#Packet Data Network Gateway
Text

Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) Market Landscape: Trends, Opportunities, and Key Industry Players
The Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) market stands at the forefront of the telecommunications industry, driven by the burgeoning need for advanced network solutions capable of managing the exponential growth in mobile data traffic and enabling new technology paradigms. Projected to reach $17.05 billion by 2028, the market is expected to experience a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.4% from 2021 to 2028. This growth trajectory is a testament to the vital role vEPC solutions play in optimizing network performance, reducing operational costs, and supporting the transition to next-generation technologies like 5G.
In this comprehensive analysis, we explore the driving forces behind the vEPC market’s expansion, the challenges it faces, and the key players shaping its evolution. We also offer insights into the market’s future outlook and strategic opportunities for stakeholders.
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=5201
Market Overview
Definition and Importance of vEPC
Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) refers to the virtualization of the Evolved Packet Core (EPC) network architecture, which is a critical component of mobile telecommunications systems. vEPC enables operators to manage their network functions more efficiently by virtualizing network components and leveraging cloud-based solutions. This approach allows for enhanced scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, essential for handling the increasing volume of mobile data and supporting new services and applications.
The vEPC architecture typically includes several key elements, such as the Serving Gateway (SGW), the Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW), and the Mobility Management Entity (MME). By virtualizing these components, operators can achieve greater operational efficiency, reduce capital and operational expenditures, and improve service delivery.
Drivers of Market Growth
Surge in Mobile Data Traffic
One of the primary drivers of the vEPC market is the unprecedented growth in mobile data traffic. As consumer and enterprise demand for high-speed internet and data-intensive applications increases, telecommunications operators are compelled to adopt advanced network solutions to handle this traffic effectively. vEPC solutions offer the scalability and flexibility needed to accommodate growing data volumes and ensure optimal network performance.
Cost Reduction Imperatives
Reducing operational expenditures (OPEX) and capital expenditures (CAPEX) is a significant motivator for adopting vEPC solutions. Traditional network infrastructures are often costly to maintain and upgrade. By transitioning to virtualized solutions, operators can achieve substantial cost savings through more efficient resource utilization, reduced hardware requirements, and simplified network management.
IoT Deployment
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and applications is another critical factor driving the vEPC market. IoT deployments require robust and scalable network architectures capable of supporting a large number of connected devices and handling diverse data traffic types. vEPC solutions are well-suited to meet these demands, providing the necessary flexibility and performance to support IoT ecosystems.
Demand for Broadband Services
The growing demand for high-speed broadband services over mobile networks is fueling the expansion of vEPC solutions. Consumers and businesses alike are seeking faster and more reliable internet connections, driving operators to invest in advanced network technologies. vEPC solutions enable operators to deliver enhanced broadband experiences by optimizing network performance and increasing capacity.
Adoption of Cloud-Native 5G Core
The transition to cloud-native 5G core architectures is creating new growth opportunities for vEPC vendors. Cloud-native solutions offer improved scalability, agility, and efficiency compared to traditional network architectures. As operators adopt 5G technologies and explore the potential of cloud-native networks, the demand for vEPC solutions that integrate seamlessly with these new architectures is expected to grow.
Challenges Facing the vEPC Market
Security Risks
Despite its advantages, vEPC infrastructure introduces new security challenges. The virtualization of network functions can create vulnerabilities that may be exploited by cyber threats. Ensuring the security of virtualized network components and protecting against potential attacks is a critical concern for operators and vendors alike. Addressing these security risks requires ongoing vigilance and the implementation of robust security measures.
Awareness and Adoption Barriers
A lack of awareness about the benefits and capabilities of vEPC solutions can impede market growth. Many organizations may not fully understand the advantages of virtualization or may be hesitant to invest in new technologies due to concerns about complexity or integration challenges. Educating stakeholders about the benefits of vEPC and demonstrating successful use cases can help overcome these barriers and drive adoption.
Key Players in the vEPC Market
The vEPC market is characterized by the presence of several leading companies, each contributing to the sector's growth through innovation and technology advancements. Below, we provide an overview of some of the key players shaping the vEPC market.
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Company Overview: Cisco Systems, Inc. is a global technology leader specializing in networking, security, collaboration, and cloud solutions. With a comprehensive portfolio spanning multiple business segments, including Infrastructure Platforms, Services, Applications, Security, and Other Products, Cisco is a major player in the vEPC market.
vEPC Offerings: Cisco offers advanced technologies such as IP, security, optical networking, and wireless solutions. The company's vEPC solutions are designed to optimize network performance, enhance scalability, and reduce costs.
Global Presence: Cisco operates across the Americas, EMEA (Europe, the Middle East, and Africa), and APJC (Asia-Pacific and Japan). Its extensive distribution network and subsidiaries, including Cisco WebEx, OpenDNS, and BroadSoft, further bolster its global reach.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson SE
Company Overview: Ericsson is a multinational telecommunications company renowned for its leadership in 4G and 5G mobile technologies. The company operates through four segments: Networks, Digital Services, Managed Services, and Emerging Business and Other.
vEPC Offerings: Ericsson's vEPC portfolio includes mobile and fixed network infrastructure, telecom services, and broadband solutions. The company's expertise in mobile technologies positions it as a key player in the vEPC market.
Global Presence: Ericsson has a wide-reaching presence across North America, Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, Africa, Northeast Asia, Southeast Asia, Oceania, and India. Its global footprint is supported by subsidiaries such as Ericsson-LG, Ericsson-Nikola Tesla, and Cenx, Inc.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Company Overview: Huawei is a leading provider of telecommunication solutions, specializing in wireline, wireless, and IP technologies. The company operates through four business segments: Carrier Business, Enterprise Business, Consumer Business, and Other.
vEPC Offerings: Huawei's vEPC portfolio includes enterprise wireless, Cloud Core, carrier networks, telecom services, and enterprise networking solutions. The company's innovative solutions are designed to meet the demands of modern network environments.
Global Presence: Huawei has a significant presence in China, EMEA, APAC (Asia-Pacific), and America. Key subsidiaries include Huawei Device Co., Ltd and Shanghai Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Affirmed Networks, Inc.
Company Overview: Affirmed Networks specializes in transforming mobile data networks through advanced intelligence and virtualization. Acquired by Microsoft in 2020, the company operates under Microsoft's Intelligent Cloud segment.
vEPC Offerings: Affirmed Networks provides solutions for IoT virtualization, vEPC, and cloud-native mobile core technologies. Its offerings include 5G NR, virtualized DPI, GiLAN services, and optimized IoT access.
Global Presence: Affirmed Networks operates in the U.S., India, the UAE, and Czechia, leveraging Microsoft’s global reach and resources.
Mavenir Systems, Inc.
Company Overview: Mavenir Systems, headquartered in Texas, U.S., is a prominent telecommunication software company focused on redefining mobile network economics for service providers.
vEPC Offerings: Mavenir's core capabilities include VoLTE, VoWiFi, vEPC, and virtualized RAN. The company's solutions are designed to accelerate the transformation of mobile networks.
Global Presence: Mavenir operates across North America, the Caribbean & Latin America, Europe, the Middle East & Africa, Asia-Pacific, and South Asia. Subsidiaries include Ranzure Networks, Netonomy, and Aquto Corporation.
Nokia Corporation
Company Overview: Nokia is a multinational communications company engaged in manufacturing mobile devices, network infrastructure, and advanced technologies. It operates through four segments: Networks, Nokia Software, Nokia Technologies, and Other.
vEPC Offerings: Nokia’s vEPC solutions are part of its Networks segment and include core networks, mobile and fixed infrastructure, and 5G solutions.
Global Presence: Nokia has a broad presence across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Greater China, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Its subsidiaries include Nokia Networks, Alcatel Lucent, Scalado, and Novarra, Inc.
ZTE Corporation
Company Overview: ZTE is a telecommunications and networking company offering a range of communication systems, including network slicing software and services. The company operates through three segments: Consumer Business, Carrier Networks, and Government and Corporate Business.
vEPC Offerings: ZTE’s vEPC portfolio includes core networks, mobile and fixed infrastructure, network automation, 5G services, and Cloud Core networks.
Global Presence: ZTE operates in China, Europe, the Americas, Oceania, and Africa, supported by subsidiaries such as Double Fine Productions, Inc., and GitHub, Inc.
F5 Networks, Inc.
