#chinese culture
Text
Emei Kung Fu Queen Ling Yun 🔥🔥🔥
#kung fu#wushu#chinese martial arts#kung fu girl#martial arts girls#kung fu cinema#kung fu star#chinese culture#kung fu world
111 notes
·
View notes
Text











First Post!
I deleted my old tumblr because... man idk why it was covid-times and the prefrontal cortex was not in the room with us!! Anyways, I was reminded by my lovely friend @repecca that tumblr exists, and that some of my work has been going around on here, so I decided to post some of my work up officially!
Starting off with my most notable (?) work to date, here's my LOTR: The Middle Kingdom Project.
Now, it's been over a year since I posted this, and at the time I was... really searchingfor myself artistically, and I decided to go all in on something that I'd been ruminating on for a long time.
So, hello, again. I'm Leia. I do visual development/BG design, and I'm also a writer of things. I love fantasy and transformative work. It's nice to meet you.
#lotr#lord of the rings#the middle kingdom#chinese culture#hanfu#frodo#visual development#visdev#concept art
8K notes
·
View notes
Video
茶宠chachong/tea pet (clay handicrafts for chinese tea culture)
9K notes
·
View notes
Note
do you have any idea when people in china stopped bowing to each other as a greeting? it seems like the most common forms of greeting now is to shake hands or wave both which were introduced from the west. it's the same in taiwan too.
Tldr: It never stopped because Chinese people never had the practice of bowing in greeting the way that Japanese people did/do.
-
(Note: there are types of greetings that involve a sort of bowing (ketou), but this is reserved for special occasions)
Back in the day there was greetings were made by clasping one's hands in front of them in the direction of the person being greeted. There might be some head lowering/slight bowing involved but it's done in conjunction with the hand greeting. You can see various forms of this in historical dramas and even hanfu shows and shortform videos. The exact way one held their hands changed in some years but the general idea is the same.
Women's and men's hand greetings differed back in the day. A women's greeting was called 万福礼 wànfùlǐ and consisted of holding the hands in front of oneself and bending the legs, or holding hands at the hip, etc. The exact way to hold the hands also changes through the years. Women also do what is called 肃拜 sù bài, which is an earlier form of a women's greeting and includes getting on one's knees (thus the 拜).
Some examples of greetings:

Men's vs women's hand positions



拱手礼 gōngshǒu lǐ ("cupped hands greeting"). The most common greeting. Top photo shows the gendered difference for proper etiquette for nowadays if you ware going to do it, for example, as a new year's greeting.
Bottom photos: I think if you look carefully in modern society, you can still see examples of this greeting in China. It is a gesture that can also be used to expresses one's gratitude. It is still there, it's just fell out of vogue in favor for waving and hand shaking.
This can also be seen in The video above shows Ming era 万福礼 as well as men's 揖礼. 作揖礼 zuòyī lǐ ("bow with clasped hand greeting") is kind of the same thing as 拱手礼, but 作揖 specifically includes a slight bow whereas 拱手礼 is merely the raising of the hands.

叉手礼 chāshǒu lǐ ("crossed hands greeting") popularised during the Western Jin - Song dynasties, seen in the drama "The Longest Day in Chang'an", which takes place in the Tang Dynasty. This particular greeting started out as one used by Buddhists in the Eastern Han dynasty.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/489897518

抱拳礼 bàoquán lǐ ("cupped fist greeting"). This one is something done more so by martial artists. For men, you use your left hand to cover your right hand. For women, the opposite is true. It is also called 吉拜 jíbài when showing respect. If you flip your hand (keep in mind men/women do this the opposite way), it is called 凶拜 xiōngbài and it used to show respect to the dead. So one has to pay attention to this.
There's kind of a lot more etiquette rules you could get into but this answer has already sort of gone beyond the scope of your question lol. Chinese people wrote rites books over the many dynasties so actually there are descriptions of how these greetings were done and over time and that's how they are replicated in dramas and movies.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


