#culture celtic
Text
'Wool waulking is a traditional Scottish process of finishing and strengthening newly woven woolen fabrics. It is a significant social and cultural activity, often carried out by women in the Highlands of Scotland. The Gaelic songs that are sung during waulking have a distinctive rhythmic pattern that aids in synchronising the work.'
(Video and text via Inverness Outlanders)
#so obsessed with waulking songs so i had to share this#folk#folk culture#scotland#scottish folklore#celtic folk#scottish gaelic
14K notes
·
View notes
Text

traditional welsh dress miku and a celtic warrior miku too :D
#hatsune miku#international miku#artists on tumblr#anime#cute#reblogs welcome#reblogs encouraged#digital artist#idkkkk I just love all the international mikus I've seen and i thought this would be fun#and it was!#welsh culture#wales#cymru#celtic#sorry for wonkiness as far as clothing goes#kinda going by memory mostly
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Not to mention that the Triple Goddess "archetype" reinforces gender roles/stereotypes and sometimes bioessentialism when placed in the "right" hands.
#also morgan is an actual expert on this culture/time period#not just some pagan all in their feelings#morgan daimler#irish paganism#celtic paganism#triple goddess#paganism#pagan#witchcraft#witchblr#the white goddess#robert graves
495 notes
·
View notes
Text


The 'Carnyx' Nightmare of the Roman Soldiers
The Carnyx was a brass musical instrument used as a psychological weapon of war by the ancient Celts between 300 BC and 200AD in western and central Europe and beyond.
The carnyx was once widespread throughout much of Europe, although only a dozen or so fragments are known to us.
It was carried by bands of Celtic mercenaries; it was present at the attack on the Greek sanctuary at Delphi in 279 BC; it defied Julius Caesar in Gaul; and it faced Claudius when he invaded Britain. They are even shown on a Buddhist sculpture in India, proof of the far-flung connections of the Iron Age world.
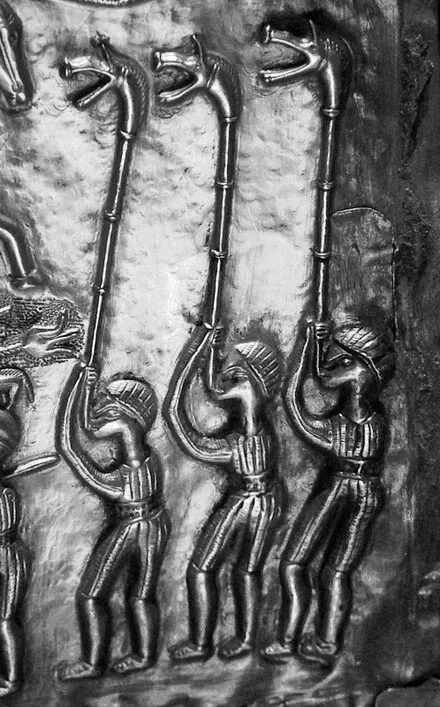

However, they were not only used by the Celts; they were also used by the Dacians in modern Romania. The term “Celtic” is a complicated one. The concept of a pan-European Celtic culture is a myth; rather, aspects of art and technology were shared across vast distances by diverse cultures. The carnyx was one example of this.
A 12-foot-long, thin bronze tube with right-angle bends on both ends made up the carnyx. The lower end ended in a mouthpiece, and the upper end flared out into a bell that was usually decorated to look like a wild boar’s had. Historians believe it had a tongue that flapped up and down, increasing the noise made by the instrument. The carnyx was played upright so that the boar’s head bell protruded well above the warriors’ heads. Its primary goal was to create more noise and confusion on the battlefield.



The Greek historian Polybius (206-126BC) was so impressed by the clamor of the Gallic army and the sound of the carnyx, he observed that “there were countless trumpeters and horn blowers and since the whole army was shouting its war cries at the same time there was such a confused sound that the noise seemed to come not only from the trumpeters and the soldiers but also from the countryside which was joining in the echo”.
