#indigenous american cuisine
Photo



sumac lemonade.
#foodedit#food#food gifs#foodcore#recipes#mine#gifs#sumac lemonade#sumac#drinks#native american cuisine#native american recipes#indigenous american cuisine#indigenous american recipes
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
One thing that always irks me without fail is when ppl outside the US take jabs at American food for being "unhealthy" and then proceed to spew the most anti-Black, anti-Indigenous commentary they can to try and "own" the US-ians.
#jelly.txt#not to mention the obvious fatphobia too but like this is the aspect where it's especially infuriating because chances are they're not even#aware of just how many staple American foods are actually a result of enslavement and/or are influenced by Indigenous cuisine#EMBARRASING! anyway.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
dont forget theres no food culture in the usa outside of what bland white-ass people make i guess -_-
#like even if youre going to ignore the vast swaths of previously enslaved black people#are you just going to ignore indigenous cuisine? the cuisine of immigrants?#HELL even american italian descendants have smth going on...#tell me youve never spoken to a nonwhite american without telling me youve never spoken to a nonwhite american
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
reclaiming Native American food : NPR
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
When I try modernizing Palestinian cuisine, I am not trying to make it acceptable to people. When I think of a dish, I don’t ask myself: “Is this gonna please the Europeans or the Americans or the Chinese?” I try to create a dish that is respectful of the flavors, and that has an identity that is very much mine. For instance, I love working with freekeh and I know you hate it. Still in my set menu, I try to force down your throat some freekeh. You know I could make an effort when ì know you’re coming over for dinner and not cook it but if I happen to have a vegetable that works well with it, well I still cook freekeh, whether you like it or not!
Don’t forget, cooking is a magic act, a sacred moment. This is why I am in the kitchen. I was recently speaking to Paris-based Japanese writer, Ryoko Sekiguchi, and we came up with this concept of “cooking of light,” “la cuisine de lumière”) [”hikari no ryôri”] and she linked it to another concept that she came up with Japanese chef Shûichirô Kobori, namely “cooking of prayer,” “la cuisine de prière” [”inori no ryôri”]. Cooking is a sacred moment of intimacy and of creation, which requires respect.
We have such particularities in our kitchen, that we should be putting forward and that we should be protecting from all those coexistence and peace initiatives, which are not really about peace and coexistence. Peace is about justice. When sometimes people ask me: “Would you work with an Israeli chef?” I say: “My conditions if an Israeli chef wants to work with me are that she or he has to accept a Palestinian state with the 1967 borders, accept Jerusalem as the capital of two states, accept the right of return of Palestinians refugees. If there is a resolution that is just to our rights as Palestinians of course I will work with an Israeli chef.” But as long as there is no justice and equality there’s no way I could work with an Israeli chef.
122 notes
·
View notes
Note
Who do you think would have the best food if they only cooked by their own indigenous resources (spices, veggies, fruits, etc)?
(Also sorry if there's a mistake, it's almost 5am and I can't sleep)
Sorry but I can't really answer that question because for one, I don't know that much about the geographic origin of spices. Second, my palate is the result of over 500 years of columbian exchange. Most modern cuisines whether North American, Latin American, Asian, European, or African are the result of that exchange. In addition the modern world makes it so that any food or spice is easily available in the grocery store or with the click of a mouse. Even way back in the Roman era there were dishes where the Romans used food and spices from Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
As a result I can't judge any culture's or geographic region's food by that parameter because I can't even comprehend what that would be like. For example, Chinese, Vietnamese, and Thai foods are some of my favorite cuisines. What would they be like without chili peppers which is a new world spice? IDK. I would have to do a lot of research and experimental archaeology to find out. Something I don't have the time and energy to do.
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
Little hc of mine but I love to imagine a Native American / indigenous yuu/mc who sometimes speaks in their native language and the octavinelle trio absolutely adoring them or looking at them with admiration and love for them.
Idk it would just be sweet to think.