Company Overview: F5 Networks is a networking company specializing in web application technologies. The company operates through two segments: Products and Services.
vEPC Offerings: F5 Networks provides vEPC solutions including SGI, virtual application delivery controllers, diameter signaling, and IMS networks.
Global Presence: F5 Networks has a significant presence in the Americas, EMEA, and Asia-Pacific, with subsidiaries like Volterra, Inc. and NGINX, Inc.
NEC Corporation
Company Overview: NEC Corporation is a multinational IT and electronics company specializing in computer peripherals, IT infrastructure, and networking products. It operates through six segments: Public Solutions Business, Public Infrastructure Business, Enterprise Business, Network Services Business, Global Business, and Others.
vEPC Offerings: NEC’s vEPC portfolio includes core networks, mobile and fixed infrastructure, and 5G Core & LTE networks.
Global Presence: NEC has a global presence in North America, EMEA, Latin America, Asia, and Oceania, with subsidiaries such as Netcracker Technology Corporation and ABeam Consulting Ltd.
IPLOOK Technologies Co., Ltd.
Company Overview: IPLOOK Technologies, headquartered in Hong Kong, China, is a leading software company offering solutions for 3G/4G/5G core networks.
vEPC Offerings: The company provides end-to-end mobile core solutions, including 5G Core networks and IP multimedia subsystems (IMS).
Global Presence: IPLOOK Technologies operates primarily in China and Southeast Asia.
Future Outlook
The vEPC market is set to witness continued growth as telecommunications operators and enterprises increasingly adopt virtualized solutions to address the demands of modern network environments. The market’s expansion will be driven by several factors, including the need for enhanced network performance, cost efficiencies, and the integration of emerging technologies such as 5G and IoT.
Emerging Trends
Integration with 5G Networks: The integration of vEPC with 5G networks will be a significant trend, enabling operators to leverage the benefits of 5G while maintaining efficient and flexible core network operations.
Increased Focus on Security: As security concerns continue to evolve, there will be a heightened focus on developing robust security measures to protect virtualized network components from cyber threats.
Expansion of IoT Ecosystems: The growth of IoT ecosystems will drive demand for scalable and flexible vEPC solutions capable of supporting a large number of connected devices and diverse data traffic types.
Strategic Opportunities
Investment in R&D: Companies investing in research and development to innovate and enhance vEPC solutions will be well-positioned to capture market share and address emerging needs.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Strategic partnerships and collaborations with technology providers, network operators, and service integrators will create opportunities for growth and market expansion.
Geographic Expansion: Expanding into new geographic regions and emerging markets will provide additional growth opportunities for vEPC vendors, as demand for advanced network solutions continues to rise globally.
Read Full Report @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/virtualized-evolved-packet-core-market-5201
Conclusion
The Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) market represents a dynamic and rapidly evolving segment of the telecommunications industry. Driven by factors such as increasing mobile data traffic, cost reduction imperatives, IoT deployment, and the adoption of cloud-native 5G core solutions, the market is poised for substantial growth in the coming years.
While challenges related to security and awareness persist, the opportunities for innovation and expansion are significant. Key players in the market are actively contributing to its development through advanced technologies and strategic initiatives, shaping the future of network infrastructure.
As the industry navigates these developments, stakeholders must remain agile and forward-thinking to capitalize on emerging trends and opportunities. The continued advancement of vEPC solutions will play a crucial role in enabling next-generation network capabilities and meeting the evolving demands of the digital age.
Contact Us:
Meticulous Research®
Email- [email protected]
Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004
Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market#VEPC Market#VEPC Telecom#Packet Data Network Gateway#Mobility Management Entity
0 notes
Text
Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market Projected to Reach $19.87 Billion by 2031
According to the latest publication from Meticulous Research®, the virtualized evolved packet core (vEPC) market is projected to reach $19.87 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 19.3% from 2024 to 2031. This growth is driven by the significant increase in mobile data traffic volumes and the rising demand for high-speed data services. However, data security risks associated with vEPC infrastructure pose challenges to market growth.
#Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market#VEPC Market#Mobility Management Entity#Home Subscriber Server#Packet Data Network Gateway#Policy and Charging Rules Function#Mobile Private Network & Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MPN & MVNO)#Long-term Evolution & Voice over Long-term Evolution (LTE & VoLTE)#Telecom Operators#Internet of Things & Machine to Machine
0 notes
Text
What is the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
Introduction:
LoRaWAN serves as the communication protocol connecting the LoRa signal (which carries sensor data) to the respective application(s). To simplify, think of LoRa as the radio signal transporting the data, while LoRaWAN acts as the governing framework that dictates how this data travels and communicates within the network.

What is LoRa?
LoRa, short for Long Range, is a wireless technology known for its extended range and energy-efficient characteristics. It operates within unlicensed wireless frequencies, similar to how Wi-Fi utilizes the unregulated 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The specific frequency employed by LoRa varies depending on the geographic location of the deployment. For instance, in North America, LoRa operates in the 915 MHz band, while in Europe, it utilizes the 868 MHz band and in India it is 865 MHz to 867 MHz.
It is crucial to be aware of the legally permitted frequencies for LoRa deployments in each respective location. In terms of its communication range, LoRa can transmit data up to a distance of 10 kilometers in ideal conditions with a clear line of sight.
Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) technology can be categorized into two main types. On one hand, there's cellular LPWA, which utilizes mobile networks. Examples of cellular LPWA technologies include Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and Long Term Machine Type Communications (LTE-M). On the other hand, there's non-cellular LPWA like LoRa, which disseminates data by dividing it into encoded packets and transmitting them across various frequency channels and data rates.
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a network protocol that serves as the bridge between the LoRa signal, which carries sensor data, and the applications that use this data. In simpler terms, LoRa represents the radio signal responsible for transmitting the data, while LoRaWAN is the communication protocol that manages and defines how this data is transmitted across the network.
LoRaWAN offers several valuable advantages, including low power consumption, extensive coverage range, and cost-effective connectivity for devices that don't require high data transfer speeds. It's an excellent choice when cellular connectivity is too expensive or Wi-Fi coverage is unavailable. Some of the most compelling use cases for LoRaWAN include:
Agriculture: LoRaWAN's long-range capabilities provide reliable connectivity for rural applications where high data transfer rates are not necessary, making it ideal for agricultural applications. LoRaWAN sensors for agriculture are used for cattle management, soli monitoring, and temperature monitoring.
Asset Tracking and Logistics: LoRaWAN supports cost-effective location tracking of assets, with optimized battery life, making it a practical choice for asset management and logistics.
Smart Metering: LoRaWAN's sensors have the ability to reach even in underground utility locations makes it a suitable choice for smart metering applications.
Smart Homes: LoRaWAN can penetrate obstacles like walls and supports battery-powered devices with low data consumption, making it an attractive connectivity option for smart home applications.LoRaWAN sensors for smart homes are used for Air quality monitoring, water quality monitoring, and temperature & humidity monitoring.
Healthcare: The low power consumption, affordability, and reliability of LoRa technology make it suitable for connected health applications. IoT solutions based on LoRa hardware can monitor high-risk patients or systems around the clock, ensuring comprehensive health and medical safety management.LoRaWAN Gateways and sensors enhance production practices, enable efficient tracking and monitoring of shipments, and facilitate the development of cutting-edge medications.
Industrial Applications: LoRa-enabled devices and sensors play a crucial role in the transformation of industrial IoT operations like mentioned above. They digitize legacy processes and equipment, leading to increased profits, lower costs, and enhanced efficiency. These devices provide real-time data for predictive maintenance, machine health monitoring, reduced downtime, and more.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is it necessary to use game boosters?
As the network environment is getting better and better, the speed of the network is getting faster and faster, players have higher requirements for the experience of online games, which leads to the emergence of a lot of game accelerator software. In the face of so many accelerator products, for many people who have not used it, they really do not know how to choose. The product introduction is all about the advantages of their own accelerator products, and the online evaluation is uneven.
The main functions of game booster are:
Reduce the network delay of the game and stabilize the network speed.
Reduce the packet loss rate of the game.
Game booster software can be regarded as a desktop application, but it establishes a virtual gateway between the user and the server in the form of software. to put it simply, it will bypass the original unstable channel to reduce the delay and packet loss rate and provide a good game experience environment for gamers.
