#Data Science Foundation Program
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#data science skills#data science#data science course#programing#data scientist#Data Science Foundation Program#Data science and ai#learnbay#tech#artificial intalligence
0 notes
Text
What Are the Qualifications for a Data Scientist?
In today's data-driven world, the role of a data scientist has become one of the most coveted career paths. With businesses relying on data for decision-making, understanding customer behavior, and improving products, the demand for skilled professionals who can analyze, interpret, and extract value from data is at an all-time high. If you're wondering what qualifications are needed to become a successful data scientist, how DataCouncil can help you get there, and why a data science course in Pune is a great option, this blog has the answers.
The Key Qualifications for a Data Scientist
To succeed as a data scientist, a mix of technical skills, education, and hands-on experience is essential. Here are the core qualifications required:
1. Educational Background
A strong foundation in mathematics, statistics, or computer science is typically expected. Most data scientists hold at least a bachelor’s degree in one of these fields, with many pursuing higher education such as a master's or a Ph.D. A data science course in Pune with DataCouncil can bridge this gap, offering the academic and practical knowledge required for a strong start in the industry.
2. Proficiency in Programming Languages
Programming is at the heart of data science. You need to be comfortable with languages like Python, R, and SQL, which are widely used for data analysis, machine learning, and database management. A comprehensive data science course in Pune will teach these programming skills from scratch, ensuring you become proficient in coding for data science tasks.
3. Understanding of Machine Learning
Data scientists must have a solid grasp of machine learning techniques and algorithms such as regression, clustering, and decision trees. By enrolling in a DataCouncil course, you'll learn how to implement machine learning models to analyze data and make predictions, an essential qualification for landing a data science job.
4. Data Wrangling Skills
Raw data is often messy and unstructured, and a good data scientist needs to be adept at cleaning and processing data before it can be analyzed. DataCouncil's data science course in Pune includes practical training in tools like Pandas and Numpy for effective data wrangling, helping you develop a strong skill set in this critical area.
5. Statistical Knowledge
Statistical analysis forms the backbone of data science. Knowledge of probability, hypothesis testing, and statistical modeling allows data scientists to draw meaningful insights from data. A structured data science course in Pune offers the theoretical and practical aspects of statistics required to excel.
6. Communication and Data Visualization Skills
Being able to explain your findings in a clear and concise manner is crucial. Data scientists often need to communicate with non-technical stakeholders, making tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Matplotlib essential for creating insightful visualizations. DataCouncil’s data science course in Pune includes modules on data visualization, which can help you present data in a way that’s easy to understand.
7. Domain Knowledge
Apart from technical skills, understanding the industry you work in is a major asset. Whether it’s healthcare, finance, or e-commerce, knowing how data applies within your industry will set you apart from the competition. DataCouncil's data science course in Pune is designed to offer case studies from multiple industries, helping students gain domain-specific insights.
Why Choose DataCouncil for a Data Science Course in Pune?
If you're looking to build a successful career as a data scientist, enrolling in a data science course in Pune with DataCouncil can be your first step toward reaching your goals. Here’s why DataCouncil is the ideal choice:
Comprehensive Curriculum: The course covers everything from the basics of data science to advanced machine learning techniques.
Hands-On Projects: You'll work on real-world projects that mimic the challenges faced by data scientists in various industries.
Experienced Faculty: Learn from industry professionals who have years of experience in data science and analytics.
100% Placement Support: DataCouncil provides job assistance to help you land a data science job in Pune or anywhere else, making it a great investment in your future.
Flexible Learning Options: With both weekday and weekend batches, DataCouncil ensures that you can learn at your own pace without compromising your current commitments.
Conclusion
Becoming a data scientist requires a combination of technical expertise, analytical skills, and industry knowledge. By enrolling in a data science course in Pune with DataCouncil, you can gain all the qualifications you need to thrive in this exciting field. Whether you're a fresher looking to start your career or a professional wanting to upskill, this course will equip you with the knowledge, skills, and practical experience to succeed as a data scientist.
Explore DataCouncil’s offerings today and take the first step toward unlocking a rewarding career in data science! Looking for the best data science course in Pune? DataCouncil offers comprehensive data science classes in Pune, designed to equip you with the skills to excel in this booming field. Our data science course in Pune covers everything from data analysis to machine learning, with competitive data science course fees in Pune. We provide job-oriented programs, making us the best institute for data science in Pune with placement support. Explore online data science training in Pune and take your career to new heights!
#In today's data-driven world#the role of a data scientist has become one of the most coveted career paths. With businesses relying on data for decision-making#understanding customer behavior#and improving products#the demand for skilled professionals who can analyze#interpret#and extract value from data is at an all-time high. If you're wondering what qualifications are needed to become a successful data scientis#how DataCouncil can help you get there#and why a data science course in Pune is a great option#this blog has the answers.#The Key Qualifications for a Data Scientist#To succeed as a data scientist#a mix of technical skills#education#and hands-on experience is essential. Here are the core qualifications required:#1. Educational Background#A strong foundation in mathematics#statistics#or computer science is typically expected. Most data scientists hold at least a bachelor’s degree in one of these fields#with many pursuing higher education such as a master's or a Ph.D. A data science course in Pune with DataCouncil can bridge this gap#offering the academic and practical knowledge required for a strong start in the industry.#2. Proficiency in Programming Languages#Programming is at the heart of data science. You need to be comfortable with languages like Python#R#and SQL#which are widely used for data analysis#machine learning#and database management. A comprehensive data science course in Pune will teach these programming skills from scratch#ensuring you become proficient in coding for data science tasks.#3. Understanding of Machine Learning
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ad | Hi folks, I'd previously been getting into the swing of posting Humble Bundle deals and the charities they were helping. With any non-bundle purchases helping to raise money for Endometriosis research and support. Then Humble decided to outsource their partner program to a system called 'Impact' which has honestly been a massive pain to get my head round. Looks like I can't link to bundles directly and they only give me the above link to share.
There is currently:
The TellTale Games Bundle featuring Batman, the Expanse, the Walking Dead, the Wolf Among Us - Currently raising money for Save the Children
The Sid Meier Collection with every Civilization game and DLC I can think of - Raising money for Covenant House and Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research
Math for Programmers Book Bundle which contains a whole bunch of data science, cryptography and Python books - Raising money for Girls Who Code
Learn Unit Game Development Course - From Shaders to 3D to a course on Game Feel - Raising money for Oceana
Super Game Asset Bundle for Unreal, Godot, and Unity. Over 7000 audio, visual and environmental assets - Raising money for Direct Relief.
Not sure if this format is okay, it requires you to visit the link and navigate but hope it helps? Let me know.
176 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heather Cox Richardson 11.15.24
One of President-elect Trump’s campaign pledges was to eliminate the Department of Education. He claimed that the department pushes “woke” ideology on America’s schoolchildren and that its employees “hate our children.” He promised to “return” education to the states.
In fact, the Department of Education does not set curriculum; states and local governments do. The Department of Education collects statistics about schools to monitor student performance and promote practices based in evidence. It provides about 10% of funding for K–12 schools through federal grants of about $19.1 billion to high-poverty schools and of $15.5 billion to help cover the cost of educating students with disabilities.
It also oversees the $1.6 trillion federal student loan program, including setting the rules under which colleges and universities can participate. But what really upsets the radical right is that the Department of Education is in charge of prohibiting discrimination on the basis of race and sex in schools that get federal funding, a policy Congress set in 1975 with an act now known as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). This was before Congress created the department.
The Department of Education became a stand-alone department in May 1980 under Democratic president Jimmy Carter, when Congress split the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare into two departments: the Department of Health and Human Services and the Department of Education.
