Text
10,000-Year-Old Sandals from Fort Rock Cave in Oregon (c.8000 BCE): these sandals are the oldest known footwear ever discovered

The oldest shoes in the world come from Oregon's Fort Rock Cave, where a team of archaeologists unearthed more than 70 sandals dating back to about 10,000 years ago. They had been buried beneath a layer of volcanic ash during the eruption of Mount Mazama in 7,600 BCE (the same eruption that produced Crater Lake). Some of the sandals still show signs of charring from the hot pumice that rained down over the site.
Each sandal is woven with ropes made of twisted sagebrush bark, and their design represents a distinctive stylistic tradition.

From the Oregon Encyclopedia:
While sandals have been found at sites other than Fort Rock Cave, no other site has produced the unusual quantity found at Fort Rock. They range from child-size to large adult size. Most are heavily worn or broken, which suggests that they were discarded rather than being stored for later use.
I briefly mentioned these sandals in my previous post, but I decided that it would be better to just give them their own separate, dedicated post instead, because they really are amazing.
Sources & More Info:
Oregon Encyclopedia: Fort Rock Sandals
Museum of Natural and Cultural History at the University of Oregon: Great Basin Sandals
Wikipedia: Fort Rock Cave
#archaeology#history#anthropology#artifact#prehistory#oregon#fort rock cave#crafting#prehistoric clothing#fashion#native american history#ancient history#world's oldest shoes
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
World's Oldest Leather Shoe, from Armenia, c.3500 BCE: this prehistoric shoe dates back to about 5,500 years ago, making it the oldest leather shoe in the world
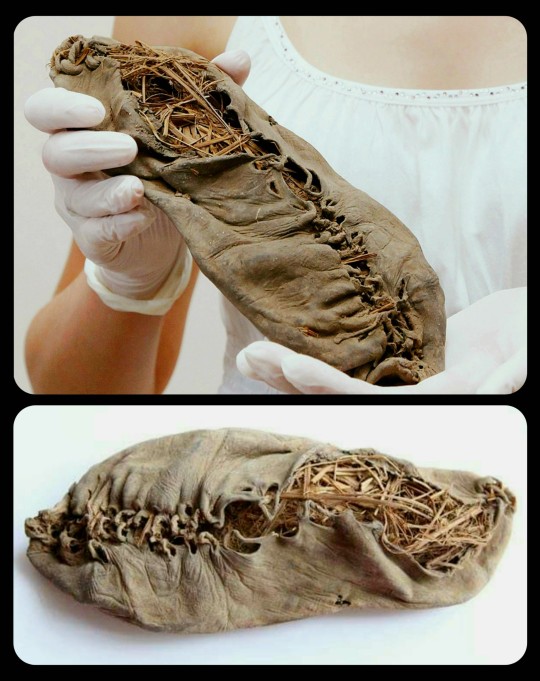
The shoe was found within a cave in the Vayots Dzor province of Armenia, where it had been preserved beneath a layer of sheep dung for more than five millennia.
From the BBC:
At 5,500 years old, the well preserved cow-hide shoe pre-dates Stonehenge by 400 years and the Pyramids of Giza by 1,000 years.
It was made of a single piece of leather and was shaped to fit the wearer's foot, researchers say.
The shoe contained grass, although the archaeologists are uncertain as to whether this was to keep the foot warm or to maintain the shape of the footwear.
Archaeologists put the shoe's remarkable preservation down to the stable, cool and dry conditions in the cave, and the fact that the floor of the cave was covered by a thick layer of sheep dung. This layer of excrement acted as a solid seal, preserving it over the millennia.
According to researchers, the shoe was deliberately buried in a clay-lined pit located within the cave system, though it's unclear why it was originally buried there. The evidence suggests that the shoe was more than just a ritual object -- an imprint of the wearer's big toe is still visible in the leather, and there is a significant amount of wear along the heel and ball of the foot.
This is the oldest leather shoe that has ever been discovered, but older shoes made of plant fiber have been found at sites in Missouri and Oregon. The oldest shoes ever discovered come from Oregon's Fort Rock Cave, where archaeologists unearthed dozens of sandals dating back to about 10,000 years ago.

Sandals from Fort Rock Cave, Oregon
Sources & More Info:
National Geographic: World's Oldest Leather Shoe Found--Stunningly Preserved
BBC: 'Oldest Leather Shoe' Discovered
The Bulletin: Viral Story about World's Oldest Shoes Failed to Mention Ancient Fort Rock Footwear
Oregon Encyclopedia: Fort Rock Sandals
#archaeology#history#artifact#anthropology#prehistoric#fashion#leather shoe#armenia#prehistoric clothing#preservation#crafting#leather work#ancient history#fort rock cave#oregon#prehistoric footwear#sandals#native american history#world's oldest shoes
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Oriental Blue Clearwing Moth: these moths were regarded as a "lost species" for more than 130 years, until they were finally sighted again in 2013
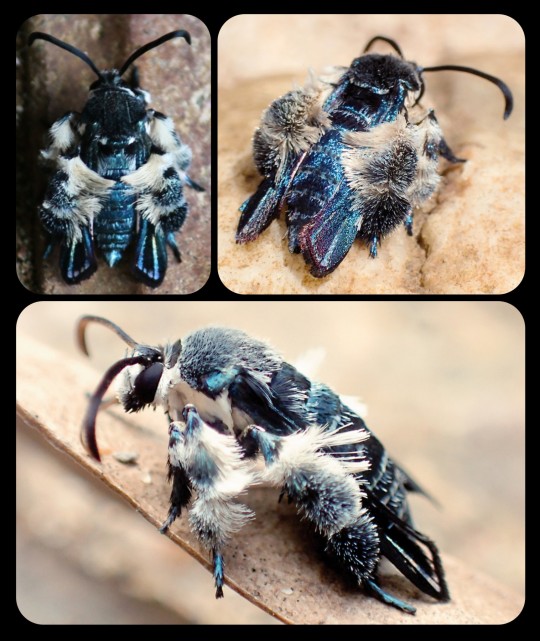

For more than 130 years, the Oriental blue clearwing moth (Heterosphecia tawonoides) was known only from a single, badly damaged specimen that was collected in Sumatra in 1887. There were no recorded sightings of this species again until 2013, when entomologist Dr. Marta Skowron Volponi unexpectedly found the moths feeding on salt deposits that had accumulated along the riverbanks in Malaysia's lowland rainforest.
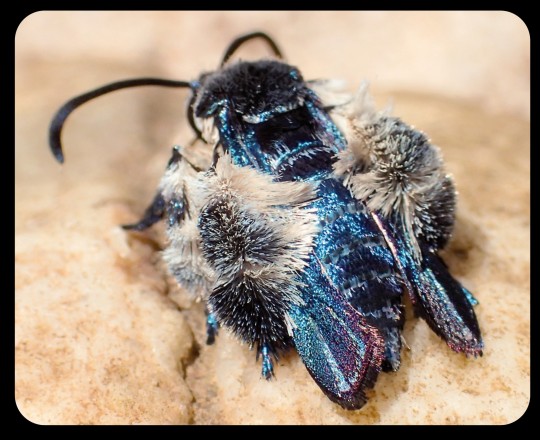

These moths were observed by researchers again in 2016 and 2017, and research indicates that the moths are actually bee-mimics, as they mimic the appearance, sound, behavior, and flight patterns of local bees. Their fuzzy, bright blue appearance might seem a little out of place for a bee-mimic, but those features do appear in several different bee species throughout Southeast Asia.
When the moths are in flight, they bear a particularly strong resemblance to the bees of the genus Thyreus (i.e. cuckoo bees, otherwise known as cloak-and-dagger bees), several of which are also bright blue, with banded markings, dark blue wings, fuzzy legs, and smooth, rounded antennae. The physical resemblance is compounded by the acoustic and behavioral mimicry that occurs when the moths are in flight.
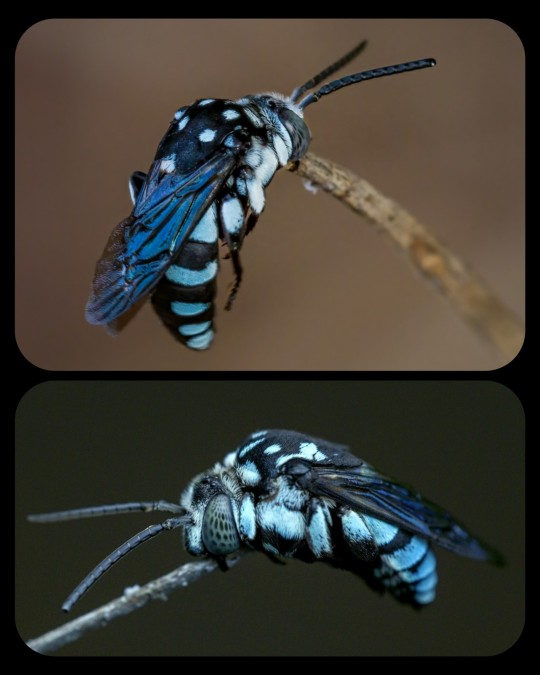

