#textiles
Text
Man, there is a huge bias in the way that hobby fibercrafters approach and think about textiles—and I say that as a hobby fibercrafter myself! See, weaving has a high barrier to entry relative to knitting, crochet, spinning—even embroidery or sewing, these days, as the sewing machine automated much of the tedium of the craft. All of those crafts require a lot less in terms of startup costs to the hobby crafter than the machinery of a loom does.
But... look, if you want to understand mass produced textiles or textiles in any historical context, you have to understand weaving. If you want to understand how most of the cloth that people wear is made, you have to understand weaving, because weaving is the oldest art for mass producing cloth that can then be turned into garments.
Spinning is also very important, of course. Spinning is how you get the thread that you can turn into cloth any number of ways. Historically speaking, though, the most common way that thread or yarn becomes cloth is inarguably weaving. More to the point, weaving is also a historical center of industry and labor organizing. Ironically enough for the argument about how no one asked a woman, the industrialization of weaving is actually an interesting early case example of men organizing to push women out of a newly profitable position.
Besides that, knitting and crocheting in particular are incredibly modern crafts. Most modern knitting as we would understand the craft is shaped by the inventions of Elizabeth Zimmerman, and even things like the circular knitting needle date back only to the past century. Historically speaking, the great innovation of knitting as a tool for fiber craft is the ability to construct garments for small, odd shapes that can stretch and grip: stockings, gloves, underwear. Even that great innovation, the knit sweater, is an artifact of the 1850s—and the familiar cable knit sweaters of the Aran Isles are even newer than that. Crochet is even younger: the entire craft originated in the 1820s as far as anyone can document.
None of that is any shade on anyone. Like I said, I knit; that's the locus of my personal interest in textiles. I just think that textile history is neat, but if you're going to make big pronouncements about the historical development of textiles, it's important to think about what changed about the technology of textile production in the most common ways of turning raw fiber into cloth—and you cannot stop at the level of understanding how to make thread or yarn, because the properties of the cloth are always going to be an artifact of the construction of the cloth.
That's technology, baby! It's literally weavecraft. But it's not obvious that weaving is missing from the bounds of a person's experience with textile manipulation until and unless they're trying to understand and work with a wide range of fabric types—and when you can quite reasonably go from raw fiber to a finished garment using modern popular craft techniques that don't rely on anything that appears difficult for a medieval craftsman to make, it's easy to forget the role of weaving in the creation of cloth as a finished product.
I suppose the point I am making is: think deeply about what your own areas of expertise are not bringing to your understanding of history. It's easier to miss things you'd think.
222 notes
·
View notes
Text
The one bizarre thing to me about textiles is that warp-weighted weaving is at least 6500 years old, but our oldest knitted artifacts are only ~1000 years old, and crochet 200 years old. Even though you need less equipment to knit (two sticks) or crochet (one hook) compared to warp-weighted weaving (frame, loom weights, batting, heddles). Why the big gaps between these inventions? And why did each one appear and spread when it did?
#seriously if any textile historians have answers i'd love to find out!#knitting isn't even hard to derive from weaving. just turn the warp on its side and use a hook to pull up a column of loops#repeat a few times and boom you have knit fabric#weaving#knitting#crochet#textiles#jlrrt speaks
96 notes
·
View notes
Text

In Ernesto Neto’s Largest Installation to Date, the World Is a Crocheted Ship Moving to a Single Rhythm
114 notes
·
View notes
Text

La Mode Illustree 1890
#historical fashion#historical#fashion#history#historical clothing#historical dress#long dress#textiles#victorian#victorian era#fashion plate#histocial magazine#fashion magazine#magazine#1890s dress#1890s art#1890s fashion#1800s dress#1800s art#1800s fashion#19th century fashion#19th century#old fashioned#high fashion#dress#dresses#victorian clothing#victorian dress#victorian history#the gilded age
57 notes
·
View notes
Text


