#Cypherpunk
Text
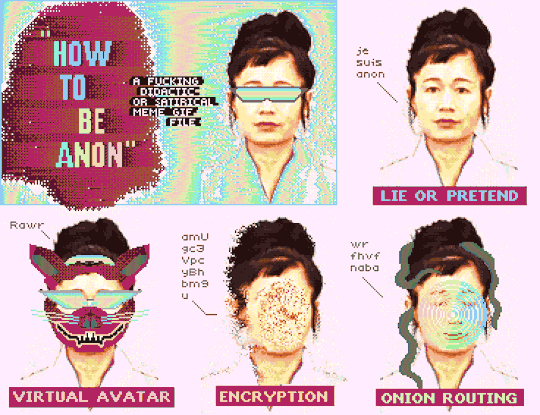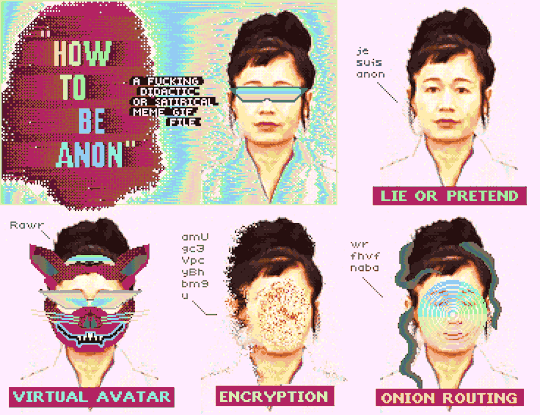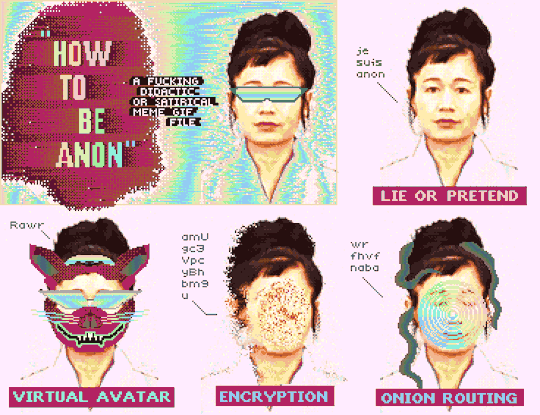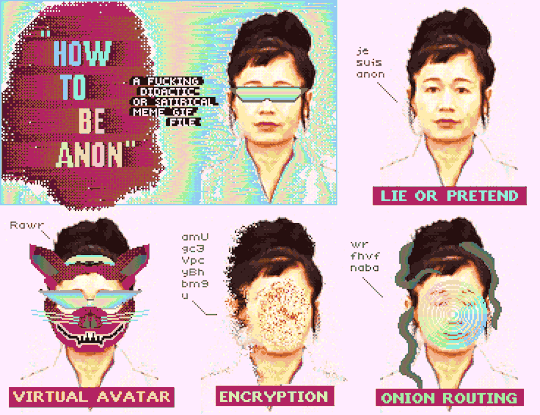
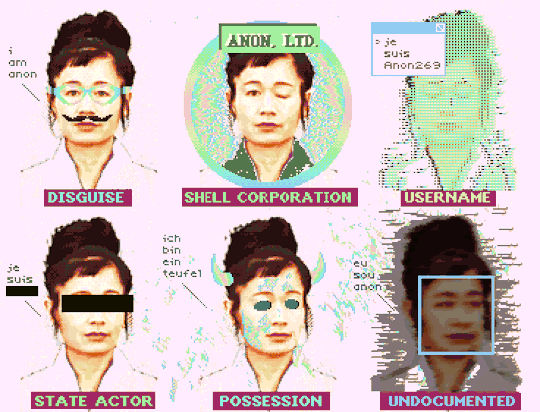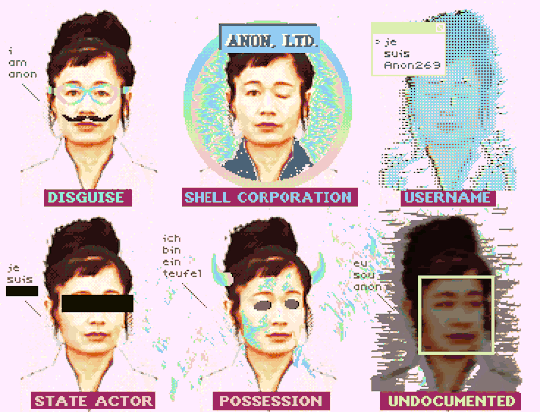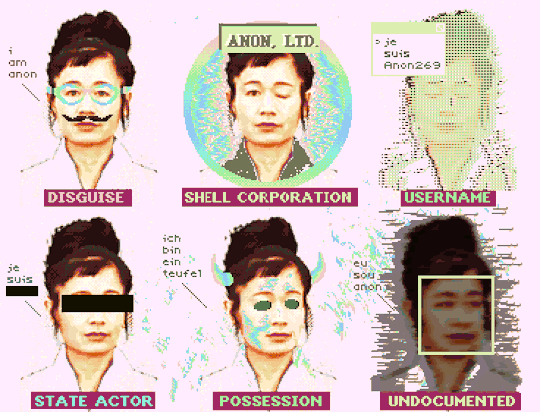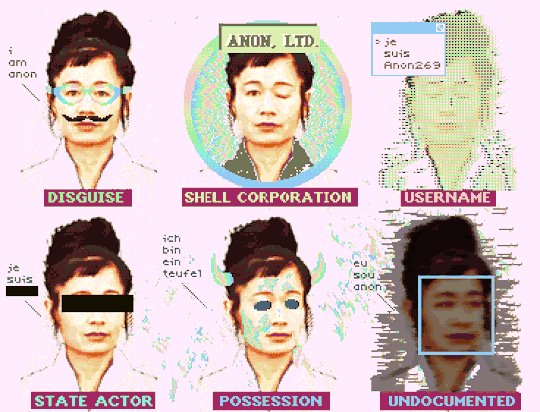

