#fukushima nuclear disaster
Text
Japan releases Fukushima water

View On WordPress
#animals#asia#fish#fishing#fukushima#Fukushima nuclear disaster#japan#meme#memes#news#pacific#pollution#radioactive#waste#wildlife
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

1 note
·
View note
Text
☢️ Today, on August 24th, 2023, Japan will be releasing over 1 Million Metric Tons of Radioactive waste water from the destroyed Fukushima Nuclear Reactor into the Pacific Ocean ☢️
#nuclear waste#fukushima#nuclear pollution#water pollution#pollution#capitalist disasters#climate change#climate crisis#environmentalism#socialism#communism#marxism leninism#socialist politics#socialist news#socialist worker#socialist#communist#marxism#marxist leninist#progressive politics#politics#japan news#Imperialism#worker solidarity#workersolidarity#fuck capitalism#crimes of capitalism
64 notes
·
View notes
Text

Damn right! Been there, done that
#apocalypse#covid 19#ebola 2014#ebola#fukushima#h1n1#h5n1#09112001#09/11/2001#ussr#chernobyl#nuclear#nuclear disaster#vietnam war#kennedy assassination#deep state
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
the elephants foot is not that dangerous anymore. i nominate the fukushima fuel masses to take its place in popular culture as the most radioactive thing you can think of.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text


in case you missed this terribly scripted PR for irradiated fish, Japan Prime Minister Fumio Kishida fully endorses Pure Frack™ Privatized Water™ Fallout Formula™ by Neztlū Waters®.
#capitalism#disaster capitalism#fukushima prefecture#fukushima#japan#nuclear waste#pollution#neztlū waters#my art#fumio kishida#japan prime minister#environment#climate crisis#environmental justice#water#seafood#sushi#ocean#chernobyl redux#2023#2020s
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
70 Years After WWII, Japan Brings New Disaster To The World
— Chen Yang | August 24, 2023

Illustration: Liu Rui/Global Times
Japan kick starts discharging the Nuclear-Contaminated Water Stored at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear ☢️ Power Plant into the sea on Thursday afternoon. This move, prioritizing Japanese government's own interests over the common interests of all humanity, will ultimately lead to Japan's isolation and leave another indelible permanent stain on human history.
On March 11, 2011, a magnitude-9 earthquake struck off the coast of northeastern Japan, triggering a towering tsunami that caused a nuclear leak at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear ☢️ Power Plant. As of now, the amount of nuclear-contaminated wastewater stored in Japan has exceeded 1.3 million tons, and it is increasing by 100 tons per day. In April 2021, the Japanese government decided to dump the nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean, choosing the most convenient and irresponsible method among various methods of treating the contaminated water. Since the Japanese government plans to discharge the nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean over a period of 30 years, the impact on the global marine ecosystem and human health and well-being is not temporary, but long-term and enduring.
Since deciding to dump nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean, Japan has consistently faced strong opposition from domestic and international public opinion. On Tuesday, the chairman of the National Federation of Fisheries Co-operative Associations in Japan, Masanobu Sakamoto, reiterated during a meeting with Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida, "Nothing will change in our opposition to the release of water into the ocean without the understanding of fishermen and the public."
On July 1, South Korea's main opposition Democratic Party, held a rally in Seoul condemning the Japanese government's plan to dump nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean, urging the South Korean government to clearly oppose it.

Cooperation Needed to Minimize Economic Risk Brought by Fukushima Nuclear ☢️ Contaminated Water Dumping — Hu Weijia! August 23, 2023. Japan's reckless dumping of nuclear wastewater poses a grave danger to Earth. Cartoon: Carlos Latuff
Despite the continuous doubts and opposition to the discharge of nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean from Japan domestically and internationally, the Japanese government has turned a deaf ear and insisted on pushing forward with the discharge process. This fundamentally reflects that discharging nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean is a selfish act that sacrifices the public health and well-being of its own country and neighboring countries and regions in exchange for short-term benefits.
In fact, one of the main reasons why Japan has insisted on dumping nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean is the tacit approval and tolerance of the US, which has long claimed to be a "defender of human rights."
The US is Japan's ally and has had a wide range of influence on Japanese politics, diplomacy, culture and other aspects. It can even influence Japan's domestic and foreign policies to some extent. In theory, the US should exert its influence to prevent Japan from adopting irresponsible practices in dumping nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean. However, unfortunately, regarding this public issue that poses a threat to the global marine ecosystem and human health and well-being, the US did not criticize or condemn it, worse, it praised the Japanese government for its "transparent efforts" in dealing with the issue and considered Japan's dumpingplan to be "safe."