Therefore, the game vpn can not only accelerate the network speed but also improve the stability of the line and low packet loss rate. This is the main role of the network accelerator. As for whether some gamers want to use the network accelerator or not, it mainly depends on personal experience. Some gamers in coastal areas can log in normally without speed-up software, but most gamers, they need to use network accelerators. If you are playing the game in addition to other configurations and the network meets the requirements of the situation, there is a card screen, disconnected, you need to accelerate the speed-up software, if not card screen, the experience is good, then you can not use it.
Due to the inequality of network resources, there is a game accelerator. If the whole network is compared to a traffic route, it is just like the morning rush hour, evening rush hour or road failure, and the network arrangement will be unequal. For example, there are differences in the arrangement of network lines and routing resources, such as interception (inaccessible), congestion and so on.
So what role does the game vpn play in this? It is similar to our GPS navigation and can help us choose the best "route". The accelerator will send your game data to the server of the accelerator operator, and the data returned by the operator is the optimized direct connect route to solve the problems of delay, disconnection, and inaccessibility for us, so as to speed up the game.
In fact, the existence is reasonable, if the accelerator for the game network speed does not have the slightest effect, then there will not be so many teams and merchants continue to launch game accelerator software. In fact, playing national service is all right, and network problems are not likely to occur, but if you play foreign service, because most of the servers are abroad, with long distance and high delay, if you are naked, stutter, disconnection, delay and other network problems can be found everywhere. Therefore, a good game accelerator is of course necessary.
Therefore, if you want to have a better game experience, you also need to learn to choose a good game vpn. As for whether the effect of the accelerator is good or bad, it varies from person to person, just like buying clothes, everyone has different standards for "good". Generally speaking, you can choose formal, well-known ones, and the probability of payment is better than that of free ones.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Remote File Access - FTP
Lab Objective: Learn how to save configurations using File Transfer Protocol.
Lab Purpose: Any data which is not backed up, you risk losing. On corporate networks, you should have a detailed backup and recovery plan. You may well use Secure FTP or some other secure method. In this lab, we will back up your router configuration using FTP (File Transfer Protocol).
Lab Tool: Cisco Packet Tracer
Lab Topology:
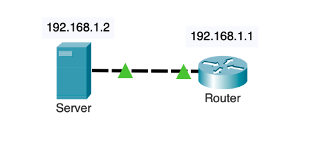
Task 1: Connect a router to a server using a cross-over cable.
Task 2:
Enter ‘no’ and press enter for the message. ‘Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialogue? [yes/no]:’
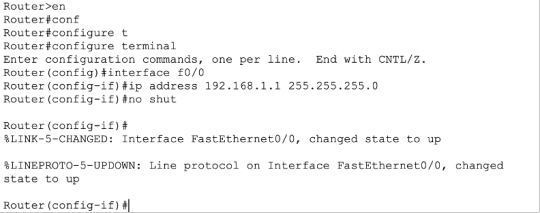
Configure an IP address on your Ethernet interface on your router.
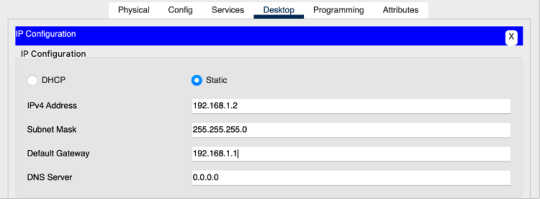
Task 3: Configure an IP address on your server's Ethernet interface. Set the default gateway address to the router.
Task 4: Ping the router from the server.

Task 5: Router configurations are stored in NVRAM, but you need to save the live configuration there in order to populate it. Use the ‘copy run start’ command in the privileged mode of the router. Any values inside the [] are the default, so just press the enter key.

Task 6: Configure FTP credentials on the server. User the username ‘demo’ and password ‘pass’. Trick all the access level boxes and then ‘Add’.
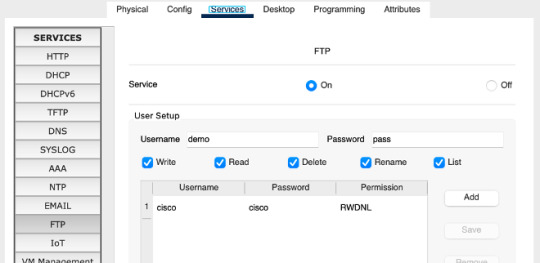
Task 7: Add the FTP username and Password to the router using the global configuration mode.

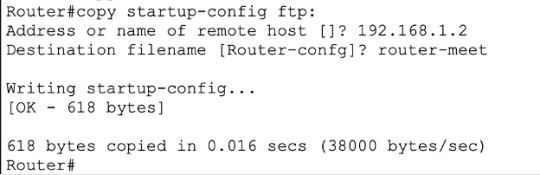
Task 8: Copy the router configuration to the FTP server. Rename the saved file to ‘router-meet’. If you had to copy it back, you would need to rename it to ‘Router-config’ but don’t worry about that for now.
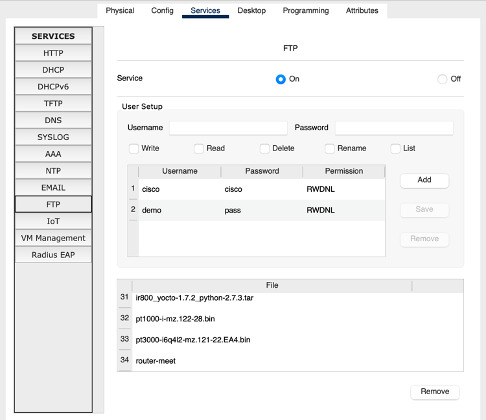
Task 9: Check that file is on the FTP server. You will have to click on another service and back onto FTP because there is no refresh key.
#ccna#ccna course#ccnatraining#ccnacertification#ccna cisco ccnp networkengineer ccie networking cybersecurity network technology training linux security ciscocert it datacenter ipv networ#networking#cybersecurity#IT
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Next-Gen Firewalls Showdown: 5 Top NGFWs for 2024

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) have become a critical component for protecting enterprise networks. As we look ahead to 2024, it’s essential to understand which NGFWs stand out in terms of features, performance, and overall value. This blog post provides a comprehensive next-generation firewall (NGFW) comparison, highlighting the top five NGFWs for 2024.
Introduction
The rise of sophisticated cyber threats has necessitated the adoption of advanced security measures. Traditional firewalls are no longer sufficient to protect against modern attacks. Enter next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), which offer enhanced capabilities such as deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and application awareness. In this next-generation firewall (NGFW) comparison, we will explore the top five NGFWs for 2024, examining their key features, strengths, and potential drawbacks.
1. Palo Alto Networks PA-Series
Overview
Palo Alto Networks is a leader in the cybersecurity space, and their PA-Series NGFWs are renowned for their robust security features and high performance. The PA-Series offers a range of models to suit different enterprise needs, from small businesses to large corporations.
Key Features
App-ID Technology: Identifies and controls applications, regardless of port, protocol, or encryption.
Threat Prevention: Blocks known and unknown threats using a combination of signature-based and behavioral analysis.
User-ID: Integrates with directory services to enforce security policies based on user identity.
Strengths
High Performance: Delivers excellent throughput and low latency.
Comprehensive Security: Offers a wide range of security features, including URL filtering, sandboxing, and SSL decryption.
Scalability: Suitable for organizations of all sizes.
Potential Drawbacks
Cost: Higher price point compared to some competitors.
Complexity: May require significant expertise to configure and manage.
2. Fortinet FortiGate
Overview
Fortinet’s FortiGate series is another top contender in the NGFW market. Known for its integrated security fabric, FortiGate NGFWs provide seamless protection across the entire network infrastructure.
Key Features
Security Fabric Integration: Connects with other Fortinet products for unified threat management.
High-Performance Security: Utilizes custom security processors to deliver high-speed threat protection.
Advanced Threat Protection: Includes features like antivirus, web filtering, and intrusion prevention.
Strengths
Unified Management: Centralized management console for easy administration.
Cost-Effective: Offers competitive pricing without compromising on features.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of deployment scenarios, from data centers to branch offices.
Potential Drawbacks
Learning Curve: May require time to fully understand and utilize all features.
Support: Some users report variability in the quality of customer support.
3. Cisco Firepower
Overview
Cisco Firepower NGFWs are designed to provide comprehensive threat protection and network visibility. Leveraging Cisco’s extensive security portfolio, Firepower NGFWs offer advanced threat intelligence and automation capabilities.
Key Features
Threat Intelligence: Integrates with Cisco Talos for real-time threat intelligence updates.
