give cost-effective treatment. Adding lifestyle changes to these therapy can lead to better results.
Before commencing any drug, consult with a healthcare expert to determine the best option for your specific needs. If you’re looking for low-cost heartburn relief drugs, check out our online pharmacy referral service. Say goodbye to acid reflux without breaking the wallet.
365scriptcare.com is an established pharmacy referral service. Order brand name and generic equivalent drugs online from a trusted Canadian drug source. Log onto http://www.365scriptcare.com to see how you can buy discounted drug prices shipped to the USA from Canada.
0 notes
Text
Digital Commerce Platform Market Developments, Trends & Opportunities till 2032
Digital Commerce Platform Market provides in-depth analysis of the market state of Digital Commerce Platform manufacturers, including best facts and figures, overview, definition, SWOT analysis, expert opinions, and the most current global developments. The research also calculates market size, price, revenue, cost structure, gross margin, sales, and market share, as well as forecasts and growth rates. The report assists in determining the revenue earned by the selling of this report and technology across different application areas.
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key regions, with sales, revenue, market share and growth Rate of Digital Commerce Platform in these regions till the forecast period
North America
Middle East and Africa
Asia-Pacific
South America
Europe
Key Attentions of Digital Commerce Platform Market Report:
The report offers a comprehensive and broad perspective on the global Digital Commerce Platform Market.
The market statistics represented in different Digital Commerce Platform segments offers complete industry picture.
Market growth drivers, challenges affecting the development of Digital Commerce Platform are analyzed in detail.
The report will help in the analysis of major competitive market scenario, market dynamics of Digital Commerce Platform.
Major stakeholders, key companies Digital Commerce Platform, investment feasibility and new market entrants study is offered.
Development scope of Digital Commerce Platform in each market segment is covered in this report. The macro and micro-economic factors affecting the Digital Commerce Platform Market
Advancement is elaborated in this report. The upstream and downstream components of Digital Commerce Platform and a comprehensive value chain are explained.
Browse More Details On This Report at @https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com/market-reports/digital-commerce-platform-market-100549
Global Growth Insights
Web: https://www.globalgrowthinsights.com
Our Other Reports:
Laboratory Analytical Instrumentation MarketMarket Size
Global Energy Harvesting System MarketMarket Share
Global Parenteral Packaging MarketMarket Growth
Stem Cells MarketMarket
Clinical Reference Laboratory Services MarketMarket Share
Concrete Waterproofing Admixture MarketMarket Growth Rate
Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Treatment Devices MarketMarket Forecast
Global Ghee MarketMarket Size
Succulent Plant MarketMarket Growth
Vanadium Redox Battery (VRB) MarketMarket Analysis
SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) MarketMarket Size
Global Automotive Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) Sensors MarketMarket Share
Global Battery Management System MarketMarket Growth
Collaborative Robots MarketMarket
Urometer MarketMarket Share
Automotive Rubber Molded Components MarketMarket Growth Rate
Throat Lozenges MarketMarket Forecast
Global UVC LED MarketMarket Size
Vascular Surgery Minimally Invasive Surgical Instruments MarketMarket Growth
Medicinal Mushroom Extract MarketMarket Analysis
Nickel-plated Steel Sheet in Batteries MarketMarket Size
Global Augmented and Virtual Reality MarketMarket Share
Global C. difficile Infection Therapeutic Drug MarketMarket Growth
Orthopedic Biomaterials MarketMarket
Electric Vehicle Battery Swapping System MarketMarket Share
Capsule Endoscopy System MarketMarket Growth Rate
Fabric Softeners and Conditioners MarketMarket Forecast
Global Civilian Less Lethal and Self Defense Weapons MarketMarket Size
Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing and Contract MarketMarket Growth
Automotive Steering Systems MarketMarket Analysis
Cloud Crew Management System MarketMarket Size
Global Silicon Carbide Wafer MarketMarket Share
Global Solution Polymerized Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SSBR) MarketMarket Growth
Aircraft Interface Device MarketMarket
Beauty Jelly MarketMarket Share
Clone Imager MarketMarket Growth Rate
Graphite Polystyrene Foam Board Market Market Forecast
Global Pneumatic On-off Guns MarketMarket Size
Methyl Chloroform MarketMarket Growth
0 notes
Text
Nosocomial Infection Treatment Market Insights: Comprehensive Global Forecast (2023-2032)

The global demand for nosocomial infection treatment was valued at USD 30154.56 Million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 35720.76 Million in 2032, growing at a CAGR of 1.90% between 2024 and 2032.
