Text
Diagnostic Laparoscopy – Purpose and Procedure
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a technique to examine the reproductive organs and abdominal organs. This procedure helps in biopsies, such as the collection of tissue samples for tests and diagnosis of various medical disorders. A laparoscopy procedure is a safe surgical method with low risks. Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/diagnostic-laparoscopy-purpose-and-procedure/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#DiagnosticLaparoscopy#LaparoscopicSurgery#ReproductiveHealth#AbdominalOrgans#MedicalDiagnosis#HealthcareTips#PreoperativeCare#PostoperativeRecovery#HomeRecuperation#PatientCare#SurgicalComplications#AnesthesiaSafety#FollowUpAppointments#WomenHealth#MenstrualCycle#SexualActivityAfterSurgery#HealthSymptoms#MedicalConsultation#HealthAwareness#Treatment
0 notes
Text
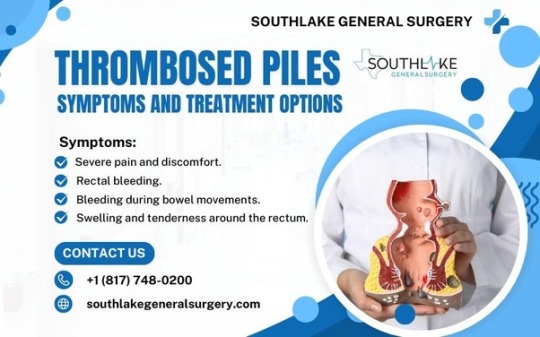
Thrombosed Piles: Symptoms and Treatment Options
Thrombosed piles, also known as thrombosed hemorrhoids, is a common and painful condition that affects the rectum and anus. Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the anal canal and can occur internally or externally. When a blood clot forms within an external hemorrhoid, it is referred to as a thrombosed pile. Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/thrombosed-piles-symptoms-and-treatment-guide/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#ThrombosedPiles#Hemorrhoids#RectalHealth#AnalHealth#PainManagement#BowelHealth#SymptomAwareness#TreatmentOptions#HealthcareProfessional#PreventiveMeasures#HomeRemedies#PostTreatmentCare#LongTermHealth#HealthAndWellness#HemorrhoidsSurgeryTexas#MedicalIntervention#ColorectalHealth#SurgicalInterventions#RecoveryProcess#HealthyLifestyle
0 notes
Text
Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical Removal of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove hemorrhoids that have not responded to other treatments or have caused serious complications. It is often recommended when hemorrhoids have prolapsed, thrombosed (developed a blood clot), or become strangulated (blood supply cut off). Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/hemorrhoidectomy-surgical-removal-of-hemorrhoids-procedure/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellness#wellbeing#health#healthcare#fitblr#Hemorrhoidectomy#SurgicalRemoval#InternalHemorrhoids#ExternalHemorrhoids#PainManagement#SitzBaths#StoolSofteners#DrValeriaSimone#PreSurgeryConsultation#HemorrhoidectomyProcedures#TraditionalHemorrhoidectomy#AdvancedSurgicalTechniques#RecoveryProcess#PostoperativeCare#PainManagementOptions#LongTermHealing#HemorrhoidSurgery#HealthcareExpert#FrequentlyAskedQuestions#Treatment
0 notes
Text
Ventral Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Surgical Solutions
Ventral hernias are a prevalent issue where the intestines or other tissues protrude through a weak spot or opening in the abdominal wall. These hernias can cause discomfort, pain, and potential complications if left untreated. Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/ventral-hernia-repair-essential-guide/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#VentralHernia#AbdominalWallWeakness#HerniaSymptoms#HerniaDiagnosis#HerniaTreatment#SurgicalSolutions#NonSurgicalManagement#LaparoscopicSurgery#MeshPlacement#PostoperativeCare#PhysicalRehabilitation#DrValeriaSimoneMD#HerniaAwareness#MedicalIntervention#HealthyRecovery#PatientEducation#HerniaPrevention#ExpertiseInHerniaRepair#QualityHealthcare#LaparoscopicHerniaRepairTexas
0 notes
Text
HIDA Scan: A Comprehensive Guide
The liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder play vital roles in the digestive process. When these organs are not functioning properly, it can lead to various symptoms and conditions. One imaging procedure commonly used to diagnose and evaluate issues with these organs is a HIDA scan. Let's explore more: Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/hida-scan-understanding-the-procedure/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellness#wellbeing#health#healthcare#fitblr#HIDAScan#GallbladderIssues#MedicalImaging#Radiology#Healthcare#BiliarySystem#LiverHealth#Gallstones#Cholecystitis#GammaCamera#HealthPreparation#SurgicalIntervention#DiagnosticTests#RadiationSafety#HealthAwareness#PatientEducation#GallbladderSurgery#NuclearMedicine#HealthcareGuidance#Treatment
0 notes
Text
Managing Porcelain Gallbladder: Patient Guide
A porcelain gallbladder, a rare condition characterized by the calcification of the gallbladder wall, poses significant health risks if left untreated. Understanding the implications of this condition is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention. Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/porcelain-gallbladder-patient-management-tips/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#PorcelainGallbladder#GallbladderHealth#GallbladderAwareness#EarlyDetection#GallbladderCancer#Cholecystectomy#HealthAwareness#MedicalAdvice#SurgicalTreatment#LifestyleAdjustments#GallbladderSymptom#DietaryModifications#PostoperativeCare#Gallstones#HealthCheckUps#PatientGuide#LaparoscopicSurgeryTexas#LifeAfterSurgery#DigestiveHealth#SouthlakeGeneralSurgery
0 notes
Text
Gallbladder Stones (Cholelithiasis): Symptoms & Solutions
Gallbladder stones or gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis, are hardened pieces of solid material that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. Let's explore more: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/signs-of-gallbladder-stones-symptoms-and-solutions/
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#Gallstones#Cholelithiasis#DigestiveHealth#LaparoscopicSurgery#Bile#GallbladderHealth#CholesterolStones#PigmentStones#SymptomAwareness#GallbladderFunction#BiliaryColic#EarlyDetection#PreventiveMeasures#LifestyleChanges#HealthyDiet#GallbladderRemoval#SurgicalOptions#NonSurgicalTreatments#PostSurgeryRecovery#DietaryAdjustments
0 notes
Text
Thrombosed Piles: Symptoms and Treatment Options
Thrombosed piles, also known as thrombosed hemorrhoids, is a common and painful condition that affects the rectum and anus. Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the anal canal and can occur internally or externally. When a blood clot forms within an external hemorrhoid, it is referred to as a thrombosed pile.
Thrombosed piles can cause severe pain, swelling, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements. The condition has the potential to be disabling and impact an individual’s quality of life. It is important to understand the symptoms and treatment options available for thrombosed piles to find relief and manage the condition effectively.
In this blog, we will discuss what thrombosed piles are, the symptoms associated with them, the causes and risk factors, as well as the various treatment options available. We will also explore the recovery process and management strategies for long-term health and prevention.
It is important to note that while there are home remedies and non-surgical treatments available, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Key Highlights
Thrombosed piles are swollen vessels in the rectum and anus that can cause severe pain and discomfort.
Symptoms of thrombosed piles include severe pain, swelling, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements.
Common risk factors for thrombosed piles include constipation, pregnancy, and sitting for long periods of time.
Treatment options for thrombosed piles range from at-home remedies and care to non-surgical and surgical interventions.
Recovery and after treatment include post-treatment care and long-term prevention strategies.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of thrombosed piles or if the condition worsens.
Understanding Thrombosed Piles
Thrombosed piles are a condition where there is a blood clot within an external hemorrhoid. Hemorrhoids are blood vessels located in the anal canal and can become swollen and inflamed, leading to various symptoms. Thrombosed piles can cause severe pain and discomfort, making it difficult to engage in daily activities.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thrombosed piles is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What Are Thrombosed Hemorrhoids?
Thrombosed piles, also known as thrombosed hemorrhoids, occur when a blood clot forms within an external hemorrhoid. Enlarged blood vessels located in the anal canal are known as hemorrhoids. While everyone has hemorrhoids, they only become a problem when they become swollen or inflamed.
Thrombosed piles are characterized by severe pain and discomfort. The blood clot within the hemorrhoid causes the affected area to become swollen and tender. This can make it painful to sit, walk, or have a bowel movement.
Thrombosed piles usually occur suddenly and can last for several days or weeks. The pain and discomfort gradually subside as the body absorbs the blood clot. However, in some cases, medical intervention may be required to relieve the symptoms and promote healing.
The Difference Between Thrombosed and Regular Hemorrhoids
Thrombosed piles are a specific type of hemorrhoid that is characterized by the presence of a blood clot within an external hemorrhoid. While both regular hemorrhoids and thrombosed piles can cause similar symptoms such as pain, itching, and bleeding, there are a few key differences between the two.
Regular hemorrhoids, also known as internal or external hemorrhoids, occur when the blood vessels in the anal canal become swollen or inflamed. Internal hemorrhoids are situated within the rectum, whereas external hemorrhoids are situated outside the anus. They can cause discomfort and may bleed during bowel movements.
On the other hand, thrombosed piles are external hemorrhoids that have developed a blood clot. This blood clot can cause severe pain and swelling, making it difficult to sit or have a bowel movement. Thrombosed piles usually require medical intervention to relieve the symptoms and promote healing.
Identifying Symptoms of Thrombosed Piles

