#reenactment
Text


Medieval Posture ™
#medieval reenactment#medieval#14th century#14th century reenactment#reenactment#medievalcore#costuming#photography#medieval clothing#medieval manuscript#sca#innilgard#i’ll be on my merry way now
304 notes
·
View notes
Text
Accurate Reenactments Based On Facts
Most cultures across the Galaxy do their utmost to preserve and remember their history, both the great achievements, and the terrible mistakes. Humans go a few dozen steps further.
They introduced us to a concept called "Historical reenactments" - accurate recreations of the situations and conditions of ancient events, usually battles, played out with prop equipment by real people. They also said they sometimes do these just for fun and don't care about being 100% accurate.
This particular reenactment was of a battle called Thermopylae. Using numerous historical records, they recreated the location, printed slightly lighter versions of the armor (well, helmets only for some) they wore, and dull weapons with embedded stun shockers that would create a kinetic "bump" upon contact to prevent actual injury by pushing the person back instead.
Once everyone was geared up the atmosphere changed, both visually as the holographic projectors did their thing, and from the Humans themselves - their demeanor became that of... wilderness. Ferocity. Deadly focus. It was quite fear inducing even from afar.
Then the defenders in red, the "Spartans", created a sort of spiky dome with their shields and spears. Then the attackers in blue, the "Persians" unleashed a terrifying volley of arrows, the sky hologram went darker, then a bright beam of light shone upon the defenders as they swept off arrows stuck to their shields in dramatic fashion before proceeding to charge towards their assaulting foes.
We noticed the "Spartans" were all much larger than the "Persians", and actually were equipped with subtle and very modern exoskeletons. Perplexed by this we asked if these Spartans had a very particular technological advantage for their time:
"Well, not as far as we can tell, but based on the materials we have, Spartans were, like, really buff and super strong compared to the average person of the time. Plus, according to the feats of strength they supposedly displayed, we suspect they became an extinct branch of Humanity at some point, so the exoskeletons are there to mimic what we think they were like. Anyway, look, this is the coolest part."
As they spoke, the artificial gravity was lowered slightly and there was a spike in the power output from the exoskeleton equipped Spartans. Now they were flinging the approaching Persians dozens of feet into the air, a single bare-chested man kicked three of them at once backwards at a whole group, knocking the wind out of them.
This sort of extreme violence continued for several minutes.
Suddenly, an incredibly large Persian man on a throne was carried to what was effectively the center stage. Him and a heavily bearded Spartan exchanged a dramatic dialogue, the Spartan threw his spear at the Persian, who dodged it with a single turn of his head, then proceeded to summon a massive horde of small Persians who quickly began to overrun the Spartans.
There were bodies and shields and spears and pieces of armor flying everywhere, but gradually all the red became engulfed by the blue, and only one remaining Spartan managed to wriggle his way out of the carnage and make a run for it back to their city in the distance.
Seemingly satisfied after plucking out the bearded Spartan from the pile, the giant Persian roared in triumph and this is when the reenactment ended and everyone gathered for a feast.
So this is how ancient Human Battles went, huh.
"Well, not all of them. Usually it's between more equal forces in large open fields, or prolonged sieges, which can be a bit boring to recreate.
You should come back next month, we'll be doing an old naval battle between the British Empire and Independent Pirates Lords. It ends with a really sweet whirlpool showdown. Man, what are the odds of that happening, eh?"
#humans are space orcs#humans are space oddities#humans are space australians#humans are deathworlders#humanity fuck yeah#story#carionto#300#reenactment#pirates of the caribbean#humans like movies#movies are historically accurate if you've gone through several civilization collapses
184 notes
·
View notes
Text


Digging these eighteenth-century highlander reenactors from an event in Georgia earlier this year. Not all perfect (how many reenactors can claim they are anyway?) but overall better fare than Hollywood's "big beards and open shirts and drab tartans."
#scotland#scottish#highlander#highlanders#18th century#reenactment#history#scottish history#tartan#kilt#kilts
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is going so much better than I thought!
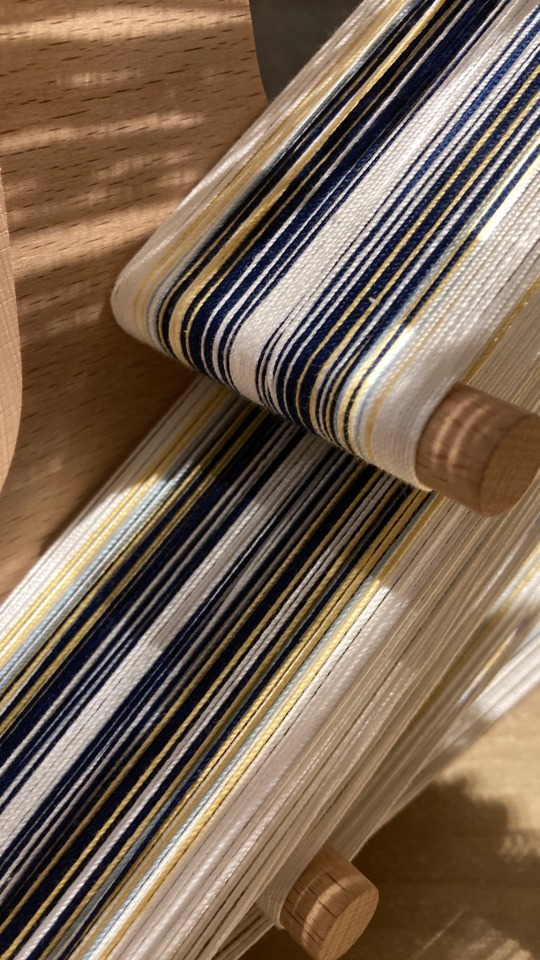
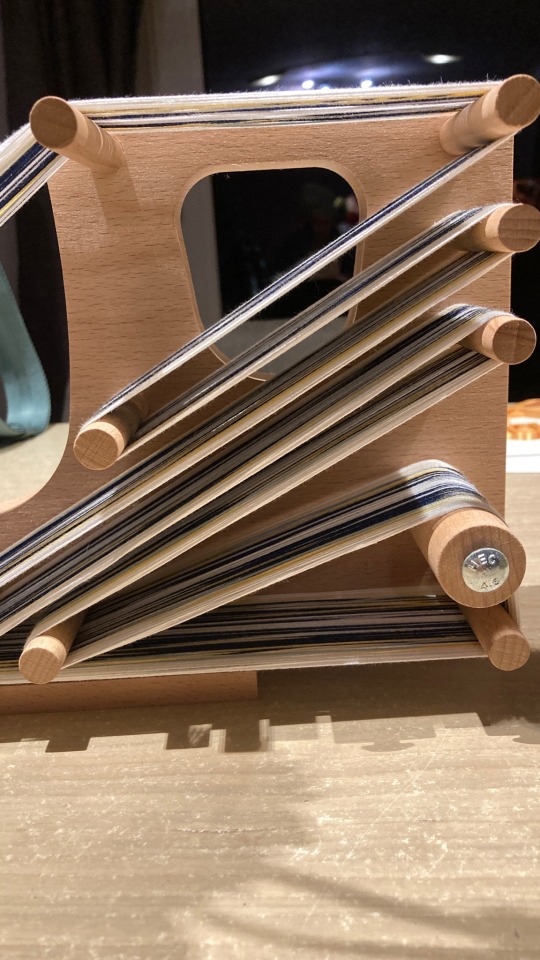



