#mancozeb
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Carbendazim Mancozeb
Say goodbye to worries about pests and diseases damaging your crops with Kisan Pesticides. Our special blend of Carbendazim and Mancozeb ensures that your plants receive the ultimate protection they deserve. With our products, you can feel confident that your hard work will yield healthy and bountiful harvests. Choose Kisan Pesticides for peace of mind in your farming endeavors.
0 notes
Text
Brazil’s new pro-agribusiness pesticide law threatens Amazon biodiversity

A priority project of Brazil’s congressional agribusiness caucus, the so-called Poison Bill eases restrictions on the sale and use of a wide range of agrochemicals dangerous to humans and the environment.
The bill went into effect as the use of pesticides banned long ago in the European Union exploded in the Brazilian Amazon.
In the rainforest, use of the fungicide mancozeb skyrocketed by 5,600%, and the use of the herbicide atrazine increased by 575% in just over a decade.
Experts warn that lax pesticide controls will worsen impacts at the edge of the Amazon, where the chemicals affect intact biodiversity and aggravate risks to Indigenous people, riverside communities and small farmers.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmentalism#amazon rainforest#farming#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 5 Common Plant Diseases Controlled by Fungicides
Plant diseases caused by fungi can severely damage crops, reduce yields, and disrupt the global food supply chain. Fortunately, fungicides—chemical or biological agents used to control fungal diseases—play a vital role in protecting plants from these invisible enemies.
Here’s an in-depth look at five common plant diseases that fungicides help manage, along with how they work to prevent or treat them.

1. Blight
🌾 Affects:
Potatoes, tomatoes, onions, and other vegetables
🔍 Disease Details:
Blight is a fast-spreading fungal disease that causes browning, wilting, and eventual decay of plant tissue, especially leaves and stems. The most notorious type is late blight, responsible for the Irish potato famine.
🛡️ How Fungicides Help:
Preventive fungicides (e.g., mancozeb, chlorothalonil) are applied before visible signs to create a protective barrier.
Systemic fungicides penetrate plant tissues and provide internal protection, stopping blight from spreading.
2. Mildew (Powdery & Downy)
🌾 Affects:
Grapes, cucurbits (e.g., cucumbers), roses, wheat, and legumes
🔍 Disease Details:
Powdery mildew appears as white, dust-like spots on plant leaves.
Downy mildew leads to yellowing leaves and fuzzy, grayish growth on the undersides.
🛡️ How Fungicides Help:
Sulfur-based products and triazole fungicides are commonly used.
Sprays are applied in early stages or as a preventive measure during high humidity and mild temperatures.
3. Rust
🌾 Affects:
Wheat, coffee, beans, and ornamental plants
🔍 Disease Details:
Rust diseases form orange, red, or brown pustules on leaves and stems, weakening plants and reducing grain or fruit production.
🛡️ How Fungicides Help:
Preventive and systemic fungicides, such as strobilurins and DMIs (demethylation inhibitors), are effective.
Crop rotation and resistant varieties help enhance chemical control.
4. Smut
🌾 Affects:
Corn, wheat, sugarcane, and other cereal crops
🔍 Disease Details:
Smut fungi infect seeds and growing tips, leading to galls, distorted kernels, or black, sooty growth.
🛡️ How Fungicides Help:
Seed treatments with fungicides are the most effective approach to smut prevention.
Infected plants are often removed to stop disease spread.
5. Leaf Spot Diseases
🌾 Affects:
Peanuts, bananas, soybeans, beets, and ornamental plants
🔍 Disease Details:
Fungal leaf spots cause brown or black lesions on leaves, reducing photosynthesis and weakening plant vigor.
🛡️ How Fungicides Help:
Copper-based fungicides and synthetic options like azoxystrobin are used.
Sprays are typically applied at early signs of disease or during favorable conditions (warm and wet).

