#so heroku it is
Text
The sixty-seventh free, unedited chapter of my upcoming book, “The Heist at Cordia Aquarium” is now available on its website (or click here to read from the beginning).
It's dark. Cramped and humid and hot. Thea tightens her arms around her knees; each breath comes rough. Haggard. Harsh against her throat, dry and raw as it is.
It's my fault. I could have said something; I could have stayed out of this and let them find someone better. Then Ivan could become a wrestler; Waylon could help whoever it was that needs him. But no, I'm selfish. I took everything from them.
Her thoughts bounce around inside her head, repeating — never-ending. Those that she escapes just add to the weight of the air around her. Floating at the edge of her perception, like specters waiting for another turn to haunt her.
She presses her head into her knees and she wretches. A dry, tearless sound — just as it's been for a while now. How long am I going to sit here, useless?
[...]

#heroku deleted my websites database so I'm a day late#did they send me an email that they were going to delete the free tier of databases? maybe#did I read it? most certainly not#and am I going to claim responsibility? I'll leave the answer to that open ended#anyway book tags#queer author#queer novel#queer lit#asexual protagonist#tw: anxiety#tw: negative thoughts#cat that thinks they're the protagonist
623 notes
·
View notes
Text
death to services that ask for ur payment info even tho they are free >:( then why in the good goddamn hell would u need that info then hhUH ???
#trying to use fly.io to get this stupid app to the internet and dude I do not want to put my credit card info there#it’s for one (1) course I don’t want to suddenly wake up some day and see that I have a big ass bill for something I thought was free#bc i don’t trust anything to actually stay free#and fly.io ’’ we don’t offer free-tier. instead we offer some free resource allowances that include enough usage per month to run a small#app for free’’ but like that seems sketchy?? like are they going to inform me like hey so if u don’t take this down we are going to start#billing you?? seems like it’ll be ’’hey so ur app is actually not what we consider ’’small’’ so we took the liberty to rob ur entire#apartment for payment thanxx <3’’#stupid heroku deciding that u now how to pay for it like literally what can u do in this world without putting ur bank account on the line??#literally nothing#september 2023#2023
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
We want to apologise for slow updates. This next one is supposed to be a heavy hitter. So far:
1. The site will have an updated UI to be more mobile friendly while maintaining a unique design. We hate to do it but banner and background images are getting phased out due to strobing, data usage for the user and us trying to upload updates. It sucks but the semi-skeuomorphic design of the site will not change.
2. Strobing is expected to be minimised because we’re also dropping Twemoji (Twitter emoji). Twemoji shut down early last year and we don’t really think parsing emojis are the most important thing for Lighthouse right now.
3. The site is now getting the basic infrastructure to be fully translatable into other languages. This push comes from current events, where English is not the primary language.
4. We’re also looking into new hosting platforms. When we were younger and thought Lighthouse wouldn’t go anywhere, we put it on Heroku. But as time as gone on, we’re learning that Lighthouse’s needs are changing as well as Heroku’s ability to deliver on those needs. We will email our users with a 7-day warning when we decide to do this so everyone is aware.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
With the resurgence of people becoming interested in setting up their own websites and platforms, one thing I'd encourage people to look into is something called "static site generators." If you're looking to stand up a really simple site without a lot of dynamic content, this is probably the easiest way to do so.
Static-site generators allow you to automate the development of html pages that are ready to serve. The biggest difference between static sites and dynamic sites is that the latter cobbles together the page your users see by pulling all sorts of data from databases upon request time. In contrast, static sites allow you to serve ready-made html pages, making them much faster, secure, and cheaper to host.
(You do need to know a bit of back-end programming to run some simple commands and setup configuration files, but if you're already dabbling in HTML, CSS, and JS, I'm guessing you're up for the challenge.)
Here are a few resources if you want to try it out.
What is a static site generator?
A list of static site generators you can choose from
There's a lot on that list, but these are the ones I often see people using: Next.js, Jekyll, Hugo, Pelican
Places that host static sites, often for free, mostly for little charge:
Github Pages
GitLab Pages
Render
Heroku
The process of updating your website will be quite different than if you're used to platforms like Wordpress or Weebly. But if you're okay with using markdown editors and syncing your files manually, the amount of control you get back over your own content is totally worth it. There are also a lot of plugins and resources already out there to make the experience much smoother.
#static site generators#html#css#js#web development#feel free to ask me anything if you're curious#i personally use pelican for my personal site#and i haven't regretted migrating from both wordpress and django
134 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey Loa, your project-streak is so amazing.
Just wanted to ask which hosting platforms would you recommend for deploying full-stack projects?

