#International Agreement
Text
Somaliland's Firm Stance On Implementing MoU With Ethiopia
By reasserting its sovereign right to int'l agreements, #Somaliland demonstrates its preparedness to engage with the global community on its own terms, safeguarding its autonomy & pursuing its #NationalInterests, particularly the #MoU with #Ethiopia
Continue reading Somaliland’s Firm Stance On Implementing MoU With Ethiopia
#2024 Ethiopia-Somaliland Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)#Diplomacy#Ethiopia#Ethiopia-Somaliland Relations#Horn of Africa#Implementation#International agreement#Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)#Ministry Of Foreign Affairs (MOFA)#Somalia#Somaliland#Sovereignty#Turkey
0 notes
Text
The US Sent Cluster Munitions to Ukraine But Activists Still Seek to Bolster a Treaty Banning Them
Backers of an international agreement that bans cluster munitions are striving to prevent erosion in support for it after what one leading human rights group calls an “unconscionable” U.S. decision to ship such weapons to Ukraine for its fight against ...
— By Jamey Keaten | September 5, 2023

Police officers look at collected fragments of the Russian rockets, including cluster rounds, that hit Kharkiv, in Kharkiv, Ukraine, on Dec. 3, 2022. Backers of an international agreement that bans cluster munitions are striving to prevent erosion in support for it after what one leading human rights group calls an “unconscionable” U.S. decision to ship such weapons to Ukraine for its fight against Russia. Advocacy groups in the Cluster Munitions Coalition released their latest annual report on Tuesday Sept. 5, 2023. AP Photo/Libkos . The Associated Press
Geneva, Switzerland — Backers of an international agreement that bans cluster munitions are striving to prevent erosion in support for the deal after what one leading human rights group calls an “unconscionable” U.S. decision to ship such weapons to Ukraine for its fight against Russia.
Advocacy groups in the Cluster Munitions Coalition released their latest annual report on Tuesday, ahead of a meeting next week of envoys from the 112 countries that have acceded to or ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions. The treaty prohibits the explosives and calls for clearing areas where they litter the ground because they harm and kill many more civilians than combatants,
A further 12 countries have signed the convention. The United States and Russia are not among them.
Mary Wareham of Human Rights Watch, who has long championed the 15-year-old convention, says the coalition was “extremely concerned” about the U.S. move in July, after an intense debate among U.S. leaders, to transfer unspecified thousands of 155mm artillery-delivered cluster munition rounds to Ukraine.
More than 20 government leaders and officials have criticized that decision, the coalition says.
Hoping to avoid defections from the convention, Wareham says supporters hope signatories will “stay strong — that they do not weaken their position on the treaty as a result of the U.S. decision. And we don’t see that happening yet. But it’s always a danger.”
U.S. officials argue that the munitions — a type of bomb that opens in the air and releases smaller “bomblets” across a wide area — could help Kyiv bolster its offensive and push through Russian front lines.

Photo: Sergei Supinsky/AFP Via Getty Images
U.S. leaders have said the transfer involves a version of the munition that has a reduced “dud rate,” meaning fewer of the smaller bomblets fail to explode. The bomblets can take out tanks and equipment, as well as troops, hitting multiple targets at the same time.
But Wareham cited “widespread evidence of civilian harm that (is) caused by these weapons. It was just an unconscionable decision.”
The report says civilians accounted for 95% of cluster munition casualties that were recorded last year, totaling some 1,172 in eight countries: Azerbaijan, Iraq, Laos, Lebanon, Myanmar, Syria, Ukraine, and Yemen. The monitor noted efforts in places like Bulgaria, Peru and Slovakia to destroy their stockpiles of the munitions in 2022 and earlier this year.
Children made up 71% of casualties from explosions of cluster-munition remnants last year, the report said.
It said Russia had “repeatedly” used cluster munitions in Ukraine since President Vladimir Putin ordered Russian forces to invade Ukraine in February last year, while Ukraine had used them “to a lesser extent.”
Washington’s decision “is certainly a setback,” said Wareham, “but it’s not the end of the road for the Convention on Cluster Munitions by far.”
#US 🇺🇸 | Ukraine 🇺🇦#Cluster Munitions#Activists#International Agreement#Human Rights Group#Russia 🇷🇺#Geneva Switzerland 🇨🇭#Cluster Munitions Coalition#112 Countries | Ratified#United States 🇺🇸 | Russia 🇷🇺 | No Ratification#Mary Wareham | Human Rights Watch#95% | Casualties | 1172 | Eight Countries#Azerbaijan 🇦🇿 Iraq 🇮🇶 | Laos 🇱🇦 | Lebanon 🇱🇧 | Myanmar 🇲🇲 | Syria 🇸🇾 | Ukraine 🇺🇦 | Yemen 🇾🇪#Bulgaria 🇧🇬 | Peru 🇵🇪 | Slovakia 🇸🇰 | Destroyed | Stockpiles | 2022#Children | 71% Casualties
0 notes
Text
If the United States were to be the first to release this new means of indiscriminate destruction upon mankind, she would sacrifice public support throughout the world, participate in the race for armaments and prejudice the possibility of reaching an international agreement on the future control of such weapons.