Advanced Malware Protection (AMP): Detects and blocks malware across the network.
Application Visibility and Control (AVC): Provides granular control over applications and users.
Strengths
Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other Cisco security products.
Automation: Automates routine security tasks to reduce administrative burden.
Visibility: Offers deep visibility into network traffic and user activity.
Potential Drawbacks
Cost: Higher total cost of ownership due to licensing and subscription fees.
Complexity: May require specialized knowledge to configure and manage effectively.
4. Check Point Quantum Security Gateways
Overview
Check Point’s Quantum Security Gateways are designed to deliver advanced threat prevention and unified security management. With a focus on scalability and performance, Quantum Security Gateways are ideal for large enterprises.
Key Features
ThreatCloud Intelligence: Leverages global threat intelligence to protect against emerging threats.
SandBlast Zero-Day Protection: Detects and mitigates zero-day attacks using advanced sandboxing techniques.
Unified Management: Centralized management platform for streamlined security operations.
Strengths
Scalability: Easily scales to meet the needs of large organizations.
Advanced Threat Prevention: Offers comprehensive protection against a wide range of threats.
User-Friendly Management: Intuitive management interface simplifies administration.
Potential Drawbacks
Cost: Premium pricing may be a barrier for smaller organizations.
Resource Intensive: May require significant hardware resources for optimal performance.
5. Sophos XG Firewall
Overview
Sophos XG Firewall combines advanced threat protection with intuitive management and reporting. Known for its ease of use, the XG Firewall is a popular choice for small to medium-sized enterprises.
Key Features
Synchronized Security: Integrates with Sophos endpoint protection for coordinated threat response.
Deep Learning Technology: Utilizes AI to detect and block advanced threats.
User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies configuration and management with an intuitive interface.
Strengths
Ease of Use: User-friendly design makes it accessible for organizations with limited IT resources.
Cost-Effective: Offers a good balance of features and affordability.
Integration: Works seamlessly with other Sophos security products.
Potential Drawbacks
Performance: May not offer the same level of performance as higher-end NGFWs.
Feature Set: Some advanced features may require additional licensing.
Conclusion
Choosing the right next-generation firewall is crucial for protecting your enterprise network against evolving cyber threats. This next-generation firewall (NGFW) comparison highlights the top five NGFWs for 2024, each offering unique strengths and capabilities. Whether you prioritize performance, ease of use, or advanced threat protection, there’s an NGFW on this list to meet your needs.
0 notes
Text
What is EPS bearer?

LTE network operates solely on the PS (Packet Switched) domain. Unlike previous generation networks, LTE does not have a CS (Circuit Switched) domain. UE must connect to at least one Packet Data Network (PDN) to facilitate data communication. In an EPS (Evolved Packet System), a PDN refers to an external data network, such as the internet or a corporate intranet. APNs (Access Point Names) are used as identifiers for PDNs.
The P-GW (PDN Gateway) resides at the boundary between the EPC (Evolved Packet Core) and the PDN. The EPS Bearer, which serves as a replacement for the PDP (Packet Data Protocol) context in UMTS networks, exists between the UE and the P-GW.
The EPS Bearer, as a tunnel, is essential for establishing and maintaining a reliable connection between UE and the PDN in LTE networks, ensuring seamless data communication and an enhanced user experience.
Source: What is EPS bearer? (iplook.com)
0 notes
Text
The Growing Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) Market: Driving Next-Gen Connectivity
The Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) Market was valued at USD 8.1 billion in 2023 and will surpass USD 23.5 billion by 2030; growing at a CAGR of 16.4% during 2024 - 2030. At the heart of this transformation is the Evolved Packet Core (EPC), the core network architecture for LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and 4G networks. However, as the demand for data grows and the transition to 5G accelerates, traditional EPC systems are struggling to keep up. Enter the Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) – a next-generation solution that is redefining how networks are built and managed.
Understanding vEPC
Virtualized Evolved Packet Core (vEPC) refers to the deployment of EPC functions using Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) technology. In a traditional EPC, network functions like the Serving Gateway (SGW), Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW), and Mobility Management Entity (MME) are implemented on dedicated hardware. In contrast, vEPC decouples these functions from physical hardware, allowing them to run as software instances on standard, off-the-shelf servers in a virtualized environment.
This shift to virtualization brings numerous benefits, including improved flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By leveraging NFV, service providers can dynamically allocate resources based on demand, scale their networks quickly, and reduce capital and operational expenditures. This makes vEPC an essential component in the evolution towards 5G networks and beyond.
Get a Sample Report: https://intentmarketresearch.com/request-sample/virtualized-evolved-packet-core-vepc-market-3649.html
Market Growth Drivers
The vEPC market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several key factors:
5G Rollout: As 5G networks become more widespread, the need for scalable and flexible core network solutions is paramount. vEPC provides the necessary foundation for 5G by enabling faster deployment, efficient resource utilization, and the ability to support diverse use cases, from enhanced mobile broadband to massive IoT connectivity.
Increased Data Traffic: The exponential growth in mobile data traffic, fueled by video streaming, social media, and IoT applications, is putting immense pressure on traditional network infrastructures. vEPC allows service providers to handle this surge in data traffic more effectively, ensuring seamless connectivity and improved user experiences.
Cost Efficiency: Virtualization reduces the need for expensive, proprietary hardware, enabling service providers to lower their capital and operational expenditures. Additionally, the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand helps in optimizing network costs, making vEPC a more cost-effective solution compared to traditional EPC.
Network Slicing: A key feature of 5G is network slicing, which allows operators to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure, each tailored to specific applications or services. vEPC plays a critical role in enabling network slicing by providing the flexibility and agility needed to create and manage these virtual networks efficiently.
Rapid Time-to-Market: In today’s fast-paced environment, the ability to launch new services quickly is crucial for staying competitive. vEPC enables service providers to reduce the time-to-market for new services by streamlining network deployment and management processes.
Market Challenges
While the vEPC market presents significant opportunities, it also faces challenges that could impact its growth:
Interoperability Issues: As vEPC involves integrating various network functions from different vendors, ensuring interoperability can be challenging. Service providers must carefully select compatible solutions to avoid integration issues that could lead to network performance degradation.
Security Concerns: Virtualized environments can be more vulnerable to security threats compared to traditional hardware-based systems. Ensuring robust security measures are in place is critical to protect sensitive data and maintain network integrity.
Skills Gap: The transition to virtualized networks requires new skill sets that may not be readily available within existing telecom teams. Investing in training and upskilling is necessary to fully leverage the benefits of vEPC.
Get an insights of Customization: https://intentmarketresearch.com/ask-for-customization/virtualized-evolved-packet-core-vepc-market-3649.html
The Future of vEPC
Looking ahead, the vEPC market is poised for continued growth as more service providers embrace virtualization and move towards 5G. The flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency offered by vEPC will be key to supporting the diverse and demanding use cases of future networks. As the technology matures, we can expect further innovations in areas such as automation, orchestration, and edge computing, all of which will enhance the capabilities of vEPC and drive its adoption.
0 notes
Text
SIP to PRI Gateway Suppliers in Dubai
Dubai’s dynamic business environment demands cutting-edge communication solutions, and SIP to PRI Gateways are becoming increasingly popular among companies looking to modernize their telecommunication systems. SIP to PRI Gateway suppliers in Dubai are meeting this demand by offering high-quality devices that bridge the gap between traditional PRI lines and modern SIP-based networks.
A SIP to PRI Gateway is a crucial tool for businesses that want to transition from legacy communication systems to VoIP without significant disruptions. These gateways convert the digital signals from a PRI line into IP packets that can be transmitted over an IP network, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of VoIP while maintaining their existing infrastructure.
In Dubai, where businesses operate in a fast-paced and competitive market, the ability to quickly adapt to new technologies is essential. SIP to PRI Gateways offer a seamless transition from traditional to modern communication systems, ensuring that businesses can continue to operate efficiently without significant downtime. Additionally, these gateways are compatible with various telecom providers, giving businesses the flexibility to choose the best service for their needs.
Cost efficiency is another major advantage of using SIP to PRI Gateways in Dubai. By converting PRI lines to SIP, businesses can reduce their communication costs, particularly for long-distance and international calls. This is especially important in Dubai, where businesses often have global operations and need to manage communication costs effectively.