Teaching Azul or Jade their native language and both of them trying to speak it to mc
Or them telling Floyd their culture stories and Floyd listening to them, since he loves stories (as long as he finds them interesting)
This example is more specific, but mc trying to explain clans to the three of them (I’m Navajo, but I’m still trying to understand how clans work myself 😭), jade would probably understand after explaining, but Azul and Floyd still struggling to understand.

Mc making frybread for them and native cuisines (Azul would probably try to sell it at the restaurant for a special time), I think Floyd’s favorite would be navajo tacos, and Jade’s would probably be the three sisters stew (bout to be a fourth sister since you know he probably add mushrooms to that shit-). Azul’s would probably enjoy three sisters stew too.
Idk, as someone who really didn’t grow up with the representation, I just enjoy making these little hcs for my native ocs sharing their culture with my favorite fictional characters are a huge comfort, especially me myself who is starting to reconnect with my roots, just a nice way to make me feel good about myself.
Are there any native/indigenous or just different people from different cultures who also play Twisted wonderland? If so what are your personal hcs for your indigenous mc sharing their culture with the NRC boys? (I would love to hear em)

#twisted wonderland#azul ashengrotto#twisted wonderland mc#jade leech#floyd leech#twst azul#twst mc#azul x mc#azul x yuu#twst jade x mc#twst headcanons#twst floyd x mc#azul ashengrotto x reader#jade leech x reader#floyd leech x reader#twisted wonderland x reader#twisted wonderland x yuu#twst x reader#twst x yuu#native#native oc
110 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's just so weird to see posts that talk about how many cultures influence American cuisine and then those same posts reduce indigenous influence down to corn, beans, and squash as if we aren't living and thriving communities with evolving cuisines and strong influences on American food, fashion, and language. We aren't dead. There is more to us than just the creations of our ancestors.
205 notes
·
View notes
Text
The complete refusal by many Europeans to listen to and understand how ethnic identity “works” in America will always get to me, because why am I having a long winded argument with someone who refuses to recognize “Irish Catholic” as an identity in America because it doesn’t include “American” tacked on after it. “Why don’t you add American onto it?” - because it’s redundant when you’re obviously in America talking about an ethnic diaspora you belong to.
For context, it’s on a video response where an American Irish Catholic family makes a light hearted joke about Irish Catholic identity in America but some snarky person from Ireland stitched the video with an “Are ye now?” when the family said “We’re Irish Catholic.” The original video contains jokes that an Irish Catholic in America would understand to be about their diaspora community. While it may contain some stereotypes, none of them are particularly harmful (e.g. no references to drinking and fighting).
You cannot tell me that Europeans with their “superior” education systems can’t figure out that an American saying they’re Irish Catholic means something different from a person in Ireland saying the same thing. You cannot confess to me that you need that clarification on a video where people with “American” accents are talking about their ethnic identity. Furthermore, insisting that people identify as Irish American in the context of their original video is absurd given that “Irish Catholic” is it’s own unique cultural identity here.
There are churches and schools that are largely Irish Catholic here. There are neighborhoods that are traditionally Irish Catholic here. There are accents and dialects that are largely based around Irish Catholic immigrant communities here. There are ways of dress. There are foods and festivals. Naming rituals. Family structures. Religious practices. Folklore. There are remnants of our culture here from when our ancestors left their homelands that eventually grew into their own unique ethnic identity - the Irish Catholic identity in America.
I’m just using Irish Catholic as an example because this video sparked the discussion, but this goes for any ethnic identity here. We’ve been shaped by our ancestors, good and bad. We all deal with a certain level of disconnection and alienation because of choices made before we were born. Enforcing the “American” label onto ethnic groups specifically when it’s not necessary to comprehend that they’re distinct from “modern day” cultures in Europe serves no great purpose other than promoting “White American” identity.