"Brighter than a Thousand Suns: A Personal History of the Atomic Scientists – Appendix B: The 'Franck Report'" - Robert Jungk, translated by James Cleugh
#book quote#brighter than a thousand suns#appendix#robert jungk#james cleugh#nonfiction#franck report#united states#indiscriminate#destruction#sacrifice#public support#international agreement#control#regulation#nuclear weapons
0 notes
Text
This is not a situation of waging war according to the laws of war and the Geneva Convention — this is a completely different philosophy of war where civilian lives are disregarded entirely.
Pavlo Kovtoniuk quoted in an article by Stephanie Nolen in Japan Times, originally published in The New York Times. In global conflict zones, hospitals and doctors are no longer spared
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
Strikes to the groin are discouraged, if not flat-out prohibited in muay Thai which I think is hilarious considering that's what Vegas does in ep 10 as if saying he's not playing by the rules.
#kinnporsche#vegaspete#boxer!pete phongsakorn saengtham#it seems there's some variation within the rules depending on whether the match is domestic or international one#although at the beginning of every match the contestants are told not strike below the belt#you could say that in thailand avoiding the groin is more about gentleman's agreement than written rule#or so i've understood#which makes me cackle even more
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The last twelve months were the hottest twelve months ever on record.
x
“In the case of climate, we are not the dinosaurs. We are the meteor. We are not only in danger. We are the danger.”
- António Guterres, Secretary-General of the United Nations
#international politics#politics#climate change#climate crisis#global warming#united nations#paris agreement#quote#article#cnn
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hitler observed the Munich agreement for less than 24 weeks. And the invasion of Poland began just over 11 months after Munich. Appeasement is not the road to peace.
Ethnonationalist dictators are not interested in the rule of law – including international law. That's usually how they got to be dictators in the first place.
Putin violated a host of international agreements and treaties when he invaded Ukraine. That includes the United Nations Charter, the 1975 Helsinki agreement, and the 1994 Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances. And all through this war, Putin has been violating the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide which went into effect in 1951.
Anybody who believes that Putin would adhere to any future agreements on Ukraine has to score in the top 1% of the population for gullibility.
#invasion of ukraine#UkraineAidNow#neville chamberlain#adolph hitler#1938 munich agreement#czechoslovakia#scrap of paper#gullibility#appeasement#dictators#vladimir putin#genocide#violations of international law#russia's war of aggression#путлер#россия#владимир путин#путин хуйло#добей путина#путин - военный преступник#геноцид#нарушение россией будапештского меморандума#путина в гаагу!#диктатура#руки прочь от украины!#геть з україни#адольф гитлер#невілл чемберлен#слава україні!#героям слава!
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
me trying to explain why i think mike is gay and is aware that he’s not in love with el cause he has feelings for someone else since atleast the end of season 3, but he also doesn’t know the feelings attached to the painting are will’s yet and he was consciously lying in the monologue by trying to follow what will told him in the van (giving el the courage to fight on by emphasizing her abilities as a superhero, something that makes her different and “better” apparently!) cause he thinks that’s the only way to save el...so the painting is a plot device for byler to get together (and mlvn bones cause it made mike misunderstand what el truly needed, leading to his words not being enough for el to win and save max in time) but not in the sense that mike fell in love with will’s feelings for him or the person behind the painting, just that it was used to show who’s always been the right person for mike based on compatibility and understanding and true unconditional love, and for him to realize that things aren’t hopeless and his feelings are requited once he finds out the full truth behind the painting cause without it he would’ve continued forcibly conforming due to societal expectations and pressure, and trapping himself in a loveless relationship because of his fear of losing el and hurting her

#so im finally coming out as a full fledged gay mike truther 🙏#but there are certain things im not in agreement with when it comes to how gay mike truthers commonly perceive the narrative#like mike figuring out will in the van scene...cause i dont think hes there just yet#hes still too wrapped up in low self worth to ever comprehend that someone loves him the way will does#but i do agree that he’s self aware of his own feelings for will and has been struggling/dealing with it#i think s5 will reveal all his internal conflicts surround it#so i dont think hes gonna have a “feelings realization” in s5 but rather come to terms with/accept said feelings#the reason i believe this is bc if s5 is when he’ll figure out his own feelings#i dont think there would be enough time to depict his internal struggles/conflicts with it#as a lot of people have said...it would look like mike realizes hes in love with will then just#immediately jumps into a relationship with him without any internal struggles in between#i dont think thats what theyre trying to convey storytelling wise#i have more thoughts on why i believe in gay mike now but i still dont know how to piece them together in a coherent analysis yet#maybe i’ll post about it someday but for now take this 👍#byler#byler analysis
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sometimes I make little bets and agreements with myself over the smallest things. Like 'okay, we'll get up when the cat isn't on our lap anymore' or 'next time YouTube throws on an ad we'll make a cup of coffee'
Which is all fun and games until the trigger never comes and you're stuck in limbo wishing you hadn't made a binding pact that has tethered you into the space between spaces. Certainly you could break the pact. But an agreement means something, dammit!