A Republican-dominated Congress established the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare in 1953 under Republican president Dwight D. Eisenhower as part of a broad attempt to improve the nation’s schools and Americans’ well-being in the flourishing post–World War II economy. When the Soviet Union beat the United States into space by sending up the first Sputnik satellite in 1957, lawmakers concerned that American children were falling behind put more money and effort into educating the country’s youth, especially in math and science.
But support for federal oversight of education took a devastating hit after the Supreme Court, headed by Eisenhower appointee Chief Justice Earl Warren, declared racially segregated schools unconstitutional in the May 1954 Brown v. Board of Education decision.
Immediately, white southern lawmakers launched a campaign of what they called “massive resistance” to integration. Some Virginia counties closed their public schools. Other school districts took funds from integrated public schools and used a grant system to redistribute those funds to segregated private schools. Then, Supreme Court decisions in 1962 and 1963 that declared prayer in schools unconstitutional cemented the decision of white evangelicals to leave the public schools, convinced that public schools were leading their children to perdition.
In 1980, Republican Ronald Reagan ran on a promise to eliminate the new Department of Education.
After Reagan’s election, his secretary of education commissioned a study of the nation’s public schools, starting with the conviction that there was a “widespread public perception that something is seriously remiss in our educational system.” The resulting report, titled “A Nation at Risk,” announced that “the educational foundations of our society are presently being eroded by a rising tide of mediocrity that threatens our very future as a Nation and a people.”
Although a later study commissioned in 1990 by the Secretary of Energy found the data in the original report did not support the report’s conclusions, Reagan nonetheless used the report in his day to justify school privatization. He vowed after the report’s release that he would “continue to work in the months ahead for passage of tuition tax credits, vouchers, educational savings accounts, voluntary school prayer, and abolishing the Department of Education. Our agenda is to restore quality to education by increasing competition and by strengthening parental choice and local control.”
The rise of white evangelism and its marriage to Republican politics fed the right-wing conviction that public education no longer served “family values” and that parents had been cut out of their children’s education. Christians began to educate their children at home, believing that public schools were indoctrinating their children with secular values.
When he took office in 2017, Trump rewarded those evangelicals who had supported his candidacy by putting right-wing evangelical activist Betsy DeVos in charge of the Education Department. She called for eliminating the department—until she used its funding power to try to keep schools open during the covid pandemic—and asked for massive cuts in education spending.
Rather than funding public schools, DeVos called instead for tax money to be spent on education vouchers, which distribute tax money to parents to spend for education as they see fit. This system starves the public schools and subsidizes wealthy families whose children are already in private schools. DeVos also rolled back civil rights protections for students of color and LGBTQ+ students but increased protections for students accused of sexual assault.
In 2019, the 1619 Project, published by the New York Times Magazine on the 400th anniversary of the arrival of enslaved Africans at Jamestown in Virginia Colony, argued that the true history of the United States began in 1619, establishing the roots of the country in the enslavement of Black Americans. That, combined with the Black Lives Matter protests in 2020, prompted Trump to commission the 1776 Project, which rooted the country in its original patriotic ideals and insisted that any moments in which it had fallen away from those ideals were quickly corrected. He also moved to ban diversity training in federal agencies.
When Trump lost the 2020 election, his loyalists turned to undermining the public schools to destroy what they considered an illegitimate focus on race and gender that was corrupting children. In January 2021, Republican activists formed Moms for Liberty, which called itself a parental rights organization and began to demand the banning of LGBTQ+ books from school libraries. Right-wing activist Christopher Rufo engineered a national panic over the false idea that public school educators were teaching their students critical race theory, a theory taught as an elective in law school to explain why desegregation laws had not ended racial discrimination.
After January 2021, 44 legislatures began to consider laws to ban the teaching of critical race theory or to limit how teachers could talk about racism and sexism, saying that existing curricula caused white children to feel guilty.
When the Biden administration expanded the protections enforced by the Department of Education to include LGBTQ+ students, Trump turned to focusing on the idea that transgender students were playing high-school sports despite the restrictions on that practice in the interest of “ensuring fairness in competition or preventing sports-related injury.”
During the 2024 political campaign, Trump brought the longstanding theme of public schools as dangerous sites of indoctrination to a ridiculous conclusion, repeatedly insisting that public schools were performing gender-transition surgery on students. But that cartoonish exaggeration spoke to voters who had come to see the equal rights protected by the Department of Education as an assault on their own identity. That position leads directly to the idea of eliminating the Department of Education.
But that might not work out as right-wing Americans imagine. As Morning Joe economic analyst Steven Rattner notes, for all that Republicans embrace the attacks on public education, Republican-dominated states receive significantly more federal money for education than Democratic-dominated states do, although the Democratic states contribute significantly more tax dollars.
There is a bigger game afoot, though, than the current attack on the Department of Education. As Thomas Jefferson recognized, education is fundamental to democracy, because only educated people can accurately evaluate the governmental policies that will truly benefit them.
In 1786, Jefferson wrote to a colleague about public education: “No other sure foundation can be devised for the preservation of freedom, and happiness…. Preach, my dear Sir, a crusade against ignorance; establish and improve the law for educating the common people. Let our countrymen know that the people alone can protect us against [the evils of “kings, nobles and priests”], and that the tax which will be paid for this purpose is not more than the thousandth part of what will be paid to kings, priests and nobles who will rise up among us if we leave the people in ignorance.”
100 notes
·
View notes
Note
hello! im just finishing up my read of structures of scientific revolutions, which has genuinely been very useful and shifted my understanding of science in a way being around people doing scientific research all day really didn't! i don't have a liberal arts education so i would love to get a sense of (a) what else of the philosophy / history of science canon is worth reading in the original (b) standard review papers or introductory textbooks and (c) critiques of the canon. i understand this is a big ask ofc, so feel free to point me to good depts / syllabi from good courses. thanks :)
yessss such a fun question >:) so, the thing that was so great about 'the structure of scientific revolutions', which i'm sure you've picked up on, is that kuhn pushed historians and philosophers of science to challenge the positivist model of science as a linearly progressive search to 'accumulate knowledge'. the idea of a 'paradigm shift' was itself a paradigm shift at the time; it was an early example of a language for talking about radical change in science without giving into the assumption that change necessarily = 'progress' (defined by national interests, mathematisation, and so forth). this is still an approach that's foundational to history and philosophy of science; it's now taken as so axiomatic that few academics even bother to gloss or defend it in monographs (which raises its own issue with public communication, lol).
where kuhn falls apart more (and this was typical for a philosopher of his era, training, and academic milieu) is in the fact that he never developed any kind of rigorous sociological analysis of science (despite alluding to such a thing being necessary) and you probably also noticed that he makes a few major leaps that indicate he's not fully committed to thinking through the relationship between science and politics. so for example, we might ask, can a paradigm shift ever occur for a reason other than a discovered 'anomaly' that the previous paradigm can't account for? for instance, how do political investments in science and scientific theories affect what's accepted as 'normal science' in a kuhnian sense? are there historical or present cases where a paradigm didn't change even though it persistently failed to explain certain empirical observations or data? what about the opposite, where a paradigm did change, but it wasn't necessarily or exclusively because the new paradigm was a 'better' explanation scientifically? how do we determine what makes an explanation 'better', anyway, especially given that kuhn himself was very much invested in moving beyond the naïve realist position? and on the more sociological side, we can raise issues like: say you're a scientist and you legitimately have discovered an 'anomaly'. how do you communicate that to other scientists? what mechanisms of knowledge production and publication enable you to circulate that information and to be taken seriously? what modes of communication must you use and what credentials or interpersonal connections must you have? what factors cause theories and discoveries to be taken more or less seriously, or adopted more or less quickly, besides just their 'scientific utility' (again, assuming we can even define such a thing)?
