#cosmologis
Text




31K notes
·
View notes
Text
“there are plenty of fish in the sea” = there are more people out there who you could get with
“sleeping with someone” = having sex with them
“sleeping with the fishes” = got murdered
my proposal: “there are plenty of other fish to sleep with” = next person you fuck will kill you
#we're working on a sex = death = fish cosmology here.#thats why they call orgasms 'the petit mort'.#because of the fish connection.
53K notes
·
View notes
Text

Observations from both NASA’s James Webb and Hubble space telescopes created this colorful image of galaxy cluster MACS0416. The colors of different galaxies indicate distances, with bluer galaxies being closer and redder galaxies being more distant or dusty. Some galaxies appear as streaks due to gravitational lensing — a warping effect caused by large masses gravitationally bending the space that light travels through.
Like Taylor Swift, Our Universe Has Gone Through Many Different Eras
While Taylor's Eras Tour explores decades of music, our universe’s eras set the stage for life to exist today. By unraveling cosmic history, scientists can investigate how it happened, from the universe’s origin and evolution to its possible fate.
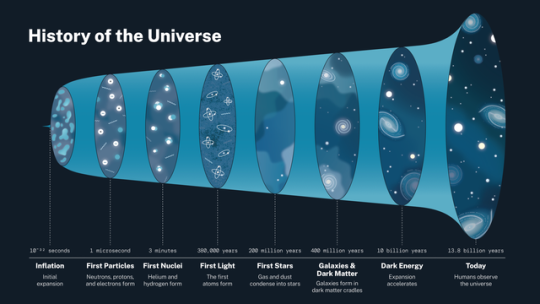
This infographic outlines the history of the universe.
0 SECONDS | In the beginning, the universe debuted extremely small, hot, and dense
Scientists aren’t sure what exactly existed at the very beginning of the universe, but they think there wasn’t any normal matter or physics. Things probably didn’t behave like we expect them to today.

