#Microsoft Azure vs Amazon AWS
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, two giants stand out as the go-to choices for businesses and individuals alike: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. As organisations increasingly migrate their infrastructure to the cloud, understanding the key differences and similarities between these two leading platforms becomes crucial. In this comprehensive overview, we’ll delve into the core aspects that differentiate AWS and Azure, helping you make informed decisions about which cloud provider aligns best with your needs.
#AWS#Azure#Cloud Computing#Amazon Web Services#Microsoft Azure#Cloud Service Providers#Cloud Infrastructure#Cloud Comparison#AWS vs Azure#Cloud Services#Decision Making#Cloud Migration#Technology Overview
0 notes
Text
Internet Solutions: A Comprehensive Comparison of AWS, Azure, and Zimcom
When it comes to finding a managed cloud services provider, businesses often turn to the industry giants: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. These tech powerhouses offer highly adaptable platforms with a wide range of services. However, the question that frequently perplexes businesses is, "Which platform truly offers the best value for internet solutions Surprisingly, the answer may not lie with either of them. It is essential to recognize that AWS, Azure, and even Google are not the only options available for secure cloud hosting.
In this article, we will conduct a comprehensive comparison of AWS, Azure, and Zimcom, with a particular focus on pricing and support systems for internet solutions.
Pricing Structure: AWS vs. Azure for Internet Solutions
AWS for Internet Solutions: AWS is renowned for its complex pricing system, primarily due to the extensive range of services and pricing options it offers for internet solutions. Prices depend on the resources used, their types, and the operational region. For example, AWS's compute service, EC2, provides on-demand, reserved, and spot pricing models. Additionally, AWS offers a free tier that allows new customers to experiment with select services for a year. Despite its complexity, AWS's granular pricing model empowers businesses to tailor services precisely to their unique internet solution requirements.
Azure for Internet Solutions:
Microsoft Azure's pricing structure is generally considered more straightforward for internet solutions. Similar to AWS, it follows a pay-as-you-go model and charges based on resource consumption. However, Azure's pricing is closely integrated with Microsoft's software ecosystem, especially for businesses that extensively utilize Microsoft software.
For enterprise customers seeking internet solutions, Azure offers the Azure Hybrid Benefit, enabling the use of existing on-premises Windows Server and SQL Server licenses on the Azure platform, resulting in significant cost savings. Azure also provides a cost management tool that assists users in budgeting and forecasting their cloud expenses.
Transparent Pricing with Zimcom’s Managed Cloud Services for Internet Solutions:
Do you fully understand your cloud bill from AWS or Azure when considering internet solutions? Hidden costs in their invoices might lead you to pay for unnecessary services.
At Zimcom, we prioritize transparent and straightforward billing practices for internet solutions. Our cloud migration and hosting services not only offer 30-50% more cost-efficiency for internet solutions but also outperform competing solutions.
In conclusion, while AWS and Azure hold prominent positions in the managed cloud services market for internet solutions, it is crucial to consider alternatives such as Zimcom. By comparing pricing structures and support systems for internet solutions, businesses can make well-informed decisions that align with their specific requirements. Zimcom stands out as a compelling choice for secure cloud hosting and internet solutions, thanks to its unwavering commitment to transparent pricing and cost-efficiency.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cloud Computing in Africa: Why Local Startups Are Saving 40% on IT Costs

Cloud computing adoption in Africa has reached a remarkable milestone, with 45% of African business workloads already on the public cloud. We're witnessing a significant digital transformation across the continent as local startups embrace these technologies to dramatically reduce their IT costs. According to recent McKinsey research, the global cloud value is projected at $3 trillion, with $797 billion of this value sitting in Africa and Europe.
What is cloud computing exactly, and why has it become so critical for African businesses? At its core, cloud computing provides scalable, cost-effective IT solutions that support digital transformation across industries. The benefits of cloud computing for African startups are particularly compelling – it currently accounts for an average of 38% of total IT expenditure among organizations surveyed, compared to the projected global cloud spend of about 50% by 2025. Additionally, the types of cloud computing options available, particularly public cloud services, are gaining popularity because they allow companies to quickly provision resources. This trend is accelerating primarily due to businesses' need for faster time-to-market.
In this article, we'll explore how African startups are leveraging cloud computing to save up to 40% on IT costs, examine the leading cloud service providers in South Africa and across the continent, and address the unique challenges and opportunities in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Why African Startups Are Turning to Cloud
African startups enjoy a unique advantage when adopting cloud technologies – the absence of extensive legacy systems that often hamper digital transformation elsewhere. This "leapfrog effect" allows businesses to embrace modern cloud solutions without the burden of technical debt.
Limited Legacy Infrastructure and Technical Debt
Legacy systems across Africa typically create significant barriers to innovation. These outdated technologies require constant maintenance, struggle with modern integration, and consume valuable resources. Furthermore, organizations spend weeks on system upgrades, diverting engineers from more valuable projects. When Old Mutual migrated to cloud services, they eliminated these version updates entirely, reducing upgrade time from 2-4 weeks to zero days. Subsequently, many African businesses recognize that freedom from technical debt enables faster digital adoption and innovation.
Public Cloud vs Private Cloud in African Context
African companies overwhelmingly prefer public cloud solutions over private infrastructure. Research indicates that approximately 45% of African business workloads run on public cloud platforms, while merely 23% utilize private cloud environments. This preference stems primarily from infrastructure limitations that make establishing private cloud at scale challenging across the continent. Currently, 50% of African companies have adopted cloud capabilities throughout most parts of their business, with projections showing 61% will have all operations cloud-based within two years. Nevertheless, only 12% of these businesses demonstrate high cloud maturity.
Cloud Service Providers in South Africa and Nigeria
In South Africa, Google Cloud leads with 41% market share, followed by Microsoft Azure at 35% and Amazon Web Services at 21%. Google's January launch of its Johannesburg cloud region significantly boosted its position. Conversely, in Nigeria, despite five local providers lobbying for government contracts, over 70% of government ministries and agencies still host data on AWS and Microsoft Azure. Local Nigerian providers include CloudFlex Computing, Cybercloud Platform, Layer3Cloud, and Velvot. Essentially, while international hyperscalers dominate, growing investment in local cloud infrastructure positions Africa for substantial growth in this sector.
How Startups Are Saving 40% on IT Costs
Switching to cloud services creates immediate financial impact for African startups, often cutting IT expenses by up to 40% through several innovative approaches.
Pay-as-You-Go Pricing Models vs Traditional CapEx
The fundamental shift from capital expenditure (CapEx) to operational expenditure (OpEx) represents perhaps the most significant cost advantage. Unlike traditional IT infrastructure requiring substantial upfront investments, cloud computing operates on a subscription basis with no initial capital outlay. This transition brings multiple financial benefits:
OpEx costs are fully tax-deductible within the same year, unlike CapEx which must be depreciated over several years
Pay-as-you-go pricing means businesses pay only for resources actually consumed
Small and medium enterprises using cloud solutions reduce IT costs by approximately 36%
Reduced Hardware and Maintenance Overheads
Cloud adoption eliminates numerous expenses associated with physical infrastructure. Beyond initial hardware costs, startups avoid ongoing maintenance expenses as cloud providers handle all infrastructure management. Moreover, businesses require less physical space for servers, reducing associated security and energy costs. Since vendors manage all updates and upgrades, IT teams can focus on innovation rather than maintenance.
Elastic Scaling for Seasonal Demand
Traditional infrastructure requires overprovisioning to handle peak loads, resulting in wasted resources during normal operations. In contrast, cloud elasticity allows African startups to instantly scale resources up or down based on actual demand. This approach proves especially valuable for businesses experiencing seasonal fluctuations or unpredictable traffic patterns. Auto-scaling systems automatically adjust resources using real-time data, eliminating manual intervention.
Serverless Architectures for Cost Efficiency
Serverless computing represents the ultimate cost optimization strategy. For startups with websites serving fewer than 1,000 visitors, switching to serverless can slash backend maintenance costs by up to 90%. Real-world examples demonstrate dramatic savings—Heavywater reduced monthly infrastructure costs from ZAR 72,002 to just ZAR 540. Similarly, Postlight cut expenses from ZAR 180,005 to merely ZAR 6,660 monthly. At approximately ZAR 3.60 per million requests, serverless architecture eliminates costs during idle periods.
Sector-Specific Use Cases Driving Cloud ROI
Cloud adoption across Africa shows how sector-specific implementations yield substantial returns on investment. Throughout different industries, cloud solutions address unique challenges while providing tangible benefits.
Fintech: M-Pesa and Cloud-Native Mobile Payments
Safaricom's M-PESA exemplifies successful cloud migration in African fintech. After implementing Red Hat OpenShift cloud platform, this mobile payment system now supports 51 million customers conducting over ZAR 5652.17 billion in annual transactions. The cloud migration yielded remarkable improvements: system availability increased from 93% to 99.98%, deployment times halved, and cluster deployment time reduced from two days to just two hours. Most notably, Safaricom launched Hustler Fund—a digital financial inclusion initiative—in merely one month from concept to market.
Healthcare: Cloud-Based Patient Record Systems
Healthcare facilities across Africa increasingly adopt cloud-based Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems to overcome paper-based record limitations. These cloud solutions address critical challenges including real-time access constraints, inability to share data among stakeholders, and incomplete medical information. In South Africa, the Netcare Group implemented a cloud-based electronic medical record system enabling healthcare workers to access patient information instantly via mobile devices. This technology facilitates multi-disciplinary collaboration through shared access to patient records, improving treatment outcomes.
Retail: Inventory and CRM on SaaS Platforms
Retail businesses leverage cloud-based inventory management to avoid costly stock issues. Cloud platforms help prevent both stockouts (which risk losing customers to competitors) and excess inventory (which ties up capital in unsold goods). SaaS-based inventory systems enable real-time tracking across multiple locations, identifying consumer behavior trends, and implementing just-in-time inventory strategies. African retailers particularly benefit from cloud CRM solutions, which allow sales, production, billing, customer service, and distribution departments to collaborate effectively through shared data access.