Cloak-and-Dagger Bees: the image at the top shows an Indo-Malayan cloak-and-dagger bee (Thyreus novaehollandiae) in a sleeping position, holding itself upright with its mandibles clamped onto a twig, while the image at the bottom shows a Himalayan cloak-and-dagger bee (T. himalayensis) resting in the same position
The moths also engage in "mud-puddling" among the various bees that congregate along the riverbanks; mud-puddling is the process whereby an insect (usually a bee or a butterfly) draws nutrients from the fluids found in puddles, wet sand, decaying plant matter, carrion, animal waste, sweat, tears, and/or blood. According to researchers, the Oriental blue clearwing moth was the only lepidopteran that was seen mud-puddling among the local bees.
Dr. Skowron Volponi commented on the unusual appearance and behavior of these moths:
You think about moths and you envision a grey, hairy insect that is attracted to light. But this species is dramatically different—it is beautiful, shiny blue in sunlight and it comes out during the day; and it is a master of disguise, mimicking bees on multiple levels and even hanging out with them. The Oriental blue clearwing is just two centimeters in size, but there are so many fascinating things about them and so much more we hope to learn.
This species is still incredibly vulnerable, as it faces threats like deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The president of Global Wildlife Conservation, which is an organization that seeks to rediscover "lost species," added:
After learning about this incredible rediscovery, we hope that tourists visiting Taman Negara National Park and picnicking on the riverbanks—the home of these beautiful clearwing moths—will remember to tread lightly and to take their trash out of the park with them. We also recommend that Americans learn about palm oil production, which is one of the primary causes of deforestation in Malaysia.
Sources & More Info:
Phys.org: Bee-Mimicking Clearwing Moth Buzzes Back to Life After 130 Years
Mongabay News: Moth Rediscovered in Malaysia Mimics Appearance and Behavior of Bees to Escape Predators
Journal of Tropical Conservation Science: Lost Species of Bee-Mimicking Clearwing Moth, H. tawonoides, Rediscovered in Peninsular Malaysia's Primary Rainforest
Frontiers in Zoology: Southeast Asian Clearwing Moths Buzz like their Model Bees
Royal Society Publishing: Moving like a Model - mimicry of hymenopteran flight trajectories by clearwing moths of Southeast Asian rainforests
Medium: Rediscovery in a Glint of Blue
re:wild.org: The "Search for Lost Species" Project
#lepidoptera#moths#heterosphecia tawonoides#oriental blue clearwing moth#entomology#insects#cute bugs#nature#animals#lost species#mimicry#evolution#bees#southeast asia#Malaysia#colorful moths#bee mimic#science
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Princely Tiger Moth: these strikingly colorful moths can be found in Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras
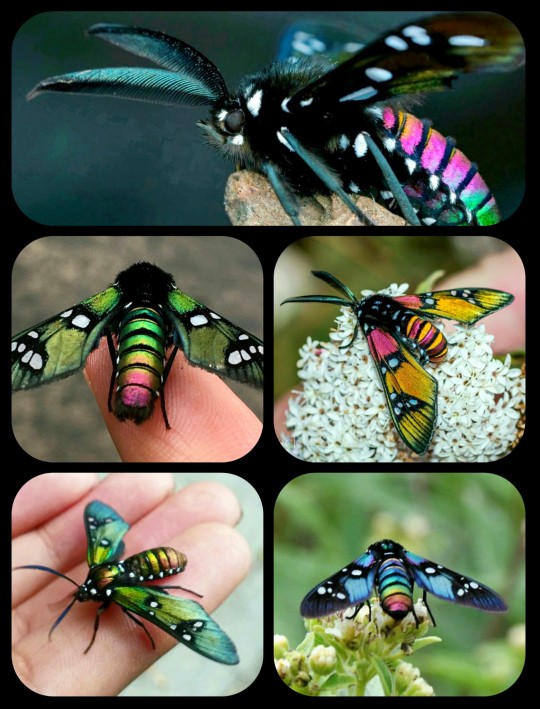

The princely tiger moth (Chrysocale principalis) has a unique, almost rainbow-like appearance, with iridescent/metallic scales that produce a broad range of colors across the wings, thorax, and abdomen. These colors can include shades of pink, gold, green, blue, and purple.

This species is particularly colorful, but aposomatic coloration in general is a trait that occurs in many different species of tiger moth; the moths often store toxic and/or unpalatable compounds within their own bodies as a way to discourage predators from eating them, and their brightly-colored markings then warn the predators to stay away.
Moths are often viewed as the boring, more plainly-colored version of butterflies, but they are much more diverse, more interesting, and more colorful than people generally realize -- as the princely tiger moth (and many other species) clearly demonstrates.
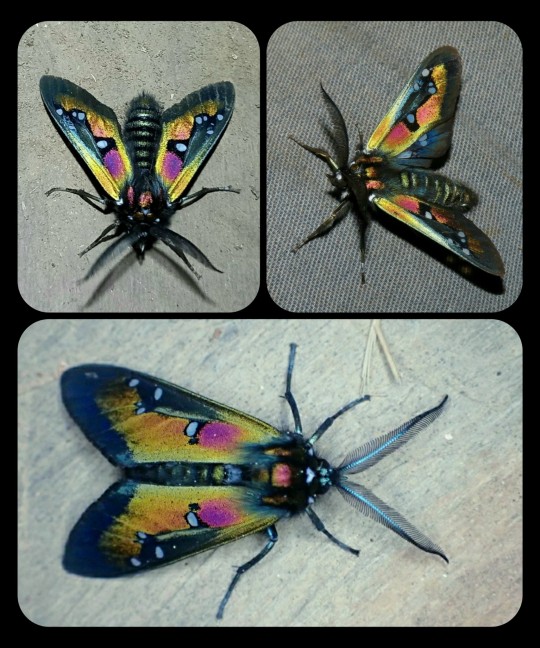

Chrysocale regalis: this species belongs to the same genus, and has a similarly colorful appearance

Chrysocale ignita: also known as the ignita wasp moth
Sources & More Info:
The Lives of Moths: Page 73
Texas Entomology: The Princely Tiger Moth
The Macrolepidoptera of the World: Chrysocale principalis
iNaturalist: photos of C. principalis, C. regalis, and C. ignita
#entomology#moths#lepidoptera#princely tiger moth#chrysocale principalis#chrysocale#colorful moths#animals#insects#central america#mexico#aposomatic coloration#colorful#wildlife#cute bugs#moths are amazing#and wildly underrated
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rare images of a leafcutter bee sharing its nest with a wolfspider:
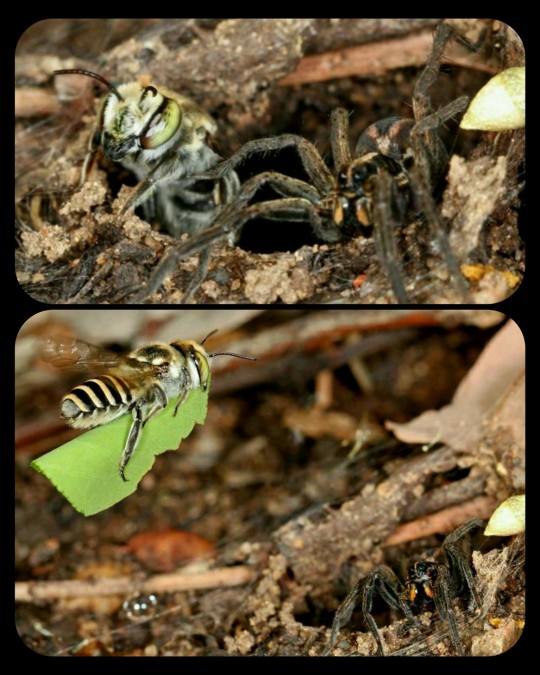

These photographs were taken in Queensland, Australia, by an amateur photographer named Laurence Sanders.
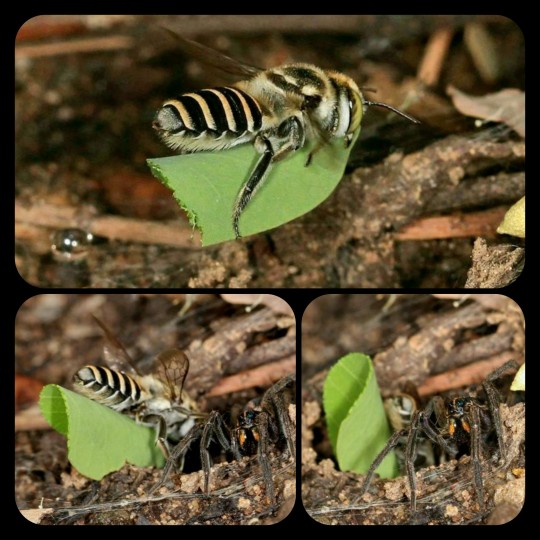