Artist's interpretation of the beginning of the universe, with representations of the early cosmos and its expansion.
10^-32 SECONDS | The universe rapidly, fearless-ly inflated
When the universe debuted, it almost immediately became unstable. Space expanded faster than the speed of light during a very brief period known as inflation. Scientists are still exploring what drove this exponential expansion.
youtube
1 MICROSECOND | Inflation’s end started the story of us: we wouldn’t be here if inflation continued
When inflation ended, the universe continued to expand, but much slower. All the energy that previously drove the rapid expansion went into light and matter — normal stuff! Small subatomic particles — protons, neutrons, and electrons — now floated around, though the universe was too hot for them to combine and form atoms.
The particles gravitated together, especially in clumpy spots. The push and pull between gravity and the particles’ inability to stick together created oscillations, or sound waves.
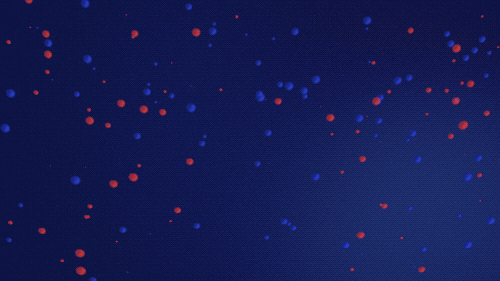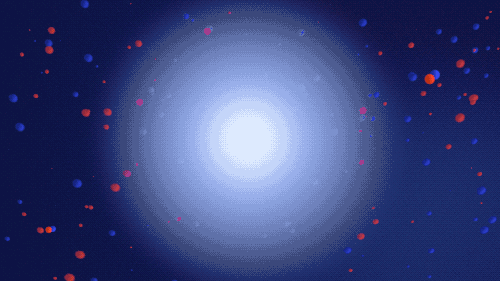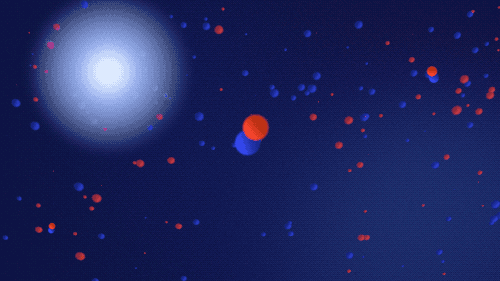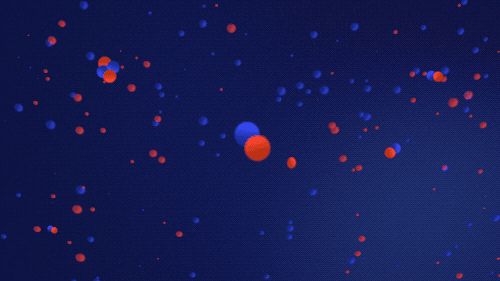
Artist's interpretation of protons and neutrons colliding to form ionized deuterium — a hydrogen isotope with one proton and one neutron — and ionized helium — two protons and two neutrons.
THREE MINUTES | Protons and neutrons combined all too well
After about three minutes, the universe had expanded and cooled enough for protons and neutrons to stick together. This created the very first elements: hydrogen, helium, and very small amounts of lithium and beryllium.
But it was still too hot for electrons to combine with the protons and neutrons. These free electrons floated around in a hot foggy soup that scattered light and made the universe appear dark.
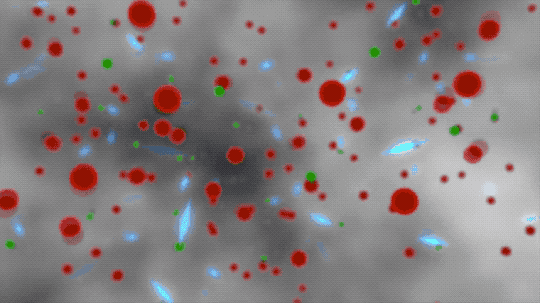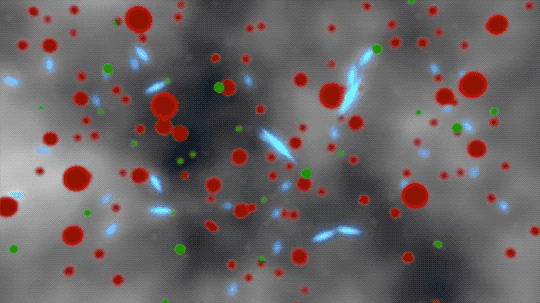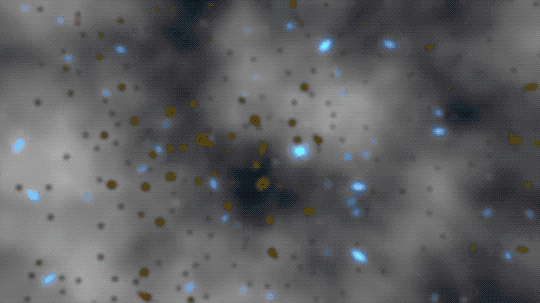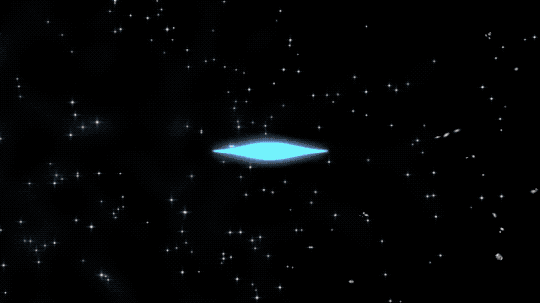
This animated artist’s concept begins by showing ionized atoms (red blobs), free electrons (green blobs), and photons of light (blue flashes). The ionized atoms scattered light until neutral atoms (shown as brown blobs) formed, clearing the way for light to travel farther through space.
380 THOUSAND YEARS | Neutral atoms formed and left a blank space for light
As the universe expanded and cooled further, electrons joined atoms and made them neutral. With the electron plasma out of the way, some light could travel much farther.

An image of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) across the entire sky, taken by ESA's (European Space Agency) Planck space telescope. The CMB is the oldest light we can observe in the universe. Frozen sound waves are visible as miniscule fluctuations in temperature, shown through blue (colder) and red (warmer) coloring.
As neutral atoms formed, the sound waves created by the push and pull between subatomic particles stopped. The waves froze, leaving ripples that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The excess matter attracted even more matter, both normal and “dark.” Dark matter has gravitational influence on its surroundings but is invisible and does not interact with light.