I said it before and I’ll say it again - it’s good that White Americans remain connected or even reconnect with their cultural roots, because “White American” as an identity was made possible by white supremacy. There’s nothing wrong with diaspora in American referring to themselves by the name of their ethnic group. You can be critical about how people appropriate or bastardize ethnic identities, but Irish Catholic and ethnic identities like it are unique in America and there’s no reason to refer to ourselves by names imposed on us.
When Americans talk about their ethnic identities, that’s not the time to be snarky with a “well actually you’re not from x, y, z.” Just let Americans talk about their own experiences. Maybe learn why diaspora communities behave similarly and differently from you. Correct practices that you think are perhaps misinformed, stereotypical, or problematic,* but realize that not all cultural practices have to be scrutinized for authenticity outside of their cultural context in America.
*e.g. You can correct someone claiming they have “Viking” ancestry to defend wearing ahistorical dress that appropriates from indigenous communities, but yelling at Americans for modifying their ethnic cuisines to suit where they live because it’s not “authentic” enough to you is rude. There’s a difference between appropriation and adaptation. Being from a country doesn’t give you the right to define diaspora communities and impose your definitions on them.
58 notes
·
View notes
Note
can you explain what the difference between texmex and other mexican food is? also thank you for your post because i'm one of these ignorant europeans lol, i thought texmex was like mexican food adapted for western tastes! i've never had it
you are so fine. im not an expert at all, but this is what i know. if someone with more culinary knowlege wants to come in and correct me, or expand upon what im saying, please feel free.
texmex is specifically the cuisine developed by tejanos (texans with mexican descent). the cuisine is shaped by a variety of factors. after the border change of the mexican-american war as well as the creation of rail lines after the american civil war, the resources tejanos had radically changed from those from across the border in mexico; consequently tejanos were working with a different set of ingredients than mexicans. the cuisine was also influenced by neighboring cuisines of the various cultures surrounding them, both american settlers and indigenous groups (this sort of syncretism is pretty is natural occurrence when it comes to cuisine).
texmex spread considerably across the united states in the 20th century beyond the borders of texas via a growing number of mexicans and chicanos moving northward. many of these people created mexican restaurants, which became quite popular amongst americans of many backgrounds. a lot of these restaurants serve a variety of chicano dishes from along the southern US. this is done to appeal to a larger market... but that's not necessarily a bad thing. you might find some sonoran, new mex, or cal-mex alongside texmax at an American mexican restaurant.
texmex is honestly similar to what you already eat from mexican restaurants in EU, from my experience eating here. though, i have to say the food is certainly changed when crossing the atlantic (done in part likely due to a different market as well as a limited access to certain ingredients). in my opinion, the closer one is to texas, the tastier the texmex is. although, i have had some great texmex in ireland.
some food you might recognize as being "texmex" would be nachos, chili con carne, and fajitas. texmex is known for being very cheesy in comparison with other chicano cuisines.
121 notes
·
View notes
Text

November is National Native American Heritage month in the USA! Did you know that many of the UK’s favourite kitchen garden plants were originally domesticated by indigenous peoples in the Americas? The Native Americans’ domesticated plants now feed most of the world and have become an integral part of cuisines in Europe, Africa, and Asia.
1. Potato: Potato (Solanum tuberosum) was domesticated by indigenous Americans in the Andes at least 10,000 years ago. Genetic studies indicate hybridization of different wild potato varieties in the species Solanum brevicaule in Southern Peru produced the original domesticated potato. Today, indigenous people in Peru have over 4000 varieties of potato, each with their culinary and cultural significance. The Chuño potato can be preserved for up to 15 years, making it an important food source during lean times in the days of the Inca Empire.
2. Corn: Indigenous Americans domesticated corn (Zea mays) from the wild grass Teosinte (Zea mays parviglumis) of southwestern Mexico approximately 9,000 years ago. The wild Teosinte is a miniature corn, with ears containing only 5-12 hard seeds. From the initial domestication in Mexico, corn spread north and south to become the iconic food plant of indigenous America. Native American corn differs from the familiar sweetcorn because it was selectively bred to be dried and preserved rather than eaten fresh. Native American corn varieties can be a kaleidoscope of beautiful colours and are either flint corn (dried for preservation and then soaked for food purposes), flour corn (processed into masa harina flour), or popcorn.