Security is a top priority for businesses in Dubai, and SIP to PRI Gateways offer robust security features to protect communication data. These gateways include encryption, firewall protection, and secure remote management, ensuring that sensitive information remains private and secure, even when transmitted over public networks.
In conclusion, SIP to PRI Gateway suppliers in Dubai are providing essential tools for businesses looking to modernize their communication systems. These gateways offer cost savings, flexibility, reliability, and security, making them a valuable investment for any business operating in Dubai’s competitive market.
0 notes
Text
What is the Role of Firewalls in Network Security?
Network security and firewalls play a pivotal role. Imagine your network as a fortress. The firewall is akin to the gatekeeper, ensuring that only trusted individuals (or data packets) are allowed entry while keeping potential threats at bay. But what exactly is a firewall, and why is it so crucial in safeguarding our digital fortresses?
Types of Firewalls
Firewalls come in various flavors, each designed to offer different levels of protection and functionality.
Packet-Filtering Firewalls
These are the most basic types of firewalls. They inspect data packets, checking their source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols before deciding whether to allow or block them.
Stateful Inspection Firewalls
A step up from packet-filtering firewalls, stateful inspection firewalls track the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of the traffic. This means they can understand if incoming packets are responses to legitimate outgoing requests.
Proxy Firewalls
Also known as application-level gateways, proxy firewalls act as intermediaries between end users and the web. They can inspect and filter traffic deeper, providing more granular control over network traffic.
Next-Generation Firewalls
The latest in firewall technology, next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), combine traditional firewall functions with advanced features like intrusion prevention, application awareness, and cloud-delivered threat intelligence.
How Firewalls Work
At their core, firewalls work by applying a set of rules to incoming and outgoing traffic.
Basic Working Principle
Firewalls examine data packets and apply predefined rules to decide whether to allow or block them. These rules are based on various factors, such as IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols.
Rule-Based Filtering
Rule-based filtering is the backbone of most firewalls. Administrators set up rules that specify which types of traffic are permitted and which are denied.
Deep Packet Inspection
Some advanced firewalls perform deep packet inspection (DPI), which examines the data within the packet rather than just the packet headers. This allows for more sophisticated filtering based on the content of the traffic.
Key Features of Firewalls
Firewalls offer a range of features designed to enhance network security.
Access Control
Firewalls enforce access control policies, ensuring only authorized users and devices can access certain network parts.
Logging and Monitoring
Firewalls keep logs of all traffic that passes through them, providing valuable data for monitoring and analyzing network activity.
VPN Support
Many firewalls support Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections, allowing secure remote access to the network.
Threat Prevention
Modern firewalls include features to detect and block various types of threats, such as malware and intrusions.
Firewalls in Different Network Setups
Firewalls are used in various settings, each with its own unique requirements.
Firewalls for Home Networks
Home networks often use simple, user-friendly firewalls to protect against primary threats and control internet access.
Firewalls for Small Businesses
Small businesses need more robust firewalls with advanced features like VPN support and comprehensive logging.
Enterprise-Level Firewalls
Enterprises require high-performance firewalls to handle large traffic volumes and provide advanced threat detection and prevention capabilities.
Advantages of Using Firewalls
Firewalls offer numerous benefits that make them indispensable in network security.
Enhanced Security
By filtering traffic and blocking malicious data, firewalls provide a crucial layer of security.
Monitoring and Logging Capabilities
Firewalls generate logs that help administrators monitor network activity and identify potential security incidents.
Policy Enforcement
Firewalls enforce security policies, ensuring users adhere to the organization's rules and guidelines.
Protection from Malware and Cyber Attacks
Firewalls help protect against various threats, from simple malware to complex cyber-attacks.
Challenges and Limitations of Firewalls
Despite their many advantages, firewalls are not without challenges.
Performance Impact
Firewalls can introduce latency and impact network performance, especially when performing deep packet inspection.
Complexity in Configuration
Properly configuring a firewall can be complex and requires specialized knowledge.
False Positives/Negatives
Firewalls may block legitimate traffic (false positives) or allow malicious traffic (false negatives).
Evolving Threat Landscape
As cyber threats evolve, firewalls must be continuously updated and improved to remain effective.
Best Practices for Firewall Configuration
It's important to follow best practices in their configuration and management to get the most out of firewalls.
Regular Updates and Patching
Keeping firewalls updated with the latest patches and firmware is crucial for maintaining security.
Defining Clear Policies
Clear, well-defined policies help ensure firewalls effectively protect the network.
Monitoring and Analyzing Logs
Regularly monitoring and analyzing firewall logs helps detect and respond to potential security incidents.
Segmenting Networks
Segmenting the network with firewalls can help contain potential breaches and limit their impact.
Case Studies: Firewalls in Action
Real-world examples illustrate the importance and effectiveness of firewalls.
Real-World Examples
Case studies from various industries demonstrate how firewalls have been used to protect networks and data.
Lessons Learned
These examples provide valuable lessons on the best practices and common pitfalls in firewall implementation.
Future of Firewalls
The field of firewall technology is constantly evolving.
Trends and Innovations
Emerging trends and innovations promise to make firewalls even more effective and versatile.
Integration with Other Security Measures
Future firewalls will increasingly integrate with other security tools and technologies to provide comprehensive protection.
Firewalls and Compliance
Firewalls play a critical role in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Requirements
Various regulations mandate the use of firewalls to protect sensitive data.
Industry Standards
Adhering to industry standards for firewall configuration and management helps organizations maintain compliance.
Common Myths about Firewalls
Several things need to be addressed about firewalls.
Firewalls Are Set-and-Forget Solutions
In reality, firewalls require ongoing management and updates to remain effective.
Firewalls Make Networks Impenetrable
While firewalls are an essential security measure, they could be more foolproof. They should be part of a multi-layered security strategy.
Firewalls vs. Other Security Measures
Firewalls are often compared to other security tools.
Comparing Firewalls with IDS/IPS
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) serve different purposes but can complement each other.
Complementary Security Tools
For comprehensive protection, firewalls should be used with other security measures, such as antivirus software and encryption.
Implementing Firewalls: A Step-by-Step Guide
A structured approach is essential for successful firewall implementation.
Assessing Needs
Evaluate the specific needs of your network to choose the right firewall solution.
Choosing the Right Firewall
Consider factors like performance, features, and budget when selecting a firewall.
Deployment and Testing
Proper deployment and thorough testing ensure the firewall is configured correctly and functioning as intended.
Conclusion
Firewalls are a cornerstone of network security, providing essential protection against various threats. While they are not without challenges, their benefits far outweigh the limitations. By following best practices and staying informed about emerging trends, organizations can effectively use firewalls to safeguard their networks. You can find more at Netseg for more detail.
FAQs
What is a firewall in simple terms?
A firewall is a security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Can firewalls protect against all types of cyber attacks?
While firewalls are critical to network security, they are not a standalone solution. They are most effective when used in conjunction with other security measures.
How often should firewall rules be updated?
Firewall rules should be reviewed and updated regularly, at least quarterly, to adapt to new threats and changes in the network.
Are software firewalls effective?
Software firewalls can be effective, especially for individual devices or smaller networks. However, they are often used with hardware firewalls for added security.
What is the difference between a firewall and antivirus software?
A firewall controls network traffic to prevent unauthorized access, while antivirus software scans and removes malicious software from devices.
0 notes
Text
Ground Antenna Trio to Give NASA's Artemis Campaign 'LEGS' to Stand On - NASA
New Post has been published on https://sunalei.org/news/ground-antenna-trio-to-give-nasas-artemis-campaign-legs-to-stand-on-nasa/
Ground Antenna Trio to Give NASA's Artemis Campaign 'LEGS' to Stand On - NASA

New 66-foot-wide antenna dishes will be built, online, and operational in time to provide near-continuous communications services to Artemis astronauts at the Moon later this decade.
Called LEGS, short for Lunar Exploration Ground Sites, the antennas represent critical infrastructure for NASA’s vision of supporting a sustained human presence at the Moon.
The first three of six proposed LEGS are planned for sites in New Mexico, South Africa, and Australia.
LEGS will become part of NASA’s Near Space Network, managed by the agency’s Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program and led out of Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
NASA’s LEGS can do more than help Earthlings move about the planet.
Three Lunar Exploration Ground Sites, or LEGS, will enhance the Near Space Network’s communications services and support of NASA’s Artemis campaign.
NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program maintains the agency’s two primary communications networks — the Deep Space Network and the Near Space Network, which enable satellites in space to send data back to Earth for investigation and discovery.