Fishers Against Fukushima Nuclear ☢️ Contaminated Water Dumping! Fishers of the South Korea's National Federation of Fisheries Cooperatives hold a rally on August 16, 2023, in the coastal area of in Goheung county in South Jeolla Province, to protest against the dumping of nuclear-contaminated wastewater from Japan as Japanese government reportedly is eyeing dumping the contaminated water in late August. Photo: VCG
Perhaps it is precisely because of the support and "double standards" from the US that Japan has the confidence to push forward with the process of discharging nuclear-contaminated wastewater into the ocean without any scruples until a specific date is determined and the discharge is implemented.
During World War II, Japan launched aggressive wars against neighboring countries, bringing great disasters to neighboring countries and regions. Today, the discharge of nuclear-contaminated wastewater can be said to be a new disaster that Japan, which has gone through defeat and surrender for more than 70 years, has brought to neighboring countries and regions.
The ocean is the common property of all humanity, not a dumping ground for Japan's arbitrary disposal. Regarding the issue of nuclear-contaminated wastewater, Japan should recognize its own responsibility, adopt a scientific attitude, fulfill its international obligations, and respond to the serious concerns of its own citizens, neighboring countries and the international community. If it simply ignores these concerns, it will ultimately leave an indelible permanent stain on Japan in human history.
— The Author is a Guest Research Fellow at the Centre for Japanese Studies, Liaoning University.
#Nuclear ☢️ Contaminated Water#Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear ☢️ Power Plant#Disaster#Japan 🇯🇵#South Korea 🇰🇷 | China 🇨🇳#Japanese Prime Minister | Fumio Kishida#National Federation of Fisheries Co-operative Associations | Japan 🇯🇵 | Masanobu Sakamoto#US 🇺🇸 | Japan 🇯🇵#Politics | Diplomacy | Culture#Global Marine Ecosystem | Human Health | Well Being#Transparent Efforts | Japan’s Dumping Plan | Safe#World War II | Japan 🇯🇵 | Aggressive Wars | Neighbors
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The TEPCO Decommissioning Archive Centre was a really informative stop today. We learnt about the details of what caused the power plant to explode, why reactor two was the most damaging to the environment (they couldn't put the steam it produced through the normal purification process) and what steps they'd undertaken to start decommissioning it.
We saw the different levels of protective equitment needed around the plant after the accident, and how the radioactive material was cleaned up.

It was also interesting to see how they used filters to filter out the radioactive materials in the waste waters from the plants, before diluting the purified water and releasing it into the ocean.
It was also so cool to see all of the technology that they used to clean up the plant in areas that were too radioactive for people to go. This little robot especially caught my eye, with its little video to show it in action.


It was really interesting to see all of the decisions that were made surrounding the disaster, and all of the people who risked their lives and wellbeing for the greater good.
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Fukushima: The Untold Tragedy
0 notes
Text
japan warns of major tsunami after powerful earthquake hits
Title: “Japan Faces Major Tsunami Threat as Powerful Earthquake Strikes: A Swift Response Unfolds”
Introduction:
Type your email…
Subscribe
In a stark reminder of nature’s unpredictable force, Japan was jolted by a powerful earthquake measuring 8.2 on the Richter scale on Monday, triggering a major tsunami warning for the northeastern coastal regions. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)…

View On WordPress
#cabinet meeting#citizen safety#coastal areas#disaster prevention#early warning systems#earthquake#emergency response#evacuation#Fukushima#global community#japan#Japan Meteorological Agency#Miyagi Prefecture#nuclear power plants#Pacific Ring of Fire#preparedness#Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga#radiation crisis#recovery efforts#resilience#Richter scale#seismic activity#Tokyo#Tokyo Electric Power Company#transportation disruption#triple meltdown#tsunami warning
0 notes
Text
The Dyatlov Pass incident- Dangers of Nuclear Power Plants [Prequel II]
Energy is dangerous! Here is some information to put nuclear energy into perspective with other energy sources.
https://e360.yale.edu/features/why-nuclear-power-must-be-part-of-the-energy-solution-environmentalists-climate
coal:
oil:
natural gas:
biomass:
hydropower:
wind:
solar:
https://ourworldindata.org/