Haha, my project-streak! 💗✨ Thanks, I didn't know I had a streak going on! But I just code random things when I'm bored and I get bored a lot I post a lot of my projects - finished or unfinished (ノ´ヮ´)ノ*: ・゚
Hosting platforms, here are some I know you could try out:
Heroku
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Microsoft Azure
Netlify
Vercel
Replit
I've used Microsoft Azure (for work) and Netlify (because of the bootcamp I was in) in the past and the rest I know my friends have used for their projects!
#my asks#resources#codeblr#coding#programming#progblr#studying#studyblr#dev logs#comp sci#computer science#programmer#deployment websites#deployment
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
SW Randomizer - new host
So, Heroku no longer offers a free tier and that broke my randomizer. Because I’m too cheap to pay for a custom domain for such a tiny project, that means if you have the link saved it won’t work anymore.
The Star Wars Randomizer is now located at https://sw-randomizer.netlify.app/
And if this is the first time hearing about it, this is NOT a name generator. Pick a topic and it’ll spit out a selection of thousands of Legends or Canon things. Give your fanworks some SW flavoring even when you don’t feel like making up something new
Remember, it’s fake and in space
25 notes
·
View notes
Note
Please tell us more about the journalling game you’re working on! It sounds really interesting.
It's a few different things, because I'm a Slack-addicted solipsist:
A bot that (presumably) follows you around anonymously, logging information about you and sending it to a central server
A game, played by a group of people, which tries to explain who the bot really is
An interactive "social environment" which is rendered in a sort of "window" within your browser. In this environment, you may meet and interact with people who are also playing the game, and chat with any of them. You may also chat with the bot anonymously.
(1) is probably the least interesting, but it needs to be done to make (2) work.
(2) and (3) can probably be summed up as "social interaction with people who are both real and fake."
(3) is the one that's closest to finished. In this state, it can be played locally (using an in-person game / telephone game) or by people in different physical locations, using text chat (which is like an IRC or MMO channel). It runs using a language called Elixir, which is based on Erlang.
The bot is in a sense the "creator" or "moderator" of the game, which is run by a group of itsa players. As the game starts, the bot tells the players about each other. In this early state, the bot's characterization of each player -- their "demographic profile" and "lifestyle" -- is based only on the bot's own logging, and is necessarily incomplete. (Anyone in the game can send chat messages to the bot that are saved as data.)
The bot's computing environment is provided by a cloud service called Heroku. This allows players to operate on the bot from anywhere, and lets the bot harvest data from anywhere. I am not "in charge" of this environment, I am merely a subscriber.
Over time, as the game progresses, players get more data about each other, plus some "special abilities" from the bot. The bot's data is supposed to increase in accuracy as it gains new data about people. Somewhere around 10-15 people should be able to play at once, except that this depends on what sort of environment they're in.
The game spontaneously ends when a player receives 100 "dots" from the bot. The bot says, "You have been fitted for a Helmet of Damnation." The game now officially begins. The Helmet of Damnation is supposed to track players so that everyone can see each other's movements. So far, the Helmet of Damnation has worked via a poorly-implemented copper wire solution, but it works. I'm not making an actual "augmented reality" environment, because a lot of the fun would depend on local, face-to-face social interactions.
What actually happens after the Helmet of Damnation is yet to be decided. But the Helmet's presence should at least have some disruptive impact on players' relationships with each other.
A final state, which is still imaginary, is that the game would be played in an augmented reality environment -- using, say, Kinect and maybe some sort of messy motion-tracking software. This would allow the bot to move around players' physical space, but I
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Inuyasha Osmosis
Glowfic is doing an Inuyasha thread. Before I start actually learning things about the setting and characters, here is my not-actually-dashboard osmosis of what I know about the characters. Mainly from the Adult Swim Flash game ‘Inuyasha: Demon Tournament’ though I think I must have looked some of this up somewhere at some point.

Inuyasha
wolf boy
I Am Not Protagonist
SO ANGERY
probably tsundere
defector from Always Chaotic Evil
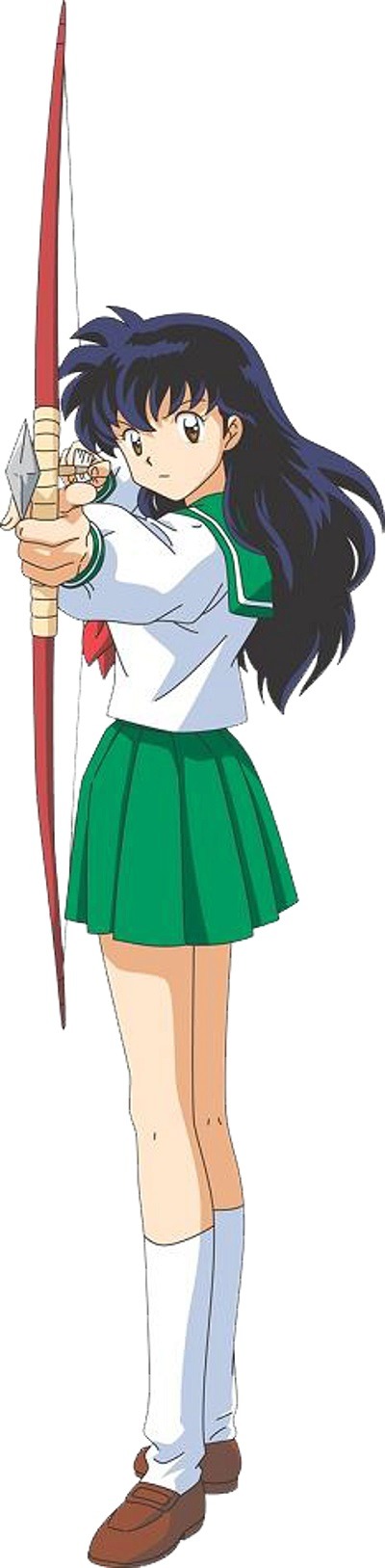

Kagome
I Am Protagonist
from the future
not going to change clothes ever so that you don’t forget I’m from the future
argh why am I here why are so many Things happening
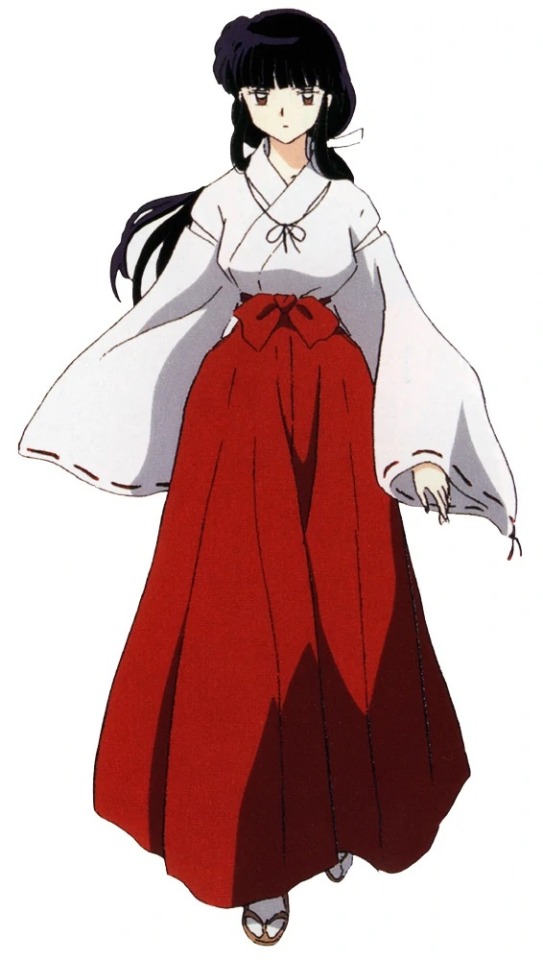