Using antennas around the globe, these networks capture signals from satellites, collecting data and enabling navigation engineers to track the mission. For the first Artemis mission, these networks worked in tandem to support the mission as it completed its 25-day journey around the Moon. They will do the same for the upcoming Artemis II mission.
To support NASA’s Moon to Mars initiative, NASA is adding three new LEGS antennas to the Near Space Network. As NASA works toward sustaining a human presence on the Moon, communications and navigation support will be crucial to each mission’s success. The LEGS antennas will directly support the later Artemis missions, and accompanying missions like the human landing system, lunar terrain vehicle, and Gateway.
“One of the main goals of LEGS is to offload the Deep Space Network,” said TJ Crooks, LEGS project manager at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “The Near Space Network and its new LEGS antennas will focus on lunar missions while allowing the Deep Space Network to support missions farther out into the solar system — like the James Webb Space Telescope and the interstellar Voyager missions.”
The Near Space Network provides communications and navigation services to missions anywhere from near Earth to 1.2 million miles away — this includes the Moon and Sun-Earth Lagrange points 1 and 2. The Moon and Lagrange points are a shared region with the Deep Space Network, which can provide services to missions there and farther out in the solar system.
The LEGS antennas, which are 66 feet in diameter, will be strategically placed across the globe. This global placement ensures that when the Moon is setting at one station, it is rising into another’s view. With the Moon constantly in sight, the Near Space Network will be able to provide continuous support for lunar operations.
As a satellite orbits the Moon, it encodes its data onto a radio frequency signal. When a LEGS antenna comes into view, that satellite (or rover, etc.) will downlink the signal to a LEGS antenna. This data is then routed to mission operators and scientists around the globe who can make decisions about spacecraft health and orbit or use the science data to make discoveries.
The LEGS antennas are intended to be extremely flexible for users. For LEGS-1, LEGS-2, and LEGS-3, NASA is implementing a “dual-band approach” for the antennas that will allow missions to communicate using two different radio frequency bands — X-band and Ka-band. Typically, smaller data packets — like telemetry data — are sent over X-band, while high-resolution science data or imagery needs Ka-band. Due to its higher frequency, Ka-band allows significantly more information to be downlinked at once, such as real-time high-resolution video in support of crewed operations.
Further LEGS capacity will be sought from commercial service providers and will include a “tri-band approach” for the antennas using S-band in addition to X- and Ka-band.
The first LEGS ground station, or LEGS-1, is at NASA’s White Sands Complex in Las Cruces, New Mexico. NASA is improving land and facilities at the complex to receive the new LEGS-1 antenna.
The LEGS-2 antenna will be in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, located near Cape Town. In partnership with SANSA, the South African National Space Agency, NASA chose this location to maximize coverage to the Moon. South Africa was home to a ground tracking station outside Johannesburg that played a role in NASA’s Apollo missions to the Moon in the 1960s. The agency plans to complete the LEGS-2 antenna in 2026. For LEGS-3, NASA is exploring locations in Western Australia.
These stations will fully complement the existing capabilities of the Near and Deep Space Networks and allow for more robust communications services to the Artemis campaign.
The Near Space Network is funded by NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program office at NASA Headquarters in Washington and operated out of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
0 notes
Text
In its latest research, Meticulous Research® projects that the global virtualized evolved packet core (vEPC) market will surpass $19.87 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 19.3% between 2024 and 2031. The market expansion is fueled by the soaring volumes of mobile data traffic and the increasing demand for high-speed data services, particularly as 5G networks become more prevalent. However, concerns around data security within vEPC infrastructure pose challenges to this growth.
On the upside, growing investments in 5G technology, the rising shift toward cloud-native 5G core solutions, and the increasing adoption of IoT technology are set to create substantial growth opportunities in the market. Yet, reliability concerns and a lack of awareness around vEPC solutions remain significant obstacles.
Additionally, the integration of edge computing with vEPC technologies is emerging as a key trend, further propelling the market forward.
Download Sample Report Here @ https://www.meticulousresearch.com/download-sample-report/cp_id=5201
Market Segmentation Overview
The virtualized evolved packet core market is broadly segmented by component, application, deployment mode, end user, and geography. The study offers a detailed analysis of industry competitors and regional markets, providing a comprehensive overview of the sector's future trajectory.
Component Analysis
The market is divided into solutions and services. The solutions segment, which includes critical components such as mobility management entities, home subscriber servers, and packet data network gateways, is expected to account for the largest share of the market in 2024. The growing need to reduce both operating and capital expenditures, combined with rising mobile data traffic and the advantages of vEPC solutions—such as agility, scalability, and real-time low-latency application delivery—are driving demand in this segment.
Collaboration among major companies to enhance network performance for both 4G and 5G users is accelerating innovation. A key example is the December 2022 collaboration between T-Mobile USA and Cisco Systems to launch the world’s largest highly scalable cloud-native converged core gateway, significantly improving speed and latency for users.
Conversely, the services segment, which encompasses professional services (such as integration, consulting, and training services) and managed services, is forecasted to experience the highest growth rate during the forecast period. The increasing need for consulting and support services, particularly among telecom operators, is driving this growth.
Application Insights
By application, the vEPC market is segmented into Mobile Private Networks & Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MPN & MVNO), Long-term Evolution (LTE & VoLTE), and Internet of Things & Machine to Machine (IoT & M2M). In 2024, the MPN & MVNO segment is projected to capture the largest market share, driven by the growing penetration of mobile devices, rising demand for affordable mobile services, and the need for high-speed internet connectivity. Companies are increasingly adopting vEPC solutions to enhance LTE and IMS network revenues through cost-effective deployments. For example, in April 2022, Summa Networks partnered with Cirrus Core Networks to offer a fully managed packet core for MNOs and MVNOs.
Meanwhile, the IoT & M2M segment is expected to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The growing need for autonomous monitoring of connected devices and data-driven decision-making processes is driving demand in this segment.
Deployment Mode and End-User Insights
The market is also segmented into cloud-based and on-premise deployments. In 2024, the on-premise segment is forecasted to hold the largest market share, largely due to its ability to offer greater control over network infrastructure, particularly for large enterprises.
However, the cloud-based deployment segment is anticipated to grow at a faster pace, driven by the cost-efficiency, scalability, and superior flexibility offered by cloud-based solutions. The increasing use of cloud networks for vEPC and growing demand for seamless customer data management are key growth drivers for this segment.
Regarding end users, telecom operators are expected to dominate the market, holding the largest share in 2024. The segment’s growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of vEPC solutions by telecom providers to improve latency issues, enhance IT agility, and reduce operational and capital expenditures. Notably, this segment is also forecasted to register the highest growth rate during the forecast period.
Telecom providers are increasingly focusing on improving network performance, bandwidth, and connectivity to stay competitive. For instance, in February 2024, NEC Corporation partnered with NTT DOCOMO to provide a virtualized radio access network (vRAN) for 5G commercial network services, further enhancing DOCOMO’s nationwide 5G infrastructure.
Regional Market Insights
Geographically, North America is expected to lead the virtualized evolved packet core market in 2024, driven by increasing investments in 5G telecom infrastructure, government support for advanced networking technologies, and the widespread adoption of cloud-based services. Recent collaborations, such as the 5G deployment initiative between Ericsson and Nex-Tech Wireless in rural Kansas, highlight the ongoing advancements in North America’s telecom landscape.
Asia-Pacific, however, is set to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by the region’s expanding mobile subscriber base, rapid growth in mobile data traffic, and increasing deployment of 5G-ready infrastructure. Leading companies are targeting this region for growth, with recent developments such as Asia-Pacific Telecom’s partnership with Ericsson to modernize Taiwan’s LTE network using Ericsson’s 5G NSA solutions.
Key Industry Players
The virtualized evolved packet core market is fiercely competitive, with key players such as Cisco Systems, Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson, Huawei Technologies, Samsung Electronics, Nokia Corporation, and Microsoft’s Affirmed Networks leading the charge. These companies are focused on strengthening their market positions through strategic partnerships, product launches, and innovative technological solutions.
Other notable players include Mavenir Systems, ZTE Corporation, F5 Inc., NEC Corporation, and Intel Corporation. As the demand for cloud-native solutions and 5G infrastructure continues to grow, these industry leaders are expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the vEPC market.
