#textiles books
Text












Woven Histories
Textiles and Modern Abstraction
Production by Brad Ireland and Christina Wiginton, Editing by Magda Nakassis,
National Gallery of Art, Washington copublished by The University of Chicago Press, 2023, 284 pages, ISBN 978-0-226-82729-2
euro 65,00
email if you want to buy [email protected]
Exhibition dates : Los Angeles County Museum Art 2023, Washington Nat.Gall.Art 2024, Ottawa Nat.Gall.Canada 2024,New York MoMA 2025
Richly illustrated volume exploring the inseparable histories of modernist abstraction and twentieth-century textiles.
Published on the occasion of an exhibition curated by Lynne Cooke, Woven Histories offers a fresh and authoritative look at textiles—particularly weaving—as a major force in the evolution of abstraction. This richly illustrated volume features more than fifty creators whose work crosses divisions and hierarchies formerly segregating the fine arts from the applied arts and handicrafts.
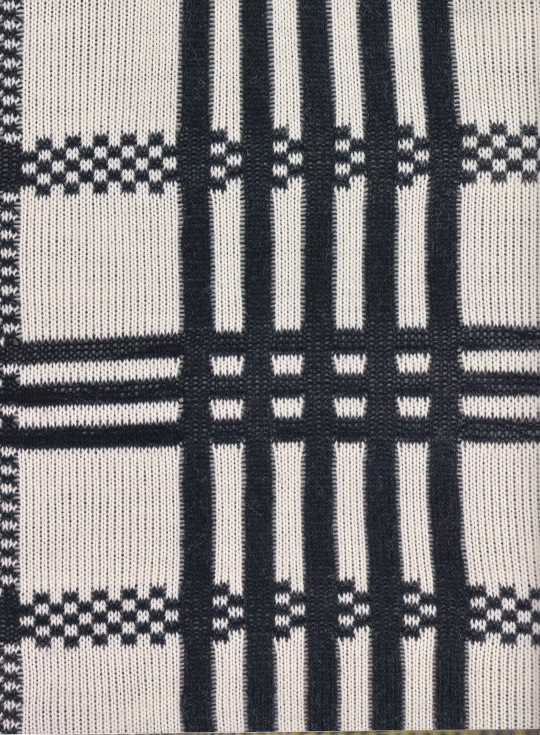
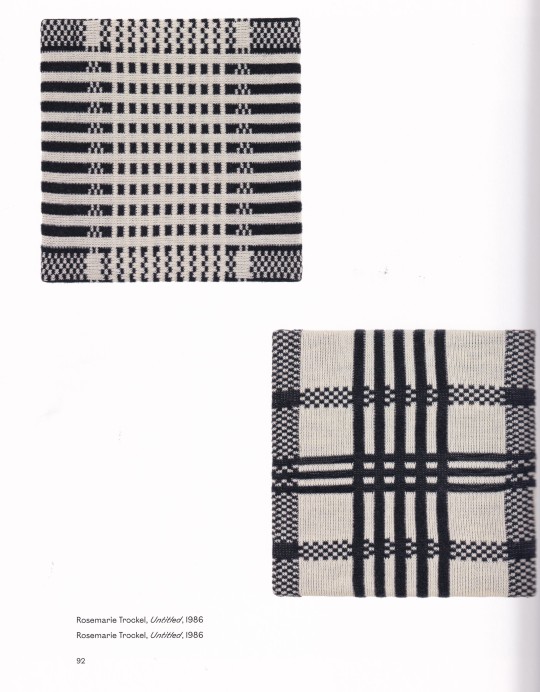
Woven Histories begins in the early twentieth century, rooting the abstract art of Sophie Taeuber-Arp in the applied arts and handicrafts, then features the interdisciplinary practices of Anni Albers, Sonia Delaunay, Liubov Popova, Varvara Stepanova, and others who sought to effect social change through fabrics for furnishings and apparel. Over the century, the intersection of textiles and abstraction engaged artists from Ed Rossbach, Kay Sekimachi, Ruth Asawa, Lenore Tawney, and Sheila Hicks to Rosemarie Trockel, Ellen Lesperance, Jeffrey Gibson, Igshaan Adams, and Liz Collins, whose textile-based works continue to shape this discourse. Including essays by distinguished art historians as well as reflections from contemporary artists, this ambitious project traces the intertwined histories of textiles and abstraction as vehicles through which artists probe urgent issues of our time.
24/12/23
#Woven Histories#textiles#modern abstraction#Anni Albers#Sonia Delaunay#Popova#Stepanova#Lenore Tawney#Sheila Hicks#textiles books#fashion books#fashionbooksmilano
58 notes
·
View notes
Text









