#PCB Electronic Board
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How PCB Electronic Boards Depend on Reliable Electronic Component Distributors
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics manufacturing, PCB electronic boards are essentially the core of many devices, starting from consumer gadgets to industrial machinery. However, the major performance and endurance factors really come into play when these parts are chosen from a dependable electronic component’s distributor.

Quality Components Make the Difference
To ensure efficient functioning of a PCB electronic board, each resistor, capacitor, and semiconductor must conform to rigid specifications. Quality implies being accountable for the stability, durability, and functionality of the end product, and reputable suppliers ensure just that. Since well-established distributors can provide certified components with proof of conformity to international standards, the defects or failures of any component are highly unlikely.
Timely Supply Chain Management
In today's fiercely competitive market, any kind of delay in getting components on-site can literally halt the production line and add costs, if not threaten the reputation. On-time delivery is a service guarantee by the trustworthy distributors with uninterrupted customs clearance and stock availability. This, thus, lays reassurance for the manufacturers to maintain their production cycle without compromising on quality for market requirements.
Advanced Testing and Certification
The best of distributors should test and provide quality assurance of components, which would detect counterfeits or defects before the components hit the assembly floor. That protects the integrity of the electronic board and minimizes product recall cases and customer discontent.
Enabling Access to Upcoming Technologies
Working with distributors who keep track of the trends allows the manufacturer to have access to innovative components and new technologies. This greatly helps these manufacturers involved in making next-generation devices that require higher functionality and energy efficiency.
Establishment of Long-Standing Partnerships
Such a trustworthy distributor-client relationship enables better pricing as well as technical support through customizing their requests to meet their needs. Close working relations with suppliers also help manufacturers streamline their own procurement processes and thereby enhance the performance of their products.
Enhancing Cost Efficiency
Reliable electronic parts distributors are able to present manufacturers with the ability to obtain cost-effective bulk pricing for solutions with tight tolerances. Strategic sourcing and haggling with suppliers often bring further price cuts without sacrificing quality of production. Simplified logistics and inventory management also assists in preventing over or under-stocking, thus significantly improving operational costs.
Supporting Innovation and Customization
It is in the capacity of an esteemed distributor to take care of its differentiation in customizing high-end power solutions from development to design. These innovations will eventually lead to products that will necessitate definition in time with changing market needs. Access to cutting-edge technology and expert guidance should broaden their scope to experiment with new designs, improved functionalities, and an enhanced overall performance.
Wrapping Up
The quality and reliability of the components that go into assembling the PCB electronic board are prime determinants of success. With the partnership of a trustworthy distributor of electronic components, manufacturers can better assure product quality, market demand, and their competitive edge in the electronics arena.
0 notes
Text
PCB Electronic Board and the Role of Electronic Components Distributors
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential to advanced innovation, serving as the establishment upon which electronic components are fastened to make utilitarian gadgets. From shrewd phones to mechanical apparatus, PCBs are fundamental in nearly each industry. In this article, we’ll investigate the part of the PCB electronic board, the significance of an electronic components merchant, and the centrality of circuit board components in guaranteeing smooth gadgets manufacturing.
What is a PCB Electronic Board?
A PCB Electronic Board is a pivotal component in any electronic gadget. It serves as a physical stage to interface and organize electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors through conductive pathways, flag follows, or tracks. The essential work of a PCB is to mechanically bolster and electrically interface different components, permitting them to work together seamlessly.
Types of PCB Electronic Boards
1. Single-Sided PCB: This is a clear sort where components are put on one side, whereas conductive copper follows are found on the inverse side.
2. Double-Sided PCB: In differentiate, this sort obliges components on both sides of the board, with conductive layers too on both sides.
3. Multi-Layer PCB: Numerous layers of PCBs stacked together, utilized for more complex electronic circuits, frequently seen in progressed computing frameworks and communication devices.
Importance of PCB Electronic Boards in Cutting edge Electronics
• Compact Plan: PCBs permit for the miniaturization of gadgets, empowering the creation of littler, more capable contraptions like smart phones, portable workstations, and wearable devices.
• Cost-Efficiency: Mass generation of PCBs guarantees that electronic gadgets can be made cost-effectively, whereas still guaranteeing tall performance.
• Reliability: A well-designed PCB moves forward the in general unwavering quality and toughness of electronic gadgets, as components are safely mounted and connected.
Defining an Electronic Components Distributor
An Electronic Components Distributor is crucial within the electronics supply chain. These merchants act as mediators between producers and businesses, giving a wide run of components required to collect PCBs and other electronic frameworks. Whether you're a large-scale hardware producer or a little commerce, having get to dependable merchants guarantees that you get high-quality components on time.

Role of Electronic Components Distributors
1. Wide Item Accessibility: Wholesalers give a wide choice of components, from essential things like resistors and capacitors to progressed chip and coordinates circuits.
2. Quality Confirmation: Legitimate wholesalers work with certified producers to guarantee that all components meet industry measures and are free from defects.
3. Supply Chain Productivity: Wholesalers guarantee convenient conveyance of components, lessening the hazard of delays in generation due to supply shortages.