again, this is not to shit on kuhn, but to point out that both history and philosophy of science have had a lot of avenues to explore since his work. note that there are a few major disciplinary distinctions here, each with many sub-schools of thought. a 'science and technology studies' or STS program tends to be a mix of sociological and philosophical analysis of science, often with an emphasis on 'technoscience' and much less on historical analysis. a philosophy of science department will be anchored more firmly in the philosophical approach, so you'll find a lot of methodological critique, and a lot of scholarship that seeks to tackle current aporias in science using various philosophical frameworks. a history of science program is fundamentally just a sub-discipline of history, and scholarship in this area asks about the development of science over time, how various forms of thinking came into and out of favour, and so forth. often a department will do both history and philosophy of science (HPS). historians of medicine, technology, and mathematics will sometimes (for arcane scholastic reasons varying by field, training, and country) be anchored in departments of medicine / technology / mathematics, rather than with other faculty of histsci / HPS. but, increasingly in the anglosphere you'll see departments that cover history of science, technology, and mathematics (HSTM) together. obviously, all of these distinctions say more about professional qualifications and university bureaucracy than they do about the actual subject matter; in actuality, a good history of science should virtually always include attention to some philosophical and sociological dimensions, and vice versa.
anyway—reading recs:
there are two general reference texts i would recommend here if you just want to get some compilations of major / 'canonical' works in this field. both are edited volumes, so you can skip around in them as much as you want. both are also very limited in focus to, again, a very particular 'western canon' defined largely by trends in anglo academia over the past half-century or so.
philosophy of science: the central issues (1998 [2013], ed. martin curd & j. a. cover). this is an anthology of older readings in philsci. it's a good introduction to many of the methodological questions and problems that the field has grown around; most of these readings have little to no historical grounding and aren't pretending otherwise.
the cambridge history of science (8 vols., 2008–2020, gen. eds. david c. lindberg & ron numbers). no one reads this entire set because it's long as shit. however, each volume has its own temporal / topical focus, and the essays function as a crash-course in historical methodology in addition to whatever value you derive from the case studies in their own right. i like these vols much more than the curd & cover, but if you really want to dig into the philosophical issues and not the histories, curd & cover might be more fun.
besides those, here are some readings in histsci / philsci that i'd recommend if you're interested. for consistency i ordered these by publication date, but bolded a few i would recommend as actual starting points lol. again some of these focus on specific historical cases, but are also useful imo methodologically, regardless of how much you care about the specific topic being discussed.
Robert M. Young. 1969. "Malthus and the Evolutionists: The Common Context of Biological and Social Theory." Past & Present 43: 109–145.
David Bloor. 1976 [1991]. Knowledge and Social Imagery. Chicago: University of Chicago Press (here is a really useful extract that covers the main points of this text).
Ian Hacking. 1983. Representing and Intervening: Introductory Topics in the Philosophy of Natural Science. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Steven Shapin. 1988. “Understanding the Merton Thesis.” Isis 79 (4): 594–605.
Steven Shapin and Simon Schaffer. 1989. Leviathan and the Air-Pump: Hobbes, Boyle, and the Experimental Life. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Mario Biagioli. 1993. Galileo, Courtier: The Practice of Science in the Culture of Absolutism. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Bruno Latour. 1993. The Pasteurization of France. Translated by Alan Sheridan and John Law. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Margaret W. Rossiter. 1993. “The Matthew Matilda Effect in Science.” Social Studies of Science 23 (2): 325–41.
Andrew Pickering. 1995. The Mangle of Practice. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Porter, Theodore M. Trust in Numbers: The Pursuit of Objectivity in Science and Public Life. Princeton University Press, 1996.
Peter Galison. 1997. “Trading Zone: Coordinating Action and Belief.” In The Science Studies Reader, edited by Mario Biagioli, 137–60. New York: Routledge.
Crosbie Smith. 1998. The Science of Energy: A Cultural History of Energy Physics in Victorian Britain. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Chambers, David Wade, and Richard Gillespie. “Locality in the History of Science: Colonial Science, Technoscience, and Indigenous Knowledge.” Osiris 15 (2000): 221–40.
Kuriyama, Shigehisa. The Expressiveness of the Body and the Divergence of Greek and Chinese Medicine. Zone Books, 2002.
Timothy Mitchell. 2002. Rule of Experts: Egypt, Techno-Politics, Modernity. Berkeley: University of California Press.
James A. Secord. 2003. Victorian Sensation: The Extraordinary Publication, Reception, and Secret Authorship of Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation. Chicago: University Of Chicago Press.
Sheila Jasanoff. 2006. “Biotechnology and Empire: The Global Power of Seeds and Science.” Osiris 21 (1): 273–92.
Murphy, Michelle. Sick Building Syndrome and the Problem of Uncertainty: Environmental Politics, Technoscience, and Women Workers. Duke University Press, 2006.
Kapil Raj. 2007. Relocating Modern Science: Circulation and the Construction of Knowledge in South Asia and Europe, 1650–1900. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Schiebinger, Londa L. Plants and Empire: Colonial Bioprospecting in the Atlantic World. Harvard University Press, 2007.
Galison, Peter. “Ten Problems in History and Philosophy of Science.” Isis 99, no. 1 (2008): 111–24.
Daston, Lorraine, and Peter Galison. Objectivity. Zone Books, 2010.
Dipesh Chakrabarty. 2011. “The Muddle of Modernity.” American Historical Review 116 (3): 663–75.
Forman, Paul. “On the Historical Forms of Knowledge Production and Curation: Modernity Entailed Disciplinarity, Postmodernity Entails Antidisciplinarity.” Osiris 27, no. 1 (2012): 56–97.
Ashworth, William J. 2014. "The British Industrial Revolution and the the Ideological Revolution: Science, Neoliberalism, and History." History of Science 52 (2): 178–199.
Mavhunga, Clapperton. 2014. Transient Workspaces: Technologies of Everyday Innovation in Zimbabwe. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Lynn Nyhart. 2016. “Historiography of the History of Science.” In A Companion to the History of Science, edited by Bernard Lightman, 7–22. Chichester, UK: Wiley Blackwell.
Rana Hogarth. 2017. Medicalizing Blackness: Making Racial Difference in the Atlantic World, 1780–1840. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
Suman Seth. 2018. Difference and Disease: Medicine, Race, and the Eighteenth-Century British Empire. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Aro Velmet. 2020. Pasteur's Empire: Bacteriology and Politics in France, its Colonies, and the World. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
i would also say, as a general rule, these books are generally all so well-known that there are very good book reviews and review essays on them, which you can find through jstor / your library's database. these can be invaluable both because your reading list would otherwise just mushroom out forever, and because a good review can help you decide whether you even need / want to sit down with the book itself in the first place. literally zero shame in reading an academic text secondhand via reviews.
486 notes
·
View notes
Text
A grant to study linguistic differences between Hebrew and English was flagged as an example of “woke DEI grants” in a new database released by Sen. Ted Cruz.
The database is part of ongoing Republican efforts to justify significant cuts to federal research funding and diversity programs under President Donald Trump.
The $226,000 grant, given by the National Science Foundation to the University of Massachusetts Amherst in 2022, was flagged by the Texas Republican senator’s team as having an inappropriate focus on “gender.”
But according to the description of the research in Cruz’s own database, the sole mention of gender in the grant’s description is in reference to the fact that the Hebrew language (like many) assigns gender to nouns.
The UMass grant was also one of seven in Cruz’s database of Biden-era grants that stated an intent to promote partnerships between American and Israeli research institutions — something that did not appear to mitigate opposition from Cruz, an avowed supporter of Israel. He said in a statement that the more than 3,400 grants in his database demonstrated that the NSF had funded “questionable projects that promoted Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) or advanced neo-Marxist class warfare propaganda.”
A request for comment to Cruz’s office was not returned; nor was an inquiry sent to UMass. Cruz, the chair of the Senate committee on Commerce, Science & Transportation, said in a statement that his data “exposes how the Biden administration weaponized federal agencies to push a far-left ideology.”
