#utilities
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
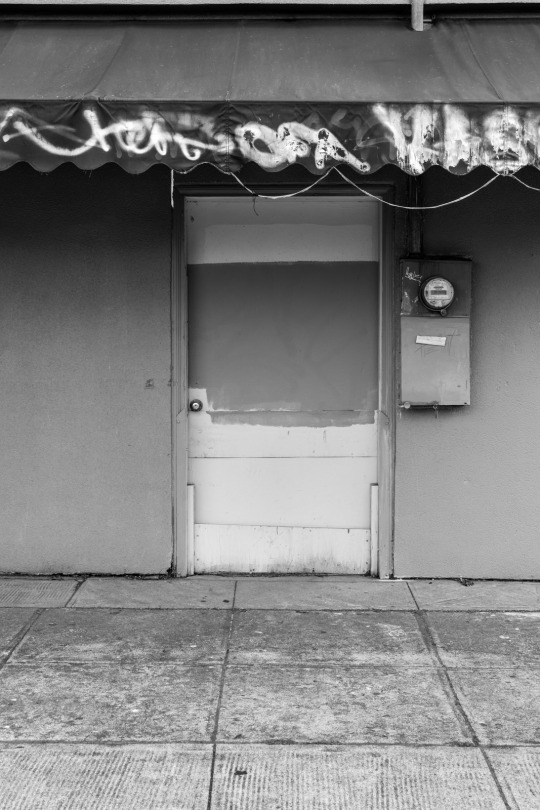

Facade, Portland, OR © Robert Pallesen
#Facade#Street Scene#Doors#Utilities#Storefront#Awnings#PDX#Portland#Urban Landscape#Black and White Photography#Robert Pallesen
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
How an obscure advisory board lets utilities steal $50b/year from ratepayers

I'm on a 20+ city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in NYC on WEDNESDAY (26 Feb) with JOHN HODGMAN and at PENN STATE on THURSDAY (Feb 27). More tour dates here. Mail-order signed copies from LA's Diesel Books.

Two figures to ponder.
First: if your local power company is privately owned, you've seen energy rate hikes at 49% above inflation over the last three years.
Second: if your local power company is publicly owned, you've seen energy rates go up at 44% below inflation over the same period.
Power is that much-theorized economic marvel: a "natural monopoly." Once someone has gone to the trouble of bringing a power wire to your house, it's almost impossible to convince anyone else to invest in bringing a competing wire to your electrical service mast. For this reason, most people in the world get their energy from a publicly owned utility, and the rates reflect social priorities as well as cost-recovery. For example, basic power to run lights and a refrigerator might be steeply discounted, while energy-gobbling McMansions pay a substantial premium for the extra power to heat and cool their ostentatious lawyer-foyers and "great rooms."
But in America, we believe in the miracle of the market, even where no market could possibly exist because of natural monopolies. That's why about 70% of Americans get their power from shareholder-owned companies, whose managers' prime directive is extracting profit, not serving their communities. To check this impulse, these private utilities are overseen by various flavors of public bodies, usually called Public Utility Commissions (PUCs).
For 40 years, PUCs have limited private utilities to a "rate of return" based on a "just and reasonable profit." They always gamed this to make it higher than was fair, but in recent years, the "experts" who advise PUCs on rate-setting have been boiled down to a tiny number of economists, who have discovered that the true "just and reasonable profit" is much higher than it's ever been considered.
Mark Ellis worked for one of those profit-hiking "experts," but he's turned whistleblower. On paper, Ellis looks like the enemy: former chief economist at Sempra Energy, an ex-Exxonmobile analyst, a retired McKinsey Consultant, and a Socal Edison engineer. But Ellis couldn't stomach the corruption, and he went public, publishing a report for the American Economic Liberties Project called "Rate of Return Equals Cost of Capital" that lays out the con in stark detail:
https://www.economicliberties.us/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/20250102-aelp-ror-v5.pdf
I first encountered Ellis last week when he was interviewed on Matt Stoller and David Dayen's excellent Organized Money podcast, where he memorably referred to these utilities as "pocket-picking machines":
https://www.organizedmoney.fm/p/the-pocket-picking-machine
Dayen followed this up with a great summary in The American Prospect (where he is editor-in-chief):
https://prospect.org/environment/2025-02-21-secret-society-raising-your-electricity-bills/
At the center of the scam is a professional association called the Society of Utility and Regulatory Financial Analysts (SURFA). The experts in SURFA are dominated by just four consulting companies, who provide 90% of the testimony for rate-setting exercises. Just two people account for half of that input.