4. Technical Bolster: Numerous merchants offer extra administrations such as specialized back and plan exhortation, making a difference producers select the right components for their particular needs.
Key Circuit Board Components
A PCB electronic board requires a assortment of components to work accurately. Here are a few of the most basic Circuit Board Components:
1. Resistors: These components direct the stream of electrical current, guaranteeing that circuits work inside secure working limits.
2. Capacitors: Capacitors store electrical vitality and discharge it when required. They are pivotal in sifting signals and stabilizing voltage in circuits.
3. Diodes: Diodes permit current to stream in one heading as it were, securing the circuit from harm due to switch current.
4. Transistors: These components act as switches or speakers, playing a critical portion in controlling the stream of electrical signals in a circuit.
5. Integrated Circuits (ICs): ICs are small chips that contain distinctive components like transistors, diodes, and resistors, allowing complex capacities to be performed on a single piece of silicon.
6. Inductors: Inductors store vitality in a attractive field when current passes through them, commonly utilized in sifting applications and control supplies.
How to Select the Right Circuit Board Components
• Compatibility: Guarantee that the components are congruous with the plan of your PCB, counting measure, control prerequisites, and execution specifications.
• Reliability: Select high-quality components from trusted producers or wholesalers to guarantee the long-term unwavering quality of your devices.
• Availability: Guarantee that the components you select are promptly accessible in the showcase, particularly if you're arranging for large-scale production.
Conclusion
PCB electronic Boards, electronic components merchants, and circuit board components are basic in the world of hardware fabricating. A well-designed PCB, combined with high-quality components sourced from dependable merchants, guarantees the effective generation of tough, high-performance electronic gadgets. Understanding these components permits producers to enhance and create the innovation that powers our advanced world.
0 notes
Text
How a Computer Works - Part 3 (Miniaturization and Standardization)
For anyone just joining in, I'm writing a series of posts explaining perhaps haphazardly all there is to know about how a computer works, from the most basic fundamental circuitry components to whatever level of higher functionality I eventually get to. As explained in the first post on this subject, I am doing this just in pure text, so that if you are inclined you can straight up print these posts out or narrate them onto some audio tape or whatever and have full access to them should every computer in the world suddenly collapse into a pile of dust or something. Part 1 mainly covered the basic mechanical principles of circuitry and how to physically construct a logic gate. Part 2 covered logic gates in detail and how to use them to create a basic working architecture for a general purpose computer. Today we're going to be talking more about what you're looking at when you crack a machine open so you can make sense of all the important fiddly bits and have maybe a starting point on how to troubleshoot things with a multimeter or something.
Before getting into it though, I do have to shake my little donation can again and remind you that I do not know how I am going to get through the winter without becoming homeless, so if this is valuable to you, I'd appreciate some help.
Boards of Bread and Printed Circuits
With the things I've explained so far, you could totally build a computer right now, but it'd be a bit messy. You can totally buy resistors, transistors, capacitors, and diodes by the bagful for basically nothing, and cheap rolls of insulated wire, but there's all these long exposed pins to cut short and soldering things in mid-air is a messy nightmare and you'd just have this big tangle of wires in a bag or something that would almost certainly short out on you. So let's look into ways to organize stuff a little.
If you start playing around with electronics on your own, one of the first things you want to hook yourself up with besides raw components and wires is a breadboard or 12. And if you're watching people explain these things with visual aids, you'll also see a lot of them, so it's good to know exactly what they are and how they work. Your standard breadboard is a brick of plastic with a bunch of little holes in it. Incidentally, the name comes from how the first ones were literally just named after the wooden cutting boards for slicing bread people recycled to make them. Inside these holes there's some pinching bits of conductive metal which connect to each other in a particular way (pretty sure you can just see the strips that connect one if you pry the bottom off), so you can just jam a thing wire or prong into a hole, have it held in place, and make a connection to every other hole its connected to on the other side.
There is a ton of standardization to all of this. The holes should always be 0.1 inches apart () and split into two big grids. Everyone I've ever seen has 63 rows, each with 5 holes labeled A-E, a shallow channel through the middle of the board, and then another 5, F-J, and we generally have numbers printed every 5 rows. Down underneath, for any given row, the set of 5 pins on each side of the channel are connected. So, holes 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D, and 1E are all connected to each other, and nothing else. Holes 1F, 1G, 1H, 1I, and 1J are also connected to each other. There's no connection though between 1E and 1F, or 1A and 2A.
Most breadboards will also have a couple of "power rails" along the sides. These are just going to be labeled with a long red line and +, and a long blue or black line and -, and have holes in 2x5 blocks staggered out. With these, all 25 or 50 or whatever holes near the red + line connect with each other, and all the ones near the black line connect with each other. The gaps every 5 holes don't serve any purpose beyond looking different enough from the big grid so you hopefully don't mix it up and forget that these ones all connect down the length, and not in in little clumps across the width like everything else. The idea, for the sake of convention, is you plug a wire connected directly to the positive side of your battery or DC adapter or whatever into any red line hole, the negative side to any blue/black hole, and then tada, you can make a circuit just by plugging a wire in from red to a normal grid line, whatever bits you want span from that grid line to another, and eventually you connect the far end back anywhere on the black/blue line.