Identifying the symptoms of thrombosed piles is crucial for seeking appropriate medical attention and starting the necessary treatment. Symptoms may differ between individuals, but there are certain typical signs to be aware of.
Thrombosed piles are typically accompanied by severe pain and discomfort in the anal region. Activities like sitting, walking, or having a bowel movement can make this pain worse. Other symptoms may include swelling, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements.
It is crucial to seek advice from a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment plan if you encounter any of these symptoms.
Early Signs to Watch For
Early signs of thrombosed piles can vary from person to person, but there are some common symptoms to watch out for. These early signs may indicate the presence of a thrombosed hemorrhoid and the need for medical attention.
Severe pain and discomfort in the anal region
Swelling and tenderness around the anus
Discomfort and itching in the impacted region
Bleeding during bowel movements
If you experience any of these early signs, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can offer a precise diagnosis and suggest suitable treatment options, depending on the seriousness of your condition. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and promote faster healing.
When Symptoms Worsen
While thrombosed piles can cause significant pain and discomfort, there are instances when the symptoms worsen and require immediate medical attention. It is important to be aware of these signs and seek prompt medical care to prevent further complications.
Severe and persistent pain that does not subside with home remedies or over-the-counter pain relievers
Increasing swelling and tenderness around the anus
Cough, fever, or other symptoms that can indicate an infection
Rectal bleeding that is excessive or does not stop
If you experience any of these worsening symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your healthcare provider can assess your condition, provide appropriate treatment, and address any potential complications. Do not delay seeking medical care if you are concerned about the worsening of your symptoms.
Causes Behind Thrombosed Piles
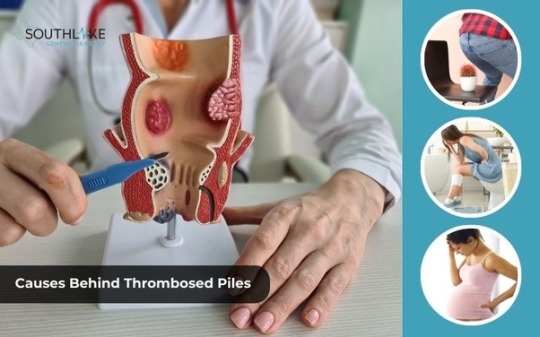
Understanding the causes behind thrombosed piles can help in taking preventive measures and managing the condition effectively. While the exact cause of thrombosed piles is not always clear, certain factors contribute to the development of this condition.
Some common causes of thrombosed piles include:
Increased pressure on the veins situated in the rectum and anus
Experiencing difficulty during defecation, particularly in cases of constipation
Diarrhea or irregular bowel movements
Pregnancy may result in heightened pressure on the veins
Extended periods of sitting, like on lengthy car trips or during office hours
By identifying and addressing these causes, you can reduce the risk of developing thrombosed piles and manage the condition effectively.
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing thrombosed piles. By understanding these risk factors, you can take preventive measures and manage the condition effectively.
Some common risk factors for thrombosed piles include:
Chronic constipation or exerting pressure during defecation
Pregnancy or childbirth, which can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus
Obesity or being overweight, can put extra strain on the veins
Prolonged sitting or standing can lead to increased pressure in the anal region
Aging occurs as the tissues in the rectum and anus become weaker over time
Genetics, as some people may be more prone to developing hemorrhoids
By addressing these risk factors and making appropriate lifestyle changes, you can reduce the likelihood of developing thrombosed piles and manage the condition effectively.
How Lifestyle Affects Thrombosed Piles
Lifestyle factors can play a significant role in the development and management of thrombosed piles. By making certain changes to your lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of developing this condition and alleviate symptoms.
Some lifestyle factors that can affect thrombosed piles include:
Diet: Consuming a high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing the strain on the rectum and anus.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can promote proper bowel function and prevent the development of hemorrhoids.
Hygiene: Maintaining good anal hygiene, such as using moist wipes instead of dry toilet paper, can help prevent irritation and inflammation.
Avoiding straining: Straining during bowel movements should be avoided, as it can put pressure on the veins in the anal region.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of developing thrombosed piles and manage the condition effectively.
Expert Diagnosis Procedures
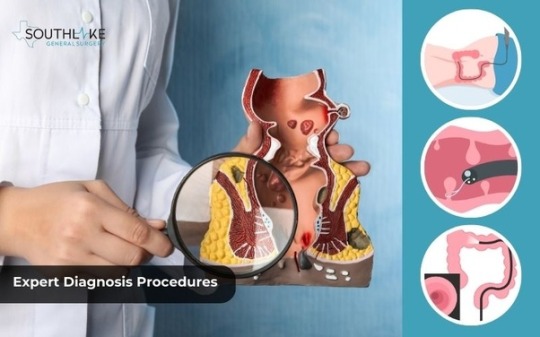
When it comes to diagnosing thrombosed piles, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate assessment. Healthcare professionals have access to various diagnostic procedures to determine the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Professional Assessment by Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Dr. Valeria Simone, a renowned healthcare provider in the field of colorectal medicine, can provide a professional assessment for thrombosed piles. Dr. Simone specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of various colorectal conditions, including hemorrhoids.
During a professional assessment, Dr. Simone may perform a flexible sigmoidoscopy, a procedure that allows for the visualization of the lower part of the colon and rectum. This procedure can help identify the presence of thrombosed piles and assess their severity.
Consulting with a healthcare professional such as Dr. Simone is crucial for receiving an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment plan. Dr. Simone’s expertise and experience can ensure that you receive the best possible care for your thrombosed piles.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Diagnostic tools and techniques are essential for accurately diagnosing thrombosed piles and determining the appropriate treatment options. Healthcare professionals have access to various tools and techniques to assess the condition and provide the best possible care.
Some common diagnostic tools and techniques for thrombosed piles include:
Physical examination: Healthcare professionals may perform a physical examination to assess the anal region and identify any visible signs of thrombosed piles.
Digital rectal exam: This procedure involves the insertion of a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for any lumps or abnormalities. This can help determine the presence and severity of thrombosed piles.
These diagnostic tools and techniques, along with the expertise of healthcare professionals, can ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for thrombosed piles.
Comprehensive Treatment Options
Treatment options for thrombosed piles range from at-home remedies and care to non-surgical and surgical interventions. Treatment options are based on the patient’s preferences and the severity of their condition. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and the right treatment plan.
At-Home Remedies and Care
For mild cases of thrombosed piles, at-home remedies, and care can often provide relief and promote healing. These remedies can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further irritation.
Some at-home remedies and care options for thrombosed piles include:
Warm sitz baths: Immersing in lukewarm water for 10-15 minutes multiple times daily can aid in decreasing pain and swelling.
Over-the-counter creams or ointments: Applying topical creams or ointments that contain ingredients like witch hazel or aloe vera can soothe the affected area and reduce discomfort.
Ice packs: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the anal region can help numb the area and reduce pain and swelling.
High-fiber diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing strain on the rectum and anus.
These at-home remedies and care options can provide temporary relief and help manage the symptoms of thrombosed piles. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss the best treatment options for your specific condition.
Non-Surgical Thrombosed Piles Treatments
In cases where at-home remedies and care are not sufficient, non-surgical treatments may be recommended to provide relief and promote healing. Healthcare professionals typically perform these treatments and can offer long-term solutions for thrombosed piles.
Some non-surgical treatment options for thrombosed piles include:
Hemorrhoid creams or ointments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments that contain ingredients like hydrocortisone or lidocaine can help reduce pain, itching, and swelling.
Rubber band ligation: In this process, a tiny rubber band is placed around the hemorrhoid’s base to stop its blood flow, leading it to shrink and detach.
Sclerotherapy: During this process, a chemical solution is inserted into the hemorrhoid, leading it to reduce in size and eventually vanish.
Non-surgical treatments can provide effective relief for thrombosed hemorrhoids and are often less invasive than surgical interventions. It is important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
Surgical Interventions by Dr. Valeria Simone
When non-surgical treatments are not effective, or the thrombosed piles are severe, surgical interventions may be recommended. Dr. Valeria Simone, a highly skilled colorectal and general surgeon, offers surgical interventions for thrombosed piles.
Some common surgical interventions for thrombosed piles include:
Local anesthesia: Dr. Simone can perform a surgical excision of the thrombosed hemorrhoid under local anesthesia. This procedure involves making a small incision to remove the blood clot and relieve the symptoms.
General anesthesia: In some cases, general anesthesia may be required for more complex surgical interventions. Dr. Simone can provide expert care and ensure your comfort throughout the procedure.
By consulting with Dr. Simone, you can discuss the surgical options available, understand the potential risks and benefits, and make an informed decision regarding your treatment. Dr. Simone’s expertise and compassionate approach to patient care ensures that you receive the highest quality treatment for your thrombosed piles.
Let’s explore more: Thrombosed Piles: Symptoms And Treatment Guide - Southlake General Surgery
Make an Appointment
If you are experiencing symptoms of thrombosed piles or if your condition worsens, it is important to make an appointment with our healthcare expert at +1 (817) 748-0200. You can also make an online appointment with us. They will be able to evaluate your health, diagnose you correctly, and suggest treatments that will work.
Relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting faster recovery can all be achieved with early management. Don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you are concerned about your symptoms or if they are impacting your quality of life.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: Thrombosed Piles: Symptoms And Treatment Guide - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellness#wellbeing#health#healthcare#fitblr#ThrombosedPiles#Hemorrhoids#RectalHealth#AnalHealth#PainManagement#BowelHealth#SymptomAwareness#TreatmentOptions#HealthcareProfessional#PreventiveMeasures#HomeRemedies#PostTreatmentCare#LongTermHealth#HealthAndWellness#HemorrhoidsSurgeryTexas#MedicalIntervention#ColorectalHealth#SurgicalInterventions#RecoveryProcess#HealthyLifestyle
0 notes
Text
Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical Removal of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove hemorrhoids that have not responded to other treatments or have caused serious complications. It is often recommended when hemorrhoids have prolapsed, thrombosed (developed a blood clot), or become strangulated (blood supply cut off).
During a hemorrhoidectomy, the affected hemorrhoidal tissue is excised, and the blood vessels are sealed to promote healing. The procedure can provide long-term relief from hemorrhoid symptoms and prevent recurrence.
While hemorrhoidectomy is an effective treatment option, it is important to understand the risks and the recovery process associated with the procedure.
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen blood vessels in the anal canal and rectum. They can be internal, located inside the rectum, or external, located under the skin around the anus. Hemorrhoids can cause discomfort, pain, itching, and bleeding.
While most cases of hemorrhoids can be managed with conservative treatments such as dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and over-the-counter medications, there are instances where surgical intervention may be necessary.
This blog will provide an overview of hemorrhoidectomy, including when it may be necessary, the different types of procedures, the recovery and aftercare, and the potential risks and complications. It will also highlight the approach of Dr. Valeria Simone at Southlake General Surgery and the benefits of choosing their healthcare services for hemorrhoidectomy.
Key Highlights
Both internal and external hemorrhoids can be surgically removed through a hemorrhoidectomy surgery.
It is often recommended when other treatments have failed or when there are complications such as prolapse, thrombosis, or strangulation.
The procedure involves cutting out the affected hemorrhoidal tissue and sealing the blood vessels.
Recovery time can vary, but most people can expect to see an improvement within two to four weeks.
Pain management, sitz baths, and stool softeners are important aspects of the recovery process.
Hemorrhoidectomy has a high success rate and provides long-term relief from hemorrhoid symptoms.
Understanding Hemorrhoids and the Need for Surgery
Hemorrhoids, whether internal or external, can cause discomfort in the anal area due to swollen blood vessels. When less invasive treatments fail to provide relief, surgical options like hemorrhoidectomy become necessary.
Signs indicating the need for surgery include severe bleeding, prolapse, or thrombosis. Understanding the nature of hemorrhoids and the potential need for surgical intervention is crucial in managing this condition effectively.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are enlarged blood vessels located in the rectum or anus, which can result in discomfort and bleeding. They can be internal or external and are common due to straining during bowel movements. Hemorrhoids may require surgical removal if conservative treatments fail.
Signs That You May Need Surgical Intervention

If you experience severe pain, excessive bleeding, or prolapsed hemorrhoids that do not retract on their own, surgical intervention such as a hemorrhoidectomy may be necessary.
Other indications include recurrent hemorrhoids that do not respond to non-invasive treatments like sitz baths or over-the-counter remedies. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider if you notice persistent symptoms despite conservative measures.
Seeking timely medical advice can help address potential complications and provide relief from discomfort.
Dr. Valeria Simone’s Approach to Hemorrhoidectomy