The leafcutter bee (Megachile macularis) can be seen fetching freshly-cut leaves, which she uses to line the inner walls of her nest. The wolfspider moves aside, allowing the bee to enter the nest, and then simply watches as the leaf is positioned along the inner wall.
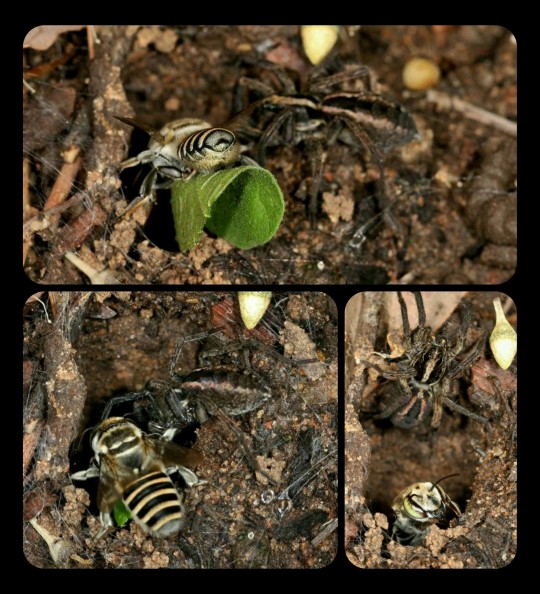

After inspecting the nest together, they return to their resting positions -- sitting side-by-side in the entryway to the nest.
The bee seems completely at ease in the presence of the wolfspider, which is normally a voracious predator, and the spider seems equally unfazed by the fact that it shares its burrow with an enormous bee.
This arrangement is completely unheard of, and the images are a fascinating sight to behold.
Sources & More Info:
Brisbane Times: The Odd Couple: keen eye spies bee and spider bedfellows in 'world-first'
iNaturalist: Megachile macularis
#entomology#arachnology#leafcutter bee#wolfspider#symbiosis#cool animals#cool bugs#bees#spiders#nature#cute#insects#arachnids#australia#props to the photographer#laurence sanders#this is a cute couple#but their babies would be terrifying
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient Necklace with Mosaic Glass Beads, from the Eastern Mediterranean, c.100 BCE-100 CE: this necklace is composed of 30 glass beads, most of which are decorated with stylized faces

From the John Paul Getty Museum:
The beads are made of multi-colored opaque glass and are decorated with heads and floral designs. The necklace is in good condition; some beads are chipped or cracked.

The exact origin of this piece is unknown, but it can be traced back to the Eastern Mediterranean, where it was likely made by a Greek or Roman artist.
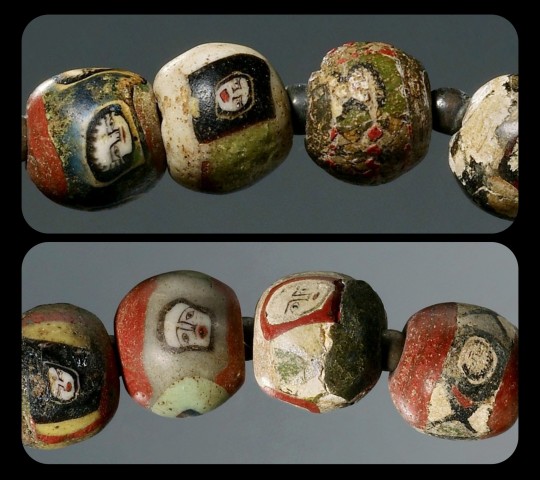

Each bead has a width of about 1.2cm (roughly half an inch); they're decorated with remarkably intricate details, and each face is depicted in its own unique style.

Sources & More Info:
John Paul Getty Museum: Necklace with Mosaic Glass Beads
#archaeology#artifact#history#ancient history#art#greek#roman#ancient art#antiquity#jewelry#beading#glass art#mosaic#crafting#greek art#roman art#eastern mediterranean#ancient#necklace#fashion#style#classical archaeology
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Moths in Disguise: these are all just harmless moths that have developed the ability to mimic wasps, bees, and/or hornets
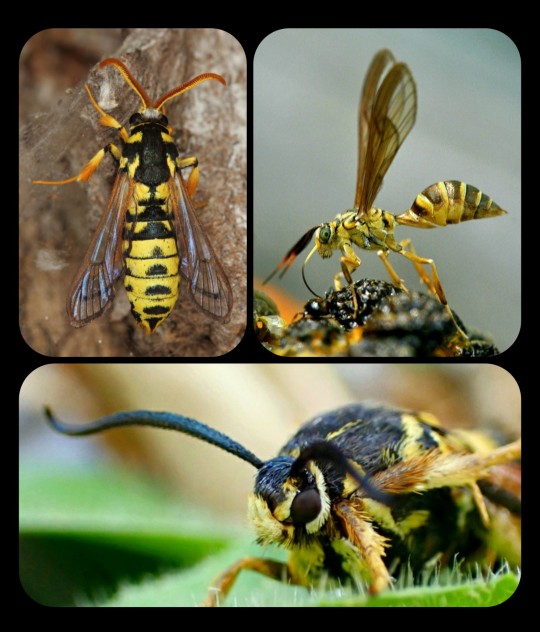

Top Row (left to right): Eusphecia pimplaeformis and Myrmecopsis polistes; Bottom Row: Pennisetia marginatum
Moths are exceptionally skilled when it comes to mimicry, and there are hundreds of moth species that rely on that tactic as a way to protect themselves from predators. Their disguises are numerous and varied, but hymenopteran mimicry is particularly common, especially among the moths that belong to subfamily Sesiidae and family Arctiinae.

Yellowjacket-Mimicking Moths: Pseudosphex sp. (top and bottom left) and Myrmecopsis polistes (bottom right)
Some of their disguises involve more than just a physical resemblance -- there are some moths that also engage in behavioral and/or acoustic mimicry, meaning that they can imitate the specific sounds and behaviors of their hymenopteran models. In some cases, these moths are so convincing that they can even fool the actual wasps/bees that they are mimicking.
Such a detailed and intricate disguise is unusual even among mimics, and researchers believe that it developed partly as a way to trick the wasps into treating the mimic like one of their own. Wasps tend to prey upon moths (and many other insects), but they are innately non-aggressive toward their own nest-mates, which are identified by sight -- so if the moth can convincingly impersonate its model, then it can avoid being eaten by predatory wasps.
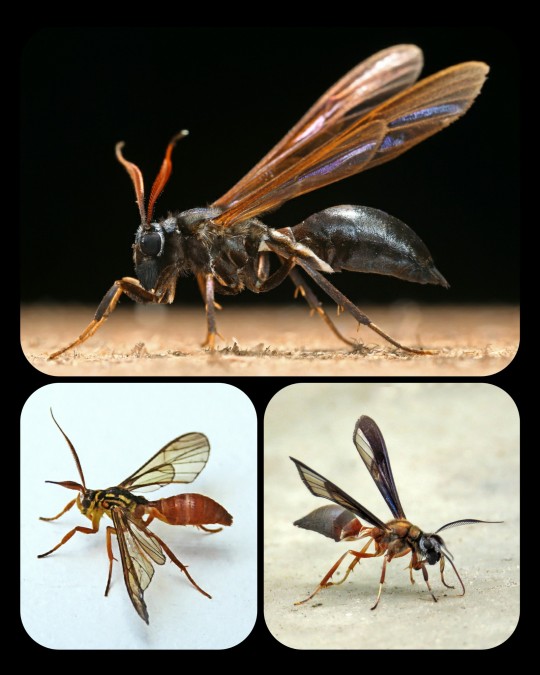

Wasp-Mimicking Moths: Pseudosphex ichneumonea (top), Myrmecopsis sp. (bottom left), and Pseudosphex sp. (bottom right)
There are many moths that can also mimic hornets, bumblebees, and carpenter bees.
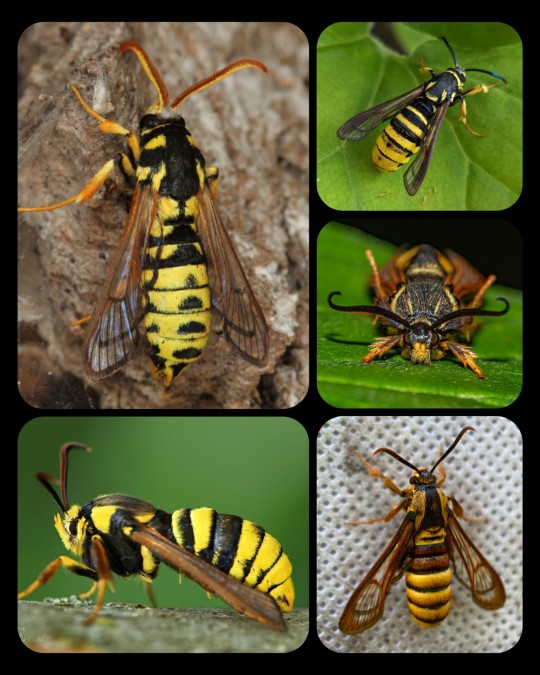

Hornet-Mimicking Moths: Eusphecia pimplaeformis (top left), Sesia apiformis (bottom left), Paranthrene simulans (top right), Pennisetia marginatum (middle right), and Sphecodoptera scribai (bottom left)