The nosocomial infection treatment market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing incidence of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), advancements in diagnostic techniques, and the development of new and effective treatment options. Nosocomial infections, also known as healthcare-associated infections, are infections that patients acquire while receiving treatment for other conditions within a healthcare setting. Common HAIs include infections like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile (C. diff), urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and surgical site infections. The rising prevalence of these infections is attributed to factors such as the growing number of surgical procedures, prolonged hospital stays, the increasing use of invasive devices like catheters and ventilators, and the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Advancements in diagnostic technologies are playing a crucial role in the early detection and management of nosocomial infections. Rapid diagnostic tests and molecular diagnostic tools have significantly improved the ability to quickly identify pathogens, allowing for timely and targeted treatment. This is particularly important in controlling the spread of infections within healthcare facilities and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, the development of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technologies has enabled precise identification of microbial strains, aiding in the selection of appropriate antimicrobial therapies.
The treatment landscape for nosocomial infections is evolving with the introduction of new antibiotics, antifungals, and antiviral agents. The growing problem of antibiotic resistance has spurred research and development efforts to discover novel antimicrobial agents that are effective against resistant strains. Pharmaceutical companies are also exploring combination therapies that enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics and reduce the risk of resistance development. Immunotherapy and bacteriophage therapy are emerging as promising alternatives, offering targeted approaches to infection treatment.
The key findings of the study on the nosocomial infection treatment market highlight the current state of the market, its driving factors, challenges, and future prospects. These findings provide valuable insights into the dynamics of the market and its growth trajectory. Here are the key findings:
1. Rising Incidence of Nosocomial Infections
The study reveals a significant increase in the prevalence of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) globally. Factors contributing to this rise include the growing number of surgical procedures, increased use of invasive devices, longer hospital stays, and the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Common HAIs such as MRSA, C. difficile, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and surgical site infections are major concerns for healthcare facilities.
2. Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies
Rapid advancements in diagnostic technologies are enhancing the early detection and precise identification of pathogens causing HAIs. The development and adoption of rapid diagnostic tests, molecular diagnostics, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are improving the speed and accuracy of diagnosis. This allows for timely and targeted treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes and controlling the spread of infections.
3. Emergence of Novel Antimicrobial Agents
The growing problem of antibiotic resistance is driving research and development efforts to discover new antimicrobial agents. Pharmaceutical companies are focusing on the development of novel antibiotics, antifungals, and antiviral agents that are effective against resistant strains. Combination therapies, immunotherapy, and bacteriophage therapy are emerging as promising treatment approaches, offering targeted solutions to combat resistant infections.
4. Importance of Infection Control Measures
The study emphasizes the critical role of infection control measures in reducing the incidence of HAIs. Healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting stringent hygiene practices, antimicrobial stewardship programs, and advanced sterilization and disinfection technologies. The implementation of infection control guidelines and protocols by regulatory bodies such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) has further bolstered efforts to prevent HAIs.
5. Aging Population and Chronic Diseases
The growing aging population and the rise in chronic diseases such as diabetes and cancer contribute to the increased risk of HAIs. Older adults and individuals with chronic conditions often require frequent hospital visits and medical procedures, making them more susceptible to infections. This demographic trend underscores the need for effective nosocomial infection treatments and preventive measures.
6. Regional Variations
The study identifies regional variations in the nosocomial infection treatment market. North America and Europe dominate the market due to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and strong regulatory frameworks. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by increasing healthcare investments, rising awareness about infection control, and the growing burden of HAIs in countries like China and India. Latin America and the Middle East and Africa are gradually improving their healthcare systems, focusing on enhancing infection control measures.
7. Competitive Landscape
The market is highly competitive, with major players focusing on strategic collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, and product innovations to strengthen their market positions. Leading companies such as Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Johnson & Johnson, and GlaxoSmithKline plc are continuously investing in R&D to develop new antimicrobial agents and improve existing treatments. Emerging players are also contributing to market growth with innovative solutions and targeted therapies.
8. Future Prospects
The nosocomial infection treatment market is poised for robust growth, driven by the rising prevalence of HAIs, advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic technologies, and increased efforts towards infection prevention and control. The continuous evolution of treatment options, the implementation of stringent infection control measures, and the growing adoption of advanced technologies will be crucial in addressing the challenges posed by nosocomial infections and improving patient care outcomes in healthcare settings.