With a nice circuit board, there's also little snap-together pegs along the sides, and the power rails are just snapped on with those. So you can just kinda cut through the backing with a knife or some scissors, snap those off, connect multiple boards together without redundant power rails in the middle, and then just have these nice spare long lines of linked sockets. In the computer I'm building on these, I'm just using spare power rails for the bus. Oh and the big grooved channel down the middle also has a purpose. Bigger electronic components, like our good good friend the integrated circuit, are generally designed to be exactly wide enough (or more, but by a multiple of 0.1 inches) to straddle that groove as you plug their legs into the wires on either side, so they nicely fit into a breadboard, and there's a handy gap to slide something under and pry them off later on.
Typically though, you don't see breadboards inside a computer, or anything else. They're super handy for tinkering around and designing stuff, but for final builds, you want something more permanent. Usually, that's a printed circuit board, or PCB. This is pretty much what everyone's going to picture when they think about the guts of a computer. A big hard (usually) green board with a bunch of intricate lines, or "traces" running all over made of (usually) copper. And maybe with some metal ringed holes punched all the way through (they call those vias). These tend to look really complicated and maybe even a little magical, but they're honestly they're just pre-placed wires with a sense of style.
Most of the material of the board is insulated. The copper traces conduct real well, and manufacturers have done the math on just how close together they can be run without connecting to each other in places you don't want. The holes that go all the way through are for either plugging other bits in that tend to come with long legs you maybe want to keep intact, or just ways to run a trace through to the other side, where we often have traces on the back too to maximize our space. Most of what makes them look all cool and magical is how the traces run as close packed as possible to conserve space, and tend to only turn at 45 degree angles, which is just an artifact of how the machinery used to etch them out sued to be iffy about anything else.
So tada, you have all your wires pre-stuck to a nice sturdy board, and maybe even have labels printed right on there for where you solder all the various components to finish the thing. Oh and when you hear people talk about like, motherboards and daughterboards? The big main board you have for everything is a motherboard. Sometimes you need more than that, so you make smaller ones, and connect them up ether with some soldering or cartridge style with end-pins sliding snugly into sockets, and those we call daughterboards.
Integrated Circuits, or as they're also known, "chips"
The last thing you're likely to find if you crack open a computer, or just about any other electronic device that isn't super old or super super simple, are integrated circuits. Generally these are think black plastic bars that look like you'd maybe try to awkardly use them to spread cheese or peanutbutter on crackers in a prepacked snack or something, with rows of tiny little legs that running along either side. Kinda makes them look like little toy bugs or something. Sometimes they're square with pins along every edge, because sometimes you need a lot of pins. These are integrated circuits, or microchips, or just chips, and wow are they handy.
Sometime back in the 60s when people were really getting their heads around just how ridiculously small they could make electronic components and still have them work, we started to quite rapidly move towards a point where the big concern was no longer "can we shrink all this stuff down to a manageable size" and more "we are shrinking everything down to such an absurdly tiny size that we need to pack it all up in some kind of basically indestructible package, while still being able to interact with it."
So, yeah, we worked out a really solid standard there. I kinda wish I could find more on how it was set or what sort of plastic was used, but you take your absurdly shrunken down complex circuit for doing whatever. You run the teensiest tiniest wires you can out from it that thicken up at the ends into standard toothy prongs you can sink into a breadboard or a PCB with that standardized pin spacing, and you coat it all in this black plastic so firmly enveloping it that nothing can move around inside or get broken, hopefully.
And honestly, in my opinion, this is all TOO standardized. The only real visible difference between any two given integrated circuits is how many legs they have, and even those tend to come to some pretty standard numbers. They're always the same size shape and color, they all have the same convention of having a little indented notch on one side so you know which end is which, and they all seem to use just the worst ink in the world to print a block of numbers on the back with their manufacturer, date of assembly, a catalog number, and some other random stuff.
For real if there's any real comprehensive standard for what's printing on these, I can't for the life of me find it. All I know is, SOMEWHERE, you've got a 2 or 3 letter code for every manufacturer, a number for the chip, and a 4 digit date code with the last 2 digits of the year, and which week of that year it was. These three things can be in any order, other things can also be on there, probably with zero spacing, and usually printed in ink that wipes away like immediately or at least is only readable under really direct light, it sucks.
Once you know what a chip is though and look up the datasheet for it, you should have all sorts of handy info on what's inside, and just need to know what every leg is for. For that, you find which end has a notch in it, that's the left side, sometimes there's also a little dot in the lower left corner, and hopefully the label is printed in alignment with that. From there, the bottom left leg is pin 1, and then you count counterclockwise around the whole chip. You're basically always going to have positive and negative power pins, past that anything goes. You can cram a whole computer into a single chip, yo can have someone just put like 4 NAND gates on a chip for convenience, whatever.
OK, but how do they make them so small?