#tablet weaving#fabric weaving#vikings#archaeology#history#field archaeologist#reenactment#traditional handicraft#Celtic#halstatt#inkle loom#inklette loom#card weaving
165 notes
·
View notes
Text

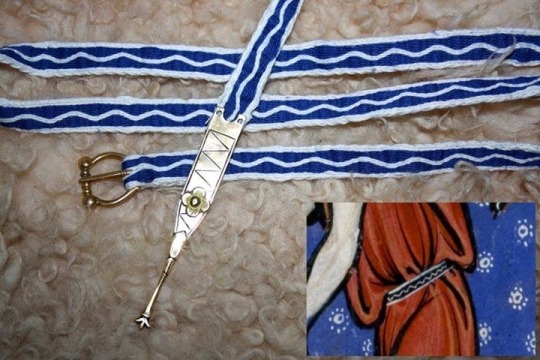
13th century tablet woven belt
#15th century#13th century#medieval#tablet weaving#loom weaving#belt#christianity#reenactment#living history#medieval clothing#reenactor#manuscript
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
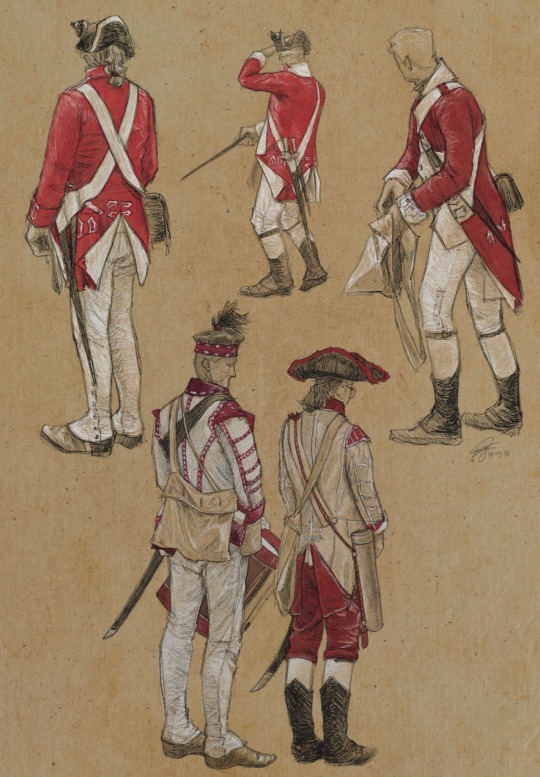

Some studies I did of the British at Monmouth this past June, featuring soldiers and musicians from the 22nd, 33rd, and 71st regiments of foot, inspired by William Barns Wollen’s 1911 sketchbook. Fantastic event and I can’t wait to do it again.
(Alternate, color-less version below cut)

#I never post my art mostly because I don’t have anything Postable but I liked this one#also the closest thing I’ve ever done to a self portrait lol#I had so much fun at this event this was the result of me not knowing what to do with myself afterward#my art#art#british military#amrev#revwar#reenactment#revolutionary war#american revolution#redcoats#god save the cheshire regiment#I am Scared to post this but whatever#historical art#history#monmouth#battle of monmouth#the captain draws#redcoatposting#awi
216 notes
·
View notes
Text
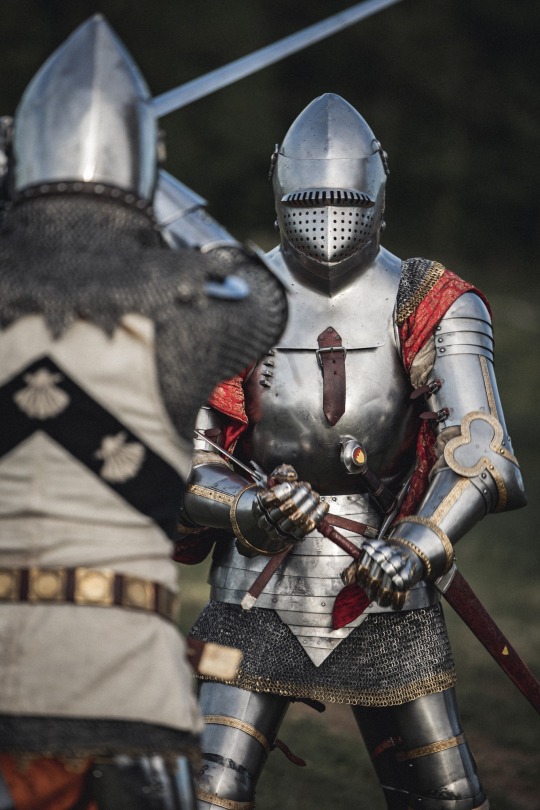