And the Roman historian Diodorus Siculus wrote, “Their trumpets are also of a peculiar and barbaric kind which produce a harsh, reverberating sound suitable to the confusion of battle.”
Archaeologists discovered a hoard of ritually destroyed weapons in 2004, including a dozen swords, scabbards, spearheads, a shield, bronze helmets, an iron helmet shaped like a swan, a cauldron, animal remains, and seven carnyces. Before the Tintignac discovery, the remains of only five actual carnyces had been found.
The finest was unearthed in Deskford, Scotland in 1816. The Deskford carnyx only has the boar’s head bell and is missing the mane, tongue, and tubing. Images of Carnyx players have been found as well. A Roman denarius, dating from 48 BC bears a representation of a Carnyx. Three carnyx players are featured prominently on the Gundestrup Cauldron, which was found in a Danish peat bog.
One of the seven found at Tintignac, on the other hand, was almost entirely complete. The Tintignac Carnyx was broken into 40 pieces. When puzzled back together, it was found to be just an inch short of six feet long with a single missing section of the tube. The bell was a boar’s head with protruding tusks and large pointed ears. Once restored, the Tintignac Carnyx proved to be the first virtually complete carnyx ever found.
By Leman Altuntaş.
Music video by John Kenny.
#The Carnyx#The 'Carnyx' Nightmare of the Roman Soldiers#Iron Age war trumpet#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#celtic mythology#celtic history#roman history#roman empire#roman legion
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Saint Fin Barre's Cathedral.
Cork, Munster, Ireland.
#cork#cork city#cork ireland#ireland#irish#celtic#europe#european#irish art#irish culture#irish monument#place to visit#visit ireland#visit#travel#trip#monument#cathedral#church#religion#christianity#history#culture#heritage#art#neogothic#munster#canon#canonphotographer#canonphotography
280 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fellow pagans. Remember that the pagan experience is not purely an ex Christian experience. That experience is worth talking about, but please don't talk about the pagan experience as if leaving Christianity is universal to being neopagan.
Ex atheist pagans deserve to have their experiences acknowledged by the community.
Ex Muslim pagans deserve to have their experiences acknowledged by the community.
Non practicing Jewish pagans deserve to have their experiences acknowledged by the community.
Pagans who have been pagan for most or all of their life deserve to have their experiences acknowledged by the community.
#196#paganism#paganblr#pagan community#pagan culture#pagan#hellenic pagan#hellenic polytheism#norse paganism#norse polytheism#norse heathen#heathenism#heathenry#celtic paganism#celtic polytheism#ex christian#ex muslim#ex atheist#atheism#jewish#non practicing jew
298 notes
·
View notes
Text

Iron Age Netherurd Gold Torc Terminal, 1st Century BCE, National Museums Scotland, Edinburgh
This terminal for a gold neck ring and two gold coins are all that remain of a large hoard of gold coins and neck rings found at Netherurd in Peeblesshire. The coins were minted in Gaul in the 1st century BCE, while the terminal fragment is an East Anglian type.
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#iron age#prehistoric#prehistory#neolithic#mesolithic#paleolithic#torc#gaul#celtic#archaeology#ancient crafts#ancient cultures#ancient living#metalwork#gold#wealth#status#Scotland#hoard
200 notes
·
View notes
Text




Unfinished portraits of Irish gods from 2021
#celtic#celtic paganism#celtic mythology#celtic polytheism#irish paganism#irish mythology#irish#paganachd#pagan#paganism#druidism#druidry#irish culture#ireland#eire#ancient ireland#ancient celts#mythology#digital art#digital illustration#portrait#art wip#unfinished
243 notes
·
View notes
Text
See, I personally find this quest to find pagan/pre-Christian elements in Welsh/Irish literature quite unnerving - I don't know about anyone else.
There's something to be said about genuinely discovering pre-Christian elements in a narrative or story and that being where evidence and study has led you. But I see some people on this fruitless quest to find pagan elements in very Christian texts and sometimes it feels like if no pagan elements can be found, people start making stuff up out of whole cloth - and that can be very dangerous for already not-well known texts in minoritised languages!