Rachid Koraïchi 7 Variations autour de l'indigo
René Guitton, Danièle Giraudy
Photographies Jean Bernard, Rachid Koraïchi, Jean Pierre Linuésa
Éditions Alors Du Temple/Musées de Marseille, 2003, 48 pages, 21x27,5cm, ISBN 978291793248
euro 40,00
email if you want to buy : [email protected]
Exposition du 28 janvier au mars 2003 Galeries de la Vieille Charité, Musées de Marseille
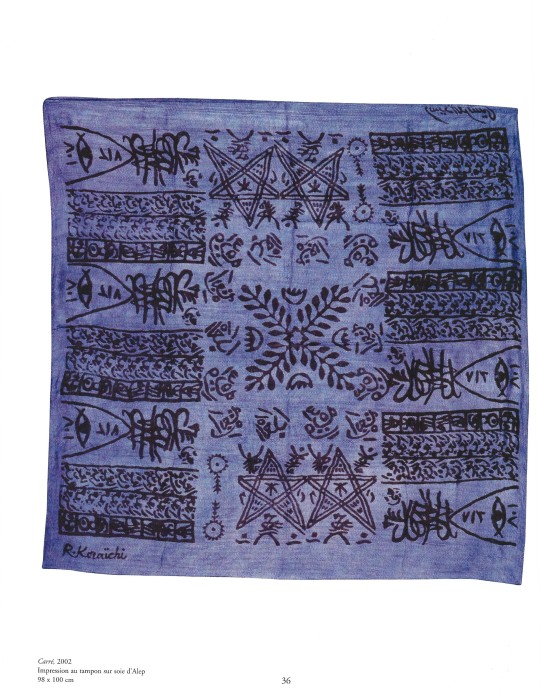
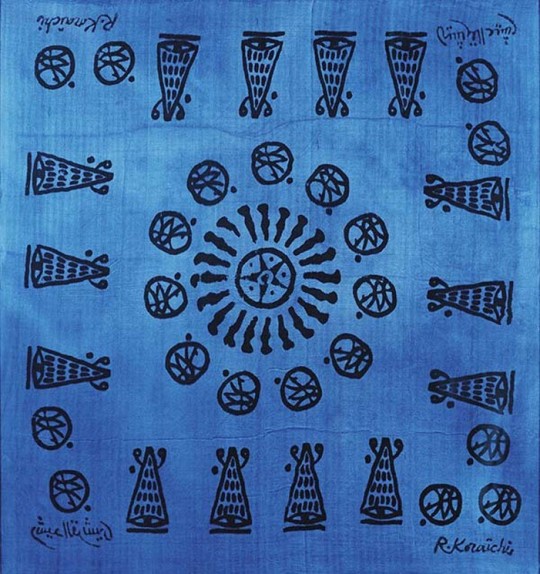
Associant les techniques ancestrales des tampons de bois en usage à Alep (Syrie) et la couleur traditionnelle des indigotiers marseillais, R. Koraïchi a créé de nouvelles étoffes : aujourd'hui exposées sous forme de bannières ou de carrés, elles se déclinent autour du chiffre 7 et de sa mystique. L'artiste méditait. Il était venu chercher l'inspiration dans cette cité vieille de plusieurs millénaires. Alep au nord de la Syrie. Comme les couleurs voyagent, il voulait retrouver des traces de bleu sur cette route de l'Inde d'où venait l'indigo. Car en Alep, au fil des siècles, cette teinture avait été l'objet de nombreuses études dont certains secrets furent peu à peu révélés: indigo mêlé d'écorce de grenade avec addition d'eau de dattes ou de suc de raisin noir broyé ou de figues piétinées. Ces macérations étranges conféraient à l'indigo d'Alep une haute réputation dans toute la Méditerranée, Rachid Koraïchi souhaitait aussi acquérir de la soie, chiner de ces tampons anciens que les imprimeurs de tissu utilisaient encore au début du XXe siècle. Il les mêlerait aux siens qu'il allait créer ici, inspiré, comme nulle part ailleurs, par les étoffes imprimées. L'ambassade de France, à Damas, et les responsables des services culturels, sensibles au projet à ce point prometteur lui accordèrent une aide chaleureuse et il fut hébergé en une demeure, vestige du Mandat français, toute proche de la citadelle. L'artiste allait y travailler en paix et remonter la mémoire de l'indigo et des routes de la soie.
23/09/23
#Rachid Koraïchi#indigo#art exhibition catalogue#Marseille 2003#tampons de bois#routes de la soie#textiles books#fashionbooksmilano
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo
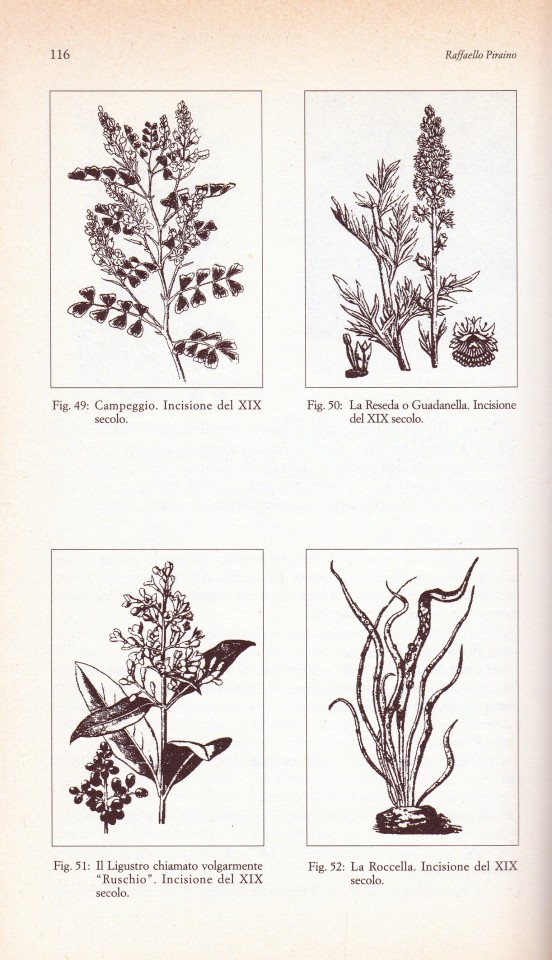