Education: E-learning Platforms on IaaS
Africa's e-learning market, valued at USD 3,411.38 million in 2024, demonstrates cloud computing's educational impact. Cloud infrastructure powers numerous platforms addressing geographical barriers to education. With over 500 million Africans online by 2023, these platforms deliver affordable education to remote areas. Organizations like FAO, UNESCO, and WHO offer specialized e-learning resources through cloud platforms, creating accessible learning opportunities across various disciplines. These solutions prove particularly valuable given that 98 million children in sub-Saharan Africa remain out of school.
Challenges and Strategic Responses
Although cloud computing offers substantial benefits, African startups must navigate several critical challenges. These hurdles require strategic responses to ensure successful adoption across the continent.
Data Residency Laws in Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa
Regulatory compliance stands as the foremost barrier to cloud adoption, with over 50% of leading African firms citing legal constraints as their primary obstacle. Kenya's Data Protection Act mandates that strategically important state data must be processed through servers located within Kenya. Likewise, Nigeria enforces strict data localization, requiring financial institutions to store customer data locally under the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation. This has forced companies like Flutterwave to adopt hybrid cloud strategies, storing sensitive financial data on local servers. South Africa's Data and Cloud policy, published in May 2024, asserts data sovereignty rights yet aims to enable cross-border data transfers through collaborative partnerships.
Shortage of Cloud Talent and Upskilling Initiatives
The technical skills gap presents another major challenge. Africa will require over 700,000 cloud engineers by 2030 to support digital transformation efforts. Currently, 79% of South African businesses report difficulty hiring tech talent. In response, several upskilling programs have emerged. Google Cloud has partnered with NEMISA to offer cybersecurity training for up to 12,000 students. AWS has expanded its re/Start cloud training program to nine African countries. Meanwhile, Vodacom aims to upskill 1 million young people across eight African nations by 2027.
Connectivity and Power Supply Constraints
Unreliable infrastructure further complicates cloud adoption. Load shedding in South Africa alone cost the economy an estimated R1.6 trillion in 2023. Ironically, these power challenges are driving cloud migration as businesses seek to mitigate disruptions. Many cloud providers already maintain backup electricity systems, allowing companies to transfer power reliability concerns to their providers. Beyond power issues, limited internet connectivity hinders cloud usage, primarily in rural areas.
Multi-cloud Adoption to Avoid Vendor Lock-in
To address these challenges, businesses increasingly implement multi-cloud strategies. Approximately half of organizations now use more than one public cloud provider. This approach reduces dependency on single vendors, minimizes downtime risks, and provides flexibility to navigate regulatory requirements. However, managing multiple cloud environments introduces complexity through differing tools, security protocols, and skills requirements.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has undeniably transformed the African startup ecosystem, offering a compelling combination of cost savings and operational efficiency. African businesses now save approximately 40% on IT costs while gaining access to enterprise-grade technology previously beyond their reach. This technological shift particularly benefits the continent because many companies can bypass legacy infrastructure challenges entirely.
The public cloud dominance across Africa reflects both infrastructure realities and strategic business decisions. Companies choose flexible, scalable solutions that align with their growth trajectories rather than investing in costly private infrastructure. Consequently, we see rapid adoption across sectors from fintech to healthcare, each demonstrating remarkable returns on investment.
Pay-as-you-go models stand out as the primary financial advantage, eliminating substantial upfront investments that would otherwise create significant barriers to entry. Additionally, serverless architectures present particularly dramatic savings, with some companies reducing monthly costs by over 99% compared to traditional infrastructure approaches.
Nevertheless, challenges remain. Data residency laws continue to evolve across countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa, creating compliance complexities. Furthermore, the talent shortage represents a critical bottleneck despite numerous upskilling initiatives. Power and connectivity constraints likewise persist, though ironically, these limitations often accelerate cloud adoption as businesses seek reliability.
Looking ahead, multi-cloud strategies will likely become standard practice as African businesses balance regulatory requirements with service availability. Though adoption has grown significantly, substantial untapped potential remains across the continent. African startups that embrace cloud technologies today position themselves for remarkable competitive advantages tomorrow, creating a foundation for innovation that extends well beyond simple cost savings.
FAQs
Q1. How much are African startups saving on IT costs by using cloud computing? African startups are saving up to 40% on IT costs by adopting cloud computing solutions. This significant reduction is primarily due to pay-as-you-go pricing models, reduced hardware and maintenance overheads, and the ability to scale resources based on demand.
Q2. What are the main advantages of cloud computing for African businesses? The main advantages include cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. Cloud computing allows businesses to avoid large upfront investments in hardware, provides access to enterprise-grade technology, and enables companies to quickly adjust their IT resources based on their needs.
Q3. Which sectors in Africa are benefiting the most from cloud computing? Several sectors are seeing significant benefits from cloud adoption, including fintech, healthcare, retail, and education. For example, fintech companies are leveraging cloud-native mobile payment systems, while healthcare providers are implementing cloud-based patient record systems for improved efficiency.
Q4. What challenges do African startups face when adopting cloud computing? The main challenges include data residency laws in countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa, a shortage of skilled cloud professionals, connectivity and power supply constraints, and concerns about vendor lock-in. However, businesses are developing strategies to address these issues.
Q5. How are African companies addressing the shortage of cloud talent? To address the skills gap, various upskilling initiatives have been launched. Companies like Google Cloud and AWS are partnering with local organizations to provide cloud training programs. Additionally, some telecom companies are investing in upskilling millions of young people across multiple African countries to meet the growing demand for cloud professionals.
#CloudComputingAfrica#AfricanStartups#CloudSavings#DigitalAfrica#TechInAfrica#CloudInSouthAfrica#UAECloudSolutions#IndiaCloudTech#SmartITInvestments#CloudForStartups#DubaiTechStartups#SouthAfricaInnovation#IndianTechLeaders#CloudTransformation#DigitalGrowthAfrica#AffordableCloudSolutions#EmergingMarketsTech#DevOpsAfrica#CloudInfrastructureIndia#DigitalDubai
0 notes
Text
Generative AI Coding Assistants Market Gains Momentum in Agile and DevOps Workflows
TheGenerative AI Coding Assistants Market Size was valued at USD 18.34 Million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 139.55 Million by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 25.4% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Generative AI Coding Assistants Market is rapidly transforming the software development landscape as developers across industries adopt AI-powered tools to enhance code efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. These assistants are redefining workflows, supporting real-time suggestions, debugging, and code refactoring at scale, especially in high-demand environments like enterprise IT, fintech, and SaaS platforms.
U.S. Market Sees Strong Adoption in Enterprise DevOps and Cloud-Native Projects
Generative AI Coding Assistants Market continues to gain traction as organizations seek intelligent coding support that integrates seamlessly with development pipelines. With rising pressure to deliver quality software faster, businesses in the U.S. and beyond are investing in AI assistants to reduce manual overhead, lower error rates, and optimize team collaboration.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6493
Market Keyplayers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) (Amazon CodeWhisperer, AWS Cloud9)
CodeComplete (CodeComplete AI Assistant, CodeComplete API)
CodiumAI (CodiumAI Test Generator, CodiumAI Code Review Assistant)
Databricks (Databricks AI Code Assistant, Databricks Lakehouse AI)
GitHub (GitHub Copilot, GitHub Copilot X)
GitLab (GitLab Duo, GitLab Code Suggestions)
Google LLC (Google Gemini Code Assist, Vertex AI Codey)
IBM (IBM Watsonx Code Assistant, IBM AI for Code)
JetBrains (JetBrains AI Assistant, JetBrains Fleet)
Microsoft (Microsoft Copilot for Azure, Visual Studio IntelliCode)
Replit (Replit Ghostwriter, Replit AI Code Chat)
Sourcegraph (Sourcegraph Cody, Sourcegraph Code Search)
Tableau (Tableau AI Code Generator, Tableau GPT)
Tabnine (Tabnine AI Autocomplete, Tabnine Pro)
Market Analysis
The market is witnessing significant growth due to the increasing complexity of software systems and the shortage of skilled developers. Generative AI coding tools address these gaps by enabling faster prototyping, enforcing code standards, and improving time-to-market for digital products. The U.S. leads in adoption, driven by tech-forward enterprises and a strong innovation ecosystem, while Europe is focusing on ethical AI integration and data compliance in development tools.
Market Trends
Surge in demand for pair-programming AI tools like GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer
Integration of coding assistants into IDEs (VS Code, JetBrains, etc.) for seamless workflow
Enhanced support for multiple programming languages and frameworks
Use of LLMs (Large Language Models) to improve context-aware suggestions
AI-driven code documentation, test case generation, and refactoring
Emphasis on ethical AI use and bias reduction in automated code generation
Collaborative tools allowing AI assistants to align with team coding conventions
Market Scope
The Generative AI Coding Assistants Market is expanding across industries, empowering both experienced developers and newcomers with intelligent support systems. These tools are not only increasing code speed and quality but also democratizing software creation through intuitive interfaces.
Real-time syntax and logic suggestions
Automated bug detection and correction
Support for agile and DevOps workflows
Enhanced code security through AI-enabled scans
Integration with CI/CD and cloud platforms
Scalable solutions for startups to large enterprises
Forecast Outlook
The outlook for the Generative AI Coding Assistants Market is highly optimistic. As digital transformation accelerates globally, coding assistants are expected to become standard across development environments. Future trends point toward even deeper integration with DevSecOps pipelines, greater multilingual code support, and proactive AI co-pilots that anticipate developer intent. With the U.S. spearheading adoption and Europe ensuring regulatory robustness, the market is poised for widespread maturity.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/generative-ai-coding-assistants-market-6493
Conclusion
The Generative AI Coding Assistants Market represents a paradigm shift in how software is written and maintained. By blending artificial intelligence with human creativity, these tools are streamlining development cycles, enhancing code reliability, and driving innovation at every level. As businesses race to modernize their tech stacks, adopting intelligent coding assistants will be a competitive advantage—not just a convenience.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Related Reports:
U.S.A Enterprise A2P SMS Market continues to expand with rising adoption in customer engagement platforms
U.S.A Fleet Management Software Market Poised for Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Real-Time Tracking
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
Mail us: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Which is Better for Your Business: Cloud-Based or Web-Based Solutions?