This animation illustrates the absorption of photons — light particles — by neutral hydrogen atoms.
ALSO 380 THOUSAND YEARS | The universe became dark — call it what you want, but scientists call this time period the Dark Ages
Other than the cosmic microwave background, there wasn't much light during this era since stars hadn’t formed yet. And what light there was usually didn't make it very far since neutral hydrogen atoms are really good at absorbing light. This kicked off an era known as the cosmic dark ages.

This animation illustrates the beginning of star formation as gas begins to clump due to gravity. These protostars heat up as material compresses inside them and throw off material at high speeds, creating shockwaves shown here as expanding rings of light.
200 MILLION YEARS | Stars created daylight (that was still blocked by hydrogen atoms)
Over time, denser areas pulled in more and more matter, in some places becoming so heavy it triggered a collapse. When the matter fell inward, it became hot enough for nuclear fusion to start, marking the birth of the first stars!
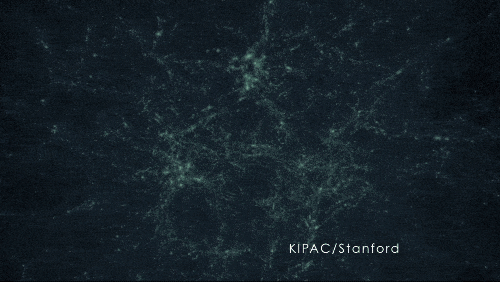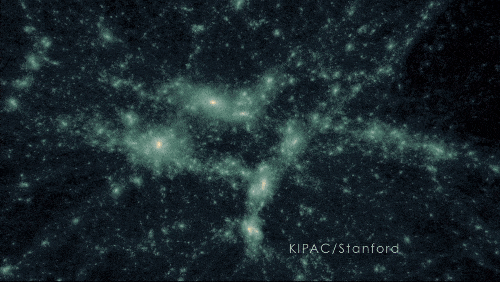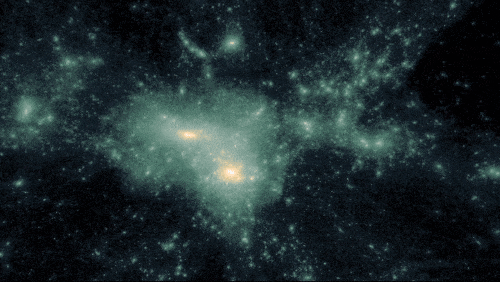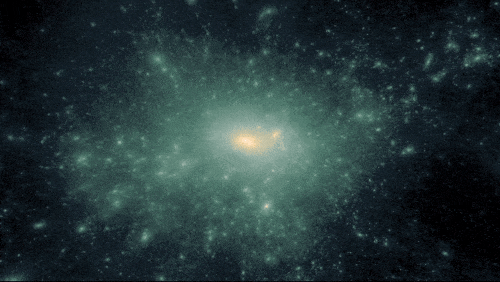
A simulation of dark matter forming structure due to gravity.
400 MILLION YEARS | Dark matter acted like an invisible string tying galaxies together
As the universe expanded, the frozen sound waves created earlier — which now included stars, gas, dust, and more elements produced by stars — stretched and continued attracting more mass. Pulling material together eventually formed the first galaxies, galaxy clusters, and wide-scale, web-like structure.
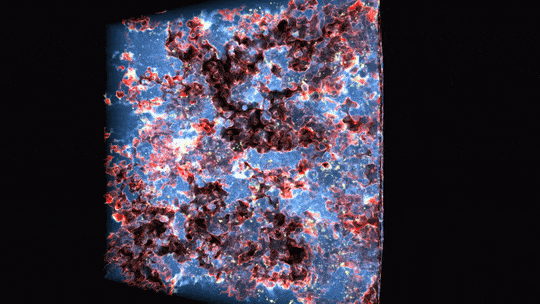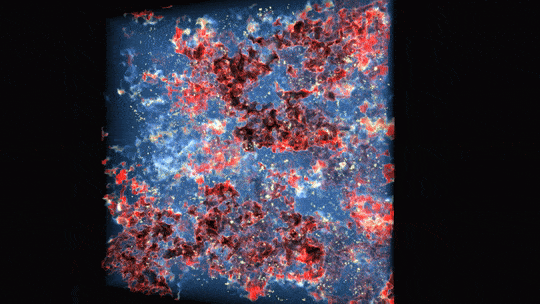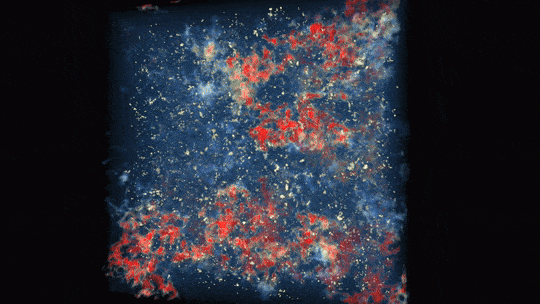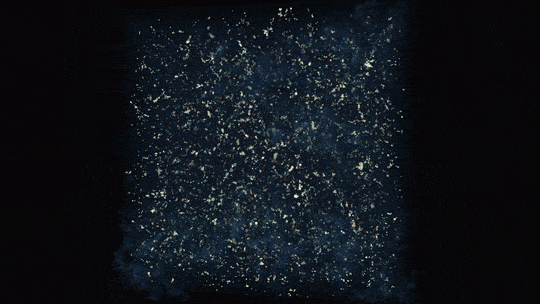
In this animation, ultraviolet light from stars ionizes hydrogen atoms by breaking off their electrons. Regions already ionized are blue and translucent, areas undergoing ionization are red and white, and regions of neutral gas are dark and opaque.
1 BILLION YEARS | Ultraviolet light from stars made the universe transparent for evermore
The first stars were massive and hot, meaning they burned their fuel supplies quickly and lived short lives. However, they gave off energetic ultraviolet light that helped break apart the neutral hydrogen around the stars and allowed light to travel farther.