Dr. Valeria Simone prioritizes patient care and precision in performing hemorrhoidectomies. With a focus on utilizing advanced surgical techniques for optimal outcomes, Dr. Simone ensures thorough pre-surgery consultations to address individual needs.
At Southlake General Surgery, patients benefit from her expertise in both traditional and innovative hemorrhoidectomy procedures. Dr. Simone’s approach emphasizes patient comfort and safety throughout the surgical process. Her dedication to delivering exceptional results makes her a trusted choice for hemorrhoid surgery.
Why Choose Southlake General Surgery?
When opting for hemorrhoidectomy, Southlake General Surgery stands out for its specialized care and expertise. With a focus on patient well-being and successful outcomes, their team ensures personalized attention and top-notch surgical techniques.
The Pre-Surgery Consultation Process
During the pre-surgery consultation process, your health information and specific details about your hemorrhoids will be thoroughly reviewed. Your healthcare provider will discuss the type of surgery required based on the severity of your condition.
They will also provide instructions on preparing for the procedure, which may include avoiding certain medications like blood thinners.
This consultation ensures that you are well informed about the upcoming surgery and are ready both physically and mentally for the hemorrhoidectomy procedure.
Types of Hemorrhoidectomy Procedures
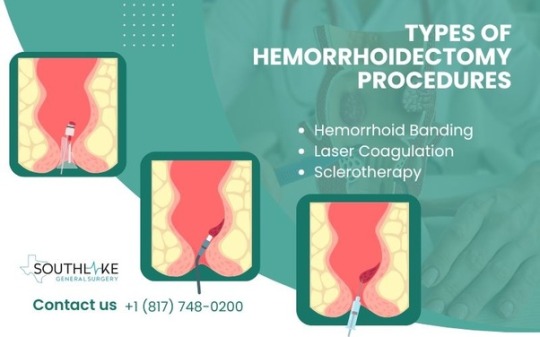
Surgical removal of hemorrhoidal tissue is the standard procedure for hemorrhoidectomy. Another method is hemorrhoid banding, where a rubber band is used to cut off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid.
Advanced techniques like laser coagulation or infrared light can treat hemorrhoids non-surgically. A closed hemorrhoidectomy involves wound closure post-procedure, while an open hemorrhoidectomy leaves the wound open.
Your surgeon will recommend the most suitable type based on your condition and factors like recovery time and postoperative discomfort.
Traditional Hemorrhoidectomy Explained
Traditional hemorrhoidectomy involves surgically removing hemorrhoids using a scalpel. Under general anesthesia, this operation is usually carried out.
During the surgery, the hemorrhoidal tissue is excised, and the wound is closed using sutures. Recovery time can vary, but patients may experience postoperative pain.
Stool softeners and pain medications are usually prescribed to manage discomfort. It is essential to follow postoperative care instructions diligently for optimal healing and to minimize the risk of complications.
Advanced Surgical Techniques for Hemorrhoid Removal
Advanced surgical techniques for hemorrhoid removal involve innovative procedures like hemorrhoidopexy and sclerotherapy.
Hemorrhoidopexy lifts and fixes prolapsed hemorrhoids back to their normal position, reducing discomfort and prolapse.
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution to shrink hemorrhoids.
These methods offer less postoperative pain and faster recovery compared to traditional options, making them appealing choices for patients seeking effective and efficient hemorrhoid removal treatments.
Preparing for Your Hemorrhoid Surgery
Prior to your hemorrhoidectomy, it is essential to follow your doctor’s pre-surgery instructions diligently. Steps may include adjusting your diet to include more fiber, staying hydrated, and possibly using stool softeners.
Your healthcare provider may advise stopping certain medications, like blood thinners. Ensure all necessary arrangements are made for transportation post-surgery.
Understanding and adhering to these guidelines can help facilitate a smoother surgical experience and aid in your recovery.
Steps to Take Before Your Procedure
Ensure to inform your surgeon of any blood thinners you may be taking and follow their guidance on their usage.
Keep yourself hydrated by drinking plenty of water and try to maintain a healthy diet rich in fiber.
Consult with your healthcare provider regarding the adjustment of any prescription medicine and inform them about any supplements you are taking.
Additionally, remember to prepare your home environment for a comfortable recovery post-surgery.
What to Anticipate on the Day of Surgery

On the day of your hemorrhoidectomy surgery, expect to arrive at the hospital or surgical center early in the morning. Prior to the procedure, fasting will be necessary. Once admitted, you will change into a hospital gown and be prepared for the operation.
An anesthesiologist will discuss the type of anesthesia you will receive — either local, regional, or general anesthesia. Before the surgery, your surgeon will also explain the details of the procedure and answer any last-minute questions you might have.
The Hemorrhoidectomy Procedure

During a hemorrhoidectomy procedure, the surgeon removes hemorrhoidal tissue, offering relief from painful symptoms. This surgery can be done under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
The process usually involves cutting out excessive tissue from the anal area. Depending on the severity, healthcare providers may opt for open or closed hemorrhoidectomy.
With advancements like infrared light or scalpel-free techniques, patients can experience less postoperative pain and a faster recovery time. This surgical intervention aims to address uncomfortable symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
An Overview of the Surgical Process
During a hemorrhoidectomy, the surgeon carefully removes hemorrhoidal tissue located in the anal canal. The procedure can address both internal and external hemorrhoids, improving symptoms like bleeding or discomfort.
Surgical techniques may involve using a scalpel, a laser, or infrared light to treat the affected area. Prior to surgery, patients are likely to receive local or general anesthesia for pain management.
Wound closure methods vary depending on the type of surgery, with options including open or closed hemorrhoidectomy procedures. Postoperatively, patients are advised on recovery steps and potential complications.
Pain Management and Anesthesia Options
Pain management and anesthesia options are crucial aspects of a hemorrhoidectomy. Patients undergoing this procedure can typically choose between local anesthesia, spinal block, or general anesthesia based on their needs and the complexity of the surgery.
These options ensure that the patient remains comfortable throughout the operation and experiences minimal discomfort. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable option for your procedure. Effective pain management is essential for a smooth recovery process post-surgery.
Recovery and Aftercare Following Hemorrhoidectomy

After a hemorrhoidectomy, recovery and aftercare are crucial for a smooth healing process. You may experience some discomfort and pain post-surgery, which can be managed with prescribed pain medication.
It is advisable to consume stool softeners, stay hydrated, and maintain a high-fiber diet to avoid constipation. Engage in light physical activities and avoid heavy lifting to aid the recovery process.
Following hygiene practices like using gentle wipes or taking sitz baths can promote healing and reduce the risk of infection. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you notice excessive bleeding, severe pain, or any concerning symptoms during your recovery period.
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
Following a hemorrhoidectomy, immediate post-surgery care plays a crucial role in recovery. Patients should expect some discomfort in the anal area, which can be managed with prescribed pain medication.
Adhering to a soft diet, including plenty of water and fiber-rich foods, aids in smoother bowel movements. Avoiding heavy lifting and straining during bowel movements is vital to prevent stress on the surgical site.
Additionally, maintaining hygiene through gentle cleansing with baby wipes instead of toilet paper can promote healing and reduce irritation.
Long-Term Healing and Recovery Tips
After undergoing a hemorrhoidectomy, focus on long-term care for efficient healing.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water to aid digestion and bowel movements.
Consume a fiber-rich diet to prevent constipation, a common post-surgery issue.
Regular exercise can promote healthy blood flow and reduce the risk of future hemorrhoids.
Do not lift large objects or strain while you are doing bowel movements.
Implement healthy habits, like using baby wipes instead of rough toilet paper.
Monitor any discomfort or itching and consult your healthcare provider promptly if any concerns arise.
Regular follow-ups ensure optimal recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
Potential risks and complications associated with hemorrhoidectomy include bleeding, infection, and difficulty in controlling bowel movements.
In rare cases, serious complications such as fecal incontinence or damage to the anal canal’s muscles, may occur. It’s important to follow post-operative care instructions diligently to minimize these risks.
Let’s explore more: Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical Removal of Hemorrhoids Procedure - Southlake General Surgery
Make an Appointment
To schedule a consultation or make an appointment for a hemorrhoidectomy, contact our healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748-0200. You can also make an online appointment with us.
Our team, led by Dr. Valeria Simone, specializes in the surgical removal of hemorrhoids using advanced techniques. Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial if you are experiencing persistent symptoms that may necessitate surgical intervention.
Don’t hesitate to reach out for personalized care and information regarding hemorrhoid surgery. Make your health a priority and take the first step towards relief.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical Removal of Hemorrhoids Procedure - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#lifestyle blog#health blog#Hemorrhoidectomy#SurgicalRemoval#InternalHemorrhoids#ExternalHemorrhoids#PainManagement#SitzBaths#StoolSofteners#DrValeriaSimone#PreSurgeryConsultation#HemorrhoidectomyProcedures#TraditionalHemorrhoidectomy#AdvancedSurgicalTechniques#RecoveryProcess#PostoperativeCare#PainManagementOptions#LongTermHealing#HemorrhoidSurgery#HealthcareExpert
0 notes
Text
Diagnostic Laparoscopy – Purpose and Procedure
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a technique to examine the reproductive organs and abdominal organs. This procedure helps in biopsies, such as the collection of tissue samples for tests and diagnosis of various medical disorders. A laparoscopy procedure is a safe surgical method with low risks.

What is laparoscopy?
According to Dr. Valeria Simone MD, an experienced board-certified general surgeon and expert in diagnostic laparoscopy at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, a laparoscopy procedure is a diagnostic surgical treatment, to examine the reproductive and abdominal organs in your body. This procedure is also used to collect sample tissues for analysis. A laparoscope is a small cylindrical tube with a camera on top inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to examine the organs. This will help the surgeon view inside the abdomen and examine organs such as:
Gallbladder
Spleen
Pancreas
Ovaries
Liver
Stomach
Uterus
Fallopian tubes
If ultrasound and X-ray fail to reveal the underlying cause of a disease, your doctor may advise a laparoscopy. Your doctor may suggest a laparoscopy procedure to:
A tissue mass examination
Check for fallopian tube obstruction or other infertility factors.
Identify the source of any abdominal and pelvic pain.
It verifies pelvic inflammatory disease or endometriosis.
What should I do to get ready for a laparoscopy?
An individual needs to adhere to the following guidelines prior to the hospital for a laparoscopy:
The night before your surgery, avoid eating, drinking (even water), and smoking after midnight.
On the day for Laparoscopic Surgery, wear flat shoes. You may feel sleepy and struggle to walk due to the anesthesia effect.
Remove all jewelry. (Wedding rings are permitted.) Nail paint must be removed before surgery.
Put on comfortable clothing. After surgery, you can experience some cramping and abdominal soreness.
What tests are usually performed prior to a laparoscopy?
Before your diagnostic laparoscopy, your doctor may need to perform a few tests and collect some medical information about your health. This includes:
Report from Pathology
Lab tests
Earlier X-rays from a different facility.
Tissue samples
Operative report
Slides from Cytology
Additionally, your doctor might request other tests, such as CT scan, Ultrasound, and MRI.
In what way is laparoscopy performed?
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed on a patient who is unconscious and lying on their back in a posture that is slightly inclined, with their head lower than their feet. During surgery, you will be given general anesthesia to help keep you from feeling any pain and to relax your muscles.
After that, a short incision is created close to the navel. After making this incision, the laparoscope will be put through it. Your abdomen will be expanded so the surgeon can more easily see your inside organs. The laparoscope can be fitted with surgical instruments, allowing for the removal of scar tissue and the collection of tissue samples.
Your doctor may additionally create a second incision along the pubic hairline as part of the procedure. This incision creates a second aperture that can be used to insert instruments that are necessary for performing minor surgical procedures.
In most cases, you will spend the first hour or so following surgery in a special room designated as a recovery area. After that, you will be transferred to an outpatient surgery unit to undergo further observation.
Once you receive the instructions for your home recuperation, then you will be released from the hospital. After a laparoscopy, the typical recovery time for a patient is between three and four hours, once the doctor allows, you will be free to leave the hospital. For individuals who undergo this treatment, it is quite uncommon for them to require a bed in the hospital for the night.
Between two and eight weeks after your laparoscopy, you will need to go back to your doctor’s office for follow-up appointments. Before you leave the hospital, you should check with your doctor about when your follow-up appointment will be.
Before undergoing surgery, it is essential to be aware that you will be unable to drive for 24 hours afterward. You must have a designated friend or a family member who can pick you up and be with you for the first 24 hours of your trip.
Is laparoscopy a safe procedure to perform?
In general, laparoscopy is a relatively risk-free procedure. It is one of the advantages of this process that your doctor will be able to provide a precise diagnosis of your problem. Three out of every 1,000 women who undergo the procedure experience difficulties. The following are a few examples of prospective issues:
Anesthesia-related issues.
A blood clot could move to the heart or brain and can lead to a heart attack or stroke. It is extremely unlikely and rare.
Infection.
Injury to surrounding organs and blood veins.
Bleeding.
Abdominal wall inflammation.
A blood clot could get into the bloodstream and cause clotting in the legs, pelvis, or lungs.
Before your procedure, talk to your doctor about any doubts. Your doctor will be able to tell you about any possible risks and tell you how likely you are to have them.
After a laparoscopy, what can you expect?
Laparoscopy patients are usually able to return home within a few hours. You’ll have to wait until the effects of the anesthesia have gone off and your doctor has confirmed that the treatment hasn’t caused any complications for you. At home, you’ll rest and heal after your laparoscopy.
How do I recover from a laparoscopic procedure at home?
It is important to note a couple of things when you are recuperating at home after a laparoscopy. These recommendations include the following:
After surgery, you are free to take a shower or a bath whenever you like.
In the first 24 hours following surgery, refrain from consuming alcohol or operating a motor vehicle.
The bandage can be taken off the day after surgery. Two to three days after surgery, the tape-like STERIS strips can be taken off.
If your urine is green, don’t worry about it. It’s possible that a blue dye was used to see if your fallopian tubes were open during the procedure.
Most people can go back to work three days after having surgery. If you require a doctor’s note excused from work, you can ask for one during your pre-operative appointment.
Do laparoscopy procedures cause discomfort?
Like many other surgical procedures, laparoscopy may result in some discomfort. These annoyances could include:
The possibility exists that you’ll feel a little queasy. The night before surgery, eat a light dinner. Tea, soup, toast, or crackers may help alleviate your stomach cramps.
Your throat could be sore for a couple of days. Use a throat lozenge if you’re experiencing a sore throat.
There may be some discomfort in your neck, shoulder, and chest for 24 to 72 hours after surgery due to abdominal gas. You can use a heating pad, take a warm shower, or go for a walk to relieve stress.
It is possible that following surgery, you will experience swelling in your abdominal region for many days. To alleviate the discomfort, you could try taking some acetaminophen.
Can I anticipate vaginal bleeding following laparoscopy?
Up to one month after a laparoscopy, it’s usual to have vaginal bleeding. For many women, it takes 4 to 6 weeks after surgery before they may resume their regular menstrual cycle. Heavy bleeding and discomfort may occur when your regular period returns.
Let’s explore more: Diagnostic Laparoscopy - Purpose and Procedure - Southlake General Surgery
Appointment
For more information on Laparoscopy, Laparoscopic Surgery, and Diagnostic Laparoscopy. You can contact our healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748-0200. You can also make an online appointment with us
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: Diagnostic Laparoscopy - Purpose and Procedure - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#DiagnosticLaparoscopy#LaparoscopicSurgery#ReproductiveHealth#AbdominalOrgans#MedicalDiagnosis#SurgicalProcedure#HealthcareTips#PreoperativeCare#PostoperativeRecovery#HomeRecuperation#PatientCare#SurgicalComplications#AnesthesiaSafety#FollowUpAppointments#WomenHealth#MenstrualCycle#SexualActivityAfterSurgery#HealthSymptoms#MedicalConsultation#HealthAwareness
0 notes
Text
Ventral Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Surgical Solutions
Ventral hernias are a prevalent issue where the intestines or other tissues protrude through a weak spot or opening in the abdominal wall. These hernias can cause discomfort, pain, and potential complications if left untreated.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for ventral hernias is essential for anyone who may be at risk or experiencing related symptoms.
In this blog, we will provide a comprehensive overview of ventral hernia repair. We will discuss the definition and types of ventral hernias, the causes and risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options available.
We will also delve into the importance of choosing a skilled healthcare provider for ventral hernia repair, including the evaluation of risk and the potential need for component separation, and provide information on recovery and rehabilitation after the procedure.
By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of ventral hernias, their treatment options, and how to ensure a successful recovery. It is important to note that individual cases may vary, and it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.