In order to calculate the "just and reasonable profit," these experts make use of economic models. Even in normal economics, these models are the source of infinite mischief and suffering, built on assumptions that legitimize the most abusive conduct:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/03/all-models-are-wrong/#some-are-useful
But even by the low standards of normal economic models, the utility models are really bad. They rely on unique "risk premium" and "expected earnings" calculations that no one else in finance will touch. As Dayen explains, these models are "perfectly circular."
This might be a bit confusing, but only because it's one of those scams that you assume you must have misunderstood because it's so, well, scammy. In the "expected earnings" analysis, the "just and reasonable profit" a utility is allowed to build into its rates is defined as "the amount of money it would like to make." In other words, if a utility projects future revenues of $10 billion over the next ten years, that is its "expected earnings." "Expected earnings" are treated as equivalent to "just and reasonable profits." So under this model, whatever number the utility puts in its financial projections is the number that it's allowed to take out of the pockets of ratepayers.
This is just as bad as it sounds. In 2022, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission said that it "defied financial logic." No duh – even SURFA's own training manual says it "does not square well with economic theory."
In the world of regulated utilities, this kind of mathing isn't supposed to be possible. The PUC and its "consumer advocates" are supposed to listen to these outlandish tales and laugh the utility out of the room.
But it's SURFA that trains the consumer advocates who work for the PUCs, the large energy customers, and community groups. These people – who are supposed to act as the adversaries of the companies that pay SURFA members to justify rate-hikes – are indoctrinated by SURFA to treat its absurd models as accepted economic gospel. SURFA has co-opted its opposition, transformed it into a botnet that parrots its own talking-points.
Because of this, the private power companies that serve 70% of US households made an extra $50b last year, about $300 per household. What's more, because the excess profits available to companies that simply bamboozle their regulators are so massive, they swamp all the other tools regulators use to attempt to improve the energy system. No incentive offered for conservation or efficiency can touch the gigantic sums energy companies can make by ripping off ratepayers, so nearly all the incentive programs approved by PUCs have been dead on arrival.
What's more, utilities are allowed to fold the cost of hiring the experts who get them rate hikes onto the ratepayers. In other words, if a utility hires a $10,000,000 expert who successfully argues for a $1,000,000,000 rate-increase, they get to recoup the ten mil they spent securing the right to rip you off for a billion dollars on top of that cool bill.
We often talk about regulatory capture in the abstract, but this is as concrete as it can be. Ellis's report makes a raft of highly specific, technical regulatory changes that states or cities could impose on their PUCs. These are shovel-ready ideas: if you find yourself contemplating a sky-high power bill, maybe you could call your state rep and read them aloud.
If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/02/24/surfa/#mark-ellis
#pluralistic#surfa#organized money#david dayen#matthew stoller#matt stoller#the american prospect#whistleblowers#power#utilities#monopolies#antitrust#Society of Utility and Regulatory Financial Analysts#Mark Ellis#PUCs#podcasts
274 notes
·
View notes
Text


#utilities#low income#trump administration#trump admin#politics#political#us politics#news#donald trump#president trump#american politics#elon musk#jd vance#law#money#finance#jobs#america#americans#us news#utility bills#bills#payments#federal government#federal spending#lifelines
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
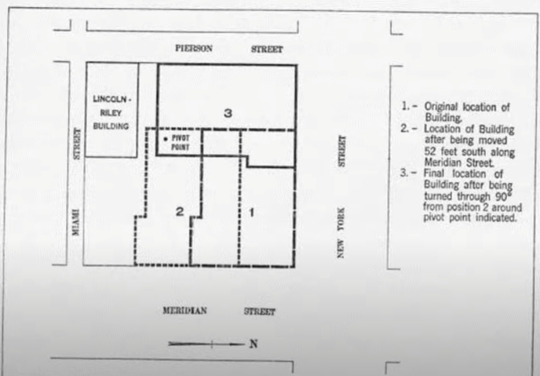
In 1930 the Indiana Bell building in Evansville, Indiana was moved over 34 days the 11,000-ton building was moved 16 meters from its original location and rotated 90 degrees, a process that was completed in mid-November 1930, without interrupting or the service of calls nor the supply of gas, water, and electricity of the building. Over a month, the structure was moved 15 inch/hr all while 600 employees still worked there. According to reports, ‘no one inside felt it move’
The move was planned by engineers Bevington, Taggert & Fowler, while contractors John Eichlea Co. carried out the feat.