Kikyo(?)
Mary Sue
“stop telling people I’m dead!”
but probably actually dead
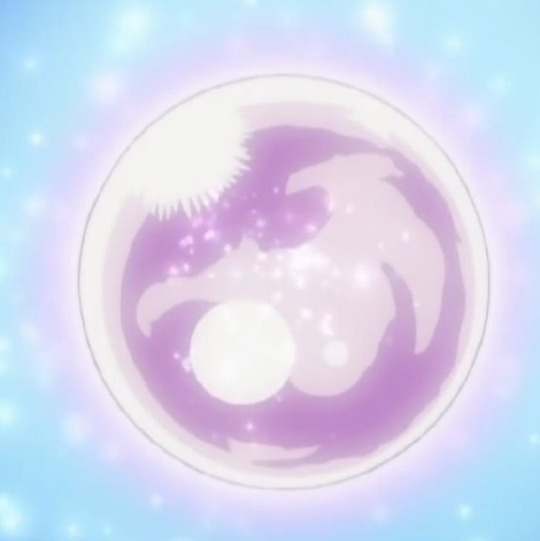

The Shiny Object
MacGuffin
gets broken into pieces?
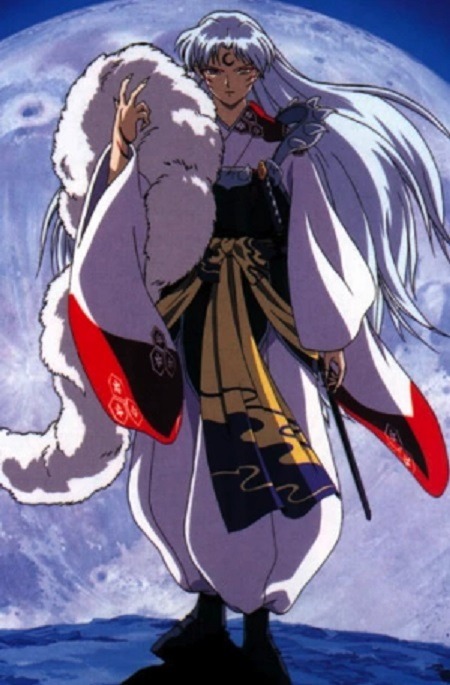

Kobayashi Maru Sesshomaru(?)
thinks he’s much cooler than you
he’s probably right
Disc One Final Boss
the kind of villain who will team up with you against the scarier villain
probably Inuyasha’s father or brother or uncle or something

Heroku
monk
designated pervert
generally kind of an asshole even besides that?
will do the right thing once he’s exhausted all other options
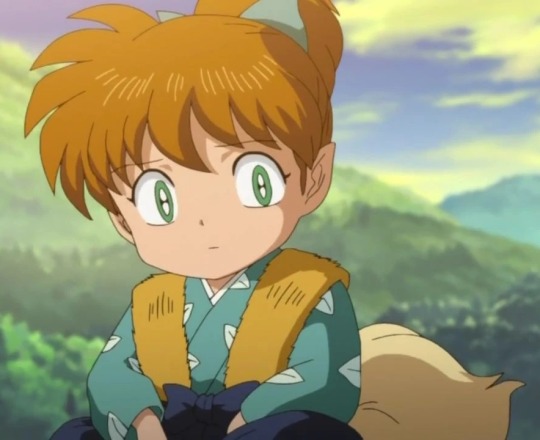

Zeppo Marx Shippo
Rule 63 Squirrel Girl
designated cute smol
extremely annoying
metacausally very happy Miroku is around so he doesn’t also have to be designated pervert
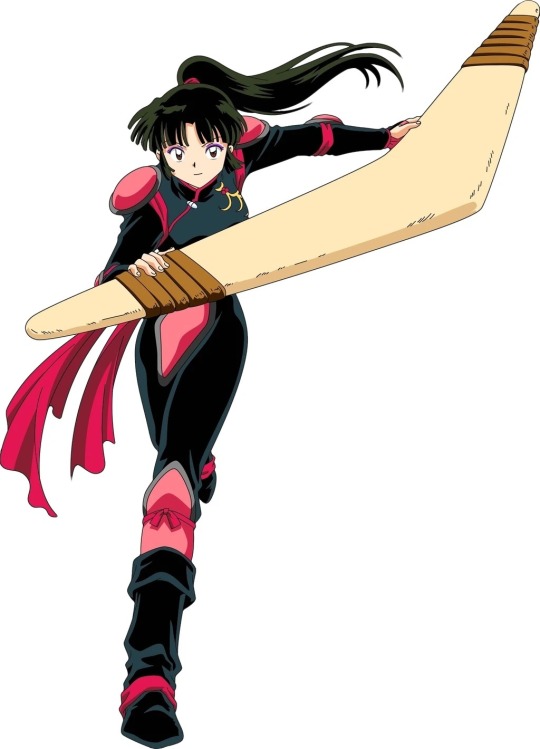

Xena Sango
not compensating for anything
makes Kagome feel insecure about not being as cool as her
bet she’s some kind of mercenary or something
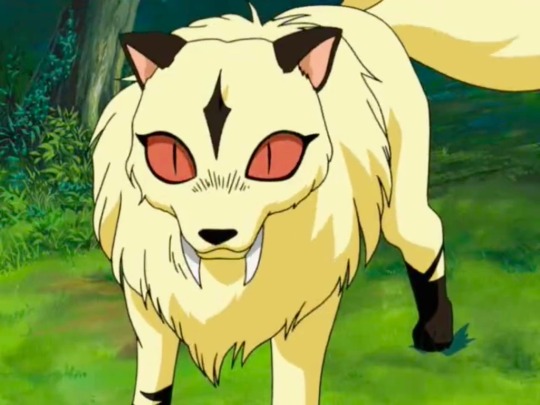

Kirara
Danger Kitty Fox
friends with Xena
probably a person?
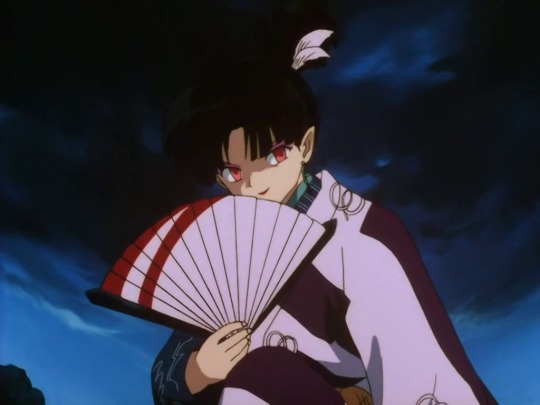

Kagura
also thinks she’s cooler than you
bet she’s the Big Bad’s daughter or something
the kind who flirts constantly but has absolutely no romantic tension with anybody
definitely not going to team up with you against anyone, you’re not cool enough