As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, one of the most important decisions they face is choosing between cloud-based vs web-based solutions. While both offer distinct advantages, understanding their differences and how they align with your business needs is crucial. With the rapid shift to remote work, scalability needs, and the growing reliance on software-as-a-service (SaaS), this decision can have a profound impact on your business’s efficiency, security, and cost structure.
In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamental differences between cloud-based and web-based solutions, discuss the unique benefits and limitations of each, and help you make an informed decision on which technology is best suited for your organization.
Understanding Cloud-Based vs Web-Based Solutions
To start, it’s important to clarify what we mean by cloud-based vs web-based solutions. While both types of systems can be accessed via the internet, they have key distinctions in how they operate and where they store and process data.
Cloud-Based Solutions: These are services that run on remote servers (the cloud) and are typically accessed over the internet via a web browser or a dedicated application. Cloud-based systems offer greater flexibility in terms of scalability, as businesses can increase or decrease their resource usage depending on their needs. Popular cloud-based platforms include Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
Web-Based Solutions: Web-based applications, on the other hand, are software that runs directly in a web browser. Unlike cloud-based solutions, which often involve storing and processing data remotely, web-based apps may or may not rely on the cloud. They are usually designed to offer a simpler interface, and the data they work with may be stored on a local server or the internet.
The key difference comes down to the infrastructure and the extent to which data and resources are distributed across the internet. Cloud-based solutions are typically more robust and scalable because they leverage distributed data centers, while web-based solutions are typically simpler and more streamlined, focusing primarily on providing a user-friendly interface.
Key Benefits of Cloud-Based Solutions
1. Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most significant advantages of cloud-based systems is scalability. Cloud infrastructure allows businesses to scale resources up or down with minimal effort, which is ideal for growing businesses that experience fluctuating demands. Whether you need to expand your storage capacity, increase server power, or add more users, cloud-based solutions can easily accommodate these changes.
For example, a retail business can use cloud services to scale up during busy seasons and scale down during off-peak times, only paying for the resources they need. This flexibility makes cloud solutions an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
2. Enhanced Security
Cloud-based solutions typically offer robust security features, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular backups. Cloud service providers invest heavily in security to protect the vast amounts of data stored on their platforms. This makes them an excellent choice for businesses that handle sensitive customer data or operate in industries with strict compliance requirements (e.g., finance, healthcare).
3. Collaboration and Remote Access
Cloud-based platforms are designed for collaboration. Since the data is stored remotely, teams can access it from anywhere, at any time. This is a significant advantage for businesses with remote teams or those that operate across multiple locations. With real-time collaboration features built into cloud platforms, employees can work on shared documents, communicate, and manage projects efficiently without the need for physical proximity.
Key Benefits of Web-Based Solutions
1. Lower Initial Costs
Web-based applications typically come with lower upfront costs compared to cloud-based solutions. Since web-based apps don’t require extensive infrastructure or specialized resources, businesses can often deploy them quickly and at a lower cost. Many web-based apps are available on a subscription basis, with flexible pricing depending on usage.
2. Simplicity and Ease of Use
Web-based applications tend to have a simpler setup and user interface. These apps are designed to run in a browser without the need for installation, making them easy for businesses to deploy and use. For smaller businesses or those with limited IT resources, web-based solutions can provide the tools they need without the complexity of more robust cloud services.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Web-based applications often integrate more seamlessly with other on-premise systems. For businesses that have legacy software or infrastructure, web-based solutions can work as an additional tool that enhances existing workflows. Since they don’t rely on extensive cloud resources, they can be more easily connected to in-house servers or other technologies already in place.
How to Choose Between Cloud-Based and Web-Based Solutions for Your Business
When deciding between cloud-based and web-based solutions, businesses should consider several factors, including:
Scalability Needs: If your business is growing quickly or expects high fluctuation in traffic or resource demand, a cloud-based solution may be better suited to meet your needs.
Budget: For businesses with limited budgets or those just starting, web-based applications might be more cost-effective in the short term.
Security and Compliance: If you handle sensitive data or are subject to strict industry regulations, the enhanced security of cloud-based solutions may make them a more attractive choice.
Ease of Use: If your business needs simple software that can be deployed quickly and with minimal setup, a web-based application could be the right choice.
Remote Access and Collaboration: For businesses with distributed teams or a remote workforce, cloud-based solutions offer more flexibility and collaboration features.
If you’re unsure which option is best for your business, a mobile app cost calculator can help provide a rough estimate of the costs associated with both cloud-based and web-based app development. This tool can help you understand the financial investment required for each solution based on your specific requirements.
If you're interested in exploring the benefits of cloud-based vs web-based services for your business, we encourage you to book an appointment with our team of experts.
Book an Appointment
Conclusion
In the debate of cloud-based vs web-based solutions, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Both have distinct advantages and drawbacks depending on your business’s specific needs. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, security, and flexibility, making them ideal for growing companies or those with complex infrastructure needs. On the other hand, web-based solutions are simpler, cost-effective, and easier to deploy, making them a solid choice for businesses looking for straightforward tools.
Ultimately, the best solution for your business depends on factors such as your budget, growth projections, and the complexity of your operations. If you’re looking to build a customized solution tailored to your unique needs, consider reaching out to a web app development company that can guide you through the process of selecting, building, and deploying the right technology for your business.
0 notes
Text
Azure vs AWS: Why Microsoft Azure Is the Right Choice for Your Cloud Migration

In today’s fast-paced digital world, migrating to the cloud isn’t just about infrastructure—it's about setting your business up for long-term agility, innovation, and growth. Regarding cloud service providers, two names dominate the landscape: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
While AWS was the early leader in the cloud race, Microsoft Azure has rapidly emerged as the preferred choice for businesses looking for a secure, scalable, and enterprise-ready cloud platform. Whether you're running a small business or managing a large enterprise, Azure offers advantages that go beyond basic cloud functionality.
So, why should you choose Microsoft Azure over AWS for your cloud migration? Let’s dive into the key reasons Azure is becoming the go-to platform for forward-thinking organizations.
1. Deep Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem
If your organization already uses Microsoft products like Windows Server, Active Directory, Office 365, or Dynamics 365, Azure offers seamless compatibility that AWS can’t match.
Single Sign-On (SSO) through Azure Active Directory
Direct integration with Power BI, SharePoint, and Microsoft Teams
Easier migration of legacy Microsoft applications to the cloud
This level of integration means lower migration friction, reduced complexity, and a more familiar environment for IT teams and end-users.
2. Hybrid Cloud Capabilities That Lead the Market
Azure is the undisputed leader in hybrid cloud. While AWS has attempted to enter this space with services like Outposts, Azure was built from the ground up with a hybrid in mind.
Azure Arc lets you manage servers, Kubernetes clusters, and apps across on-premises and multi-cloud environments
Azure Stack brings cloud capabilities to your data center
Seamless VPN, ExpressRoute, and Active Directory sync
These capabilities allow businesses to move to the cloud at their own pace, keeping sensitive workloads on-prem while still benefiting from Azure’s cloud infrastructure.
3. Enterprise-Grade Security and Compliance
Security is often the top concern when migrating to the cloud, and Azure excels in this area.
Microsoft spends over $1 billion annually on cybersecurity R&D
Azure has more than 90 compliance certifications—the most in the industry
Integrated Security Center, Sentinel, and Defender provide unified threat management
For industries with strict regulatory requirements—like finance, healthcare, and government—Azure’s compliance-first approach is a game-changer.
4. Better Support for Windows and Linux Workloads
While AWS supports Windows workloads, Azure is optimized for them. Microsoft has engineered Azure to run Windows-based services more efficiently, offering:
Cost-effective licensing with Azure Hybrid Benefit
Extended support for Windows Server and SQL Server
Better performance benchmarks for Windows virtual machines
At the same time, Azure also supports open-source technologies, including Linux, Kubernetes, PostgreSQL, and more—offering flexibility for diverse IT environments.
5. Competitive and Flexible Pricing
Cost is a major consideration in any cloud migration. While AWS is often perceived as cheaper, that’s not always the case when you look at the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Azure offers:
Pay-as-you-go pricing
Reserved instances for predictable workloads
Azure Hybrid Benefit to reuse on-prem licenses
Free extended security updates for legacy systems
Businesses often find that Azure provides more value for money, especially when they leverage existing Microsoft licenses.
6. Global Reach with Local Presence
Azure is available in more regions than any other cloud provider, offering a truly global footprint with data sovereignty in mind.
60+ regions worldwide
Presence in Australia, UAE, Europe, North America, and more
Local data centers help meet compliance and latency requirements
If your business operates globally or needs local hosting for compliance reasons, Azure provides unmatched flexibility.
7. Developer Productivity and DevOps Integration
Azure empowers development teams with tools and services that accelerate app development and deployment.
Visual Studio and GitHub integration for seamless CI/CD
Azure DevOps for agile project management and release automation
Azure Functions and Logic Apps for low-code serverless solutions
Azure helps businesses shorten development cycles, improve app quality, and bring innovation to market faster.
8. AI, ML, and Data Services for Innovation
Beyond infrastructure, Azure provides cutting-edge services in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data.
Azure OpenAI Service for advanced generative AI models
Azure Cognitive Services for speech, vision, and language
Azure Synapse Analytics and Databricks for enterprise data integration
These tools allow businesses to turn data into actionable insights and automate workflows, driving digital transformation across departments.