This is normal human behavior, right?
#camden posting#this post brought to you by me waiting to get out of bed when my phone battery goes below 95%#damn it all I want coffee#why did I agree to this?!#I can't decide not to or we'll realize that's an option for anything#and for this to work we need to always honor our internal agreements#even if they're stupid and wrong
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Friendly reminder that Francesco Coppino and Prospero di Camulio, contemporaries who were literally getting their information from predominantly Yorkist circles, were both explicitly clear that it was Henry VI who decided to surrender Berwick to Scotland.
Camulio: "King Henry has given away a castle [town] called Berwick, which is one of the keys of the frontier between England and Scotland."
Coppino: "[Scotland has] received from the same Henry the town of Berwick, on the frontiers of Scotland, which the Scots have long claimed as their right from the English, as the excellently well furnished guardian of their frontiers, and the place to which King Henry repaired as an asylum after the battle."
The idea that Margaret of Anjou was principally involved in the surrender, or that she was the one who actually made the decision, is based on nothing but assumption. Two direct contemporaries, both speaking of ongoing events as they unfolded, who were both getting information from Yorkist-held England, both clearly believed it was Henry who was responsible for this course of action. Neither of them mention Margaret. Sure, you can argue that it was merely rhetorical, and that they were simply automatically attributing such an important decision to the King rather than the queen - but rhetoric is nonetheless extremely important and helps us understand how historical figures were perceived at the time. Margaret's enemies would surely not have hesitated to broadcast her involvement had it actually been true, and Coppino in particular had shown no qualms about criticizing her in favor of the Yorkists before. If she was genuinely believed to have been responsible, and if the Yorkists were actually claiming that she was at the time, I see no reason why Coppino or Camulio would not have emphasized her role in their letters. What these samples instead indicate is literally the opposite: that their contemporaries - probably including the Yorkists who were putting out the information that Coppino and Camulio reported - actually believed that Henry was the one making the decision. I think it's a very large and very unnecessary stretch to go against actual evidence and claim otherwise by placing the responsibility on Margaret instead.
Additionally, these small samples may also reveal what people at the time - once again including the Yorkists - actually thought of Henry's role in the war on a broader level, away from direct Yorkist propaganda which would obviously and perhaps understandably seek to de-emphasize it: namely, that Henry was perceived as the one making decisions and deciding the courses of action for his own side.
Source: Excerpts from the Calendar of State Papers and Manuscripts, Existing in the Archives and Collections of Milan
#henry vi#margaret of anjou#english history#my post#I want to make a longer post detailing the clear indications we have that Henry *was* perceived as the active decision maker of his side#which indicates that contemporaries did not really think that there was some kind of giant 'role-reversal' between him and MoA#but until then the gist is:#after Henry was rescued in 1461 contemporary letters clearly emphasize his own actions; they mostly did not attribute decisions to Margaret#we also know he and Margaret separated when she headed off to the continent;#that he seems to have been involved in border-raids against Yorkist England;#*and* that he avoided capture until 1465#if Henry was entirely passive throughout it all and entirely dependent on Margaret to make decisions#I do not understand how any of this would have been possible#Instead Henry & Margaret seemed to have had more of a partnership with Margaret focusing on gaining international support#which she was very well-suited for given her powerful foreign connections#& with her taking on leadership in his absence (mainly due to imprisonment/incapacity) rather than all the time/when they were together#and like I said when it comes to Berwick contemporaries clearly believed it was Henry's decision#but also like. let's hypothetically assume that Margaret was the driving force behind it. please think of this situation logically.#whoever's idea it was Scotland was very obviously going to want a proper confirmation from the *king*#who was. yk. the actual authority of the country#even if Margaret was the one encouraging this surrender Henry's approval and agreement would have still been required#if not by the Lancastrian party then by Scotland#and again this is assuming that Margaret was actually the driving force behind it. there's no indication that she was#but ultimately contemporaries very clearly believed *Henry* was responsible#we don't know what MoA actually thought of it or what her actual involvement was (she could may encouraged it; she may have misliked it;#she may have simply been told after the decision had already been made)#but ultimately even in the most extreme case - which is contradicted by actual evidence - the final say would have been Henry's#it would be nice if this was reflected by historians?