#reddit#nextfuckinglevel#Natchos09#imgur#archdaily.com#1930#1930s#architecture#engineering#indiana bell building#engineers#bevington taggert & fowler#john eichlea co#relocation#rotation#indiana#evansville#video#telephone#phone#gas#water#electricity#utilities
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Master the Logistics and Etiquette of Moving Out
On a recent episode of the award-winning highly acclaimed scandalous homoerotic merely adequate “moms love it!” Bitches Get Riches podcast, we discussed how to get your first apartment.
It’s an exciting time! You’re moving into your very own place, getting one of your very first Adulthood Merit Badges!
But what do you do when your time in that first apartment comes to an end? In short, how do you handle moving out?
As tempting as it might be to toss the keys over your shoulder and just walk the fuck away, there is definitely an etiquette for moving out.
Keep reading
Did we just help you out? Say thanks by donating to our Patreon!
37 notes
·
View notes
Text

♠️_Le mie virtù le ho utilizzate come ho potuto. Dei miei vizi ne ho fatto buon uso!🖤🌹
©️Licaonia Lupe
#virtù#utilities#vizio#buoni propositi#cuore#frasi#legami#romantic#amore#frasi pensieri#peccati#leggerezza#mind control#emozioni#donna#femminilità#essenza#bellezza#saggezza#avvenire#adorable#fine art#beautiful women#white women evolving#evolve
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
Utility Companies, capitalism, and climate change
@ian.outside
#tiktok#climate change#climate crisis#michigan#capitalism#act of god#DTE#detroit#insurance#accountability#utilities#ian outside#floods#flooding#disaster capitalism
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
NO ES AMOR,
SI NO HAY CELOS
#pensamientos#amor#poesia#textos#poemas#love#quotes#cosas que escribo#escribir#citas#CELOS#celosa#sentimientos#escritos#frases#recuerda#ten en cuenta#util#utilities#loveee#this is so pretty#obsessed with this#oh i love this#this is gorgeous#poetry#citas quotes
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 pieces of Trump's "big, beautiful bill" that could impact your life





#big beautiful bill#donald trump#trump administration#federal government#republicans#gop#gambling#philanthropy#charity#utility bill#utilities#cost of living#consumer protection#consumer financial protection bureau#cfpb#civil rights#social justice#us politics
12 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
#fafo Season: Alabama MAGA Voters BETRAYED After Trump Order Cancels Energy Grant & Hikes Power Bill | Red States
Awwww
#youtube#red states#maga cult#energy#utilities#fafo#maga fafo#donald trump#republicans#trump supporters#economy#leopards eating people's faces party#politics#black lives matter#maga congress#trump
20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Street Scene, Portland, OR © Robert Pallesen
#Street Scene#Cars#Houses#Windows#Utilities#PDX#Portland#Urban Landscape#Black and White Photography#Robert Pallesen
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
What’s a “public internet?”

I'm in the home stretch of my 24-city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in LONDON (July 1) with TRASHFUTURE'S RILEY QUINN and then a big finish in MANCHESTER on July 2.