Kuga
wolf boy... two!
the kind who’s raised by wolves this time
doesn’t have anything against the heroes but they keep getting in his way for some reason
not going to team up with you because teaming up with people is lame
teaming up with wolves is fine though

Toad Boy
minion
likes fire
probably gets used as a stress ball by whichever villain he’s working for
lame

Voldemort Heroku Naraku
actual final boss
this isn’t even my final form!
gloats too much
might actually be just a normal guy under the toothy mask and big-ass cloak
would kill all the heroes even if they were absolutely no threat or impediment to him
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Build Websites Like a Pro with a Full Stack Course

In the modern world of technology, creating a professional website is crucial for all entrepreneurs and individuals. It does not matter whether you are a beginner, a freelancer, or a person who wants to get an additional profession, familiarizing yourself with website development provides an opportunity to enter many spheres.
And so, the question arises: how to progress from a complete beginners’ level to a professional one? The answer is quite simple and that is by enrolling at the Best Fullstack Development Institutes.
What is Full Stack Development?
Full-stack development is the process to create both the interface that the user will be interacting with (front end) and the side that the user is not likely to see or directly interface with (back end) of a web application. Full stack developers are able to write code in various programming languages and are also aware of the use of different tools for web development.
Main components of Full Stack Development
1. Front End Development
Front end development is about the final interfaces of a website the users see and interact with. The key components of front-end development include, HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), JavaScript and frameworks like React.js, Angular, and Vue.js.
2. Back End Development
Back end development entails handling the actual programming of how a website actually works, along with the handling of databases and API, with languages like Node.js. web frameworks including Python, PHP and Ruby for application development and SQL and NoSQL databases such as MySQL and MongoDB for data management.
3. Deployment and DevOps
Full stack developers have to be aware of specific deployment methods, and should have at least a basic understanding of DevOps and its tools, including integration, delivery, and monitoring. It involves hosting web applications using cloud platforms like AWS or Heroku so as to enable the users to access the applications.
Search “Best Web Development Course Near Me”, and choose Career Boss to know more about full stack development courses.
Why Choose a Full Stack Course?
Comprehensive Learning: It’s the step-by-step process, hence, you will find out how to create a website, how to include server-side code, work with databases and, eventually, place your website on the Internet.
Increased Job Opportunities: Full Stack developer jobs are increasing, as employers rather seek to employ people who can work on both front end and back end since it is cheaper as well as time saving to work with a single person instead of several specialised persons.
Versatility and Flexibility: Because of full stack knowledge, you are not restricted to any one position. It is possible to work as a front-end, back end, or full stack developer. Also, the skills you learn can also be extended to project types, ranging from small business sites to complex web applications.
Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: In line with a full stack course, you will also learn problem solving skills in tackling any problem that comes your way.
Opportunity to Work on Freelance Projects: If you want to work for yourself or become a business owner, full stack development is a perfect skill set. Thus, because of the possibility to create websites from scratch, clients can be found, projects can be handled, and regular earnings can be achieved.
What You Will Learn in a Full Stack Course?
In a course at the Best Fullstack Development Institutes, you are taught everything that is required to create and manage the front end and back end of an application. This having an expertise in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript interactive and designing a web page user interface and the server-side languages like Node. java script or Python, for managing all the application processing and the databases.
You will also be skilled in using databases (SQ/NoSQL), version control (Git, API interoperation and cloud-based deployment. Also, the course will include topics as security, performance, and collaboration practices that lets you design and deliver full-scale web projects from scratch.
How to Choose the Right Full Stack Course?
Make sure to look for the following factors before choosing among many programs out there:
Curriculum: Make sure that both the front end and back end development areas should be taught in the course in-depth.
Instructor Expertise: Choose those classes that are delivered by tutors with ample academic records in web development.
Hands-On Projects: There can be no substitute for experience therefore, practical experience is mandatory. Select a course that comes with practical activities in terms of projects and assignments so that you can easily practise all that is learnt.
Career Support: Some of the courses at the Best Fullstack Development Institutes are designed with option facilitation for career employment and business networking. These can be very useful when one moves from a learning state to practise in the field of interest.
Reviews and Testimonials: Check out comments and testimonials of former students in different courses in order to get the feel of what it is like.
Conclusion
Learning full stack development is quite effective when developing websites like a professional. Full stack course helps you learn a number of skills which are necessary to create and launch impressive web platforms in the modern context of competition.
When you grasp the significant areas of full stack development, take advantage of the comprehensive course, get acquainted with the trends in the IT sphere, and select the appropriate course, you can create the best conditions for a successful Web development career. Do not wait any longer and start your journey toward becoming a full stack expert right now. Contact Career Boss Institute- the Best Fullstack Development Institutes.
#Best Fullstack Development Institutes#Best Fullstack Development#Fullstack Development Institutes#Fullstack Development
0 notes
Text
Building a Strong Full-Stack Foundation: Essential Skills and Tools
Introduction
In the dynamic world of web development, mastering full-stack development is a powerful way to enhance your skill set and increase your marketability. A solid foundation in full-stack development not only makes you versatile but also equips you to handle both the frontend and backend aspects of web applications. Whether you're a budding developer or an industry professional looking to expand your expertise, understanding the core components of a full-stack foundation is crucial.
What is Full-Stack Development?
Full-stack development involves working on both the client-side (frontend) and server-side (backend) of web applications. A full-stack developer is proficient in a range of technologies that allow them to build complete web solutions from scratch.
Key Components of a Full-Stack Foundation
Frontend DevelopmentHTML/CSS: The building blocks of web development, crucial for structuring and styling web pages.JavaScript: Essential for creating interactive elements and improving user experience. Familiarity with frameworks like React, Vue.js, or Angular can be beneficial.Responsive Design: Understanding how to create layouts that work well on various devices using frameworks like Bootstrap or material design principles.
Backend DevelopmentProgramming Languages: Knowledge of server-side languages such as Node.js (JavaScript), Python, Ruby, or PHP.Frameworks and Libraries: Familiarity with backend frameworks like Express.js for Node.js, Django for Python, or Rails for Ruby.Database Management: Understanding both SQL databases (like PostgreSQL or MySQL) and NoSQL databases (like MongoDB) is crucial for data storage and retrieval.
Version ControlGit: Proficiency with Git and platforms like GitHub or GitLab is essential for managing code changes and collaboration in development projects.
APIs and Web ServicesRESTful APIs: Knowledge of creating and consuming RESTful APIs to enable communication between the frontend and backend.GraphQL: An alternative to REST for querying and manipulating data, offering more flexibility.
DevOps and DeploymentServer Management: Basic understanding of server environments and deployment strategies, including using platforms like AWS, Heroku, or DigitalOcean.CI/CD Pipelines: Familiarity with continuous integration and continuous deployment practices to automate testing and deployment processes.
Soft SkillsProblem-Solving: Strong analytical skills to troubleshoot and resolve issues.Communication: Ability to articulate technical concepts clearly to non-technical stakeholders and work effectively in teams.
Building Your Full-Stack Foundation
Start with Projects: Apply what you've learned by building real-world projects. This hands-on experience is invaluable for reinforcing your skills.
Stay Updated: Technology evolves rapidly, so keeping up with industry trends and new tools is important.
Join a Community: Engage with developer communities through forums, meetups, or online groups to learn from others and stay motivated.
Conclusion
Developing a strong full-stack foundation is an investment in your career as a developer. By mastering both frontend and backend technologies and understanding the tools and practices that support modern development workflows, you'll be well-equipped to tackle complex projects and adapt to the ever-changing tech landscape. Whether you're just starting out or looking to deepen your expertise, focusing on these core areas will set you on a path to success in the world of full-stack development.
#web developers#web development#android development#app development#web design#web developing company
1 note
·
View note
Text
Charity Majors, CTO & Co-Founder at Honeycomb – Interview Series
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/charity-majors-cto-co-founder-at-honeycomb-interview-series/
Charity Majors, CTO & Co-Founder at Honeycomb – Interview Series
Charity is an ops engineer and accidental startup founder at Honeycomb. Before this she worked at Parse, Facebook, and Linden Lab on infrastructure and developer tools, and always seemed to wind up running the databases. She is the co-author of O’Reilly’s Database Reliability Engineering, and loves free speech, free software, and single malt scotch.
You were the Production Engineering Manager at Facebook (Now Meta) for over 2 years, what were some of your highlights from this period and what are some of your key takeaways from this experience?
I worked on Parse, which was a backend for mobile apps, sort of like Heroku for mobile. I had never been interested in working at a big company, but we were acquired by Facebook. One of my key takeaways was that acquisitions are really, really hard, even in the very best of circumstances. The advice I always give other founders now is this: if you’re going to be acquired, make sure you have an executive sponsor, and think really hard about whether you have strategic alignment. Facebook acquired Instagram not long before acquiring Parse, and the Instagram acquisition was hardly bells and roses, but it was ultimately very successful because they did have strategic alignment and a strong sponsor.