There's already so much misinformation out there about Irish/Welsh texts and literature in general - so it hurts to see people carelessly adding to the misinformation either out of ignorance or lack of respect for the source material.
I promise you the source material being Christian doesn't ruin it - you can in fact, enjoy these myths without making them into something they're not!
#I feel like general ire towards (particularly) colonial Christianity has informed how people think of and view anything that is associated#with Christianity - and ire towards some of the ills committed in the name of Christianity is very valid actually#but what it isn't is approaching any text written in a Christian context and immediately disregarding it for having anything unique or#insightful to say. And in a Celtic languages context#this can be especially othering and almost fetishistic of an imagined pagan Ireland and Wales which was 'covered up' by Christianity#and that desire for people outside of Ireland and Wales to impose a kind of 'pagan faerie culture' onto the modern countries directly feeds#into false depictions of Ireland and Wales as 'lost in time' or as magical places full of latent pagan culture &c. which can be really#damaging in its own way against people who live in Wales or Ireland or who speak Welsh or Irish#this goes for other Celtic speaking nations too like Scotland Brittany Isle of Man and Cornwall#But Wales and Ireland tend to be the most focused on for this kind of treatment#luke's originals#Welsh#Wales#Cymblr#Irish#Ireland#welsh mythology#irish mythology#irish literature#welsh literature#Arthurian legends#arthurian literature
353 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which deities do you personally associate with change/transformation?
#hellenic polytheism#norse polytheism#kemetic polytheism#celtic polytheism#gaelic polytheism#irish polytheism#welsh polytheism#roman polytheism#slavic polytheism#gaulish polytheism#deity work#deity worship#pop culture polytheism
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, why do people care so much about Cornish identity? Cornwall’s just a part of England right? Another county with some distinct foods and a funny accent, and they moan about the tourists- when they should be grateful for the money.
Except it’s not.
Whilst the rest of England was forming with a character influenced by Germanic and Norse cultures, Cornwall was holding itself separate as an independent Celtic kingdom, with strong links with Wales, Ireland and Brittany- as well as trading with the wider Mediterranean. For a long time, this kingdom included parts of Devon, but eventually the Celtic people were forced back past the Tamar, and at some point started referring to the land as Kernow, rather than Dumnonia (probably).
Even after the Norman conquest, in part because Cornwall came under the control of the Duke of Brittany, Cornwall retained elements of its unique culture, and certainly its language. There are existing works of literature written in the Cornish language (also called Kernewek) during the medieval period. Due to the active tin mining industry and the Stannary courts, they even had a separate legal system.
All of this continued until the start of the Tudor period, when Henry VII, desperate for money for his wars with Scotland, suspended the operation of the Cornish Stannaries, and imposed greater taxes. This ultimately led to the Cornish Rebellion of 1497. An army of as many as 15000 rebels marched towards Somerset, and ultimately to London, where the rebels met with Henry VII’s armies. Unfortunately, the Cornish lost the ensuing battle, and the rebel leaders were captured, killed and quartered, with their quarters being displayed in Cornwall and Devon. From 1497 to 1508, Cornwall was punished with monetary penalties, impoverishing the people, and land was given to the king’s (English) allies.
However, this wasn’t the death of Cornish culture or dreams of independence from England. Until 1548, Glasney college was still producing literature in Cornish- when it was destroyed in the dissolution of the monasteries, during the English reformation. The following year, 1549, the Cornish rose again- this time to demand a prayer book in their own language, which was still the first (and often only) language of most people in the region. The rebellion was also about the ordinary people vs the landowners, as shown by their slogan “kill all the gentlemen”.
Unfortunately, this rebellion failed too, and this time, it wasn’t just the leaders who were killed, but up to 5,500 Cornishmen- which would have been a significant proportion of the adult male population at the time. These factors combined are widely thought to have contributed to the decline of the Cornish language- although it was still widely in use centuries later.
Despite the failings of these rebellions, the Cornish retained a distinct language and their own culture, folklore and festivals. Mining, farming and fishing meant that the region itself wasn’t economically impoverished, as it was today. Even towards the end of the 1700s, there were still people who spoke Cornish fluently as a first language (including Dolly Pentreath, who definitely wasn’t the last Cornish speaker).