🌞 Sun and Moon Pagodas | 日月双塔 🌚
Originally built in Guilin, Guangxi during the Tang dynasty (618-917) the pagodas were reconstructed in 2001.
#chinese culture#chinese history#Chinese architecture#buddhism#pagodas#tang dynasty#asian architecture#China#east asia#east Asian cultures#dynastic china
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Curious Ming Dynasty Hairpins in the shape of two shrimps. Found on a gilt silver hair cover excavated in a tomb in Shanghai. Exhibited at the Shanghai Museum of Art.
#ming dynasty#ming#chinese art#ancient china#chinese culture#hairpins#shrimps#shrimps art#antique jewelry#headdress#chinese jewelry#jewelry#jewelry design
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
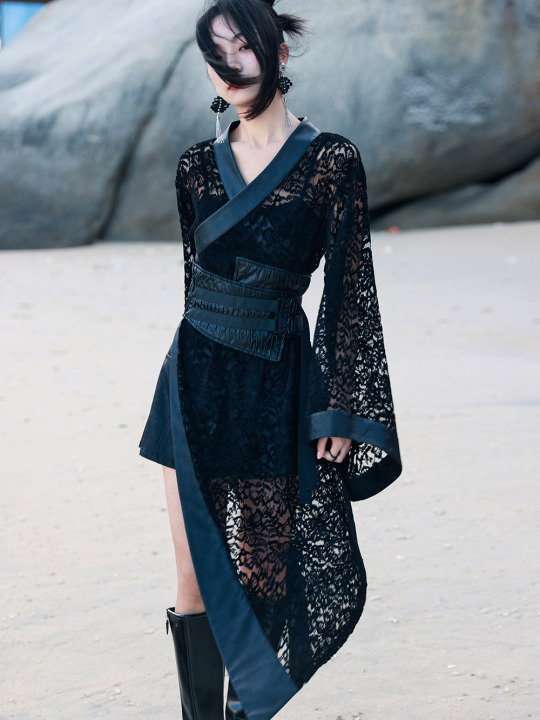
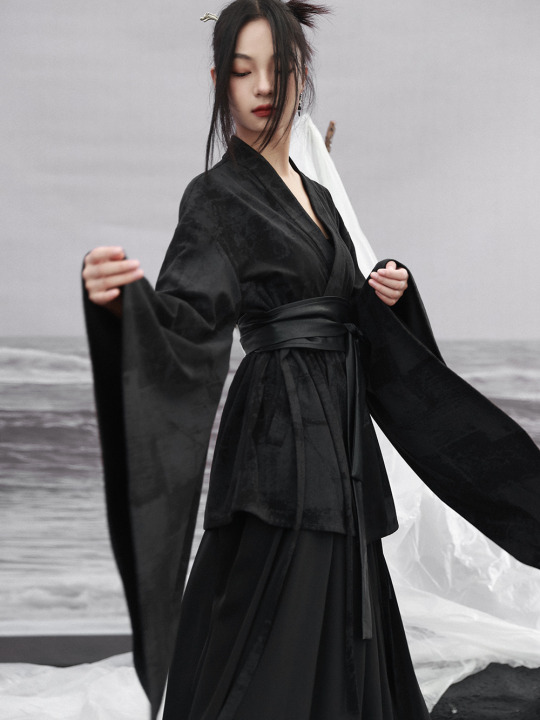
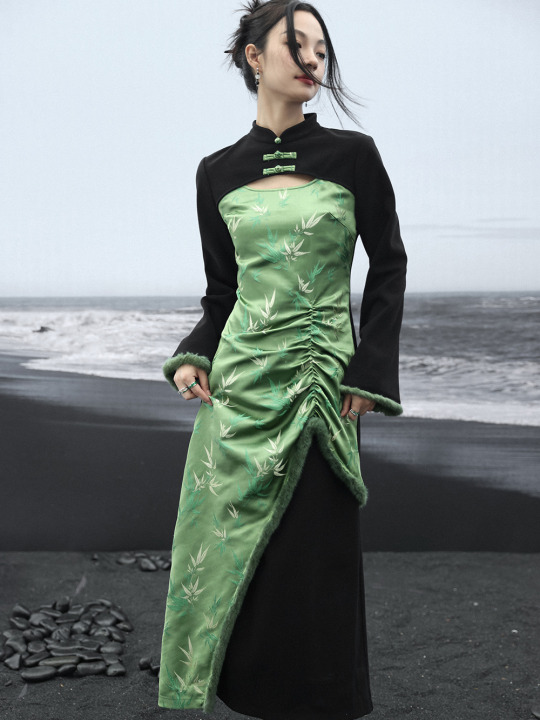
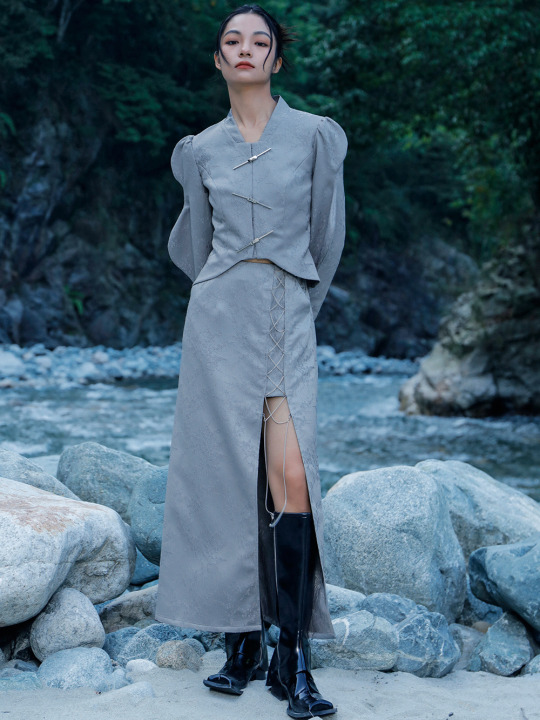
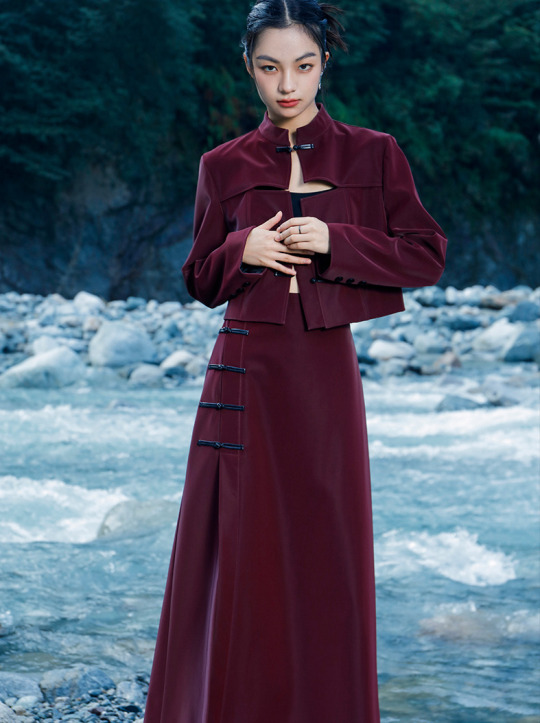
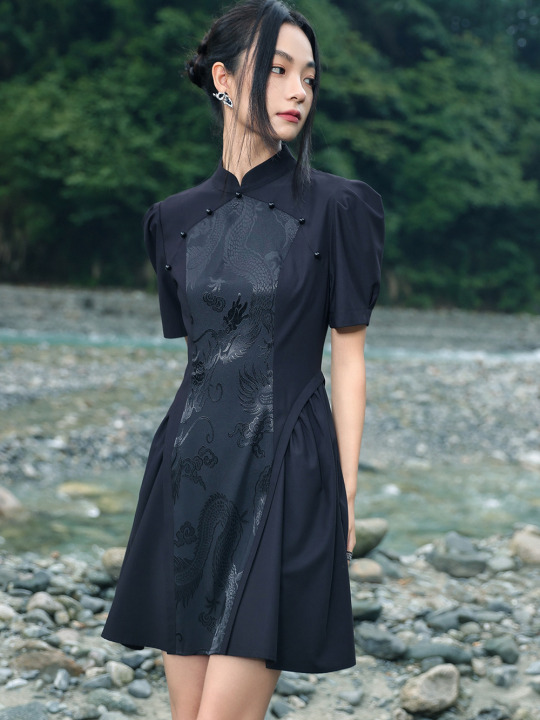
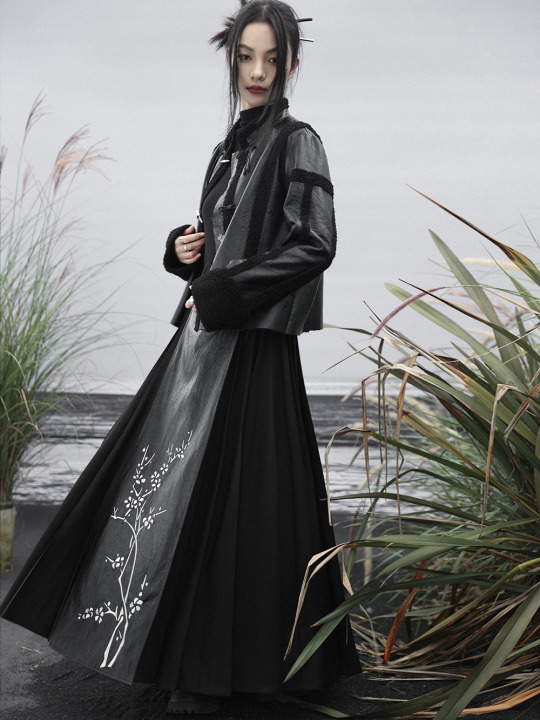
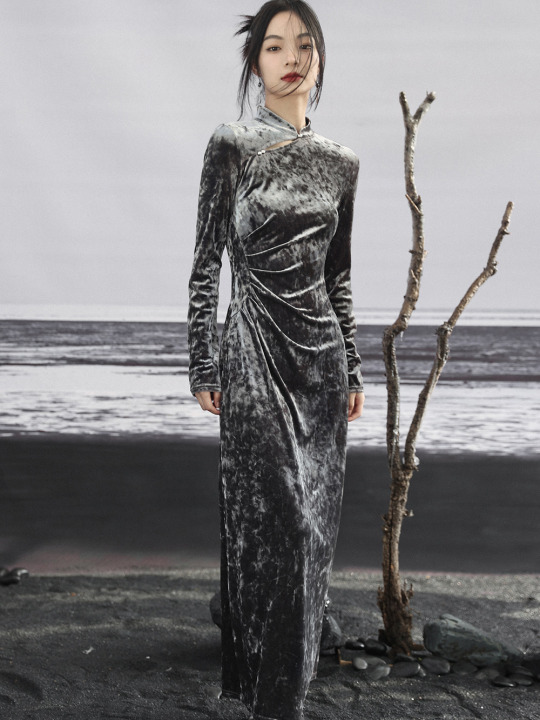
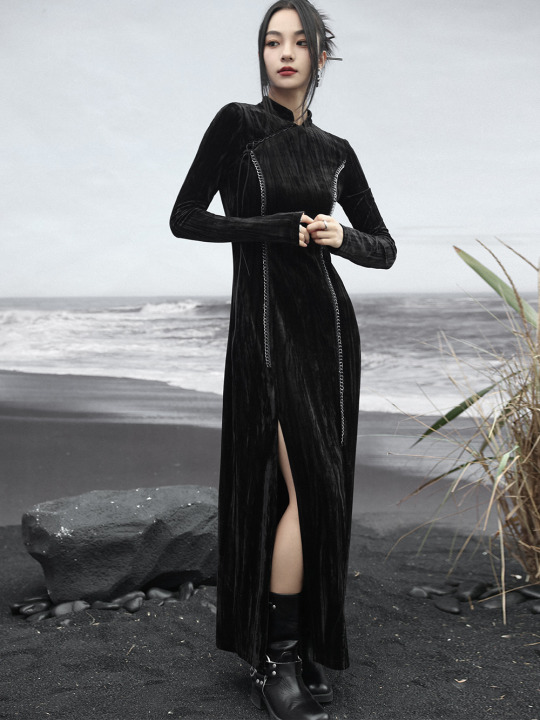

