Key Highlights
Ventral hernias occur when the intestines or other tissues protrude through a weakness in the abdominal wall.
Symptoms of ventral hernias include a visible bulge in the abdomen, discomfort or pain, and potential complications such as intestinal blockage or tissue death.
Diagnosis involves a physical examination and may include imaging techniques like CT scans or ultrasounds.
Treatment options for ventral hernias include surgical repair and non-surgical management strategies.
Surgical repair can be done through open surgery or laparoscopic techniques, and mesh may be used to reinforce the abdominal wall.
Recovery and rehabilitation after ventral hernia repair involve postoperative care and physical rehabilitation.
Understanding Ventral Hernias
Ventral hernias occur when abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. These can manifest as incisional or umbilical hernias, affecting the blood supply and requiring surgical repair.
Risk factors include obesity, heavy lifting, and previous abdominal surgery. Physical examination and imaging techniques like CT scans aid in diagnosis. Surgical techniques such as laparoscopic repair or open surgery, which is a common surgery, are performed by general surgeons. Understanding ventral hernias is vital for timely intervention and successful management.
Definition and Types of Ventral Hernias
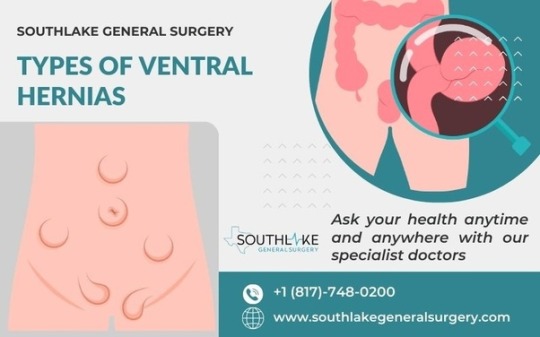
Ventral hernias occur when abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall, also known as the abdominal cavity. The three main types are umbilical, epigastric, and incisional hernias.
Umbilical hernias develop near the belly button, epigastric hernias form above the navel, and incisional hernias occur at the site of a previous surgical incision.
Proper diagnosis and treatment require a thorough understanding of these differences. Each type presents unique challenges that require tailored hernia repair approaches.
Causes and Risk Factors
Ventral hernias can develop due to factors like abdominal surgery, weakened abdominal wall, or heavy lifting. Patients with a history of hernias or connective tissue disorders are at a higher risk.
Obesity and chronic cough can also contribute to their occurrence. Factors such as aging and pregnancy may weaken the abdominal muscles, increasing the likelihood of developing a ventral hernia.
Symptoms of a Ventral Hernia
Ventral hernia symptoms may include a noticeable bulge or swelling in the abdomen, especially when straining or standing. Patients might also experience abdominal pain, discomfort, or a feeling of heaviness at the hernia site.
Additional signs can involve nausea, vomiting, or constipation, particularly if the intestine becomes trapped within the hernia. In some cases, a ventral hernia may present as a tender lump under the skin, which can cause hernia pain. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention.
Recognizing the Signs
A ventral hernia can present various signs, including a noticeable bulge or swelling in the affected area. Pain or discomfort during activities like lifting or straining may also indicate a ventral hernia.
It’s essential to pay attention to any changes in your abdominal wall, especially if there is tenderness or a feeling of pressure in the area. Seek medical advice if you experience persistent symptoms or have concerns about a possible hernia.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent pain, visible bulging, or changes in the appearance of a ventral hernia, seek medical attention promptly. Other warning signs include nausea, vomiting, and difficulties with bowel movements.
Additionally, sudden severe pain or redness at the hernia site may indicate serious complications needing immediate evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Early intervention is key to managing ventral hernias successfully, so never delay seeking medical help when experiencing concerning symptoms.
Diagnosis of Ventral Hernias

Ventral hernias are diagnosed through physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging techniques. During a physical exam, healthcare providers assess the abdomen for bulges or weak spots.
Blood tests may be conducted to check for signs of infection or other underlying conditions that could affect hernia treatment. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may also be used to confirm the presence and extent of a ventral hernia. It also helps determine the size and location of the hernia.
These diagnostic tools are crucial in identifying the appropriate treatment plan, whether it involves non-surgical management or surgical repair. Prompt diagnosis is essential to ensuring effective management of ventral hernias and preventing potential complications.
Physical Examination Findings
During a physical examination for ventral hernias, doctors may palpate the abdomen to locate the hernia. They assess for any bulges or unusual areas in the abdominal wall.
In some cases, a cough test might be performed to observe hernia protrusion during increased intra-abdominal pressure. Additionally, doctors may inquire about symptoms like pain or discomfort at the site and possible causes, such as previous abdominal surgeries or obesity.
These physical examination findings help in confirming the presence and size of the hernia, guiding further diagnostic and treatment decisions.
Imaging Techniques and Their Importance
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing and planning treatment for ventral hernias. Modalities such as CT scans and ultrasound provide detailed insights into the size and location of the hernia, aiding surgeons in determining the most appropriate approach.
These imaging tools are essential in assessing the extent of the hernia and identifying any associated complications, guiding healthcare providers towards the most effective treatment strategies.
Treatment Options Available
For ventral hernias, treatment options include both non-surgical and surgical approaches. Non-surgical management focuses on lifestyle modifications to alleviate symptoms, while surgical repair methods involve techniques like robotic surgery, laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, or open surgery with synthetic mesh placement.
In some cases, biological mesh may be used to reduce the risk of infection and promote the development of scar tissue for reinforcement. Your healthcare provider will guide you in selecting the most suitable option based on the size of the hernia, your overall health, and the risk factors involved. Understanding these choices is essential for making informed decisions regarding your care.
Non-Surgical Management Strategies
Non-surgical management strategies for ventral hernias, also known as groin hernias, primarily focus on lifestyle modifications and symptom control. These strategies typically involve weight management, avoiding heavy lifting, and maintaining physical activity within limits that do not exacerbate the hernia.
In some cases, wearing supportive garments may provide relief. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure these strategies are appropriate for individual cases and to monitor the hernia’s progression closely.
These strategies, along with surgical options, are outlined in international guidelines for groin hernia management, providing a comprehensive approach to treating this common medical condition.
Surgical Repair Methods

To address ventral hernias surgically, various methods are employed, depending on the size and complexity of the hernia.
Surgical repair methods commonly include open hernia repair surgery, laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, or minimally invasive surgery.
Open surgery involves making a larger incision to directly access and repair the hernia, while laparoscopic surgery utilizes smaller incisions and a camera for a minimally invasive approach.
Minimally invasive surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, involves using specialized tools and techniques to perform the hernia surgery through small incisions, resulting in less pain, scarring, and a faster recovery time.
Both laparoscopic and minimally invasive surgeries may involve the use of synthetic mesh to reinforce the abdominal wall and reduce the risk of hernia recurrence.
Preparing for Surgery