Bumblebee-Mimicking Moths: Hemaris tityus (top and bottom left) and Hemaris affinis (bottom right)
Moths are some of the most talented mimics in the natural world, as illustrated by their mastery of hymenopteran mimicry. But it's not just bees, hornets, and wasps -- there are many other forms of mimicry that can be found among moths, and the resemblance is often staggering.
Moths deserve far more credit than they receive, to be honest, because they are so incredibly interesting/diverse.
Sources & More Info:
Journal of Ecology and Evolution: A Hypothesis to Explain the Accuracy of Wasp Resemblances
Frontiers in Zoology: Southeast Asian clearwing moths buzz like their model bees
Royal Society Publishing: Moving like a model: mimicry of hymenopteran flight trajectories by clearwing moths of Southeast Asian rainforests
#lepidoptera#moths#Sesiidae#entomology#insects#animals#cool bugs#mimicry#nature#evolution#Arctiinae#bees#hymenoptera#hymenopteran mimic#wasp#bumblebee#acoustic mimicry#evolutionary arms race#I spend way too much time#reading about moths
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Namib Sand Geckos: these nocturnal geckos have biofluorescent markings that emit a bright, neon-green glow when exposed to the moonlight
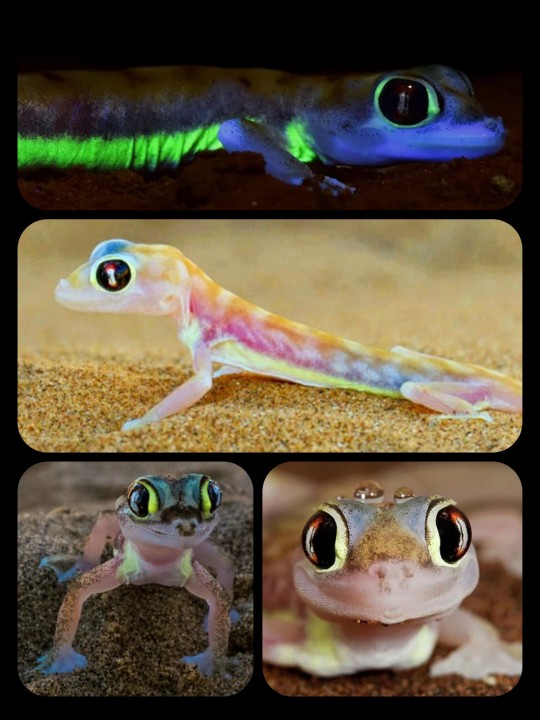

This species (Pachydactylus rangei) is found only in the Namib Desert, which stretches across Namibia, Angola, and South Africa; the geckos typically inhabit the arid, coastal region known as the Skeleton Coast.
In order to escape from the blistering heat of the desert, they use their webbed feet to burrow down into the sand during the day, and then emerge only at night, when the temperature has finally dropped. The webbing on their feet also enables them to run more easily across the dunes.
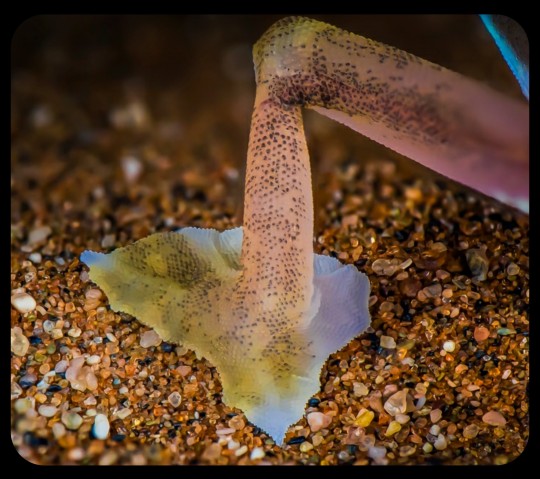

Namib sand geckos are covered in translucent scales, but they also have a strangely colorful appearance, as the colors/shades of their circulatory system, spinal column, internal organs, and optical membranes remain partially visible through the skin, producing various shades of pink, dark blue, purple, magenta, orange, and yellow.
They also have several distinctive markings running along their lower flank and encircling their eyes; these markings are known to fluoresce when exposed to UV light (including moonlight), emitting a bright, neon-green glow.
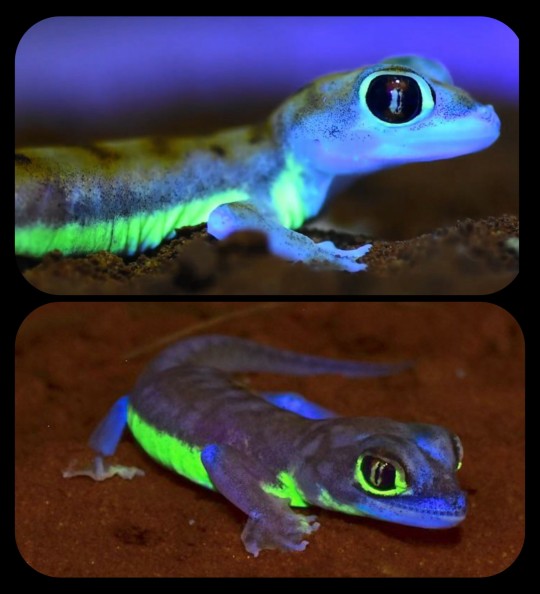

Some researchers have theorized that the biofluorescent markings may act as a signal to other geckos, allowing them to locate one another in the vast, desolate expanse of the desert, as this paper explains:
The fluorescent areas of P. rangei are concentrated around the eyes and along the lower flanks. This positioning is practically invisible to predators with a higher perspective (e.g. birds and jackals), but highly conspicuous from a gecko’s perspective. As P. rangei is sociable but generally solitary, and occurs at low population densities, such a signal might serve to locate conspecifics over greater distances ...
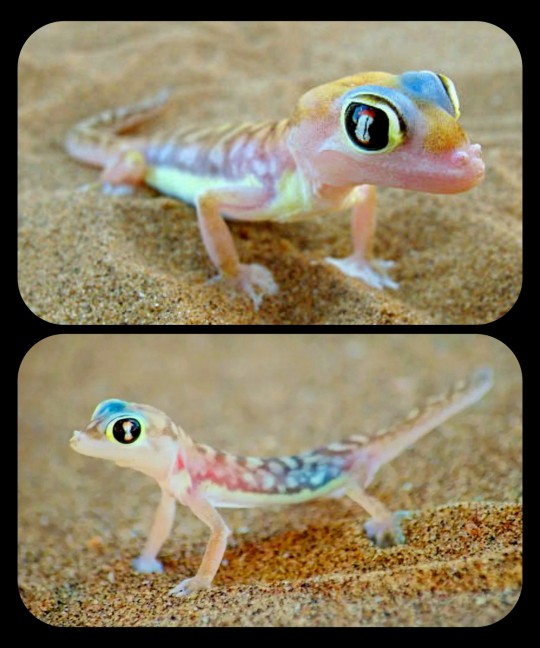

Encounters in P. rangei might serve purposes beyond mating opportunities: as the Namib desert has extremely low precipitation, fog is a key water source for its flora and fauna. Fog condenses on the bodies of the geckos, and they lick it from their faces. In husbandry, we have observed individuals licking water from conspecifics, taking advantage of a much greater available surface area.
Additionally, after short periods of isolation, the geckos run to meet each other. The combination of vital hydration with socialisation might reinforce signals that enable such meetings, and the cost of visibility to predators with higher vantage points, might constrain the signals to regions best visible from eye-level and below.
The Namib sand gecko is the only terrestrial vertebrate that is known to use an iridophore-based form of biofluorescence (you can find a more detailed explanation of that mechanism in the article mentioned above). The fluorescent dermal markings are also unique to this species.

Sources & More Info:
Scientific Reports: Neon-green fluorescence in the desert gecko Pachydactylus rangei caused by iridophores
Animal Diversity Web: Pachydactylus rangei
Dr. Mark D. Scherz's Blog: A Neon-Green Glowing Gecko!
Australian Geographic: Skeleton Coast - Namibia's strange desert dwellers
#herpetology#reptiles#gecko#Pachydactylus rangei#namib sand gecko#palmatogecko#namib desert#namibia#biofluorescence#animals that glow#lizards#cute animals#biology#nature#africa#squamata#web-footed gecko#cool animals#geckos#South Africa#Angola#Skeleton Coast#wildlife#not an arthropod#but still pretty cool
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
Figurine from Georgia (South Caucasus), c.300-200 BCE: this figurine was found buried in a pit beneath the ruins of an ancient temple; it was decorated with gold jewelry, wrapped in a burial shroud, and then placed in its own special "grave"
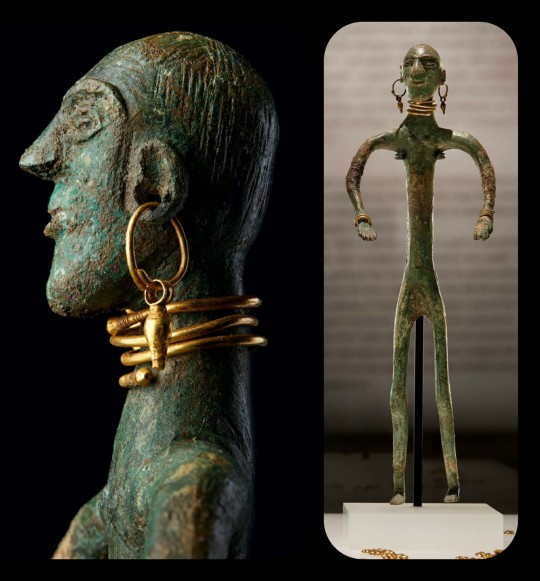