However, over time, the tin mines became less profitable, and Cornwall’s economy started to suffer. Especially in the latter part of the 19th century, many Cornish began to emigrate, especially to places like Australia, New Zealand (or Aotearoa), Canada and South America. Cornish miners were skilled, and were able to send pay back home, and along with the Welsh, influenced culture and sport in many of these places. Many mining terms also have their roots in Cornish language and dialect.
Throughout the 20th Century, Cornwall went through an economic decline- to the point where, when the UK was an EU member, Cornwall was receiving funding intended for only the most deprived regions in Europe. It was one of very few places in the UK to receive this funding- due to the levels of poverty and lack of infrastructure.
Part of the decline was also linked to the decline of historic fish stocks, such as mackerel. In the 70s and 80s, there was a mackerel boom- and large fishing trawlers came from as far away as Scandinavia (as well as Scotland and the north of England) to fish in Cornish waters. The traditional way of fishing in Cornwall used small boats and line fishing. The local fishermen couldn’t compete, and ultimately stocks were decimated by the trawlers. Many more families had to give up their traditional way of life. One could draw parallels here with worldwide indigenous struggles over fishing rights.
Despite this, Cornish communities retained their traditional folklore and festivals, many of which are still celebrated to this day. And throughout the 20th Century, efforts were made to preserve the Cornish language. Although there may not be any first language Cornish speakers left, it is now believed that community knowledge of the language was never truly lost.
Cornwall has since become a popular tourist destination. This brings its own problems- many people want to stay in self-catering accommodation and, more recently, air bnbs. This, alongside second homes, has gutted many Cornish communities. The gap between house prices and average wages is one of the largest in the country. Land has become extremely expensive, which hurts already struggling farmers. Roads can’t cope with the level of traffic. The one (1) major hospital can’t cope with the population in the summer. All of last winter, most Cornish households faced a “hosepipe ban” due to lack of water- yet in the summer, campsites and hotels can fill their swimming pools and hot tubs for the benefit of tourists.
Does this benefit Cornwall? Only about 13% of Cornwall’s GDP comes from tourism. The jobs associated with tourism are often poorly paid and may only offer employment for part of the year. People who stay in Air BnBs may not spend that much money in the community, and the money they pay for accommodation often goes to landlords who live upcountry and aren’t Cornish. Many major hotels and caravan sites are also owned by companies that aren’t Cornish, taking money out of the local economy.
Match this with a housing crisis where it’s increasingly difficult to rent properties long term, and buying a flat or house in Cornwall is out of reach of someone on the average salary and it’s easy to see why people are having to leave communities where their family lived for generations. This damages the local culture, and means centuries-old traditions can come under threat.
All of this feeds into the current situation; it feels like middle class families from London see Cornwall as their playground, and moan about tractors on the road, or the lack of services when they visit. People talk about theme park Cornwall- a place that’s built for entertainment of outsiders, not functionality for those who live here. More widely, a lot of people around the UK have never heard of the Cornish language, or view it as something that’s “extinct” or not worth preserving.
The Cornish are one of Britain’s indigenous cultures, alongside Welsh, Gaelic, Scots, Manx and others. And it’s a culture that’s increasingly under threat economically and culturally. We’ve been clinging on to our homes for a long time, and even now it still feels like we might be forced from them (indeed some of us are). So yes, Cornish people can seem excessively defensive about our identity and our culture- but there’s good reason for it!