Before undergoing ventral hernia repair, thorough preparation is crucial. Understanding what to expect before the procedure is vital. Mentally and physically, preparing yourself can positively impact the outcome. Follow pre-surgery guidelines diligently to ensure a smooth experience.
Maintaining good overall health and adhering to any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider is essential. Being well-prepared can help reduce postoperative complications and aid in a speedier recovery. Take proactive steps to ensure you are fully ready for the surgical intervention.
What to Expect Before the Procedure
Clear communication with your healthcare team is crucial. Before the ventral hernia repair, you will likely undergo preoperative tests. It’s important to follow instructions related to fasting and medication intake. Expect a discussion on the procedure and anesthesia options, including the use of general anesthesia to make you asleep and pain-free during the surgery.
Your surgeon will provide information on potential risks and complications. Mental preparedness plays a significant role, so feel free to ask any questions or express concerns. Ensuring you understand the process will help you approach the surgery with confidence.
How to Prepare Mentally and Physically
Preparing mentally and physically for ventral hernia surgery is essential. Stay informed about the procedure, ask questions, and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. Engage in relaxation techniques to alleviate anxiety and maintain a positive mindset.
Physically, follow any preoperative instructions provided, such as fasting guidelines. Stay active within the limits set by your doctor to promote better recovery outcomes. Being mentally and physically prepared can significantly contribute to a smoother surgical experience and improved rehabilitation.
The Role of Dr. Valeria Simone MD and Southlake General Surgery
Dr. Valeria Simone MD, from Southlake General Surgery, is essential in performing skilled ventral hernia repair procedures. With a focus on patient outcomes and utilizing advanced techniques like laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, they ensure comprehensive care.
Dr. Valeria Simone MD’s expertise in managing ventral hernias of the abdomen is evident through successful surgical interventions. Patients benefit from the innovative approaches and personalized treatment plans offered by Southlake General Surgery, making them a top choice for hernia patients seeking quality care.
Expertise in Ventral Hernia Repair
Dr. Valeria Simone MD at Southlake General Surgery specializes in ventral hernia repair, offering expert knowledge and skill in abdominal wall surgery. With a focus on patient outcomes and using advanced surgical techniques, Dr. Simone ensures the highest level of care.
Southlake General Surgery is renowned for handling large ventral hernias with precision, including complex cases requiring intricate repair methods. Trust in their expertise for comprehensive management of ventral hernias, emphasizing both medical and surgical solutions.
Why Choose Southlake General Surgery?
Choosing Southlake General Surgery ensures expert ventral hernia repair by Dr. Valeria Simone MD. With a proven track record and specialized expertise in hernia treatments, patients benefit from personalized care and successful outcomes. Make the right choice for your hernia repair needs with Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after ventral hernia repair is crucial for successful outcomes. Postoperative care guidelines recommend avoiding strenuous activities and heavy lifting to prevent complications. Patients should follow instructions diligently for a smooth recovery.
Tips like maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adhering to the prescribed medication regimen aid in the healing process. Physical rehabilitation may be necessary to regain strength and mobility.
Let’s explore more: Ventral Hernia Repair: Essential Guide - Southlake General Surgery
Make an Appointment
To schedule your ventral hernia repair consultation, contact Southlake General Surgery healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748–0200. You can also make an online appointment with us.
Our experienced team, led by Dr. Valeria Simone MD, specializes in abdominal wall surgeries and ensures individualized care for optimal patient outcomes.
Whether you require surgical intervention for an abdominal hernia or need further evaluation, our practice is dedicated to your health and well-being. Don’t delay in addressing potential complications; make an appointment with us to begin your journey towards recovery and improved quality of life.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: Ventral Hernia Repair: Essential Guide - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#VentralHernia#AbdominalWallWeakness#HerniaSymptoms#HerniaDiagnosis#HerniaTreatment#SurgicalSolutions#NonSurgicalManagement#LaparoscopicSurgery#MeshPlacement#PostoperativeCare#PhysicalRehabilitation#DrValeriaSimoneMD#HerniaAwareness#MedicalIntervention#HealthyRecovery#PatientEducation#HerniaPrevention#ExpertiseInHerniaRepair#QualityHealthcare#LaparoscopicHerniaRepairTexas
0 notes
Text
HIDA Scan: A Comprehensive Guide
The liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder play vital roles in the digestive process. When these organs are not functioning properly, it can lead to various symptoms and conditions. One imaging procedure commonly used to diagnose and evaluate issues with these organs is a HIDA scan.
A HIDA scan, also called hepatobiliary scintigraphy or cholescintigraphy, is a non-invasive imaging procedure that monitors the movement of bile from the liver to the small intestine. It helps healthcare providers assess the function of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder to diagnose conditions such as acute cholecystitis, chronic cholecystitis, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, biliary atresia, and biliary leak.
A radioactive tracer is injected into the bloodstream during a HIDA scan. The liver absorbs the tracer and then releases it into the gallbladder and small intestine. A gamma camera detects the energy emitted by the tracer and creates detailed images that show the flow of bile through the biliary system.
HIDA scans are performed in the Department of Nuclear Medicine in Radiology. They are commonly used alongside other imaging tests, such as X-rays and ultrasounds, to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide a detailed understanding of HIDA scans, their importance in diagnosing gallbladder issues, how they work from a surgeon’s perspective, preparation for the scan, what to expect during and after the procedure, and potential findings and next steps. We will also address common concerns, risks, and considerations associated with HIDA scans.

Key Highlights
A HIDA scan is an imaging procedure that tracks the flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine, helping to diagnose gallbladder issues.
It is used to evaluate conditions such as acute cholecystitis, chronic cholecystitis, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, biliary atresia, and biliary leak.
The scan involves injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, where it is absorbed by the liver and later released into the gallbladder and small intestine.
Preparation for a HIDA scan requires fasting for a specific period and informing your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking.
During the scan, a gamma camera captures images of the tracer as it moves through the biliary system, allowing healthcare providers to assess its function.
After the scan, you can go about your day as usual, and the remaining radioactive tracer will be eliminated from your body within a day or two.
Understanding HIDA Scans
A HIDA scan, also referred to as hepatobiliary scintigraphy, is a medical imaging technique that monitors the movement of bile from the liver to the small intestine. It uses a radioactive tracer, usually hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA), which is injected into the bloodstream.
The tracer is taken up by the liver cells and released into the bile ducts. It then flows through the gallbladder and into the small intestine. During the scan, a gamma camera detects the radioactive energy emitted by the tracer and creates images that show the function of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder.
Significance of HIDA Scans in Identifying Gallbladder Problems
HIDA scans play a crucial role in diagnosing and evaluating gallbladder issues. They are particularly important in diagnosing conditions such as acute cholecystitis, which is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder that can be caused by gallstones. Acute cholecystitis often requires gallbladder surgery to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
By tracking the flow of bile through the biliary system, HIDA scans can help healthcare providers identify any obstructions or abnormalities in the gallbladder or bile ducts. This information is vital in determining the appropriate treatment plan, whether it involves surgical intervention, medication, or monitoring.
HIDA scans provide valuable insights into the function and health of the gallbladder, allowing healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and provide timely treatment for patients with gallbladder issues.
How HIDA Scans Work: A Surgeon’s Perspective
From a surgeon’s perspective, a HIDA scan provides valuable information about the function of the gallbladder and the flow of bile. One essential parameter that can be measured during a HIDA scan is the gallbladder ejection fraction. This refers to the percentage of bile that is released from the gallbladder when it contracts.
During the scan, a radioactive tracer is injected into the bloodstream, and as it moves through the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder, a series of images are taken using a gamma camera. These images help surgeons assess the flow of bile from the liver to the gallbladder and ultimately to the small intestine.
By analyzing these images, surgeons can determine if there are any abnormalities or blockages in the bile ducts or gallbladder. This information is crucial in guiding treatment decisions and determining whether surgery or other interventions are necessary to address the underlying issue.
HIDA scans provide valuable insights into the function of the biliary system, allowing surgeons to make informed decisions and provide optimal care for their patients.
Preparing for Your HIDA Scan

Before undergoing a HIDA scan, there are certain preparations you need to follow to ensure accurate results. Your healthcare provider will provide you with specific instructions, but here are some general guidelines to keep in mind:
Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as some medications may interfere with the accuracy of the scan.
Fasting for a minimum of four hours before the scan is necessary, which involves refraining from consuming any food or beverages except water.
Remove any jewelry or accessories that may interfere with the scan, and wear comfortable clothing.
By following these preparations, you can help ensure a smooth and successful HIDA scan procedure. It is essential to communicate openly with your healthcare provider and ask any questions you may have before the scan.
Steps to Prepare for a HIDA Scan: Tips from Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Preparing for a HIDA scan is relatively straightforward, but there are a few important steps to keep in mind. Dr. Valeria Simone MD, shares some tips to help you navigate the preparation process:
Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding fasting. Usually, you will need to avoid food and drink for at least four hours before the scan, although specific requirements may vary.
Inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as they may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued.
Dress comfortably and remove any jewelry or accessories that might interfere with the scan.
During the scan, you may experience slight discomfort from the injection of the radioactive tracer while lying still on the scanning table. Nevertheless, this discomfort is usually slight and short-lived.
Rest assured that the amount of radiation exposure during a HIDA scan is considered safe and within acceptable limits.
By following these steps and staying informed, you can prepare for your HIDA scan with confidence and ensure accurate results.
Eating and Drinking: What You Need to Know Before Your Scan
One of the key preparations for a HIDA scan is fasting. Fasting is typically required for at least four hours before the scan to ensure accurate results. It is important to follow these fasting guidelines to avoid interference with the scan.
During the fasting period, you should refrain from consuming any food or drink, except water. It is essential to drink enough water to stay hydrated, but avoid consuming anything else, including juice, coffee, or tea.
Fasting helps ensure that the radioactive tracer used during the scan is not influenced by the digestion process, allowing for clearer and more accurate imaging of the biliary system.
If you have any concerns or questions about fasting before your HIDA scan, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can provide specific instructions based on your circumstances and help alleviate any concerns you may have.
During the HIDA Scan
During a HIDA scan, you will be positioned on a scanning table, and a gamma camera will be used to capture images of the radioactive tracer as it moves through your biliary system. It is essential to stay still during the scan to achieve clear and accurate images.
The scan usually takes about an hour, during which you may be asked to change positions or hold your breath briefly. The healthcare team will provide instructions and guide you through the process to ensure optimal imaging.
If you experience any discomfort or have any questions or concerns during the scan, do not hesitate to communicate with the healthcare team. They are there to support you and ensure your comfort throughout the procedure.
What to Expect During the Procedure
During a HIDA scan, you can expect a non-invasive imaging test that tracks the flow of bile through your biliary system. The process generally includes these steps:
You will be positioned on a scanning table.
A gamma camera, which is a specialized imaging device, will be placed over your abdomen.
The healthcare team will inject a radioactive tracer into your bloodstream. This tracer is taken up by the liver and released into the gallbladder and small intestine.
The gamma camera will capture a series of images as the radioactive tracer moves through your biliary system.
It is crucial to remain still during the procedure to ensure clear and accurate images.
The healthcare team will guide you throughout the procedure and provide any necessary instructions. The entire process usually takes about an hour, after which you can resume your regular activities.
Understanding the Role of the Radiologist and Surgeon During Your Scan
During a HIDA scan, both the radiologist and surgeon play important roles in interpreting the images and assessing the function of the biliary system.
The radiologist is responsible for analyzing the images captured by the gamma camera. They will interpret the flow of the radioactive tracer and assess how well bile is flowing from the liver to the gallbladder and small intestine. Based on their findings, they can identify any abnormalities or obstructions in the biliary system.
The surgeon, on the other hand, relies on the information provided by the radiologist to guide treatment decisions. The images from the HIDA scan help the surgeon determine the appropriate course of action, whether it involves surgical intervention or other treatment options.
By working together, the radiologist and surgeon ensure that patients receive accurate diagnoses and the most appropriate care for their biliary system issues.
After the HIDA Scan
After a HIDA scan, there are a few important steps to follow to ensure optimal recovery and to allow the remaining radioactive tracer to be eliminated from your body.
Drink plenty of fluids, particularly water, to help flush the tracer out of your system.
Use the restroom frequently to eliminate any radioactive tracer that may have been excreted in your urine or stool.
Remember to wash your hands properly after using the bathroom.
Resume your normal activities and diet unless otherwise instructed by your healthcare provider.
It is important to note that the amount of radiation exposure during a HIDA scan is minimal and poses no significant risk to your health or the health of those around you.
Immediate Steps Post-Scan: A Guide
After your HIDA scan, you can take some immediate steps to ensure comfort and well-being. Here is a guide to help you through the post-scan period:
Slowly get up from the scanning table to avoid dizziness or light-headedness.
Drink plenty of fluids, particularly water, to help flush the remaining radioactive tracer out of your system.
Be aware of any signs of redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site. If you notice any of these signs, inform your healthcare provider.
Resume your regular activities and diet, unless otherwise instructed by your healthcare provider.
Wash your hands thoroughly after using the restroom to eliminate any traces of the tracer.
By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth recovery after your HIDA scan and minimize any potential discomfort or concern.
Reading Your HIDA Scan Results: Dr. Simone’s Insights
Interpreting the results of a HIDA scan requires expertise and experience, and provides valuable insights into understanding the scan results:
The scan image will show the flow of the radioactive tracer through your biliary system.
The overall quality of the scan, including the clarity and consistency of the images, is crucial in assessing the function of the biliary system.
Any abnormalities or obstructions in the flow of bile can indicate issues such as gallbladder inflammation or other conditions affecting the biliary system.
Your healthcare provider will provide you with a comprehensive interpretation of the images and explain the implications for your health. By understanding the scan results, you can make informed decisions about your treatment and care.
Potential Findings and Next Steps
During a HIDA scan, various findings can be identified, providing valuable information about the function of the biliary system. Some potential findings include:
Normal flow of bile, indicating healthy biliary function.
Slow movement of the radioactive tracer, suggesting a possible blockage or obstruction.
No tracer was seen in the gallbladder, indicating acute inflammation of the gallbladder.
Abnormally low gallbladder ejection fraction, which may indicate chronic inflammation.
Based on the scan findings, your healthcare provider will determine the next steps in your treatment plan. This may involve further imaging, additional tests, or consultation with a specialist.
Common Gallbladder Issues Identified by HIDA Scans
HIDA scans are particularly useful in identifying and evaluating common gallbladder issues. Some of these issues include:
Gallbladder disease: This term encompasses a range of conditions that affect the gallbladder, such as gallstones, inflammation, or infection.
Chronic cholecystitis: This refers to repeated episodes of gallbladder inflammation, often caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct intermittently.
Biliary tree abnormalities: HIDA scans can detect obstructions or abnormalities in the bile ducts, which make up the biliary tree.
By identifying these issues through HIDA scans, healthcare providers can develop appropriate treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific condition and needs.
When Surgery Is Recommended: Navigating Your Options in Texas
In some cases, surgery may be recommended based on the findings of a HIDA scan. Gallbladder surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, is a common procedure used to remove the gallbladder in cases of severe gallbladder disease or chronic cholecystitis.
In more complex cases, a liver transplant may be necessary to address issues with the biliary system. This procedure involves replacing a diseased liver with a healthy liver from a donor.
The decision to undergo surgery depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and the gallbladder ejection fraction measured during the HIDA scan.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in hepatobiliary surgery to discuss your options and make an informed decision.
Risks and Considerations
As with any medical procedure, there are some risks and considerations associated with HIDA scans. It is essential to be aware of these potential risks and discuss them with your healthcare provider. Some of the key considerations include:
Allergic reactions to medications containing radioactive tracers used during the scan, although they are rare.
Bruising at the injection site of the radioactive tracer.
Minimal radiation exposure, which is within safe limits.
Precautions for pregnant individuals, as nuclear medicine tests are generally not performed during pregnancy due to potential harm to the developing fetus.
By understanding these risks and addressing any concerns with your healthcare provider, you can make informed decisions regarding your medical care.
Understanding the Risks Associated with HIDA Scans
HIDA scans are generally considered safe with minimal risks. However, it is important to be aware of potential risks associated with the procedure. These risks may include:
Allergic reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to the radioactive tracer. It is important to inform your healthcare provider of any known allergies before the scan.
Bruising: Bruising at the injection site of the tracer is possible, but it is typically minimal.
Radiation exposure: HIDA scans involve the use of a small amount of radiation, but the exposure is within safe limits and not considered a significant risk.
Your healthcare provider will assess the potential risks and benefits of a HIDA scan based on your situation. They will provide guidance and address any concerns you may have before proceeding with the procedure.
Addressing Patients’ Concerns: Safety Measures in Place