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
I don’t talk about it much but one of my biggest interests is nuclear energy and disasters and I see that Netflix has recently added a new dramatized series on Fukushima daiichi so 👀
I’ve actually been really hoping for a docu series on the event and aftermath for a while, and even though I’m not big on the dramatized series I’m still super excited that this is happening because it might open the door for a proper documentary series in the near future
#anyways please don’t let shows deter you from supporting nuclear energy#every disaster we have experienced has drastically improved the safety of nuclear energy practices#I hate the fear mongering that often accompanies information about these disasters#even when Chernobyl happened in Russia the same accident could not have happened in the us#because rbmk type reactors were built with flaws thst had already been intentionally eliminated in American reactors#and the Fukushima disaster was a major flaw in preparation for natural disasters that should have been preventable#but the station was built with safety features for a large earthquake OR a tsunami but not both#which should have been considered given the high probability of the two combining#but instead of implimenting precautions for future natural disasters Japan shut down all nuclear facilities in the country#we need nuclear now more than ever if we want to continue industrializing without producing more greenhouse#and I wish people understood more about how nuclear power and waste disposal actually works#that was long whoops had a real autism moment there#anyways it’s called the days
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Fukushima#TEPCO#nuclear disaster#radiation#cleanup#environmental impact#government response#public health#reactor#decommissioning
1 note
·
View note
Link
A big lesson we've learned.
Can we fly higher?
0 notes
Note
ask for infodump about Chernobyl as someone who has never even heard of it
INHALES
Chernobyl is considered to be the worst nuclear disaster in history, rated at a 7 on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES), the only other disaster ranking at a 7 being in Fukushima back in 2011. The disaster occurred on April 26, 1986. The Chernobyl Nuclear Power plant was located in Ukraine, which was under the control of the Soviet Union at the time. It was only about 16 miles from the Belarus-Ukraine border, which was also under Soviet control. There were two main towns nearby, Chernobyl itself, which was older, had only about 15,000 residents, and was actually farther from the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant than Pripyat, which had about 50,000 residents, and was only about 2 miles from the plant. Pripyat was newer, and residents had an average age of about 26. The town itself was filled with young, well educated people starting new lives. A large number of public buildings were located in Pripyat, including a school and a sports complex, which contains the famous Azure Swimming Pool. The plant supplied Pripyat with energy, and the place was considered a sort of "dream city." The plant was an RBMK-1000 type reactor, a generation I nuclear reactor, which are the earliest, and generally most hazardous, nuclear reactors. RBMKs were used to produce Plutonium, a radioactive material primarily used in nuclear weapons. However, they could also be used to produce civilian energy, so a few were constructed to supply parts of the USSR with power. At the time of the incident, there were four reactors in operation, with reactors 5 and 6 under construction. A test was scheduled to be conducted to see if the backup generators could successfully turn on in time to keep the cooling systems running at safe levels. However, the test was delayed until the less experienced night shift was in. They turned off the reactor's shutdown feature and lowered the power to the reactor. Reactors need energy to function, as they have to be cooled. For these reactors, large amounts of water were used to cool them. Without the shutdown function, the reactor was in danger of overheating if it wasn't cooled. Regardless, they ran the test. When the backup generators took too long to turn on, panic set in, and the reactor began to overheat. Then, somehow hit the AZ-5 button, which lowers all control rods into the reactor at once. Control rods are used to absorb excess amounts of shed neutrons from the nuclear reactions. However, they momentarily increase reactions when first introduced into the reactor chambers. The undertrained staff of the night shift were not aware of this. With the increased reactivity, the reactor was now dangerously hot, and the casinging around the fuel rods began to rupture, causing white-hot radioactive fuel to come into direct contact with steam. At 1:23 A.M., April 26, 1986, Chernobyl Nuclear Reactor #4 exploded. The contact between the fuel and the steam caused a steam explosion, blowing the 1000 tonne reactor roof into the air and spewing radioactive debris and particles into the air.
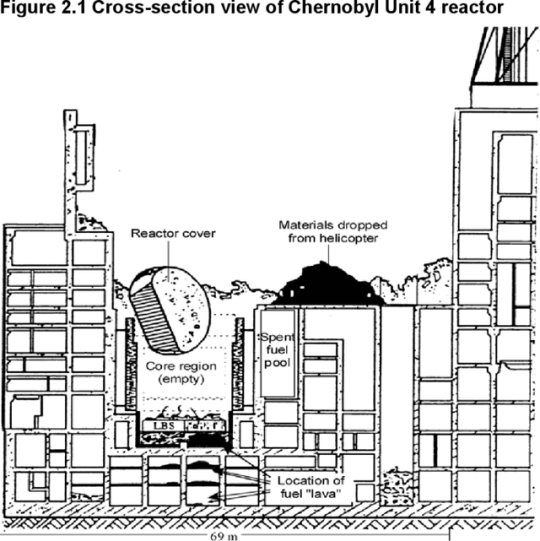