Genz d'armes 1415
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
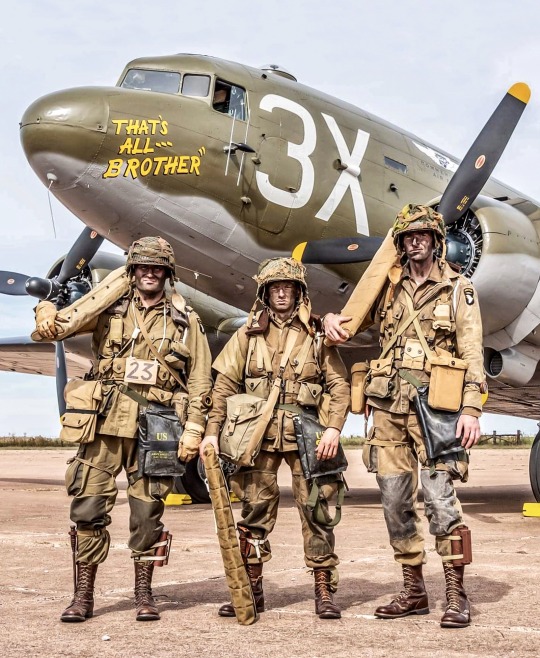

Three members of the WWII Airborne Demonstration Team display the typical loadout of gear worn by US Paratroopers of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Divisions on D-Day.
The WWII ADT was one of several groups of airborne re-enactors that jumped in period-correct uniforms and gear, with authentic military canopy parachutes, from a fleet of C-47 ‘Dakotas’ onto original D-Day drop zones during the 75th anniversary of D-Day on June 6, 2019.
(Photo by: Gary Daniels)
#d day#operation overlord#us army#paratroopers#101st airborne#82nd airborne#reenactment#military#history
378 notes
·
View notes
Text
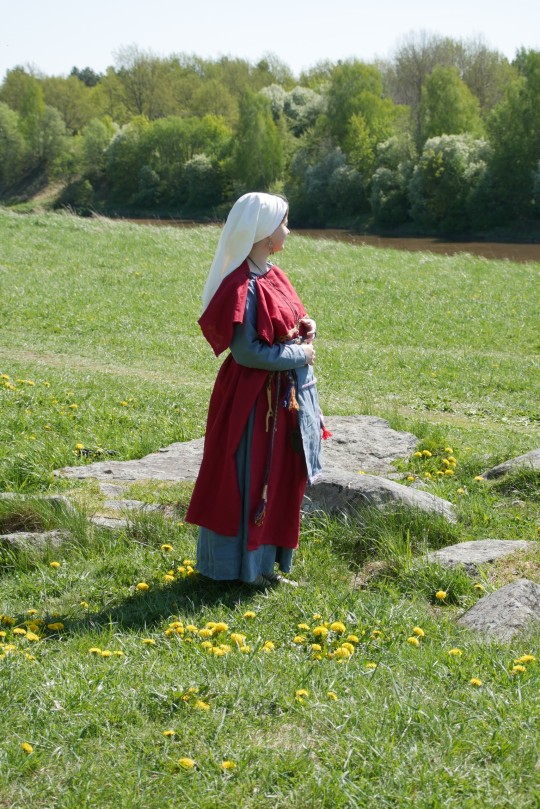
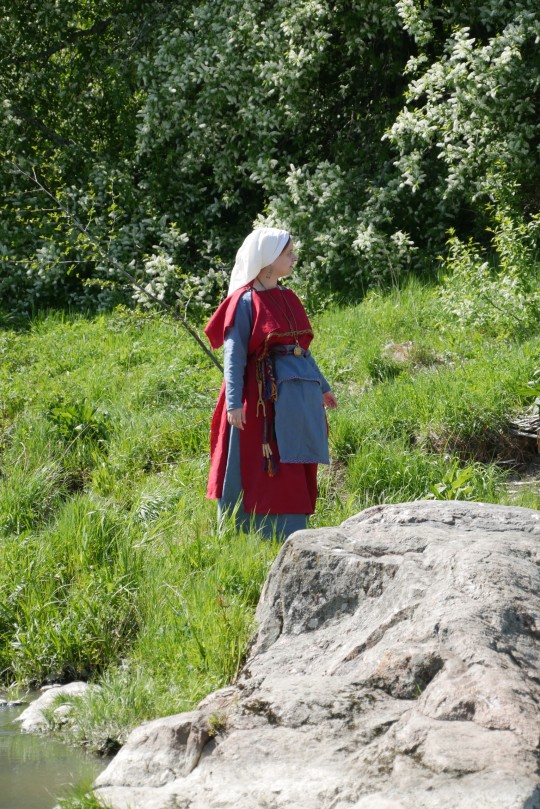