I didn’t have an easy time at Facebook, but I am very grateful for the time I spent there; I don’t know that I could have started a company without the lessons I learned about organizational structure, management, strategy, etc. It also lent me a pedigree that made me attractive to VCs, none of whom had given me the time of day until that point. I’m a little cranky about this, but I’ll still take it.
Could you share the genesis story behind launching Honeycomb?
Definitely. From an architectural perspective, Parse was ahead of its time — we were using microservices before there were microservices, we had a massively sharded data layer, and as a platform serving over a million mobile apps, we had a lot of really complicated multi-tenancy problems. Our customers were developers, and they were constantly writing and uploading arbitrary code snippets and new queries of, shall we say, “varying quality” — and we just had to take it all in and make it work, somehow.
We were on the vanguard of a bunch of changes that have since gone mainstream. It used to be that most architectures were pretty simple, and they would fail repeatedly in predictable ways. You typically had a web layer, an application, and a database, and most of the complexity was bound up in your application code. So you would write monitoring checks to watch for those failures, and construct static dashboards for your metrics and monitoring data.
This industry has seen an explosion in architectural complexity over the past 10 years. We blew up the monolith, so now you have anywhere from several services to thousands of application microservices. Polyglot persistence is the norm; instead of “the database” it’s normal to have many different storage types as well as horizontal sharding, layers of caching, db-per-microservice, queueing, and more. On top of that you’ve got server-side hosted containers, third-party services and platforms, serverless code, block storage, and more.
The hard part used to be debugging your code; now, the hard part is figuring out where in the system the code is that you need to debug. Instead of failing repeatedly in predictable ways, it’s more likely the case that every single time you get paged, it’s about something you’ve never seen before and may never see again.
That’s the state we were in at Parse, on Facebook. Every day the entire platform was going down, and every time it was something different and new; a different app hitting the top 10 on iTunes, a different developer uploading a bad query.
Debugging these problems from scratch is insanely hard. With logs and metrics, you basically have to know what you’re looking for before you can find it. But we started feeding some data sets into a FB tool called Scuba, which let us slice and dice on arbitrary dimensions and high cardinality data in real time, and the amount of time it took us to identify and resolve these problems from scratch dropped like a rock, like from hours to…minutes? seconds? It wasn’t even an engineering problem anymore, it was a support problem. You could just follow the trail of breadcrumbs to the answer every time, clicky click click.
It was mind-blowing. This massive source of uncertainty and toil and unhappy customers and 2 am pages just … went away. It wasn’t until Christine and I left Facebook that it dawned on us just how much it had transformed the way we interacted with software. The idea of going back to the bad old days of monitoring checks and dashboards was just unthinkable.
But at the time, we honestly thought this was going to be a niche solution — that it solved a problem other massive multitenant platforms might have. It wasn’t until we had been building for almost a year that we started to realize that, oh wow, this is actually becoming an everyone problem.
For readers who are unfamiliar, what specifically is an observability platform and how does it differ from traditional monitoring and metrics?
Traditional monitoring famously has three pillars: metrics, logs and traces. You usually need to buy many tools to get your needs met: logging, tracing, APM, RUM, dashboarding, visualization, etc. Each of these is optimized for a different use case in a different format. As an engineer, you sit in the middle of these, trying to make sense of all of them. You skim through dashboards looking for visual patterns, you copy-paste IDs around from logs to traces and back. It’s very reactive and piecemeal, and typically you refer to these tools when you have a problem — they’re designed to help you operate your code and find bugs and errors.
Modern observability has a single source of truth; arbitrarily wide structured log events. From these events you can derive your metrics, dashboards, and logs. You can visualize them over time as a trace, you can slice and dice, you can zoom in to individual requests and out to the long view. Because everything’s connected, you don’t have to jump around from tool to tool, guessing or relying on intuition. Modern observability isn’t just about how you operate your systems, it’s about how you develop your code. It’s the substrate that allows you to hook up powerful, tight feedback loops that help you ship lots of value to users swiftly, with confidence, and find problems before your users do.
You’re known for believing that observability offers a single source of truth in engineering environments. How does AI integrate into this vision, and what are its benefits and challenges in this context?
Observability is like putting your glasses on before you go hurtling down the freeway. Test-driven development (TDD) revolutionized software in the early 2000s, but TDD has been losing efficacy the more complexity is located in our systems instead of just our software. Increasingly, if you want to get the benefits associated with TDD, you actually need to instrument your code and perform something akin to observability-driven development, or ODD, where you instrument as you go, deploy fast, then look at your code in production through the lens of the instrumentation you just wrote and ask yourself: “is it doing what I expected it to do, and does anything else look … weird?”
Tests alone aren’t enough to confirm that your code is doing what it’s supposed to do. You don’t know that until you’ve watched it bake in production, with real users on real infrastructure.
This kind of development — that includes production in fast feedback loops — is (somewhat counterintuitively) much faster, easier and simpler than relying on tests and slower deploy cycles. Once developers have tried working that way, they’re famously unwilling to go back to the slow, old way of doing things.
What excites me about AI is that when you’re developing with LLMs, you have to develop in production. The only way you can derive a set of tests is by first validating your code in production and working backwards. I think that writing software backed by LLMs will be as common a skill as writing software backed by MySQL or Postgres in a few years, and my hope is that this drags engineers kicking and screaming into a better way of life.
You’ve raised concerns about mounting technical debt due to the AI revolution. Could you elaborate on the types of technical debts AI can introduce and how Honeycomb helps in managing or mitigating these debts?
I’m concerned about both technical debt and, perhaps more importantly, organizational debt. One of the worst kinds of tech debt is when you have software that isn’t well understood by anyone. Which means that any time you have to extend or change that code, or debug or fix it, somebody has to do the hard work of learning it.
And if you put code into production that nobody understands, there’s a very good chance that it wasn’t written to be understandable. Good code is written to be easy to read and understand and extend. It uses conventions and patterns, it uses consistent naming and modularization, it strikes a balance between DRY and other considerations. The quality of code is inseparable from how easy it is for people to interact with it. If we just start tossing code into production because it compiles or passes tests, we’re creating a massive iceberg of future technical problems for ourselves.
If you’ve decided to ship code that nobody understands, Honeycomb can’t help with that. But if you do care about shipping clean, iterable software, instrumentation and observability are absolutely essential to that effort. Instrumentation is like documentation plus real-time state reporting. Instrumentation is the only way you can truly confirm that your software is doing what you expect it to do, and behaving the way your users expect it to behave.
How does Honeycomb utilize AI to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of engineering teams?
Our engineers use AI a lot internally, especially CoPilot. Our more junior engineers report using ChatGPT every day to answer questions and help them understand the software they’re building. Our more senior engineers say it’s great for generating software that would be very tedious or annoying to write, like when you have a giant YAML file to fill out. It’s also useful for generating snippets of code in languages you don’t usually use, or from API documentation. Like, you can generate some really great, usable examples of stuff using the AWS SDKs and APIs, since it was trained on repos that have real usage of that code.
However, any time you let AI generate your code, you have to step through it line by line to ensure it’s doing the right thing, because it absolutely will hallucinate garbage on the regular.
Could you provide examples of how AI-powered features like your query assistant or Slack integration enhance team collaboration?
Yeah, for sure. Our query assistant is a great example. Using query builders is complicated and hard, even for power users. If you have hundreds or thousands of dimensions in your telemetry, you can’t always remember offhand what the most valuable ones are called. And even power users forget the details of how to generate certain kinds of graphs.
So our query assistant lets you ask questions using natural language. Like, “what are the slowest endpoints?”, or “what happened after my last deploy?” and it generates a query and drops you into it. Most people find it difficult to compose a new query from scratch and easy to tweak an existing one, so it gives you a leg up.
Honeycomb promises faster resolution of incidents. Can you describe how the integration of logs, metrics, and traces into a unified data type aids in quicker debugging and problem resolution?
Everything is connected. You don’t have to guess. Instead of eyeballing that this dashboard looks like it’s the same shape as that dashboard, or guessing that this spike in your metrics must be the same as this spike in your logs based on time stamps….instead, the data is all connected. You don’t have to guess, you can just ask.
Data is made valuable by context. The last generation of tooling worked by stripping away all of the context at write time; once you’ve discarded the context, you can never get it back again.
Also: with logs and metrics, you have to know what you’re looking for before you can find it. That’s not true of modern observability. You don’t have to know anything, or search for anything.
When you’re storing this rich contextual data, you can do things with it that feel like magic. We have a tool called BubbleUp, where you can draw a bubble around anything you think is weird or might be interesting, and we compute all the dimensions inside the bubble vs outside the bubble, the baseline, and sort and diff them. So you’re like “this bubble is weird” and we immediately tell you, “it’s different in xyz ways”. SO much of debugging boils down to “here’s a thing I care about, but why do I care about it?” When you can immediately identify that it’s different because these requests are coming from Android devices, with this particular build ID, using this language pack, in this region, with this app id, with a large payload … by now you probably know exactly what is wrong and why.