OK, so, mostly a circuit we're going to want to shrink down and put on a chip is just gonna be a big pile of logic gates, we can make our logic gates just using transistors, and we can make transistors just by chemically treating some silicon. So we just need SUPER flat sheets of treated silicon, along with some little strands of capacitive/resistive/insulating material here and there, and a few vertically oriented bits of conductive metal to pass signals up and down as we layer these together. Then we just need to etch them out, real real small and tight.
And we can do that etching at like, basically infinite resolution it turns out. It just so happens we have access to special acids that eat through the materials we need them to eat through, but that only work when they're being directly hit with fairly intense UV light. And a thing about light is when you have say, a big cut out pattern that you hold between a light and a surface, it casts a shadow on it... and the scaling of that shadow depends entirely on the distances between the light, the pattern, and the surface. So if you're super careful calibrating everything, you can etch a pattern into something at a scale where the main limiting factors become stuff like how many molecules thick things have to be to hold their shape. Seriously, they use electron microscopes to inspect builds because that's the level of tininess we have achieved.
So yeah, you etch your layers of various materials out with shadow masks and UV acid, you stack them up, you somehow align microscopic pins to hold them together and then you coat the whole mess in plastic forever. Tada. Anything you want in a little chip.
ROMs, maybe with various letters in front
So there's a bunch of standard generally useful things people put into ICs, but also with a computer you generally want some real bespoke stored values with a lookup table where you'll keep, say, a program to be run by feeding whatever's inside out to the bus line by line. For that we use a chip we call Read Only Memory, or ROM. Nothing super special there, just... hard wire in the values you need when you manufacture it. Manufacturing these chips though is kind of a lot, with the exacting calibrations and the acid and the clean rooms and all. Can't we have some sort of Programmable ROM? Well sure, just like build it so that all the values are 1, and build a special little thing that feeds more voltage through than it can handle and physically destroy the fuse for everything you don't want to be a 1.
OK that's still kind of a serious commitment. What if I want to reuse this later? Oh, so you want some sort of Erasable PROM? OK someone came up with a funky setting where you overload and blow out the fuses but then if you expose the guts of the chip to direct UV light through this little window, everything should reform back to 1. Just like, throw a sticker on there when you don't want to erase it. Well great, but can we maybe not have me desolder it and take it out to put under a lamp? Oh la de da! You need Electronically Erasable PROMs? EEPROMs? I guess we can make THAT work, somehow. They're still gonna be slow to write to though, can't have anything. I mean, not unless we invented like, flash memory. Which somehow does all this at speeds where you can use it for long term storage without it being a pain. So that's just kinda the thing we have now. Sorry I don't quite get the principles behind it enough to summarize. Something about floating components and needing less voltage or whatever. Apparently you sacrifice some read speed next to older options but hey, usable rewritable long term storage you just plug in, no jumping through extra hoops.
So OK. I think that's everything I can explain without biting the bullet and explaining ALUs and such. Well, there's keyboards (they're just buttons connecting input lines), monitors (these days, LEDs wired up in big grids), and mice (there's spokes in wheels that click X times or cameras checking the offset values of dust on your desk or whatnot).
Maybe throw me some money before we move on ?
CONTINUED IN PART 4
#computers#computer science#pcb#printed circuit board#integrated circuits#microchip#breadboards#education#electronics
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
PCB layout--MakerPCB
PCB or PCB assembly quickly offer, feel free email to [email protected]
https://www.linkedin.com/in/marcia-liu-0566a11b1/
#electronic#uav#pcb assembly#pcb#pcb manufacturer#flexible pcb board#flex pcb#electrical design#engineering#electrical#electricity
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
We provide a reliable, cost effective and efficient service to various industries throughout the UK and indeed worldwide. Our key areas of expertise are repairing, variable speed drives including; Frequency Inverters, Spindle, Servo, Stepper; HMI’s, Power Supplies, Programmable Logic Controller’s (PLC’s), Printed Circuit Boards (PCB’s), Servo Motors, Encoders and many other types of industrial equipment. Occasionally we use our worldwide network of suppliers to effect a repair.
#electronic restoration services#circuit board repair#printed circuit board repair#electronics repairs#pcb repair
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Benefits of Ordering Printed Circuit Boards Online: A Guide to Choosing the Right PCB Manufacturer
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in various electronic devices, from smartphones to industrial machinery. As demand for these essential components grows, businesses and hobbyists alike seek efficient and cost-effective solutions for obtaining high-quality PCBs. One of the most convenient methods is to order printed circuit boards online. In this article, we will explore the advantages of ordering PCBs online and provide insights into selecting a reputable PCB manufacturer.
Why Order Printed Circuit Boards Online?
Ordering printed circuit boards online offers several benefits, making it an attractive option for many businesses and individuals:
Convenience: The ability to order PCBs from the comfort of your home or office eliminates the need for in-person visits to manufacturers or suppliers. This convenience saves time and effort, allowing you to focus on your projects or business operations.
Wide Range of Options: Online PCB manufacturers offer a variety of options in terms of materials, layer counts, finishes, and more. This flexibility allows you to customize your PCBs according to your specific requirements and budget.