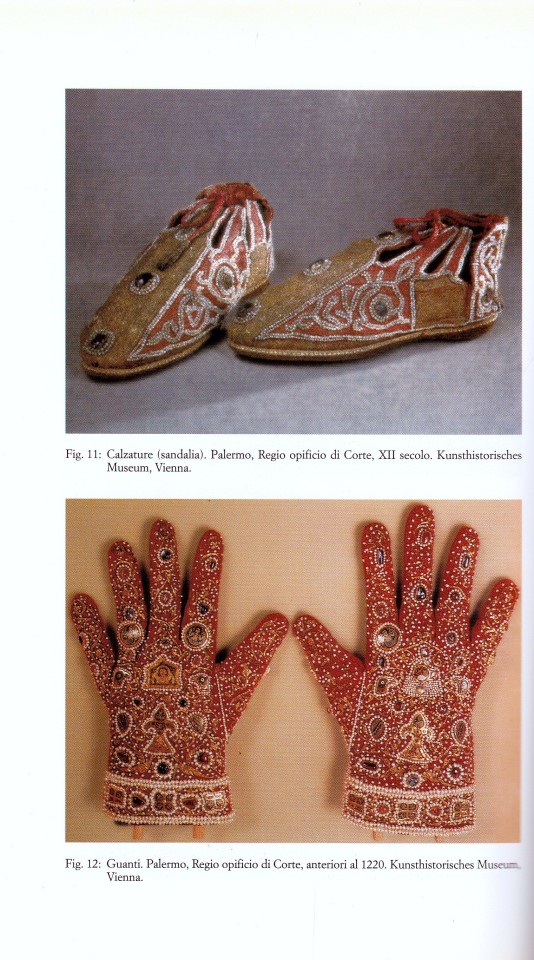





Il tessuto in Sicilia
Raffaello Piraino, Foto di Fulvio Abate
L’Epos, Palermo 1998, Collana Sumptuaria,140 pagine, 15,24 cm, ISBN 9788883020940
euro 52,00 n/a
email if you want to buy [email protected]
Raffaello Piraino tratta in questo volume dell’arte e della tecnica tessile in Sicilia a partire dalla colonizzazione greca e via via, attraverso i secoli, sino ai giorni d’oggi, soffermandosi su quei momenti in cui ha raggiunto gli apici della qualità e della competitività con gli altri paesi del Mediterraneo.

17/04/23
orders to: [email protected]
ordini a: [email protected]
twitter: @fashionbooksmi
instagram: fashionbooksmilano, designbooksmilano tumblr: fashionbooksmilano, designbooksmilano
#tessuto Sicilia#stoffe#industria tessile#Raffaello Piraino#Fulvio Abate#textiles books#rare books#fashion books#fashionbooksmilano
9 notes
·
View notes
Text







Unknown, Dyer's textile pattern book
mid 19th century
Part of RISD Museum (Rhode Island School of Design)
Woodcut on paper; Cotton plain weave, resist printed
30.8 x 23.5 x 2.5 cm (12 1/8 x 9 1/4 x 1 inches)
#unknown#set#textiles#pattern#pattern design#books#japanese art#woodblock print#color woodblock#japanese#woodcut
644 notes
·
View notes
Text
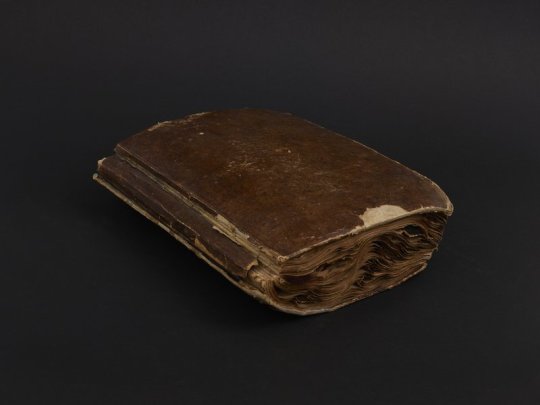
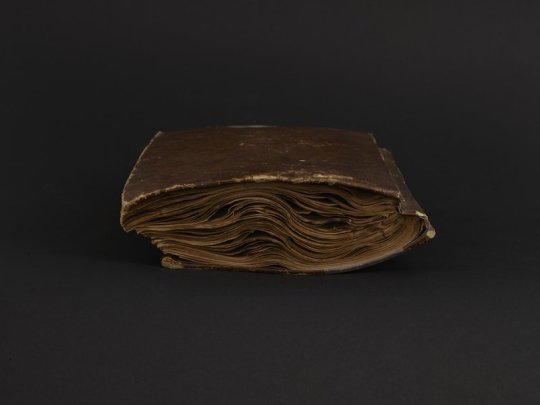




Italian Dyer's Notebook
Autograph manuscript, circa 1856-1866
This warped and worn nineteenth-century Italian manuscript appears to be a working manual and color inventory of a wool dyer in mid-nineteenth-century Italy. The handwritten entries are dated between 1856 and 1866, suggesting that the notebook was used and added to over a period of time. The work includes more than 500 numbered and itemized recipes for dyes. Recipes are illustrated with more than 800 wool and fabric samples adhered to the pages. The samples range in colors from shades of brown to vivid fuchsia, turquoise, and mustard. The samples include fabrics of wool, felt, and cotton, as well as raw wool and coils of yarn. Ingredients listed include mud, urine, arsenic, and vitriol. Pages 192-219 contain longer descriptions of dying processes, one attributed to Giacomo Udinese and another to Cesare Bizzi.
Check it out on our digital collections site.
#colors#colors in textiles#colorfastness#dyes#dyes and dyeing#textiles#wool#italian manuscripts#manuscripts#rare books#old books#rare book#dye samples#19th century#othmeralia
526 notes
·
View notes
Text