9. Enterprise Agreements and Migration Incentives
Microsoft offers generous incentives and support for businesses looking to move to Azure:
Azure Migration and Modernization Program (AMMP) to guide you step-by-step
FastTrack for Azure provides personalized onboarding
Financial support, training, and consulting through Microsoft partners
This ensures a low-risk, high-value migration experience, with expert help every step of the way.
10. Trusted Partner Ecosystem
Azure boasts a vast ecosystem of certified partners, including cloud consultants, migration experts, and managed service providers.
Certified Microsoft Partners can help plan, execute, and optimize your move
Support for industry-specific solutions
Access to Azure Marketplace for third-party integrations
This means your cloud journey is supported not just by Microsoft, but a community of trusted experts.
✅ Final Thoughts: Choose Azure for Your Cloud Future
AWS may have been the first to the cloud, but Microsoft Azure has become the top choice for organizations that want more than just storage and servers. With unmatched hybrid capabilities, better integration with enterprise tools, robust security, and a strong global presence, Azure offers a more comprehensive and cost-effective cloud platform for business growth.
Whether you’re migrating a single application or your entire data center, Azure gives you the flexibility, control, and innovation edge you need to succeed.
#cloud migration services#azure cloud solution#azure cloud migration#azure migration services#microsoft azure migration#azure migration strategy#cloud migration services companies
0 notes
Text
Which Cloud Computing Platform Is Best to Learn in 2025?

Cloud computing is no longer optional—it’s essential for IT jobs, developers, data engineers, and career switchers.
But here’s the question everyone’s Googling: Which cloud platform should I learn first? Should it be AWS, Azure, or GCP? Which one gets me hired faster? And where do I start if I’m a fresher?
This article answers it all, using simple language, real use cases, and proven guidance from NareshIT’s cloud training experts.
☁️ What Is a Cloud Platform?
Cloud platforms let you run software, manage storage, or build apps using internet-based infrastructure—without needing your own servers.
The 3 most popular providers are:
🟡 Amazon Web Services (AWS)
🔵 Microsoft Azure
🔴 Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
🔍 AWS vs Azure vs GCP for Beginners
Let’s compare them based on what beginners care about—ease of learning, job market demand, and use case relevance.
✅ Learn AWS First – Most Versatile & Job-Friendly
Best cloud certification for freshers (AWS Cloud Practitioner, Solutions Architect)
Huge job demand across India & globally
Tons of free-tier resources + real-world projects
Ideal if you want to land your first cloud job fast
✅ Learn Azure – Best for Enterprise & System Admin Roles
Works great with Microsoft stack: Office 365, Windows Server, Active Directory
AZ-900 and AZ-104 are beginner-friendly
Popular in government and large MNC jobs
✅ Learn GCP – Best for Developers, Data & AI Enthusiasts
Strong support for Python, ML, BigQuery, Kubernetes
Associate Cloud Engineer is the top beginner cert
Clean UI and modern tools
🧑🎓 Which Cloud Course Is Best at NareshIT?
No matter which provider you choose, our courses help you start with real cloud labs, not theory. Ideal for:
Freshers
IT support staff
Developers switching careers
Data & AI learners
🟡 AWS Cloud Course
EC2, IAM, Lambda, S3, VPC
Beginner-friendly with certification prep
60 Days, job-ready in 3 months
🔵 Azure Cloud Course
AZ-900 + AZ-104 covered
Learn Azure Portal, Blob, AD, and DevOps
Perfect for enterprise IT professionals
🔴 GCP Cloud Course
Compute Engine, IAM, App Engine, BigQuery
30–45 Days, with real-time labs
Ideal for developers and data engineers
📅 Check new batches and enroll → Both online and classroom formats available.
🛠️ Beginner Cloud Engineer Guide (In 4 Simple Steps)
Choose one platform: AWS is best to start
Learn core concepts: IAM, storage, compute, networking
Practice using free-tier accounts and real labs
Get certified → Apply for entry-level cloud roles
🎯 Final Thought: Don’t Wait for the “Best.” Start Smart.
If you're waiting to decide which cloud is perfect, you’ll delay progress. All three are powerful. Learning one cloud platform well is better than learning all poorly.
NareshIT helps you start strong and grow faster—with hands-on training, certifications, and placement support.
📅 Start your cloud journey with us → DevOps with Multi Cloud Training in KPHB
At NareshIT, we’ve helped thousands of learners go from “I don’t get it” to “I got the job.”
And Articles are :
What is Cloud Computing? A Practical Guide for Beginners in 2025
Where to Start Learning Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide for 2025
Entry level cloud computing jobs salary ?
Cloud Computing Job Roles for Freshers: What You Need to Know in 2025
Cloud Computing Learning Roadmap (2025): A Realistic Path for Beginners
How to Learn Cloud Computing Step by Step (From a Beginner’s Perspective)
How to Become a Cloud Engineer in 2025
How to become a cloud engineer ?
Cloud Computing Salaries in India (2025) – Career Scope, Certifications & Job Trends
Where to Start Learning Google Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide by NareshIT
Future Scope of Cloud Computing in 2025 and Beyond
#BestCloudToLearn#AWSvsAzurevsGCP#NareshITCloudCourses#CloudForBeginners#LearnCloudComputing#CareerInCloud2025#CloudCertificationsIndia#ITJobsForFreshers#CloudLearningRoadmap#CloudTrainingIndia
0 notes
Text
Hosting Game Servers: Cloud vs. Self-Hosted Solutions
In the world of game development, one of the most critical decisions developers face is choosing how to host their game servers. Whether you're building an online multiplayer game or a persistent world, the server infrastructure you choose can directly impact your game's performance, scalability, and player experience. Two main options are available: cloud hosting and self-hosted solutions. Both have their advantages and challenges, and selecting the right one depends on your specific needs.

Cloud Hosting for Game Servers
Cloud hosting refers to renting server space from third-party providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. These services offer flexible, on-demand server resources that can scale up or down based on player demand.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting
Scalability One of the biggest advantages of cloud hosting is the ability to scale resources automatically based on the number of active players. During peak times, cloud providers can allocate additional servers to prevent lag and downtime, while scaling back when traffic is low.
Reliability Cloud providers typically have robust infrastructure with data centers in multiple regions, reducing the risk of downtime. Many cloud services also offer built-in failover solutions, ensuring minimal disruption during server issues.
Global Reach With cloud hosting, you can deploy servers across the world, ensuring low-latency experiences for players regardless of their location. This is essential for global multiplayer games where players from different regions interact.
Cost Efficiency for Small to Medium Projects For indie developers or small studios, cloud hosting allows you to pay only for what you use. You don’t need to invest upfront in hardware or worry about maintaining a server farm.
Challenges of Cloud Hosting
Ongoing Costs While cloud hosting offers flexibility, it can become expensive over time, especially as your player base grows. The costs of data transfer, server uptime, and storage can add up, particularly for large-scale games.
Dependence on Third-Party Providers Cloud hosting means you're relying on external services for uptime, security, and performance. If there's an issue with the cloud provider, it can affect your game.
Self-Hosting Game Servers
Self-hosting refers to the practice of setting up and maintaining your own physical servers or renting dedicated hardware from a provider, where you have complete control over the hardware and software environment.
Benefits of Self-Hosting
Complete Control Self-hosting gives developers full control over the server environment. You can optimize the hardware, choose specific configurations, and customize the server software to meet your game's exact needs.
Fixed Costs Once the initial investment in hardware is made, self-hosting can be more cost-effective in the long term, especially for large games with steady traffic. You won’t face variable costs that scale with player numbers like you do with cloud hosting.
Customization and Flexibility With self-hosted solutions, you're not restricted to the infrastructure or limits of cloud providers. This gives you more freedom to fine-tune your server setup, security, and performance.
Challenges of Self-Hosting
Infrastructure and Maintenance Self-hosting requires a significant investment in hardware, along with the expertise to manage, secure, and maintain servers. It's a continuous process of monitoring, updates, and troubleshooting.
Limited Scalability Unlike cloud hosting, scaling a self-hosted solution involves purchasing additional hardware or renting more server space. This can lead to longer response times and higher costs during periods of rapid growth.
Geographic Limitations Hosting servers in a specific region can result in high latency for players located far away. Expanding to multiple regions requires significant effort and expense.
Cloud vs. Self-Hosting: Which is Right for You?
Cloud Hosting is ideal for games that require flexibility, scalability, and global reach, especially for projects with fluctuating player bases or rapid growth.
Self-Hosting is better for larger studios or developers who have the infrastructure and resources to manage servers themselves and need complete control over their environment.
The decision between cloud and self-hosted solutions ultimately depends on your specific game’s requirements, your team’s technical expertise, and your budget. Both approaches offer distinct advantages, and many developers opt for a hybrid solution, utilizing cloud servers for scalability while keeping critical infrastructure self-hosted for more control.
Choosing the right server hosting solution is essential to ensuring a smooth, reliable gaming experience for players and a scalable, maintainable backend for developers.
#GameDevelopment#GameServers#CloudHosting#SelfHosting#OnlineGaming#ServerManagement#GameInfrastructure#MultiplayerGames#HostingSolutions#ScalableGaming
1 note
·
View note
Text
Big Tech vs AI Startups: Who Will Lead the AI Race in 2025?

The focus keyword Big Tech vs AI Startups: Who Will Lead the AI Race in 2025? is on everyone's radar as we see unprecedented growth in artificial intelligence globally. While the world watches in awe, the question becomes clear—will massive tech corporations maintain dominance, or will agile, innovative AI startups take the lead in shaping our intelligent future?
The Current AI Landscape in 2025
Artificial Intelligence in 2025 is no longer a futuristic concept. From voice assistants and autonomous vehicles to predictive healthcare and intelligent manufacturing, AI is embedded into the fabric of our daily lives. At the heart of this AI revolution stand two forces:
Big Tech (Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, Apple)
AI Startups (Tagbin, OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face, Stability AI, and countless new disruptors)
Each brings unique strengths to the table, but the battle for AI supremacy is heating up like never before.