Animation showing a graph of the universe’s expansion over time. While cosmic expansion slowed following the end of inflation, it began picking up the pace around 5 billion years ago. Scientists still aren't sure why.
SOMETIME AFTER 10 BILLION YEARS | Dark energy became dominant, accelerating cosmic expansion and creating a big question…?
By studying the universe’s expansion rate over time, scientists made the shocking discovery that it’s speeding up. They had thought eventually gravity should cause the matter to attract itself and slow down expansion. Some mysterious pressure, dubbed dark energy, seems to be accelerating cosmic expansion. About 10 billion years into the universe’s story, dark energy – whatever it may be – became dominant over matter.

An image of Earth rising in the Moon’s sky. Nicknamed “Earthrise,” Apollo 8 astronauts saw this sight during the first crewed mission to the Moon.
13.8 BILLION YEARS | The universe as we know it today: 359,785,714,285.7 fortnights from the beginning
We owe our universe today to each of its unique stages. However, scientists still have many questions about these eras.
Our upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will look back in time to explore cosmic mysteries like dark energy and dark matter – two poorly understood aspects of the universe that govern its evolution and ultimate fate.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#space#science#Nancy Grace Roman#STEM#cosmology#YouTube#Taylor Swift#the eras tour
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Ruvina, goddess of winter and sorrow
#ruvina#d20 fantasy high#fantasy high junior year#dimension 20#fhjy#fantasy high#fhjy spoilers#d20 fhjy#lucy frostblade#d20 fanart#yeah so im spinning in circles in my mind like gorgug when he was losing it over mango soda#ribbittrobbit#completely normal about the cosmology of fantasy high#my ipad says i worked on this & ankarna for 12 hours#ice is hard to draw so its just little lines now lol#now i need to go do actual work instead lol
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I like how MP100 fully sidesteps the "But Who Deserves Redemption?" question bc honestly it's a bad framing that gets extremely bogged down in philosophical debates about Good and Evil and who gets to make the call and becomes an awful quagmire and is also not necessary. the better questions are:
Is this person capable of change? (Answer: Yes, always.)
Are they actually going to change? (Answer: That's up to them.)
Do you want them in your life? (Answer: That's up to you.)
12K notes
·
View notes
Text