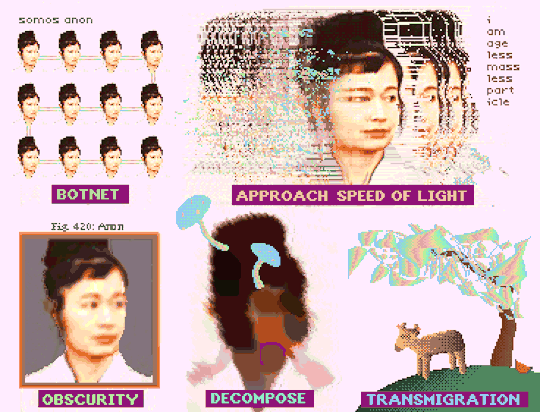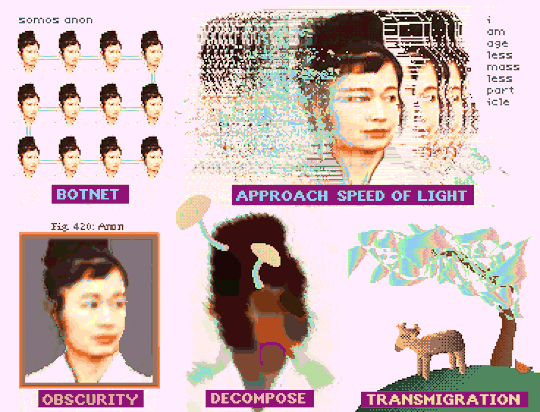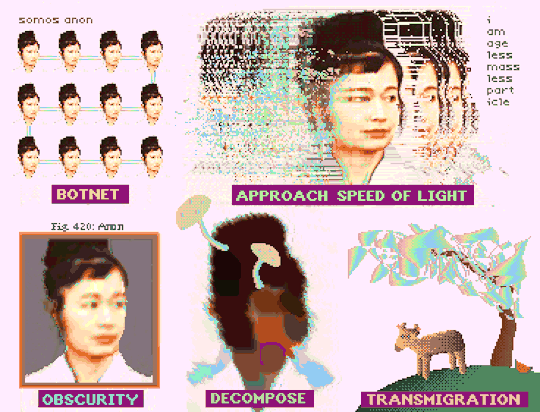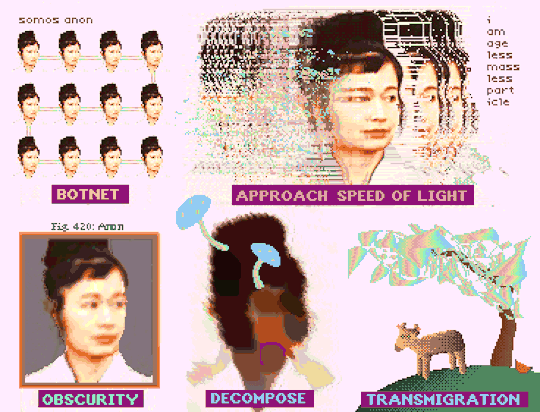
"How To Be Anon" (Deluxe Paint IV + Frames from Hito Steyerl's "How Not to Be Seen: A Fucking Didactic Educational .MOV File)
#art#glitch#hito steyerl#anon#pixel art#pixels#new media#aesthetic#post-internet#digital art#glitchcore#webcore#cypherpunk#how to
17K notes
·
View notes
Text