What Big Tech Brings to the Table
1. Infrastructure & Scale
Big Tech firms have vast computational resources, data centers, and access to proprietary user data. This enables them to train large-scale AI models like GPT-5 or Gemini Ultra at a scale most startups cannot match.
2. Talent Acquisition
These companies are able to attract and retain top-tier AI researchers by offering unmatched salaries and research environments.
3. Deployment Power
Thanks to global reach, Big Tech can deploy AI systems at scale���across billions of devices, apps, and ecosystems like Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud.
Why AI Startups Are Disrupting the Game
1. Speed and Agility
Startups move fast. Without bureaucratic red tape, they innovate rapidly, test bold ideas, and push boundaries without fear.
2. Niche Innovation
AI startups often focus on niche problems—drug discovery, ethical AI, quantum AI integration, or local language NLP—which are overlooked by larger players.
3. Open Source & Community Power
Companies like Hugging Face are democratizing AI by creating open-source models, creating a strong developer community and collaboration culture.
The Ethical Divide: AI for Profit vs AI for Purpose
2025 is also seeing an ethical shift. The world wants responsible AI. Big Tech faces criticism over data privacy, algorithmic bias, and monopolistic behavior. Meanwhile, startups often embrace ethical AI principles from inception, building trust among users and regulators.
This divide may give AI startups an edge—especially in regions like Europe and India where AI ethics and regulation are tightening.
Collaboration or Competition?
It’s not always a battle. Many AI startups collaborate with Big Tech through cloud partnerships or acquisitions. OpenAI, initially a startup, is now heavily funded by Microsoft. This shows a symbiotic trend: Startups bring ideas; Big Tech brings scale.
But the question remains—will such collaborations lead to innovation, or consolidation and control?
2025's Most Promising AI Startups
Anthropic – Championing “constitutional AI” for safer LLMs
Mistral AI – Developing compact, open-source foundation models
Hugging Face – Powering the open-source AI revolution
Runway ML – Leading the creative AI space (text-to-video, generative art)
LightOn – Merging AI with physics for ultra-efficient computing
Can AI Startups Win?
Despite being outspent, AI startups in 2025 are winning on creativity, ethics, and accessibility. With decentralization and open-source movements growing, the barriers to entry are falling. If they can scale responsibly and sustainably, the balance could tilt.
Future Outlook: The Next 5 Years
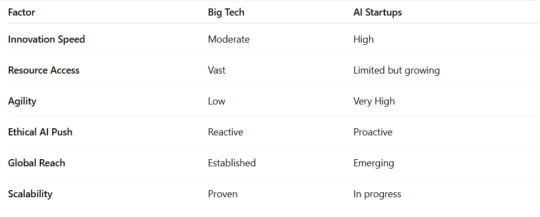
In conclusion, the AI race in 2025 isn’t just about who is bigger—it's about who is bolder, more ethical, and more community-driven. Whether it’s Big Tech or AI startups, the future of artificial intelligence will be shaped by the choices made today.
#tagbin#writers on tumblr#artificial intelligence#technology#tumblr#ai trends 2025#big tech vs ai startups 2025#ai race 2025#best ai startups 2025#ethical ai companies 2025#big tech in artificial intelligence#ai startup trends 2025#who will lead ai in 2025#ai competition 2025
0 notes
Text
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Which is Better for IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing how we interact with technology. IoT devices, from smart homes to industrial automation, collect and process data in real-time. But where does this data go, and how is it processed? This is where Edge Computing and Cloud Computing come into play.
We understand the importance of choosing the right technology for IoT applications at Wavy Informatics, a leading Drupal Development Company. In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing, their benefits, and which one is better for IoT.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing allows devices to send data to remote servers for storage and processing. These servers, also known as the cloud, are managed by companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
How Cloud Computing Works in IoT
When an IoT device collects data, it sends the data to the cloud through the internet. The cloud processes this data and sends back insights or commands to the device.
Benefits of Cloud Computing for IoT
Scalability – Cloud platforms can handle large amounts of data from multiple devices.
Easy Management – Cloud providers handle maintenance, updates, and security.
Cost-Effective – Businesses only pay for the resources they use.
Challenges of Cloud Computing for IoT
Latency – Sending data to the cloud and back takes time, which can slow down real-time applications.
Internet Dependency – A stable internet connection is required for cloud computing to function properly.
Security Risks – Transmitting data over the internet increases the risk of cyberattacks.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing processes data closer to the source, meaning directly on the IoT device or a nearby network node instead of sending it to a distant cloud server.
How Edge Computing Works in IoT
IoT devices collect and analyze data locally before sending only essential information to the cloud. This reduces the time needed to process data.
Benefits of Edge Computing for IoT
Low Latency – Since data is processed locally, responses are much faster.
Better Security – Less data is sent over the internet, reducing the risk of cyber threats.
Reduced Bandwidth Costs – Less data transmission means lower network usage and cost savings.
Challenges of Edge Computing for IoT
Higher Initial Costs – Setting up edge computing requires advanced hardware and software.
Limited Storage & Processing Power – Edge devices have less storage and computing power than cloud servers.
Complex Maintenance – Managing multiple edge devices can be challenging.
Cloud vs. Edge: Which One is Better for IoT?
Both Cloud Computing and Edge Computing have their strengths and weaknesses. The choice depends on the specific needs of your IoT project.
Feature
Cloud Computing
Edge Computing
Speed
Slower (higher latency)
Faster (low latency)
Security
Higher risk due to internet dependency
More secure as data stays local
Cost
Lower initial cost but ongoing cloud fees
Higher initial investment but lower long-term costs
Scalability
Highly scalable
Limited by local hardware
Reliability
Depends on internet availability
Works even with poor connectivity
When to Use Cloud Computing for IoT?
Your IoT system requires a lot of storage and processing power.
Easy expansion and organized data handling are your priorities.
Real-time data processing is not a major requirement.
When to Use Edge Computing for IoT?
Fast data processing with little delay is useful for self-driving cars and factory machines.
Better security comes from keeping data nearby.
IoT devices in remote areas work better with local processing.
Combining Edge and Cloud Computing for IoT
Many businesses use a hybrid approach that combines both edge and cloud computing. This means:
Critical data is processed at the edge for real-time responses.
Less urgent data is sent to the cloud for storage and deeper analysis.
This method offers the best of both worlds—speed and efficiency from edge computing, plus the power and scalability of the cloud.
Final Thoughts
There is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to Edge vs. Cloud Computing for IoT. The best choice depends on your business needs, budget, and application type.
At Wavy Informatics, we specialize in IoT solutions, Web Design, and Drupal development. Whether you need a cloud-based IoT platform or an edge computing system, our team can help you make the right choice.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Computing vs. DevOps: What Should You Learn?
If you’re starting out in tech or planning to upgrade your skills, you’ve probably come across two terms everywhere: Cloud Computing and DevOps. Both are in demand, both offer strong career growth, and both often show up together in job descriptions.
So how do you decide which one to focus on?
Let’s break it down in simple terms so you can choose the one that best fits your interests and goals.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is about delivering computing services—like storage, servers, databases, and software—over the internet. Instead of buying expensive hardware, companies can rent resources on platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
These services help businesses store data, run applications, and manage systems from anywhere, anytime.
Key Roles in Cloud Computing:
Cloud Engineer
Cloud Architect
Solutions Architect
Cloud Administrator
Skills You’ll Need:
Understanding of networking and storage
Basics of operating systems (Linux, Windows)
Knowledge of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP
Some scripting (Python, Bash)
What Is DevOps?
DevOps is a practice that focuses on collaboration between development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams. It’s all about building, testing, and releasing software faster and more reliably.
DevOps isn’t a tool—it’s a culture supported by tools. It brings automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery into one process.
Key Roles in DevOps:
DevOps Engineer
Release Manager
Site Reliability Engineer
Automation Engineer
Skills You’ll Need:
Strong scripting and coding knowledge
Familiarity with tools like Jenkins, Docker, Git, Kubernetes
Understanding of CI/CD pipelines
Basic cloud knowledge helps
Cloud vs. DevOps: Key Differences
Aspect
Cloud Computing
DevOps
Focus
Infrastructure and service delivery
Process improvement and automation
Tools
AWS, Azure, GCP
Docker, Jenkins, Git, Kubernetes
Goal
Scalable, cost-efficient computing
Faster and reliable software releases
Learning Curve
Starts simple, grows with experience
Needs a good mix of coding and tools
Job Demand
Very high, especially in large enterprises
High in tech-focused and agile teams
What Should You Learn First?
If you enjoy working with infrastructure, managing systems, or want to work for companies that are moving to the cloud, cloud computing is a strong starting point. You can always build on this foundation by learning DevOps later.
If you love automation, scripting, and speeding up software delivery, then DevOps might be a better fit. It often requires some cloud knowledge too, so you’ll likely learn a bit of both anyway.
Many students from a college of engineering in Bhubaneswar often begin with cloud fundamentals in their curriculum and then expand into DevOps through workshops, online courses, or internships.
Can You Learn Both?
Absolutely. In fact, many companies look for professionals who understand both areas. You don’t have to master both at the same time—but building skills in one will make it easier to transition into the other.
For example, a cloud engineer who understands DevOps practices is more valuable. Similarly, a DevOps engineer with solid cloud knowledge is better equipped for real-world challenges.
Learning paths are flexible. The key is to get hands-on practice—build small projects, join open-source contributions, and use free or student credits from cloud providers.
Career Scope in India
In India, both cloud and DevOps are growing quickly. As more startups and large companies move to the cloud and adopt automation, the demand for skilled professionals continues to rise.
Recruiters often visit top institutions, and a college of engineering in Bhubaneswar that focuses on tech training and industry tie-ups can give students a solid head start in either of these fields.