Calligraphy exam: Write down the number 37, spelled out, nicely.
Exam Numbers [Explained]
Transcript Under the Cut
[6 different math test questions.]
[The first panel:]
Kindergarten math final exam
Q. Write down the biggest number you can think of
A. [empty box]
[The second panel:]
Pre-algebra final exam
Q. Write down the value of x if x=3x-8
A. [empty box]
[The third panel:] Calculus final exam
Q. Write down the value of [integral sign, from 0 to pi] x sin^2 x dx
A. [empty box]
[The fourth panel:] PhD cosmology final exam
Q. Write down the Hubble constant to within 1%
A. [empty box]
[The fifth panel:] Game theory final exam
Q. Write down 10 more than the average of the class's answers
A. [empty box]
[The sixth panel:] Postgraduate math final exam
Q. Write down the biggest number you can think of
A. [empty box]
#xkcd#xkcd 2966#exam numbers#mathematics#kindergarten#pre-alebra#calculus final exam#phd cosmology#ame theory
985 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kikuji Kawada, from The Last Cosmology, 1988
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

512 notes
·
View notes
Text








" Jupiter the most badass planet in the Solar System...
It is the largest & the oldest planet in the Solar System.
It has 79 moons, some of which are even larger than planet Mercury!
It is large enough to fit 1300 Earths.
It is covered with giant storms some of which are even larger than Earth!
jupiter is called a 'Failed Star If it had enough mass, its core could've sustained nuclear fusion like the Sun.
And most importantly..
lts gravity protects Earth from asteroids & comets & also helps stabilize the Solar System"
//© Quantum Royco
#space#Planets#earth#moon#mercury#Venus#Mars#Jupiter#Saturn#Uranus#Neptune#Pluto#solarsystem#cosmos#cosmology#universe#astronomy#spacescience#spaceexploration#physics#science#quantumphysics#astrobiology#planet#planets#galaxy#galaxies#NASA#explore#follow
3K notes
·
View notes
Text





and i knowwww it doesn't really work with how americans write dates but who cares
273 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sam Chivers — Steam-Oxygene (New Scientist, illustration, 2010)
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Pluto in Colorized Infrared NASA
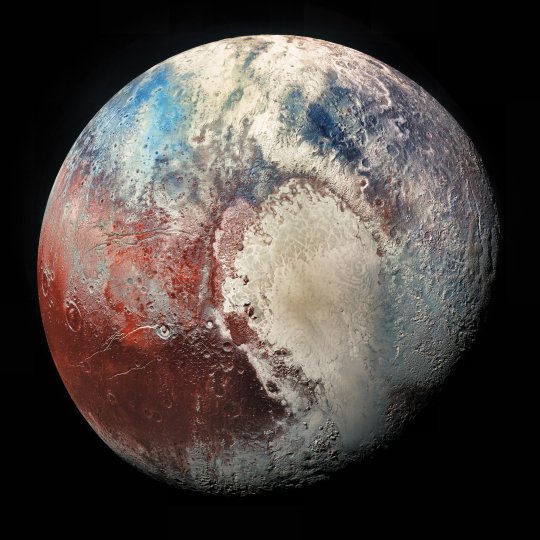