From: Maria Lai, Libro dei telai, (thread and ink on paper, twenty pages), 1979 [Private Collection. © Archivio Maria Lai, Lanusei (NU)]
574 notes
·
View notes
Text
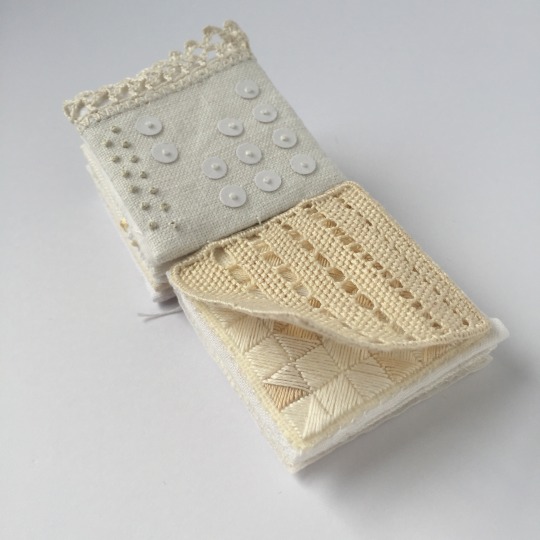
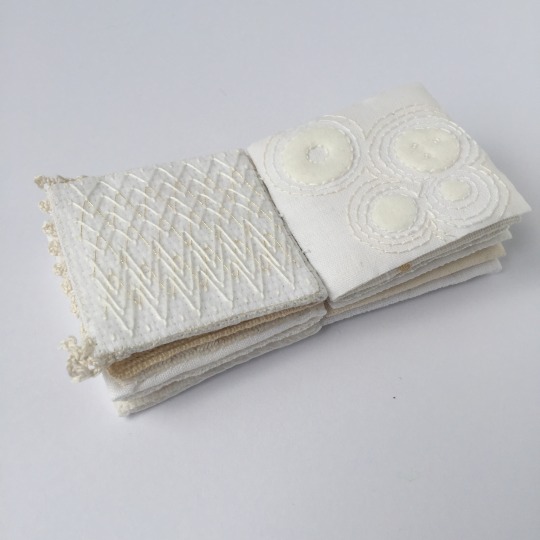