Wrapping Up
Both cloud computing and DevOps offer promising careers. They’re not competing paths, but rather parts of a larger system. Whether you choose to start with one or explore both, what matters most is your willingness to learn and apply your skills.
Pick a starting point, stay consistent, and take small steps. The opportunities are out there—you just need to start.
#top 5 engineering colleges in bhubaneswar#top engineering colleges in odisha#bhubaneswar b tech colleges#college of engineering and technology bhubaneswar#best colleges in bhubaneswar#college of engineering bhubaneswar
0 notes
Text
Google Cloud Next 2025: Doubling Down on AI with Silicon, Software, and an Open Agent Ecosystem
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/google-cloud-next-2025-doubling-down-on-ai-with-silicon-software-and-an-open-agent-ecosystem/
Google Cloud Next 2025: Doubling Down on AI with Silicon, Software, and an Open Agent Ecosystem
Las Vegas is playing host to Google Cloud Next 2025, an event unfolding at a critical moment for the technology industry. The artificial intelligence arms race among the cloud titans – Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – is escalating rapidly. Google, often cast as the third contender despite its formidable technological prowess and deep AI research roots, seized the Cloud Next stage to articulate a comprehensive and aggressive strategy aimed squarely at the enterprise AI market.
The narrative, delivered by Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian and echoed by Google and Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai, centered on moving AI transformation from mere possibility to tangible reality. Google underscored its claimed momentum, citing over 3,000 product advancements in the past year, a twentyfold surge in Vertex AI platform usage since the previous Cloud Next event, more than four million developers actively building with its Gemini family of models, and showcasing over 500 customer success stories during the conference.
However, Google Cloud Next 2025 was more than a showcase of incremental updates or impressive metrics. It also unveiled a multi-pronged offensive. By launching powerful, inference-optimized custom silicon (the Ironwood TPU), refining its flagship AI model portfolio with a focus on practicality (Gemini 2.5 Flash), opening its vast global network infrastructure to enterprises (Cloud WAN), and making a significant, strategic bet on an open, interoperable ecosystem for AI agents (the Agent2Agent protocol), Google is aggressively positioning itself to define the next evolutionary phase of enterprise AI – what the company is increasingly terming the “agentic era.”
Ironwood, Gemini, and the Network Effect
Central to Google’s AI ambitions is its continued investment in custom silicon. The star of Cloud Next 2025 was Ironwood, the seventh generation of Google’s Tensor Processing Unit (TPU). Critically, Ironwood is presented as the first TPU designed explicitly for AI inference – the process of using trained models to make predictions or generate outputs in real-world applications.
The performance claims for Ironwood are substantial. Google detailed configurations scaling up to an immense 9,216 liquid-cooled chips interconnected within a single pod. This largest configuration is claimed to deliver a staggering 42.5 exaflops of compute power. Google asserts this represents more than 24 times the per-pod compute power of El Capitan, currently ranked as the world’s most powerful supercomputer.
While impressive, it’s important to note such comparisons often involve different levels of numerical precision, making direct equivalency complex. Nonetheless, Google positions Ironwood as a greater than tenfold improvement over its previous high-performance TPU generation.
Beyond raw compute, Ironwood boasts significant advancements in memory and interconnectivity compared to its predecessor, Trillium (TPU v6).
Perhaps equally important is the emphasis on energy efficiency. Google claims Ironwood delivers twice the performance per watt compared to Trillium and is nearly 30 times more power-efficient than its first Cloud TPU from 2018. This directly addresses the growing constraint of power availability in scaling data centers for AI.
Google TPU Generation Comparison: Ironwood (v7) vs. Trillium (v6)
Feature Trillium (TPU v6) Ironwood (TPU v7) Improvement Factor Primary Focus Training & Inference Inference Specialization Peak Compute/Chip Not directly comparable (diff gen) 4,614 TFLOPs (FP8 likely) – HBM Capacity/Chip 32 GB (estimated based on 6x claim) 192 GB 6x HBM Bandwidth/Chip ~1.6 Tbps (estimated based on 4.5x) 7.2 Tbps 4.5x ICI Bandwidth (bidir.) ~0.8 Tbps (estimated based on 1.5x) 1.2 Tbps 1.5x Perf/Watt vs. Prev Gen Baseline for comparison 2x vs Trillium 2x Perf/Watt vs. TPU v1 (2018) ~15x (estimated) Nearly 30x ~2x vs Trillium
Note: Some Trillium figures are estimated based on Google’s claimed improvement factors for Ironwood. Peak compute comparison is complex due to generational differences and likely precision variations.
Ironwood forms a key part of Google’s “AI Hypercomputer” concept – an architecture integrating optimized hardware (including TPUs and GPUs like Nvidia’s Blackwell and upcoming Vera Rubin), software (like the Pathways distributed ML runtime), storage (Hyperdisk Exapools, Managed Lustre), and networking to tackle demanding AI workloads.
On the model front, Google introduced Gemini 2.5 Flash, a strategic counterpoint to the high-end Gemini 2.5 Pro. While Pro targets maximum quality for complex reasoning, Flash is explicitly optimized for low latency and cost efficiency, making it suitable for high-volume, real-time applications like customer service interactions or rapid summarization.
Gemini 2.5 Flash features a dynamic “thinking budget” that adjusts processing based on query complexity, allowing users to tune the balance between speed, cost, and accuracy. This simultaneous focus on a high-performance inference chip (Ironwood) and a cost/latency-optimized model (Gemini Flash) underscores Google’s push towards the practical operationalization of AI, recognizing that the cost and efficiency of running models in production are becoming paramount concerns for enterprises.
Complementing the silicon and model updates is the launch of Cloud WAN. Google is effectively productizing its massive internal global network – spanning over two million miles of fiber, connecting 42 regions via more than 200 points of presence – making it directly available to enterprise customers.
Google claims this service can deliver up to 40% faster performance compared to the public internet and reduce total cost of ownership by up to 40% versus self-managed WANs, backed by a 99.99% reliability SLA. Primarily targeting high-performance connectivity between data centers and connecting branch/campus environments, Cloud WAN leverages Google’s existing infrastructure, including the Network Connectivity Center.
While Google cited Nestlé and Citadel Securities as early adopters, this move fundamentally weaponizes a core infrastructure asset. It transforms an internal operational necessity into a competitive differentiator and potential revenue stream, directly challenging both traditional telecommunication providers and the networking offerings of rival cloud platforms like AWS Cloud WAN and Azure Virtual WAN.
(Source: Google DeepMind)
The Agent Offensive: Building Bridges with ADK and A2A
Beyond infrastructure and core models, Google Cloud Next 2025 placed an extraordinary emphasis on AI agents and the tools to build and connect them. The vision presented extends far beyond simple chatbots, envisioning sophisticated systems capable of autonomous reasoning, planning, and executing complex, multi-step tasks. The focus is clearly shifting towards enabling multi-agent systems, where specialized agents collaborate to achieve broader goals.
To facilitate this vision, Google introduced the Agent Development Kit (ADK). ADK is an open-source framework, initially available in Python, designed to simplify the creation of individual agents and complex multi-agent systems. Google claims developers can build a functional agent with under 100 lines of code.
Key features include a code-first approach for precise control, native support for multi-agent architectures, flexible tool integration (including support for the Model Context Protocol, or MCP), built-in evaluation capabilities, and deployment options ranging from local containers to the managed Vertex AI Agent Engine. ADK also uniquely supports bidirectional audio and video streaming for more natural, human-like interactions. An accompanying “Agent Garden” provides ready-to-use samples and over 100 pre-built connectors to jumpstart development.
The true centerpiece of Google’s agent strategy, however, is the Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol. A2A is a new, open standard designed explicitly for agent interoperability. Its fundamental goal is to allow AI agents, regardless of the framework they were built with (ADK, LangGraph, CrewAI, etc.) or the vendor who created them, to communicate securely, exchange information, and coordinate actions. This directly tackles the significant challenge of siloed AI systems within enterprises, where agents built for different tasks or departments often cannot interact.
This push for an open A2A protocol represents a significant strategic gamble. Instead of building a proprietary, closed agent ecosystem, Google is attempting to establish the de facto standard for agent communication. This approach potentially sacrifices short-term lock-in for the prospect of long-term ecosystem leadership and, crucially, reducing the friction that hinders enterprise adoption of complex multi-agent systems.
By championing openness, Google aims to accelerate the entire agent market, positioning its cloud platform and tools as central facilitators.
How A2A works (Source: Google)
Recalibrating the Cloud Race: Google’s Competitive Gambit
These announcements land squarely in the context of the ongoing cloud wars. Google Cloud, while demonstrating impressive growth often fueled by AI adoption, still holds the third position in market share, trailing AWS and Microsoft Azure. Cloud Next 2025 showcased Google’s strategy to recalibrate this race by leaning heavily into its unique strengths and addressing perceived weaknesses.
Google’s key differentiators were on full display. The long-term investment in custom silicon, culminating in the inference-focused Ironwood TPU, provides a distinct hardware narrative compared to AWS’s Trainium/Inferentia chips and Azure’s Maia accelerator. Google consistently emphasizes performance-per-watt leadership, a potentially crucial factor as AI energy demands soar. The launch of Cloud WAN weaponizes Google’s unparalleled global network infrastructure, offering a distinct networking advantage.
Furthermore, Google continues to leverage its AI and machine learning heritage, stemming from DeepMind’s research and manifested in the comprehensive Vertex AI platform, aligning with its market perception as a leader in AI and data analytics.
Simultaneously, Google signaled efforts to address historical enterprise concerns. The massive $32 billion acquisition of cloud security firm Wiz, announced shortly before Next, is a clear statement of intent to bolster its security posture and improve the usability and experience of its security offerings – areas critical for enterprise trust.
Continued emphasis on industry solutions, enterprise readiness, and strategic partnerships further aims to reshape market perception from a pure technology provider to a trusted enterprise partner.