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
How tech does regulatory capture
If you want to know which industries have the most influence in DC, study the trade deals struck by the US Trade Representative, whose activities are the most obvious manifestation of American corporate power over state. Take the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF). As David Dayen notes, this treaty is a kind of Big Tech wishlist:
https://prospect.org/power/2023-04-18-big-tech-lobbyists-took-over-washington/
If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/18/cursed-are-the-sausagemakers/#how-the-parties-get-to-yes
The USTR’s playbook has changed over the years, reflecting the degree of control over the US government exerted by different sectors of the US economy. Today, with Big Tech in the driver’s seat, US trade deals embody something called the “digital trade agenda,” a mix of policies ranging from limiting liability, privacy protection, competition law, and data locatization.
The Digital Trade Agenda is a relatively new phenomenon. A decade ago, when the USTR went abroad to twist the arms of America’s trading partners, the only “digital” part of the agenda was obligations to spy on users and to swiftly remove materials claimed to have violated US media monopolies’ copyright. But as the tech sector grew more concentrated, they were able to seize a greater share America’s trade priorities.
One person who had a front-row seat for this transformation was Wendy Li, a PhD candidate in sociology at the University of Wisconsin, who served in the USTR’s office from 2015–17, and who leveraged her contacts among officials and lobbyists (and ex-lobbyists turned officials and vice-versa) to produce a fascinating, ethnographic account of a very specific form of regulatory capture. That account appears in “Regulatory Capture’s Third Face of Power,” in Socio-Economic Review. The article is paywalled, but if you access it via this link, you can bypass the paywall:
https://pluralistic.net/wendi-li-reg-capture
Li’s paper starts with a taxonomy of types of regulatory capture, drawn from the literature. The first kind — the “first face of power” — is when an industry wins some battle over a given policy, triumphing over the public interest. Li notes that defining “public interest” is sometimes tricky, which is true, but still, there are some obvious examples of this kind of capture.
My “favorite” example of horrible regulatory capture is from 2019, when Dow Chemical — working through the West Virginia Manufacturers Association — convinced the state of West Virginia to relax the limits on how much toxic runoff from chemical processing could be present in the state’s drinking water. Dow argued that the national safe levels reflected a different kind of person from the typical West Virginian. Specifically, Dow argued, the people of West Virginia were much fatter than other Americans, so their bodies could absorb more poison without sickening. And besides, Dow concluded, West Virginians drink beer, not water, so poisoning their drinking water wouldn’t affect them:
https://washingtonmonthly.com/2019/03/14/the-real-elitists-looking-down-on-trump-voters/
This isn’t even a little ambiguous. Dow’s pleading wasn’t just absurd on its face — it was also scientifically bankrupt — there’s no evidence that being overweight makes you less susceptible to carcinogens. And yet, the state regulator bought it. Why? Well, maybe because chemical processing is WV’s largest industry, and Dow is the largest chemical company in the state. Regulatory capture, in other words.
The second kind of regulatory capture is the “revolving door”: when an executive from industry rotates into a role in government, where they are expected to guard the public interest from their former employers. There’s some of this in every presidential administration — think of Obama’s ex-Morganstanley and ex-Goldmansachs finance officials.
But while Obama and other “normal” pols sketched their corruption with a fine-tipped pen, making the overall shape hard to discern, Trump scrawled large, crude, unmissable figures with a fisted Sharpie. Remember Scott Pruitt, the disgraced Trump EPA who wanted to abolish the EPA? Pruitt was was such a colossal asshole that even the lobbyists who’d been bribing him with free housing actually evicted him:
https://www.cnn.com/2018/04/06/politics/pruitt-trump/index.html
After Pruitt resigned in the midst of chaotic scandal, he was succeeded by his deputy, Andrew Wheeler — a former coal lobbyist:
https://www.nytimes.com/2018/07/05/climate/scott-pruitt-epa-trump.html
That’s the “second face of power.” What’s the third? It’s taking over the shape of the debate, getting to define its axioms. Think of the reflexive idea that government projects are “wasteful” and “inefficient.” Once all players internalize this idea, the debate shifts from “what should the public sector do?” to “which private-sector entity should the government pay to do this?” Anyone who says, “Wait, why doesn’t the government just do this?” just gets blank stares.
We can see this in the cramped and inadequate debate over the SVB bailout; apologists for the bailout insist that it was necessary because if SVB’s depositors had been forced to take a haircut, every large depositor in America would pile into Morganstanley, making it so “too big to fail” that it could tank the nation.
This is probably true — but only if you discount the possibility of establishing a public bank. Public banks are hardly a radical idea: America had nationwide public banking through the postal service until 1966:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/15/socialism-for-the-rich/#rugged-individualism-for-the-poor
Li summarizes: “the first face of power is measured through the winner of the game, and the second face of power can be understood as the referee. The third face of power is the field, the rulebook, and agreement that there is even a game at all.”