Cost-Effectiveness: Many online PCB manufacturers provide competitive pricing, especially for bulk orders. Additionally, you can easily compare prices and services from different providers, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
Quick Turnaround Times: Online ordering often comes with expedited production and shipping options, allowing you to receive your PCBs faster. This is particularly beneficial for projects with tight deadlines or when you need quick prototypes.
Access to Advanced Technologies: Many online PCB manufacturers offer advanced technologies such as high-frequency PCBs, flexible PCBs, and more. This access to cutting-edge technology ensures your designs are compatible with the latest industry standards.
Choosing the Right PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is crucial to ensuring the quality and reliability of your printed circuit boards. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a PCB manufacturer:
Experience and Reputation: Look for a manufacturer with a solid track record and positive reviews from previous customers. Experienced manufacturers are more likely to produce high-quality PCBs and provide reliable service.
Quality Assurance: Ensure the manufacturer follows strict quality control measures, such as ISO certification and regular testing. High-quality PCBs are essential for the proper functioning and longevity of your electronic devices.
Customer Support: Good customer support is vital, especially if you encounter issues during the ordering process or with the final product. Choose a manufacturer that offers responsive and helpful customer service.
Manufacturing Capabilities: Check the manufacturer’s capabilities, including the types of PCBs they can produce, their layer count capacity, and the materials they use. Make sure they can meet your specific design requirements.
Lead Times and Shipping: Consider the manufacturer’s production lead times and shipping options. Quick turnaround times are crucial for meeting project deadlines, so choose a manufacturer that can deliver within your required timeframe.
Pricing and Payment Terms: While cost is an important factor, it should not be the sole consideration. Ensure the manufacturer offers transparent pricing and flexible payment terms that suit your budget.
Conclusion
Ordering printed circuit boards online is a convenient and cost-effective way to obtain high-quality PCBs for your projects. By choosing a reputable PCB manufacturer, you can ensure the reliability and performance of your electronic devices. Whether you are a business looking to streamline your supply chain or a hobbyist working on a personal project, ordering PCBs online provides a seamless and efficient solution.
For those ready to place a printed circuit board order online, consider the factors outlined above to select the right PCB manufacturer for your needs. With the right partner, you can bring your electronic designs to life with precision and quality.
#printed circuit board#pcb manufacturer#pcb supplier#printed circuit board order online#pcb design & manufacturing services#pcb circuit manufacturer in ahmedabad#electronic circuit design company
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
PCB Assembly Prototypes Manufacturer
PCB Assembly
What is a prototype PCB assembly?
PCB prototyping is the experimentation pilot stage of the product which is to be mass produced at a later stage. This is more of an experiment which is done after the initial discussions and the design. This offers a pre-production analysis of the boards that are to be manufactured, reducing the possible number of errors in the PCB design. PCB prototypes help the manufacturer analyze the strengths as well as weak areas of their proposed circuit boards. Prototypes also serve as a reference point for future versions of the same product. At Hitechpcba, we handle PCB prototype assembly in quantities from one to hundred printed circuit boards.
We have acquired capabilities that enable us to serve our clients better. All these years, we have worked on many complex prototype PCB assembly projects, and we believe the following capabilities have helped us serve our clients better.
Prototype PCB Assembly Services: We specialize in the following prototype printed circuit board assembly services.
SMT: We can provide single-sided and double-sided surface mount PCB assemblies in different specifications.
Plated Through Hole: We offer plated through hole assembly with selective soldering.
Mixed Assemblies: We often work on projects involving mixed assemblies – through-hole and SMT and electromechanical assemblies.
PCBA Testing: All the PCBA functional testing is performed in-house. Over the years, we have invested in various test fixtures and equipment, which helps us ensure the quality of PCBA. Currently, we provide the following types of PCBA testing services:
Flying probe testing for PCB
Functional testing including system and board-level testing
General PCB Assembly Capabilities: Our general PCB assembly capabilities are not limited to these:
RoHS, leaded or lead free, clean and no chemistries
PCB components including various types of QFNs, BGAs, 0105, 0201, 0804, and press fit components in small quantities.

What are the benefits of a prototype PCB assembly?
Prototype PCB assembly comes with several advantages. These benefits play a major role in the facilitation of your PCB manufacturing. Some of these benefits include:
Detection of Flaws Early
With prototype PCB, you will easily detect whatever flaws are present during the product’s development stages. This will allow you to solve the issues thereby saving you some money if you had gone ahead to make the production having the flaws in them.
If you go ahead to make changes during the production, there may be a need for more technicalities, and this may be expensive.
Testing of Each Component
With a prototype, you will be able to test all your system’s elements individually before you go ahead to set it up. You should do this because it is important especially for very complex projects composed of several parts that are PCB based.
When you validate each of these components, you will be able to identify those areas having issues that you should look into. This is the only way the project can function the right way.
Reduction in Total Costs
Utilizing the prototype bare PCB for any of your projects could go a long way in reducing what you’ll have spent in total for the project. With prototyping, you will be able to notice those errors in your project and then make corrections before you start the real production.
As soon as these flaws have been checked and rectified, then you may continue with the manufacturing of your Printed circuit boards in large quantities, thereby saving you unnecessary costs.