Key Players:
3M Company
Abbott Laboratories
Advanced Sterilization Products Services Inc. (ASP)
Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
Belimed AG
BioMérieux SA
Cantel Medical Corp.
Getinge Group
Johnson & Johnson
Merck & Co., Inc.
Pfizer Inc.
Roche Diagnostics Corporation
Stryker Corporation
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Steris Corporation
Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc.
Ansell Limited
Molnlycke Health Care AB
Cantel Medical Corp.
More About Report- https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/nosocomial-infection-treatment-market
The nosocomial infection treatment market exhibits distinct regional characteristics, driven by variations in healthcare infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, awareness levels, and prevalence of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). Here's an overview of the regional insights:
North America
Key Characteristics:
Advanced Healthcare Infrastructure: North America, particularly the United States, boasts a highly advanced healthcare system with well-equipped hospitals and clinics. This supports the adoption of advanced diagnostic and treatment technologies for nosocomial infections.
High Healthcare Expenditure: The region's significant healthcare spending enables substantial investment in infection control measures, antimicrobial research, and the implementation of advanced treatment protocols.
Strong Regulatory Framework: Agencies like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforce stringent guidelines and regulations for infection control and the approval of new treatments.
Research and Development Hub: North America is a major hub for pharmaceutical and biotechnology research, leading to the continuous development of novel antimicrobial agents and diagnostic tools.
Europe
Key Characteristics:
Robust Infection Control Policies: Europe has established comprehensive infection control policies and guidelines, supported by organizations such as the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC).
High Awareness and Education: There is a high level of awareness and education regarding HAIs among healthcare professionals and the general public, promoting adherence to hygiene and infection control practices.
Government Initiatives: European governments actively invest in healthcare infrastructure and infection control programs, facilitating better management and treatment of nosocomial infections.
Collaborative Research: Europe benefits from collaborative research initiatives and funding from the European Union, driving advancements in diagnostics and treatments for HAIs.
Asia-Pacific
Key Characteristics:
Rapidly Developing Healthcare Infrastructure: The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in healthcare infrastructure, particularly in countries like China, India, and Japan. This expansion supports the increased adoption of advanced medical technologies.
Rising Prevalence of HAIs: The growing burden of HAIs in densely populated countries necessitates effective infection control and treatment strategies.
Increasing Healthcare Investments: Governments in the region are investing heavily in healthcare improvements, including infection prevention and control measures.
Awareness and Education Campaigns: Efforts to raise awareness about the importance of infection control are gaining momentum, leading to better implementation of hygiene practices and protocols.
Latin America
Key Characteristics:
Developing Healthcare Systems: Latin American countries are working towards improving their healthcare systems, with a focus on enhancing infection control measures and access to advanced treatments.
High Burden of HAIs: The prevalence of HAIs is relatively high, driving the need for effective diagnostic and therapeutic solutions.
Government and NGO Initiatives: Both government bodies and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are playing active roles in promoting infection control and funding healthcare improvements.
Middle East and Africa
Key Characteristics:
Emerging Healthcare Infrastructure: The region is witnessing gradual improvements in healthcare infrastructure, with a focus on modernizing hospitals and clinics.
High Infection Rates: The high incidence of HAIs, coupled with limited resources, presents significant challenges in infection control and treatment.
Government Efforts: Governments are increasingly prioritizing healthcare investments and infection control programs to address the rising burden of HAIs.
International Support: International organizations and partnerships are providing support for healthcare improvements and infection control initiatives.
Segmentation:
By Type of infection
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Surgical Site Infections (SSIs)
Pneumonia
Bloodstream Infections
Gastrointestinal Infections
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
By Treatment Type
Antibiotics
Antifungal Agents
Antiviral Drugs
Surgical Interventions
Supportive Care
By End User
Hospitals
Long-Term Care Facilities
Ambulatory Surgical Centers
Clinics and Outpatient Settings
Home Healthcare
Browse the full report – https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/nosocomial-infection-treatment-market
Browse Our Blog: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/nosocomial-infection-treatment-market-pmq0f
Contact Us:
Phone: +91 6232 49 3207
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.credenceresearch.com
0 notes
Text
Antimicrobial Coatings in Action_ Real-World Case Studies and Success Stories with Chuck Brodsky (DC)
Charles Brodsky DC
Antimicrobial Coatings in Action: Real-World Case Studies and Success Stories with Chuck Brodsky (DC)
Antimicrobial coatings have emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in hospitals and healthcare facilities. These coatings, which are applied to environmental surfaces such as walls, floors, and medical equipment, help to inhibit the growth and spread of harmful microorganisms, reducing the risk of infections among patients and healthcare workers. In this blog, we will explore real-world case studies and success stories that highlight the effectiveness of antimicrobial coatings in healthcare settings, showcasing their impact on infection prevention and patient safety.