It’s the creation of this third face that Li’s paper dissects — the creation of “Type I” ideas that form the unquestioned assumptions for all other debate. Sociologist call these ideas “schemas.” Li describes two ways that the tech industry changed the schemas used in trade negotiations. First, schemas are changed through “knowledge production” — creating reports and data.
Second, schemas are embedded through “recursive institutional reproduction” — a bit of unfortunately opaque academic jargon that is roughly equivalent to what activists call “policy laundering.” That’s when an industry can’t get its way in its home country, so it leans on trade reps to include that policy in a treaty or trade deal, which transforms it into an obligation at home.
In tech policy, the Ur-example of this is the DMCA, a 1998 digital copyright law that has profoundly changed the way we relate to everything from online services to our coffee makers. The origins of the DMCA are wild. In 1991, Al Gore kicked off the National Information Infrastructure hearings — AKA the “Information Superhighway” project. One of the most prominent proposals for the future of the internet came from Bruce Lehman, Bill Clinton’s Copyrigh tCzar. Lehman had been the head of IP enforcement for Microsoft, and he had some genuinely batshit ideas for the internet, like requiring a separate, negotiated copyright license for every transitory copy made by RAM, or a network buffer, or drive cache:
https://www.wired.com/1996/01/white-paper/
Gore laughed Lehman out of the room and told him to hit the road. So Lehman did, scurrying over to Geneva, where he turned his batshit ideas into the WIPO Copyright Treaty (WCT) and the WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty (WPPT). Then he raced back to DC where he told Congress that they had to get on board with those UN treaties. In 1998, Congress passed the DMCA, turning a failed regulatory policy into a federal law that endures to this day.
That’s “policy laundering.” Lehman couldn’t get his ideas though the US government, so he rammed them through a UN agency, converting his proposal into an obligation, which Congress duly assumed.
The Digital Trade Agenda triumphed by both knowledge production and recursive institutional reproduction (AKA policy laundering). Under Obama, trade officials created the Digital Trade Working Group in consultation with industry, through the US Chamber of Commerce. This group worked with the US International Trade Commission (USITC) — a quasi-governmental research body — to produce copious reports, testimony and data in support of a focus on “digital trade.”
In particular, they inflated the value of digital trade to US officials, convincing them that getting wins for the digital industry would have an outsized impact on the US economy. This is reflected in the terms of the Trans-Pacific Partnership, a trade deal that was negotiated in the utmost secrecy, in hotels all over the world surrounded by armed guards, where neither the press nor activists were welcome.
TPP represented a kind of farcical wishlist for America’s corporate giants, including the tech sector, and it looked like a done deal — until Trump. Trump unilaterally withdrew from TPP, so the tech industry’s reps simply tacked around TPP. They took everything they’d wanted to get out of TPP and crammed it into the USMCA, Trump’s rewrite of NAFTA. This makes perfect sense — corporate America’s priority was TPP’s policies, not TPP itself.
Li’s paper doesn’t just document this shift, she also gives us interviews with (anonymized) officials and lobbyists who speak frankly about how this happened behind the scenes. For example, a former Commerce official turned tech lobbyist describes how he lobbies his former coworkers: “Sometimes, [meetings are like] hey, let’s grab lunch, let’s grab coffee, and catch up. And half of it is about our kids, and half of it is about this [work related issue]. We’ll have a formal meeting [with government officials], but obviously we chitchat before and after. Because we’re human. So, a lot of it is just normal human interaction, right?”
This social coziness lets lobbyists position themselves as “stakeholders,” which legitimizes — and even requires — their participation in policymaking. As a trade negotiator says, “So to get your handle on a problem, you’ve got to pull the right people together, and you’ve got
to sift through all the various ideas, so we obviously have a lot of regular interaction with companies [. . .] I spend a lot of time with the companies trying to understand their business model, try ing to understand how they interact with the governments in different countries, and then of course, socializing it within the building.”
Once lobbyists are “stakeholders,” they get to define not just what position the US takes — they get to define which positions can even be considered. As a trade negotiator says, “[Lobbyists aren’t] coming in and spouting talking points. They’re not giving us draft text because
we haven’t gotten to the text phase yet. The way these meetings go is, generally we provide an update on what is happening and what approach we’re taking. The remainder is usually devoted to companies talking about their particular interests, and inquiring as to whether and how their issues are being addressed in that forum.”
That’s not just winning the game — it’s defining the rules.
Li’s paper is a fascinating tour of the sausage-factory and a close examination of the gunk that litters the factory floor. That said, I think there are areas where she drops policies and fights into neat categories that are much messier. For example, Li contrasts the rules in TPP with the rules in ACTA, the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement, a failed international treaty from 2010.
Li characterizes ACTA as being an anti-tech proposal because it imposed copyright liability on tech companies, which would have raised their costs by forcing them to police their users’ speech, items for sale and uploads for copyright infringement. But that’s not quite right: ACTA was much broader. First, because “counterfeiting” doesn’t mean what you think it does: in an international trade agreement, counterfeiting concerns itself with all kinds of totally legitimate activities.