Finnish iron age (AD 500 - 1300) dress
Iron brooches, shoes and knife: Rautaportti
Necklace and earrings: Kalevala Koru
Cross necklace: Kimmo Tulimetsä
Ring: Takomo Alkutuli
Lucet: VytuVatu (Etsy)
Rosary cross: FenrirS (Etsy)
Veil pin (not even visible): Elävä keskiaika ry
Sock garters (also not visible): an old lady in the local Karelian association
Everything else by me
Pictures by my friend who doesn't use social media
#personal#suomi#fashion history#reenactment#iron age#rautakausi#ok to rb#spot the subtle tolkien reference#i probably need a tetanus shot after walking in that disgusting river#aurajoki ♥️
272 notes
·
View notes
Text
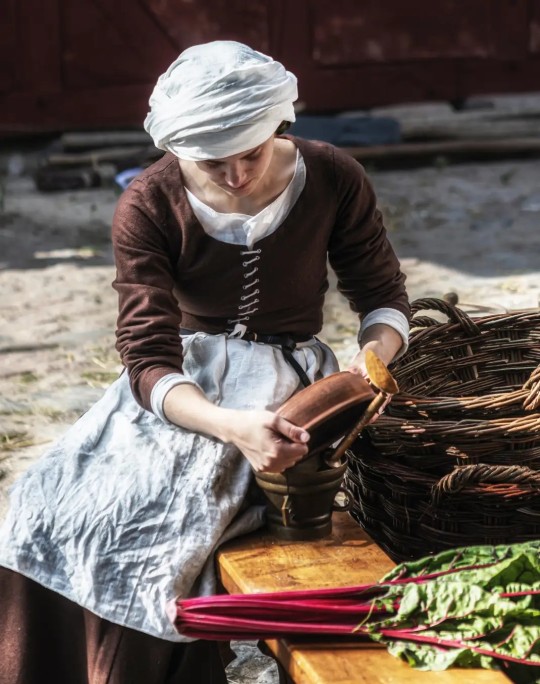




some more pictures from my 8 day reenactment event :) hard at work in the kitchen!
#medievalcore#personal#myface#medieval reenactment#reenactment#historical reenactment#15th century#historical fashion#medieval fashion#these are two different dresses btw#theybare just both brown#medieval
194 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sometimes, during events, you need to find alternative uses for your spinning equipment and make something funny... Maybe recreate a miniature?

291 notes
·
View notes
Text
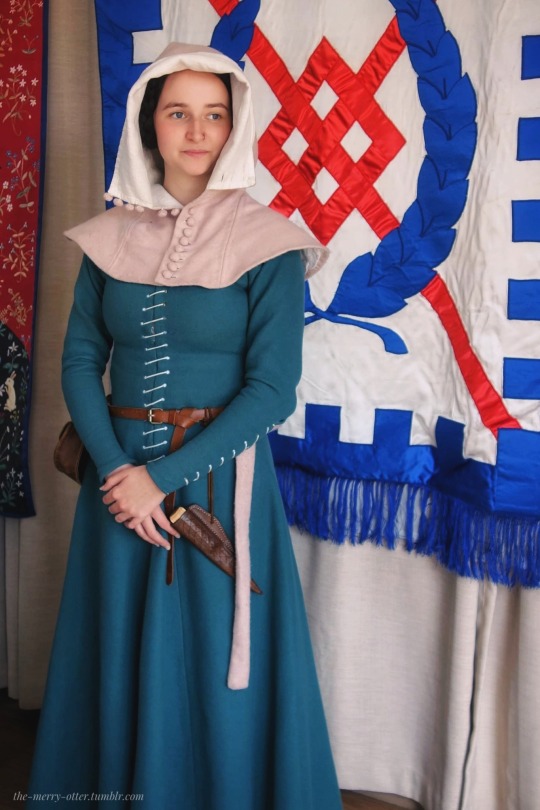
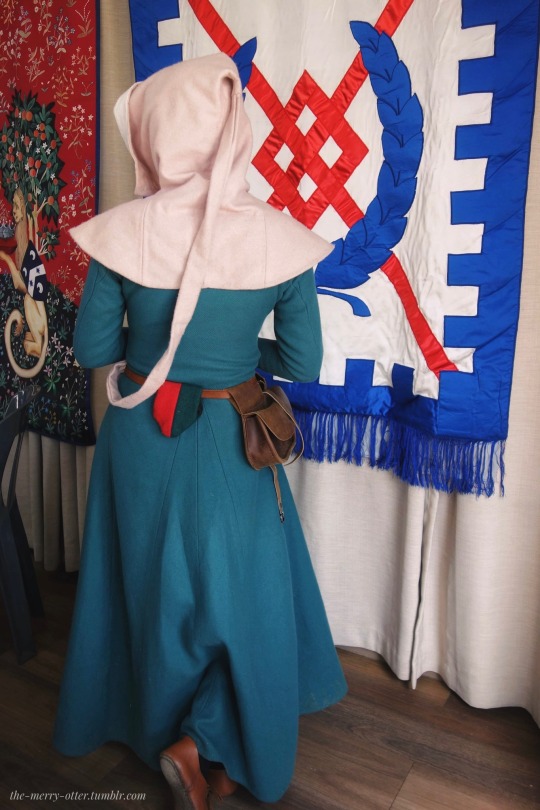


Photos of my 14th century garb from the camping event
#medieval reenactment#14th century#medieval#middle ages#history#historical reenactment#medievalcore#medieval aesthetic#sca#innilgard#lochac#reenactment#photography#costuming#fashion#medieval costume#i’ll be on my merry way now#something something it isn’t perfect yet shh
286 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sully-sur-Loire 2023
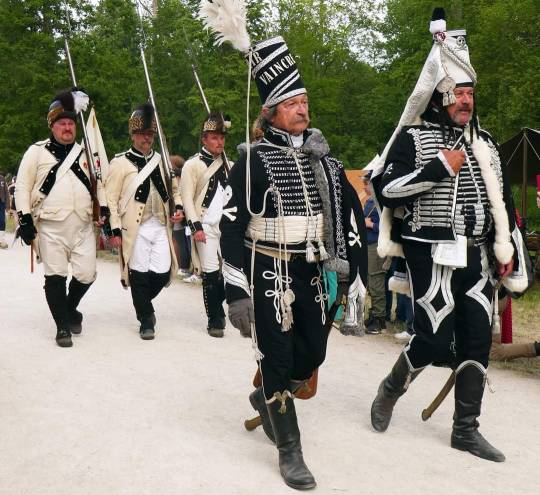