New chapter of Fisheye Placebo is out!
You can read the entire comic here Yuumeiart.com/fisheye-placebo
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

65 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is a Cypherpunk?
The term "cypherpunk" refers to a movement and a community of activists advocating for the widespread use of strong cryptography and privacy-enhancing technologies as a route to social and political change. Emerging in the late 1980s and early 1990s, the cypherpunk movement is a confluence of libertarian political philosophy, hacker ethos, and cryptographic science.
The Core Traits of Cypherpunks
1. Advocacy for Privacy and Anonymity: Cypherpunks champion the right to privacy, emphasizing that individuals should have control over their personal information and digital footprints. This advocacy is often in direct opposition to government surveillance and corporate data collection practices.
2. Use of Cryptography: The cornerstone of the cypherpunk movement is the use of strong cryptography to secure communications and transactions. Cypherpunks believe that through cryptographic techniques, individuals can protect their privacy in the digital world.
3. Open Source and Decentralization: A significant trait among cypherpunks is the belief in open-source software and decentralized systems. This ethos promotes transparency, security, and resistance to censorship and control by central authorities.
Who are the Cypherpunks?
The cypherpunk community consists of programmers, activists, academics, and technologists. Notable figures include Julian Assange, the founder of WikiLeaks; Jacob Appelbaum, a former spokesperson for the Tor Project; and Hal Finney, a pioneer in digital cash systems. The manifesto "A Cypherpunk's Manifesto" by Eric Hughes (1993) [https://www.activism.net/cypherpunk/manifesto.html] eloquently encapsulates the philosophy and ideals of this movement.
The Cypherpunk Movement
Cypherpunks are not a formal organization but rather a loosely associated group sharing common interests in cryptography and privacy. The movement's origins can be traced to the “Cypherpunks” mailing list, started in 1992 by Eric Hughes, Timothy C. May, and John Gilmore. This list served as a platform for discussing privacy, cryptography, and related political issues.
Relation to Cyberpunk Principles
While cypherpunks share some overlap with the cyberpunk genre of science fiction, they are distinct in their real-world activism. Cyberpunk literature, like William Gibson's "Neuromancer" (1984) [https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/6088006-neuromancer], often presents a dystopian future where technology is pervasive and oppressive. In contrast, cypherpunks aim to use technology, specifically cryptography, as a tool for empowerment and resistance against such dystopian futures.
Notable Contributions and Technologies
The cypherpunk movement has been instrumental in the development of technologies that emphasize privacy and security:
Tor (The Onion Router): A free and open-source software for enabling anonymous communication [https://www.torproject.org/].
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP): A data encryption and decryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication [https://www.openpgp.org/].
Bitcoin: The creation of Bitcoin by an individual or group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto was heavily influenced by the ideas of the cypherpunk movement. It embodies principles of decentralization and financial privacy [https://bitcoin.org/en/].
Wikileaks: Founded by Julian Assange, WikiLeaks is a multinational media organization that publishes news leaks and classified media provided by anonymous sources [https://wikileaks.org/].
Conclusion
The cypherpunk movement is a critical lens through which to view the ongoing dialogue about privacy, security, and freedom in the digital age. While not an organized group, the collective impact of cypherpunks on modern cryptography, internet privacy, and digital rights is profound. As digital technology continues to permeate every facet of our lives, the principles and contributions of the cypherpunk community remain more relevant than ever. - REV1.
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Philosophy Behind Bitcoin