The "Eurostack" is a (long overdue) project to publicly fund a European "stack" of technology that is independent from American Big Tech (as well as other powers' technology that has less hold in Europe, such as Chinese and Russian tech):
https://www.euro-stack.info/
But "technological soveriegnty" is a slippery and easily abused concept. Policies like "national firewalls" and "data localization" (where data on a country's population need to be kept on onshore servers) can be a means to different ends. Data localization is important if you want to keep an American company from funneling every digital fact about everyone in your country to the NSA. But it's also a way to make sure that your secret police can lay hands on population-scale data about anyone they might want to kidnap and torture:
https://doctorow.medium.com/theyre-still-trying-to-ban-cryptography-33aa668dc602
At its worst, "technological sovereignty" is a path to a shattered internet with a million dysfunctional borders that serve as checkpoints where thuggish customs inspectors can stop you from availing yourself of privacy-preserving technology and prevent you from communicating with exiled dissidents and diasporas.
But at its best, "technological sovereignty" is a way to create world-girding technology that can act as an impartial substrate on which all manner of domestic and international activities can play out, from a group of friends organizing a games night, to scientists organizing a symposium, to international volunteer corps organizing aid after a flood.
In other words, "technological sovereignty" can be a way to create a public internet that the whole public controls – not just governments, but also people, individuals who can exercise their own technological self-determination, controlling crucial aspects of their own technology usage, like "who will see this thing I'm saying?" and "whose communications will I see, and which ones can I block?"
A "public internet" isn't the same thing as "an internet that is operated by your government," but you can't get a public internet without government involvement, including funding, regulation, oversight and direct contributions.
Here's an example of different ways that governments can involve themselves in the management of one part of the internet, and the different ways in which this will create more or less "public" internet services: fiber optic lines.
Fiber is the platinum standard for internet service delivery. Nothing else comes even close to it. A plastic tube under the road that is stuffed with fiber optic strands can deliver billions of times more data than copper wires or any form of wireless, including satellite constellations like Starlink:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/03/30/fight-for-44/#slowpokes
(Starlink is the most antifuturistic technology imaginable – a vision of a global internet that gets slower and less reliable as more people sign up for it. It makes the dotcom joke of "we lose money on every sale but make it up in volume" look positively bankable.)
The private sector cannot deliver fiber. There's no economical way for a private entity to secure the rights of way to tear up every street in every city, to run wires into every basement or roof, to put poles on every street corner. Same goes for getting the rights of way to string fiber between city limits across unincorporated county land, or across the long hauls that cross national and provincial or state borders.
Fiber itself is cheap like borscht – it's literally made out of sand – but clearing the thicket of property rights and political boundaries needed to get wire everywhere is a feat that can only be accomplished through government intervention.
Fiber's opponents rarely acknowledge this. They claim, instead, that the physical act of stringing wires through space is somehow transcendentally hard, despite the fact that we've been doing this with phone lines and power cables for more than a century, through the busiest, densest cities and across the loneliest stretches of farmland. Wiring up a country is not the lost art of a fallen civilization, like building pyramids without power-tools or embalming pharoahs. It's something that even the poorest counties in America can manage, bringing fiber across forbidden mountain passes on the back of a mule named "Ole Bub":
https://www.newyorker.com/tech/annals-of-technology/the-one-traffic-light-town-with-some-of-the-fastest-internet-in-the-us
When governments apply themselves to fiber provision, you get fiber. Don't take my word for it – ask Utah, a bastion of conservative, small-government orthodoxy, where 21 cities now have blazing fast 10gb internet service thanks to a public initiative called (appropriately enough) "Utopia":
https://pluralistic.net/2024/05/16/symmetrical-10gb-for-119/#utopia
So government have to be involved in fiber, but how should they involve themselves in it? One model – the worst one – is for the government to intervene on behalf of a single company, creating the rights of way for that company to lay fiber in the ground or string it from poles. The company then owns the network, even though the fiber and the poles were the cheapest part of the system, worth an unmeasurably infinitesimal fraction of the value of all those rights of way.
In the worst of the worst, the company that owns this network can do anything they want with its fiber. They can deny coverage to customers, or charge thousands of dollars to connect each new homes to the system. They can gouge on monthly costs, starve their customer service departments or replace them with mindless AI chatbots. They can skimp on maintenance and keep you waiting for days or weeks when your internet goes out. They can lard your bill with junk fees, or force you to accept pointless services like landlines and cable TV as a condition of getting the internet.