Taken together, Google’s strategy appears less focused on matching AWS and Azure service-for-service across the board, and more concentrated on leveraging its unique assets – AI research, custom hardware, global network, and open-source affinity – to establish leadership in what it perceives as the next crucial wave of cloud computing: AI at scale, particularly efficient inference and sophisticated agentic systems.
The Road Ahead for Google AI
Google Cloud Next 2025 presented a compelling narrative of ambition and strategic coherence. Google is doubling down on artificial intelligence, marshaling its resources across custom silicon optimized for the inference era (Ironwood), a balanced and practical AI model portfolio (Gemini 2.5 Pro and Flash), its unique global network infrastructure (Cloud WAN), and a bold, open approach to the burgeoning world of AI agents (ADK and A2A).
Ultimately, the event showcased a company moving aggressively to translate its deep technological capabilities into a comprehensive, differentiated enterprise offering for the AI era. The integrated strategy – hardware, software, networking, and open standards – is sound. Yet, the path ahead requires more than just innovation.
Google’s most significant challenge may lie less in technology and more in overcoming enterprise adoption inertia and building lasting trust. Converting these ambitious announcements into sustained market share gains against deeply entrenched competitors demands flawless execution, clear go-to-market strategies, and the ability to consistently convince large organizations that Google Cloud is the indispensable platform for their AI-driven future. The agentic future Google envisions is compelling, but its realization depends on navigating these complex market dynamics long after the Las Vegas spotlight has dimmed.
#000#2025#acquisition#adoption#agent#agents#ai#AI adoption#ai agent#AI AGENTS#ai inference#ai model#ai platform#AI research#AI systems#Alphabet#Amazon#Amazon Web Services#amp#Analytics#Announcements#applications#approach#architecture#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#assets#audio#autonomous#AWS
0 notes
Text
Cloud Services Software: Powering a Connected World
Imagine running your business, storing your files, or collaborating with a team—all without a single hard drive in sight. Cloud services software makes this a reality, delivering tools and resources over the internet with unmatched flexibility and scale. These platforms transform how we work, play, and innovate, offering everything from storage to computing power on demand. What makes cloud services software a cornerstone of modern life, and how can it elevate your digital game? Let’s dive in.

What is Cloud Services Software?
Cloud services software refers to applications and platforms that operate via the internet, hosted on remote servers rather than local machines. It’s the engine behind online storage, app hosting, team collaboration, and more think Google Drive, AWS, or Microsoft Teams. Instead of owning hardware, you tap into a shared pool of resources, paying only for what you use.
Today, these tools harness artificial intelligence (AI), real-time syncing, and robust security to serve individuals, small businesses, and global enterprises, making tech accessible anywhere, anytime.
Why Cloud Services Software Matters
The shift to cloud isn’t just a trend it’s a necessity. Physical servers tie you down with costs, maintenance, and limits, while the cloud frees you up. Cloud services software matters because it:
Boosts Flexibility: Access your work from any device, anywhere.
Cuts Costs: Skip hardware investments and scale as needed.
Speeds Collaboration: Sync teams across cities or continents instantly.
Future-Proofs You: Adapt to growth or change without a tech overhaul.
X posts often praise tools like Dropbox for simplicity, proving their grip on our digital lives.
Key Features of Cloud Services Software
Top cloud services software offers a versatile toolkit:
Storage: Save files, from docs to terabytes of data, securely online.
Computing Power: Run apps or process data with virtual servers.
Collaboration: Share, edit, and chat in real time with teammates.
Backup & Recovery: Protect data with automatic saves and restores.
Scalability: Add resources instantly as demand spikes.
AI Tools: Analyze data or automate tasks with cloud-based smarts.
These features make the cloud a one-stop shop for digital needs.
Top Benefits for Users
Cloud services software delivers standout wins:
Mobility: Work from a café or couch with zero lag.
Savings: Slash IT budgets by 30%, per user insights.
Reliability: Trust uptime with pro-grade server management.
Innovation: Launch ideas fast with ready-to-use infrastructure.
A freelancer using Google Drive might never lose a file, while a startup on AWS scales an app overnight.
Popular Cloud Services Software
The cloud market sparkles with options:
Google Drive: Simple storage and collaboration for all.
AWS (Amazon Web Services): King of cloud computing for devs and firms.
Microsoft Azure: Enterprise-ready with deep Office integration.
Dropbox: User-friendly file syncing and sharing.
Heroku: Developer-loved platform for app hosting.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Services Software
Finding your cloud fit takes a plan:
Purpose: File storage (Dropbox) or app hosting (Heroku)?
Scale: Personal use (Google Drive) or business (Azure)?
Ease: Test for simplicity—complexity slows you down.
Integrations: Sync with tools like Slack or QuickBooks.
Cost: Free tiers (Drive) vs. pay-as-you-go (AWS at $0.01/hour+).
The Future of Cloud Services Software
The cloud’s future is sky-high. AI will optimize resource use—think auto-scaling servers or predicting your storage needs. Edge computing will cut latency by processing closer to you, while 5G will make everything instant. Green cloud initiatives might lower energy use, and hybrid models will blend public and private clouds for max control. The trend is toward faster, smarter, and greener services.
Challenges to Watch For
There are quirks. Downtime is rare but real can halt work, so check uptime guarantees. Costs can balloon; AWS bills sneak up if you’re not careful. Data migration takes effort moving in or out isn’t instant. Security is king to ensure encryption and compliance with laws like GDPR, or risks multiply. Internet reliance means a weak signal could stall you.
Real-World Impact
Individuals: A student uses Drive to back up years of work.
Teams: A remote crew on Azure builds an app together.
Businesses: A retailer with AWS handles Black Friday traffic flawlessly.
Conclusion
Cloud services software is your digital lifeline—unshackling you from hardware and opening a world of possibility. It’s not just about storage or speed—it’s about working smarter, scaling effortlessly, and staying connected. Whether you’re saving a photo or launching a startup, the right cloud tool can lift you up. Explore the options, find your match, and soar into the cloud.
Frequently asked questions
What is cloud services software? It’s a set of tools and platforms hosted online, offering storage, computing, or collaboration without local hardware.
Who uses cloud services software? Individuals, teams, businesses, and devs needing flexible, internet-based resources.
How does it improve workflows? It speeds access, cuts costs, and syncs teams with scalable, on-demand tech.
Is it secure? Top providers encrypt data and meet privacy laws—check uptime and security specs.
What’s the difference between public and private cloud software? Public shares resources (AWS); private dedicates them for one user (custom setups).
How much does cloud services software cost? Ranges from free (Google Drive) to cents-per-hour (AWS) or $5-$50/month (Dropbox).
Can it integrate with other tools? Most sync with apps, CRMs, or storage—verify what fits your stack.
How long until I see benefits? Basic use—like file access—is instant; deeper gains grow with adoption.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Computing Service Providers in 2025
In today’s digital era, businesses are rapidly adopting cloud computing services to enhance scalability, security, and cost-efficiency. With numerous cloud service providers available, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. This guide explores the best cloud computing services, compares cloud computing costs, and highlights key features like hybrid cloud computing solutions and cloud computing security services.
Whether you're a startup or an enterprise, understanding cloud-based computing services will help you make an informed decision. Let’s dive in!

What Are Cloud Computing Service Providers?
Cloud computing service providers offer on-demand computing resources over the internet, including storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. These cloud solutions eliminate the need for physical infrastructure, allowing businesses to scale efficiently.
Types of Cloud Services
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Virtualized computing resources (e.g., AWS, Azure).
Platform as a Service (PaaS) – Development platforms for app building (e.g., Google Cloud).
Software as a Service (SaaS) – Ready-to-use applications (e.g., Salesforce, Dropbox).
Top Cloud Computing Companies in 2025
Here are the leading cloud computing providers dominating the market:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Key Features: Scalable, extensive global infrastructure, AI & ML integration.
Best For: Enterprises needing high-performance cloud-based services.
2. Microsoft Azure
Key Features: Seamless integration with Microsoft products, strong hybrid cloud computing solutions.
Best For: Businesses already using Microsoft ecosystems.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Key Features: Advanced data analytics, AI tools, and cost-effective pricing.
Best For: Data-driven organizations.
4. IBM Cloud
Key Features: Strong focus on AI and cloud computing security services.
Best For: Industries requiring high compliance (finance, healthcare).
5. Oracle Cloud
Key Features: High-performance databases and enterprise-grade cloud solutions.
Best For: Large-scale database management.
For businesses seeking tailored cloud consulting companies, CloudAstra offers expert guidance on migration and optimization.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Cloud Service Providers
Selecting the right cloud computing providers depends on several factors:
1. Pricing & Cloud Computing Cost
Pay-as-you-go vs. subscription models.
Hidden costs (data transfer, support fees).
2. Security & Compliance
Look for cloud computing security services like encryption, DDoS protection, and compliance certifications (GDPR, HIPAA).
3. Scalability
Ensure the provider supports auto-scaling for growing businesses.
4. Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Support
Hybrid cloud computing solutions allow seamless integration between on-premise and cloud environments.
5. Customer Support & SLAs
24/7 support and guaranteed uptime (99.9% SLA).
Cloud Computing Cost: How to Optimize Expenses?
Managing cloud computing cost is crucial for ROI. Here’s how to optimize:
✔ Right-Sizing Resources – Avoid over-provisioning. ✔ Reserved Instances – Save up to 75% with long-term commitments. ✔ Spot Instances – Use unused cloud capacity at lower rates. ✔ Monitor Usage – Tools like AWS Cost Explorer help track spending.
For cost-effective cloud-based computing services, consult CloudAstra’s Cloud Computing Services for expert advice.
Why Are Cloud Computing Security Services Essential?
With rising cyber threats, cloud computing security services protect:
Data Encryption – Secures data in transit and at rest.
Identity & Access Management (IAM) – Controls user permissions.
DDoS Protection – Prevents downtime from attacks.