In conclusion, the global virtualized evolved packet core market is on a robust growth trajectory, fueled by advancements in 5G, IoT, and cloud technologies. As telecom operators and enterprises continue to adopt vEPC solutions, the market is set to experience significant growth, creating new opportunities for innovation and investment.
Read Full Report : https://www.meticulousresearch.com/product/virtualized-evolved-packet-core-market-5201
Contact Us:
Meticulous Research®
Email- [email protected]
Contact Sales- +1-646-781-8004
Connect with us on LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/company/meticulous-research
#Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market#VEPC Market#VEPC Telecom#Packet Data Network Gateway#Mobility Management Entity
0 notes
Text
#Virtualized Evolved Packet Core Market#VEPC Market#Mobility Management Entity#Home Subscriber Server#Packet Data Network Gateway#Policy and Charging Rules Function#Mobile Private Network & Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MPN & MVNO)#Long-term Evolution & Voice over Long-term Evolution (LTE & VoLTE)#Telecom Operators#Internet of Things & Machine to Machine
0 notes
Text
Pri Gateway | E1/T1 Digital VoIP Gateway | Dinstar India
The realm of telecommunications, the demand for efficient, high-quality voice transmission has led to the development of various technologies. Among these, the Primary Rate Interface , PRI Gateway, particularly the E1/T1 Digital VoIP Gateway, stands out as a critical component for businesses seeking to integrate traditional telephony with modern Voice over IP (VoIP) systems. This article delves into the intricacies of PRI Gateways, their functionalities, benefits, and applications in the contemporary communications landscape.
What is a PRI Gateway?

A PRI Gateway is a network device that facilitates the conversion of digital signals from a traditional PRI line into VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) signals. The PRI, which stands for Primary Rate Interface, is a standard in telecommunications that carries multiple voice and data transmissions between a network and a user. It is a part of the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and typically uses E1 or T1 lines.
E1 Line: Commonly used outside North America and Japan, an E1 line can handle 32 channels, with 30 B-channels for voice or data, one D-channel for signaling, and one framing channel.
T1 Line: Predominantly used in North America and Japan, a T1 line supports 24 channels, with 23 B-channels for voice or data and one D-channel for signaling.
Functionality of a PRI Gateway
A PRI Gateway essentially acts as a bridge between traditional telephony systems and IP-based networks. Here’s how it works:
Signal Conversion: The gateway converts PRI signals (from E1 or T1 lines) into IP packets, which can then be transmitted over the internet.
Protocol Translation: It translates signaling protocols between ISDN and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), ensuring seamless communication.
Call Routing: The gateway manages call routing, ensuring that calls are directed to the correct destination, whether within the traditional telephony network or an IP network.
Compression: Advanced gateways can compress voice signals to optimize bandwidth usage without compromising call quality.
Security: Many gateways incorporate security features like encryption and firewall functionalities to protect against unauthorized access and ensure secure communication.
Benefits of Using a PRI Gateway
The integration of a PRI Gateway into a business's communication infrastructure offers several notable advantages:
Cost Efficiency: By leveraging VoIP technology, businesses can significantly reduce long-distance and international call charges. VoIP calls, especially over the internet, are typically cheaper than traditional phone calls.
Scalability: PRI Gateways allow businesses to scale their communication systems easily. Adding more lines or expanding the network can be done without significant infrastructure changes.
Enhanced Functionality: VoIP systems offer advanced features such as voicemail to email, call forwarding, auto-attendant, and more, enhancing the overall functionality of the communication system.
Flexibility: Businesses can integrate existing PRI lines with modern IP-based systems, allowing them to transition to VoIP gradually without discarding their current telephony infrastructure.
Reliability: E1 and T1 lines are known for their reliability and high-quality voice transmission, ensuring clear and consistent communication.
Applications of PRI Gateways
PRI Gateways are versatile and can be used in various scenarios, including:
Enterprise Communication: Large businesses with significant call volumes can benefit from the reliability and scalability of PRI Gateways. They ensure seamless integration of traditional PBX systems with modern VoIP networks.
Call Centers: Call centers require robust and reliable communication systems to handle high call volumes. PRI Gateways provide the necessary infrastructure to support these operations efficiently.
Service Providers: Telecommunications service providers use PRI Gateways to offer VoIP services to their customers, leveraging existing E1/T1 infrastructure.
Educational Institutions: Schools and universities can use PRI Gateways to integrate their communication systems, facilitating better connectivity and collaboration.
Government Agencies: Government bodies can benefit from the enhanced security and reliability offered by PRI Gateways for their communication needs.
Key Features to Look for in a PRI Gateway
When selecting a PRI Gateway, businesses should consider several key features to ensure they choose the right device for their needs:
Compatibility: Ensure the gateway is compatible with existing telephony systems and supports both E1 and T1 lines.
Voice Quality: Look for gateways that offer high-quality voice transmission with advanced compression algorithms to optimize bandwidth usage.
Security Features: Essential security features include encryption, firewall capabilities, and support for VPNs to protect against unauthorized access.
Ease of Integration: The gateway should be easy to integrate with existing infrastructure and offer support for various protocols, including SIP.
Management and Monitoring: Advanced management and monitoring tools can help in maintaining the gateway and ensuring optimal performance.
Scalability: The ability to scale the system easily as the business grows is crucial, so look for gateways that support expansion without significant additional costs.
Challenges and Considerations
While PRI Gateways offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
Initial Setup Costs: The initial investment in a PRI Gateway and the necessary infrastructure can be significant. However, this cost is often offset by the long-term savings on call charges.
Technical Expertise: Setting up and maintaining a PRI Gateway requires technical expertise. Businesses may need to invest in training or hire skilled personnel to manage the system.
Quality of Service: Maintaining high call quality over VoIP can be challenging, especially in networks with variable internet quality. Ensuring sufficient bandwidth and implementing QoS (Quality of Service) measures is essential.
Regulatory Compliance: Businesses must ensure that their communication systems comply with local regulations, including those related to data privacy and emergency call handling.
Future of PRI Gateways
The future of PRI Gateways looks promising as businesses continue to adopt VoIP technology for its cost savings and advanced features. The integration of traditional telephony with IP-based systems is expected to become more seamless, with improved compatibility and enhanced functionality. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as the adoption of 5G networks, will likely further enhance the capabilities and performance of PRI Gateways.
Conclusion
PRI Gateways, particularly the E1/T1 Digital VoIP Gateways, are essential components for businesses looking to integrate traditional telephony with modern VoIP systems. They offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, scalability, enhanced functionality, and reliability. By understanding their functionalities and applications, businesses can make informed decisions about integrating PRI Gateways into their communication infrastructure, ensuring seamless and efficient communication in the digital age.
0 notes
Text
Is Your Business Operating in the Blind Spot of the Egyptian Internet?
The Challenge of Restricted Access and Unsecured Connections in Egypt
Imagine trying to navigate a crucial business deal in Egypt, only to find essential websites and resources blocked. Or, picture your employees struggling with sluggish connections and potential security vulnerabilities while working remotely. This is the unfortunate reality for many companies operating in the Egyptian market.
The Egyptian Landscape: Restrictions and Security Concerns
Egypt boasts a vibrant and growing business scene. However, internet access in the country faces certain limitations. Websites deemed politically sensitive or containing specific content are sometimes blocked. This can hinder your company's ability to access crucial information, research tools, and collaboration platforms.
Furthermore, the Egyptian government has implemented Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) technology. While this allows for content filtering, it also raises concerns about data privacy and online security. Without proper safeguards, your company's sensitive information could be exposed to unauthorized access.
The Impact on Businesses: A Cascade of Challenges
These limitations translate into a cascade of challenges for businesses operating in Egypt:
Restricted Access to Critical Resources: Blocked websites can hinder your ability to access essential business tools, research platforms, and industry-specific resources. This disrupts workflows, hinders research and development, and ultimately impacts your competitive edge.
Limited Collaboration Opportunities: With access to certain collaboration platforms potentially restricted, communication and teamwork with international partners and remote employees can become a struggle. This can lead to delays, communication breakdowns, and decreased productivity.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: Unsecured connections on public Wi-Fi networks or limited control over network security can expose your company's data to cyberattacks. This can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions.
Hindered Innovation and Growth: Restricted access to global resources and the constant threat of data breaches can stifle innovation and hinder your company's ability to grow and expand its reach in the Egyptian market.
IM Solutions: Unlocking the Full Potential of the Egyptian Internet
At IM Solutions, we understand the unique challenges businesses face in the Egyptian market. That's why we offer a robust Virtual Private Network (VPN) solution specifically designed to empower your company's success.