They can also play favorites with local businesses: maybe they give great service to every Domino's pizza place at knock-down rates, and make up for it by charging extra to independent pizza parlors that want to accept internet orders and stream big sports matches on the TV over the bar.
They can violate Net Neutrality, slowing down your connection to sites unless their owners agree to pay bribes for "premium carriage." They can censor your internet any way they see fit. Remember, corporations – unlike governments – are not bound by the First Amendment, which means that when a corporation is your ISP, they can censor anything they feel like:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/15/useful-idiotsuseful-idiots/#unrequited-love
Governments can improve on this situation by regulating a monopoly fiber company. They can require the company to assume a "universal service" mandate, meaning they must connect any home or business that wants it at a set rate. Governments can ban junk fees, set minimum standards for customer service and repair turnarounds, and demand neutral carriage. All of this can improve things, though its a lot of work to administer, and the city government may lack the resources and technical expertise to investigate every claim of corporate malfeasance, and to perform the technical analysis to evaluate corporate excuses for slow connections and bungled repairs.
That's the worst model: governments clear the way for a private monopolist to set up your internet, offering them a literally priceless subsidy in the form of rights of way, and then, maybe, try to keep them honest.
Here's the other extreme: the government puts in the fiber itself, running conduit under all the streets (either with its own crews or with contract crews) and threading a fiber optic through a wall of your choice, terminating it with a box you can plug your wifi router into. The government builds a data-center with all the necessary switches for providing service to you and your neighbors, and hires people to offer you internet service at a reasonable price and with reasonable service guarantees.
This is a pretty good model! Over 750 towns and cities – mostly conservative towns in red states – have this model, and they're almost the only people in America who consistently describe themselves as happy with their internet service:
https://ilsr.org/articles/municipal-broadband-skyrocket-as-alternative-to-private-models/
(They are joined in their satisfaction by a smattering of towns served by companies like Ting, who bought out local cable companies and used their rights of way to bring fiber to households.)
This is a model that works very well, but can fail very badly. Municipal governments can be pretty darned kooky, as five years of MAGA takeovers of school boards, library boards and town councils have shown, to say nothing of wildly corrupt big-city monsters like Eric Adams (ten quintillion congratulations to Zohran Mamdani!). If there's one thing I've learned from the brilliant No Gods No Mayors podcast, it's that mayors are the weirdest people alive:
https://www.patreon.com/collection/869728?view=condensed
Remember: Sarah Palin got her start in politics as mayor of Wasilla, Alaska. Do you want to have to rely on Sarah Palin for your internet service?
https://www.patreon.com/posts/119567308?collection=869728
How about Rob Ford? Do you want the crack mayor answering your tech support calls? I didn't think so:
https://www.patreon.com/posts/rob-ford-part-1-111985831
But that's OK! A public fiber network doesn't have to be one in which the government is your only choice for ISP. In addition to laying fiber and building a data-center and operating a municipal ISP, governments can also do something called "essential facilities sharing":
https://transition.fcc.gov/Bureaus/Common_Carrier/Orders/1999/fcc99238.pdf
Governments all over the world did this in the late 1990s and early 2000s, and some do it still. Under an essential facilities system, the big phone company (BT in the UK, Bell in Canada, AT&T and the Baby Bells in the USA) were required to rent space to their competitors in their data centers. Anyone who wants to set up an ISP can install their own switching gear at a telephone company central office and provide service to any business or household in the country.
If the government lays fiber in your town, they can both operate a municipal fiber ISP and allow anyone else to set up their own ISP, renting them shelf-space at the data-center. That means that the town college can offer internet to all its faculty and students (not just the ones who live in campus housing), and your co-op can offer internet service to its members. Small businesses can offer specialized internet, and so can informal groups of friends. So can big companies. In this model, everyone is guaranteed both the right to get internet access and the right to provide internet access. It's a great system, and it means that when Mayor Sarah Palin decides to cut off your internet, you don't need to sue the city – you can just sign up with someone else, over the same fiber lines.