Since there's quite a lot of interest in Chinese-inspired cyberpunk and adjacent aesthetics, just wanted to share these neat "Chinese style meets the Matrix"-esque looks from popular brand 大青龙肆/Da Qing Long Si. There's also an English website here.
#大青龙肆#daqinglongsi#hanfu inspired#hanyuansu#qipao inspired#and etc#guofeng#xinzhongshi#cyberpunk#taobao#recs#chinese fashion#chinese clothing#chinese culture#china
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
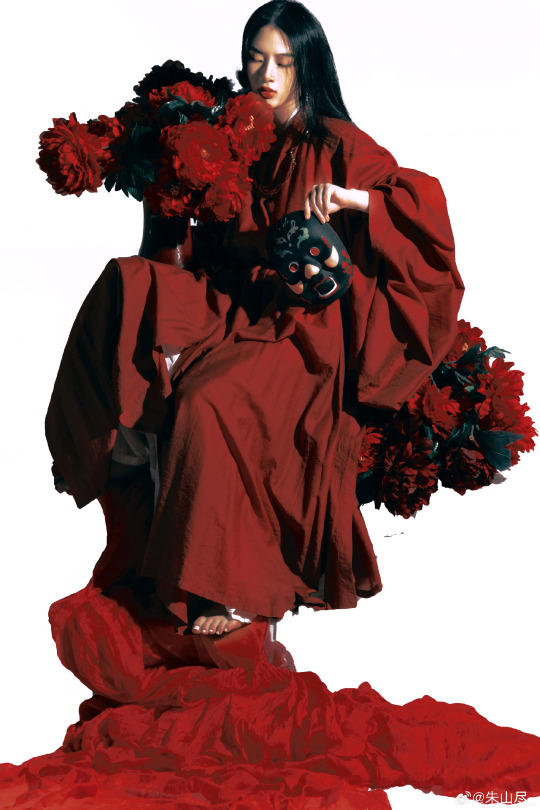
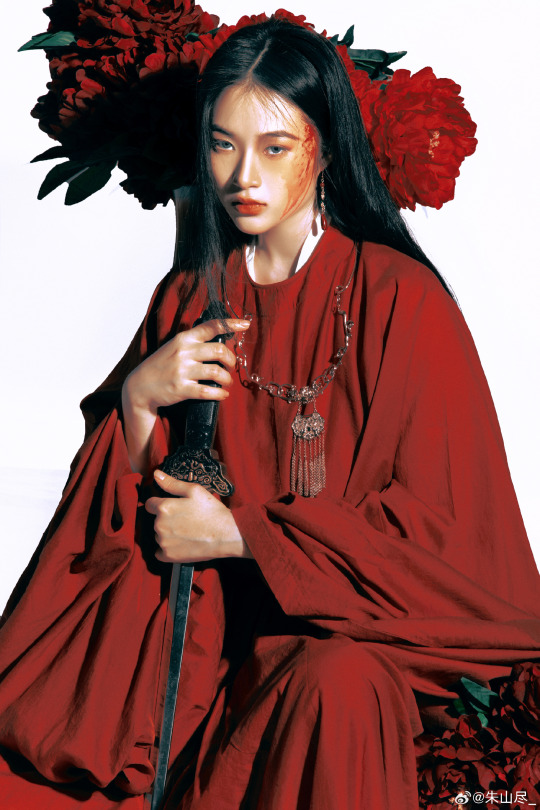
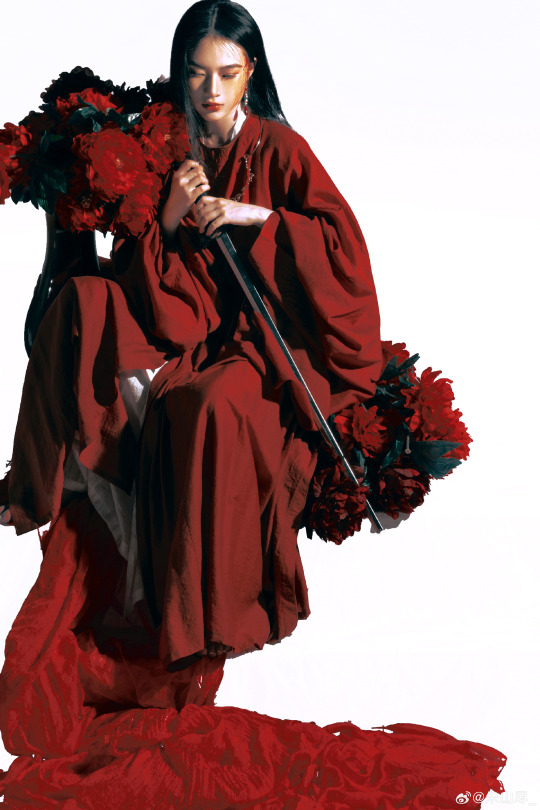
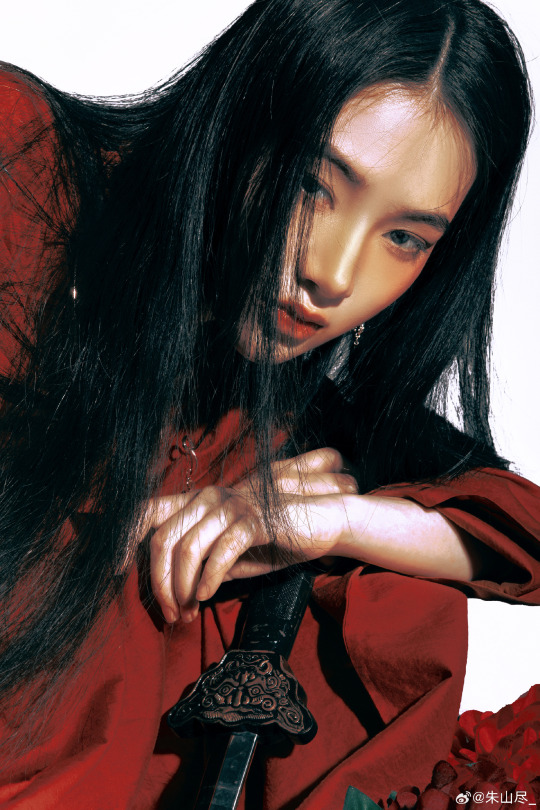
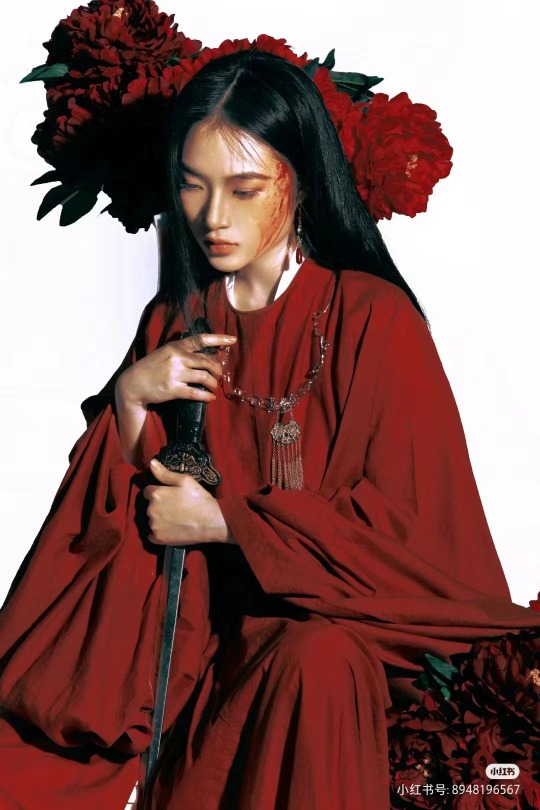
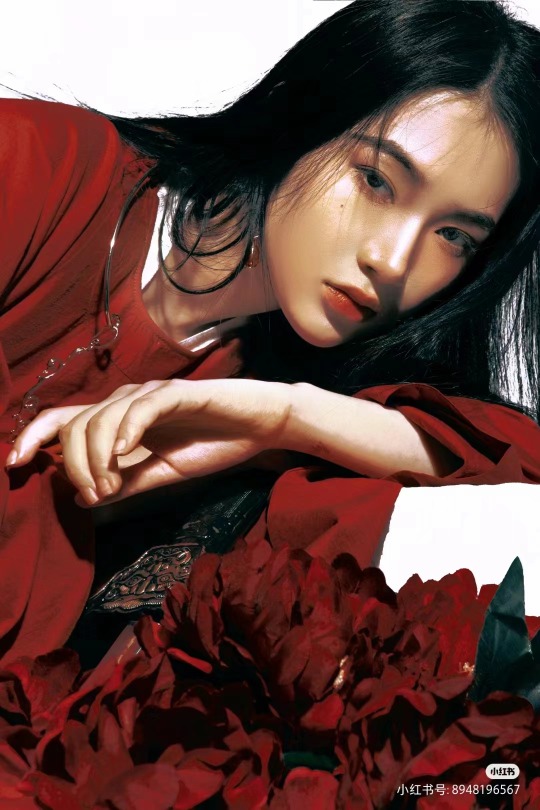