Conclusion
Fungicides are essential tools in the fight against fungal plant diseases. By understanding which diseases are most common and how to apply fungicides effectively, farmers and growers can protect their crops, enhance yields, and contribute to a more stable food supply. However, effective use must be paired with best agricultural practices like crop rotation, resistant varieties, and timely scouting for long-term success.
0 notes
Link
#Alternaria brassicae#Brassica napus L#Milor MZ fungicide#Pseudomonas fluorescens PF83#Raphanus brassica#Salicylic acid
1 note
·
View note
Text
Fungicides Market Size, Share, and Industry Analysis
Increasing Crop Protection Needs and Agricultural Productivity Drive Growth in the Fungicides Market.
The Fungicides Market Size was valued at USD 22.1 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 37.8 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 6.2% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The Fungicides Market is witnessing significant growth due to increasing global demand for crop protection solutions. Fungicides are chemical or biological agents used to prevent and control fungal infections in crops, ensuring higher yields and improved food security. With climate change, rising incidences of fungal diseases, and the need for enhanced agricultural productivity, the adoption of fungicides is expanding worldwide. Additionally, the shift toward bio-based and eco-friendly fungicides is driving innovation in the industry.
Key Players in the Fungicides Market
Adama Agricultural Solutions (Signum, Sencor, Bravo)
BASF SE (Headline, Cantus, Teldor)
Bayer CropScience (Corbel, Flint, Bayfidan)
Cheminova A/S (Carbendazim, Folicur, Topguard)
Dow AgroSciences (Quadris, Rally, Inspire Super)
DuPont (Chlorothalonil, Fontelis, Cabrio)
FMC Corporation (Ridomil Gold, Pristine, Topguard)
Lanxess AG (Opera, Amistar, Folicur)
Monsanto (Stratego, Pristine, Headline)
Nufarm Ltd (Score, Nativo, Mancozeb)
Future Scope of the Market
The fungicides market is expected to grow due to:
Rising demand for food security and higher agricultural productivity.
Increasing prevalence of fungal diseases affecting crop yields.
Government initiatives and subsidies for sustainable farming practices.
Advancements in bio-based and organic fungicide solutions.
Expanding applications in horticulture, cereals, and oilseeds farming.
Emerging Trends in the Fungicides Market
The market is shifting toward biofungicides and eco-friendly alternatives due to concerns about chemical residues and environmental impact. Farmers are increasingly opting for integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, combining chemical and biological fungicides for sustainable crop protection. Additionally, the development of nanotechnology-based fungicides is enhancing efficacy and targeted application. With advancements in precision agriculture and smart farming technologies, the demand for efficient and residue-free fungicides is set to grow.
Key Points:
Increasing demand for fungicides due to crop losses caused by fungal diseases.
Growing preference for bio-based and organic fungicides.
Advancements in nanotechnology and precision agriculture solutions.
Government regulations promoting sustainable pesticide use.
Expanding applications in grains, vegetables, and fruit crops.
Conclusion
The Fungicides Market is poised for steady expansion, driven by the growing need for effective crop protection solutions. As the industry shifts toward sustainable and bio-based alternatives, leading players are focusing on innovation and eco-friendly formulations. With increasing agricultural challenges and climate-related threats, the demand for advanced fungicide solutions will continue to rise, ensuring higher yields and global food security.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/fungicides-market-3548
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Fungicides Market#Fungicides Market Size#Fungicides Market Share#Fungicides Market Report#Fungicides Market Forecast
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Pesticide Spraying: Importance, Types, and Preventive Measures
Pesticide Spraying: Importance, Types, and Preventive Measures Introduction Pesticide spraying is one of the most important methods used to combat harmful pests and insects that may cause serious health, agricultural, and economic damage. Pesticides are used in various fields such as agriculture, public health, and homes, with the aim of eliminating harmful insects, bacteria, fungi, and unwanted weeds. Despite their effectiveness, the incorrect use of pesticides may lead to negative effects on the environment and human health.