It’s not just about the unified data, either — although that is a huge part of it. It’s also about how effortlessly we handle high cardinality data, like unique IDs, shopping cart IDs, app IDs, first/last names, etc. The last generation of tooling cannot handle rich data like that, which is kind of unbelievable when you think about it, because rich, high cardinality data is the most valuable and identifying data of all.
How does improving observability translate into better business outcomes?
This is one of the other big shifts from the past generation to the new generation of observability tooling. In the past, systems, application, and business data were all siloed away from each other into different tools. This is absurd — every interesting question you want to ask about modern systems has elements of all three.
Observability isn’t just about bugs, or downtime, or outages. It’s about ensuring that we’re working on the right things, that our users are having a great experience, that we are achieving the business outcomes we’re aiming for. It’s about building value, not just operating. If you can’t see where you’re going, you’re not able to move very swiftly and you can’t course correct very fast. The more visibility you have into what your users are doing with your code, the better and stronger an engineer you can be.
Where do you see the future of observability heading, especially concerning AI developments?
Observability is increasingly about enabling teams to hook up tight, fast feedback loops, so they can develop swiftly, with confidence, in production, and waste less time and energy.
It’s about connecting the dots between business outcomes and technological methods.
And it’s about ensuring that we understand the software we’re putting out into the world. As software and systems get ever more complex, and especially as AI is increasingly in the mix, it’s more important than ever that we hold ourselves accountable to a human standard of understanding and manageability.
From an observability perspective, we are going to see increasing levels of sophistication in the data pipeline — using machine learning and sophisticated sampling techniques to balance value vs cost, to keep as much detail as possible about outlier events and important events and store summaries of the rest as cheaply as possible.
AI vendors are making lots of overheated claims about how they can understand your software better than you can, or how they can process the data and tell your humans what actions to take. From everything I have seen, this is an expensive pipe dream. False positives are incredibly costly. There is no substitute for understanding your systems and your data. AI can help your engineers with this! But it cannot replace your engineers.
Thank you for the great interview, readers who wish to learn more should visit Honeycomb.
#acquisitions#Advice#ai#AI-powered#android#API#APIs#APM#app#apps#author#AWS#Best Of#bugs#Building#Business#change#Charity#chatGPT#code#Collaboration#complexity#Containers#course#CTO#dashboard#data#data pipeline#Database#databases
0 notes
Text
Global Windows IT Outage
In the early hours of this morning, major banks, media airlines and many more organisations were impacted by an IT outage. Whilst originally attributed to Microsoft, the cause appears to be a security tool “Crowdstrike”, causing Windows machines to crash and be unable to restart.
Torchbox and its operations are not impacted directly, as we do not use Windows. Heroku, our hosting partner, along with AWS and Cloudflare, are also not showing signs of impact. Some services used internally and by our applications are reporting being affected, however so far the impact is minimal and not visible.
We therefore don’t believe there’s a risk to the applications we host. However, we will be monitoring the situation closely to ensure continuity.
If you have any questions or concerns, contact your delivery manager. We will update this page if the situation develops.
0 notes
Text
Migrating to the Cloud: Best Practices and Strategies for Success
In the realm of technology, cloud computing stands out as one of the most transformative innovations of the 21st century. It has fundamentally altered how businesses operate, how data is managed, and how software and services are delivered. The essence of cloud computing lies in its ability to provide on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources, such as servers, storage, applications, and services, over the internet. This article explores the key aspects of cloud computing, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be defined as the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Instead of owning their own computing infrastructure or data centers, companies can rent access to anything from applications to storage from a cloud service provider.
Cloud computing services are typically divided into three broad categories:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This is the most basic category of cloud computing services. With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. PaaS is designed to make it easier for developers to quickly create web or mobile apps, without worrying about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure. Examples include Google App Engine and Heroku.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the Internet. Common examples are email, calendaring, and office tools (like Microsoft Office 365). SaaS provides a complete software solution that you purchase on a pay-as-you-go basis from a cloud service provider.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The rise of cloud computing has introduced numerous benefits that have revolutionized how organizations and individuals operate:
Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running on-site data centers—the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and cooling, the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It offers a pay-as-you-go model that aligns costs with actual usage.
Scalability: With cloud computing, you can easily scale up or down your IT resources as needed. For example, you can easily increase your computing capacity during peak seasons and scale down when the demand is lower. This flexibility is crucial for businesses with fluctuating demands.
Performance: Major cloud services run on a worldwide network of secure data centers, which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate data center, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
Speed and Agility: Most cloud computing services are provided self-service and on-demand, so even vast amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks. This gives businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning.
Global Scale: The benefits of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In cloud speak, that means delivering the right amount of IT resources—for example, more or less computing power, storage, bandwidth—right when it is needed and from the right geographic location.
Security: Many cloud providers offer a set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats.
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Despite its numerous advantages, cloud computing also presents several challenges that organizations must navigate:
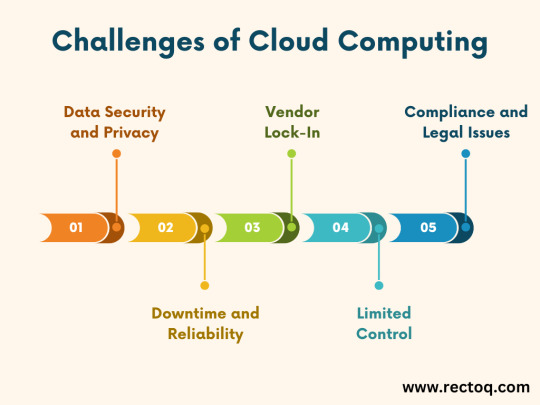
Data Security and Privacy: One of the primary concerns about cloud computing is data security and privacy. Storing data and critical applications in the cloud introduces new risks. Organizations must ensure their data is protected and that they comply with regulatory requirements.
Downtime and Reliability: Cloud service providers may experience outages and downtime. While many providers offer robust uptime guarantees, outages can still happen, affecting the availability of services.
Vendor Lock-In: Once an organization starts using a cloud service, it may find it difficult to move to another provider due to the complexities of migration and integration. This dependency on a single provider is known as vendor lock-in.
Limited Control: Because the cloud infrastructure is entirely owned and managed by the provider, businesses may have limited control over their operations and performance. This can be an issue for companies with specific compliance or regulatory needs.
Compliance and Legal Issues: Different countries have different laws regarding data storage and transfer. Organizations need to ensure that their use of cloud services complies with all applicable regulations.
Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing looks promising, with several emerging trends poised to drive further innovation and adoption:
Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to where it is generated rather than relying on a centralized data center. This trend is gaining traction as it reduces latency, improves performance, and enhances data security.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Cloud providers are increasingly integrating AI and ML capabilities into their services. This enables businesses to harness advanced analytics, automate processes, and derive insights from large datasets.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Organizations are adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to leverage the best features of different cloud providers and on-premises infrastructure. This approach offers greater flexibility, cost savings, and redundancy.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing is an execution model where the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation of machine resources. This allows developers to focus on writing code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Quantum Computing: While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize cloud computing by solving complex problems much faster than classical computers. Cloud providers are beginning to offer quantum computing services to researchers and developers.
Sustainability: As environmental concerns grow, cloud providers are investing in sustainable practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes using renewable energy sources and optimizing data center operations for energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has undeniably revolutionized the digital landscape, providing unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. As organizations continue to embrace this technology, it will drive further innovation and transformation across various industries. However, it is crucial to address the challenges associated with cloud computing to fully harness its potential. With ongoing advancements and emerging trends, the future of cloud computing promises to be dynamic, offering new opportunities and solutions for businesses and individuals alike.
Phone: +91 7975244680
Website: https://rectoq.com/
0 notes
Text
We might also put the site into "maintenance mode" while we move the site over from Heroku to DigitalOcean.
This would be of great benefit to us because we've used both platforms for years. Only Heroku has been getting progressively more difficult to manage and they've been less than great the last few months, like charging us twice for one service and then having to refund us... This has been going on for the past couple months at the least, so we're going to plan a time to move. For everyone's sake.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Depths of Full Stack Development: A Roadmap to Mastery
Introduction: Embarking on a Voyage of Discovery
It's thrilling and intimidating to start the journey to become a full stack developer. It's important to have reasonable expectations and recognise the commitment needed to succeed, even with the promise of mastering a wide range of technologies and frameworks. Your career in software development will be shaped by a longer learning journey, of which the completion of an online course is only the first step.
For those looking to master the art of Full Stack, enrolling in a reputable Full Stack Developer Training in Hyderabad can provide the essential skills and knowledge needed for navigating this dynamic landscape effectively.