#uk politics#cornwall#cornish#kernow#kernewek#celtic languages#minority languages#minority cultures#Cornish history#cornish langblr
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
Valyrian Wedding Rituals & Its Parallels

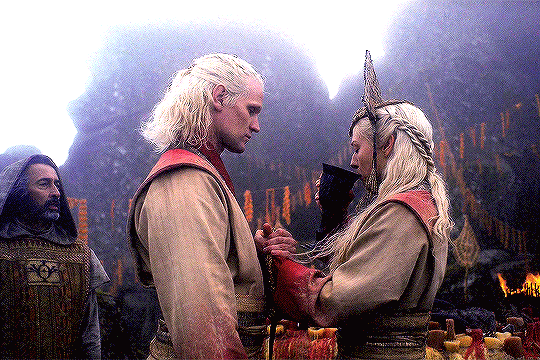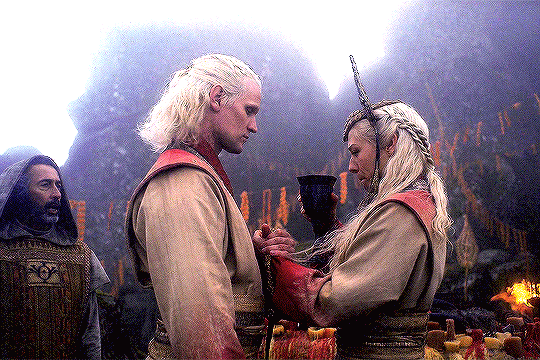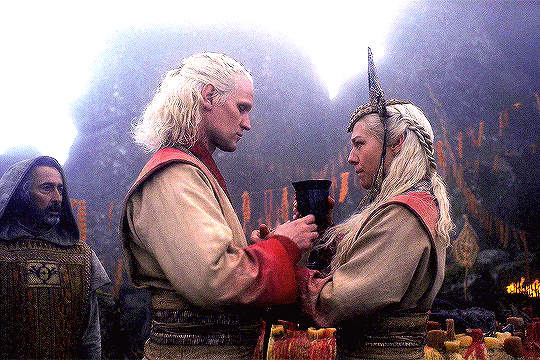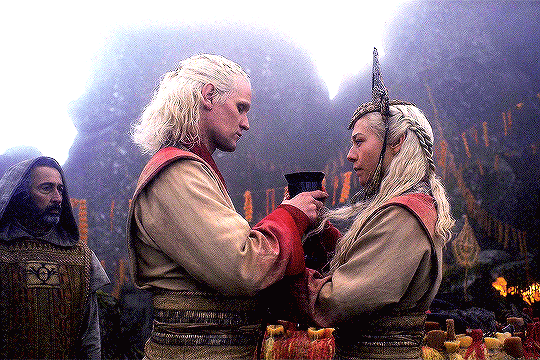




“Among the people who came to inhabit Northumbria and the Lothians, as well as among other Germanic peoples, the nuptials were completed in two distinct phases. (…) The parties plighted their troth and the contract was sealed, like any other contract, by a hand-shake. This joining of hands was called handfæstung in Anglo-Saxon, and the same word is found in different forms in the German, Swedish and Danish languages. In each it means a pledge by the giving of the hand.”
Handfasting' in Scotland - The Scottish Historical Review; Anton, A. E. (1958)
“In ancient Rome, a wedding was a sacred ritual involving many religious practices. (…) In a Roman wedding both sexes had to wear specific clothing. Men had to wear the toga virilis while the bride to wear a wreath, a veil, and a yellow hairnet.”
Women's Costume and Feminine Civic Morality in Augustan Rome; Sebesta, Judith Lynn (1997)
“ When the terms of the ketubah were accepted a cup of wine was shared to seal the marriage covenant. (…) The bride and groom shared the same cup, symbolizing the shared life that would be theirs. (…) Wine in Judaism has always symbolized joy. (…) Wine also symbolized blood. The marriage covenant is a blood covenant in the eyes of God. Two lives become one in a lifelong commitment.”