This is one of seven figurines that have been unearthed from similar burial pits throughout the city of Vani, which once served as the cultural, religious, and administrative center for the Kingdom of Colchis. Each figurine was crafted from bronze or iron, decorated with pieces of gold jewelry, wrapped in a special shroud, and then buried in a small "grave" that had been dug beneath (or near) one of the many temples that once stood throughout the city.
From The Golden Graves of Ancient Vani:
... other discoveries at Vani have shed light on Colchian culture. Most compelling are seven metal figurines, dating to 300–200 B.C., that have been discovered both in and near sacred structures at Vani. Adorned with gold jewelry and apparently wrapped in decorated garments, the figures were carefully buried in a way that seems to mimic the human burials at the site. Their precise function remains unclear, but they probably related to local religious and funerary customs.
And the Fitzwilliam Museum (which exhibited some of the artifacts from Vani back in 2008) adds:
Distinct local ritual practices are suggested during [the 3rd century BCE] as can bee seen from the four bronze and iron figurines displayed in the exhibition. These were discovered on the city’s upper terrace and were all buried in or near a sanctuary; this placement may well indicate a religious or funerary function for the figurines. The example illustrated here was placed between two terracotta tiles that were buried in a pit cut into the bedrock, thus mimicking contemporary human burials.
The figurine has a head with disproportionately large features, a low sloping brow, and an elongated torso with bowed arms and stiffly rendered legs. Most striking is its lavish gold jewellery, some of which reflects types worn by those buried at Vani. In addition to gold earrings, a torque (neck ring), and bracelets, five gold rosettes appear to have been strung around the figurine’s head and several pendants were found in its chest area.
The form and detail of their jewellery date the four figurines to the 3rd century BC. Their precise function, surely of local religious nature, still remains a subject of discussion. However, it is worth noting that the intriguing practice of burying such figurines in a ritualistic manner appears to be specific to Vani during its phase as a sanctuary city.
During antiquity, the Kingdom of Colchis covered the Western half of what is now the nation of Georgia, located in the South Caucasus. Colchis was famous for its talented goldsmiths, and it ultimately came to be known as the homeland of the fabled Golden Fleece -- the destination of Jason and the Argonauts, according to the Greek Argonautica.
Sources & More Info:
J. Paul Getty Museum: The Golden Graves of Ancient Vani
Fitzwilliam Museum: Ritual
Fitzwilliam Museum: From the Land of the Golden Fleece
Institute for the Study of the Ancient World: Wine, Worship, and Sacrifice
Journal of Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies: Vani: An Ancient City of Colchis (PDF download)
#archaeology#history#artifact#ancient history#art#vani#colchis#kolkheti#sakartvelo#georgia#caucasus#ritual artifact#religion#mythology#anthropology#ancient greece#crafting#sculpture#paganism#ancient ruins#ancient temple
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
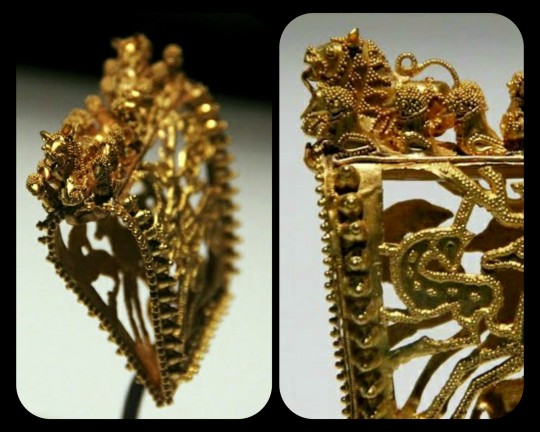
Gold Headdress Ornament from Ancient Colchis (Georgia/South Caucasus) c. 350-300 BCE: this is a stunning example of Colchian goldsmithing, and it reflects a blend of cultural influences from both Europe and Asia

Ancient Colchis was located in what is now the nation of Georgia, nestled in the South Caucasus (modern-day Georgia can be seen on this map). It stood right on the boundary between the Eastern and Western worlds, with Europe on one side and Asia on the other; as a result, there are many Colchian (and Georgian) artifacts that combine the different styles and techniques of cultures from throughout Eastern Europe, the Mediterranean, the Middle East, and Central Eurasia.
From the Wine, Worship, and Sacrifice exhibition at NYU:
In technique and form, the piece is firmly rooted in local Colchian production. What makes the piece so fascinating, however, is its wide array of cultural influences.
Framed on three sides by rounded studs, the central area features a stylized stag and three smaller deer set around it––a motif also present in the gold work of the nomadic Scythians in the northwest. The piece’s openwork design recalls objects produced in Luristan in the southeast. Along the folded upper edge is a pair of outward-facing lions that, in composition, seem loosely related to Assyrian door guardians. Between them are three birds, a motif that occurs throughout ancient cultures, but which is particularly present in the goldwork at Vani.
The Colchians were also renowned for their talent as goldsmiths, and Colchis itself was famous as the place where Jason and the Argonauts were said to have acquired the Golden Fleece (according to the Greek Argonautica).
There are many incredible pieces of goldwork that have been unearthed from Colchian sites, but this has always been one of my favorites.

Sources & More Info:
Institute for the Study of the Ancient World: Wine, Worship, and Sacrifice
J. Paul Getty Museum: Golden Graves of Ancient Vani
J. Paul Getty Museum: About Colchis and Vani
World History: Portion of a Colchian Headdress
#archaeology#artifact#history#ancient history#colchis#georgia#caucasus#vani#goldsmithing#art#ancient greece#mythology#greek mythology#jason and the argonauts#golden fleece#sakartvelo#kolkheti#gold#crafting#scythian#stag#ancient art#jewelry#goldwork
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bronze Age Libation Vessel from Crete, c. 1600-1450 BCE: the body of this 3,600-year-old vessel was carved from a single block of rock crystal
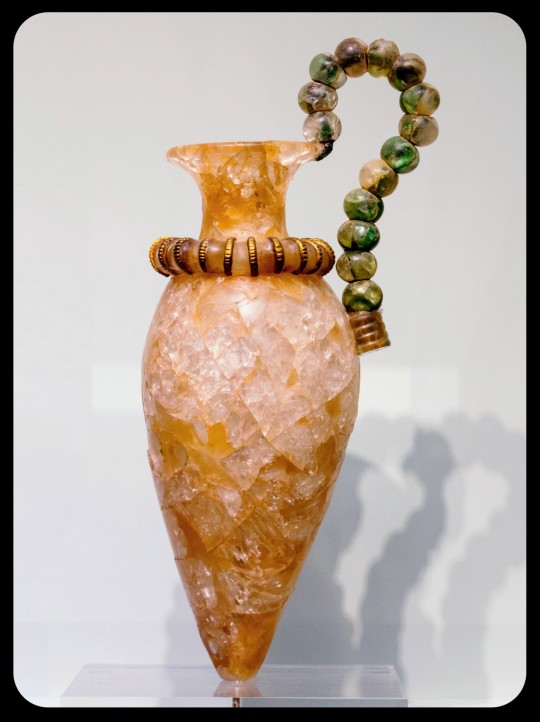

The collar of this libation vessel is decorated with discs of gilded ivory, while the handle is formed by a length of bronze wire and fourteen beads made of rock crystal. The vessel itself is about 16.5cm tall (roughly 6.5 inches) when measured from the base up to the rim.
Libation vessels such as this were widely used to pour ritual offerings, such as wine (or other alcoholic substances), water, honey, olive oil, milk, or grain, usually in honor of a deity or in remembrance of the dead. These ritual vessels are also known as rhyta (or the singular rhyton). They were especially common among ancient cultures, but have also been used by many other peoples throughout history, and similar libation vessels are still used within certain religious/cultural traditions today.
This particular vessel was crafted and used by the Minoans -- a Bronze Age civilization that once flourished on the island of Crete. It was unearthed from the ruins of the Central Palace of Zakros.
According to The Heraklion Archaeological Museum:
This small libation vessel, a true masterpiece of Minoan art, is one of the most valuable ritual vessels of the Central Sanctuary of Zakros. The body and neck are made separately. The body of the rhyton is carved from a particularly large block of rock crystal. The vase was found shattered into hundreds of tiny pieces, which were restored with marvellous skill by the conservators of the Heraklion Archaeological Museum. The collar around the join between neck and body is decorated with gilded ivory discs. The tall, curved handle is formed of fourteen crystal beads threaded on bronze wire and was found almost intact during the excavation, with the beads still in place.
The skill of the Minoan craftsman is evident not only from the decorative details of the rhyton but also from the fact that he was able to create such a fine-walled vessel without cracking the particularly hard raw material. The aesthetic perfection of the rhyton is as impressive as the technical skill required to produce it. Its symbolic value as a ritual vessel is heightened by the precious ivory and the metals, all of which were imported to Crete from distant parts of the East Mediterranean.
Sources & More Info:
Heraklion Archaeological Museum: Rock Crystal Libation Vessel/Rhyton
World History Encyclopedia: Minoan Rock-Crystal Vase
Minoan Crete: Zakros
#archaeology#history#artifact#ancient history#art#bronze age#minoan#crete#greece#europe#rhyton#ritual artifact#religious art#ancient religion#rock crystal#ancient art#crafting#crystals#stonework#ritual
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
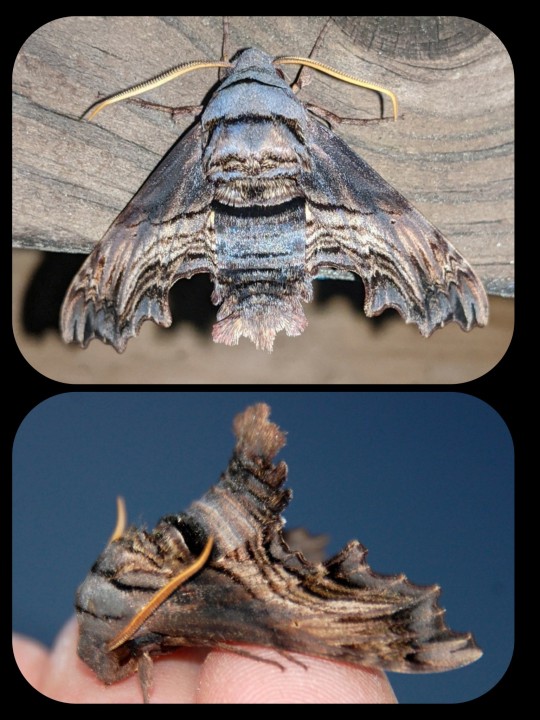
Abbott's Sphinx Moth: this caterpillar has a false eye on its rump; it mimics the features of a vertebrate's eye, and even includes a white reflection spot