Patient safety is a top priority during HIDA scans, and various safety measures are in place to minimize risks. These measures include:
Let’s explore more: HIDA Scan: Understanding the Procedure - Southlake General Surgery
Make An Appointment
If you are experiencing symptoms related to your gallbladder or have concerns about your biliary system, it is important to seek medical advice and schedule an appointment with our healthcare expert at +1 (817) 748-0200 and click the link to book an online appointment with us. They can evaluate your symptoms, discuss your medical history, and recommend appropriate diagnostic tests, including HIDA scans.
Remember, early diagnosis and timely intervention are key to effective treatment and better outcomes for gallbladder issues.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: HIDA Scan: Understanding the Procedure - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#HIDAScan#GallbladderIssues#MedicalImaging#Radiology#Healthcare#BiliarySystem#LiverHealth#Gallstones#Cholecystitis#GammaCamera#HealthPreparation#SurgicalIntervention#DiagnosticTests#RadiationSafety#HealthAwareness#PatientEducation#GallbladderSurgery#DigestiveHealth#NuclearMedicine#HealthcareGuidance
0 notes
Text
Managing Porcelain Gallbladder: Patient Guide
A porcelain gallbladder, a rare condition characterized by the calcification of the gallbladder wall, poses significant health risks if left untreated. Understanding the implications of this condition is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention.
Recent studies have shed light on the correlation between porcelain gallbladder and an increased risk of gallbladder cancer, emphasizing the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment. Surgical approaches, such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, are often recommended to mitigate the risks associated with this condition.
With insights into its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their health effectively. Regular health check-ups and lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in preventing complications related to the porcelain gallbladder and understanding its natural history.

Understanding Porcelain Gallbladder
Porcelain gallbladder, also known as calcified gallbladder or PGB refers to a condition where the gallbladder wall becomes calcified, leading to a brittle consistency. In some cases, this calcification can be a result of chronic inflammation, often linked to gallstones or other gallbladder diseases.
Understanding this condition is crucial due to its association with a higher risk of gallbladder cancer. Recent reports have highlighted the importance of early detection and treatment to prevent potentially serious complications.
Imaging techniques, such as CT scans and ultrasounds, play a significant role in diagnosing this condition. Surgical interventions like laparoscopic cholecystectomy are often recommended in cases where the risk of malignancy is present, emphasizing the need for prompt medical attention.
What is a Porcelain Gallbladder?
Porcelain gallbladder is a rare condition where the gallbladder wall becomes calcified. This can lead to an increased risk of gallbladder cancer. It is essential to comprehend this condition for timely detection and proper treatment.
The Importance of Early Detection
Identifying the porcelain gallbladder early is crucial, as it can help prevent serious complications like gallbladder cancer. The early detection of porcelain gallbladder is key to initiating timely treatment to avoid the progression of the condition.
Recent reports emphasize the significance of identifying the calcification of the gallbladder in its early stages. Individuals with risk factors such as chronic cholecystitis should be particularly vigilant and undergo regular screenings for gallbladder abnormalities.
Early detection allows for prompt intervention, reducing the risk of malignant degeneration and potential complications. Therefore, awareness of the signs and symptoms of porcelain gallbladder is essential for ensuring timely diagnosis and appropriate management.
Causes and Risk Factors
Porcelain gallbladder, characterized by calcification of the gallbladder wall, has intricate causes and risk factors. The major contributor to this condition is the presence of gallstones, especially cholesterol stones.
Additionally, chronic cholecystitis, a result of chronic inflammation, can lead to the calcification of the gallbladder. Other risk factors include emphysematous cholecystitis and dystrophic calcification.
Recent studies have shown a potential causal relationship between calcium deposits and the development of this rare condition.
Understanding these factors is crucial for early detection and appropriate management, including early cholecystectomy. Timely intervention, such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is recommended to prevent complications like gallbladder cancer and malignant degeneration of the lumen.
How Gallstones Contribute to Porcelain Gallbladder?
Gallstones play a significant role in the development of a porcelain gallbladder. The chronic presence of gallstones within the gallbladder results in inflammation, leading to the calcification of the gallbladder wall.
The calcification process occurs over time, causing the once flexible gallbladder to become brittle due to calcium deposits. This transformation ultimately gives the gallbladder a porcelain-like appearance in imaging studies.
Research indicates a causal relationship between long-standing gallstones and the formation of a porcelain gallbladder, with a higher frequency of gallstones found in patients with a porcelain gallbladder compared to the general population.
Therefore, individuals with a history of gallstones are at a higher risk of developing this unusual condition. Early detection and management of gallstones are crucial in preventing the progression to a porcelain gallbladder.
Other Risk Factors Leading to Porcelain Gallbladder
Porcelain gallbladder can be influenced by various factors beyond gallstones. Chronic cholecystitis, a condition characterized by long-term inflammation, poses a significant risk.
Moreover, the presence of emphysematous cholecystitis, where gas accumulates within the gallbladder, can contribute to the development of a porcelain gallbladder. Dystrophic calcification, a process where calcium deposits form in damaged tissues, is another risk factor to consider.
Recent studies also suggest a potential link between gallbladder sludge and the calcification of the gallbladder wall, raising concerns about its impact on gallbladder health. Understanding these additional risk factors is crucial for comprehensive management and prevention strategies for porcelain gallbladder.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of porcelain gallbladder are often absent, making early diagnosis challenging. However, if present, symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
In some cases, patients may experience weight loss or jaundice. Diagnostic tests like CT scans and ultrasounds are crucial for accurate identification. Calcifications seen in imaging studies signify advanced disease.
If a porcelain gallbladder is suspected, prompt medical evaluation is essential to rule out potential complications. Given the lack of specific symptoms, regular health check-ups and imaging screenings play a crucial role in the early detection of this condition.
Early diagnosis can significantly impact treatment outcomes and improve patient prognosis.
Common Symptoms of Porcelain Gallbladder
Brittle consistency of the gallbladder wall due to calcification often leads to the absence of symptoms in patients with a porcelain gallbladder.
However, when symptoms are present, they can mimic those of gallbladder disease. Common symptoms may include vague abdominal discomfort, nausea, and bloating in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen.
In severe cases, patients might experience weight loss and signs of chronic inflammation. Diagnostic imaging techniques such as ultrasound and CT scans play a vital role in identifying these symptoms.
Early detection through these methods is crucial in managing the condition effectively and preventing potential complications like gallbladder cancer. Regular health check-ups are recommended to monitor any changes in symptomatology.
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging Techniques
When diagnosing porcelain gallbladder, healthcare providers may rely on various diagnostic tests and imaging techniques to confirm the condition.
Commonly used methods include ultrasounds, CT scans, and plain abdominal radiographs. These tools allow specialists to visualize the gallbladder and detect any calcifications or abnormalities in the gallbladder wall indicative of a porcelain gallbladder.
Additionally, more advanced imaging techniques, like MRI scans and radiography, may provide detailed insights into the extent of calcification and the overall health of the gallbladder.
Precise diagnosis through these methods is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan and ensuring the best possible outcome for individuals with porcelain gallbladder.
Treatment Options for Porcelain Gallbladder

Surgical treatment for porcelain gallbladder typically involves cholecystectomy, the removal of the gallbladder. This procedure is commonly done laparoscopically, offering a less invasive approach with quicker recovery times.
Non-surgical management strategies may be considered for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery or prefer non-invasive options. These strategies often focus on symptom management and lifestyle modifications to prevent complications.
Individuals with porcelain gallbladder need to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific case. Understanding the available treatment options and their potential outcomes is crucial in managing porcelain gallbladder effectively.
Surgical Treatment: Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the primary surgical treatment for porcelain gallbladder in the United States. This procedure involves the removal of the gallbladder, usually due to complications like gallstones, chronic inflammation, or the increased risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
A laparoscopic gallbladder surgery, compared to open cholecystectomy, is commonly preferred for its minimally invasive nature and faster recovery times.
Studies indicate that patients undergoing cholecystectomy experience relief from symptoms and a reduced risk of complications associated with porcelain gallbladder. Surgical intervention aims to prevent potential malignancy and alleviate symptoms caused by the calcification of the gallbladder wall.
The mean age of patients undergoing cholecystectomy for porcelain gallbladder is 58.6 years, with a range of 19–94 years. Individuals with porcelain gallbladder need to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment recommendations.
Non-Surgical Management Strategies
For individuals with porcelain gallbladder who are not suitable candidates for surgery, non-surgical management strategies play a crucial role in symptom control and disease management.
Dietary modifications aimed at reducing fat intake can help alleviate symptoms associated with gallbladder disease. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition and regular physical activity can further aid in managing the condition.
Some patients may benefit from medications to dissolve gallstones or alleviate pain. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive non-surgical management plan tailored to individual needs and health conditions.
Monitoring symptoms and adapting the management strategy as needed are key aspects of long-term care.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care

After undergoing a cholecystectomy for a porcelain gallbladder, a crucial aspect is the recovery and post-operative care. Following surgery, patients can typically resume their normal activities within a week. Physical therapy may aid in a quicker recovery.
It’s essential to adhere to any prescribed pain management regimen and follow dietary recommendations to prevent discomfort. Monitoring for signs of infection or complications is paramount during the recovery period.
Patients should contact their healthcare provider if they experience persistent pain, fever, or unusual symptoms. Embracing a gradual return to regular activities is advised, with close attention to any post-operative guidelines provided by the medical team.
What to Expect After Gallbladder Removal Surgery
After gallbladder removal surgery, patients can expect a period of recovery. Initially, some may experience mild pain and discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed medication. It’s normal to feel tired and have a reduced appetite for a few days post-surgery.
Gradually, individuals can resume their regular activities, but heavy lifting should be avoided for a few weeks. Changes in bowel habits may occur but usually normalize over time. A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor progress and address any concerns.
Adhering to dietary recommendations, staying hydrated, and slowly increasing physical activity are crucial aspects of a smooth recovery process.
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments for Recovery