The Ancient Jewish Wedding; Lash, Jamie (2012)
#daemon targaryen#daemon x rhaenyra#daemyra#hotd#fantasy#game of thrones#rhaenyra targaryen#house of the dragon#house targaryen#asoiaf#wedding vows#old valyria#ancient rome#roman empire#roman history#jewish history#judaism#jewish culture#celtic paganism#scottish
249 notes
·
View notes
Text
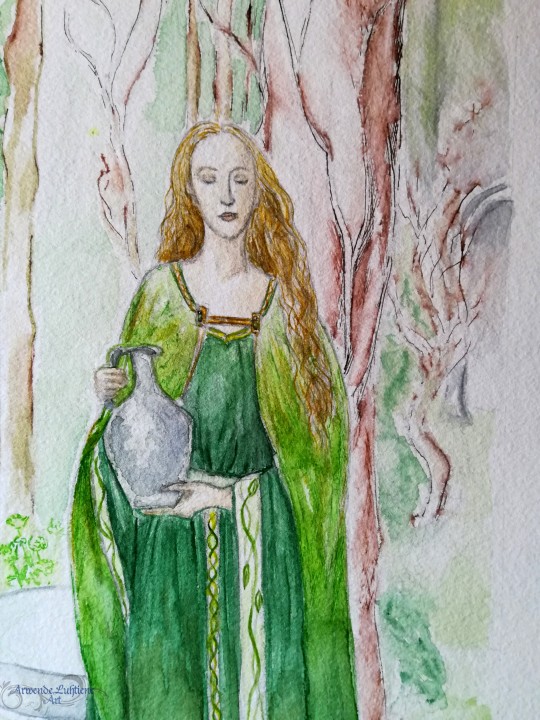
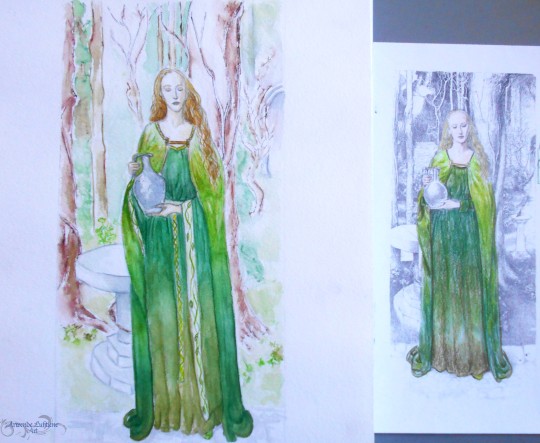
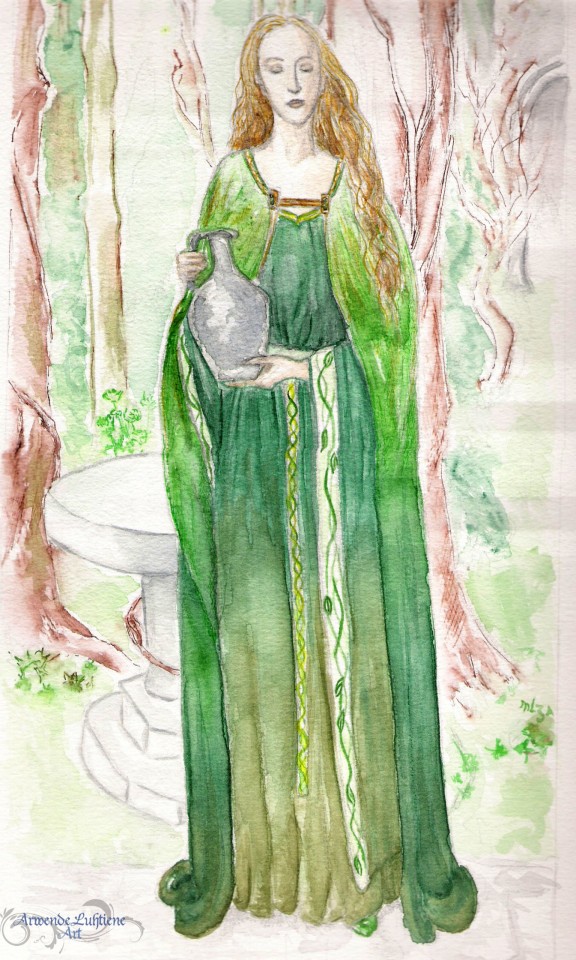








Happy Ostara/Easter/belated Spring Equinox 😊🌸🌿 🐰🥚🍫!
.
✨Valar and Valier series (late 2000s)✨ - 🌳🌿Yavanna Kementári🌿🌳 Initial practice sketch, the final painting and a couple of details.