#french history#military history#cavalry#history#military aesthetic#napoleon#dragoon#napoleon bonaparte#reenactment#hussar#light cavalry#napoleonic era#napoleonic wars
99 notes
·
View notes
Photo

One seriously badass photo from this year's Monmouth reenactment - British light infantry and jägers leading out Loyalists, Highlanders, dismounted dragoons. Courtesy of the 40th Foot Light Infantry/Bloodhounds and Bruce Neumann.
#reenactment#history#military history#redcoat#redcoats#british army#light infantry#british light infantry#american revolution#revwar#american war of independence
175 notes
·
View notes
Text

Going a-viking this long weekend!
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
16th c. Costume Books, a Problematic Source for Dress History

But did they really dress like this?
Costume books and costume albums are a popular source for dress historians, historical costumers, and reenactors researching 16th and early 17th c. Europe. There are good reasons for this. They are primary source documents (at least sometimes), and they show the clothing of cultures and social groups that are difficult-to-impossible to find in other types of period art, like the Irish and rural peasants. Examples of these books include Trachtenbuch des Christoph Weiditz, Habiti antichi et moderni di tutto il Mondo di Cesare Vecellio, and Théâtre de tous les peuples et nations de la terre avec leurs habits et ornemens divers. These books are, however, deeply problematic as a dress history source for several reasons. In this post, I will discuss the ways they are problematic and how those of us researching historical dress can gain a better understanding of what the people shown in these books were actually wearing. I have broken down the problems with using these images into 4 areas.
Embodied biases:
The creators of these books were, at least sometimes, prejudiced against the cultures they were portraying, and these biases may have affected how they characterized these cultures. Hans Weigel, author of Habitus praecipuorum populorum, characterized his native German fashion as modest and virtuous and characterized elaborate Italian fashions as decadent and corrupt. Weigel considered these 'strange' foreign fashions a threat to the 'civilized' German fashion he favored (Bond 2018). This bias might have motivated Weigel to idealize his portrayal of German fashion or to exaggerate the strangeness of Italian fashion in order to scare his readers away from trying it.
Weigel's dislike of flashy foreign fashions seems mild in comparison to the bigotry of some of his peers. Flemish artist Lucas de Heere and French artist François Desprez both labeled the Scottish 'savages' in their books. Jost Amman's description of a purported Turkish sex worker in the German edition of Gynaeceum, sive Theatrum mulierum, is appallingly bigoted:
"A Turkish Wh*re: This is a prostitute, who sells her impure body for dirty money to a lover that pleases her. With the earnings of this sin she dresses herself prettily and beautifully, in order to attract the Turks even more easily with her false ornaments." (translation from Ilg 2004)
Considering the blatant bigotry he shows here, I wouldn't anything about trust Amman's depictions of sex workers, Turks, or any other non-Western Europeans. Or any other women, really.
Sights unseen:
Even when costume book creators weren't actively trying to perpetuate their biases through their work, their ignorance could still cause problems. These artists did not always visit the countries whose costumes they painted. They relied on other artists' work or even just verbal descriptions to fill in the gaps in their knowledge. The resulting images can distort the cut, construction, and material of the clothing.
For example, the Turkish women in this original woodcut by Pieter Coecke van Aelst are wearing shawls or scarves with long fringe wrapped around their heads and shoulders. In the Christoph von Sternsee costume album's illustration based off Coecke van Aelst's print, the fringed shawl has become a strange, tailored hood with a panel of pleated cloth attached to either it or the gown below.