For example, Apple engraves microscopic Apple logos on every part in an iPhone; no user ever sees these parts. But Apple uses the presence of an Apple trademark on these tiny components to lodge trademark claims with US border officials in order to block the importation of parts harvested from dead iPhones, as part of the company’s war on repair:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/30/80-lbs/#malicious-compliance
Likewise, companies like Rolex and Cartier have national subsidiaries in countries all over the world with the exclusive license to sell their goods in each country. These companies then claim that, say, an official Mexican Rolex watch becomes a counterfeit Rolex the minute it crosses the US border, because Rolex Mexico doesn’t have the right to use Rolex International’s trademarks outside of Mexico.
Asking tech companies to police “counterfeits” isn’t just about stopping knockoffs — it’s about letting multinational corporations control all secondary markets for their goods, giving them total control over repair and used goods.
Beyond that: creating an affirmative duty for platforms to police their users’ uploads and speech for copyright infringement is one of those things that not only won’t prevent copyright infringement (beating filters is easy for dedicated copyright infringers), but it will also compromise users’ speech (because filters are rife with false positives) — and it will hand eternal dominance to the largest tech firms (both Youtube and Facebook support mandatory filters, because they’ve spent hundreds of millions on them, and know that their small rivals can’t).
ACTA wasn’t a way to “punish” tech to make life better for media companies — it was a way to shift some of the oligarchic control of both tech and media around, while shoring up its dominance. Yes, parts of the tech sector hated ACTA, but it died because millions of people campaigned against it.
And of course, ACTA got policy-laundered into law in 2019, when the EU adopted the Digital Single Market Directive and created a filtering mandate, ignoring the largest petition in EU history and the people who marched in 50 cities. That was recursive institutional reproduction in action all right.
Likewise, TPP can’t be understood as the tech sector sidelining the entertainment companies — because both of them rallied for the parts of TPP that feathered all their nests. For example, the entertainment sector and the tech sector both love rules against reverse-engineers (like Section 1201 of the DMCA), which make it a felony to unlock your books, music, games and videos from the store that sold them to you and take them with you to another player.
Tech loves this because it gets them lock-in — if you break up with Amazon, you have to kiss your Kindle and Audible books goodbye. Media loves it because it gives them control — DRM stops you from recording Christmas movies between Feb and Dec, when they come free with your streaming service, and that means you have to pay-per-view them in December, when you want to watch them.
In other words, the Big Tech and Big Content’s policy fights aren’t so much about which policies we get — they’re about who gets to profit from them. They both want the same stuff — no taxes, no unions, no minimum wage, no consumer rights, no privacy — but they each want to hoard the benefits from that stuff.
Both tech and media love “IP” — not in the sense of “copyright” or “trademark,” but in the sense of “any law that lets me control the conduct of my competitors, critics and customers”:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
In USMCA, it wasn’t just the “Digital Trade Agenda” that made it into the final agreement — it was mandatory DRM laws, massive copyright extensions, and the evisceration of fair use and its equivalents in Mexico and Canada:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/08/01/set-healthy-boundaries/#la-ley
There’s another important factor missing from Li’s analysis of the rise of the Digital Trade Agenda: monopoly. Tech used to be composed of hundreds of competing firms that hated each other’s guts and were incapable of working together. The entertainment industry, by contrast, was already hugely consolidated and able to lobby effectively as a body.
That was hugely important in the Napster Wars, when international copyright proposals like the Database Right and the Broadcast Treaty were popping up at the UN and in country-to-country trade deals. While the tech industry was competing to give users a better deal, Big Content was able to solve the collective action problem and come up with a common lobbying position, getting nearly identical (and absolutely ghastly) tech bills introduced in dozens of state legislatures at once:
https://web.archive.org/web/20030425210736/https://www.eff.org/IP/DMCA/states/200304_sdmca_eff_analysis.php
The rise of the Digital Trade Agenda is downstream of tech industry consolidation, the orgy of mergers that saw the internet transformed into “five giant websites, each filled with screenshots of text from the other four”:
https://twitter.com/tveastman/status/1069674780826071040
Li’s taxonomy of regulatory capture is useful and important, and it’s complimented by an analysis of failures in antitrust enforcement. Market consolidation has produced firms that are more powerful than the governments that are supposed to keep them honest. When the teams have more power than the ref, the game will never be fair:
https://doctorow.medium.com/small-government-fd5870a9462e
The tech industry aren’t really adverse to the entertainment industry, at least not where it counts. They are all part of the business lobby, whose regulatory priorities are broadly shared, even if they disagree at the margins. Dayen describes how the Digital Trade Agenda is playing out in IPEF, the treaty with more than a dozen Pacific Rim countries: “It would prohibit governments from reviewing or prescreening algorithms for violations of labor law, competition policy, or nondiscrimination statutes. It would bar limitations on data flows or storage. And it would treat policies that have greater impacts on the large tech firms as illegal trade barriers. These terms could block signatory countries from writing laws that take on any of these issues.”