i have so many mini-bundles of hand dyed and blended wool from various dye and carding experiments and i'm trying to spin them up to make more room in my stash. these yarns are roughly akin to fingering weight. i like spinning small amounts of yarn at a time unless i need a lot of a specific fibre for a project, if i spin the same colour for too long i get bored (< has adhd)
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
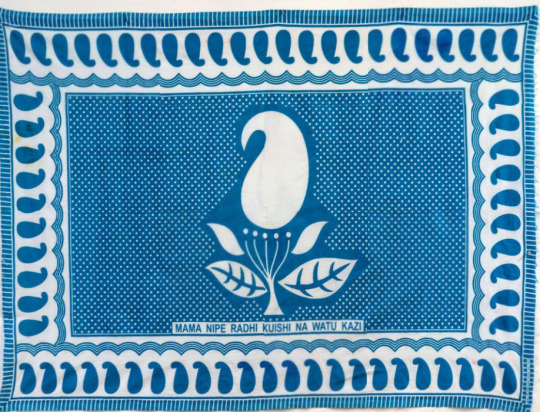

“MAMA NIPE RADHI KUISHI NA WATU KAZI”
English Translation: “Mother give me pleasure, living with people is hard”
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

Pieced Quilt (Friendship Sampler Strips) 1843 by Lizzie C. Jones.
Chintzes, calicoes and white cotton.
SAAM.
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
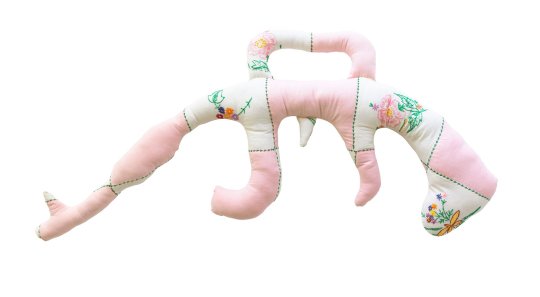

Natalie Baxter, Warm Gun | Flag Quilt
#natalie baxter#soft sculpture#american gothic#textile art#protest art#textile design#appalachain gothic#southern gothic#angelcore#pastel grunge#soft gothic#quilting#quilt#floral#flag#⭒* ·˚ ☾ ⊹.#textiles
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
My finished toile
After great efforts I was finally able to complete my practice garment. I was able to spot mistakes and errors and have them corrected so that I will not be making them on my final piece. I am really happy with the way it turned out and cannot wait to see the way the dress is elevated when it is created in colour.
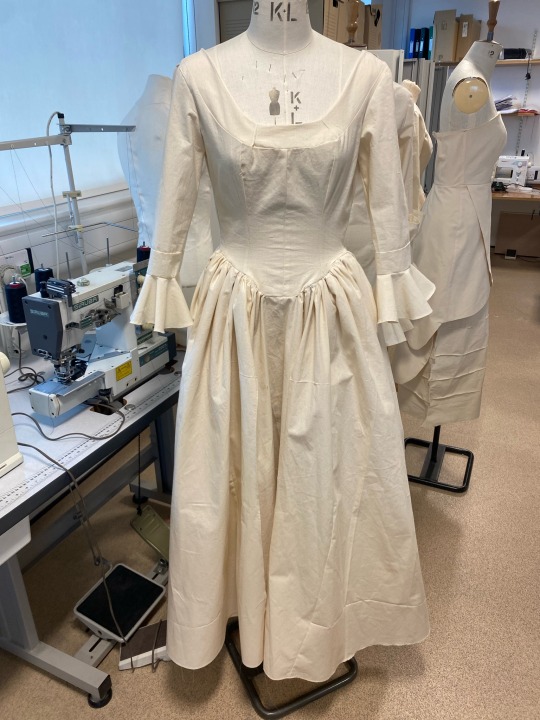
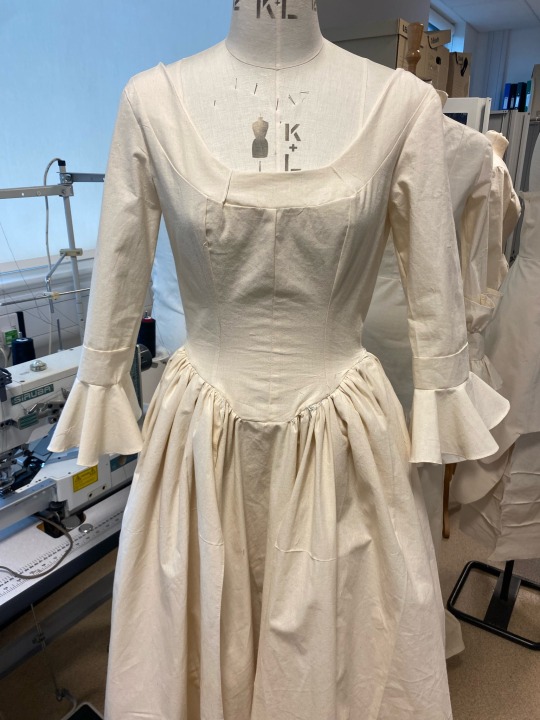
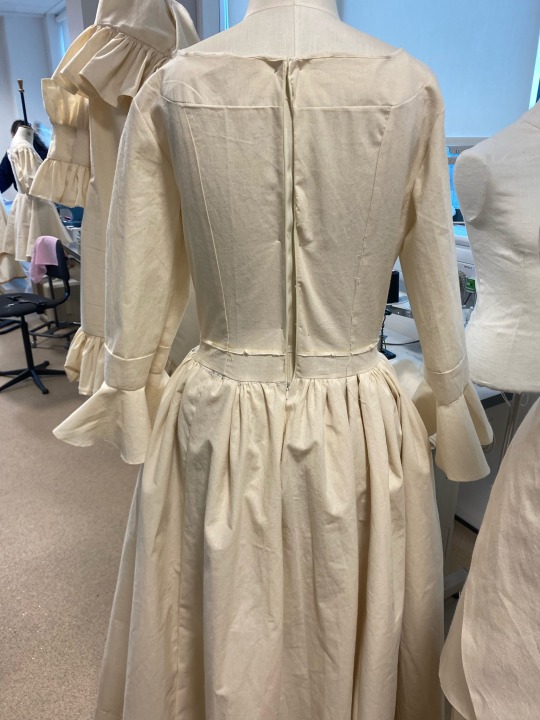