3. Beans: Our familiar kitchen garden beans all come from indigenous American agriculture. The fresh green beans and most of the dried beans belong to the same species, the Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) which was domesticated via hybridization of several wild species in Mesoamerican around 4,000 years ago. The Lima Bean (Phaseolus lunatus) was domesticated in South America around 4,000 years ago and spread north of the Rio Grande by the 1300’s.
#katia plant scientist#plants#gardening#agriculture#crops#potatoes#corn#beans#native american#native american heritage month#indigenous food#history#native american culture#native american food#domestication#botany#plant based
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
EAST INDIGENOUS NORTH AMERICAN RESOURCES
The Anthropological Masterlist is HERE.
The Midwestern United States is a North American region that constitutes the northern central part of the United States.
HURON ─ “The Wyandot, or Huron, people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the north of Lake Ontario.”
─ Huron Information
─ Huron History
─ Huron Language
LAKOTA ─ “The Lakota people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to North and South Dakota.”
─ Lakota Language
─ Lakota Language Reclamation Project
─ Lakota Dictionary
SENECA ─ “The Seneca people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the south of Lake Ontario.”
─ Seneca Information
─ Seneca Culture
─ Seneca Language
The Northeast United States is a North American region that constitutes the northeastern part of the United States.
BLACKFOOT ─ “The Blackfoot people are an Indigenous North American military confederation that share the Blackfoot language. They are native to northeastern America.”
─ Blackfoot Culture
─ Blackfoot Language
LENAPE ─ “The Lenape, or Leni Lenape, people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the Northeastern Woodlands.”
─ William Penn on the Lenape
─ Lenape Language
─ Lenape Dictionary
NARRAGANSETT ─ “The Narragansett people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to Rhode Island.”
─ Narragansett Records
─ Narragansett Language
─ Narragansett Language
WAMPANOAG ─ “The Wampanoag, or Wôpanâak, people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to southeastern Massachusetts.”
─ Chappaquiddick Wampanoag Information
─ Wampanoag Culture
─ Wampanoag Language Reclamation Project
The Southern United States is a North American region that constitutes the southern part of the United States.
CADDO ─ “The Caddo people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States.”
─ Caddo History
─ Caddo Language
─ Caddo Alphabet
CHEROKEE ─ “The Cherokee are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States.”
─ Cherokee Information
─ Cherokee Culture and History
─ Cherokee Dictionary
CHICKASAW ─ “The Chickasaw people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the southeastern United States.”
─ Chickasaw History
─ Chickasaw Language
─ Chickasaw Language and Word Stress
CHOCTAW ─ “The Choctaw, or Chahta, people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to Alabama and Mississippi.”
─ Choctaw Information
─ Choctaw Culture
─ Choctaw Mythology
CREEK ─ “The Creek, or Muskogee, people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to the Southeastern Woodlands in the United States.”
─ Creek Information
─ Creek Language
*GULLAH ─ “The Gullah people are an African American people. They live in the Lowcountry Region of the United States.”
─ Gullah Culture
─ Gullah Cuisine
KIOWA APACHE ─ “The Plains Apache are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to Oklahoma and Texas.”
─ Apache Information
─ Apache Culture
─ Apache Creation Myth
PAWNEE ─ “The Pawnee people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to Oklahoma.”
─ Pawnee Information
─ Tirawa of Pawnee Legend
─ Pawnee Dictionary
POWHATAN ─ “The Powhatan, or Powatan, people are an Indigenous North American people. They are native to eastern Virginia.”
─ Important Powhatan People
─ Powhatan History
─ Powhatan Language
* - The Gullah are not indigenous North American people. They are an African diasporic people.