Case Study: Reduced Infection Rates
One notable case study comes from a large hospital system that implemented antimicrobial coatings on high-touch surfaces throughout its facilities. After the application of the coatings, the hospital observed a significant reduction in the incidence of HAIs among patients. Specifically, rates of infections such as MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and C. difficile (Clostridioides difficile) decreased, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
The success of this case study underscores the importance of antimicrobial coatings in preventing the transmission of pathogens within healthcare environments. By creating a protective barrier on surfaces, these coatings with the help of experts like Chuck Brodsky (DC) help to minimize the risk of contamination and subsequent infections, ultimately contributing to better patient care and safety.
Success Story: Enhanced Environmental Hygiene
Another success story comes from a research hospital that adopted antimicrobial coatings as part of its infection control measures. By incorporating these coatings into its environmental hygiene protocols with the help of experts like Chuck Brodsky (DC), the hospital was able to maintain cleaner and more hygienic surfaces, even in high-traffic areas such as patient rooms and operating theaters.
As a result, the hospital saw a decrease in the prevalence of healthcare-associated infections, as well as a reduction in the spread of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs). Healthcare workers also reported feeling more confident in their ability to provide safe and effective care, knowing that the risk of cross-contamination from environmental surfaces had been significantly mitigated.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of antimicrobial coatings are clear, their implementation in healthcare settings can present challenges. One common obstacle is the need for thorough surface preparation prior to coating application, which may require extensive cleaning and disinfection to remove existing biofilms and contaminants.
To address this challenge, hospitals and facilities may need to invest in specialized cleaning protocols and equipment to ensure that surfaces are properly prepared for coating. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of antimicrobial coatings over time.
Cost-Effectiveness and Return on Investment
Despite the initial investment required for the application of antimicrobial coatings, many hospitals have found that the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. By reducing the incidence of HAIs and associated complications, hospitals can save significant amounts of money on healthcare expenditures, including treatment costs, extended hospital stays, and additional resources required for infection control measures.
Furthermore, the intangible benefits of improved patient outcomes and satisfaction cannot be overlooked. Hospitals that prioritize infection prevention and patient safety through the use of antimicrobial coatings demonstrate their commitment to quality care and accountability, which can enhance their reputation and competitiveness in the healthcare industry.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
As the use of antimicrobial coatings becomes more widespread, hospitals must ensure compliance with regulatory guidelines and standards governing their use. This includes considerations such as safety testing, environmental impact assessments, and adherence to antimicrobial efficacy requirements.
By working closely with regulatory agencies and manufacturers, hospitals can ensure that they are using antimicrobial coatings responsibly and effectively. This may involve conducting regular audits and inspections to verify compliance with regulatory requirements and address any issues or concerns that arise.
Future Directions and Innovations
Looking ahead, the field of antimicrobial coatings continues to evolve with advancements in technology and research. Innovations such as nanotechnology-based coatings, self-disinfecting surfaces, and antimicrobial peptides hold promise for further improving infection prevention and control in healthcare settings.
As hospitals strive to stay ahead of emerging pathogens and antimicrobial resistance threats, they will likely continue to explore new strategies and technologies for enhancing environmental hygiene and patient safety. By embracing innovation and collaboration with the help of experts like Chuck Brodsky (DC), healthcare facilities can leverage the power of antimicrobial coatings to protect the health and well-being of patients and staff alike.
Patient and Staff Satisfaction
In addition to the tangible benefits of reduced infection rates and improved environmental hygiene, the implementation of antimicrobial coatings in hospitals can also lead to increased patient and staff satisfaction. Patients and their families often perceive hospitals that prioritize infection prevention measures, such as antimicrobial coatings, as safer and more trustworthy institutions.
By demonstrating a commitment to patient safety and well-being with the help of experts like Chuck Brodsky (DC), hospitals can enhance the overall patient experience and build stronger relationships with their communities. Additionally, healthcare workers who feel supported in their efforts to maintain a clean and hygienic environment may experience higher job satisfaction and morale, leading to increased retention rates and a more positive work culture.