Introduction
In the world of finance, few innovations have sparked as much intrigue and debate as Bitcoin. But beyond its role as a digital currency, Bitcoin embodies a profound philosophy that challenges traditional financial systems and proposes a new paradigm for economic freedom. Understanding the philosophy behind Bitcoin is essential to grasp its potential impact on our world.
The Origins of Bitcoin
In 2008, amid the global financial crisis, a mysterious figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper. This document outlined a revolutionary idea: a decentralized digital currency that operates without the need for a central authority. The financial turmoil of the time, characterized by bank failures and government bailouts, underscored the need for a system that could function independently of traditional financial institutions.
Core Philosophical Principles
Decentralization-Decentralization lies at the heart of Bitcoin’s philosophy. Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on centralized authorities such as banks and governments, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes). Each node maintains a copy of the blockchain, Bitcoin's public ledger, ensuring that no single entity has control over the entire network. This decentralization is crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of the system, as it prevents any one party from manipulating the currency or its underlying data.
Trustlessness-Bitcoin's trustless nature is another fundamental principle. In traditional financial systems, trust is placed in intermediaries like banks and payment processors to facilitate transactions. Bitcoin eliminates the need for these intermediaries by using blockchain technology, where transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography. This system ensures that transactions are secure and reliable without requiring trust in any third party.
Transparency-The transparency of Bitcoin’s blockchain is a key philosophical aspect. Every transaction that has ever occurred on the Bitcoin network is recorded on the blockchain, which is publicly accessible. This transparency allows anyone to verify transactions and ensures accountability. However, while the ledger is public, the identities of the individuals involved in transactions remain pseudonymous, balancing transparency with privacy.
Immutability-Immutability is the concept that once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This is achieved through cryptographic hashing and the decentralized nature of the network. Immutability ensures the integrity of the blockchain, making it a reliable and tamper-proof record of transactions. This principle is crucial for maintaining trust in the system, as it prevents fraudulent activities and data corruption.
Financial Sovereignty-Bitcoin empowers individuals by giving them full control over their own money. In traditional financial systems, access to funds can be restricted by banks or governments. Bitcoin, however, allows users to hold and transfer funds without relying on any central authority. This financial sovereignty is particularly valuable in regions with unstable economies or oppressive governments, where individuals may face restrictions on their financial freedom.
The Ideological Spectrum
Bitcoin’s philosophy is deeply rooted in libertarian values, emphasizing personal freedom and minimal government intervention. It also draws inspiration from the cypherpunk movement, a group of activists advocating for privacy-enhancing technologies to promote social and political change. These ideological influences shape Bitcoin's emphasis on decentralization, privacy, and individual empowerment.
Real-World Applications and Challenges
Bitcoin's philosophy extends beyond theory into practical applications. It is used for various purposes, from everyday transactions to a store of value akin to digital gold. However, this revolutionary system also faces challenges. Regulatory issues, scalability concerns, and environmental impact are some of the hurdles that need addressing to realize Bitcoin’s full potential.
Conclusion
The philosophy behind Bitcoin is a radical departure from traditional financial systems. Its principles of decentralization, trustlessness, transparency, immutability, and financial sovereignty offer a new vision for economic freedom and integrity. As Bitcoin continues to evolve, its underlying philosophy will play a crucial role in shaping its future and potentially transforming the global financial landscape.
Call to Action
Explore more about Bitcoin and consider its implications for your own financial freedom. Engage with the community, stay informed, and think critically about the role Bitcoin can play in our economic future. Let’s continue the journey of understanding and embracing the Bitcoin revolution together.
#Bitcoin#Cryptocurrency#FinancialFreedom#Decentralization#Blockchain#DigitalCurrency#CryptoPhilosophy#SatoshiNakamoto#Cypherpunk#FinancialSovereignty#BitcoinRevolution#CryptoCommunity#DigitalEconomy#TechInnovation#FutureOfFinance#EconomicFreedom#CryptoEducation#BitcoinPhilosophy#BlockchainTechnology#financial education#financial empowerment#financial experts#finance#unplugged financial#globaleconomy
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo

n-hp.png
#photography#photo manipulation#datamosh#cyberpunk#cypherpunk#devoidoflove#thallium art#dolcore#art#my art#design#crustpunk#crust punk#punk#stenchcore#lancer rpg#transgender#trans#nonhuman person#nhp#queer#unicode
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

9 notes
·
View notes
Photo

1993
https://archive.org/details/anarchy_Cypherpunk_Manifesto/mode/2up
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
La crittografia (1/6) - Alle origini dei Bitcoin: il mistero Satoshi - Guarda il documentario completo | ARTE in italiano
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bitcoin Man! He's Fighting for the future - Bitcoin man He's a digital warrior! The CoinHeads cypherpunk meme rock n roll
1 note
·
View note
Text
ETF e fine dell'anarchia delle criptovalute