#pluto#space#astronomy#universe#astrophotography#galaxy#nasa#astronout#galaxies#astro#astrology#nasa breaking news#nasa picture of the day#telescope#planet#solar system#astroloji#cosmos#cosmology#astro notes
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo
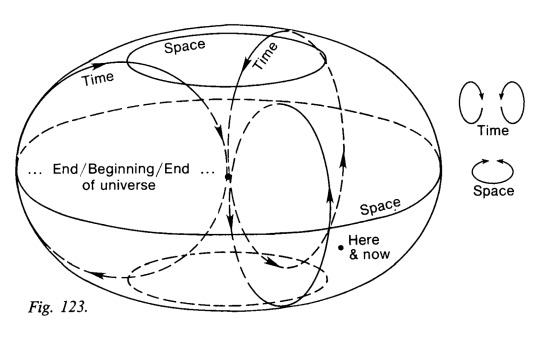
Rudy Rucker, Geometry, Relativity, and the Fourth Dimension
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
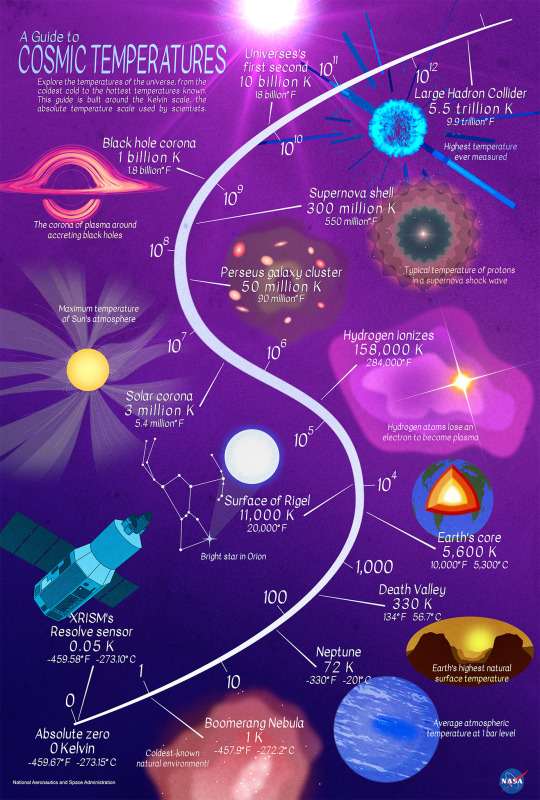
A Tour of Cosmic Temperatures
We often think of space as “cold,” but its temperature can vary enormously depending on where you visit. If the difference between summer and winter on Earth feels extreme, imagine the range of temperatures between the coldest and hottest places in the universe — it’s trillions of degrees! So let’s take a tour of cosmic temperatures … from the coldest spots to the hottest temperatures yet achieved.
First, a little vocabulary: Astronomers use the Kelvin temperature scale, which is represented by the symbol K. Going up by 1 K is the same as going up 1°C, but the scale begins at 0 K, or -273°C, which is also called absolute zero. This is the temperature where the atoms in stuff stop moving. We’ll measure our temperatures in this tour in kelvins, but also convert them to make them more familiar!
We’ll start on the chilly end of the scale with our CAL (Cold Atom Lab) on the International Space Station, which can chill atoms to within one ten billionth of a degree above 0 K, just a fraction above absolute zero.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Just slightly warmer is the Resolve sensor inside XRISM, pronounced “crism,” short for the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission. This is an international collaboration led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) with NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). Resolve operates at one twentieth of a degree above 0 K. Why? To measure the heat from individual X-rays striking its 36 pixels!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Resolve and CAL are both colder than the Boomerang Nebula, the coldest known region in the cosmos at just 1 K! This cloud of dust and gas left over from a Sun-like star is about 5,000 light-years from Earth. Scientists are studying why it’s colder than the natural background temperature of deep space.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Let’s talk about some temperatures closer to home. Icy gas giant Neptune is the coldest major planet. It has an average temperature of 72 K at the height in its atmosphere where the pressure is equivalent to sea level on Earth. Explore how that compares to other objects in our solar system!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
How about Earth? According to NOAA, Death Valley set the world’s surface air temperature record on July 10, 1913. This record of 330 K has yet to be broken — but recent heat waves have come close. (If you’re curious about the coldest temperature measured on Earth, that’d be 183.95 K (-128.6°F or -89.2°C) at Vostok Station, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.)
We monitor Earth's global average temperature to understand how our planet is changing due to human activities. Last year, 2023, was the warmest year on our record, which stretches back to 1880.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
The inside of our planet is even hotter. Earth’s inner core is a solid sphere made of iron and nickel that’s about 759 miles (1,221 kilometers) in radius. It reaches temperatures up to 5,600 K.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We might assume stars would be much hotter than our planet, but the surface of Rigel is only about twice the temperature of Earth’s core at 11,000 K. Rigel is a young, blue star in the constellation Orion, and one of the brightest stars in our night sky.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We study temperatures on large and small scales. The electrons in hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, can be stripped away from their atoms in a process called ionization at a temperature around 158,000 K. When these electrons join back up with ionized atoms, light is produced. Ionization is what makes some clouds of gas and dust, like the Orion Nebula, glow.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We already talked about the temperature on a star’s surface, but the material surrounding a star gets much, much hotter! Our Sun’s surface is about 5,800 K (10,000°F or 5,500°C), but the outermost layer of the solar atmosphere, called the corona, can reach millions of kelvins.
Our Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft to fly through the corona in 2021, helping us answer questions like why it is so much hotter than the Sun's surface. This is one of the mysteries of the Sun that solar scientists have been trying to figure out for years.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Looking for a hotter spot? Located about 240 million light-years away, the Perseus galaxy cluster contains thousands of galaxies. It’s surrounded by a vast cloud of gas heated up to tens of millions of kelvins that glows in X-ray light. Our telescopes found a giant wave rolling through this cluster’s hot gas, likely due to a smaller cluster grazing it billions of years ago.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Now things are really starting to heat up! When massive stars — ones with eight times the mass of our Sun or more — run out of fuel, they put on a show. On their way to becoming black holes or neutron stars, these stars will shed their outer layers in a supernova explosion. These layers can reach temperatures of 300 million K!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Jeremy Schnittman
We couldn’t explore cosmic temperatures without talking about black holes. When stuff gets too close to a black hole, it can become part of a hot, orbiting debris disk with a conical corona swirling above it. As the material churns, it heats up and emits light, making it glow. This hot environment, which can reach temperatures of a billion kelvins, helps us find and study black holes even though they don’t emit light themselves.
JAXA’s XRISM telescope, which we mentioned at the start of our tour, uses its supercool Resolve detector to explore the scorching conditions around these intriguing, extreme objects.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/CI Lab
Our universe’s origins are even hotter. Just one second after the big bang, our tiny, baby universe consisted of an extremely hot — around 10 billion K — “soup” of light and particles. It had to cool for a few minutes before the first elements could form. The oldest light we can see, the cosmic microwave background, is from about 380,000 years after the big bang, and shows us the heat left over from these earlier moments.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We’ve ventured far in distance and time … but the final spot on our temperature adventure is back on Earth! Scientists use the Large Hadron Collider at CERN to smash teensy particles together at superspeeds to simulate the conditions of the early universe. In 2012, they generated a plasma that was over 5 trillion K, setting a world record for the highest human-made temperature.
Want this tour as a poster? You can download it here in a vertical or horizontal version!
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Explore the wonderful and weird cosmos with NASA Universe on X, Facebook, and Instagram. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