[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Tang Dynasty Hanfu Photoshoots
————————
📸Photo:朱山尽_
💄 Makeup:@南夕叙
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/6906018733/Nb2eJyNoq
————————
#chinese hanfu#tang dynasty#hanfu#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#chinese culture#hanfu photoshoot#hanfu art#hanfu girl#hanfu fashion#chinese fashion#漢服#中華風#汉服
755 notes
·
View notes
Text
culture tips for writing asian settings: calligraphy (pt ii)
in my last post i talked about calligraphy more generally, but here i want to talk about the calligraphy from atla. all of the calligraphy from the show is written by dr siu-leung lee and i'll be using the artbook as my reference.
if you're a writer or artist approaching written chinese, you can think about how script and handwriting might tell us something about a character. dr lee certainly did, and he even tailored writing styles to who he thought might've been writing that text: "If it were a highly cultured royal attendant, he would use a refined, elegant style, but if it were a low-level clerk, he would use a more pedestrian handwriting style."
first thing: modern standard chinese coming out of mainland china uses simplified chinese. this system was developed in the mid-20th century, so it's pretty anachronistic to use this for atla. instead, you should be using traditional chinese as dr lee does (which is still used in hong kong, taiwan, and many diasporic communities). i usually use google translate to switch between the systems.

note the use of simplified 门 (door) instead of the traditional 門 from the aang's unfreezing day comic.
next i'm going to take aang's wanted poster as an example of three different chinese scripts we see in the show. the "title" is in clerical script, the body of the text is in regular script, and the seal is in seal script.

regular script is the standard way you'd learn how to write chinese nowadays. you can see (as i mentioned in part i) how the text is meant to be read up -> down, then right -> left.
clerical script is characterised by fairly compact shapes and a kind of "roundness", and was developed in the late warring states period. this is the script used for the chinese title of the show! in the context of atla, it implies to me that the writer has more specialised calligraphic training than the average person (who, if they can write, would be using regular script). you can compare the difference in styles for the same words between clerical (L) and regular (R):




seal script is the most archaic form of chinese on display; this one wouldn't have been written by the calligrapher, but carved into a seal by a craftsperson and then stamped onto the page.
what's also really interesting is dr lee implies a difference in script between the nations. some of the characters used to write water tribe-related concepts:

this is an adapted form of oracle bone script, the one of the earliest forms of chinese writing. this fascinated me because this script was—as the name suggests—written on bone, and perhaps reflects something about the material of what the water tribes were using to write. (you can input modern characters into this website to see examples of their older forms.)
finally, some cool differences in handwriting! this is from the fire day festival poster:

this uses regular script, but in contrast to the excerpt we saw before, the formation of the characters is more haphazard (excitable?). it's also written left -> right! this suggests to us the writer is a commoner, as opposed to a royal scribe.
these are some things you can keep in mind when you're writing or drawing in this universe—while you're probably writing in english, the characters would be steeped in the writing systems we've been talking about. if a character's sending a letter, what might the recipient notice about the handwriting? what does it tell them about their social status or education? could the shape of the letters signal something about where they come from, i.e. water tribe characters write a more curvy script?
disclaimer | more tips
581 notes
·
View notes
Text
wuxia and confucianism
Hey. Thought I'd answer the wuxia-confucian question very briefly. I did suggest wuxia being closely knitted to confucianism, but I do understand the other perspective of wuxia being anti-confucian. Quick answer only because I've got little time right now -- might add on to it later!!

confucianism
First the central themes of confucianism:
常 (cháng): Virtues of compassion and courtesy. 仁 (rén)、义 (yì)、礼 (lǐ)、智 (zhì)、信 (xìn)、忠 (zhōng)、孝 (xiào)、悌 (tì) (there are more). These in order in crude translation mean compassion, righteousness, courtesy, wisdom, integrity, loyalty, filial piety, and respect to one's older siblings. These are the main ideas Confucius, the founder of Confucianism, wished to spread through his philosophy.
纲 (gāng): Order. This is about the relationships between people, the filial piety of child to their parents, the relationship between significant others, between friends and teachers, and expanding outwards in the sphere of influence in our circle of life, the patriotism and loyalty of a liege to his lord.
Understand that Confucius came up with these ideas in a time of war. He lived his life traversing different kingdoms and establishing his prominence by getting emperors to trust him as a consultant and employ his school of ideas. As such, these beliefs are very much centred around creating harmony and order in society, and of course entails the respect of commoners and lieges to their lords (because why else would kings employ his beliefs over other schools of philosophy if not so?).
wuxia
Moving on to the wuxia genre, the 侠 (xiá) in wuxia emphasises righteousness. xia, as people, are itinerants and rebels in the fictitious pugilistic society who tire of the power of the aristocracy and seek to use their own, often unlawful ways, to help others through 锄强扶弱 (chú qiáng fú ruò) -- helping the needy and going against the strong (the morals are debatable but that's me trying to sum up wuxia in 5 minutes off the top of my head rip).