Understanding the Learning Journey
Mastering full stack development requires more than just completing an online course; it demands a commitment to lifelong learning and continuous improvement. The journey may seem daunting at first, but with the right mindset and approach, you can conquer the challenges ahead and emerge as a proficient full stack developer.
Essential Components: Navigating the Building Blocks of Full Stack Proficiency
Front-end Fundamentals: Delve into the world of front-end development, where you'll learn to craft captivating user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These foundational skills form the bedrock of every successful full stack developer.
Back-end Essentials: Explore the back-end realm, where you'll discover the power of server-side languages such as Python, Ruby, or Node.js, and frameworks like Django, Ruby on Rails, or Express.js. Gain a deep understanding of database management and learn to wield SQL or NoSQL databases with precision.
Version Control Mastery: Seamlessly collaborate with fellow developers and track changes to your code with version control systems like Git. Unlock the full potential of platforms like GitHub or Bitbucket to streamline your development workflow and ensure code integrity.
Deployment Domination: Learn the art of deploying your applications to the web with confidence. From Heroku to AWS, explore the myriad deployment options available to full stack developers and discover the best practices for hosting your projects online. Here's where getting certified with the Top Full Stack Online Certification can help a lot.

Putting Theory into Practice: Embarking on Real-world Projects
Theory alone can only take you so far in the world of full stack development. To truly master the craft, you must apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios. Dive headfirst into hands-on projects that challenge your skills and push you to new heights of proficiency.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Embracing Lifelong Learning
The tech industry is a rapidly evolving landscape, with new technologies and frameworks emerging at breakneck speed. Stay ahead of the curve by immersing yourself in online tutorials, documentation, and community forums. Never stop learning, and you'll always be prepared for whatever challenges lie ahead.
Conclusion: Charting Your Course to Full Stack Proficiency
Becoming a proficient full stack developer is a journey of discovery, innovation, and continuous growth. By embracing the challenges, honing your skills, and staying true to your passion for learning, you'll navigate the ever-changing currents of full stack development with confidence and emerge as a master of your craft. So hoist the sails, set your course, and embark on the adventure of a lifetime in the world of full stack development.
#full stack course#full stack developer#full stack software developer#full stack training#full stack web development#full stack#full stack online training
0 notes
Text
Salesforce Developer: A Guide To Become One