(Coecke van Aelst's woodcuts were identified as the source for the von Sternsee album's illustration in Katherine Bond's 2018 dissertation.)
Copy of a copy of what?
In spite of the problems it causes, copying from other artists' work was common in costume albums (Bond 2018). Considering that the artists did not visit all the cultures they illustrated, this is unsurprising. Some images were copied repeatedly, and the artist misunderstanding the source material wasn't the only source of distortion. Artists also made up details to compensate for bare-bones source material.
This simple line black-and-white print of an Irish woman wearing a léine (linen tunic), brat (Irish mantle), and headwear was used by several artists, all of whom made changes and additions. The first copy in this post is the most faithful to the original, but it still adds long sleeves and eyelet holes on the neckline to the léine. The coloring of the headwear suggests a wool hat crested with a tuft of horsehair and having a linen roll at the bottom. The coloring also gives the brat a contrasting lining.
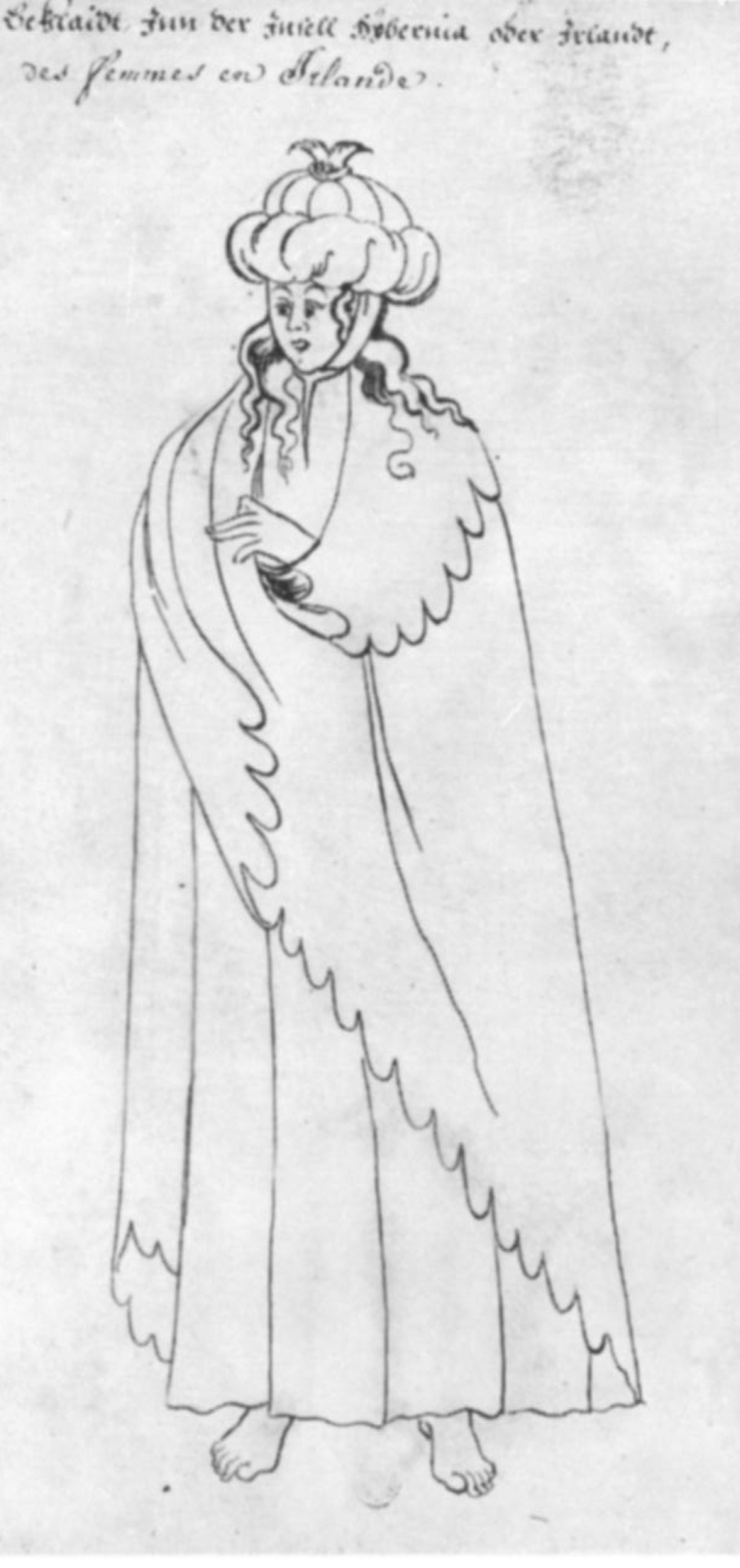
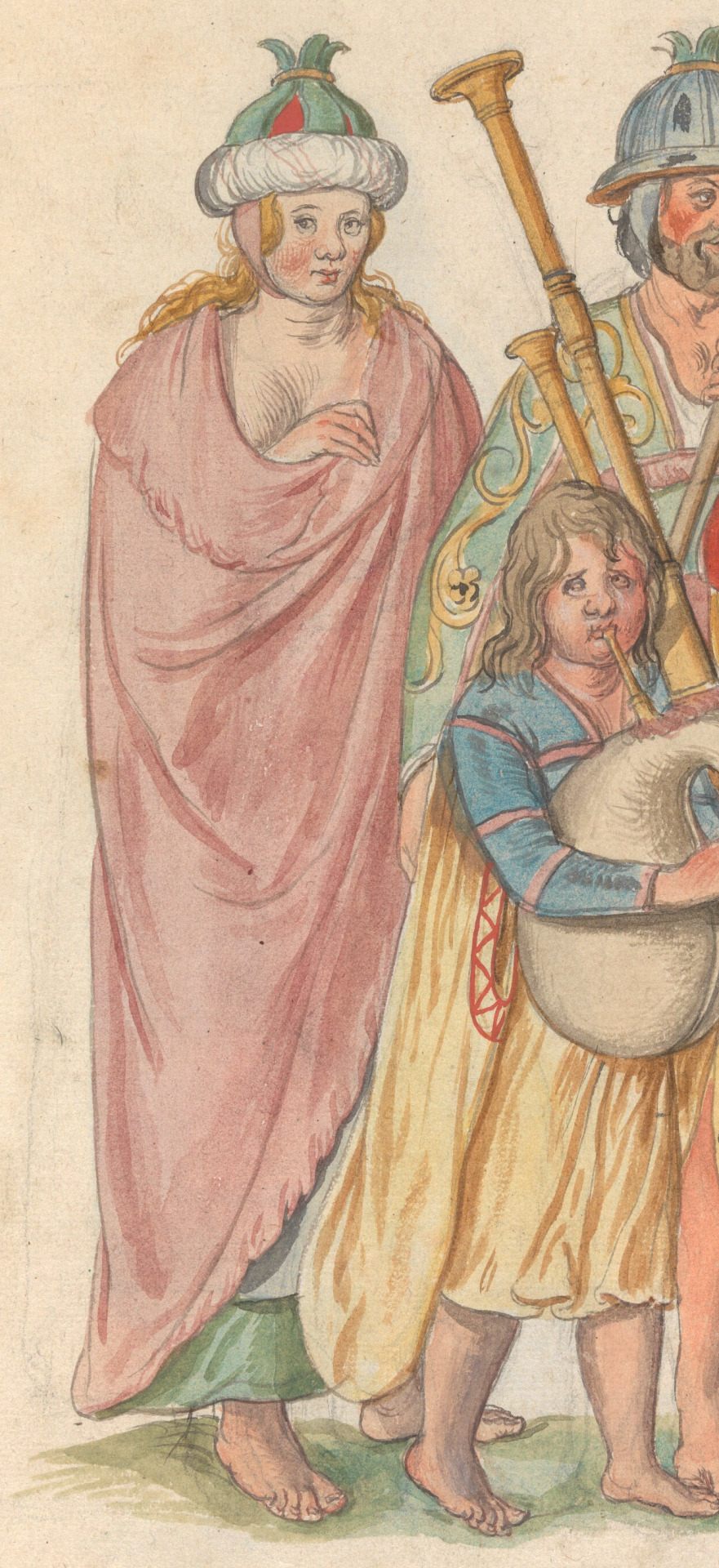