That's where essential facilities sharing starts, but that's not where it needs to stop. When the government puts conduit (plastic tubes) in the ground for fiber, they can leave space for more fiber to fished through, and rent space in the conduit itself. That means that an ISP that wants to set up its own data center can run physically separate lines to its subscribers. It means that a university can do a point-to-point connection between a remote scientific instrument like a radio telescope and the campus data-center. A business can run its own lines between branch offices, and a movie studio can run dedicated lines from remote sound-stages to the edit suites at its main facility.
This is a truly public internet service – one where there is a publicly owned ISP, but also where public infrastructure allows for lots of different kinds of entities to provide internet access. It's insulated from the risks of getting your tech support from city hall, but it also allows good local governments to provide best-in-class service to everyone in town, something that local governments have a pretty great track record with.
The Eurostack project isn't necessarily about fiber, though. Right now, Europeans are thinking about technological sovereignty through the lens of software and services. That's fair enough, though it does require some rethinking of the global fiber system, which has been designed so that the US government can spy on and disconnect every other country in the world:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/10/weaponized-interdependence/#the-other-swifties
Just as with the example of fiber, there are a lot of ways the EU and member states could achieve "technological sovereignty." They could just procure data-centers, server software, and the operation of social media, cloud hosting, mobile OSes, office software, and other components of Europeans' digital lives from the private sector – sort of like asking a commercial operator to run your town's internet service.
The EU has pretty advanced procurement rules, designed to allow European governments to buy from the private sector while minimizing corruption and kickbacks. For example, there's a rule that the lowest priced bid that conforms to all standards needs to win the contract. This sounds good (and it is, in many cases) but it's how Newag keeps selling trains in Poland, even after they were caught boobytrapping their trains so they would immobilize themselves if the operator took them for independent maintanance:
https://media.ccc.de/v/38c3-we-ve-not-been-trained-for-this-life-after-the-newag-drm-disclosure
The EU doesn't have to use public-private partnerships to build the Eurostack. They could do it all themselves. The EU and/or member states could operate public data centers. They could develop their own social media platforms, mobile OSes, and apps. They could be the equivalent of the municipal ISP that offers fast fiber to everyone in town.
As with public monopoly ISPs, this is a system that works well, but fails badly. If you think Elon Musk is a shitty social media boss, wait'll you see the content moderation policies of Viktor Orban – or Emmanuel Macron:
https://jacobin.com/2025/06/france-solidarity-urgence-palestine-repression
Publicly owned data centers could be great, but also, remember that EU governments have never given up on their project of killing working encryption so that their security services can spy on everyone. Austria's doing it right now!
https://www.yahoo.com/news/austrian-government-agrees-plan-allow-150831232.html
Ever since Snowden, EU governments have talked a good line about the importance of digital privacy. Remember Angela Merkel's high dudgeon about how her girlhood in the GDR gave her a special horror of NSA surveillance?
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-24647268
Apparently, Merkel managed to get over her horror of mass surveillance and back total, unaccountable, continuous digital surveillance over all of Germany:
https://www.hrw.org/news/2021/06/24/germanys-new-surveillance-laws-raise-privacy-concerns
So there's good reasons to worry about having your data – and your apps – hosted in an EU cloud.
To create a European public internet, it's neither necessary nor desirable to have your digital life operated by the EU and its member states, nor by its private contractors. Instead, the EU could make Eurostack a provider of technological public goods.
For example, the EU could work to improve federated social media systems, like Mastodon and Bluesky. EU coders could contribute to the server and client software for both. They could participate in future versions of the standard. They could provide maintenance code in response to bug reports, and administer bug bounties. They could create tooling for server administrators, including moderation tools, both for Mastodon and for Bluesky, whose "composable moderation" system allows users to have the final say over their moderation choices. The EU could perform and/or fund labelling work to help with moderation.
The EU could also provide tooling to help server administrators stand up their own independent Mastodon and Bluesky servers. Bluesky needs a lot of work on this, still. Bluesky's CTO has got a critical piece of server infrastructure to run on a Raspberry Pi for a few euros per month:
https://justingarrison.com/blog/2024-12-02-run-a-bluesky-pds-from-home/
Previously, this required a whole data center and cost millions to operate, so this is great. But this now needs to be systematized, so that would-be Bluesky administrators can download a package and quickly replicate the feat.