#fashion#textiles#fashion illustration#fashion marketing#history#the duchess#fashion history#development#cannon hall#print design
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

H variation quilt: Milky Way by Nettie Young, 1971
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
LEEAH JOO
Korean-American painter Leeah Joo’s work is inspired by the enigmatic and hidden. In her illusionist paintings, she teases our predisposition to probe and uncover. Intriguing parcels in her Pojagi series are enveloped by a lavish, traditional Korean wrapping cloth and beckon to be unpacked. The richly detailed paintings of lacey drapery in her Parrhasius series present an open-ended narrative, inviting us to question what lies behind the curtain. Joo studied painting and art history at Indiana University in Bloomington and received her MFA in painting from the Yale School of Art, Her paintings have been exhibited widely in the U.S. and South Korea. She is the recipient of notable awards from the Pollock-Krasner Foundation, George Sugarman Foundation, Connecticut Commission on Arts and the Puffin Foundation. Currently, Leeah Joo lives and paints in Middlebury, Connecticut and teaches at Southern CT State University and Paier College.
70K notes
·
View notes
Text
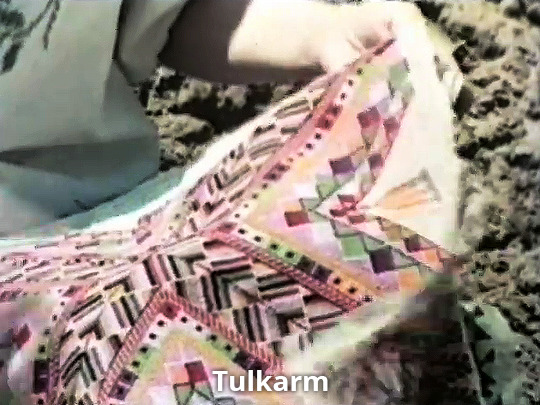
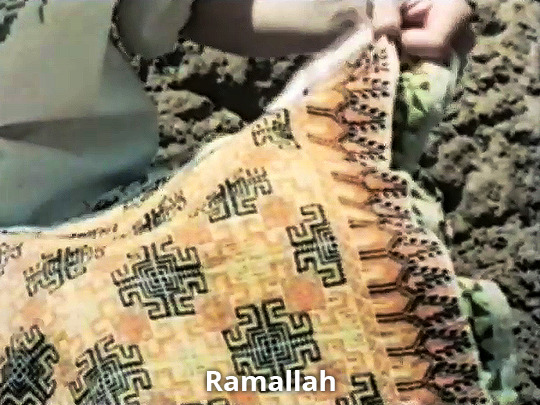