In this article, we will discuss the importance of pesticide spraying, their types, methods of use, potential risks, and preventive measures to ensure safety.
The importance of pesticide spraying Pesticide spraying is an essential step to maintain public health and the agricultural environment, and its most prominent benefits are:
Combating agricultural pests:
Protecting crops from insects and fungi that affect productivity and quality.
Reducing farmers' losses and increasing the crop. Protecting public health:
Eliminating disease-carrying insects such as mosquitoes, flies, and cockroaches. Reducing the spread of infectious diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and typhoid.
Maintaining the home environment:
Getting rid of household insects such as ants, cockroaches, and bedbugs.
Reducing the possibility of spreading diseases and unpleasant odors resulting from insects.
Types of pesticides Pesticides vary according to the type of pest targeted and the way they affect it, and the most important types include:
source
شركة مقاولات بالرياض
شركة تركيب ورق جدران بالرياض
شركة دهانات منازل بالرياض
Insecticides They are used to eliminate flying and crawling insects such as flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches, and ants.
Example: Pyrethroids, Organic Phosphides.
Fungicides They are used to protect plants from fungal diseases that affect roots, leaves, and fruits.
Example: Micronized sulfur, Mancozeb.
Herbicides They are used to eliminate harmful weeds that compete with crops for food and water.
Example: Glyphosate, Bromoxynil.
Rodenticides Targets mice and rats that cause severe damage to crops and stores and transmit diseases.
Example: Warfarin, Brodifacoum.
Nematicides Used to combat nematodes that attack plant roots and cause damage.
Example: Carbofuran, Oxamyl. Pesticide spraying methods
Manual spraying Equipment used: Backpack or manual pumps. Advantages: Low cost and easy to use in small spaces. Disadvantages: Requires great effort and exposes the worker to pesticides directly.
Automatic spraying Equipment used: Mechanical or tractor-mounted sprayers. Advantages: Effective for large agricultural areas and saves time. Disadvantages: Higher cost than manual spraying.
Aerial spraying Equipment used: Aircraft or drones. Advantages: Suitable for large farms and difficult terrain. Disadvantages: Difficulty controlling the direction of spraying and the possibility of contaminating nearby areas.
Ultraviolet (ULV) spraying It depends on converting the pesticide into fine droplets that spread in the air, and is usually used to combat mosquitoes and flies in open areas.
Preventive measures during pesticide spraying To protect human health and the environment, a set of preventive measures must be followed:
Wear personal protective equipment:
Gloves, goggles, masks, and clothing that covers the entire body.
Adhere to the specified doses:
Avoid increasing the concentration of the pesticide beyond the recommended percentage.
Choosing the appropriate time for spraying:
It is preferable to spray in the early morning or before sunset to reduce evaporation.
Avoid spraying during wind or rain.
Keep people and pets away:
Make sure the area is free of people and animals during spraying and for a certain period after completion.
Safe storage of pesticides:
Keep pesticides in closed places away from children and heat sources. Potential risks of using pesticides
Health risks: Acute poisoning: May occur as a result of inhaling the pesticide or contact with the skin and eyes. Chronic diseases: Continuous exposure to pesticides may increase the risk of respiratory diseases and nervous system diseases. Allergy: Some individuals may suffer from allergic reactions to pesticides.
Environmental risks: Water pollution: Pesticides may reach groundwater or surface water and cause pollution. Negative impact on non-target organisms: such as bees, birds and fish. Emergence of resistant pests: Excessive use of pesticides may lead to the development of resistant strains of pests. Natural alternatives to chemical pesticides Given the environmental and health risks of chemical pesticides, safer alternatives have emerged such as:
Biopesticides:
Rely on microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi to control pests. Example: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). Plant extracts:
Using natural oils such as neem oil and garlic oil to repel insects. Pheromone traps:
Attracts insects to traps using sex pheromones, reducing their numbers without using chemicals.