Bitcoin, così la finanza tradizionale ha schiacciato il sogno anarchico. Uno spettro perseguita il mondo moderno, è lo spettro della cripto anarchia. Così Timoty C. May iniziava il suo “The Crypto Anarchist Manifest”. Un’idea andata via via scemando.
Uno spettro si aggira per il mondo moderno, è lo spettro della cripto anarchia». Così Timoty C. May, richiamandosi all’incipit del Manifesto del Partito Comunista di Karl Marx e Friedrich Engels, iniziava il suo “The Crypto Anarchist Manifest” scritto nel 1988 e diffuso nel 1994. Un documento il quale avrebbe influenzato i Cypherpunk e, di conseguenza, il mondo delle criptovalute. In primis, il Bitcoin.
Certo! I Cypherpunk – un gruppo che agli inizi degli anni ’90 in California ha elaborato molte tecniche ed impostazioni socio-economiche riprese dalla cripto regina – erano eterogenei. Come ha detto, Adam Back: una realtà articolata di attivisti, avvocati, crittografi con impostazioni (anche) politiche differenti.
Dai libertari di destra agli anarco-capitalisti fino agli anarchici con vocazione più solidarista. Ciò detto, però, è innegabile che un fil rouge fosse tra di loro riscontrabile: quello di essere, seppure con diverse sfumature, anti sistema.
Di volere, unitamente alla difesa della privacy tramite la crittografia, la realizzazione di meccanismi per le transazioni, e i pagamenti, che non richiedessero la presenza di un terzo garante.
Soprattutto se questo è rappresentato da entità quali il Governo o, ancora peggio, banche commerciali e altre istituzioni finanziarie tradizionali. Insomma: un “must” era (ed è) la disintermediazione.
Lo stesso Satoshi Nakamoto riprende il concetto nel sommario del suo white paper. «Una versione puramente peer-to-peer di denaro elettronico (...) senza passare tramite un’istituzione finanziaria».
È, per l’appunto, la disintermediazione, l’essere anti sistema che costituisce una delle caratteristiche di quella che (piaccia o non piaccia) è una geniale struttura socio-tecnologica.
Il cambiamento
Sennonché, qualcosa è profondamente mutato. La stessa approvazione, da parte della Security and exchange commision (Sec), dell’Etf sul prezzo spot del token di Nakamoto ne é la riprova.
Il prezzo della cryptocurrency, già risalito nei mesi precedenti anche in scia ai rumors sul possibile arrivo del nulla osta della Sec, è balzato ulteriormente dopo la pubblicazione della notizia. Più in generale il cripto mondo – ad eccezione forse dei massimalisti –ha festeggiato.

Già, ma festeggiato cosa? Il fatto che il mondo tradizionale della finanza, il sistema istituzionale ha uno strumento in più, e molto potente, per convogliare flussi di denaro sul bitcoin. In altre parole: quelle realtà tanto osteggiate diventano, se non dominus, almeno molto influenti rispetto al token.
Il quale, va sottolineato, non da ora è sempre più definito asset e sempre meno valuta digitale. Cioè: un titolo su cui investire e non attraverso cui effettuare transazioni. Vero! In alcuni Paesi, dove ad esempio sono forti le rimesse dei migranti, la caratteristica di moneta resiste e si espande.
Inoltre la natura di oro digitale, asset che consente la riserva di valore, è presente nello stesso progetto di Nakamoto. Ancora: la micro struttura della cripto regina, e il suo funzionamento, rimangono quelli.
L’appropriazione
Ciò detto, però, l’obiezione di fondo resta valida. La finanza tradizionale si va appropriando del Bitcoin. Una dinamica che, peraltro, era già visibile nel 2022. Durante la fase dello “sboom” l’investitore istituzionale era ben presente sul bitcoin.
Ebbene: questo operatore, non conoscendo o non seguendo i meccanismi peculiari del token, si è basato su quelli della finanza tradizionale. Lo ha assimilato ad un titolo ad alta crescita e, a fronte del rischio inflazione e delle strette monetarie, lo ha venduto.
Vendite le quali hanno accelerato un’altra trasformazione del Bitcoin. Quella dei minatori. I bassi prezzi hanno creato margini limitati sulla validazione. Il che ha richiesto, ai miners, maggiori economie di scala e un approccio prettamente industriale.
Di nuovo, una caratteristica anti sistema finisce sullo sfondo: la possibilità che la singola persona possa essere realmente partecipe al mining. Certo! È la stessa programmata crescente difficoltà del “proof of work” – e del dispendio di energia – che ha fatto nascere le mining pool.
E, tuttavia, la distorsione è divenuta strutturale. Il tutto a discapito di quello che era l’utopia anarchica iniziale. Ma nel sistema capitalistico, si sa, l’utopia è destinata a lasciare il passo al profitto.
Read the full article
#aethernum#anarco-capitalisti#antisistema#criptoanarchia#cryptocurrency#Cryptovalute#Cypherpunk#finanzatradizionale#miningpool#SatoshiNakamoto#valutadigitale
0 notes
Text
Why didn't I start earlier?
Why don't you start now?
0 notes
Text

Trying a new style. Have been training SDXL models for different styles all weekend. Liking this laundromat vibe. Still need to fine tune more aspects of it, but so far SDXL is exceeding my expectations, it's what SD2.0 should've been.
0 notes