#resources#midwestern united states#northeastern united states#southern united states#huron#lakota#seneca#blackfoot#lenape#narragansett#wampanoag#caddo#cherokee#chickasaw#choctaw#creek#gullah#kiowa apache#pawnee#powhatan
382 notes
·
View notes
Text
Accidentally had a bunch of parents and kids at my local culture festival concerned for me a few weeks ago lol
So my junior high held their culture festival and I got to order some food for the two days I was there. You write what you want and send the money in an envelope to the vice principal, and I got tickets for my menu items. I saw on the menu that they had コーンパン (literally corn bread), and my Southern US self got very hyped because I didn't even know they HAD cornbread in Japan! But they seem to have corn dishes in a lot of cuisine, so I thought it made sense. So I order corn bread.
I get my bento bag and am expecting the bread of my childhood, cornbread. Warm, fluffy, like a brownie but made of cornmeal in all its redneck and indigenous-origins glory.
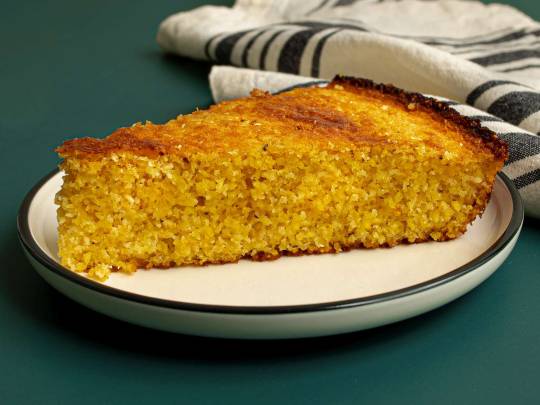

My friends and fellow hoes, I did not receive cornbread. I received...Japanese cornbread.
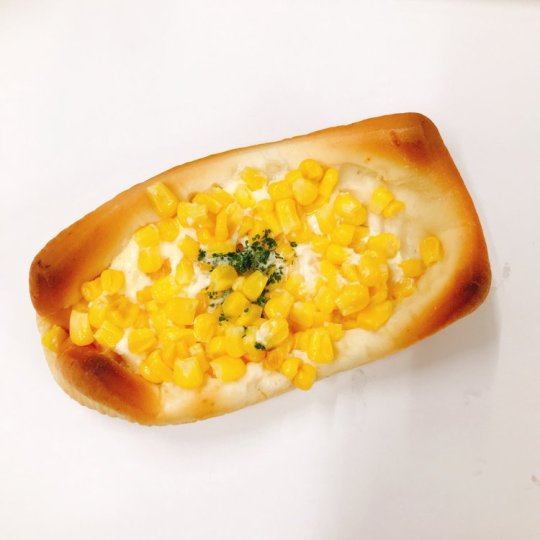

Now on its face, I like the three components of this food. I like corn. Of course I do, I'm American, we put corn in everything. I like mayo. I love bread. But when you are a Texan, you're already missing some cultural aspects of your home like its cuisine, and you are expecting CORNBREAD, and you get this?
I spent a solid thirty seconds just blinking at this corn bun and I looked so dejected that multiple students near me asked if I was okay. I live in a first-person perspective like everyone else but I imagine my face was similar to this:

26 notes
·
View notes
Text
The story of Mexican food is usually told as a happy merging of indigenous ingredients and techniques with those brought by the Spanish in the 1500s, as if the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was just a means to a better burrito. In fact, what we now know as Mexican cuisine is the result of centuries of shifting borders and tastes.
“When it came to culinary cultural exchange in the colonial period, the conquistador Bernal Díaz del Castillo referred to corn dishes as the ‘misery of maize cakes,’” says Stephanie Noell, Special Collections Librarian at the University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA). “On the other side, the Nahuas were not impressed by the Spaniards’ wheat bread, describing it as ‘famine food.’”* The eventual confluence of native and European ingredients and traditions is, of course, what defines North American cuisine to this day.