conclusions
So I guess that's enough information for you to form your own conclusions, and here's what I think, at the very least.
Against Confucianism -- Subverting the power pyramid. Many of the heroes/xia's in wuxia are lawless rebels. They aren't good, upstanding citizens of the society. Hell, xia was first popularised from 游侠列传 (yóu xiá liè zhuàn) in the Han dynasty records, talking about how a "xia" went against the officials and helped the commoners in the name of righteousness. This goes against the confucian beliefs of respecting your lord and serving the kingdom.* That's why I can understand why some would consider wuxia going against confucianism.
Align with Confucianism -- Righteousness. Ultimately, however, wuxia is about righteousness and nobility and honour, defined by society and commoners and not by royal blood. These values of etiquette, decorum, and nobility were long ingrained in the hearts of all these chinese characters, from when the courtesy and etiquette rules were defined in the Zhou dynasty, and afterwards, from the Han dynasty on, when emperors heavily employed Confucian beliefs in education and throughout society because it helps in rebuilding a harmonious society.
Confucianism is about compassion and righteousness, the staples permeating and defining chinese culture in the last two thousand years, and it is these values that serve as the central impetus of the xia and wuxia genres. People are born into these values; as such they fight against the injustice they see, and thus engenders the lost xia's of every dynasty.

*And well, even Confucius wasn't that dead set on fealty to lords. Confucian highly venerated loyalty, but when the court is corrupt, they acknowledge insurgence over the mindless following of an emperor. This is a story for another day, one I would have to back up with more quotes and citations, but I hope this answered your questions, or even better, let you form some conclusions of your own :)
Confucian philosophy is only one aspect that has correlations/influences over the "xia" genre, there are many other interesting things to say about Taoism and Buddhism as well (e.g. Jin Yong's wuxia classics have quite a bit of Buddhist values in the characters owing to author preferences), it's definitely worth looking up on these things if you're interested!
initially reblogged under the original meta post on wuxia, xianxia, and cultivation differences, but i realised it was too long and would bury the reply, so please don't mind me opening a new post for this again.
feel free to ask and discuss!!
#chinese#cdrama#danmei#philosophy#chinese language#chinese culture#wuxia#cnovel#chinese history#confucius#confucianism#chinese philosophy#fate's meta
386 notes
·
View notes
Text



Lunar New Year Zenyatta and Ramattra by eweeppy (1, 2)
#zenyatta#ramattra#eweeppy#overwatch#fan skin#fanskin#lunar new year#east asian culture#chinese culture
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
BY 换谁不迷糊呀 (fyi, don't try chinese daoism 手印shouyin/指诀zhijue in a bold manner because↓


#china#video#fun#shouyin#zhijue#the practice of making a shouyin is called 结印jieyin#chinese culture#daoism#i think he is half in jest because of that doge emoji(is he?#so don't worry it probably will just cost you two years#not twenty
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Pretty sure the name Xianyun/闲云 is a reference to the word 闲云野鹤, lit. "leisurely clouds and wild crane*" (can also be written as 闲云孤鹤, so it will be "lone crane" instead of "wild crane", but the overall meaning does not change). The word describes a leisurely and carefree lifestyle, free from worldly worries, and because it makes a reference to cranes, it's a great fit for Cloud Retainer.
This word first originated in the Song dynasty era book 《全唐诗话》.
*note: crane here refers to the red-crowned crane, which is traditionally a symbol of elegance associated with immortals, Daoism, longevity, and the literati.
232 notes
·
View notes
Text





Chinese traditional patterns. 🧶🧵
#chinese culture#hanfu#textiles#patterns#chinese history#silk#china#east asia#designs#weaving#silk weaving#tiles#Art
727 notes
·
View notes
Text
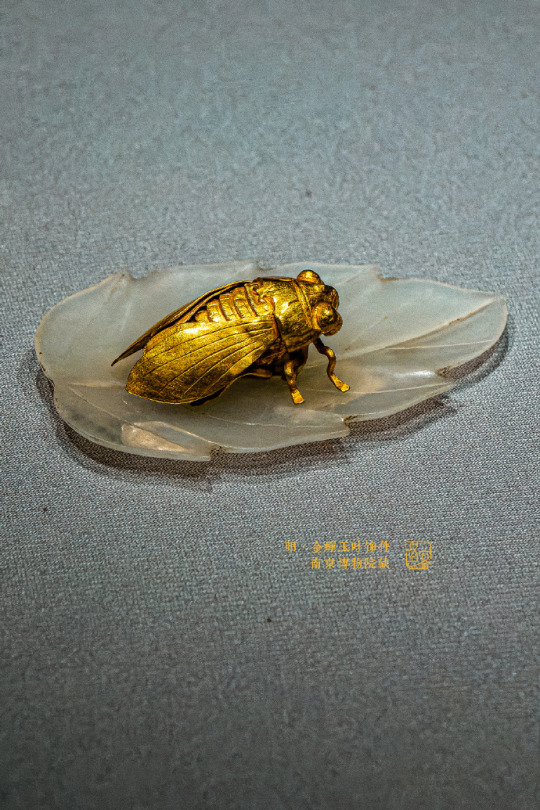
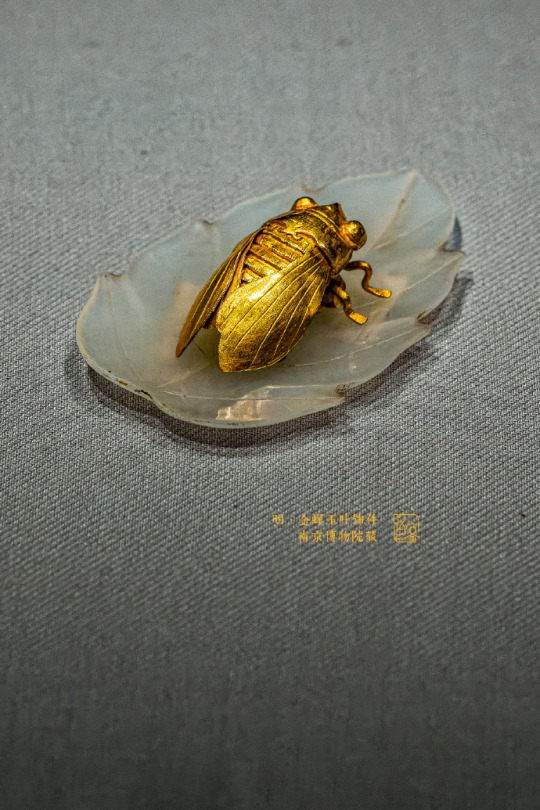