Those aren’t tech priorities — those are corporate priorities. The success of the “Digital Trade Agenda” isn’t just because tech grew up and started lobbying — it’s because the things they lobby for are the things every business wants: no labor protection, no antitrust, no privacy.
That’s the “schema” that matters: the bedrock assumption that job of US trade policy is to make sure that workers and residents abroad have no rights, with the obligation on America to dismantle the few rights that remain intact in its borders to satisfy the “obligation” it actually insisted on.
Later this week (Apr 20/21), I’m speaking in Chicago at the Stigler Center’s Antitrust and Competition Conference.
This weekend (Apr 22/23), I’m at the LA Times Festival of Books.
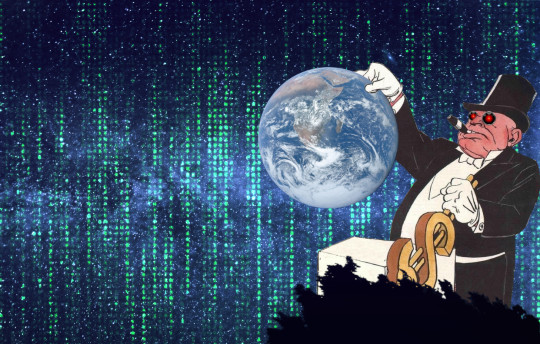
[Image ID: The Milky Way. Standing to the left of the frame is a giant ogrish figure, a top-hatted, cigar-chomping caricature of a capitalist. He emerges from behind a silhouetted tree, towering over it. With one white-gloved hand, he is yanking a golden, dollar-sign-shaped lever at a control box. With the other hand, he disdainfully dangles a 'big blue marble' image of Earth from space. The starry sky is partially blended with a green-on-black 'code waterfall' effect in the style of the Matrix movie open credits. The ogre's eyes have been replaced with the glaring red eyes of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.']
Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Andy (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:The_Milky_Way_and_Andromeda_Galaxies.jpg
CC BY 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#us trade representative#scholarship#regulatory capture#wendy li#ustr#usmca#digital trade policy#trade#anti-counterfeiting trade agreement#us canada mexico agreement#US International Trade Commission#USITC#copyfight#collective action problems#collusion#monopoly#big tech#how the sausage gets made#ipef#Indo-Pacific Economic Framework#thanks obama#Digital Trade Working Group#ethnography#third face of power
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
this song ain’t got no right to be scratchin’ my brain as much as it does
#and i mean that as a compliment#Seven.txt#music stuff#Warren Zeiders#Spotify#gonna start making more use of Tumblr’s features and putting the actual songs i’m obsessed with in the body of posts#instead of just talking abt them in tags. i like music and y’all r gonna Hear about it no matter how bad my taste may be#anyways i’m at an internal war over this song#half of me is like ‘it’s just one of a million Mainstream Country Songs where some white guy sings abt heartbreak. what’s so great abt it?’#but the other half of me is like ‘yeah but. ur weak to that shit. that’s ur kryptonite bitch. it’s in ur blood. we Know this.’#‘also. nice voice + country accent + he’s blaming Himself and not just the girl + 2:40-3:00 makes u go apeshit every time.’#‘Also the cover image is hot as hell and it makes u think of that shot of Boothill standing at that pool table.’#‘oh yeah And the whole damn thing is giving off Seth YuuriVoice vibes. so like. yeah’#and i nod my head in reluctant agreement like yeah ok i guess ur right. damn#anyways if anyone needs me i’ll be in the corner listening to this on loop until i make myself sick of it#hsr boothill#Seth YV#yea fuck it i’ll tag them too why not#if anyone disagrees with me pls keep it to yourself it’s just my opinion pls let me have it in peace
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Im sorry but this trend of "stay at home girlfriend" that's being glorified is the saddest fucking thing.
First of all never let anyone control your finances and solely rely on another for that because if they leave you're stuck with nothing. If they die you are stuck with nothing. If they are abusive and you need to get outta dodge you got nothing. Never let anyone have that power over you whether man or woman or literally anyone else.
2ndly it's also sad to say you cook, you clean, you wash the literal smudged underwear of some schmup, you're doing the full time work in their place and all for nothing but to get to call yourself "girlfriend". You don't get paid, you don't have the same tax benefits that you might have from marriage, you can't hop onto their insurance, you don't get anything because you're stuck with a person who doesn't view you as anything more than a live-in bangmaid with little value outside of that because they know you got so little self worth that you allow yourself to get used as a doormat.