High-Quality PCBs
Why prototyping your PCB is important is to help you test if your project will function effectively. When we talk of testing, it involves the identification of errors present and then rectifying and making corrections to them.
Therefore, the eventual PCB after the prototyping will be of high quality that surely meets standards set internationally.
Less Turnaround Time
With prototype PCB assembly, you will be able to reduce the total time used in producing your printed circuit board. While making use of prototype printed circuit boards, you’ll be able to see the errors and then make corrections before you start the actual production.
Therefore, the eventual prototype will be free of defects. This implies that your PCBs will be produced quickly by your manufacturer.
We are here :https://www.hitechpcba.com/pcb-assembly-manufacturer
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

keebtar
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Advanced PCB Manufacturing Cost Effective Solutions Partnership
Introducing a one-stop solution for all your advanced PCB manufacturing needs such as rigid-flex pcb. We're not just a provider; we're your partner in innovation, serving customers globally with top-notch fabrication, solutions, and services. Join our Advanced PCB Manufacturing cost effective solutions for USA, EU, Germany, Switzerland.
#Advanced pcb#pcb manufacturer#usa#europe#germany#switzerland#technology#printed circuit board#affiliate program#partnership#electronic
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Multilayer PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) offer numerous advantages over their single-layer or double-layer counterparts. These benefits arise from their enhanced design capabilities, improved performance, and greater flexibility. Here are some key advantages of multilayer PCBs:
#PCB#printed circuit board manufacturers#electronic cable assembly#pcb manufacturing#pcb assembly manufacturer#pcb assembly services#pcb board manufacturer#printed circuit board manufacturer in india#circuit board manufacturing#pcb exporters#pcba#pcb manufacturer#pcb design#pcbassembly#multilayer pcb
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
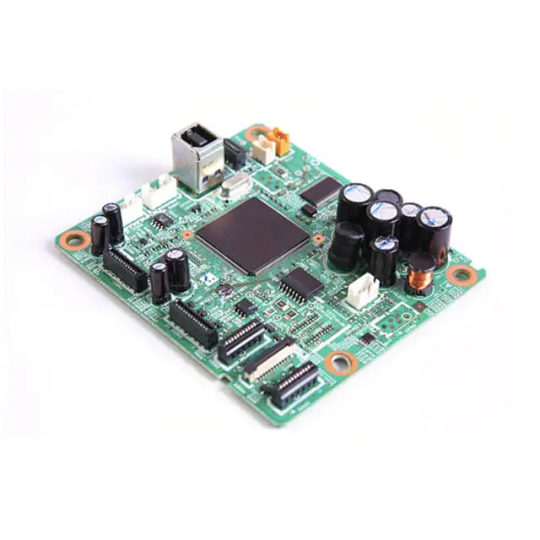

Fanway as a professional high quality Mixed PCB Assembly manufacture, you can rest assured to buy Mixed PCB Assembly from our factory and we will offer you good after-sale service and timely delivery.
0 notes
Text
Grundy Partners RM-B PCB Card | High-Performance Industrial Control Board | Ram Automations
Discover the reliability and precision of the Grundy Partners RM-B PCB Card, a trusted component in many automation and industrial control systems. Whether you’re upgrading, repairing, or maintaining your equipment, this used but fully functional PCB card is the perfect fit for high-performance applications. Now available at Ram Automations, where we specialize in genuine and hard-to-find industrial and marine spare parts from the world’s top brands.
🛒 Buy Now: https://ramautomations.com/products/grundy-partners-rm-b-pcb-card-used
🌐 Explore Our Full Product Range: https://ramautomations.com
🔍 Product Highlights:
• Product Name: RM-B PCB Card • Brand: Grundy Partners • Condition: Thoroughly Tested & Verified • Type: Printed Circuit Board (PCB) • Application: Industrial Control & Automation Systems
This RM-B PCB Card by Grundy Partners is built to ensure the longevity, reliability, and stability of your industrial control setup. It handles signal transmission and circuit management tasks effectively, making it indispensable in automation processes. Even though it’s used, it’s been quality checked and remains highly efficient.
✅ Key Features:
✔️ Trusted quality by Grundy Partners ✔️ Designed for industrial-grade applications ✔️ Enhances operational accuracy and circuit performance ✔️ Thoroughly tested and quality assured ✔️ Ideal replacement for faulty or discontinued PCB cards ✔️ Part of advanced automation, monitoring, or PLC control systems
🏭 Ideal For:
• Manufacturing Units • Electrical & Automation Control Panels • Marine Equipment Controls • Power Distribution Systems • Factory Automation • Legacy Equipment Repairs • OEM Replacement for Existing Units
📦 Why Buy from Ram Automations?
At Ram Automations, we offer a massive inventory of industrial automation and marine equipment spare parts, including rare or discontinued models from over 1000+ trusted brands. Whether you’re searching for automation parts, PLCs, drives, transmitters, power supplies, or circuit boards like the Grundy Partners RM-B PCB Card, we deliver with quality, care, and global shipping options.