0 notes
Text
Key Trends in Chilli Farming

In this Issue
Celebrating a significant milestone, this edition commemorates five years of our Q-AgriPulse Chilli Panel syndicate research. Originating in 2019 with 1000 chilli farmers spanning 10 districts across India, our panel reached its five-year mark in Kharif 2023.
We extend our deepest gratitude to all our clients and partners whose unwavering support has fueled our journey. This newsletter serves as a heartfelt token of appreciation, offering insights into key trends observed among chilli farmers over the past five years.

Overview of the Chilli Market
India is the world’s largest producer, consumer and exporter of spices, the country produces about 75 of the 109 varieties and accounts for half of the global trading in spices.
Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, the export of spices from India in 2020-21 touched USD $4 billion mark attaining an all -time high, recording a 30% increase in volume, 23% increase in rupee terms and 17% in dollar terms compared to the previous year.
Chilli holds the lion’s share of spice export from India, amounting to $1.50 billion which accounts for about 34 per cent of India’s total spices exports during 2023-24. Andhra Pradesh was the largest producer of chillies in the fiscal year 2023 among other states across India. The production volume amounted to over 627 thousand metric tons that year. This was followed by Telangana and Madhya Pradesh. India produced about two million metric tons of chili during that year.
Key trends in the crop protection category

Kharif 2023 was a year which saw high incidence of all major sucking insects. However a drop was seen in lepidopteran pest incidence. Thrips, Black Thrips and Whitefly incidence was reported by over 90% of the chilli growers in the 50-130 DAT window.
Black thrips continues to be a concern for farmers with growers spending approx. INR 7500-8000/acre in a season for its control. Currently high value G30 molecules viz Broflanilide, Fluxametamide, Tolfenpyrad are majorly used. In addition, Cyantraniliprole, Spinetoram, Fipronil are also used.
Thrips continues to be a concern to the chilli growers. Molecules like Fipronil and its combination, Cyantraniliprole, Spinetoram, Monocrotophos, Broflanilide are commonly used. At present farmer is spending INR 5500-5800/acre on its control
Despite the rise in insect incidence, the overall insecticide applications declined, especially in Andhra Pradesh. Farmers, anticipating poor yields due to adverse weather conditions and high infestation levels, were reluctant to invest in crop protection, leading to reduced applications during the later stages of the season.
On an average growers are making 4 applications of Fungicides and AP saw a decline in fungicide usage, where major molecules Carbendazim +Mancozeb and combinations of Azoxystrobin saw a decline in PAT share. The per acre spend on fungicides is approx.is INR 2200-2600/-
PGR and Biostimulants saw an increase of 15% by application number. The key driver here being protection of the plant health or to prevent flower drop or better fruit quality which could be due to higher incidence of insects this year, especially Black thrips impacting the 80-130 DAT period.
The Economics Of Chilli Cultivation

Over the past five years, chilli farmers have observed a consistent uptrend in the cost of cultivating chilli, with overall expenditure registering a robust 5.4% CAGR
Chilli, once considered a cash crop, has not been profitable for growers in recent years. Over the past five years, profitability from chilli cultivation has generally declined, with the most significant drop occurring in 2021. The primary reasons for this decline include the emergence of the invasive pest “Black Thrip,” a rise in other insect infestations, and unseasonal rains. These factors have collectively reduced yields by 8-9% annually.
Kharif 2023 too, was tough for chilli growers. Unseasonal rains and high insect infestations reduced both yield and quality. As a result, prices fell by 10-15% due to lower demand from traders, who blamed the poor quality of the crop.
The data of cultivation costs collected over a 5 year period reveals that chilli growers are incrementally spending 7.5% higher each year on crop protection products.
Digitalization of Chilli farming


The penetration (i.e. access to) of smartphones among chilli farmers has surged impressively, catapulting from 52% in 2019 to a remarkable 90% in 2023, reflecting an astounding 11. 6% CAGR.
AP and Telangana are the top 2 states with higher smartphone accessibility amongst chilli farmers.