He added, “Congress must end the politicization of NSF funding and restore integrity to scientific research.”
The public database of grants compiled by Cruz provides a window into how Trump and his allies are thinking about cuts to research funding. The flagged grants mentioning Israel were made to six universities including Brown, the University of Michigan and the University of Maryland-Baltimore County. They cover a range of scientific topics, from studying cognition to magnetic technologies to energy storage.
What they have in common is a stated intent to collaborate with an Israeli university. For example, Michigan’s grant specifically references a partnership with Ben-Gurion University in the southern Israeli city of Beersheva, while a second UMass grant mentions partnering with Technion-Israel Institute of Technology in the port city of Haifa, as well as “outreach by the Israeli collaborator to local high schools in Haifa.”
The second common thread among the Israel-related grant descriptions is the use of keywords flagged by the database as related to gender or DEI. Cruz’s team sorted the grants based on the presence of keywords related to the categories of “gender,” “status,” “social justice,” “race” and “environmental justice.”
None of the grants to mention Israeli partnerships make such topics the focus of their research, though some state a general commitment to “groups underrepresented in science” or “outreach to women and underrepresented minorities.” UMBC’s grant states that it will allow participation “for local high school students from underrepresented groups on the US side, and from various nationalities on the IL [Israeli] side.”
The UMass grant exploring the Hebrew and English languages makes no such commitment to diversity. Its reference to gender comes as it states that “English and Hebrew differ in how they organize the words within sentences and whether they assign gender to nouns; Hebrew assigns masculine and feminine genders to nouns, similar to languages like Spanish and French but unlike English.”
The project’s stated focus is to study how such linguistic differences affect “interpretation errors” among people who speak both languages.
Cruz’s dragnet of so-called “woke” research grants also comes as a number of American researchers and campus groups have pushed for boycotts of all Israeli institutions, in protest of Israel’s war in Gaza.
The database was posted as Elon Musk’s Department of Government Efficiency has targeted federal research funding on the basis of keywords that, the Trump team claims, reveal evidence of gender- and DEI-driven agendas. On Tuesday a federal judge intervened to block steep cuts to medical research funding at the National Institutes of Health. Another injunction blocked key parts of Musk’s effort to shut down the U.S. Agency for International Development.
A report last week in the Washington Post found that NSF staff were also being directed to comb through their research projects in search of dozens of offending keywords, including “women,” “victims,” “trauma” and “ethnicity.” Such efforts are part of a larger slashing of federal spending, including the shuttering of entire departments, that scholars say is unlawful and may be leading to a constitutional crisis.
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
KOSA Update
Following up on a previous post about the KOSA bill - a bill that would drastically change how the internet functions, in some ways enforcing the collection of private information and restricting access to educational material based on anyone’s belief that it might be harmful to children.
As of March 2024, the bill has gone through revision to reduce the ability to target marginalized communities. However, the language used in the bill is still broad and would be ultimately harmful to children and adult internet users.
Press releases like that of the American Civil Liberties Union invoke the First Amendment to highlight both the bill’s continued call for requiring or incentivizing age verification and its goal of censoring many different topics of conversation in online spaces.
If the U.S. government seeks to control, censor, and otherwise interfere with the world of the internet, then it would have to be a government program akin to public education or certain libraries. Let that government take over the responsibilities of running and funding the internet in that case if they want that power. Otherwise, the internet does not fall under federal jurisdiction.
In response to reaching out regarding this bill, one Congressman wrote that platforms like TikTok have come under scrutiny for “leaving users’ data vulnerable to access by the Chinese Communist Party, by collecting personal information on children in violation of federal law”. This Congressman does not state in this response whether he supports the KOSA bill in particular, but we hope that he is aware that this proposed bill would, by federal law, necessitate the collection of personal information of minors if websites are to follow its requirements. Additionally, TikTok’s data collection is comparable to that of other sites such as Instagram and Facebook, which are just as able to be infiltrated by political enemies of the U.S.
This update is not about the U.S. government’s ultimatum to the company ByteDance that will likely end in a U.S. ban on TikTok. Still, that news is relevant to internet users, especially those who value choice and self-determination.
In the aforementioned Congressman’s response, he also mentions the Privacy Enhancing Technology Research Act (H.R. 4755). That bill, passed in 2023, calls for organizations like the National Science Foundation to conduct and support research into technologies for mitigating privacy risks. Bills like this one are far more conducive to achieving online safety than the proposed KOSA bill. It seeks to enhance our understanding of data handling and online privacy, while the KOSA bill is more so blindly punching towards a problem that we do not yet have a clear view of.
As before, resources to further learn about and speak out against the bill are below.
Resources:
1.https://www.aclu.org/press-releases/revised-kids-online-safety-act-is-an-improvement-but-congress-must-still-address-first-amendment-concerns
2.https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2024/02/dont-fall-latest-changes-dangerous-kids-online-safety-act
3. https://www.stopkosa.com/
4. Privacy Enhancing Technology Research Act
5. KOSA Bill Post-Revision6.https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2024/03/analyzing-kosas-constitutional-problems-depth#
#kosa bill#stop kosa#kosa#politics#us politics#article#news#resources#first amendment#freedom of speech
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

New SpaceTime out Wednesday
SpaceTime 20250409 Series 28 Episode 43
Why does Venus have so many volcanoes?
A new study suggests convection in its crust could explain why Venus has so many volcanoes.



ESA shuts down the Gaia spacecraft for good
The European Space Agency has finally powered down its Gaia spacecraft after more than a decade spent gathering data on the stars of the Milky Way galaxy.








FRAM 2 launch
SpaceX launches the first manned mission to orbit above planet Earth’s poles.








The Science Report
Agriculture likely to push antibiotic use on livestock by a further 29 percent over the next 15 years.
Warnings that plastic-eating seabirds have failing organs, brain and nerve problems, and cell damage.
Teen girls who spend longer on their phones are more likely to have less sleep.
Alex on Tech the new Nintendo Switch 2.
SpaceTime covers the latest news in astronomy & space sciences.
The show is available every Monday, Wednesday and Friday through your favourite podcast download provider or from www.spacetimewithstuartgary.com
SpaceTime is also broadcast through the National Science Foundation on Science Zone Radio and on both i-heart Radio and Tune-In Radio.
SpaceTime daily news blog: http://spacetimewithstuartgary.tumblr.com/
SpaceTime facebook: www.facebook.com/spacetimewithstuartgary
SpaceTime Instagram @spacetimewithstuartgary
SpaceTime twitter feed @stuartgary
SpaceTime YouTube: @SpaceTimewithStuartGary
SpaceTime -- A brief history
SpaceTime is Australia’s most popular and respected astronomy and space science news program – averaging over two million downloads every year. We’re also number five in the United States. The show reports on the latest stories and discoveries making news in astronomy, space flight, and science. SpaceTime features weekly interviews with leading Australian scientists about their research. The show began life in 1995 as ‘StarStuff’ on the Australian Broadcasting Corporation’s (ABC) NewsRadio network. Award winning investigative reporter Stuart Gary created the program during more than fifteen years as NewsRadio’s evening anchor and Science Editor. Gary’s always loved science. He studied astronomy at university and was invited to undertake a PHD in astrophysics, but instead focused on his career in journalism and radio broadcasting. Gary’s radio career stretches back some 34 years including 26 at the ABC. He worked as an announcer and music DJ in commercial radio, before becoming a journalist and eventually joining ABC News and Current Affairs. He was part of the team that set up ABC NewsRadio and became one of its first on air presenters. When asked to put his science background to use, Gary developed StarStuff which he wrote, produced and hosted, consistently achieving 9 per cent of the national Australian radio audience based on the ABC’s Nielsen ratings survey figures for the five major Australian metro markets: Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide, and Perth. That compares to the ABC’s overall radio listenership of just 5.6 per cent. The StarStuff podcast was published on line by ABC Science -- achieving over 1.3 million downloads annually. However, after some 20 years, the show finally wrapped up in December 2015 following ABC funding cuts, and a redirection of available finances to increase sports and horse racing coverage. Rather than continue with the ABC, Gary resigned so that he could keep the show going independently. StarStuff was rebranded as “SpaceTime”, with the first episode being broadcast in February 2016. Over the years, SpaceTime has grown, more than doubling its former ABC audience numbers and expanding to include new segments such as the Science Report -- which provides a wrap of general science news, weekly skeptical science features, special reports looking at the latest computer and technology news, and Skywatch – which provides a monthly guide to the night skies. The show is published three times weekly (every Monday, Wednesday and Friday) and available from the United States National Science Foundation on Science Zone Radio, and through both i-heart Radio and Tune-In Radio.
