#SIPOC diagram example
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
🔄 Process Approach Across ISO & IATF Standards with 🚗 OEM Requirements in 2025
✅ Introduction: Why the Process Approach Matters in 2025 The process approach isn’t just a buzzword from ISO standards—it’s the engine behind operational excellence. As we step into 2025, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) demand more than compliance—they expect traceability, zero-defect culture, and real-time performance. In this guide, you’ll learn: 📌 How the process approach is defined…

View On WordPress
#5W2H model ISO#Automotive manufacturing#automotive quality system#clause 4.4 explained#EHS process compliance#energy management ISO 50001#environmental compliance ISO 14001#IATF 16949 process control#ISO digital integration#ISO standards 2025#lean manufacturing#occupational health ISO 45001#OEM compliance 2025#PFMEA process improvement#process approach ISO#process mapping ISO 9001#process ownership in QMS#quality management ISO 9001#risk-based thinking ISO#SIPOC diagram example#smart factory process control#Turtle diagram QMS
0 notes
Text
Conducting Effective Business Process Improvement

Business Process Improvement (BPI) is the systematic approach to helping an organization optimize its core processes for greater efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability.
1. Understand the Current State ("As-Is")
Map Out Existing Processes
Use process mapping tools like:
SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers)
Flowcharts
Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
Collect Data
Key metrics: Cycle time, error rates, cost per transaction, throughput
Interview stakeholders, observe workflows, review logs and KPIs
Tip: Get cross-functional input to avoid blind spots.
2. Define Clear Goals and Metrics
Use the SMART framework:
Specific – What process needs to improve?
Measurable – What metrics define success?
Achievable – Is it realistic with current resources?
Relevant – Does it align with strategic goals?
Time-bound – When should results be achieved?
Examples:
Reduce invoice processing time by 40% in 90 days
Eliminate 80% of manual handoffs in customer onboarding
3. Analyze the Root Causes
Use proven diagnostic tools:
5 Whys Analysis
Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram
Pareto Analysis (80/20 rule)
Process mining tools for digital workflows
Look for:
Bottlenecks
Redundancies
Manual tasks that could be automated
Communication failures
4. Design the Improved Process ("To-Be")
Use Lean, Six Sigma, and Agile Principles:
Eliminate waste (Lean: TIMWOOD – Transport, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Overproduction, Overprocessing, Defects)
Reduce variation (Six Sigma)
Shorten feedback loops (Agile)
Redesign for:
Simplicity
Speed
Scalability
Automation where possible (e.g., RPA, workflow platforms)
Create To-Be maps, RACI charts, and updated SOPs.
5. Implement the New Process
Focus Areas:
Change Management – Train teams, communicate clearly, and manage resistance
Pilot Testing – Try improvements on a small scale before a full rollout
Project Management – Use agile sprints or phased rollouts to maintain momentum
Key Tools:
Communication plan
Training modules
Feedback loops (daily standups, weekly reviews)
6. Monitor, Optimize, and Sustain
Track KPIs:
Real-time dashboards
Weekly metrics reviews
Before vs. after comparisons
Continuous Improvement:
Encourage feedback from frontline users
Use Kaizen or PDCA cycles to keep iterating
Build a culture of accountability and excellence
7. Document and Standardize
Finalize new SOPs and documentation
Create playbooks or handbooks
Assign process owners for ongoing accountability
Tip: Use a centralized knowledge base or BPM tool to manage version control.
Bonus Tools & Frameworks
Tool/MethodUse CaseLean Six Sigma (DMAIC)Structured process improvementBusiness Process Model and Notation (BPMN)Process design and documentationKPI Tree / Metrics TreeLinking process improvements to business goalsVoice of the Customer (VoC)Ensure customer impact is central to changes
Summary Cheat Sheet
StepFocus1. Assess Current ProcessMap + Measure2. Define GoalsAlign with business impact3. Root Cause AnalysisFind what's broken4. Design Future StateLean + tech + feedback5. Implement ChangesTraining + testing + rollout6. Measure & ImproveMonitor, adapt, optimize7. Document & SustainSOPs, ownership, culture shift
0 notes
Text
Business Process Mapping: A Step-by-Step Guide to Success
In today’s fast-paced business environment, optimizing efficiency is crucial for staying competitive. One of the most effective ways to enhance operations is through business process mapping. This technique allows organizations to visualize workflows, identify inefficiencies, and design solutions that streamline processes for greater success. Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, mastering business process mapping can lead to better decision-making, reduced costs, and improved performance.
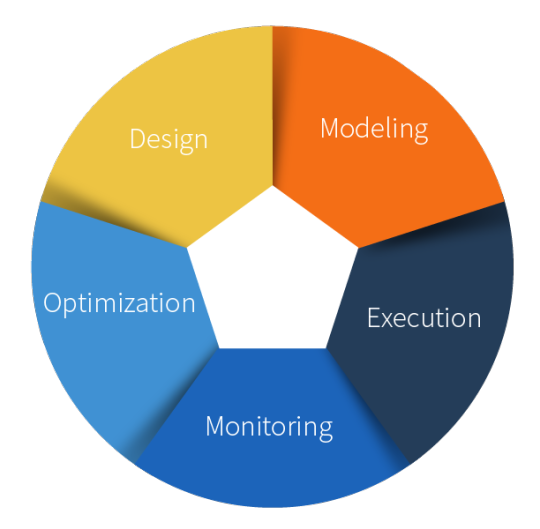