Surge in usage for digital payment apps like Paytm, BHIM, Google Pay etc. and strong growth seen from 4% in 2019 to 49% in 2023.

If you found this newsletter helpful, feel free to share it with your colleagues and your broader network.
WHAT NEXT??
The detailed chilli report including Kharif 2023 data and past trends is now available. Read more to deep dive into pest incidence, brand shares and movements, detailed farmer ROI and profitability and more.
Companies mentioned in the report

Resource Link: https://qqri.com/2024/11/29/key-trends-in-chilli-farming/
#agriculture market research#agriculture market research companies#market research companies in india#agricultural market research companies in india
0 notes
Text
FOTO: Bruno Collaço / AGÊNCIA AL Dos 175 municípios pesquisados, em 60 foram constatados resíduos de agrotóxicos na água e cinquenta deles sequer poderiam fornecer água à população se estivessem localizados na União Europeia. A informação foi repassada pela doutora em Química, Sônia Corina Hess, durante reunião do Fórum Catarinense de Combate aos Impactos dos Agrotóxicos e Transgênicos, realizada nesta segunda-feira (11), na Assembleia Legislativa, com o apoio da Comissão de Turismo e Meio Ambiente. “No Brasil a lei permite cinco mil vezes mais glifosato que na União Europeia. A gente viu amostra de água com 13 diferentes agrotóxicos e está tudo bem. Por que? Porque está dentro do normal (previsto na legislação) e não existe limite para a soma dos resultados”, criticou Sônia. O engenheiro agrônomo Matheus Fraga, da Companhia Integrada de Desenvolvimento Agrícola de Santa Catarina (Cidasc), concordou com Sônia Hess. “Já peguei amostra de água com 29 produtos diferentes”, registrou Matheus. Segundo Sônia Hess, 79% dos agrotóxicos são aplicados em somente quatro culturas: 52% na soja; 10% no milho; 10% na cana-de-açúcar; e 7% no algodão. Mas os maiores problemas, de acordo com o representante da Cidasc, estão relacionados com o uso do acefato, carbendazim e clorpirifós. “Velhos, cheios de problemas no país e continuamos usando. O tomate usa agrotóxico banido, mas usam porque não sabem que é proibido, porque é o agrotóxico que têm acesso. O nosso desafio dos próximos anos tem de ser a orientação e a tecnologia da aplicação, se utilizar corretamente já diminui a quantidade aplicada”, avaliou Matheus, acrescentando que o morango, alface, pêssego e rúcula estão entre as culturas que utilizam esses agrotóxicos proibidos na União Europeia. A lixeira do mundo De acordo com levantamento feito pela doutora Sônia Hess, em 2013 foram comercializadas 495 mil toneladas de agrotóxicos no Brasil, enquanto em 2021 a quantidade foi de 719 mil toneladas. “Foram cerca de 3,4 kg por habitante em 2021”, pontuou Hess, que comparou o crescimento no uso dos agrotóxicos com o aumento da área cultivada. “O uso entre 2013 e 2021 aumentou 45%, enquanto a área cultivada aumentou somente 19%. Conclusão? A quantidade de veneno utilizada aumentou muito por hectare”, sustentou a pesquisadora. Conforme dados levantados pela doutora Hess, em 2021 foram comercializadas 219 mil toneladas de glifosato; 62 mil toneladas de 2,4D; 50 mil toneladas de mancozeb; e 35 mil toneladas de acefato. “Aparecem em nossa comida, na água. Todos banidos na União Europeia, isso nos dá a condição de lixeira, somos a maior lixeira química do mundo”, garantiu Sônia Hess. Os campeões do agrotóxico