The second knockoff is the most famous. It comes from Lucas De Heere's illustration which purportedly shows Irish people in service to King Henry VIII. This is some thing De Heere couldn't have actually seen, as he moved to England 20 years after Henry VIII died and never went to Ireland at all. De Heere took the most liberties with his version. His Irish woman appears to be topless under her brat. The bottom of her léine has much less volume than the original, and De Heere has added an apron. For the hat, De Heere has replaced the crest with triangles of green wool.
Unlike De Heere's version, the final version is mostly loyal to the cut shown in the original, but it makes some unlikely suggestions for the materials. The léine appears to be green silk brocade. The brat also appears to be silk. Accounts from people who actually went to Ireland in the 16th and early 17th centuries state that these garments were made of linen and wool, respectively. Both the hat and its crest are now completely made of linen.
Chronological distortion:
The heavy use of copying in costume books also has the potential to mislead us in terms of when these fashions were worn, because the original images may be significantly older than publication year of the books that copy them. For example, the dress of Livonian women shown in Hans Weigel's 1577 book was almost certainly copied from Albrecht Dürer's 1521 watercolors. Weigel used references that were more than half a century old, but described them as if they were contemporary fashion in 1577.
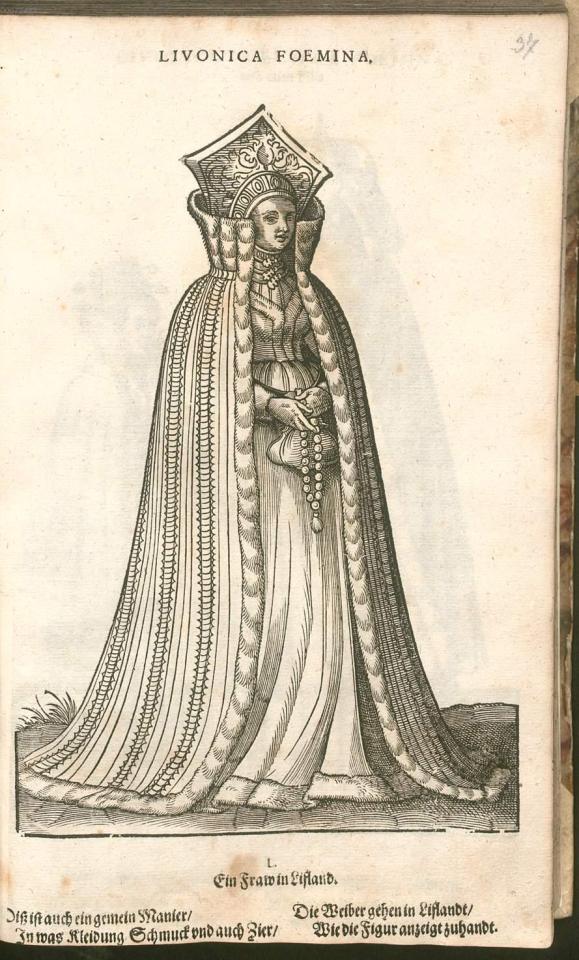
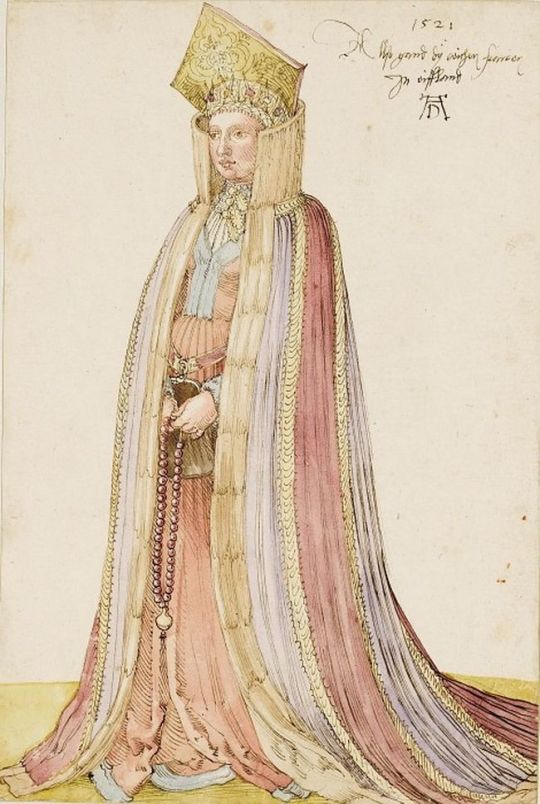
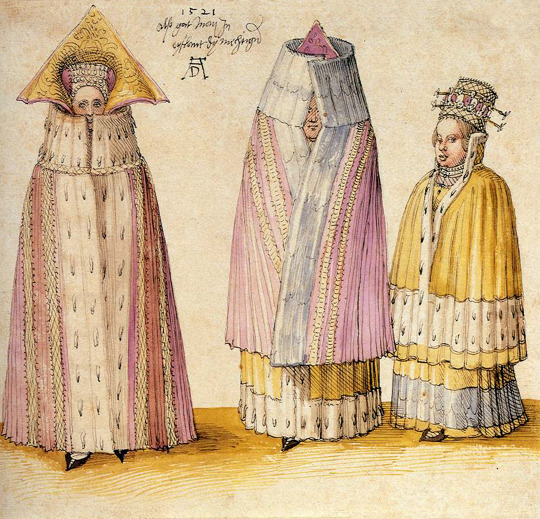