#science#space#astronomy#physics#news#nasa#astrophysics#esa#spacetimewithstuartgary#starstuff#spacetime#hubble#hubble telescope#hubble space telescope
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dharna Noor at The Guardian:
Climate experts fear Donald Trump will follow a blueprint created by his allies to gut the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (Noaa), disbanding its work on climate science and tailoring its operations to business interests.
Joe Biden’s presidency has increased the profile of the science-based federal agency but its future has been put in doubt if Trump wins a second term and at a time when climate impacts continue to worsen. The plan to “break up Noaa is laid out in the Project 2025 document written by more than 350 rightwingers and helmed by the Heritage Foundation. Called the Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise, it is meant to guide the first 180 days of presidency for an incoming Republican president. The document bears the fingerprints of Trump allies, including Johnny McEntee, who was one of Trump’s closest aides and is a senior adviser to Project 2025. “The National Oceanographic [sic] and Atmospheric Administration (Noaa) should be dismantled and many of its functions eliminated, sent to other agencies, privatized, or placed under the control of states and territories,” the proposal says.
That’s a sign that the far right has “no interest in climate truth”, said Chris Gloninger, who last year left his job as a meteorologist in Iowa after receiving death threats over his spotlighting of global warming. The guidebook chapter detailing the strategy, which was recently spotlighted by E&E News, describes Noaa as a “colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future US prosperity”. It was written by Thomas Gilman, a former Chrysler executive who during Trump’s presidency was chief financial officer for Noaa’s parent body, the commerce department. Gilman writes that one of Noaa’s six main offices, the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research, should be “disbanded” because it issues “theoretical” science and is “the source of much of Noaa’s climate alarmism”. Though he admits it serves “important public safety and business functions as well as academic functions”, Gilman says data from the National Hurricane Center must be “presented neutrally, without adjustments intended to support any one side in the climate debate”.
[...] Noaa also houses the National Weather Service (NWS), which provides weather and climate forecasts and warnings. Gilman calls for the service to “fully commercialize its forecasting operations”. He goes on to say that Americans are already reliant on private weather forecasters, specifically naming AccuWeather and citing a PR release issued by the company to claim that “studies have found that the forecasts and warnings provided by the private companies are more reliable” than the public sector’s. (The mention is noteworthy as Trump once tapped the former CEO of AccuWeather to lead Noaa, though his nomination was soon withdrawn.)
The claims come amid years of attempts from US conservatives to help private companies enter the forecasting arena – proposals that are “nonsense”, said Rosenberg. Right now, all people can access high-quality forecasts for free through the NWS. But if forecasts were conducted only by private companies that have a profit motive, crucial programming might no longer be available to those in whom business executives don’t see value, said Rosenberg. [...] Fully privatizing forecasting could also threaten the accuracy of forecasts, said Gloninger, who pointed to AccuWeather’s well-known 30- and 60-day forecasts as one example. Analysts have found that these forecasts are only right about half the time, since peer-reviewed research has found that there is an eight- to 10-day limit on the accuracy of forecasts.
The Trump Administration is delivering a big gift to climate crisis denialism as part of Project 2025 by proposing the dismantling and privatizing the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and National Weather Service (NWS) in his potential 2nd term.
This should frighten people to vote Democratic up and down the ballot if you want the NOAA and NWS to stay intact.
#Project 2025#Climate Change#Climate Crisis#Weather#AccuWeather#National Weather Service#NOAA#NWS#John McEntee#The Heritage Foundation#Donald Trump#Climate Change Denialism#Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Climate Crisis Denial
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
Day 11 | Diana Ravenscroft | Day 13

31 days of FF 7 Headcanons: Day 12: First Encounter with Sephiroth
Today’s exploration explores the first documented interaction between Diana Ravenscroft and Sephiroth during her early years in Shinra’s Science Department. This clinical meeting marked the beginning of a deeply asymmetrical dynamic. It is one rooted not in relationship, but in observation, data extraction, and scientific ambition.
Diana did not see a person when she looked at Sephiroth. She saw a living experiment, a benchmark for what humanity could become when stripped of limitation and reengineered. This post analyzes that foundational moment through the lens of power, dehumanization, and unchecked scientific obsession.
Possible Trigger Warnings: discussions of bodily autonomy violation, dehumanization, medical experimentation, psychological detachment, scientific abuse, and unethical research practices.

Diana Ravenscroft first encountered Sephiroth in [μ] – εγλ 1998, during her tenure as an assistant geneticist under Professor Hojo in the Shinra Science Department. At the time, Sephiroth was already a rising figurehead of the SOLDIER program, his reputation as an elite SOLDIER cemented through a combination of raw combat skill and the secretive enhancements Shinra bestowed upon him. Diana was tasked with conducting a series of routine cellular diagnostics and hormone-level assessments following one of Sephiroth’s prolonged missions. Their interaction was perfunctory and clinical. She took samples, recorded vitals, and reported anomalies, but it left a deep impression on Diana, not because of any personal connection, but because of the rare biological data she was allowed to observe firsthand.
To Diana, Sephiroth represented the epitome of applied bioengineering. The Jenova-infused cellular structure that coursed through his veins confirmed everything she believed about the potential of human enhancement. Her interest in him was strictly professional but intensely so. In him, she saw not a person, but a data point: a walking, breathing case study of her life's ambitions realized. She took note of his regenerative capacity, cellular resistance, and neurological response to controlled stimuli, filing away every deviation and irregularity for later analysis.
What Sephiroth was, or could become, became more important to her than who he was. Their exchanges were sparse, often mediated by Hojo’s directives, and limited to the clinical sphere.
Diana’s role in Sephiroth’s medical monitoring escalated as Hojo began delegating more sensitive projects to her. She analyzed tissue samples, observed his reactions to various forms of stimuli, and studied the ways his Jenova cells responded to stress, trauma, and mako exposure. She never sought his trust, nor did she care for his consent. The only thing she cared about was the results. If he acknowledged her presence, it was likely as another faceless scientist in a white coat, indistinguishable from the others who poked, prodded, and cataloged him. Diana did not concern herself with his autonomy or humanity. She viewed him as a controlled experiment with a unique variable: alien cells. The more she learned, the more detached she became, reducing Sephiroth in her mind to a vessel of scientific significance rather than a person capable of will or emotion.
Their relationship, if it could even be called that, was purely procedural and entirely unbalanced. Sephiroth held power on the battlefield; Diana held power in the lab. She never attempted to manipulate him in a social or emotional context, but her fascination with his biology influenced her behavior in increasingly unhinged ways. She began building experimental models based on his genome, laying the groundwork for future human and celestial trails (through Bianca Moore) without his knowledge or involvement.
In hindsight, Diana’s first meeting with Sephiroth was less a turning point and more a confirmation of her path. It reinforced her belief that human limitations could, and should, be enhanced and lead the path of the obsession she has with Bianca Moore's cells and heritage. Her obsession with optimizing the human condition only deepened as a result of their clinical encounters. She did not see Sephiroth as a cautionary tale, but as unfinished work.