The formal name for this species is Sphecodina abbottii.
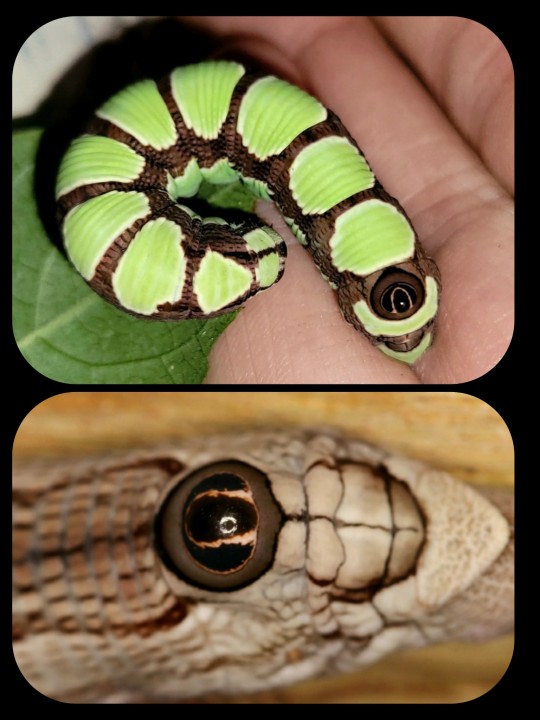

From Minnesota Seasons:
The caterpillar is up to 3″ (7.5 cm) long. Middle stage (instar) caterpillars are whitish to bluish-green. In place of the horn found on other sphinx caterpillars, there is a raised orange knob on the eighth abdominal segment (A8). Final instar caterpillars come in two color forms. The brown color form has longitudinal streaks of light and dark brown mimicking the color of a woody vine. The green form has on each abdominal segment a large, pale green, saddle-shaped spot on the upper side and a similar smaller spot on each side. The pattern is said to mimic a bunch of unripe grapes. Both forms have a black, raised, eye-like knob on A8 complete with a small white spot mimicking reflected light.
When the caterpillar is pinched or poked, it often squeaks and bites at the attacker.
The fully-developed moth also has a unique appearance -- it has an ash-grey/blue coloration with streaks of pink and black.

Sources & More Info:
Encyclopedia of Life: Sphecodina abbottii
Insect Identification: Abbott's Sphinx Moth
University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee: Saukeville Field Station
Minnesota Seasons: Abbott's Sphinx Moth
University of Minnesota Garden Extension: Abbott's Sphinx
#lepidoptera#cute bugs#moths#nature#mimicry#caterpillar#sphecodina#sphingidae#animals#insects#cool bugs#arthropods#sphinx moth#abbott's sphinx
222 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vida's Sheep Jumping Spider: researchers believe that these tiny spiders developed their "woolly" appearance as a way to mimic lacewing larvae or scale insects

The scientific name for this species is Oviballus vidae, but it has also been referred to as the "sheepy jumping spider" or "Vida's jumping spider." It was discovered in 2015, and first described (in a formal context) back in 2020.

As this article (PDF) describes:
Recently, two new salticids, R. legitima and Oviballus vidae were described from South Africa, and suggested to be mimics of either scale insects (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) or lacewing larvae (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae), due to their white colouration and the presence of peculiar tufts of white setae on the body.

The possibility of [scale insects] being the model is supported by Oviballus vidae being regularly collected from plants with woolly scales, although the movements of O. vidae quite closely resemble those of chrysopid larvae.
In fact, a fourth species of possible scale mimic, a new Rhene species, was recently discovered in a collection of salticids
from southern Mozambique, indicating that this phenomenon may be more widespread than has previously been known or even suspected.
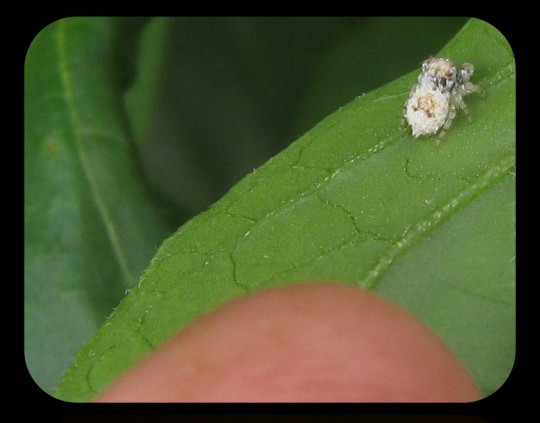

O. vidae was named after Vida van der Walt, the photographer who captured some of the first images of these spiders back in 2015, just after the species was discovered by Dr. Galina Azarkina. Vida van der Walt also took the photographs that appear in this post.
Sources & More Info:
Arthropoda Selecta (scientific journal): Rediscovery and Redescription of Rhene cooperi, another possible mimic of scale insects (PDF)
Spider Club of South Africa: Two New Species Named After SA Photographer (PDF, with the relevant info on page 5)
Field Guide to the Spiders of South Africa: Section on Vida's Sheep Jumping Spider
#arachnology#jumping spider#oviballus vidae#mimicry#cute bugs#animal facts#lacewing larvae#scale insects#south africa#wildlife#cute spider#sheep jumping spider#arthropods#cw spiders#but it's a really fluffy spider
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Skeletorus Spider: this species of jumping spider was named for its distinctive skeleton-like pattern
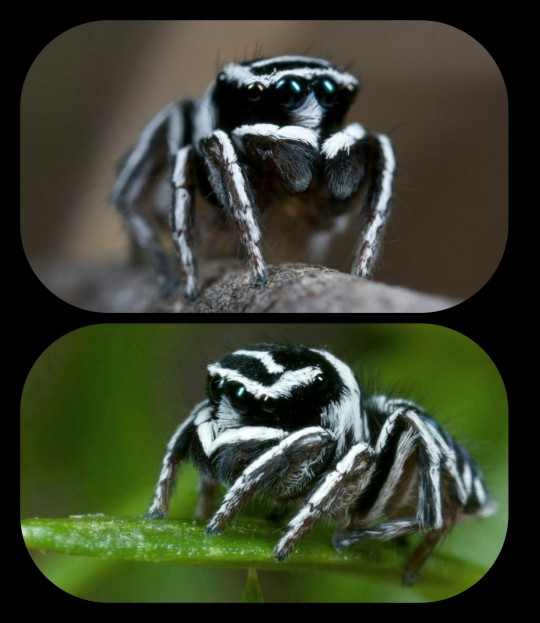

The scientific name for this species is Maratus sceletus; it's a type of peacock spider that has been found only in the southeast region of Queensland, Australia.
The species was discovered by a grad student named Madeline Girard back in 2015. For obvious reasons, she decided to give it the colloquial name "skeletorus."

The black-and-white appearance is very unusual, as male peacock spiders are generally known for their colorful/flamboyant features.
According to Dr. Jürgen Otto, who co-authored the article in which this species was first described:
[Skeletorus] looks dramatically different from all other peacock spiders known to date, making me think that this group is perhaps much more diverse than we had thought.
Peacock spiders are also famous for their charming and elaborate courtship dances, which often differ slightly from one species to the next. You can watch footage of the mating dance for this particular species here.