After undergoing gallbladder removal surgery, incorporating dietary and lifestyle modifications is crucial for a smooth recovery. Focus on a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to aid digestion and prevent complications.
Avoid high-fat and spicy foods that may trigger digestive issues. Gradually introduce physical activity, such as walking or light exercises, to regain strength and promote overall well-being. Hydration is key, so ensure adequate water intake daily.
Listen to your body’s signals and gradually resume normal activities while avoiding strenuous tasks. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice on post-operative care and any necessary adjustments for your specific recovery journey.
Complications and Risks of Untreated Porcelain Gallbladder
The complications and risks of untreated porcelain gallbladder include an increased likelihood of developing gallbladder cancer due to the chronic inflammatory state.
Research has shown a potential link between calcification of the gallbladder and the malignant degeneration of cells. Without early intervention, there is a higher risk of gallbladder carcinoma, necessitating more aggressive treatment measures.
The brittle consistency of the gallbladder wall in porcelain gallbladder increases the chances of complications such as emphysematous cholecystitis or dystrophic calcification.
Ignoring symptoms can lead to further chronic inflammation, potentially causing issues like bile duct obstruction or gallbladder wall malignancy. Timely diagnosis and treatment can help prevent these severe outcomes.
Risk of Gallbladder Cancer
Porcelain gallbladder poses a significant concern due to the potential risk of gallbladder cancer. The calcification of the gallbladder, a characteristic feature of this condition, can sometimes lead to malignancy.
Recent reports have shown that the risk of developing gallbladder cancer from gallbladder calcification, also known as the incidence of GBC, is much lower than previously believed, emphasizing the importance of early detection and prompt treatment.
Patients with porcelain gallbladder should be vigilant about any new symptoms or changes in their health, as close monitoring and intervention can help mitigate the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Understanding the potential complications, such as malignant degeneration, underscores the importance of proactive management and regular follow-ups to safeguard against adverse outcomes.
Other Potential Complications
Potential complications associated with porcelain gallbladder extend beyond the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Emphysematous cholecystitis, characterized by gas-forming bacteria in the gallbladder wall, is a rare but serious complication.
Dystrophic calcification may lead to the brittleness of the gallbladder wall, increasing the risk of perforation during surgical interventions.
Chronic inflammation associated with porcelain gallbladder can also result in other issues such as bile duct obstruction and sludge formation.
These complications highlight the importance of timely diagnosis and appropriate management strategies to prevent further health implications. In cases where complications arise, a multidisciplinary approach involving radiology, pathology, and surgical expertise may be necessary for optimal patient outcomes.
Preventative Measures
To prevent porcelain gallbladder complications, certain lifestyle adjustments are key. Maintaining a healthy weight and following a balanced diet can reduce the risk of gallbladder disease. Regular physical activity aids in overall gallbladder health.
Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial for bile production and preventing gallstones. Annual health check-ups can detect any potential issues early on, facilitating timely intervention. Monitoring cholesterol intake and opting for a low-fat diet may also lower the risk of developing gallstones.
These preventative measures can play a significant role in safeguarding against the progression of the porcelain gallbladder to more severe conditions.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Gallbladder Problems

To prevent gallbladder problems, implementing lifestyle changes is crucial. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and regular exercise can significantly lower the risk of gallbladder issues. Including fiber-rich foods and staying hydrated helps with bile function and overall gallbladder health.
Avoiding rapid weight loss methods and adopting a balanced approach to weight management is advisable. Limiting the consumption of high-fat and cholesterol-laden foods is essential to prevent the formation of gallstones.
Additionally, regular physical activity promotes overall well-being and aids in the prevention of gallbladder disease. Making these lifestyle modifications can have a positive impact on gallbladder health and reduce the likelihood of developing complications.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups play a vital role in managing porcelain gallbladder and other potential complications effectively. These routine assessments allow for the early detection of any changes in the gallbladder wall, including signs of gallbladder cancer or calcification.
Let’s explore more: Porcelain Gallbladder: Patient Management Tips - Southlake General Surgery
Make an Appointment

To address any concerns or symptoms related to the porcelain gallbladder, it is crucial to seek professional medical advice promptly. Making an appointment with a healthcare provider experienced in gallbladder conditions is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Early detection through a comprehensive evaluation can significantly influence management outcomes. By scheduling a consultation, individuals can benefit from timely interventions and access to the most appropriate treatment recommendations.
Don’t delay in seeking medical attention if you suspect any issues with your gallbladder. Take proactive steps toward your health by arranging a consultation with our specialist at +1 (817) 748-0200 today, to discuss your symptoms and explore the best course of action. You can also book an online appointment with us.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: Porcelain Gallbladder: Patient Management Tips - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellness#wellbeing#health#healthcare#fitblr#lifestyle blog#health blog#PorcelainGallbladder#GallbladderHealth#GallbladderAwareness#EarlyDetection#GallbladderCancer#Cholecystectomy#HealthAwareness#MedicalAdvice#patientcare#SurgicalTreatment#LifestyleAdjustments#GallbladderSymptom#DietaryModifications#PostoperativeCare#Gallstones#HealthCheckUps#PatientGuide#LaparoscopicSurgeryTexas
0 notes
Text
Gallbladder Stones (Cholelithiasis): Symptoms & Solutions
Gallbladder stones or gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis, are hardened pieces of solid material that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver.
The gallbladder has a significant function in the digestive process as it stores and releases bile, a liquid created by the liver to aid in fat digestion. When the balance of cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile salts in the bile is disrupted, gallstones can form.

Gallstones can range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball and can be composed of either cholesterol or pigment. Cholesterol stones are the predominant variety and typically exhibit a yellow-green color. They are made up of undissolved cholesterol and may also contain other substances such as bilirubin or bile salts. Pigment stones, on the other hand, are brown or black and are primarily made of bilirubin. People with liver disease or certain blood disorders are more likely to develop pigment stones.
Most gallstones do not cause any symptoms and are referred to as “silent gallstones.” They are typically discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions. However, when a gallstone blocks a bile duct, it can cause severe pain and lead to complications. It is important to recognize the symptoms of gallstones and seek medical attention if they occur.
Key Highlights
Gallstones are pieces of solid material that form in the gallbladder and can vary in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball.
Most gallstones do not cause any symptoms and do not require treatment.
Symptoms of gallstones typically occur when a stone blocks a bile duct, causing pain in the upper right abdomen, lower chest, or back.
Cholesterol stones are the most common type of gallstones, followed by pigment stones.
Risk factors for gallstones include obesity, high cholesterol levels, rapid weight loss, and a family history of gallstones.
Treatment options for gallstones include surgical removal of the gallbladder or non-surgical treatments to dissolve or break up the stones.
Understanding Gallbladder Stones
Gallbladder stones, also known as cholelithiasis, are solid formations that occur in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. The gallbladder stores and releases bile, a fluid produced by the liver that aids in digestion. Bile is transported from the liver to the gallbladder through the common bile duct.
Cholelithiasis, or gallbladder stones, can be classified into two main types: cholesterol stones and pigment stones. Cholesterol stones are the most common type and are formed when there is an imbalance of cholesterol in the bile. They are usually yellow-green. Pigment stones, on the other hand, are made up of bilirubin, a substance produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. These stones are usually brown or black.
Gallbladder stones can vary in size, ranging from a grain of sand to a golf ball. They can cause symptoms when they block the flow of bile, leading to pain and other complications. Understanding the different types of gallstones and their formation can help in recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
The Basics of Gallbladder Function and Health

The gallbladder has a vital function in digestion. After food is digested in the stomach, it enters the small intestine, where bile is released from the gallbladder to aid in the breakdown and absorption of fats.
Bile is a fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. It contains bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin, and other substances necessary for digestion. When food enters the small intestine, the gallbladder contracts and releases bile into the common bile duct, which transports it to the small intestine.
In cases of liver disease or gallbladder inflammation, the flow of bile may be affected, leading to the formation of gallstones. Maintaining a healthy gallbladder is essential for proper digestion and overall health.
Different Types of Gallstones Explained
Gallstones can be classified into two main types: cholesterol gallstones and pigment stones.
Cholesterol gallstones: About 80% of cases are attributed to these being the most prevalent type of gallstones. They are primarily composed of cholesterol that has not been dissolved in bile. Other substances, such as bilirubin or bile salts, may also be present in cholesterol gallstones.
Pigment stones: Pigment stones are typically brown or black and are composed mainly of bilirubin. They are more commonly seen in individuals with liver disease or blood disorders that lead to excess bilirubin production. In some cases, gallstones may consist of a combination of cholesterol and pigment.
Both types of gallstones can vary in size, ranging from tiny grains of sand to larger golf ball-sized stones. The formation of gallstones occurs when there is an imbalance in the composition of bile, resulting in the deposition of substances that can solidify into stones.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones

Symptoms of gallbladder stones may vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all. However, when gallstones cause a blockage in the bile duct or gallbladder, symptoms may occur. Common symptoms of gallbladder stones include:
Discomfort experienced in the upper right abdomen, beneath the ribcage
Pain in the lower chest, right shoulder, or back
Upset stomach
Nausea or vomiting
Additional gastrointestinal issues like dyspepsia, acid reflux, and gas
These symptoms may arise during a gallbladder attack, also known as biliary colic, which occurs when a gallstone blocks the flow of bile. It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones can often go unnoticed until they cause a blockage or inflammation in the gallbladder or bile ducts. However, there are some early warning signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of gallstones. These include:
Abdominal pain: Gallstone pain often begins as a dull ache in the upper right abdomen and may radiate to the back or right shoulder. The pain can be intermittent or persistent and may worsen after eating fatty or greasy foods.
Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss may occur due to the avoidance of certain foods that trigger gallstone symptoms or a decrease in appetite.
Nausea and vomiting: Nausea and vomiting may occur as a result of the blockage or inflammation caused by gallstones.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can perform diagnostic tests, such as an abdominal ultrasound, to confirm the presence of gallstones.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Gallstone Symptoms
While gallstone symptoms can vary in severity, there are certain situations in which it is important to seek immediate medical attention. These include:
Severe pain: If you experience severe, persistent pain that lasts for several hours, it may indicate a serious complication such as a blocked bile duct or inflammation of the gallbladder.
Inflammation of the gallbladder: Inflammation of the gallbladder, known as cholecystitis, can occur when a gallstone blocks the cystic duct. Symptoms consist of intense abdominal pain, fever, and sensitivity in the upper right abdomen.
Jaundice: The presence of gallstones can lead to the blockage of the bile duct, causing a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream. This can result in jaundice and a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Pancreatitis: Gallstones may obstruct the pancreatic duct in certain situations, causing pancreas inflammation. This can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and fever.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention, as they may indicate a serious complication related to gallstones.
Causes and Risk Factors for Gallbladder Stones
Several factors can contribute to the development of gallbladder stones. Common causes and risk factors include:
Obesity: The risk of developing gallstones is higher in individuals who are overweight or obese. Excess weight can lead to increased cholesterol levels in the bile, which can contribute to stone formation.
High cholesterol levels: Too much cholesterol in the bile can lead to the formation of cholesterol gallstones.
Excess bilirubin: Conditions that cause increased breakdown of red blood cells or impaired liver function can result in excess bilirubin in the bile, leading to the formation of pigment stones.
Rapid weight loss: Losing a significant amount of weight in a short period of time, such as after weight loss surgery, can increase the risk of developing gallstones.
Other risk factors for gallbladder stones include a sedentary lifestyle, a high-fat diet, certain medical conditions such as diabetes, and a family history of gallstones. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to reduce the risk of developing gallbladder stones.
Lifestyle and Diet: Key Contributors to Gallbladder Issues
Lifestyle and diet play a significant role in the development of gallbladder issues, including the formation of gallstones. Certain dietary habits and lifestyle choices can contribute to an increased risk of developing gallbladder stones. Some key contributors include:
Dietary fats: Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats can increase cholesterol levels in the bile, making it more likely for cholesterol gallstones to form. It is important to limit the intake of unhealthy fats and opt for healthier fats found in foods such as nuts, olive oil, and fish.
Whole grains: Incorporating whole grains into your diet, such as whole wheat bread and brown rice, can help promote regular bowel movements and prevent the buildup of gallstones.
Weight loss: Rapid weight loss or crash dieting can increase the risk of developing gallstones. It is important to approach weight loss in a gradual and sustainable manner to reduce the risk.
Bile salts: Consuming a diet low in fiber and high in refined carbohydrates can interfere with proper bile salt metabolism, increasing the risk of gallstone formation. Including fiber-rich foods in your diet can help regulate bile salt levels.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and making dietary choices that promote gallbladder health, you can reduce the risk of developing gallbladder issues, including gallstones.
Who is at Risk? Demographic and Genetic Factors
Certain demographic and genetic factors can increase the risk of developing gallbladder stones. These include:
Gender and hormones: Women, especially those who have had multiple pregnancies or are on hormonal contraceptives, have a higher risk of developing gallstones. This is because estrogen increases cholesterol levels and slows down gallbladder emptying.
Age: The risk of developing gallstones increases with age, particularly after the age of 40.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as Native Americans and Mexican Americans, have a higher prevalence of gallstones.
Genetic predisposition: A family history of gallstones can increase the likelihood of developing gallbladder stones.
Gallbladder disease: Individuals who have a history of gallbladder disease, such as inflammation or infection, are at a higher risk of developing gallstones.
It is important for individuals who fall into these high-risk categories to be aware of the potential risks and take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of gallstone formation.
Diagnosing Gallbladder Stones
Diagnosing gallbladder stones typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may use the following methods to diagnose gallbladder stones:
Abdominal ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the abdomen and can show the presence of gallstones.
HIDA scan: This nuclear medicine test involves injecting a radioactive substance into the bloodstream to evaluate the function of the gallbladder and detect blockages in the bile ducts.
Endoscopic ultrasound: This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with an ultrasound device into the digestive tract to obtain detailed images of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Blood tests: Blood tests can help identify signs of inflammation, infection, or liver dysfunction that may be associated with gallbladder stones.
A healthcare professional will review the results of these tests and make a professional diagnosis based on the findings. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of gallbladder stones.
Professional Diagnosis: What to Expect During Your Visit
During a visit to a healthcare provider for the diagnosis of gallbladder stones, several steps may be involved. These include:
Physical examination: The healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to assess any visible signs of gallbladder issues and evaluate the abdomen for tenderness or swelling.
Medical history: The healthcare provider will review your medical history and ask questions about your symptoms, lifestyle, and any previous episodes of gallstone-related pain.
Symptoms review: A detailed review of your symptoms will be conducted to understand the pattern, severity, and duration of pain or discomfort.
Blood pressure and vital signs: Vital signs, including blood pressure and heart rate, may be checked to evaluate overall health.
Liver function tests: Blood tests may be ordered to assess liver function and check for any abnormalities that may be associated with gallbladder stones.
These steps help healthcare providers gather important information to make a proper diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment for gallbladder stones.
The Role of Imaging and Lab Tests in Gallbladder Stone Diagnosis
Diagnostic imaging and lab tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis of gallbladder stones. These tests provide valuable information about the presence and characteristics of gallstones. Some common tests used for diagnosis include:
Abdominal ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the abdomen and can detect gallstones.
HIDA scan: This nuclear medicine test involves injecting a radioactive substance into the bloodstream to evaluate the function of the gallbladder and detect blockages in the bile ducts.
Blood tests: Blood tests can assess liver function, measure bilirubin levels, and check for signs of inflammation or infection associated with gallbladder stones. Liver enzyme levels may also be evaluated.
ERCP, or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: It is a diagnostic procedure used to identify and treat issues in the bile ducts and pancreas. This test can help differentiate between conditions like cholecystitis and gallstones.
The results of these tests, along with a thorough medical history and physical examination, help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individuals with gallbladder stones.
Lab Test & Purpose
Abdominal ultrasound - Non-invasive imaging test to detect gallstones.
2. HIDA scan - Evaluates gallbladder function and detects blockages in the bile ducts.
3. Blood tests - Assess liver function and check for signs of inflammation, infection, or abnormal bilirubin levels.
4. ERCP - ERCP is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the bile ducts and pancreas, diagnose issues like gallstones, and provide therapeutic relief for patients with gallbladder stones.
Modern and Traditional Solutions for Gallbladder Stones
When it comes to treating gallbladder stones, there are a variety of options available. The most common approach is gallbladder removal surgery, which can be performed using laparoscopic or open techniques. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy entails creating minor incisions and utilizing specific instruments to extract the gallbladder. Open cholecystectomy is a more traditional approach that requires a larger incision.
In some cases, non-surgical treatments and home remedies may be recommended to dissolve gallstones or manage symptoms. These can include medications such as ursodeoxycholic acid, shock wave lithotripsy to break up stones, or dietary changes to prevent further stone formation.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the size and number of gallstones, the severity of symptoms, and the individual’s overall health. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to determining the most appropriate treatment plan for gallbladder stones.
Surgical Approaches: From Open Surgery to Laparoscopic Surgery

Surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy, is a common and effective treatment for gallbladder stones. There are two main approaches to gallbladder removal: laparoscopic cholecystectomy and open cholecystectomy.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: This minimally invasive procedure involves making several small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera, and surgical tools, to remove the gallbladder. The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include smaller incisions, less scarring, and faster recovery time.
Open cholecystectomy: In some cases, open surgery may be necessary, particularly if there are complications or if the gallbladder cannot be safely removed using laparoscopic techniques. Open cholecystectomy involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the gallbladder.
The choice of surgical approach depends on various factors, including the individual’s overall health, the presence of complications, and the surgeon’s expertise. Recovery time can vary but is generally shorter with laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Home Remedies
In addition to surgical removal, non-surgical treatments, and home remedies may be considered for managing gallbladder stones. These options are typically reserved for individuals who are not suitable candidates for surgery or prefer non-invasive approaches. Some non-surgical treatments and home remedies include:
Medications: Ursodeoxycholic acid or chenodiol may be prescribed to help dissolve cholesterol gallstones over time.
Shock wave lithotripsy: This non-invasive procedure uses sound waves to break up gallstones, making them easier to pass or dissolve.
Dietary changes: Modifying your diet to reduce the intake of high-fat foods and incorporating more fiber-rich foods can help prevent further stone formation and promote gallstone dissolution.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate non-surgical treatment or home remedy based on individual circumstances and the characteristics of gallbladder stones.
Recovery and Management Post-Gallbladder Removal
After gallbladder removal surgery, it is important to make certain adjustments to your diet and lifestyle to ensure a smooth recovery and long-term management. Some key considerations include:
Diet adjustment: Following gallbladder removal, you may need to modify your diet to accommodate changes in the digestion and absorption of fats. This may involve gradually reintroducing high-fat foods and incorporating digestive enzymes or bile salts to aid in the digestive process.
Long-term management: It is important to maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor post-surgery recovery and manage any potential complications. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding rapid weight loss, can help prevent the formation of new gallstones.
By following the recommended post-surgery care and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively manage life without a gallbladder and maintain a healthy digestive process.
Adjusting Your Diet for a Healthy Gallbladder-free Life
After gallbladder removal, adjusting your diet is essential for a healthy gallbladder-free life. Here are a few things to think about when it comes to your diet:
Fat intake: Limiting your intake of high-fat foods can help prevent digestive discomfort, as your body may have difficulty digesting and absorbing fats without the gallbladder. Gradually reintroduce healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, avocados, and olive oil, to ensure a balanced diet.
Digestive enzymes: Some individuals may benefit from incorporating digestive enzyme supplements to aid in the digestion of fats. These enzymes can help break down fats and improve digestion.
Whole grains: Including whole grains in your diet can provide essential fiber and nutrients while promoting regular bowel movements.
Balanced diet: Focus on a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support overall health and digestion.
Bile salts: In some cases, bile salt supplements may be recommended to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats.
By making these dietary adjustments, individuals can maintain a healthy digestive process and minimize digestive discomfort after gallbladder removal.
Long-term Management and Care Post-Surgery
Long-term management and care following gallbladder removal surgery are essential to maintain digestive health and overall well-being. Some important considerations include:
Regular check-ups: It is important to schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor post-surgery recovery, manage any potential complications, and discuss any digestive concerns.
Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding rapid weight loss can help prevent the formation of new gallstones and support overall digestive health.
Managing complications: If you experience any complications or digestive issues post-surgery, such as diarrhea or abdominal pain, it is important to discuss these with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate management strategies.
By staying proactive and maintaining regular communication with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage life without a gallbladder and ensure optimal digestive health.
Preventative Measures Against Gallbladder Stones
Prevention is key when it comes to gallbladder stones. By adopting certain dietary and lifestyle practices, individuals can reduce the risk of developing gallstones. Some preventative measures include:
Dietary tips: Following a diet that is low in saturated fats, high in fiber, and rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help prevent the development of gallstones.
Gallstone prevention: Avoiding crash diets and rapid weight loss and maintaining a stable weight can reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
Regular health screenings: Periodic health screenings can help identify potential risk factors and allow for early detection and intervention.
By incorporating these preventative measures into daily life, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of gallbladder stones and maintain optimal digestive health.
Dietary Tips and Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Gallstones
Making certain dietary and lifestyle changes can help prevent the formation of gallstones. Here are some tips to consider:
Let’s explore more: Signs of Gallbladder Stones: Symptoms & Solutions - Southlake General Surgery
Make An Appointment
If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns about gallbladder stones, you can book an appointment with our healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748-0200. You can also make an online appointment with us.
They will be able to evaluate your symptoms, perform the necessary tests, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options based on your circumstances. Don’t hesitate to reach out and make an appointment to ensure your gallbladder health and overall well-being.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Source: Signs of Gallbladder Stones: Symptoms & Solutions - Southlake General Surgery
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#lifestyle blog#health blog#Gallstones#GallbladderStones#Cholelithiasis#DigestiveHealth#LaparoscopicSurgery#Bile#GallbladderHealth#CholesterolStones#PigmentStones#SymptomAwareness#GallbladderFunction#BiliaryColic#EarlyDetection#PreventiveMeasures#LifestyleChanges#HealthyDiet#GallbladderRemoval#SurgicalOptions
0 notes
Text

Managing Gallbladder Pain: Tips from Dr. Valeria Simone MD
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#aesthetic#pic of the day#picture of the day#picture#images#GallbladderPain#Gallstones#DigestiveHealth#LaparoscopicSurgery#HealthyDiet#PainManagement#GallbladderHealth#MedicalAdvice#SurgicalOptions#HealthcareTips#DietaryChanges#PatientCare#PreventiveHealth#PostSurgeryRecovery#MedicalFAQs
0 notes
Text

Hyperthyroidism vs Hypothyroidism: Explained Concisely
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#aesthetic#pic of the day#picture#picture of the day#picoftheday#usa#ThyroidHealth#HyperthyroidismAwareness#HypothyroidismAwareness#ThyroidSymptoms#HashimotosThyroiditis#GravesDisease#ThyroidBalance#ThyroidDisorders#ThyroidFunction#ThyroidSupport#TSHLevels#ThyroidDiagnosis#ThyroidSurgery#AutoimmuneThyroid
0 notes
Text

Understanding Hernia Surgery: FAQs Answered by Experts
#southlake#southlake general surgery#texas#southlaketx#queued#wellbeing#wellness#health#healthcare#fitblr#aesthetic#pic of the day#picture of the day#picoftheday#HerniaSurgery#HerniaTreatment#HerniaFAQs#SurgicalRecovery#MinimallyInvasiveSurgery#MedicalAdvice#laparoscopicsurgery#laparoscopic surgeon#HealthcareTips#PostOpCare#SurgicalOptions#PatientEducation#SurgicalRecoveryTips#HealthAwareness#SurgicalProcedures#HealthyRecovery
0 notes