De acordo com o representante da Cidasc, as regiões que mais consomem agrotóxicos são o Planalto Norte, o Oeste e a região de São Joaquim. “O glifosato é o mais utilizado”, apontou Matheus Fraga, completando que na cultura da soja são utilizados 10 kg de agrotóxicos por hectare; cebola, 50 kg por hectare; maçã, 94 kg por hectare; fumo, 4 kg por hectare; milho, 17 kg por hectare; tomate, 97 kg por hectare; banana, 11 kg por hectare. “Este levantamento ajuda a Cidasc a focar no que realmente tem risco, como a fruticultura, que por usar uma tecnologia de aplicação defasada, tem mais riscos. O uso correto é bem complexo e custa caro, mas temos de fazer, temos de ensinar o agricultor a utilizar de forma correta, não é difícil o desafio, dá para evoluir e trabalhar de forma diferente”, opinou Matheus Fraga. Sugestões aos legisladores Doutora Sônia sugeriu a revisão dos limites de resíduos de agrotóxicos permitidos na água e nos alimentos; a proibição da pulverização aérea; cobrança de impostos relativos à comercialização dos agrotóxicos, muitas vezes isentos; incentivo à produção de alimentos orgânicos para humanos; e a proteção dos mananciais. “Principalmente banir os banidos, para a gente deixar de ser a lixeira do mundo, porque se a gente tivesse dignidade, quando um produto for proibido em algum lugar, deveríamos proibir também”, opinou Sônia Hess.
Deliberações O deputado Marquito (Psol), presidente da Comissão de Turismo e Meio Ambiente da Alesc, participou da abertura e destacou a importância do tema. A presidente da Cidasc, Celles Regina de Matos, também esteve presente. Ela destacou o trabalho da companhia no controle de resíduos nos alimentos e na orientação dos produtores rurais. “Consideramos essa pauta muito importante”, afirmou. Durante a plenária, os membros do fórum deliberaram sobre a realização de um encontro ampliado, a ser realizado em março do ano que vem, na Alesc, além reforçarem o posicionamento do fórum contra o projeto de lei aprovado no Senado Federal, conhecido como PL dos Agrotóxicos, que modifica as regras de aprovação e comercialização desses produtos, seguindo orientação do fórum nacional. A preocupação com o uso de drones para a pulverização de lavouras também foi abordado durante a plenária. Vitor Santos AGÊNCIA AL Fonte: Agência ALESC
0 notes
Text
Pesticide sales declined by 5.6% in 2023, Brazil environmental agency says
A total of 755,400 metric tonnes of products were sold; sales had reached 800,600 metric tonnes in 2022

The latest data from Brazil’s environmental protection agency (IBAMA) indicate that pesticide sales in Brazil declined by 5.6% in 2023, totaling 755,400 metric tonnes of formulated chemical and biochemical products. This marked a drop from the record 800,600 metric tonnes sold in 2022.
Most of the products sold were domestically manufactured, accounting for 465,300 metric tonnes, while imports totaled 326,300 metric tonnes. Brazil also exported 6,000 metric tonnes of formulated pesticides last year.
Biological products, considered to have low environmental risk, experienced a significant decline, with production falling by 58% and sales dipping by 1%. In 2023, total production reached 1,900 metric tonnes, down from 3,000 metric tonnes the previous year. Sales remained steady at 3,800 metric tonnes, while exports increased from zero to 23.4 metric tonnes, and imports fell from 1,200 to 411 metric tonnes.