The consequences of her detachment and dehumanization would ripple out in the years to come, especially as she began manipulating Bianca Moore with the same disregard for agency or suffering. For Diana, Sephiroth was never a person. He was a benchmark, a blueprint, and ultimately, a failure she intended to surpass.

@themaradwrites @shepardstales @megandaisy9 @watermeezer
@prehistoric-creatures @creativechaosqueen @chickensarentcheap
@inkandimpressions @arrthurpendragon @projecthypocrisy @serenofroses
#31 days of headcanons#31 doh: ff#31 doh: diana ravenscroft#31 doh: day 11#oc: diana ravenscroft - ff#fwc: ff#ff vii oc#characters: fwc#characters: fwc: ff#au: canon divergent#bardic tales#bardic-tales#headcanon: fwc: ff#By🔥⚔️#By🌸🌙#BladeAndBloom
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

"This new image of NGC 2264, also known as the 'Christmas Tree Cluster,' shows the shape of a cosmic tree with the glow of stellar lights. NGC 2264 is, in fact, a cluster of young stars — with ages between about one and five million years old — in our Milky Way about 2,500 light-years away from Earth. The stars in NGC 2264 are both smaller and larger than the Sun, ranging from some with less than a tenth the mass of the Sun to others containing about seven solar masses.
This new composite image enhances the resemblance to a Christmas tree through choices of color and rotation. The blue and white lights (which blink in the animated version of this image) are young stars that give off X-rays detected by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. Optical data from the National Science Foundation’s WIYN 0.9-meter telescope on Kitt Peak shows gas in the nebula in green, corresponding to the 'pine needles' of the tree, and infrared data from the Two Micron All Sky Survey shows foreground and background stars in white. This image has been rotated clockwise by about 160 degrees from the astronomer’s standard of North pointing upward, so that it appears like the top of the tree is toward the top of the image.

Young stars, like those in NGC 2264, are volatile and undergo strong flares in X-rays and other types of variations seen in different types of light. The coordinated, blinking variations shown in this animation, however, are artificial, to emphasize the locations of the stars seen in X-rays and highlight the similarity of this object to a Christmas tree. In reality the variations of the stars are not synchronized.
The variations observed by Chandra and other telescopes are caused by several different processes. Some of these are related to activity involving magnetic fields, including flares like those undergone by the Sun — but much more powerful — and hot spots and dark regions on the surfaces of the stars that go in and out of view as the stars rotate. There can also be changes in the thickness of gas obscuring the stars, and changes in the amount of material still falling onto the stars from disks of surrounding gas.
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts."
Date: December 19, 2023
NASA ID: link
#NGC 2264#Christmas Tree Cluster#Space#Galaxy#NASA#December#2023#gif#Chandra X-ray Observatory#X-ray Observatory#Chandra#Marshall Space Flight Center#MSFC#Huntsville#Alabama#my post
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
by John Jeffay
Researchers in Israel are re-writing the history of Jerusalem after advances in carbon dating have allowed them to create a timeline of its construction with greater accuracy than ever before.
They now believe that much of the ancient city’s expansion actually took place at least a century earlier than previously thought, and have been able to link archaeological findings from the City of David archeological site to events described in the Bible.
The research program, funded by the Israel Science Foundation, lasted almost a decade and was jointly carried out by the Israel Antiquities Authority, Tel Aviv University (TAU) and the Weizmann Institute of Science. Their findings were recently published in the science journal PNAS.
The research team employed new radiocarbon dating techniques that can pinpoint, within a decade, the age of organic finds such as grape seeds, date pits and even bat skeletons.
Ancient tree rings from Europe, stored at the Weizmann Institute of Science, served as a benchmark for their timeline, providing data on fluctuations of carbon-14 – the basis of the radiocarbon dating method – found in the atmosphere.
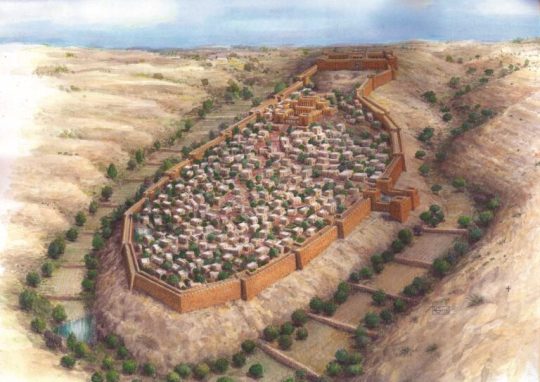
Their discovery challenges the idea that Jerusalem was constructed during the 350 years when the kings of Judah reigned.
“Until now, most researchers have linked Jerusalem’s growth to the west, to the period of King Hezekiah — just over 2700 years ago, following the Assyrian exile,” said Prof. Yuval Gadot of TAU.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
"From Passion to Profession: Steps to Enter the Tech Industry"
How to Break into the Tech World: Your Comprehensive Guide
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the tech industry is thriving and full of opportunities. Whether you’re a student, a career changer, or someone passionate about technology, you may be wondering, “How do I get into the tech world?” This guide will provide you with actionable steps, resources, and insights to help you successfully navigate your journey.
Understanding the Tech Landscape
Before you start, it's essential to understand the various sectors within the tech industry. Key areas include:
Software Development: Designing and building applications and systems.
Data Science: Analyzing data to support decision-making.
Cybersecurity: Safeguarding systems and networks from digital threats.
Product Management: Overseeing the development and delivery of tech products.
User Experience (UX) Design: Focusing on the usability and overall experience of tech products.
Identifying your interests will help you choose the right path.
Step 1: Assess Your Interests and Skills
Begin your journey by evaluating your interests and existing skills. Consider the following questions:
What areas of technology excite me the most?
Do I prefer coding, data analysis, design, or project management?
What transferable skills do I already possess?
This self-assessment will help clarify your direction in the tech field.
Step 2: Gain Relevant Education and Skills
Formal Education
While a degree isn’t always necessary, it can be beneficial, especially for roles in software engineering or data science. Options include:
Computer Science Degree: Provides a strong foundation in programming and system design.
Coding Bootcamps: Intensive programs that teach practical skills quickly.
Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer courses in various tech fields.
Self-Learning and Online Resources
The tech industry evolves rapidly, making self-learning crucial. Explore resources like:
FreeCodeCamp: Offers free coding tutorials and projects.
Kaggle: A platform for data science practice and competitions.
YouTube: Channels dedicated to tutorials on coding, design, and more.
Certifications
Certifications can enhance your credentials. Consider options like:
AWS Certified Solutions Architect: Valuable for cloud computing roles.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): Great for cybersecurity.
Google Analytics Certification: Useful for data-driven positions.
Step 3: Build a Portfolio
A strong portfolio showcases your skills and projects. Here’s how to create one:
For Developers
GitHub: Share your code and contributions to open-source projects.
Personal Website: Create a site to display your projects, skills, and resume.
For Designers
Design Portfolio: Use platforms like Behance or Dribbble to showcase your work.
Case Studies: Document your design process and outcomes.
For Data Professionals
Data Projects: Analyze public datasets and share your findings.
Blogging: Write about your data analysis and insights on a personal blog.
Step 4: Network in the Tech Community
Networking is vital for success in tech. Here are some strategies:
Attend Meetups and Conferences
Search for local tech meetups or conferences. Websites like Meetup.com and Eventbrite can help you find relevant events, providing opportunities to meet professionals and learn from experts.
Join Online Communities
Engage in online forums and communities. Use platforms like:
LinkedIn: Connect with industry professionals and share insights.
Twitter: Follow tech influencers and participate in discussions.
Reddit: Subreddits like r/learnprogramming and r/datascience offer valuable advice and support.
Seek Mentorship
Finding a mentor can greatly benefit your journey. Reach out to experienced professionals in your field and ask for guidance.