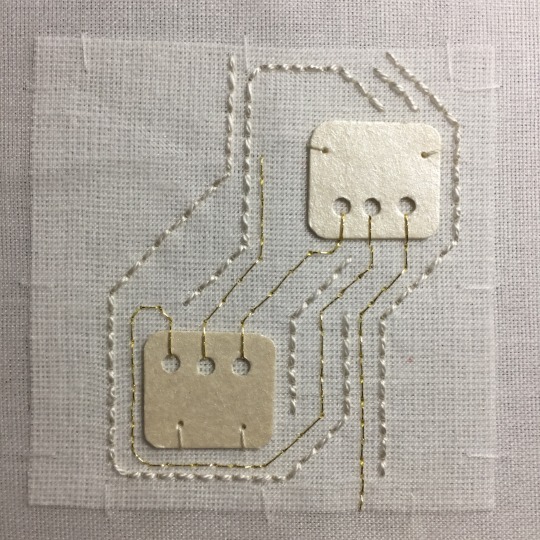

A tiny stitched book.
581 notes
·
View notes
Text

Maison Martin Margiela fall/winter 1993 ph. frédéric aufray
pregnant Paula Girardi wearing reverse-float jacquard sweater, which evoked the back of a tapestry. Her round belly stretched the knit of the sweater emphasizing its structure.
#maison martin margiela#maison margiela archive#fw93#1993#textile#fashion#book#photography#frederic aufray#my scan
304 notes
·
View notes
Text
I keep thinking everyone knows the exact same information as me, but since I'm about to make more posts about textiles and clothing, as I'm reading the book on them, I'm going to write down some basic information, just in case it's not very common, because a lot of this I only gathered recently. If I get something wrong please correct me in a kind way!
So where does the clothing come from, and how do we make it? During most of the history, textiles were made by women, from natural materials; flax, wool, cotton, silk, jute. Recently we started using more synthetic materials, like acrylic, polyester, nylon, spandex. If you want to make clothing from the natural materials, like wool or cotton, they first need to be processed, cleaned and combed, then spun into yarn, or thread. Spinning is the process where women manage to pull a thin part of the material and spin the fibres into one consistent, firm thread. It's super impressive to watch them do it and I have no idea how they manage to make it consistent, I've not yet tried to do it myself.
Once the thread is done, it can be made into a textile by knitting, crochet, or weaving. There are also other more complex, decorative methods, like tatting or lacing.
For knitting, you need two needles, or a special circular needle, or, there are also knitting machines, which you can use to make woolen fabric. For weaving, you need a loom. For crochet, you need a crochet hook. While knitting and weaving can be done by a machine, crochet can only be done by hand. Woven fabrics are firm, sturdy, durable, and not stretchy, while knit fabric is the most stretchy and soft. I'm not sure about crochet since I only have one crochet garment, but mine is very sturdy!
All of these methods were historically done by women; families were able to grow flax plants close to their homes, and women would then create linens, woven textiles made from processed flax, which was used to make sheets and clothing. Linen was specifically useful in keeping people clean, since it's very good at absorbing moisture. Used as an under-garment, it was capable of absorbing sweat, and protecting the outer layers, which were not washed. Experiments have shown that frequently changing into clean linen was more effective at keeping clean than showering and then putting on the same clothing back on.
Women's ability to create clothing was sadly exploited, and women were even banned to sell it commercially, or from competing at the commercial market, but their husbands were allowed to profit off of their craft.
In the USA, cotton was the most produced material, however for this too people were enslaved and exploited; cotton took human labour to grow, harvest and process, it also required a lot of water, and caused destruction of environment, because of the chemicals used in it's growth, and the unsustainability of monocrops.
Creating a piece of clothing out of textiles, or sewing, is a process that still cannot be completely automated; while you can use a sewing machine, you cannot make a machine that would produce a whole garment out of textiles. No mass-produced piece of clothing was sewn by a machine, it always has to be made by a human being. This is why a lot of the sewing labour is currently outsourced to third-world countries and companies use modern slavery in order to create fast fashion; there is no machine that can do it, so by the rules of capitalism, the companies are trying to get that labour as cheap as possible, often at the cost of human lives.
We didn't use to have as many garments as we do today, in the 18th century people would have two outfits, one for normal days of the week, and one for Sunday. The clothing they owned was usually made to fit them exactly, either by a female member of the family, or a seamstress, and these garments were made to last them for decades. As clothing became cheaper to buy than to make at home, and more of it became mass-produced, people started acquiring more of it, but also using it for lesser period of time. This would eventually grow into a bigger problem, due to the amount of chemicals and labour used to grow, process, dye and sew the garments, and the amount of waste we were starting to accumulate.
Introduction of synthetic materials, like acrylic, made the yarn and the textiles much cheaper, however it lacks the important properties natural materials have. Do you ever notice how synthetic garments sometimes continue smelling bad even after you wash them? That is because they'll absorb sweat, but become hydrophobic when wet, meaning they will take in your sweat, but refuse to let it go once they're in the water. This means that the longer you have them, the worst their stink becomes. This, of course, can be hidden by the generous use of scented fabric softener, but it won't exactly make the garment clean. This information I've learned recently, but it helped me identify what were the most synthetic pieces of clothing I had. Acrylic clothing had also proven to shed 1.5 more microplastics than any other polyester when put into the washing machine.
Having our clothing grown, processed, spun, woven/knit, and then sewn far out of sight, it's possible to lose the sight of where it came from, or how it's made. Only by trying to do it yourself, or learning closely about the process can one learn to appreciate what a monumental task it is, to create fabric, or a garment. Other than the synthetic textiles, of which I still know very little of, all of the natural clothing is a product of plants and animals, it takes land, farming, agriculture and water to grow the plants, raise the animals, and then labour to process and spin the fibres. It's also something people used to do in their gardens, inside of their homes, something that was normal for women to do, and to trade for anything else they needed, saving them from having to work for wages. Women making fabric was always to the benefit of everyone around them, while m*n taking over the industry and doing it commercially, ultimately brought slave labour to a lot of people, cheap and low quality garments to the select few, and money to the hands of the exploiters.
Being curious about clothing and what becomes of it, is a big benefit to the environment and the future of the earth! Knowing what the textile industry is doing, and how does it affect the planet, can be a great motivator to try and sew, or upcycle and mend clothing, or create garments. It's presented to us as something women were forced to do in the past, and it's connected to 'feminine hobbies', but in actuality, it is power to create something humans cannot do without. Women in the past used it's power too, whenever they could. And we are the only ones who ever used this power for good.
#textiles#clothing#linen#women's history#herstory#radical feminism#sewing#weaving#crochet#synthetic fiber#random information on clothing i've gathered#i feel much smarter so i wanna share!#if anyone knows more and wants to share please add#my sources are the book Worn#and dozens of youtube videos on textiles I've watched recently
139 notes
·
View notes
Text
i LOVE the teens who held the door open for us and took selfies in front of the five nights at freddies poster before the showing of Coraline tonight, a film i saw in theaters the first time too. time marches ever onwards. did you know coraline had "stunt wigs" including some with gears to raise up the hairs for bounce effects
#i was sooo weird about coraline when i was 13. and i was weird about the book when i was 10#loved seeing those textiles on the big screen !
248 notes
·
View notes
Text



Made a small batch and really love how tactile these needle booksies are. Just want to hold them forever.
#textile art#froge#frog#ferntales#etsy#australia#cuddle#tactile#cottagecore#needlebook#book#folk art#art#naive art
217 notes
·
View notes
Text
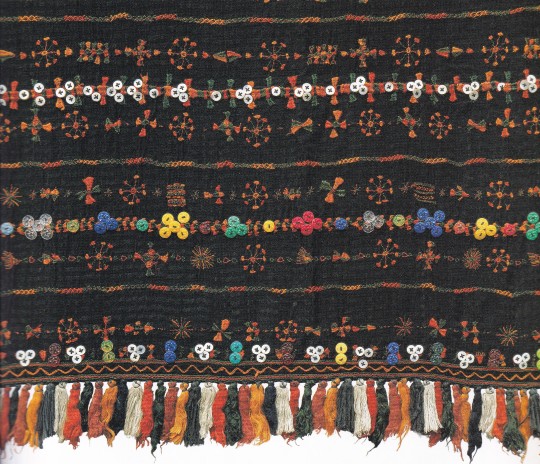