Nature Inspired: Golden Cicada Resting On a Jade Leaf
Exquisite ornament of the Ming dynasty.
Total weight of the insect figurine, made of 95% pure gold, is 4.65 g. The thickness of the finely crafted wings is only 2 mm.
Unearthed in Boshiwu (博士塢), Wufeng Mountain, Suzhou. Now exhibited in Nanjing Museum (南京博物院).
Photo: ©南京博物院
#ancient china#chinese culture#chinese art#ming dynasty#antique jewelry#chinese jewelry#jewelry design#jewelry#ancient jewelry#gold#chinese miniatures#miniature#miniature sculpture#miniature art#jade#jadeite#nephrite#carved#cicada#bug#insects#beetle#leaf art
407 notes
·
View notes
Text
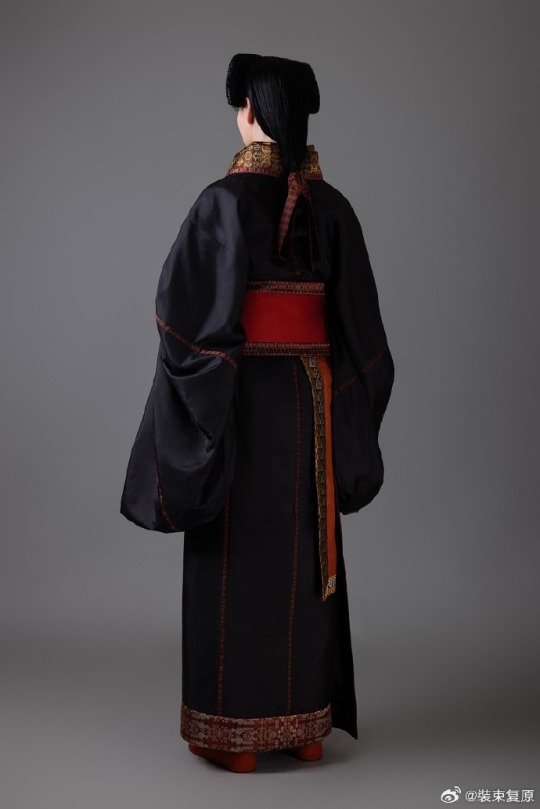
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Warring States period(475–221 BC) Chu (state) Hanfu Based On Chu (state) lacquer figure
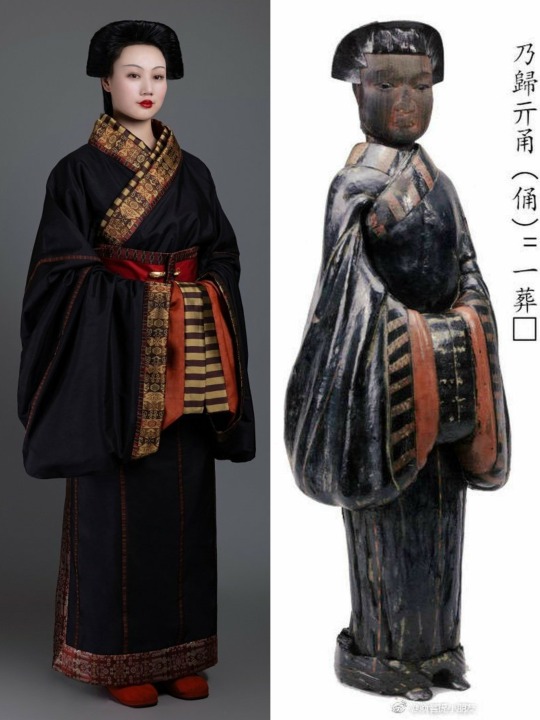
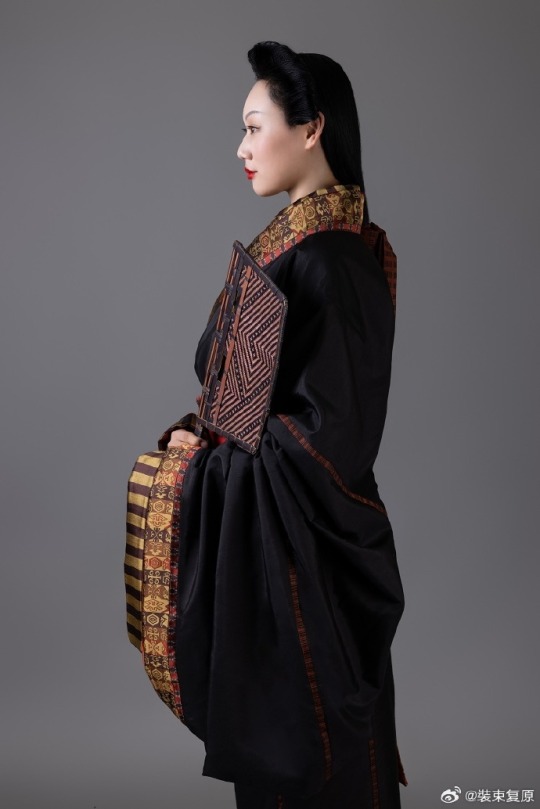
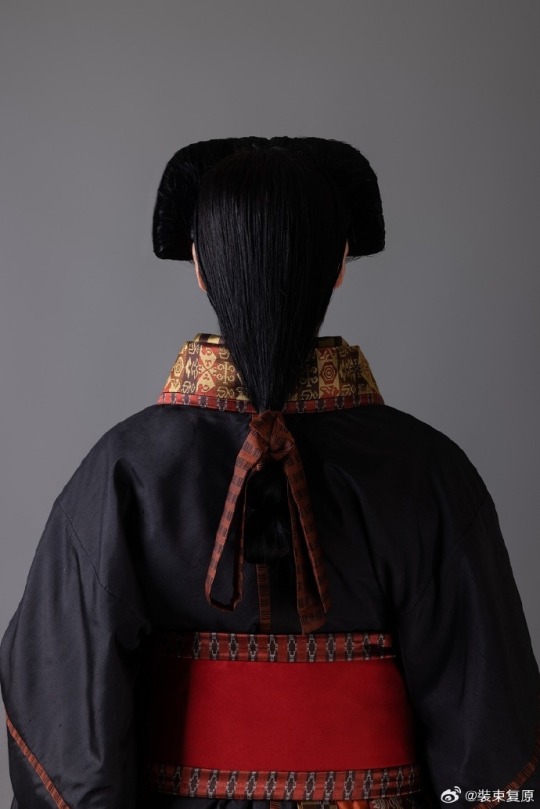
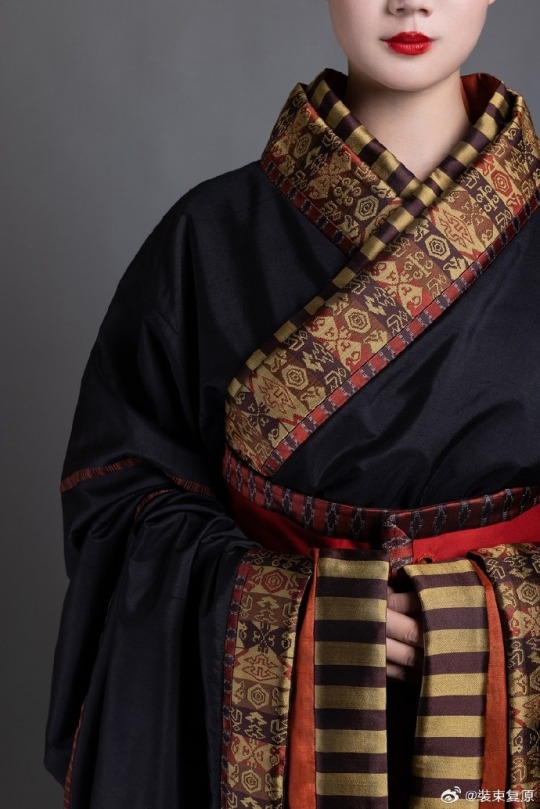