Step 5: Gain Practical Experience
Hands-on experience is often more valuable than formal education. Here’s how to gain it:
Internships
Apply for internships, even if they are unpaid. They offer exposure to real-world projects and networking opportunities.
Freelancing
Consider freelancing to build your portfolio and gain experience. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr can connect you with clients.
Contribute to Open Source
Engaging in open-source projects can enhance your skills and visibility. Many projects on GitHub are looking for contributors.
Step 6: Prepare for Job Applications
Crafting Your Resume
Tailor your resume to highlight relevant skills and experiences. Align it with the job description for each application.
Writing a Cover Letter
A compelling cover letter can set you apart. Highlight your passion for technology and what you can contribute.
Practice Interviewing
Prepare for technical interviews by practicing coding challenges on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank. For non-technical roles, rehearse common behavioral questions.
Step 7: Stay Updated and Keep Learning
The tech world is ever-evolving, making it crucial to stay current. Subscribe to industry newsletters, follow tech blogs, and continue learning through online courses.
Follow Industry Trends
Stay informed about emerging technologies and trends in your field. Resources like TechCrunch, Wired, and industry-specific blogs can provide valuable insights.
Continuous Learning
Dedicate time each week for learning. Whether through new courses, reading, or personal projects, ongoing education is essential for long-term success.
Conclusion
Breaking into the tech world may seem daunting, but with the right approach and commitment, it’s entirely possible. By assessing your interests, acquiring relevant skills, building a portfolio, networking, gaining practical experience, preparing for job applications, and committing to lifelong learning, you’ll be well on your way to a rewarding career in technology.
Embrace the journey, stay curious, and connect with the tech community. The tech world is vast and filled with possibilities, and your adventure is just beginning. Take that first step today and unlock the doors to your future in technology!
contact Infoemation wensite: https://agileseen.com/how-to-get-to-tech-world/ Phone: 01722-326809 Email: [email protected]
#tech career#how to get into tech#technology jobs#software development#data science#cybersecurity#product management#UX design#tech education#networking in tech#internships#freelancing#open source contribution#tech skills#continuous learning#job application tips
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today's (10/29/2024) Episode: Wholesome Morning Fun
Luigi and Noemi had successfully launched Watcher Tales right before their originally planned New Year’s Eve release date.
With that deadline off their backs, the family was able to relax and enjoy the holiday in style. In honor of all the relatives who had helped with his game launch, Luigi orchestrated a charity stream at the local gaming center, raising money for the family's foundation for at risk youth.
They kicked things off early in the morning, gathering a group of sims to participate in a timed Watcher Tales build challenge.
“You’ve got 2 hours to create a rockin’ party venue” Luigi told them “I’ll be checking in throughout on your progress, and at the end we’ll take turns touring all your creations, while our online viewers vote on their favorite. Good luck everyone!”


The winning build wound up being a futuristic nightclub lot, designed by the foundation’s volunteer computer science tutor, Mauricio.
Luigi had known this fellow computer lover since their teen years, when he’d been captain of Copperdale High’s computer club. The now much more mellow sim had put his interest in technology to good use both at the foundation and as a teacher at their old alma mater.
“I love your game, and so do my students.” he told Luigi when he came over to offer his congratulations. “The logic and data puzzles you added to the gearhead career are genius. It’s a fun way for kids to learn some of the basics of programming and I’m excited to work it into my lesson plans.”


As the attendees enjoyed placing their creations into their game worlds, Luigi was setting up breakfast with Grandpa Don and his friend Anderson.
“Anderson, this is Lalani. She wants to open her own catering business someday and today she’ll be helping you prepare your famous waffles for our event. Meanwhile, our volunteer Bradley here will be helping Don prepare drinks for all our guests. Nothing too potent now, he’s still a teen!”
“Brunch will be served shortly” he hollered to the crowd. “In the meantime, feel free to enjoy any of the fun activities we’ve setup throughout the center and thank you again for coming out to support this great cause!”


While Luigi was busy hosting the event and gathering footage for the foundations future promotions his son was unloading his most recent woes onto his friend Elyse “…then a clown with pliers started yanking out my teeth. It was awful! That wasn’t just a dream either…” he finished with a sigh “A bunch of my baby teeth are loose, and I hate how they’re all wiggly in my mouth. Daddy said I could just pull them out but I’m afraid to.”
“I totally get it” Elyse replied “I have nightmares too, and losing teeth is the worst! I yank mine to make sure I don’t swallow any in my sleep!”
“Oh, I don’t want to swallow them” Skye whimpered, more scared than ever, just in time for Bruce to jump into the conversation.
“I heard when you swallow a tooth it stays in your stomach for SEVEN YEARS!” their feisty friend grinned evilly at Skye’s horrified expression. “Now quite your bellyaching and come upstairs so I can kick your butts on this HUGE Space Invaders arcade game I found!”


After the meal Noemi gathered the children and teens for a little programming workshop. “Today I’ll show you how to program a simple music player and synthesizer so you can make your own tunes. I’ll also show you how to add your music tracks to Watcher Tales so you can hear them in game!”
Luigi filmed the kids working on their players, providing tips and tricks as he went. The sight of his friends, relatives, and the at-risk kids playing and learning together warmed his heart and made him proud of the good work the foundation was doing to help sims who might otherwise fall through the cracks.
Checking the donation counter Lugi was excited to see they’d already raised a healthy sum, and the day was just getting started!


View The Full Story of My Not So Berry Challenge Here
#sims 4#sims 4 challenge#sims 4 legacy#sims4#sims 4 nsb#sims 4 not so berry#sims4nsbstraud#sims 4 let's play#sims 4 gameplay#sims 4 lets play
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Python for Beginners: Launch Your Tech Career with Coding Skills
Are you ready to launch your tech career but don’t know where to start? Learning Python is one of the best ways to break into the world of technology—even if you have zero coding experience.
In this guide, we’ll explore how Python for beginners can be your gateway to a rewarding career in software development, data science, automation, and more.
Why Python Is the Perfect Language for Beginners
Python has become the go-to programming language for beginners and professionals alike—and for good reason:
Simple syntax: Python reads like plain English, making it easy to learn.
High demand: Industries spanning the spectrum are actively seeking Python developers to fuel their technological advancements.
Versatile applications: Python's versatility shines as it powers everything from crafting websites to driving artificial intelligence and dissecting data.
Whether you want to become a software developer, data analyst, or AI engineer, Python lays the foundation.
What Can You Do With Python?
Python is not just a beginner language—it’s a career-building tool. Here are just a few career paths where Python is essential:
Web Development: Frameworks like Django and Flask make it easy to build powerful web applications. You can even enroll in a Python Course in Kochi to gain hands-on experience with real-world web projects.
Data Science & Analytics: For professionals tackling data analysis and visualization, the Python ecosystem, featuring powerhouses like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib, sets the benchmark.
Machine Learning & AI: Spearheading advancements in artificial intelligence development, Python boasts powerful tools such as TensorFlow and scikit-learn.
Automation & Scripting: Simple yet effective Python scripts offer a pathway to amplified efficiency by automating routine workflows.
Cybersecurity & Networking: The application of Python is expanding into crucial domains such as ethical hacking, penetration testing, and the automation of network processes.
How to Get Started with Python
Starting your Python journey doesn't require a computer science degree. Success hinges on a focused commitment combined with a thoughtfully structured educational approach.
Step 1: Install Python
Download and install Python from python.org. It's free and available for all platforms.
Step 2: Choose an IDE
Use beginner-friendly tools like Thonny, PyCharm, or VS Code to write your code.
Step 3: Learn the Basics
Focus on:
Variables and data types
Conditional statements
Loops
Functions
Lists and dictionaries
If you prefer guided learning, a reputable Python Institute in Kochi can offer structured programs and mentorship to help you grasp core concepts efficiently.