the infinite desires
#artists on tumblr#photography#astrophotography#astrophysics#astro observations#astronomy#astro notes#astro community#astronomical objects#astronomical observation#astronomical#astronomers#astrology observations#observatories#cosmic secrets#cosmology#cosmic dreams#cosmic poetry#cosmic art#outer space#planets#space art#galaxy#other worlds#infinite universe#expanding universe#supernova
429 notes
·
View notes
Text
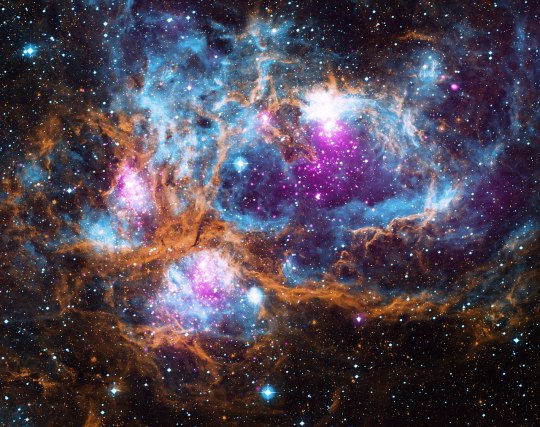

NGC 6357; The lobster nebula
Located within the Milky Way, about 5,500 light years from Earth, frosty-looking NGC 6357 is actually a "cluster of clusters" containing at least three clusters of young stars as well as the rest of the older, dimmer population of local stars.
#astronomy#astrophotography#astro community#science#photography#cosmos#nebula#outer space#space#chandraxrayobservatory#cosmology#astrophile#astrophysics
419 notes
·
View notes