✔️ 100% Genuine & Tested Products ✔️ Competitive Pricing & Bulk Order Discounts ✔️ Worldwide Shipping & Timely Delivery ✔️ Reliable Technical Assistance ✔️ Hassle-Free Returns ✔️ Trusted by Engineers Worldwide
🔎 Applications of Grundy Partners RM-B PCB Card:
• Signal Processing • PLC Interfacing • Control Logic Processing • Automation Loop Control • Circuit Integration in Industrial Machinery • Equipment Maintenance for Manufacturing Plants
📽️ Watch to Learn:
In this video, we highlight the technical features and uses of the Grundy Partners RM-B PCB Card. Learn how this component functions within your automation system and why it’s a preferred solution among engineers and industrial professionals.
🔧 We also provide installation tips, use cases, and troubleshooting info to help you deploy it effectively in your setup.
💬 Let’s Connect:
If you have any questions about this PCB card or other industrial products, drop them in the comments! 👍 Like this video if it helped you 🔔 Subscribe to stay updated on automation components
#Grundy Partners RM-B#RM-B PCB Card#Grundy RM-B Board#industrial PCB card#automation spare parts#control panel board#signal interface card#used automation board#industrial control board#circuit board automation#industrial PCB module#OEM replacement PCB#automation system PCB#Ram Automations parts#marine PCB components#electrical control board#automation PCB card#PCB for industrial system#used PCB board#Grundy automation board#automation electronics#control signal processor#legacy PCB replacement#Grundy PCB module#printed circuit board#automation spares
1 note
·
View note
Text
SMT chip mounting process--MakerPCB
PCB or PCB assembly quickly offer, feel free email to [email protected]
https://www.linkedin.com/in/marcia-liu-0566a11b1/
#pcb assembly#pcb manufacturer#pcb design#flexible pcb board#pcb#hardware#flex pcb#soldering#electronics#solderingstation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
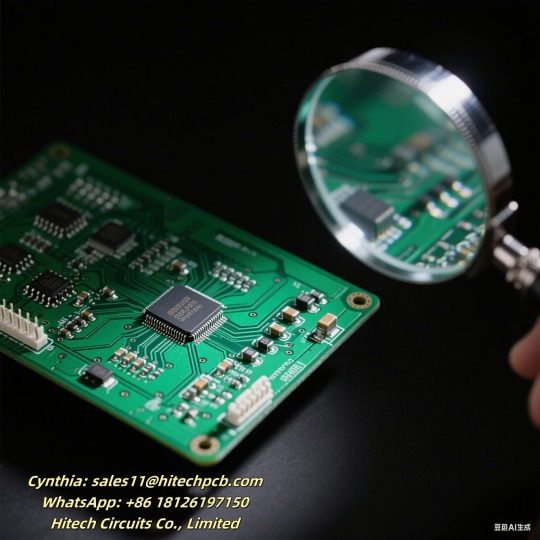


2. Why PCBA Quality is Non-Negotiable, Hitech Circuits at your service.
The quality of PCBA directly impacts the performance, reliability, and lifespan of your electronic devices. A subpar PCBA can lead to frequent malfunctions, increased product returns, and damage to your brand reputation. On the contrary, a well-crafted PCBA ensures stable operation, reduces maintenance costs, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Our PCBA manufacturing process adheres to the highest industry standards. From material selection to final inspection, every step is meticulously monitored to guarantee that each assembly meets or exceeds your specifications. We use premium-grade PCBs, genuine electronic components, and advanced soldering techniques to ensure strong connections and optimal functionality.
Email Cynthia: [email protected] if you are interested in PCB and PCBA service.
#pcb assembly#pcb manufacturer#pcba#led pcb#pcb#fr4#flexible pcb board#aluminum pcb#electronic#ceramic pcb#flex pcb
0 notes
Text
Printed Circuit Board Basics
Most of us are using Printed Circuit Board in our daily life. Printed Circuit Boards are used in almost all the Electronic products, from consumer gadgets such as PCs, tablets, smartphones, and gaming consoles to industrial and even high tech products in strategic and medical electronics domains.
Here, we have some statistics for you that shows how many electronic devices connect worldwide from 2015 to 2025. This statistic shows an increase in the use of a number of PCB in people daily life. Hence, CircuitWala took this opportunity to provide a basic knowledge about PCB via this article.
There are so many books available online which teach about Printed Circuit Board design and hardware part. There are few links available online which shows only a few basic fundamentals of PCB and few are there for Basics of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Design. Few which gives good know knowledge on Printed Circuit Board terminology. But in the end for the hobbyist, there is no such material available which make their work easy.
Now days there few online designing websites available which allow hobbyist and students to create their design and Printed Circuit Board fabrication part. These websites provide limited features and charge high for the full edition. We, @CircuitWala are in try to provide one platform which provides plenty of Printed Circuit Board knowledge digitally to make your work simple and easy.
Alternatives of PCB include wire wrap and point-to-point construction. Creating a layout of PCB is a little bit time-consuming method as compared to its alternative solution but manufacturing of PCB is cheaper and faster then other wiring methods as electronic components are mounted and wired with one single part.