The Palestinian (1977)
#the palestinian 1977#vanessa redgrave#gaza#ramallah#tulkarm#ayn ghazal#jerusalem#bethlehem#haifa#jaffa#documentary#screencaps#post#history#tatreez#artistry#jerusalem and tulkarem my favess#textiles#art
28K notes
·
View notes
Text
Today I am thinking about weaving.

I can knit and crochet, but those crafts didn't exist in Roman times. Any historically accurate Roman cloth must be woven. So when a little potholder loom jumped into my shopping basket for 50 cents, it felt like a sign I should learn.
One potholder that was 50% yarn and 50% weird gaps later, I looked up a tutorial, and realized why the damn thing was 50 cents. I needed a better, more adaptable loom. And, because I am a cheapskate and slightly loony, I decided to make one instead of buying it.
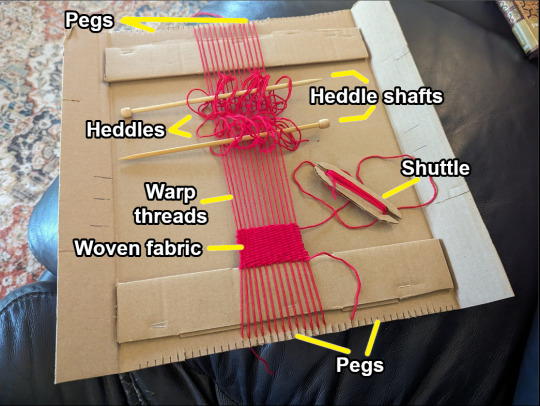
So, how does this thing work?
First, you string the warp threads up and down, around the pegs. Here, I made a zigzag shape. Then, you use a needle or shuttle to weave more yarn over and under the warp, horizontally, back and forth. This produces woven fabric.

Some looms weave from the top, some from the bottom. This Greek urn shows two weavers working from the top. The left weaver uses a rod to compact the woven fabric upward, keeping it even and sturdy. The right weaver is passing an oval-shaped shuttle through the warp threads to form another row.

Most Roman looms would have looked like this, with the finished cloth at the top. Unlike my looms, these are warp-weighted. That means you keep the warp yarns taut by hanging weights at the bottom, rather than through a bottom row of pegs.
Warp-weighted looms also have a big advantage over my little potholder loom: you can easily create multiple sheds.
A "shed" is a temporary gap between lifted strands and non-lifted strands. Instead of having to go over and under each strand individually, you raise the entire shed, then pull the shuttle or needle straight through. This saves lots of time! Then, to weave the next row, you close the shed, lift up a different set of threads to create a new shed, and send the shuttle/needle through the other direction.

On a warp-weighted loom, the sheds are opened by loops called heddles (H), which are attached to a heddle rod (G). When the rod is down, shed (1) is open (middle diagram). When you pull the rod up, shed (1) closes and shed (2) opens instead (right diagram). Most warp-weighted looms also have a pair of forks you can rest the heddle rod on, to free your hands.
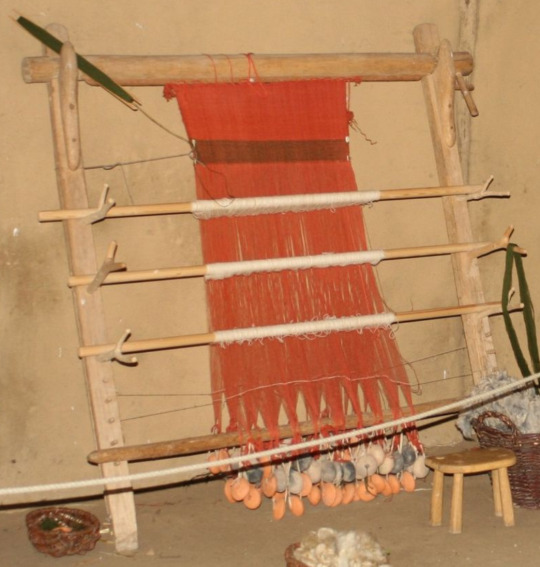