Glyphosate remained the top-selling active ingredient, accounting for nearly half of all pesticides sold in 2023. Other widely used products included mancozeb, 2,4-D, acephate, chlorothalonil, atrazine, S-metolachlor, glufosinate-ammonium salt, malathion, and diquat dibromide.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#economy#environmentalism#farming#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
0 notes
Text
Indofil Share Price Riding High on the Terrain
Introduction
Indofil Industries Ltd., a prominent player in the chemical industry, has been making waves in the stock market recently. With a strong foothold in both agricultural chemicals (ABD) and specialty and performance chemicals (SPCD), the Indofil Industries Share Price has been on a significant upward trajectory. This article delves into the reasons behind this surge in Indofil Industries Share Price and what it means for investors and the industry at large. Indofil Industries Ltd. stands out in the fields of agricultural chemicals (ABD) and specialty and performance chemicals (SPCD). As a member of the K.K. Modi Group, this comprehensive multi-product chemical company manufactures and distributes agrochemicals and specialty chemicals throughout India. It is organized into three main segments: agrochemicals, specialty and performance chemicals, and investments. Indofil offers a wide array of products, including fungicides, insecticides, herbicides, acaricides, plant growth regulators, surfactants, and plant nutrition products. The company also provides specialty performance chemicals for industries such as leather, plastics, textiles, paints, coatings, and construction. Additionally, Indofil delivers tailored solutions to support farmers, with a primary distribution network of dealers and distributors. Indofil boasts an export footprint in over 60 countries, particularly known for its mancozeb formulations. Domestically, the company excels in the strategic marketing of various insecticides, including IGRs, fungicides (like mancozeb, tricyclazole, and zineb), bactericides, herbicides, acaricides, surfactants, and plant growth regulators (PGRs). Indofil’s operations in the agricultural sector are driven by its "crop care concept," emphasizing comprehensive crop protection and growth solutions. The company operates one manufacturing facility in Thane and three in Dahej, India. These units are equipped to produce the extensive range of chemical products offered by Indofil, ensuring high standards of quality and reliability. Established in 1962 as a subsidiary of Rohm & Haas Co., USA, Indofil Industries Ltd. is headquartered in Thane, India. Over the decades, it has evolved into a major player in the chemical industry, leveraging its historical expertise and innovative approaches to dominate both agricultural and specialty chemical markets.
Strong Market Position Indofil Industries Ltd. is uniquely positioned in the chemical sector, boasting a robust presence in two critical segments. Its agricultural chemicals division is renowned for providing essential products that support the farming community, enhancing crop yield and protecting plants from various pests and diseases. On the other hand, the specialty and performance chemicals division caters to a broad range of industries, including textiles, leather, and plastics, offering high-performance solutions that meet stringent quality standards.
Financial Performance The company's recent financial performance has been impressive, with quarterly and annual results exceeding market expectations. Revenue growth has been driven by strong demand in both its primary business segments. The agricultural chemicals segment has benefited from favorable monsoon seasons and increased agricultural activities, while the specialty chemicals division has seen a surge in demand from various industries seeking high-quality and innovative chemical solutions.
Strategic Initiatives Indofil's strategic initiatives have played a crucial role in its share price ascent. The company has invested heavily in research and development, leading to the introduction of new and innovative products that cater to evolving market needs. Additionally, Indofil has expanded its global footprint, establishing a presence in key international markets through strategic partnerships and acquisitions. These initiatives have not only diversified its revenue streams but also mitigated risks associated with market fluctuations.
Sustainability Efforts In an era where sustainability is paramount, Indofil has made significant strides in adopting environmentally friendly practices. The company has implemented green chemistry principles in its manufacturing processes, reducing its carbon footprint and ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations. These efforts have not only enhanced its brand reputation but also attracted socially responsible investors, contributing to the rise in its share price.
Investor Confidence The combination of strong financial performance, strategic expansion, and a commitment to sustainability has bolstered investor confidence in Indofil Industries Ltd. Market analysts have been optimistic about the company's future prospects, leading to positive ratings and recommendations. As a result, the stock has seen increased trading volumes and heightened interest from institutional investors.
Future Outlook Looking ahead, Indofil is well-positioned to continue its growth trajectory. The global demand for agricultural and specialty chemicals is expected to rise, driven by population growth, urbanization, and the need for sustainable solutions. Indofil's ongoing investments in innovation and expansion will likely keep it at the forefront of these trends, providing a solid foundation for sustained share price growth.