Including patient and staff satisfaction as a key outcome of antimicrobial coating implementation reinforces the importance of creating a holistic approach to infection prevention and environmental hygiene in healthcare settings. By prioritizing the well-being of both patients and healthcare workers, hospitals can create a safer, more supportive environment for everyone involved.
Antimicrobial coatings represent a valuable tool in the ongoing efforts to prevent healthcare-associated infections and promote patient safety in hospitals. Through real-world case studies and success stories, we have seen how the implementation of these coatings can lead to reduced infection rates, enhanced environmental hygiene, and increased patient and staff satisfaction.
Despite implementation challenges and regulatory considerations, the long-term benefits of antimicrobial coatings far outweigh the costs, making them a worthwhile investment for hospitals and healthcare facilities. As the field of antimicrobial coatings continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements and innovations that contribute to safer, healthier healthcare environments for all.
By embracing the science of antimicrobial coatings and incorporating them into comprehensive infection prevention strategies with the help of experts like Chuck Brodsky (DC), hospitals can create environments that prioritize patient safety, support staff well-being, and ultimately improve the quality of care for all patients.
0 notes
Photo


ialling 'poo pills' to flush out dangerous superbugsUK doctors are attempting to clear dangerous superbug infections using "poo pills" containing freeze-dried faeces.The stool samples come from healthy donors and are packed with good bacteria.Early data suggests superbugs can be flushed out of the dark murky depths of the bowel and replaced with a mix of healthy gut bacteria.It is a new approach to tackling infections that resist antibiotics, which are thought to kill a million people each year.The focus is on the bowels which are "the biggest reservoir of antibiotic resistance in humans" says Dr Blair Merrick, who has been testing the pills at Guys and St Thomas' hospitals.Drug-resistant superbugs can escape their intestinal home and cause trouble elsewhere in the body – such as urinary tract or bloodstream infections."So there's a lot of interest in 'can you get rid of them from the gut?'," says Dr Merrick.The idea of poo-pills isn't as far-fetched as it might seem. Faecal transplants – also known as a trans-poo-tion - are already approved for treating severe diarrhoea caused by Clostridium difficile bacteria.But scientists noticed hints that faecal transplants for C. difficile also seemed to get rid of superbugs.New research has focused on patients who had an infection caused by drug-resistant bacteria in the past six months.They were given pills made from faeces which people had donated to a stool bank.Each stool sample is tested to ensure it does not contain any harmful bugs, undigested food is removed and then it is freeze dried into a powder.This is stored inside a pill that can pass through the stomach unscathed and reach the intestines where it dissolves to release its poopy powdery payload.The stool samples were tested to ensure they did not contain anything dangerousThe trial has taken place on 41 patients at Guy's and St Thomas' hospitals in London to lay the groundwork for a large-scale study. It showed patients were up for taking a poo pill and the donated bacteria were still being detected in the bowels at least a month later.Dr Merrick says there are "really promising signals" that poo pills could help tackle the rising scourge of superbugs and that donor bacteria could be going to microbial war with the superbugs as they compete over food and space on the lining of the gut and either rid the body of them completely or "reduce them down to a level that doesn't cause problems".The study also suggests the array of gut bacteria becomes more varied after the therapy. This is a sign of good health and "may well be promoting colonisation resistance" so it is harder for new infectious bugs to get in."It's very exciting. There's a real shift from 20 years ago where all bacteria and viruses were assumed to do you harm; to now where we realise they are completely necessary to our overall health," says Dr Merrick.Earlier this week scientists showed the good bacteria our bodies meet – in the hours after we are born – seem to halve the risk of young children being admitted to hospital with lung infections.Our body's own human cells are outnumbered by the bacteria, fungi and others that live inside us - known as the microbiome.This has led to research implicating the microbiome in everything from Crohn's disease to cancer to mental health. If poo pills are proven to work against superbugs in larger studies then the researchers think they could be used for both treatment and prevention in people at risk. Medical procedures that suppress the immune system - including cancer therapies and organ transplants - can make the body more vulnerable."A lot of these individuals come to a lot of harm from drug resistant organisms," Dr Merrick.The UK's drugs regulator – the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) – said there were more than 450 microbiome medicines currently in development."Some of them will succeed, so I do think we will see them coming through quite soon," said Dr Chrysi Sergaki, the head of microbiome researc
0 notes