Here, there are three heddle rods and sets of forks, the heddles are white, and the warp thread is red. This gives you four different sheds, and the potential to weave very complex patterns indeed. Not bad for a device invented over 6500 years ago!
I liked the multiple heddle-rod design so much, I tried incorporating it into my DIY loom, too. I've tested both yarn and paperclips as heddles:

I actually got both sheds and heddle-rods working, too. Which is pretty cool for a lap loom - every other lap loom I found only has one shed, so you have to go over-under the individual threads on alternate rows.* More time-consuming. However, the sheds here are narrow, and I'll need a smaller and smoother shuttle to pass through them smoothly. This wouldn't be an issue on a warp-weighted loom, where the warp hangs freely downward, and can move more flexibly with the heddles.
Anyway. I may get a "real" loom at some point, but I wanted to build one first, and I think it gave me more appreciation for just how resourceful ancient weavers were. They created technology, clothing, and artwork out of very basic materials, and civilization depended on these skills.
Now, I need to go finish the...whatever the hell it will be. Big thanks to Wikipedia and to the lovely Youtubers who make this craft easier to learn. I think it'll be a lot of fun.
(*Edit - found out a rotating heddle bar can make two sheds on a lap loom! Exciting!!)
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Listen I'm a little drunk but... yarn crafts are so important. Textile arts are the backbone of society. All of us take our clothing and accessories and upholstery for granted and it's honestly shocking
I used to buy affordable t-shirts and they were comfy and nice, now I buy them in the same price range and they're sandpaper. They don't wick away moisture and the print comes undone after two washes. I buy denim and the crotch falls apart in months. I read about how modern Singer sewing machines are disappointing and then look at the delicate machining and the beautiful finishes on my 1857 machine and wonder if this is progress?!
Reblog if you're desperate for clothing that doesn't feel like sandpaper or if you like machines that go thunk instead of going obsolete in two years
22K notes
·
View notes
Text


1750-1760
#historical fashion#fashion#historical#history#historical clothing#historical dress#long dress#textiles#high fashion#rococo#old fashioned#1760s fashion#1750s#1750s fashion#1700s fashion#1700s#18th century fashion#18th century#dress#gown#ball gown#historical costuming
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
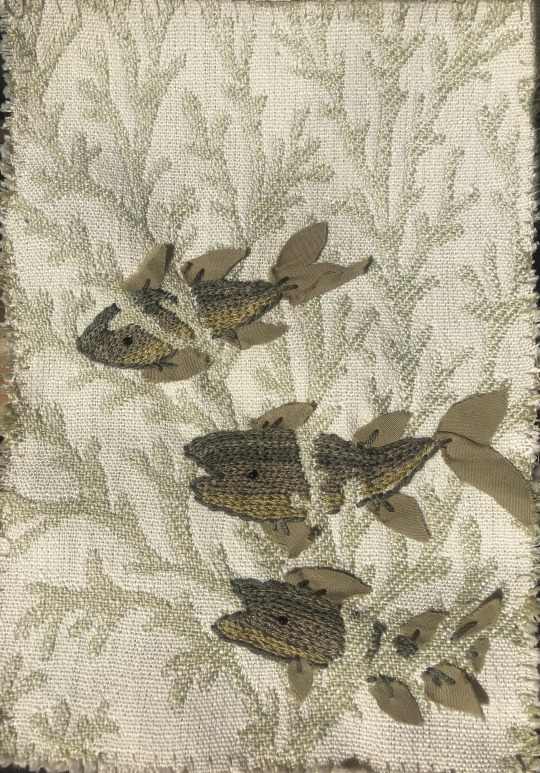

ID: three fish embroidered on an upholstery sample with a design that looks like coral. the fish are embroidered so they appear to be swimming in between the coral. the colors are shades of olive green and beige.
14K notes
·
View notes