【Historical Artifact Reference】:
Lacquered wood figurines unearthed from Chu State Tomb in Shayang Tumbun Chu Tombs/沙洋塌冢楚墓出土漆俑

Collar cloth and robe unearthed from china Mashan Chu Tomb N19

【Histoty Note】Warring States Period·Chu (state) Noble Women Fashion
Many people may wonder why this set of clothing and hairstyles are so similar to Japan, but the fact is this kind of clothing and hairstyle existed in China at least 1,000 years earlier than Japan.
During the China Warring States Period, it was popular for aristocratic men and women to wear robes.
Lacquered wood figurines and robe with similar images have been unearthed from the Shayang Tumbun Chu Tombs and the Chu Tombs at Mashan, many of which adopted the "three-dimensional structure" technique.
For example, a roughly rectangular piece is caulked at the intersection of the robe's sides, skirt sides and sleeve armpits. At the same time, the lower edge line of the top and the upper edge line of the lower skirt are incrementally extended, and then sewn into one body. It is called "Ming three-dimensional structure".
Its ingenuity is that while the outer contour of the garment remains unchanged, it effectively expands the inner space of the garment body, making it convenient for people to wrap the garment from the front to the back when wearing it, without damaging the original collar and garment forms.
The attire of aristocratic women from the Chu state in this set was restored based on the lacquered wooden figurines of the Chu tomb in Shayang. Their foreheads and temples hair are fluffy, and they have a hanging bun at the back of their heads. They wear robes that are connected up and down, and are decorated with brocade inlays at the seams.
The wearing method is the "layering method", two robes are stacked together in advance and then worn as a whole. This allows the collar edge of the lining to be show parallel to the collar edge of the outer garment, and a section of the lining to be show behind the lapel.The brocade edge is decorated with a wide belt and fixed with double belt hooks.
This "layered" wearing method shows the layers and details of Chu people's clothing, and can also show the graceful beauty of the body.
In addition, many creative clothing styles and fabric patterns emerged during the Spring and Autumn Period and the Warring States Period, bringing with them the unique atmosphere, mysterious imagination and ultimate romance of that era, becoming our inexhaustible source of art.
--------
Recreation Work by : @裝束复原
Weibo 🔗:https://weibo.com/1656910125/NhBx1oi5n
--------
#chinese hanfu#Warring States period(475–221 BC)#Chu(State)1030 BCE – 223 BCE#hanfu#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#hanfu history#hanfu fashion#imperial china#chinese culture#chinese style#historical fashion#Hanfu From China#漢服#汉服#楚国
631 notes
·
View notes