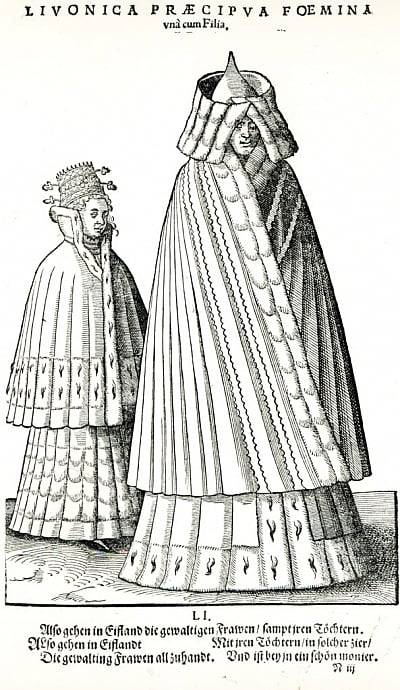

Even when costume book images are accurate portrayals of their source material, many of them lack the detail needed to identify seams, fabric types, or garment understructures. How do we deal with these problems when attempting to reconstruct what the people shown in these books actually wore?
What do we do about it?
I am not saying that we should discard these things completely as sources. Dress historians as respected as Patterns of Fashion author Janet Arnold and The Tudor Tailor authors Jane Malcolm and Ninya Mikhaila have used costume book illustrations. I definitely know less about 16th c. dress history than Jane and Ninya. I am just saying we shouldn't use them uncritically.
First, do some research on the costume book you're looking at. When was it created? Do the illustrations look suspiciously similar to those in other books? (Google image search and pinterest can be helpful for identifying this.) Did the creator, like Hans Weigel, have a particular bias they were advancing? Did they actually visit the cultures they portrayed? Christoph Weiditz actually traveled quite a bit, but he did not visit the British Isles, so his Irish and English women are probably based on someone else's art (Bond 2018). A lot of the scholarly publications about costume books are frustratingly paywalled, but some of them can be accessed for free via researchgate or academia.edu.
Avoid using copies when possible, even if the copies are more realistic-looking or more detailed art. As I discussed in the examples above, artists change things when they copy. Publication dates of copies can also be misleading in terms of dating clothing styles.
Find other sources such as: written descriptions from the time period, extant historical garments, more detailed art depicting similar fashions in related cultures, and art made by people from the culture you are studying. Period written descriptions can yield information about materials used, colors, and other details. Extant garments are your best source for information on cut and construction (unless you are lucky enough to have an extant tailor's manual from your period and culture). Detailed art depicting similar fashions can offer suggestions to fill in for missing information on construction, materials, and embellishments. Art created by the culture is valuable for identifying inaccuracies created by bigoted or ignorant artists.
Finally, remember that it's okay to not know everything. There are gaps in our knowledge about what people wore 500 years ago that will probably never be filled without a time machine. Sometimes you just have to make a plausible guess and move on. Don't let yourself get so paralyzed by doing research that you never complete the garment reconstruction/art/tumblr post you were doing the research for.
Bibliography:
Bond, K. L. (2018). Costume Albums in Charles V’s Habsburg Empire (1528-1549). https://doi.org/10.17863/CAM.25054
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
Ilg, Ulrike. (2004). The Cultural Significance of Costume Books Sixteenth-Century Europe. In Catherine Richardson (ed.), Clothing Culture, 1350-1650 (p. 29-47). Ashgate.
McClintock, H. F. (1943). Old Irish and Highland Dress. Dundalgan Press, Dundalk.
McClintock, H. F. (1953). Some Hitherto Unpublished Pictures of Sixteenth Century Irish People, and the Costumes Appearing in Them. The Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland, 83(2), 150-155. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25510871
Costume Books mentioned:
Amman, Jost. Gynaeceum, sive Theatrum mulierum.
The Costume Album of Christoph von Sternsee. not available on-line. Katherine Bond's research is your best source for this one.
Desprez, François. Recueil de la diversité des habits.
De Heere, Lucas. Corte Beschryvinghe van Engheland, Schotland, ende Irland.
Théâtre de tous les peuples et nations de la terre avec leurs habits et ornemens divers, tant anciens que modernes, diligemment depeints au naturel par Luc Dheere peintre et sculpteur Gantois.
Vecellio, Cesare, and Gratilianus, Sulstatius. Habiti antichi et moderni di tutto il Mondo di Cesare Vecellio.
Trachtenbuch des Christoph Weiditz
Weigel, Hans, and Amman, Jost. Habitus praecipuorum populorum, tam virorum quam foeminarum singulari arte depicti.
Kostüme der Männer und Frauen in Augsburg und Nürnberg, Deutschland, Europa, Orient und Afrika
Kostüme und Sittenbilder des 16. Jahrhunderts aus West- und Osteuropa, Orient, der Neuen Welt und Afrika
costume prints by an unknown artist, in the Bibliothèque nationale de France, Cabinet des Estampes. I cannot find this one online. image taken from McClintock 1953.
#dress history#historical fashion#art#16th century#17th century#historical costuming#historical dress#cw whorephobia#cw racism#irish dress#leine#irish mantle#reenactment#costume album
194 notes
·
View notes