.
I now prefer to headcanon Yavanna as dark-skinned, but I quite like how this watercolour turned out - especially the gradation of the different greens in the dress and mantle, and the trees in the background. I also love Alan Lee's original drawing on which this painting is based 🌿💚 (swipe for the comparison! Original is black and white, coloured by me as a guide for the painting).
.
Some years ago I started a 'Valar and Valier' project in which I took an existing painting/drawing as reference/inspiration to draw/paint one of the Valar. So far, I've done Varda, Yavanna, Nienna, Mandos and Aulë, and I also have some sketches of Nessa, Vána and Estë. Hope to get back to this project sometime!
.
. 🎨Media: Graphite, watercolours, inks, ink wash
. 🌱References: Alan Lee's drawing of the Celtic fae Ladies of the Land of the Young, for the book Faeries.
🎨ArtStation
🎨Instagram
🎨 DeviantArt
#tolkien#yavanna#tolkien art#silmarillion#silmarillion art#silmarillion fanart#tolkien fanart#yavanna kementári#My art#watercolour painting#alan lee#kementári#valaquenta#valier#valar#goddess art#lotr#lotr art#lotr fanart#lord of the rings#lord of the rings art#lord of the rings fanart#graphite drawing#watercolours#celtic culture#celtic mythology#irish mythology#faeries#tolkien women#ostara
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
Someday, eventually, I will get an opportunity to talk about Celtic Apollo.
I see a lot of discussions and content (light-hearted and not) talking about Greek Apollo and Roman Apollo but y'all don't understand; it wasn't just that Greek Apollo had a second Roman Apollo hidden in his pocket, it's that Greek Apollo also has a secret third Celtic Apollo hidden behind his back like a tramp stamp he got in college and refuses to acknowledge or show to anyone.
#ginger rambles#Even then it wasn't secret or hidden at all#According to a couple sources but most relevantly Pindar Apollo would spend his winters in Hyperborea because he works entirely too much#the other nine months of the year#Hyperborea was actually England y'all it was England this whole time#It's hilarious btw because obvi Boreas the literal winter wind was the Greeks' big concept of cold? And Hyperborea was considered#even more north than Boreas hence the name and I just love the idea of the thing that is more cold than even winter itself being England#Anyway Celtic Apollo is rad as hell#He was even sycretised into a bunch of other gods because when the Romans came to do their whole conquering thing#(the first time not the time they succeeded)#They were like “gee wilkers y'all have Apollo too :0” and the Celts were like “???” because they didn't speak Latin#Anyway the real secret is that Celtic Apollo is actually at least three other Apollos in a trenchcoat#Namely Maponos Belenus and Lugh (and yes this is a fun little cross cultural equivalency thing#like the greco-egyptian pantheon equivalents#I won't call Horus Egyptian Apollo because it's more like Horus and Apollo co-evolved like brothers separated at birth#But I also definitely want to call Horus Egyptian Apollo because I'm an Apolline menace#ginger chats about greek myths#apollo#greek mythology
37 notes
·
View notes
Text



Ancient Celtic Bronze Head of a Bull
5th Century BC
#Ancient Celtic Bronze Head of a Bull#5th Century BC#bronze#bronze sculpture#bronze statue#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient gaul#celtic art#ancient art#art history
386 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dom a Lloyd : Cymru Heddiw
youtube
Hiiii!! Please share this. This is a cool video regarding Black Welsh speakers and some of the progress and some of the obstacles that have been happening in the country of Wales in regarding to Black Welsh people. Everyone can be a part of revitalizing a language and in regards to revitalizing indigenous languages (like Welsh) anti-Blackness should have no place in the process. This is something I think no one really talks about and I LOVE this YouTube channel it needs more subscribers for sure!!
#welsh#black culture#black people#black girl magic#wales#celtic#welsh language#cymru#cymraeg#black pride#black history#indigenous#indigenous languages#indigenous issues#diaspora#intercultural#welsh culture#celtic pride#Youtube
193 notes
·
View notes