Compliance Certifications – Ensures adherence to industry regulations.
Leading cloud service providers like AWS and Azure offer built-in security, but third-party solutions add extra layers of protection.
The Rise of Hybrid Cloud Computing Solutions
Hybrid cloud computing solutions combine private and public clouds, offering:
✅ Flexibility – Run sensitive workloads privately and scale publicly. ✅ Cost Efficiency – Balance between CapEx and OpEx. ✅ Disaster Recovery – Enhanced backup and redundancy.
Companies like IBM and Microsoft lead in hybrid cloud deployments.
Best Cloud Consulting Companies for Migration & Optimization
If managing cloud solutions in-house is complex, consider these cloud consulting companies:
Accenture – End-to-end cloud transformation.
Deloitte – Strategy and implementation.
CloudAstra – Specialized in cost optimization and security.
Conclusion
Choosing the right cloud computing service providers is critical for business growth. Evaluate factors like cloud computing cost, security, scalability, and hybrid cloud computing solutions before deciding.
For expert guidance on best cloud computing services, explore CloudAstra’s Cloud Computing Services today!
FAQ
Q1. What are the best cloud computing companies? AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, IBM, and Oracle are the top cloud computing providers.
Q2. How can I reduce cloud computing costs? Use reserved instances, monitor usage, and right-size resources.
Q3. What is hybrid cloud computing? A mix of private and public cloud-based services for flexibility.
Q4. Why is cloud security important? Cloud computing security services protect against breaches and ensure compliance.
By leveraging the right cloud service providers, businesses can achieve agility, security, and cost savings.
#cloud computing cost#cloud based computing services#cloud computing service providers#cloud based services
0 notes
Text
Azure vs. AWS: A Detailed Comparison
Cloud computing has become the backbone of modern IT infrastructure, offering businesses scalability, security, and flexibility. Among the top cloud service providers, Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS) dominate the market, each bringing unique strengths. While AWS has held the position as a cloud pioneer, Azure has been gaining traction, especially among enterprises with existing Microsoft ecosystems. This article provides an in-depth comparison of Azure vs. AWS, covering aspects like database services, architecture, and data engineering capabilities to help businesses make an informed decision.
1. Market Presence and Adoption
AWS, launched in 2006, was the first major cloud provider and remains the market leader. It boasts a massive customer base, including startups, enterprises, and government organizations. Azure, introduced by Microsoft in 2010, has seen rapid growth, especially among enterprises leveraging Microsoft's ecosystem. Many companies using Microsoft products like Windows Server, SQL Server, and Office 365 find Azure a natural choice.
2. Cloud Architecture: Comparing Azure and AWS
Cloud architecture defines how cloud services integrate and support workloads. Both AWS and Azure provide robust cloud architectures but with different approaches.
AWS Cloud Architecture
AWS follows a modular approach, allowing users to pick and choose services based on their needs. It offers:
Amazon EC2 for scalable compute resources
Amazon VPC for network security and isolation
Amazon S3 for highly scalable object storage
AWS Lambda for serverless computing
Azure Cloud Architecture
Azure's architecture is designed to integrate seamlessly with Microsoft tools and services. It includes:
Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) for compute workloads
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) for networking and security
Azure Blob Storage for scalable object storage
Azure Functions for serverless computing
In terms of architecture, AWS provides more flexibility, while Azure ensures deep integration with enterprise IT environments.
3. Database Services: Azure SQL vs. AWS RDS
Database management is crucial for any cloud strategy. Both AWS and Azure offer extensive database solutions, but they cater to different needs.
AWS Database Services
AWS provides a wide range of managed database services, including:
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) – Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, and Oracle.
Amazon Aurora – High-performance relational database compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Amazon DynamoDB – NoSQL database for low-latency applications.
Amazon Redshift – Data warehousing for big data analytics.
Azure Database Services
Azure offers strong database services, especially for Microsoft-centric workloads:
Azure SQL Database – Fully managed SQL database optimized for Microsoft applications.
Cosmos DB – Globally distributed, multi-model NoSQL database.
Azure Synapse Analytics – Enterprise-scale data warehousing.
Azure Database for PostgreSQL/MySQL/MariaDB – Open-source relational databases with managed services.
AWS provides a more mature and diverse database portfolio, while Azure stands out in SQL-based workloads and seamless Microsoft integration.
4. Data Engineering and Analytics: Which Cloud is Better?
Data engineering is a critical function that ensures efficient data processing, transformation, and storage. Both AWS and Azure offer data engineering tools, but their capabilities differ.
AWS Data Engineering Tools
AWS Glue – Serverless data integration service for ETL workloads.
Amazon Kinesis – Real-time data streaming.
AWS Data Pipeline – Orchestration of data workflows.
Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) – Managed Hadoop, Spark, and Presto.
Azure Data Engineering Tools
Azure Data Factory – Cloud-based ETL and data integration.
Azure Stream Analytics – Real-time event processing.
Azure Databricks – Managed Apache Spark for big data processing.
Azure HDInsight – Fully managed Hadoop and Spark services.
Azure has an edge in data engineering for enterprises leveraging AI and machine learning via Azure Machine Learning and Databricks. AWS, however, excels in scalable and mature big data tools.
5. Pricing Models and Cost Efficiency
Cloud pricing is a major factor when selecting a provider. Both AWS and Azure offer pay-as-you-go pricing, reserved instances, and cost optimization tools.
AWS Pricing: Charges are based on compute, storage, data transfer, and additional services. AWS also offers AWS Savings Plans for cost reductions.
Azure Pricing: Azure provides cost-effective solutions for Microsoft-centric businesses. Azure Hybrid Benefit allows companies to use existing Windows Server and SQL Server licenses to save costs.
AWS generally provides more pricing transparency, while Azure offers better pricing for Microsoft users.
6. Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority in cloud computing, and both AWS and Azure provide strong security measures.
AWS Security: Uses AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management), AWS Shield (DDoS protection), and AWS Key Management Service.
Azure Security: Provides Azure Active Directory (AAD), Azure Security Center, and built-in compliance features for enterprises.
Both platforms meet industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, making them secure choices for businesses.
7. Hybrid Cloud Capabilities
Enterprises increasingly prefer hybrid cloud strategies. Here, Azure has a significant advantage due to its Azure Arc and Azure Stack technologies that extend cloud services to on-premises environments.
AWS offers AWS Outposts, but it is not as deeply integrated as Azure’s hybrid solutions.
8. Which Cloud Should You Choose?
Choose AWS if:
You need a diverse range of cloud services.
You require highly scalable and mature cloud solutions.
Your business prioritizes flexibility and a global cloud footprint.
Choose Azure if:
Your business relies heavily on Microsoft products.
You need strong hybrid cloud capabilities.
Your focus is on SQL-based workloads and enterprise data engineering.
Conclusion
Both AWS and Azure are powerful cloud providers with unique strengths. AWS remains the leader in cloud services, flexibility, and scalability, while Azure is the go-to choice for enterprises using Microsoft’s ecosystem.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your organization’s needs in terms of database management, cloud architecture, data engineering, and overall IT strategy. Companies looking for a seamless Microsoft integration should opt for Azure, while businesses seeking a highly scalable and service-rich cloud should consider AWS.
Regardless of your choice, both platforms provide the foundation for a strong, scalable, and secure cloud infrastructure in today’s data-driven world.
0 notes
Text
"SRE vs. DevOps: Which One is Right for Your Career?"
Introduction
As the demand for efficient software delivery and system reliability grows, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) and DevOps have emerged as critical methodologies in IT operations. While both aim to bridge the gap between development and operations, they take different approaches. This article will explore their differences and help you decide which career path is right for you.
Key Skills Gained Through SRE and DevOps
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE)
Strong programming skills (Python, Go, or Java)
System architecture and automation expertise
Incident management and troubleshooting
Monitoring and performance optimization
CI/CD pipeline implementation
DevOps
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) proficiency
CI/CD pipeline development
Cloud platform expertise (AWS, Azure, GCP)
Security and compliance in development
Collaboration and communication skills
Benefits of SRE and DevOps Certifications
Earning certifications like sre certification, site reliability engineer certification, and SRE Foundation Certification validates expertise and boosts career prospects. Similarly, DevOps certifications enhance skills in automation, cloud computing, and continuous deployment.
Why Get Certified?
Higher salary potential
Increased job opportunities
Industry recognition and credibility
Enhanced skill set and career growth
Job Opportunities After SRE and DevOps Certification
SRE Job Roles
Site Reliability Engineer
Systems Engineer
Cloud Infrastructure Engineer
Observability Engineer
DevOps Job Roles
DevOps Engineer
Release Engineer
Cloud DevOps Architect
Kubernetes Engineer
Market Demand & Industry Growth
The demand for site reliability engineering certification and DevOps professionals is skyrocketing. Companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are actively hiring SRE and DevOps professionals to maintain uptime, scalability, and automation.
Why Choose SRE or DevOps?
Choose SRE if:
You enjoy coding and automation.
You like monitoring system reliability and incident management.
Choose DevOps if:
You prefer streamlining development and operations workflows.
You are passionate about CI/CD, cloud, and containerization.
Future Trends
AI in IT Operations: AI-driven observability tools will enhance automation.
Kubernetes and Containers: Essential for both SRE and DevOps professionals.
Security Integration: DevSecOps is becoming a must-have skill.
Conclusion & Call-to-Action
Both SRE and DevOps are lucrative career choices. If you are passionate about coding and reliability, SRE is a great choice. If you love automation and CI/CD, DevOps might be the best fit. To advance your career, consider earning a site reliability engineering certification or a DevOps certification today!
For information visit: -
https://www.gsdcouncil.org/certified-site-reliability-engineer-foundation
Contact : +41444851189
#sre #srecertification #DevOps #siteReliabilityEngineer #sreFoundation
#sre certification#site reliability engineer certification#SRE Foundation Certification#site reliability engineering certification#sre certifications
0 notes