What is Business Process Mapping?
Business process mapping is a method of visually representing the steps, inputs, outputs, and resources involved in a business process. It helps businesses understand how work flows from one task to another and highlights areas that need improvement. By mapping these processes, businesses can make data-driven decisions, pinpoint redundancies, and create more efficient workflows.
Why is Business Process Mapping Important?
Clarity and Understanding: Visualizing processes makes them easier to comprehend. It enables team members at all levels to see how their tasks contribute to the overall goal of the organization.
Process Improvement: Mapping helps identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas with excessive steps. This insight allows for continuous improvements that can save time, resources, and money.
Alignment Across Teams: Business process mapping ensures all team members understand their roles, the steps they need to take, and the overall goals of the organization, reducing confusion and enhancing collaboration.
Data-Driven Decision Making: With clear visual representations, management can use process maps to make better-informed decisions about where to allocate resources and how to streamline workflows.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Business Process Mapping
1. Define the Process
The first step in business process mapping is defining the process you wish to map. This involves identifying the specific task or workflow that needs improvement. Be clear about what the process aims to achieve and the desired outcomes. For example, the process could be related to customer service, order fulfillment, or employee onboarding.
2. Identify Key Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders who are familiar with the process, including employees, managers, and other departments that interact with it. Gather input from those directly involved to understand the process flow and its pain points.
3. List the Process Steps
Break down the process into individual steps. Each step should represent a distinct action or decision. Make sure to capture all relevant activities and avoid skipping any stages, no matter how small they seem. For example, an order fulfillment process might include order receipt, payment verification, inventory check, packaging, and shipping.
4. Choose a Mapping Method
There are several techniques to map business processes. The most common methods include flowcharts, value stream mapping, SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers) diagrams, and BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation). Choose a method based on the complexity of the process and your organization’s needs.
5. Create the Process Map
Now, start creating the process map. Use appropriate symbols for different process elements: ovals for start/end points, rectangles for actions, diamonds for decision points, and arrows for flow direction. There are various tools available to create process maps, including software like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, or free tools like draw.io. Ensure that your process map is clear, easy to follow, and contains all necessary information.
6. Analyze the Process
Once the process map is created, analyze it to identify any inefficiencies, redundancies, or bottlenecks. Are there unnecessary steps that can be eliminated? Are there points where delays or errors frequently occur? This analysis is critical for improving the process and enhancing overall productivity.
7. Optimize the Process
With a clear understanding of the existing process, look for areas to optimize. This might involve eliminating unnecessary steps, automating repetitive tasks, or improving communication between departments. Reducing the complexity of the process can lead to significant time savings and cost reductions.
8. Test and Implement Changes
Before making widespread changes, test the new optimized process on a smaller scale. Gather feedback from stakeholders, and make any necessary adjustments. Once the new process is refined, implement the changes organization-wide.
9. Monitor and Iterate
After implementation, regularly monitor the process to ensure it remains efficient and effective. Business processes evolve over time, so it's important to update the process map and make adjustments when needed. Continuous improvement is key to maintaining success.
youtube
Conclusion
Business process mapping is a powerful tool for organizations looking to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance collaboration. By following these simple steps, businesses can map out their processes, identify pain points, and implement improvements that drive success. With a clear, visual representation of workflows, teams can work more cohesively, and businesses can achieve higher productivity and better overall performance.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Software Processes - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
1 note
·
View note
Text