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
Flag of the Pueblo Sultanate

This is the flag of the Pueblo Sultanate. It comes from a world where the Ottoman Empire established colonies in the New World. The Ottomans began in the Caribbean, and soon went on to conquer Mexico. Eventually, the Ottomans made their way to the American Southwest, and subjugated the Pueblo peoples. Life was harsh for the Pueblo people under Ottoman colonialism. Pueblo people were forced to toil away in silver mines to feed the Ottomans’ hunger for precious metals. Several madrasas were established with the intent to convert the Pueblo peoples to Islam. In theory, the madrasas would provide aid, education, and social services to the Pueblo people. In practice, however, the imams often subjected their charges to horrific abuse. Despite this, Islam did manage to spread among the Pueblo peoples. The Pueblo peoples begged for a savior. But where could he be?
The Pueblo people received their answer in the form of a charismatic preacher named Po’Pay. Despite the similar name, he is a separate individual from the Po’Pay of our world. This Po’Pay preached the highly syncretic religion that combined indigenous Pueblo beliefs with Islamic liberation theology. This was in sharp contrast to the Islam of the Ottomans, which frowned upon syncretism, and suppressed indigenous beliefs. Po’Pay teachings began to spread, and soon Po’Pay a revolt against the Ottomans. Though the fight was hard, at last the Pueblo peoples were free from the Ottoman yoke. The Pueblo peoples began to think of themselves not as a collection of disparate tribes, but as a united people sharing in a common destiny.
Po’Pay organized the tribes into a sultanate, with himself as the first sultan. However, the sultan would not rule alone. An assembly of tribes was created. Representatives of each tribe could voice the opinions and concerns of the tribe to the assembly. Thus, the Pueblo Sultanate became the first representative monarchy in the New World. The Pueblo Sultanate stretches over much of what would be he American Southwest.
The Pueblo Sultanate is famous for begin very tolerant, open-minded, and accepting of peoples with different beliefs. Most citizens practice Pueblo Islam, but don’t try to push it on other people. Most women do not veil, and most Pueblo citizen wear traditional indigenous-style clothing. to Po’Pay developed a written script based upon Arabic, and the Pueblo Sultanate is home to several libraries and other centers of learning. In fact, the Great Pueblo Library is world renown for its expansive collection of books. Qurans are written in the Pueblo script, and the call to prayer to announced in the various Pueblo languages. The Pueblo Sultanate is also quite famous for its cooking. Pueblo cuisine combines cooking techniques from the Eastern Mediterranean with spices and ingredients of the American Southwest. The Pueblo Sultanate has a noticeable minority of Greeks, Serbians, Bulgarians, and Amazighs. They are mostly descended from slaves brought over during the days of Ottoman colonialism.
Also, the Pueblo Sultanate isn’t actually called the Pueblo Sultanate in-universe, but I couldn’t think of a better name.
The flag includes the sun symbol of the Zia people, and the crescent moon of Islam. This is a reference to the Sultanate’s mixed indigenous and Islamic heritage. The blue band represents turquoise, an important stone to many Pueblo peoples. The green band represents prosperity, and green is a color associated with Islam. The yellow band is there because it goes well with everything else.