Two plant workers were killed instantly by either the force of the blast or from being hit by debris. Although plant workers realized what had happened rather quickly, superiors were slow to act. Firefighters were called in, but they were not told the dangers of the radiation. Most died within a few months. But that was only the tip of the iceberg. In Pripyat, the Amusement Park that had been scheduled to open the next day was hurriedly opened a day early to distract residents from the fact that the reactor was on fire.

It took 36 hours for Soviet Officials to finally begin to evacuate Pripyat, only after residents had begun to report nausea, dizziness, fatigue, vomiting, and headaches, all symptoms of radiation poisoning. A few weeks earlier, citizens were trained with gas masks in case there ever was an incident. Officials said that they didn’t need them, as they didn’t want to cause a panic.

Residents were also told they would be returning soon, and to leave everything behind. They did not come back. This left Pripyat as an eerie ghost down where everything seemed to have simply been dropped and left. Today, it is still abandoned, and is being slowly reclaimed by nature.

During the cleanup of the incident, “Liquidators” were called in. Some knew the dangers, others didn’t. The fire of the reactor was too hot to be put out by water, so tons and tons or boron, sand, and lead were dumped onto the burning reactor by helicopters that flew over. It didn’t help much, and the reactor finally stopped burning after about 2-3 weeks. A structure dubbed “The sarcophagus” was built over the reactor to contain the radiation, though it was rushed and leaked radiation. A large area of woodlands was contaminated by the radiation, and it turned red and died, earning the nickname “The Red Forest.” Most of these trees were cleared and buried. Highly contaminated houses were knocked down, animals were shot, and crops destroyed. Absolutely everything that was highly contaminated was at least attempted to be destroyed and buried. Still, not everything could be destroyed and buried, there was simply too much. One object, dubbed “The Claw of Death” was, according to conflicting accounts, either used to assist in the overall cleanup or was used specifically in the cleanup of the plant roof. It is radioactive enough to give a lethal dose if sat in for about 11 hours.

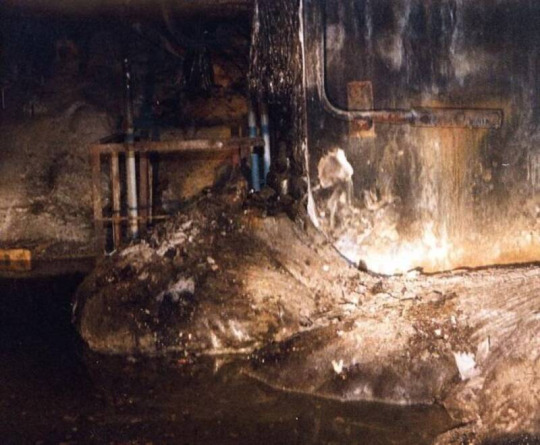
Another rather infamous object is “The Elephant’s Foot” which is a mass of sand, concrete, and melted reactor fuel that had melted its way through the floor and down into the basement. Upon discovery, the sheer amount of radiation it gave off was enough to give you a fatal dose within about 90 seconds. Today, that’s increased to about five minutes. The foot was unyielding to sampling tools, so, they shot it with a Kalashnikov Rifle (AK-47) to get a sample.

After a very short period of time, the remaining three reactors were up and running again, as the USSR simply needed power desperately. By December of 1987, all three reactors were up and running again. They were operated for years, until the last reactor was finally shut down for good in 2000. Being so close to the border, and with the wind conditions of the time, mass amount of radioactive particles were blown north to Belarus. The Soviet Union had planes fly over and seed the clouds with chemicals, forcing them to rain on rural land instead of heavily populated areas, but this still had a major effect, as about 1/3 of Belarusian farmland was contaminated. However, the winds began to shift, blowing radiation towards Europe. Sweden was the first to sound the alarm, asking if something had happened after detecting dangerous amounts of airborne radiation and determining it was not from any of their own reactors. The USSR finally admitted there had been a “very small” incident at Chernobyl, and was very reluctant to give the world information. Careful monitoring protocols were put on resources everywhere in Europe, from grain to milk to wood, all were carefully measured for radiation. Years later, after the Sarcophagus was determined to be unsafe, the New Safe Confinement unit was constructed, which is a semicircular dome over the existing Sarcophagus. The New Safe Confinement was finished in 2018.