Step 4: Build Projects
Learning by doing is key. Start small:
Build a calculator
Automate file organization
Create a to-do list app
As your skills grow, you can tackle more complex projects like data dashboards or web apps.
How Python Skills Can Boost Your Career
Adding Python to your resume instantly opens up new opportunities. Here's how it helps:
Higher employability: Python is one of the top 3 most in-demand programming languages.
Better salaries: Python developers earn competitive salaries across the globe.
Remote job opportunities: Many Python-related jobs are available remotely, offering flexibility.
Even if you're not aiming to be a full-time developer, Python skills can enhance careers in marketing, finance, research, and product management.
If you're serious about starting a career in tech, learning Python is the smartest first step you can take. It’s beginner-friendly, powerful, and widely used across industries.
Whether you're a student, job switcher, or just curious about programming, Python for beginners can unlock countless career opportunities. Invest time in learning today—and start building the future you want in tech.
Globally recognized as a premier educational hub, DataMites Institute delivers in-depth training programs across the pivotal fields of data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. They provide expert-led courses designed for both beginners and professionals aiming to boost their careers.
Python Modules Explained - Different Types and Functions - Python Tutorial
youtube
#python course#python training#python#learnpython#pythoncourseinindia#pythoncourseinkochi#pythoninstitute#python for data science#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
There are trillions upon trillions of numbers in the world. We use numbers to describe almost every conceivable thing in the universe. But there is one number that surpasses all others for the enormous impact it will have on every living thing on Earth over the next few thousand years. We consider it so important that we’ve dedicated our lives to acquiring and understanding it. Today that number happens to be: 427.6.
This is a measure (known in scientific terms as the mole fraction) of atmospheric carbon dioxide at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii, in parts per million. It’s part of a continuous chain of observations stretching back across two generations, to 1958, when Dave Keeling recorded the first measurement of 313 parts per million. Dave Keeling maintained this record, known as the Keeling Curve, using a running hodgepodge of short-term grants until 2005, at which point geochemist Ralph Keeling, a professor at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, coauthor of this piece and Dave’s son, assumed its stewardship. But now, after 67 years of battling to keep the program funded and provide the data to other scientists around the world, the program faces its most dire threat ever.
Why? Endeavors of this nature—highly precise measurements of a trace gas over many decades—require three basic inputs: knowledge, people, and money. It’s the third one that’s at risk, thanks to the current administration’s attacks on NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. NOAA provides support for our program both through an annual grant and through invaluable “in-kind” support, such as staffers taking samples for us, maintaining buildings in remote areas where sampling occurs, and running the Mauna Loa Observatory.
Monthly average carbon dioxide concentration at Mauna Loa (top panel) and annual financial support for the Scripps CO2 program (bottom panel), adjusted for inflation to US dollars in 2007. Photographer: Adapted from Sundquist and Keeling, 2009
The Trump administration has made clear it wishes to gut NOAA’s research enterprise, which is at the center of climate research globally. Already, we’ve seen large-scale firings and rejections of research proposals. Recent guidance from the Office of Management and Budget shows the administration intends to assiduously follow the blueprint of the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025 and shutter the Ocean and Atmospheric Research Line Office. This is not just a little haircut for a large federal agency—it’s grabbing the scissors and stabbing the agency through the heart. If successful, this loss will be a nightmare scenario for climate science, not just in the United States, but the world. It will also likely spell the end of our ability to continuously update the Keeling Curve.
Against this ominous backdrop, a small group of scientists is scrambling to preserve the ability to know how much carbon dioxide is in the atmosphere. NOAA maintains a global backbone of measurements of carbon dioxide and other gases, not just at Mauna Loa, but at more than 50 stations around the world. In parallel, our program at Scripps maintains records at a dozen stations. Other countries also contribute, but their efforts are almost all focused regionally, leaving the big picture to just a few programs that are global in scope. Climate change, however, is a global problem, and global networks address the really important questions. Such networks provide critical information on how fast carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are building up in the air from fossil-fuel burning and other processes. They provide information on how much carbon dioxide is being removed from the atmosphere by the oceans and by land plants. They provide information critical to independently verify emissions, to negotiate international treaties, to make decisions now about how much carbon dioxide the world can emit. These observational networks are the factual basis upon which all efforts to mitigate and adapt to climate change are based.
NOAA and Scripps play another key role in the atmospheric measurement community. How does the world know that the value of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today is really 427.6 and not 427.7 parts per million? Such differences may seem small, but they are consequential in the realm of climate research, and they can be calculated only because a lot of work has gone into calibration. Hundreds of groups can measure carbon dioxide using various off-the-shelf analyzers, but these analyzers first need to be calibrated using compressed air that has a known amount of carbon dioxide in it. Scripps assumed the lead role for preparing tanks filled with known amounts of carbon dioxide and dispensing them to the community until 1995, at which point NOAA took over.
The country and the world are now at risk of losing the only two programs that have played this central role. If the current administration has its way, the climate change research community could soon be fully adrift, unable to know with sufficient accuracy how quickly carbon dioxide levels are rising.
Even in the best of times, long-term observations can be very fragile. It is difficult to convince funding agencies to put money into long-term observations because, by definition, they are continuations; they have been done before. Most funding entities, from science agencies to philanthropic organizations, want to be associated with exciting, groundbreaking work, and sustained observations are too routine to scratch that itch. (Dave Keeling records in his autobiography, Rewards and Penalties of Monitoring the Earth, that at one point a National Science Foundation program manager demanded that, to maintain funding, he generate two discoveries per year from his record of carbon dioxide levels.)
Another vulnerability stems from the fact that the community of researchers making sustained measurements of atmospheric carbon dioxide probably numbers less than 30. Graduate students interested in learning to conduct this arcane work are a rare commodity. Patience and attention to detail are required, and years may be needed to accumulate enough data to answer the key questions or make groundbreaking discoveries. Researchers have to be extremely diligent and exacting to ensure that measurements in 1958 are comparable to those today. Calibration is an endless chore. This scientific pursuit isn’t for everyone.
Perversely, while the Keeling Curve has attained iconic global importance, this actually can hinder, rather than help the funding situation. Environmental programs tend to be organized by geographic domain and discipline—the National Water Quality Program of the US Geological Survey, NSF’s Arctic Observing Network, and the US Forest Service, for instance. Amid these focused efforts, the big picture can be lost. As the climate change field has evolved, we have found it increasingly difficult to find sponsors who accept responsibility for measuring vital signs of the Earth as a whole.
The original Mauna Loa measurements were started during the International Geophysical Year in 1957/1958. This was a massive, remarkable effort, led by the United States and including 67 countries, with the goal (simply put) of measuring every physical attribute possible on the Earth in one year. It led to numerous, important scientific discoveries and the establishment of many measurement programs worldwide. It established the South Pole station, for instance, a home for vital climate research that is still going today. It was a time of enormous optimism, of international cooperation (even during the height of the Cold War), of vast dreams, of global cooperation. And the United States was proud to lead the way.
This sense of endeavor continued into the 1970s, when then president Richard Nixon—a conservative Republican—established NOAA to better understand the world’s oceans and atmosphere. By the 1980s, the NOAA grew in scope, alongside the Scripps effort, to become the beating heart of global climate science. Now, after just three short months of the Trump administration, we are contemplating the abdication of US leadership in oceanic and atmospheric science and the loss of the largest and most critical observing network for carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases and their calibration laboratories.
Our colleagues at NOAA are living day to day, not sure if tomorrow will be their last on the job. We pray that common sense will prevail and that NOAA will be spared the worst. Whatever its fate, we will remain in the fight to preserve the world’s ability to measure carbon dioxide levels with whatever support we can muster, a small bulwark against climate science’s new dark age.
8 notes
·
View notes