➡️ SIPOC Diagram | Example | PPT Template | Excel Template Download
0 notes
Text
How to Use a Workflow Mapping Template
A workflow mapping template is a valuable tool for documenting, analyzing and better understanding your team’s business processes and associated outcomes. It’s also an essential tool for establishing and improving communication, productivity and teamwork.
Identify the Why for Process Mapping
The reason you’re creating a process map is typically because something isn’t working as well as it could be, and/or there are issues with the current process. For example, maybe a new service needs to be developed or a certain process isn’t meeting performance metrics.
Gather Information for Process Mapping
Once you’ve figured out the reason for your map, you need to start collecting the information you need. It may help to shadow employees or conduct interviews to collect the details needed. Once you’ve gathered all the information, you need to document it in a way that makes sense and is easy to understand.

Make a Flowchart or Diagram for Your Workflow
The most common type of diagram is a flowchart, which shows the end-to-end steps and their relationships to each other. Typically, arrows connect each step to demonstrate how it flows from one to the next.
Depending on the level of complexity, you can also use other diagrams. For instance, a SIPOC diagram is a high-level process map that shows the steps that start and end with inputs and outputs.
Process maps can be used for a variety of purposes, from brainstorming to identifying inefficiencies and areas of improvement to new hire training. It’s an effective way to organize a process and identify potential redundancies, bottlenecks and problems with workflow.
youtube
Also Read : meeting performance metrics
SITES WE SUPPORT
Google Docs Workflow - Blogger
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Instagram YouTube
0 notes
Text
Six Sigma in Bank Business Processes
Integrated solutions are increasingly becoming part of the banking landscape. These solutions help banks turn into customer-centric organizations and enhance customer relationships.

Business process automation is an important part of this strategy. This technology helps banks eliminate bloated workflows, streamline processes, and improve cycle times. This allows staff to focus on higher value work. It also reduces the risk of error. The use of intelligent Business Process Management Software (iBPMS) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) together drive automation efforts.
One of the most common ways to automate a process is to create a rule-based workflow. A rule-based process automatically takes repetitive decision-making steps across a full process and repurposes admin time toward high-value work.
Another way to automate a process is to document it. Detailed flow chart documentation can identify specific steps that can be automated. This can lead to improvements in cycle times, productivity, and customer service.
Another way to standardize a process is to document errors and root causes. This can identify areas of opportunity and eliminate unnecessary variation. It can also allow staff to focus on core tasks.
An example of this is the SIPOC diagram. This diagram identifies the benefits of a data collection plan and the key quality characteristics of a process.
The paper uses a graphical and descriptive approach to identify the key processes of the bank. It examines these processes to find their weaknesses, and then improves them.
The literature review provides an introduction to the application of Six Sigma management in the financial industry. This involves the creation of a management organization that promotes Six Sigma and the corresponding culture.
youtube
Also Read : Financial Industry
SITES WE SUPPORT
Finance Bank Process- Blogger
SOCIAL LINKS
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Instagram YouTube
#Business Process Management Banking Financial Industry#Banking Process Workflow#Fintech Automation#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text

➡️ SIPOC Diagram | Example | PPT Template | Excel Template Download
0 notes
Text

➡️ SIPOC Diagram | Example | PPT Template | Excel Template Download
#lean six sigma#excellence#tutorial#kaizen#iso9001#leansixsigma#tutorials#leanmanufacturing#5s#oee#industrialengineering#pokayoke#7qctools#histogram#tpm#iatf16949#g8d#iatf#qms#vsmstudy#flowchart#histograms#smartgoal#DMAIC#5Why#BlackBelt#GreenBelt#YellowBelt
0 notes
Text

➡️ SIPOC Diagram | Example | PPT Template | Excel Template Download
#lean six sigma#excellence#tutorial#kaizen#iso9001#leansixsigma#tutorials#leanmanufacturing#5s#oee#industrialengineering#pokayoke#7qctools#histogram#tpm#iatf16949#g8d#iatf#qms#vsmstudy#flowchart#histograms#smartgoal#DMAIC#5Why#BlackBelt#GreenBelt#YellowBelt
1 note
·
View note
Text

➡️ SIPOC Diagram | Example | PPT Template | Excel Template Download
#lean six sigma#excellence#tutorial#kaizen#iso9001#leansixsigma#tutorials#leanmanufacturing#5s#oee#industrialengineering#pokayoke#7qctools#histogram#tpm#iatf16949#g8d#iatf#qms#vsmstudy#flowchart#histograms#smartgoal#DMAIC#5Why#BlackBelt#GreenBelt#YellowBelt
0 notes