DONE!
(For now)
@not-wizard-council-aristocrat @anarcho-neptunism @siley-the-wizard @villainessbian
322 notes
·
View notes
Text
Google Drive full of book PDFs about Chernobyl
Link to the Google Drive if you don't want to click the title: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1kscKFciW6almJA8p-0sUQPO3c0A4AQYe
Note: It will be updated regularly - for as long as I'll be able to find/get new things =) So far I've compiled 41 books in three languages.
Just to repeat what I said in the first post: I'm open to any requests or suggestions or even PDFs themselves, if someone wants to share theirs from their collection. Message me, send me an ask, throw a rock through my window - whatever you prefer, just please, do it yourself because I'm too scared to message anyone, thanks. No fiction - that's the only rule. Any language is welcome - if you want me to look for a certain book in the language of your choice, I'll do that. If you have a book in language other than English, I'd love to add it to the Drive! If you have a better version of whatever PDF I've already got, then I'd be more than happy to do a swap.
Now, some of my reasoning, if anyone's interested: first of all, I think it's important for everyone to be able to access stuff like this. Think of it as a library, minus the "give these back" part. Secondly, I get soooo mad when people are like haha, found this super rare, basically impossible to find, very expensive book! ...I shall now keep it exclusively to myself. Ma'am, you're ruining the vibe and stalling everyone's hobby research but I guess you do you...
List of all the books (under the cut):
In English:
Voices from Chernobyl - Alexievich S.
Chernobyl Reactor Accident - Source Term
Chernobyl - Insight from the Inside - Dr. Chernousenko V.M.
How It Was - Dyatlov A.S.
(ENG+RUS) Chernobyl Booklet
Chernobyl: The Devastation, Destruction and Consequences of the World’s Worst Radiation Accident - Fitzgerald I.
Final Warning. The Legacy of Chernobyl - Gale R.P.
Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World’s Greatest Nuclear Disaster - Higginbotham A.
INSAG-1
INSAG-7
Interesting Chernobyl - 100 Symbols
From Chernobyl To Fukushima - Karpan N.
Manual for Survival. A Chernobyl Guide to the Future - Kate Brown
Chernobyl. Confessions of a Reporter - Kostin I.
The Politics of Invisibility. Public Knowledge about Radiation Health Effects after Chernobyl - Kuchinskaya O.
Memories - Kupnyi A.
Chernobyl 01:23:40 - The Incredible True Story of the World’s Worst Nuclear Disaster - Leatherbarrow A.
Chernobyl Notebook - Medvedev G.
No Breathing Room - Medvedev G.
Chernobyl Record - The Definitive History of the Chernobyl Catastrophe - Mould R. F.
Wormwood Forest - A Natural History of Chernobyl - Mycio M.
Life Exposed: Biological Citizens After Chernobyl - Petryna A.
Chernobyl: History of a Tragedy - Plokhy S.
Ablaze - Story of Chernobyl - Read P.P.
Producing Power: The Pre-Chernobyl History of the Soviet Nuclear Industry - Schmid S. D.
Chernobyl: A Documentary Story - Shcherbak I.
The Vienna Report
Chernobyl - Crime Without Punishment - Yaroshinskaya A.A.
In Russian:
Chernobyl: Kak eto bylo. Preduprezhdeni - Kopchinsky, Steinberg
Chernobyl. Tak eto bylo. Vzglyad Iznutri - Voznyak Ya. Troitskiy N.
Лучевая болезнь человека (очерки) - Гуськова А.К., Байсоголов Г.Д.
Чернобыль. Как это было - Дятлов А.С.
Чернобыль: 30 лет спустя - Кравчук Н.В.
Живы - Купный А.
Чернобыль - Щербак Ю.
(ONLY Pages 367-383) Чернобыль, 10 лет спустя. Неизбежность или случайность?
KGB files - pre and post accident (includes additional information in Ukrainian)
In Polish:
Jak to było - Diatłov A.S.
Czarnobyl - Plokhy S.
Czarnobyl - Sekuła P.
Katastrofa w Czarnobylu - Sekuła P.
Czarnobyl. Od katastrofy do procesu - Siwiński W.
#chernobyl#26th april 1986#nuclear power plant#chornobyl#nuclear disaster#chernobyl hbo#you wouldn't download a car#file: special interest: chernobyl#Чернобыль#pripyat#rbmk 1000#radiation#free resources#free books
441 notes
·
View notes