Sources & More Info:
Sci News: Two New Species of Peacock Spiders Discovered in Australia
Peckhamia Scientific Journal: Two New Peacock Spiders of the Calcitrans Group from Southern Queensland (PDF)
National Geographic: Behold Sparklemuffin and Skeletorus, New Peacock Spiders
Animal Diversity Web: Genus Maratus
#arachnology#jumping spider#cute bugs#skeletorus spider#maratus#sceletus#peacock spider#australia#queensland#wildlife#courtship dance#cw spiders#spooky#biodiversity#animals#arthropods
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Lion of Mari, from Syria (Mesopotamia) c.1782-1759 BCE: this is one of two lion statues that once guarded the entrance to a temple in ancient Mari; the lions were partially crushed when Hammurabi laid waste to the city in 1759 BCE
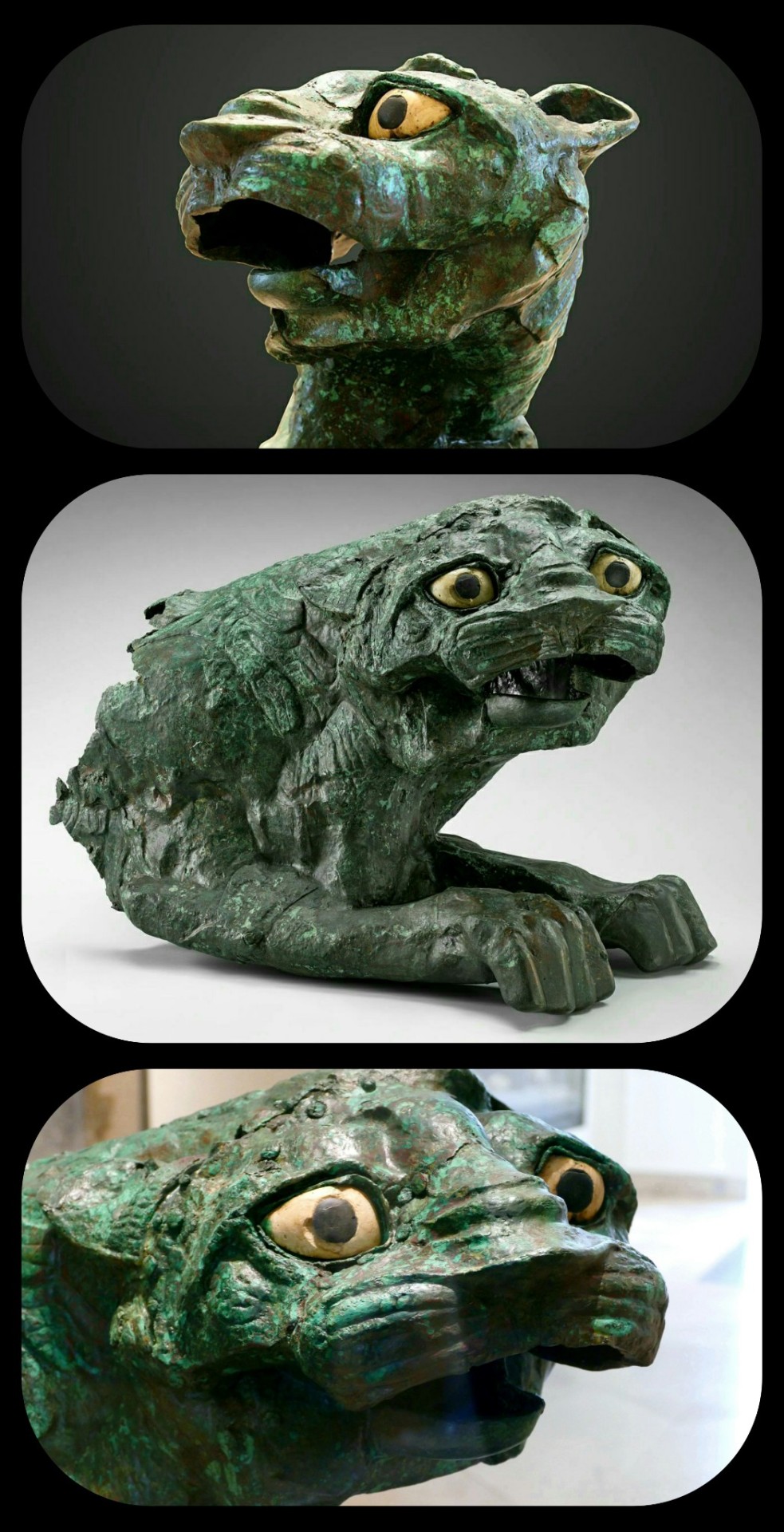

That's a pretty fitting expression, given the circumstances
Together, the two lion statues that were found at the ruined temple are known as the "Lions of Mari." They were unearthed from the ruins at Tell Hariri, where the ancient city-state of Mari once stood; this site is located near the border between modern-day Syria and Iraq.
The lions were likely designed as protomes, given their lack of hindquarters. They were originally stationed on either side of the entrance to the temple, so they are often described as the "temple guardians."

This is the same statue that appears in the first three photos, just seen from a different angle
It's believed that the temple at this site was originally built in honor of a West Semitic deity known as Dagan. Dagan was the chief deity of the Mariote pantheon; he was a particularly prominent figure in the middle and upper regions of the Euphrates, with cult centers in Mari, Terqa, Tuttul, and Ebla, but he was known throughout many parts of the ancient Near East.

The lion is primarily made of copper, with limestone and shale inlay for the eyes, and it measures 53cm tall, 77.5cm long, and 43cm wide, weighing roughly 55kg (about 21in x 30.5in x 17in, with a weight of 121lbs)
The Lions of Mari were partially crushed when their temple was destroyed (along with the rest of Mari) by Hammurabi's forces in 1759 BCE, leaving the statues badly warped...which is why they look really upset.
It's hard to find high-quality photos of the second lion, but he does have a particularly distinctive appearance:

This second lion was most recently housed at the National Museum of Aleppo, in Syria, though its current location/status (in the aftermath of the Syrian Civil War) remains unclear.
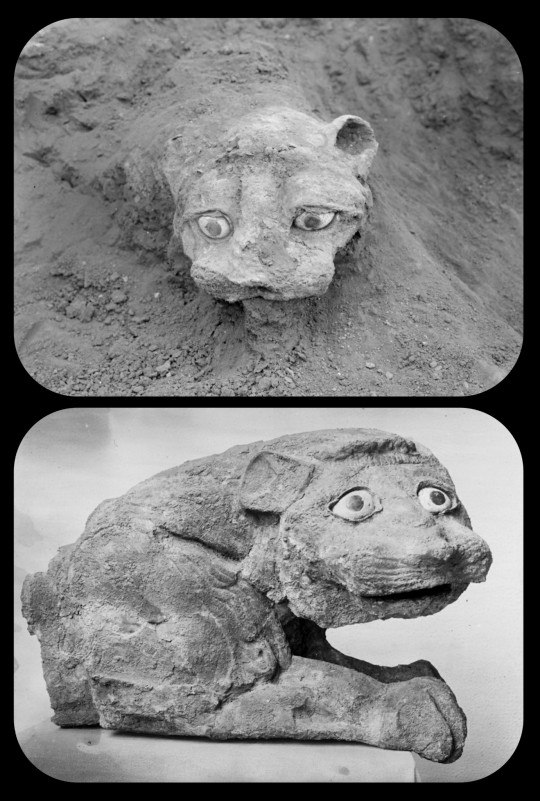

These photographs were taken during the original excavations at the ruined temple; they depict the first lion statue as it was still being unearthed (top) and the second statue shortly after it was removed (bottom)
Sources & More Info:
The Louvre: Lion of Mari
Archeologie.culture.fr: Lion Protome
Archeologie.culture.fr: Detailed Information about Ancient Mari
Virtual Museum Syria: Lion Sculpture
#archaeology#history#artifact#ancient history#art#mari#ancient temple#Syria#mesopotamia#Temple of the Lions#mesopotamian religion#ruins#hammurabi#Tell Hariri#middle east#lion#mesopotamian art#syrian archaeology#paganism#that first lion looks exactly like the way I feel
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
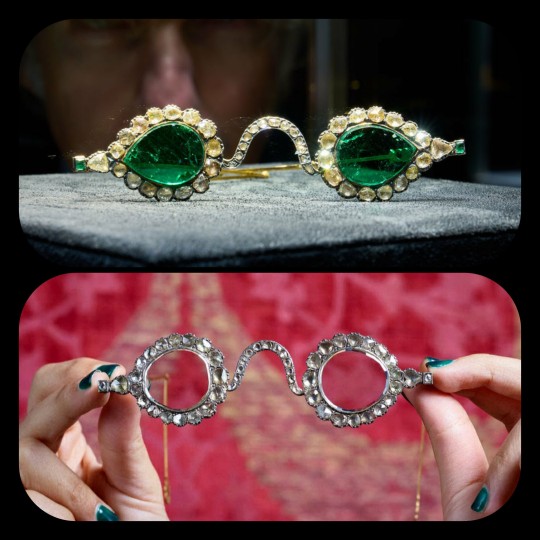
Emerald Spectacles from India, c. 1620-1660 CE: the lenses of these spectacles were cut from a single 300-carat emerald, and it was believed that they possessed mystical properties
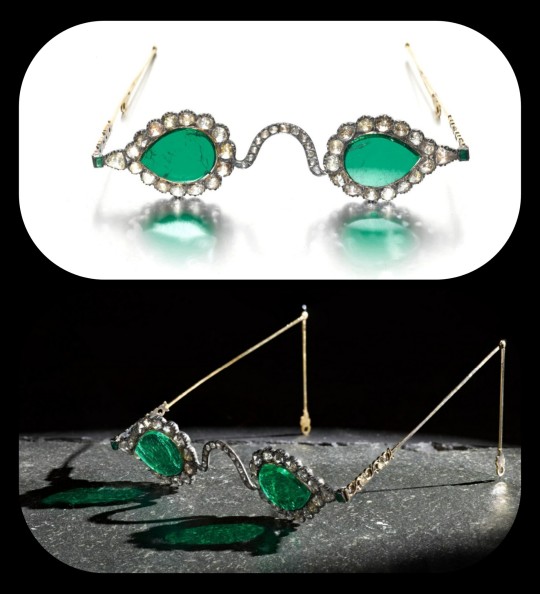

These eyeglasses are also known by the name "Astaneh-e ferdaws," meaning "Gate of Paradise," based on the perception of the color green as a symbol for spiritual salvation/Paradise. This was a common belief in Mughal-era India, where the spectacles were made.