Salesforce is a popular customer relationship management platform. Their software helps organizations expand by employing cloud-based apps for sales, marketing, and customer care to better understand their consumers’ demands.
But as no two businesses are alike, their Salesforce requirements will vary as well. It’s a good idea to have a Salesforce developer on hand when this occurs — someone who can modify the platform and provide new business solutions.
You should continue reading if that sounds like something you’d like to do or if you are now using Salesforce but would like to upskill.
Who is a salesforce developer?
A Salesforce developer is a programmer. They use the Salesforce CRM platform or other Salesforce cloud technologies to create unique business apps for clients. To tackle challenging issues, they combine Salesforce’s no-code solutions with code.
Salesforce developers create apps using frameworks like Lightning Component and tools like Apex and Visualforce. Additionally, they leverage APIs to interface with MuleSoft, modify common programs, and build web apps on Heroku.
What does a salesforce developer do?
A Salesforce developer is someone who possesses experience with the Salesforce platform and understands its functions. They complete the Salesforce Developer Training & Certification Course. Further, they attend the Salesforce Developer Certification Training.
The customer hires a developer to customize Salesforce to their specifications. Alternatively, it can be an internal coder who just so happens to be proficient with Salesforce. These developers create apps using frameworks like Lightning Component and tools like Apex and Visualforce.
How To Become A Salesforce Developer?
1. Gain experience using Salesforce
Acquiring experience on this platform can improve your abilities and show potential employers that you are prepared for the workforce. Get familiar with Salesforce by:
Enrolling in Salesforce Developer Course, such as the Salesforce Sales Operations Professional Certification
Obtaining an internship or entry-level position at Salesforce
Getting involved in a Salesforce online community
2. Pass the Salesforce Certified Administrator exam
You must pass the certification exam to be eligible for the majority of Salesforce administrator roles. This test assesses your abilities in:
Setup and configuration (20%)
Using the Lightning App Builder (20%) and Object Manager
Applications for sales and marketing (12%)
Applications for services and support (11%)
Collaboration and productivity (7%)
Analytics and data management (14%)
Automation of processes and workflow (16%)
3. Apply for salesforce jobs
Next, as you gain experience and earn your Salesforce certification as an administrator, you should start looking for and applying for positions. To focus your efforts, start by determining your desired lifestyle and professional path.
Next, search Indeed and Glassdoor employment boards for available positions. Examine each job description for a Salesforce administrator in detail to see if the duties, responsibilities, credentials needed, and pay scale fit your professional objectives.
To approach companies with confidence, make sure your resume is current and accurately reflects your experience, credentials, and talents. You should also dedicate some time to practicing your interviewing techniques.
Final words
If you dream of becoming a Salesforce certified developer, follow our guide on how to become a Salesforce developer!
0 notes