Embroidered Textiles
Sheila Paine
Thames & Hudson, London 2010, 240 pages, 24x28cm, First paperback edition, ISBN978-0-500-28858-0
euro 40,00
email if you want to buy [email protected]
Traditional patterns from five continents with a worldwide guide to identification
The art of embroidery has been practised for thousands of years. In the West, traditions have been at the mercy of trade and fashion, but in much of the rest of the world, embroidery continues to be rooted in ancient beliefs and superstitions. This beautifully illustrated book examines in detail the fascinating symbolism of the motifs and patterns that give life to these spectacular textiles, from Ghanaian patchwork banners to Egyptian headshawls. Complete with a glossary, dictionary of stitches, further reading and information on where to access public collections as well as how to collect textiles of one's own, this is an unrivalled guide for anyone interested in textiles, costume or craft.
28/01/24
#embroidered textiles#motifs and patterns#Cyprus#Ukraine#Panama#Portugal#Ghana#Egypt#five continents#textiles books#fashion books#fashionbooksmilano
35 notes
·
View notes
Text











Motifs d'Artistes
Une histoire du design dans l’industrie textile depuis le 18e siècle
Silvana Editoriale, Cinisello Balsamo 2023, 96 pagine, 20x20cm, brossura, Francese, ISBN 9788836655403
euro 20,00
email if you want to buy : [email protected]
L’exposition « Motifs d’artistes, une histoire du design dans l’industrie textile depuis le 18e siècle » revient sur l’origine du métier de designer textile et le rôle des artistes dans la création de motifs. Depuis les dessinateurs employés par les manufactures de soieries et d’indiennes, jusqu’à l’apparition des designers textiles, l’exposition questionne la diversité́ de leur statut et l’évolution de la reconnaissance de leur art. En s’adaptant aux contraintes techniques propres à ce domaine, ces inventeurs de formes ont donné naissance à de véritables ornements, reflets de leur univers artistique, des tendances et des pratiques de consommation de leur temps. Ainsi, Jean-Baptiste Huet, William Morris, Raoul Dufy ou encore Sonia Delaunay ont laissé une empreinte indélébile dans le répertoire des arts décoratifs.
Jouy-en-Josas, Musée de la Toile de Jouy
dal 16 Giugno 2023 al 14 Gennaio 2024
04/10/23
#Motifs Artistes#histoire design textile#exhibition catalogue#Musée ToileJouy 2023#textiles books#fashion books#fashionbooksmilano
1 note
·
View note
Photo



‘Wild Textiles’ Is a Practical Guide for Turning Foraged Materials into Fiber-Based Works
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
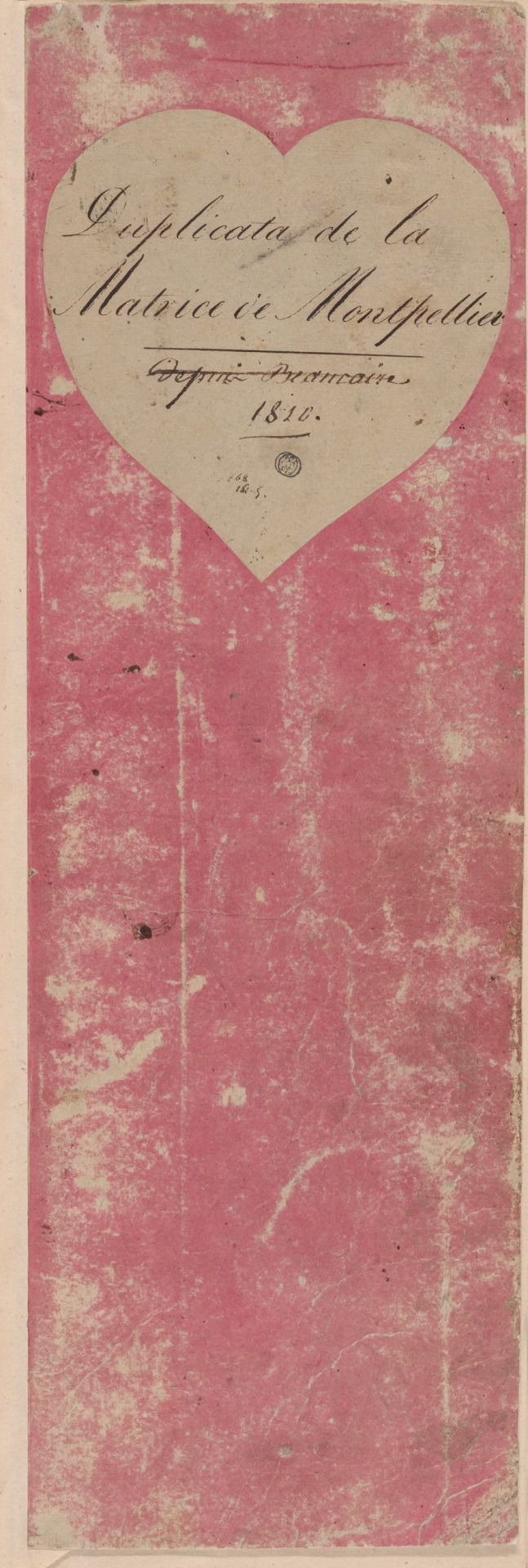
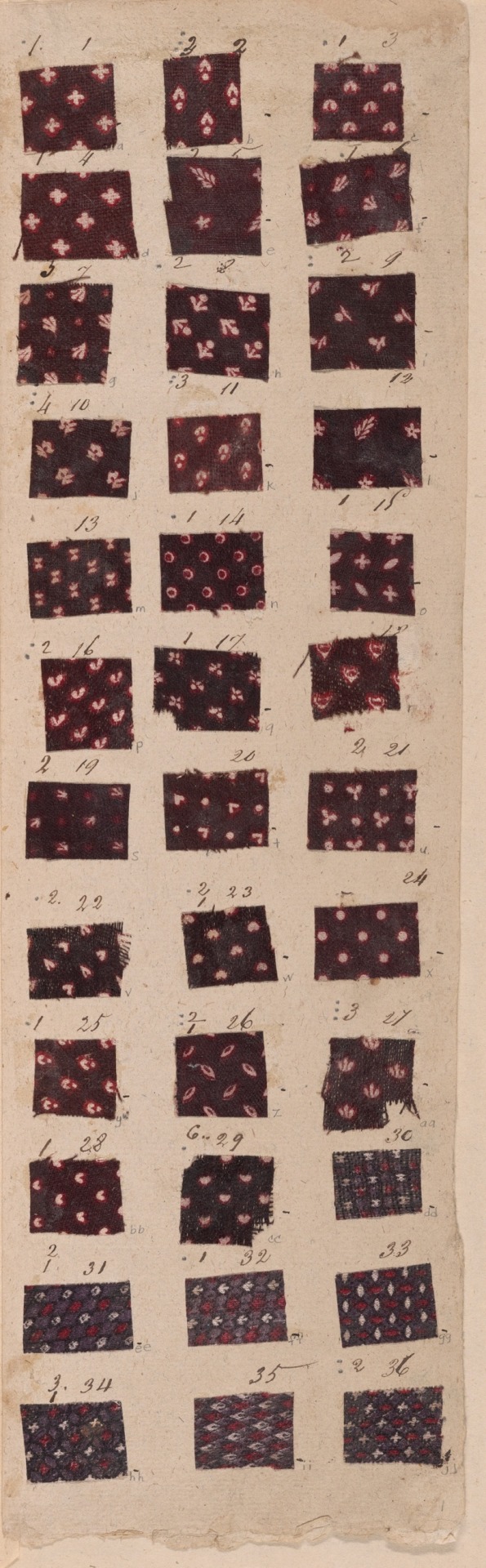