The lenses were crafted from two thin slices of the same emerald. Together, the lenses have a combined weight of about 27 carats, but given the precision, size, and shape of each lens, experts believe that the original emerald likely weighed in excess of 300 carats (more than sixty grams) before it was cleaved down in order to produce the lenses. The emerald was sourced from a mine in Muzo, Colombia, and it was then transported across the Atlantic by Spanish or Portuguese merchants.
Each lens is encircled by a series of rose-cut diamonds, which run along an ornate frame made of gold and silver. The diamond-studded frame was added in the 1890s, when the original prince-nez design was fitted with more modern frames.
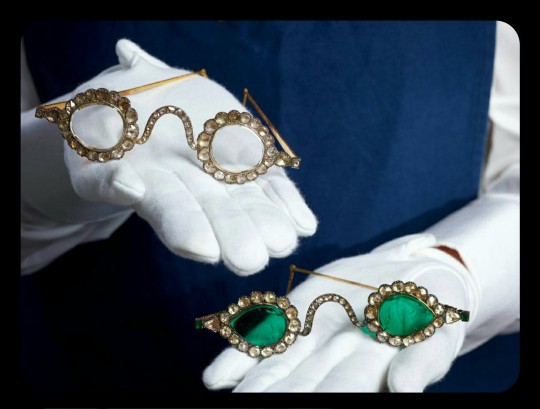

The emerald eyeglasses have long been paired with a second set of spectacles, and they were almost certainly commissioned by the same patron. This second pair is known as Halqeh-e nur, or the "Halo of Light."
The Halo of Light features lenses that were made from slices of diamond. The diamond lenses were cleaved from a single stone, just like the emerald lenses, with the diamond itself being sourced from a mine in Southern India. It's estimated that the original, uncut diamond would have weighed about 200-300 carats, which would make it one of the largest uncut diamonds ever found.
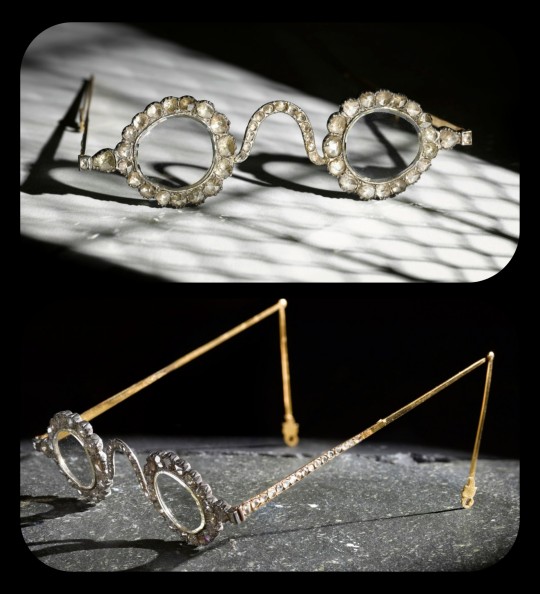

These lenses are so clear and so smoothly cut that it sometimes looks like they're not even there
Both sets of spectacles date back to the mid-1600s, and it's generally believed that they were commissioned by a Mughal emperor or prince. The identity of that person is still a bit of a mystery, but it has been widely speculated that the patron was Shah Jahan -- the Mughal ruler who famously commissioned the Taj Mahal after the death of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal. Shah Jahan did rule as the Mughal emperor from about 1628 to 1658.
The emerald and diamond lenses may have been chosen for symbolic/cultural reasons, or they may have been chosen simply because they're pretty and extravagant; their meaning/purpose is unclear. Experts do believe that the eyeglasses were designed to be worn by someone, though.
It was believed that the spectacles had spiritual properties, like the ability to promote healing, ward off evil, impart wisdom, and bring the wearer closer to enlightenment. Those beliefs are often related to Indic and Islamic traditions, some of which ascribe spiritual and/or symbolic traits to emeralds and diamonds. Emeralds can be viewed as an emblem of Paradise, divine salvation, healing, cleansing, and eternal life; diamonds are similarly associated with enlightenment, wisdom, celestial light, and mysticism.

The Gate of Paradise and the Halo of Light were both kept in the collections of a wealthy Indian family until 1980, when they were sold to private collectors, before going on auction once again back in 2021. They were valued at about $2 million to $3.4 million per pair.
Sources & More Info:
Sotheby's: Mughal Spectacles
Architectural Digest of India: At Sotheby's auction, Mughal-era eyeglasses made of diamond and emerald create a stir
Only Natural Diamonds: Auspicious Sight & the Halqeh-e Nur Spectacles
The Royal Society Publishing: Cleaving the Halqeh-Ye Nur Diamonds
Gemological Institution of America: Two Antique Mughal Spectacles with Gemstone Lenses
Manuscript: From Satan's Crown to the Holy Grail: emeralds in myth, magic, and history
CNN: The $3.5 million Spectacles Said to Ward off Evil
BBC: Rare Mughal Era Spectacles to be Auctioned by Sotheby's
#history#archaeology#artifact#mughal#india#17th century#art#emerald#diamond#glasses#indian lore#islam#religion#mysticism#indian history#anthropology#spirituality#fashion
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Grote's Bertholdia Moth: when bats are detected nearby, these moths emit a rapid series of ultrasonic clicks that act as a "jammer," interfering with the bat's sonar signals so that the moth can avoid detection

The Grote's bertholdia moth (B. trigona) is capable of emitting about 4,500 ultrasonic "clicks" per second. While there are other types of moths that use ultrasonic signals (in various ways) to avoid being preyed upon by bats, none of them have a more rapid-fire pace than this species.
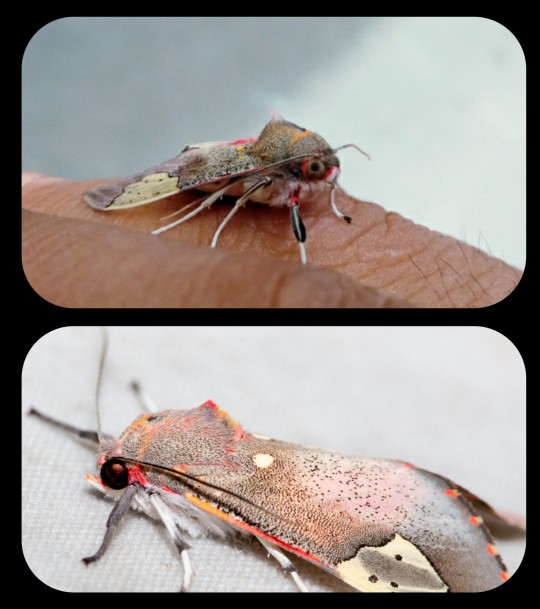

The barrage of signals provides the moth with a way to remain hidden, because it interferes with the echolocation that bats use to navigate and locate prey.
As this article from Smithsonian explains:
... when approached by the bats, the moths produced their own ultrasonic clicking sounds at a rate of 4,500 times per second, blanketing the surrounding environment and cloaking themselves from sonar detection.

This article also expands upon the use of ultrasonic signals among moths:
Like other nocturnal insects, moths need to contend with bats. Unlike grasshoppers or beetles, they have soft bodies without spines or hard cuticles to protect them. Yet bats’ reliance on echolocation has given moths a way to avoid ending up as food: by tapping into their predators’ acoustic signals. Many have evolved ears that can hear the calls of bats. Some moths make ultrasonic squeaks, chirps, or clicks to warn their predators (honestly or not) that they are poisonous. Others generate near-constant, ultrasonic buzzes capable of jamming bat sonar.
Sources & More Info:
Smithsonian Magazine: How One Moth Species Can Jam Bats' Sonar Systems
The Scientist: Many Moths Speak Up to Ward Off Bats
Science.org: Moths Block Bats' Sonar
PubMed: High Duty Cycle Moth Sounds Jam Bat Echolocation
Journal of Theoretical Biology: Neural Representation of Bat Predation Risk and Evasive Flight in Moths
#moth#lepidoptera#biology#grote's bertholdia#Bertholdia trigona#adaptation#evolutionary arms race#bats#nature#echolocation#cool bugs#tw insects#ultrasonic animals#arthropods#bugs#weird animals
152 notes
·
View notes