Ultimately, the choice of Mastodon or Bluesky shouldn't matter all that much to Europeans. These standards can and should evolve to the point where everyone on Bluesky can talk to everyone on Mastodon and vice-versa, and where you can easily move your account from one server to another, or one service to another. The EU already oversees systems for account porting and roaming on mobile networks – they can contribute to the technical hurdles that need to be overcome to bring this to social media:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/12/14/fire-exits/#graceful-failure-modes
In addition to improving federated social media, the EU and its member states can and should host their own servers, both for their own official accounts and for public use. Giving the public a digital home is great, especially if anyone who chafes at the public system's rules can hop onto a server run by a co-op, a friend group, a small business or a giant corporation with just a couple clicks, without losing any of their data or connections.
This is essential facilities sharing for services. Combine it with public data centers and tooling for migrating servers from and to the public server to a private, or nonprofit, or co-op data-center, and you've got the equivalent of publicly available conduit, data-centers, and fiber.
In addition to providing code, services and hardware, the EU can continue to provide regulation to facilitate the public internet. They can expand the very limited interoperability mandates in the Digital Markets Act, forcing legacy social media companies like Meta and Twitter to stand up APIs so that when a European quits their service for new, federated media, they can stay in touch with the friends they left behind (think of it as Schengen for social media, with guaranteed free movement):
https://www.eff.org/interoperablefacebook
With the Digital Service Act, the EU has done a lot of work to protect Europeans from fraud, harassment and other online horribles. But a public internet also requires protections for service providers – safe harbors and carve outs that allow you to host your community's data and conversations without being dragged into controversies when your users get into flamewars with each other. If we make the people who run servers liable for their users' bad speech acts, then the only entities that will be able to afford the lawyers and compliance personnel will be giant American tech companies run by billionaires like Elon Musk and Mark Zuckerberg.
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/04/kawaski-trawick/#230
A "public internet" isn't an internet that's run by the government: it's a system of publicly subsidized, publicly managed public goods that are designed to allow everyone to participate in both using and providing internet services. The Eurostack is a brilliant idea whose time arrived a decade ago. Digital sovereignty projects are among the most important responses to Trumpism, a necessary step to build an independent digital nervous system the rest of the world can use to treat the USA as damage and route around it. We can't afford to have "digital soveriegnty" be "national firewalls 2.0" – we need a public internet, not 200+ national internets.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/06/25/eurostack/#viktor-orbans-isp
#pluralistic#web theory#public ownership#infrastructure#technology#eurostack#technological soveriegnty#first amendment#utilities#1a
202 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey all,
this summer is kicking not only my ass but also the utility bill's ass. it's been in the 90s for weeks with very little reprieve, and i'm losing sleep because we have to keep the apartment 75 degrees to avoid an even higher bill than we already have, and are likely to have for the next few months. my roommate is working part-time summer hours, but has already committed to making sure rent is paid and may not be able to cover utilities in full on top of that. i'm still struggling with being unemployed due to PTSD and depression, and don't qualify for the state unemployment benefits because i have not worked in VA long enough. i get food stamps but don't qualify for utility assistance because the bill is not in my name.
if anyone is willing and able to lend a hand, it would mean so much and the kitties and i will thank you 💜
$85.00/$200

27 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Even though customers are covering all the costs of the program, the utility companies could end up squeezing them for lost profits with so-called “under-earning” fees. The utility companies lobbied the LPSC to keep a provision that allows them to tack on additional charges to make up for profits they miss out on when their customers no longer waste electricity. In other words, the utilities want their customers to pay fees for both the energy efficiency program and for the electricity they will no longer use because of the program."
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

You know we’re in a healthy, functioning society when people have to use a burger app to see if they have electricity because the local infrastructure doesn’t exist
#society#community#infrastructure#reality#earth#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#electricity#class war#utilities#utility#anti capitalism#anti colonialism#anti cop#anti colonization#dating apps#app store#mobile apps#contributor apps#apps
26 notes
·
View notes