Conclusion Indofil Industries Ltd.'s share price has been riding high, reflecting the company's strong market position, impressive financial performance, strategic initiatives, and commitment to sustainability. For investors, the company's continued growth and innovative approach present a promising opportunity. As Indofil navigates the evolving landscape of the chemical industry, it remains a stock to watch in the coming years.
0 notes
Link
#Alternaria brassicae#Brassica napus L#Milor MZ fungicide#Pseudomonas fluorescens PF83#Raphanus brassica#Salicylic acid
1 note
·
View note
Text
Fungicides Market Size, Share, and Industry Analysis
Rising Crop Losses and Demand for Higher Yields Propel Growth in the Fungicides Market.
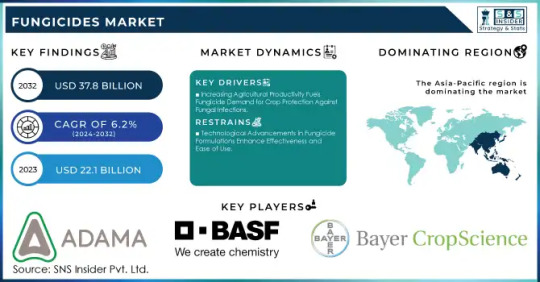
The Fungicides Market Size was valued at USD 22.1 billion in 2023, and is expected to reach USD 37.8 billion by 2032, and grow at a CAGR of 6.2% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The global fungicides market is witnessing steady growth, driven by the increasing need for crop protection, higher agricultural yields, and disease resistance. Fungicides are essential in preventing and controlling fungal infections in crops, ensuring food security and economic stability for farmers. With rising concerns over climate change, unpredictable weather patterns, and soil-borne diseases, the demand for innovative and sustainable fungicidal solutions is increasing. Additionally, advancements in biological and eco-friendly fungicides are shaping the future of the industry.
Key Players in the Fungicides Market
Adama Agricultural Solutions (Signum, Sencor, Bravo)
BASF SE (Headline, Cantus, Teldor)
Bayer CropScience (Corbel, Flint, Bayfidan)
Cheminova A/S (Carbendazim, Folicur, Topguard)
Dow AgroSciences (Quadris, Rally, Inspire Super)
DuPont (Chlorothalonil, Fontelis, Cabrio)
FMC Corporation (Ridomil Gold, Pristine, Topguard)
Lanxess AG (Opera, Amistar, Folicur)
Monsanto (Stratego, Pristine, Headline)
Nufarm Ltd (Score, Nativo, Mancozeb)
Future Scope and Emerging Trends
The fungicides market is evolving with a significant focus on sustainability and innovation. The shift toward bio-based and organic fungicides is gaining momentum due to rising concerns over chemical residues, environmental impact, and regulatory restrictions. Additionally, precision agriculture and AI-driven application techniques are optimizing fungicide usage, ensuring targeted and efficient disease management. The adoption of next-generation fungicides with multiple modes of action is also increasing to combat fungal resistance. Governments and regulatory bodies are promoting the use of biological fungicides and integrated disease management (IDM) approaches to enhance agricultural sustainability.
Key Points
Growing Demand for Sustainable Crop Protection: Rise in bio-based and organic fungicides.
Advancements in Precision Agriculture: AI and smart farming optimizing fungicide application.
Increasing Fungal Resistance: Development of multi-action fungicides.
Stricter Environmental Regulations: Push for eco-friendly and low-residue fungicides.
Emerging Markets Driving Growth: High demand in Asia-Pacific and Latin America for crop protection solutions.
Conclusion
The fungicides market is set for continued expansion, driven by technological advancements, sustainable solutions, and the need for higher crop yields. Companies investing in biological fungicides, digital farming techniques, and innovative disease management solutions will lead the market. As agriculture shifts toward eco-friendly and precision-based practices, the demand for efficient and environmentally responsible fungicides will continue to grow globally.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/fungicides-market-3548
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Fungicides Market#Fungicides Market Size#Fungicides Market Share#Fungicides Market Report#Fungicides Market Forecast
0 notes