Link to the original flag on my blog: https://drakoniandgriffalco.blogspot.com/2022/06/flag-of-pueblo-sultanate.html?m=1
#alternate history#flag#flags#alternate history flag#alternate history flags#vexillology#alt history#Pueblo Sultanate#Pueblo Tribes#Pueblo Peoples#american southwest#Ottoman Empire#Islam#native americans#native american#indigenous people#indigenous#Pueblo#america#north america#united states#USA#united states of america#Pueblo People
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some things that drive me up the goddamn wall:
Western medicine is not that old. CHARITABLY its like, 400ish years old, but all the most popular ways of defining western medicine (e.g. based on the modern scientific study) really only apply to information-generating and medicine-distribution practices that started in the late 1800s and were codified in THE TWENTIES. Sure, no ideas come out of nowhere and modern western medicine absolutely has a lineage and if you want you could make a good argument for tracing that lineage back to say, Galen. (Side note: american Doctors love to claim Galen when it makes them sound Storied and Dramatic but foist him off on us stupid herbalists as soon as anything controversial by modern standards comes up). But what's a lot more important to think about is that prior to the past hundred years or so, the diversity of actively-practiced, available medical traditions that existed in "the west" was so much greater than it is today, and if you go back another hundred or more years it's bigger and bigger. For most of human history in most parts of the world medicine has been a great, fluid cultural field (like cuisine! or religion! in fact these three subjects overlap quite a bit!!) that becomes forcibly homogenized and codified as part of nation-building. That has happened and is still happening here in the west as empire seeks to homogenize culture, through, yknow, genocide; and minority medical philosophies are deligitimized, criminalized, and culturally persecuted. Indigenous and folk traditions survive in small bubbles of people desperately trying to keep them alive.
Following from #1, the majority of people on the "left" to postleft & whatever recognize, at least nominally, that this is Bad. However, what most white people seem to be doing with the idea that Cultural Extermination Is Bad is grant some kind of nebulous exception status to their nebulous idea of "Indigenous medicine" while otherwise paying lip service to the western medical progress narrative: What "we" do now is so much better than what "we" "used to" do. First of all, "we" here is an incoherent concept unless you want to buy into the idea that dominant western culture (or civilization more broadly) is an inevitable evolution that all cultures will come to, which is uhm. Social darwinism. Second of all, "used to" is just a straight up lie in most cases unless it's very narrowly referring to any number of practices that were codified in like, 1930 by the still-budding medical establishment and have since been discarded by the extant medical establishment. Diverse, Indigenous & folk medical traditions are still fucking around and alive and being used, adapted and added to. Some are holding on by a thread and plenty are very closed practices now out of defensiveness, while others struggle to be known more widely because of medical licensure laws that claim to be about "safety" but were always about stamping out minority medical traditions. What a lot of motherfuckers miss is that when the western medical establishment tells the story about how everything is so much better now and we know the right way to be, they are telling the same story I told under heading one. The nonviolent story of progress that "we" just "discovered" "new ideas" is conveniently shuffling around the genocide and criminalization that are STILL actively trying to stamp out the """"old"""" ideas.
Does all of this mean that we should just willy nilly accept/use/treat as valid every single thought anyone has ever had about medicine? Fuck no! People have bad ideas sometimes! Medical traditions are LIVING traditions for good reasons. It just means that I wish people would sit down and THINK for a second before making a claim about non-western or historical medical traditions, ask themselves "is my only source for this claim the current western medical establishment?", and if "yes", spend any amount of time trying to find an alternate perspective. If you can't find any source that isn't affiliated with genocide and forced cultural assimilation on the practice you want to talk shit about, ask yourself "why isn't there a proponent of this practice around to defend it?" and like, go from there.
I truly do not care what medical philosophy any given individual person feels most comfortable using for themselves. Your reasons for preferring western medicine might very well be rooted in shit i disagree with/find abhorrent, I might think you could be happier (or more likely to survive climate collapse) if you were at all open to any strategy other than the one that's entirely dependent on empire and extraction, but I am frankly too tired and too busy to be remotely invested in what people I don't know are doing with their bodies. What frustrates me is how little critical thinking is being done when it comes to medicine, how comfortable everyone seems to be with incoherent cognitive dissonance when it comes to criticizing specific instances of oppression/nationalism/racism/etc in western medicine but still buy the overall narrative in a way that renders those critiques superficial, and how successful the project of western medical nationalism has been at claiming a monopoly on the story.
#theory#these thoughts are part of a big essay about disability and “alternative medicine” but that's probably going to rot in my drafts and i felt#like these parts are important. so.
10 notes
·
View notes