#i do wanna say before anyone twists my words this aint about the crowd who just doesnt want to get married#and are fine living together and just doing normal couple things#this doesnt apply to them normally because most of them have a lot of other agreements and split household things#this aint about them nor is it about most standard housewives/househusbands either#because theres a big difference and a lot of nuance and even they tend to split more responsibility#and what we got here isn't a split of responsibility its just all going on one party with no payoff other than being financially controlled#this is for the trad girlies who can't even aspire to be a tradwife and just settled for... well a whole heck of a low lower#and are often not understanding the bad and horrendous deal they are putting themselves into#because they have so much self loathing from the internalized misogyny they have#married or no again never let anyone control your money#but its just an extra layer of whack to give everything up and all possible safety nets for the title of just merely... girlfriend???
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Song of the Day: May 22
"And So It Goes” Billy Joel cover by Jennifer Warnes
#song of the day#I'd never heard this version of the song before that fanvid I reblogged earlier and it is by far my favorite now#no shade to Billy Joel but damn#'and so it goes and so it goes / and you're the only one / who knows'#truly heartbreaking delivery#in other news today I got the first third of the Idiot Project completed#(clarification: there are three segments and I've been working on them all and now one is completely done and I'm very glad#I'm not only just now 33% of the way done with the project overall. I'd become a mollusc)#I had a breakthrough with the financials data I've been trying to compile#the 'correct' numbers I've been told to compare myself to don't include all the transactions!#there are specific internals codes I should have known to exclude because they get recorded but never reported#a very frustrating epiphany but whatever. I get it#(I mean to say. the best borscht in cherry grove is money laundering but my university is operating by 'pass-along agreement'#okay sure whatever y'all say. not my business and I'm not mad. I'm just sipping my tea real loud don't mind me)#I got this information too thoroughly wrapped in 'you should already know this obvious thing' to actually get an explanation#but I can see the shape of it if I squint. there's a politics bit going on and I get it. I do get it. but y'all. it's the shape of bullshit#anyway now I know how it works and I can account for it so I've built in a little filter and now my financials data makes sense!!#it actually makes sense now babes this is huge!! two months!! two months of the Idiot Project and now it's a third-chunk down!!#tomorrow I will make no progress whatsoever because I have to work graduation but on Friday when I have my stupid awful meeting!#she will ask me again if I am done! and I will say Look!! I am 1 out of 3 done!!#she will not be impressed but I will know. I will know she is wrong
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Then you're no better than the Empire" - Rebels S3 E13 (Ezra talking to Saw)
"I'm condemned to use the tools of my enemy to defeat them" - Andor S1 E10 (Luthen)
I really really hope people don't pit Rebels and Andor against each other because together they are so interesting, two sides of the same story, getting at the same themes but in totally different ways.
Does anybody really have an answer to this philosophical question anyways, whether the ends justify the means? I'm not sure we can say who is right, only that it takes everyone in the Rebellion to ultimately overthrow the Empire
#Also now that we know Saw knows Luthen#can you imagine his internal response to hearing this from Ezra and having the whole Ghost crew nod in agreement#like wow this whole team is crazy huh#different rebellions#same empire#andor#star wars andor#star wars rebels#ghost crew#ezra bridger#saw guerrera#luthen rael#star wars
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
argh you just know there’s something a little shady under that whole retirement situation :))))
#sorry i have an unhealthy parasocial attachement to that old man but#like#either he unfollowed them bc retiring bc of health concerns is probably not fun and having the whole travel log rubs salt on the wound#which is the charitable explanation but still depressing#or he might've been forced into retirement or smth and there's bad blood :)))))#right when nikki talks about making new material#mick ''unclear status in the band as so far a touring retirement was retirement from all meaningful activities of the band'' mars#unfollows their social media#like he WAS kinda sweeped under the rug following retirement but it's not necessarily out of character for him#at least whether he likes it or not that's how he's handled it since he's been in motley#but like. is it that crazy to think it COULD have happened that he's being excluded from this hypothetical new music#and isn't taking it well#like i'm not trying to say the others are horrible evil assholes like just the geographical distance will cause exclusion#and while that would be painful to everyone to be excluded in such a way it's not necessarily ethically wrong or whatever#we don't know what they discuss or not and what kind of internal agreement they have#BUT THEY DO HAVE A HISTORY OF BEING PETTY BITCHES#AND IT WOULDN'T BE TOO FAR FETCHED TO SAY THEY MIGHT'VE WENT AND BEEN DICKS TO EACH OTHER AGAIN#WOULDN'T BE THE FIRST TIME#like idk if say. i was in mick's shoes. and i. say. learned from social media that the band i'm supposed to work with is making new music#without me#after 40 years#and didn't warn me or didn't discuss this with me or something#i'd be pretty pissed#now of course i'm not saying this is what happened#i'm just saying it might have happened#and the entire basis of this anyway is that i'm very sad my parasocially beloved old man might be upset#and the status quo of general peace and happiness my parasocially beloved band might be disturbed#and i need to talk it out#so yeah#broadcasting my misery
8 notes
·
View notes