Let’s start with some basics of Printed Circuit Board with this article. Here in this article we will discuss about history of PCB to understand the emerge of PCB, Types of PCB to make your complex PCB a very simple using different types, Usage of PCB to provide you an idea to create more Printed Circuit Board projects, Advantages and Disadvantages, Possible Future to know about new technological change in Printed Circuit Board manufacturing and also about how to destroy and manage your PCB’s e-waste? We know you are eager to know all the stuff in details but before that let’s make a simple definition of Printed Circuit Board.
What is Printed Circuit Board?Printed Circuit Board is an electronic device made of conductive material(FR-4) like copper which connects components mounted on it to to get desired output by providing an input on another end.
When the board has not mounted with any of the components is called as Printed Circuit Board or Printed Wired Board. Mounting of an electronic component on Printed Circuit Board is called as PCB assembly.
History of Printed Circuit BoardThe invention of Printed Circuit Board was by Austrian engineer Paul Eisler as part of a radio set while working in England around 1936.
In early days before Printed Circuit Board became common in use, Point-to-Point construction was used. This meant some bulky and unreliable design that required plenty of sockets and regular replacement of it. Most of this issue directly address when PCB went into regular production.
Originally, every electronic component had wire leads, and the PCB had holes drilled for each wire of each component. The components’ leads were then passed through the holes and soldered to the PCB trace. This method of assembly is called Through-Hole construction. There is one other method to mount component is called as Surface Mount.
Type of Printed Circuit BoardPCBs are produced from the different types of material and on the basis of that material PCBs are divided mainly into two parts: Rigid PCB and Flexible PCB. Nowadays, a combination of Rigid and flexible PCB is also possible and that is called as Flexi-Rigid PCBs.
Most of the PCBs are built in layers. The inner layer is the base material called as a substrate. Rigid PCBs are mainly made of material like epoxy materials and Flexible PCBs are made of plastic material that can withstand high temperatures.
Rigid PCBs are generally, hard materials that hold the component in a better way. The motherboard in the tower of a computer is the best example of Rigid PCBs. Flexible PCBs fundamental material allows PCB to fit into forms that Rigid PCBs can not. Flexible PCBs can turn round without harmful the circuit on PCB.
All Rigid and Flexible PCBs can come in three formats by layers: Single Layer, Double Layer, and Multi-Layer.
1. Single Layer PCBSingle Layer PCBs have been around since the late 1950s and still dominate the world market in sheer piece volume. Single Sided PCBs contain only one layer of conductive material and are best suited for low-density designs. Single-sided PCBs are easy to design and quick to manufacture. They serve as the most lucrative platform in the industry.
2. Double Layer PCBDouble Layered printed circuit board technology is conceivably the most popular type of PCB in the industry. Double Sided PCB (also known as Double-Sided Plated Thru or DSPT) circuits are the gateway to advanced technology applications. They allow for a closer (and perhaps more) routing traces by alternating between top and bottom layers using vias.
3. Multi Layer PCB
Multilayer PCB is a circuit board that has more than two layers. Unlike a Double-Sided PCB which only has two conductive layers of material, all multilayer PCBs must have at least three layers of conductive material which are buried in the center of the material.
Usage of Printed Circuit BoardBy reading this article till this point, we hope that you are now able to get about printed circuit boards. Now, we will make you understand about different applications of printed Circuit Board.
In this digital world, Printed Circuit Board is in almost all our daily life electronic devices and in our industrial electronics as well. Below are the industries where PCBs are used:
Possible FutureNowadays, most of the circuits are replaced to produce Printed Circuit Board from the old methods. Revolution in technology made many of the processes automated and hence it is easy to manufacture PCB. But still, these processes are a bit expensive to hire, involve toxic waste and use high temperatures and acids. With technological advances we have seen in the past years, it is not hard to imagine PCB will soon be revolutionized. Not only that but research institutes predict a more ‘green’ future for PCBs; PCBs being made of paper.
Electronic Waste (e-waste)Electronic Waste or e-waste is described as discarded electrical or electronic devices. Informal processing of e-waste in developing countries can lead to adverse human health effects and environmental pollution.
Electronic scrap components contain a hazardous substance such as lead, cadmium, beryllium, or brominated flame retardants. Recycling and disposal of e-waste may involve significant risk to health of workers and communities in developed countries and great care must be taken to avoid unsafe exposure in recycling operations
Nowadays, developing countries are encouraging electronic users to take care while recycling the e-waste or submit them to the organization who are involved in such activities.
SummaryIn this blog, we have learned the basics of Printed Circuit Board. CircuitWala is planning to write as many blogs to provide more and more knowledge of Printed Circuit Board. Either it is basics or manufacturing or usages or advantages and disadvantages of PCBs. We will also try to make our users/customers up to date for the new technology innovations, including past histories and revolution of the PCB industries.
In the next blog, we will look at more briefly about the different types of Printed Circuit Board. We also understand the process to make it and different usage and application for the same.
#electronic circuit design company#pcb circuit manufacturer in ahmedabad#pcb design & manufacturing services#printed circuit board companies#printed circuit board order online#PCB manufacturer#Printed Circuited Board#double layer PCB#PCB Quality Control
3 notes
·
View notes