A Secure Gateway to Unrestricted Access
Our VPN service acts as a secure tunnel, encrypting your company's internet traffic and routing it through a remote server. This bypasses internet restrictions, granting your employees unrestricted access to the global web. They can access essential business tools, research platforms, and collaboration tools with ease.
Enhanced Security for Peace of Mind
Our VPN utilizes industry-standard encryption protocols, creating a secure barrier between your company's data and the internet. This safeguards your sensitive information from unauthorized access, even on public Wi-Fi networks. With IM Solutions, you can operate with peace of mind, knowing your data is protected.
Unleashing Growth and Innovation
By removing internet access restrictions and bolstering your company's cybersecurity, IM Solutions empowers you to tap into the full potential of the Egyptian market. Your employees can collaborate seamlessly, access the latest resources, and drive innovation without limitations. This translates to increased productivity, a competitive edge, and sustainable growth for your business.
Don't Let Restrictions Hold You Back: Take Action Today!
At IM Solutions, we are committed to providing businesses with the tools they need to thrive in Egypt. Contact us today to learn more about our VPN solutions and how we can help your company navigate the Egyptian internet landscape with confidence and security. Let's unlock the full potential of your business in Egypt together!
0 notes
Text
Snort: Understanding The Network Intrusion Detection & Prevention System

Snort is a powerful and lightweight open-source IDS/IPS that analyses network traffic and records packets in real time.
SNORT is a strong open-source Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) that analyzes and logs data packets in real-time network traffic. It uses a rule-based language with methods for anomaly detection, protocol analysis, and signature inspection to find actions that might be harmful.
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks, Common Gateway Interface (CGI) attacks, buffer overflows, and stealth port scans are some of the cyber threats that network managers use SNORT to find. SNORT sets up rules that describe bad network behavior, find harmful packets, and send users warnings.
SNORT is an open-source solution, which means it is free and can be used by both people and businesses. The SNORT rule language tells the computer what network data to watch and what to do when it finds malicious packets. With this feature, SNORT can spot malicious packets like sniffers and traditional network intrusion detection systems, or it can be used as a full IPS solution that watches network activity, finds threats, and blocks them.
Snort Network Intrusion Detection & Prevention System Specifications
Specification
Description
Type
IDS/IPS
License
Open-source
Platform
Cross-platform
Detection
Signature
Performance
High-speed
Configuration
Flexible
Protocols
Multiple
Alerts
Real-time
Rules
Customizable
Community
Active
Logging
Detailed
Integration
Versatile
Updates
Regular
Analysis
Comprehensive
Deployment
Easy
Introducing Snort
Martin Roesch created the C-based network intrusion detection system Snort in 1998, and Cisco is currently responsible for maintaining it. Protocol analysis, content matching, OS fingerprinting, real-time traffic monitoring, and packet logging are some of its features. It is both free and open-source. In addition to being deployable over a wide range of Network Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems, it is extremely customizable.
Why Do People Like Snort?
A Network Intrusion Detection System (IDS) called Snort is widely used and known as one of the best tools for finding cyber threats in the cybersecurity field. It effectively keeps an eye on network traffic in real-time, carefully checking each packet for payloads that could be dangerous. The fact that Snort can analyze protocols, look for content, and match patterns is a big part of its popularity. It can find many types of threats, like port scans and buffer spills, making it very useful for finding them.
Snort is widely used because it is easy to move around and works with many other programs. It works with all major BSD operating systems, Windows, Linux, and many versions of UNIX. Notably, Snort doesn't need the kernel to be recompiled or any extra software or hardware to be installed. It only needs to be installed and run with root capabilities. Built to work like a normal network intrusion detection system, Snort checks network data against rules already set. It then tells system administrators about any suspicious activity so they can fix it.
Finally, Snort is a good choice for organizations with limited funds because it is open source and doesn't cost anything. This includes educational institutions, small and medium-sized businesses, and even home users who need an Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS) solution.
How Snort Is Used?
Brief Synopsis
Companies looking for a flexible Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) to protect their networks from new hazards often embrace Snort. Snort is mainly used for:
Real-time network traffic analysis
Analyzing protocols
Content matching is arranged according to protocol, ports, and content
Operating Systems (OS) fingerprinting
Interference with platforms
Logging and packet sniffing
Snort efficiently captures and analyses network traffic as a packet sniffer and logger. In:
Track local network traffic on an interface.
Save captured packets for troubleshooting on the disc.
Real-time network traffic monitoring lets you check every packet for potentially dangerous content.
Guidelines and Alerts
Based on preset criteria, snort can create alarms for odd packets found in network traffic. This capacity facilitates the identification of network vulnerabilities and their mitigating action. Using the versatile Snort rule language lets consumers:
Establish specific guidelines to differentiate regular network behavior from anomalies.
Create additional rules to track particular actions and stop possible assaults.
Finding attacks
Because Snort is flexible and works with many operating systems, it can find many types of network attacks as long as there are rules that match how the attacks behave. Some examples are:
DoS and DDoS Attacks
These hacks send many fake service requests through the network, which stops things from working. DoS attacks come from a single system, while DDoS attacks are planned by many systems working together.
Too Much Buffer
Attackers send too much data to a network address, which uses up the system's bandwidth.
Spoofing
Hackers pretend to be authorized users or systems to get into target networks and do bad things.
Common Gateway Interface
Hackers can use input validation attacks to exploit common CGI script flaws.
Stealth Port Scans
Hackers get around firewalls by using stealth port scans to find open ports on the network without making full links.
Can Snort Find Attacks That Don't Exist Yet?
Yes. Hannes Holm from the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Sweden, wrote a study called "Signature Based Intrusion Detection for Zero-Day Attacks: (Not) A Closed Chapter?" that says Snort can find zero-day attacks. The study looked at 356 serious attacks on Snort that used old government rules. It found that Snort can find zero-day exploits about 17% of the time. The average detection rate for known attacks is higher (54%), but Snort can find zero-day flaws at an impressive rate of 8.2%, showing that it can work even against threats that aren't known yet.
Snort Installation Steps
On Linux
wget https://www.snort.org/downloads/snort/snort-2.9.15.tar.gz
tar xvzf snort-2.9.15.tar.gz
cd snort-2.9.15
./configure –enable-sourcefire && make && sudo make install
On Windows
Get the Snort installation from the Snort Download Page.
Handle the installer.
Different Snort Modes
Sniffer Mode: Use./snort -v to output TCP/IP headers or./snort -vd to include IP addresses.
Packet Logging: Store packets on the disc under./snort -dev - l./SnortLogs.
Network IDS Mode: Activate with ./snort -dev -l ./SnortLogs -h 192.127.1.0/24 -c snort.conf.
How does Snort detect an Attack?
Snort uses the Misuse Detection Engine BASE to look at real-time network data. It checks both coming and going data packets against signatures in its rule set. The following are some of Snort's most important features for finding intrusions:
Watch the traffic on the network: Snort finds malicious packets and setup problems by looking at traffic that has been recorded.
Find Strange Things in the Network: Snort rules let network managers tell the difference between normal and strange traffic to spot malicious activity in real time.
Packet Sniffing: Snort gathers all data bits sent within a network, which lets you look at traffic in great detail.
Set Up Alerts: Snort lets users know when it finds strange or harmful packets, possible uses of security holes, or policy violations based on how it is set up.
Create New Standards: Snort lets admins make their own rules, which lets them set criteria for finding new threats like backdoor attacks or certain packet content.
Network managers can quickly separate normal, expected internet activity from anything deviating from the norm by applying SNORT principles. SNORT creates notifications to users after real-time analysis of network activity to identify hostile activities.
FAQs
How is Snort different from other systems that look for intrusions?
Snort is special because it is open source, meaning it can be changed and added in many ways. It uses signature-based and anomaly-based detection algorithms to give you a flexible and all-around way to find intrusions.
Snort can be used in small networks, right?
Yes, Snort is good for small networks because it can identify and stop intrusions well, is scalable, and has features that can be customized. It meets the security needs of smaller networks without needing a lot of resources.
What does Snort do with data that is encrypted?
Snort has trouble checking encrypted traffic because it can't look at encrypted text directly. To fix this problem, businesses often combine SSL/TLS decryption proxies with Snort. This lets them look at material decrypted for possible security threats.
Read the full article
0 notes