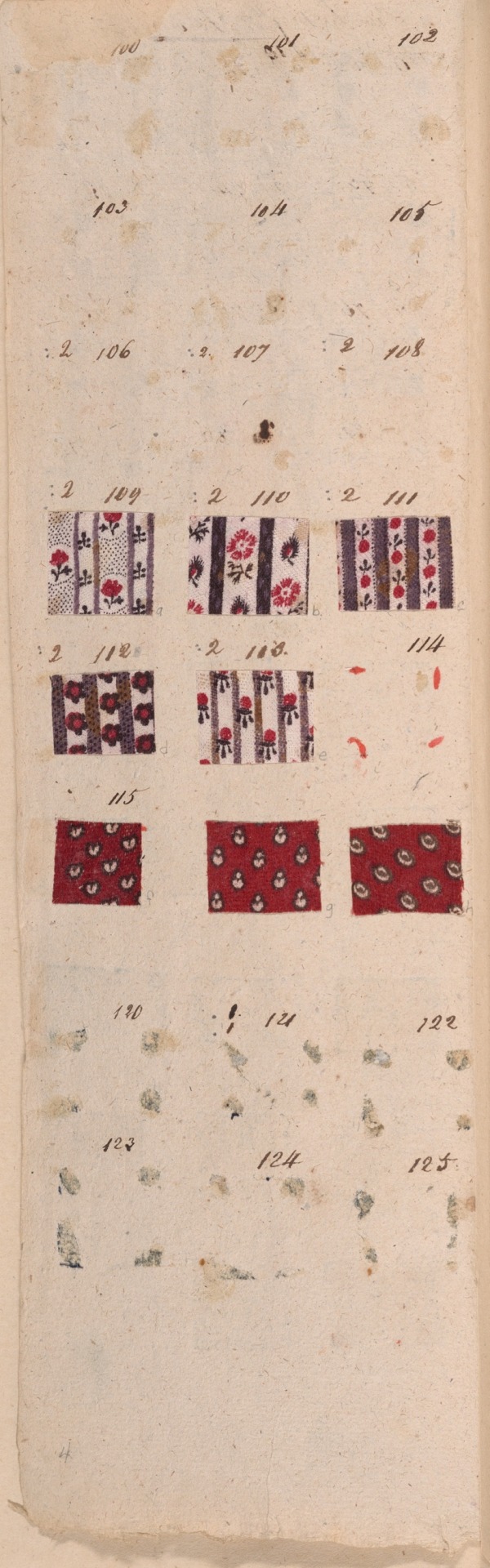

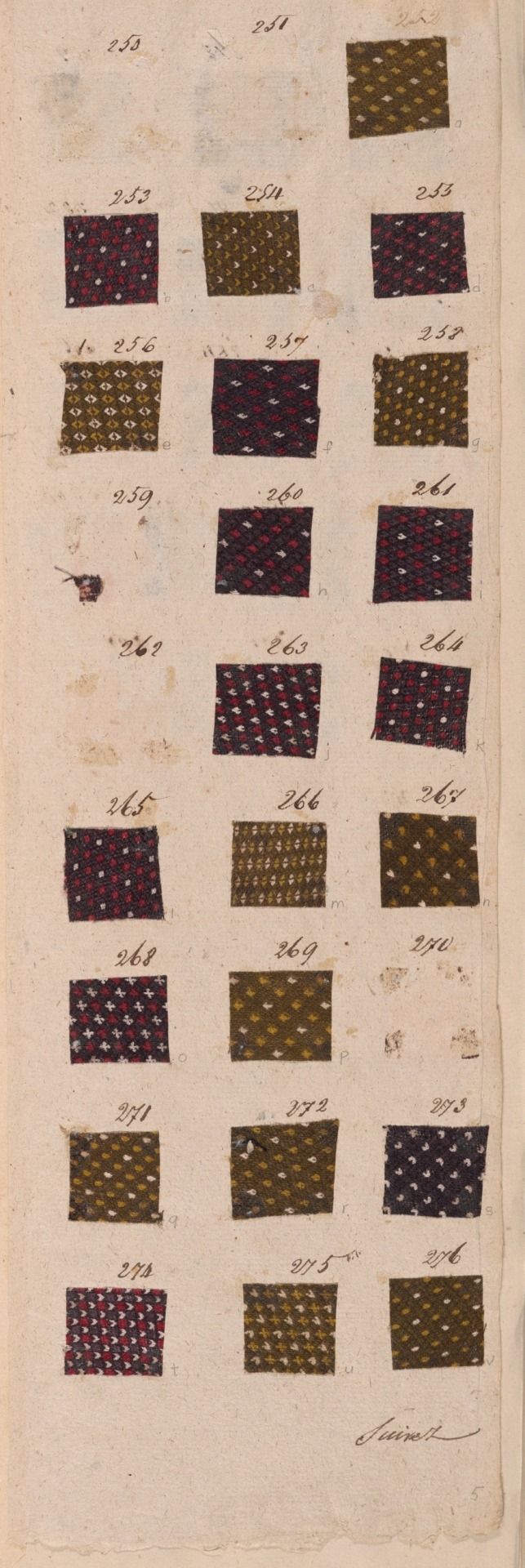
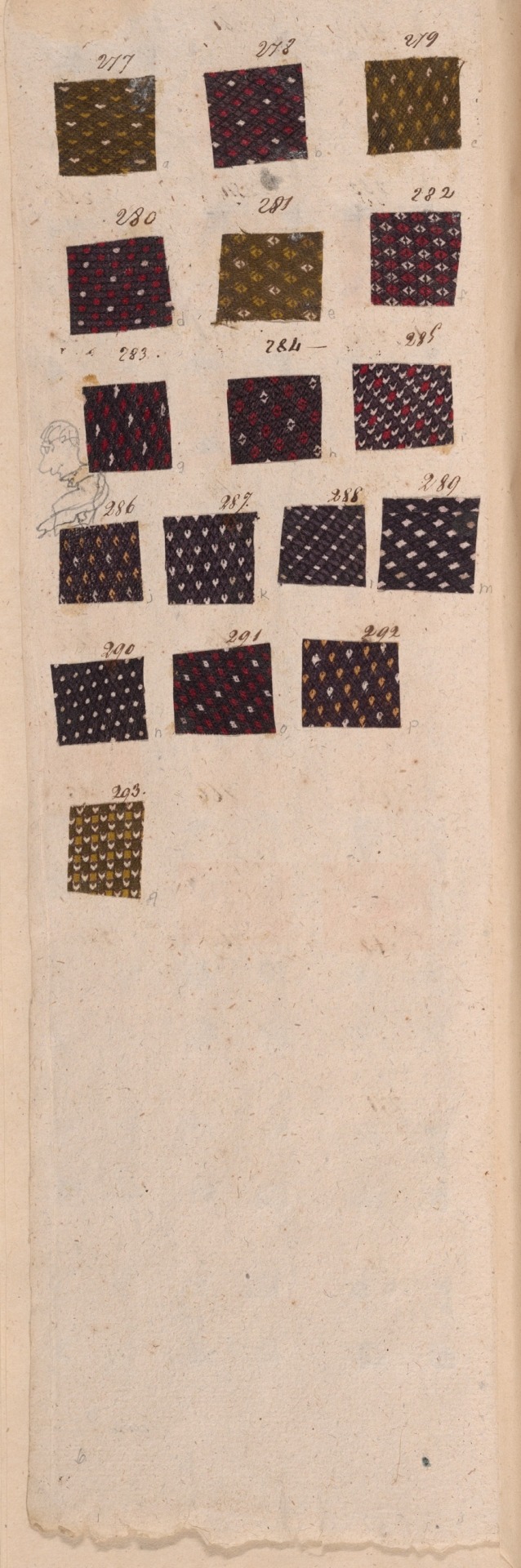
Copy of the Goods of Montpellier
France, c. 1810
Napoleonic era
This book illustrates the huge variety of intricate patterns printed in vivid colors on cotton textiles for fashion during the early 19th century. The book comes from Montpellier, a town on the southern coast of France that is not known today as a center of textile printing. Thus these samples indicate how much more widespread the textile industry was in Europe during the Industrial Revolution. This book contains more than 2,300 small samples.
Source: Art Institute of Chicago
#textiles#colors#farbric#Montpellier#book#napoleonic era#napoleonic#19th century#1800s#1810#cotton#textile#fashion#style#pretty#empire period#empire style#first french empire#french empire#french#art#France#fabric#french art#empire#napoleon#19th century art#history#women#pattern
486 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Jerome Wallace, Coolness of Water on Naked Bodies (detail), 1968
Batik on hand woven silk
377 notes
·
View notes