Text
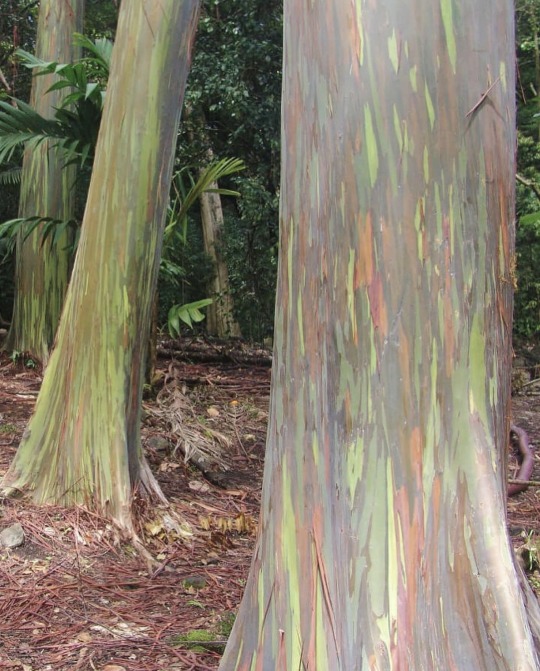
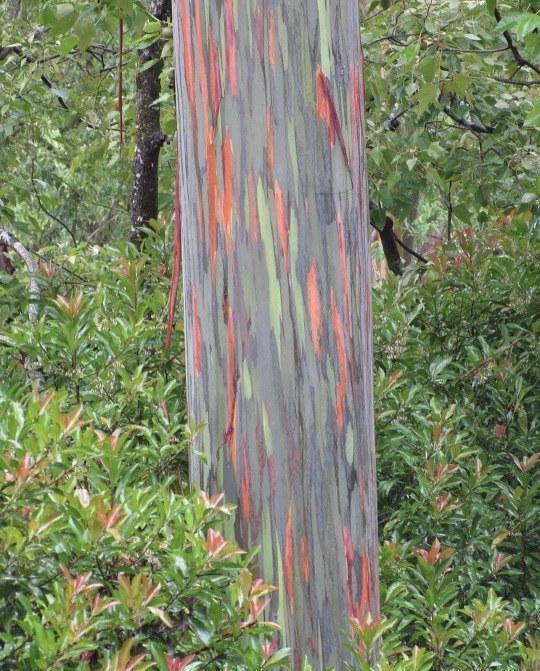
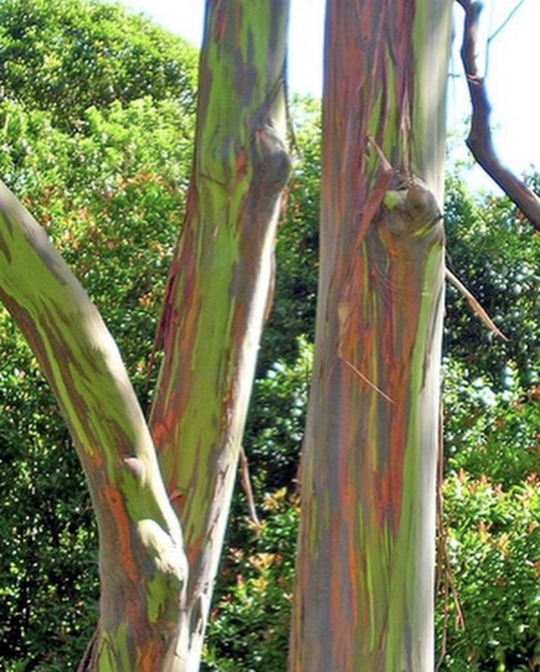
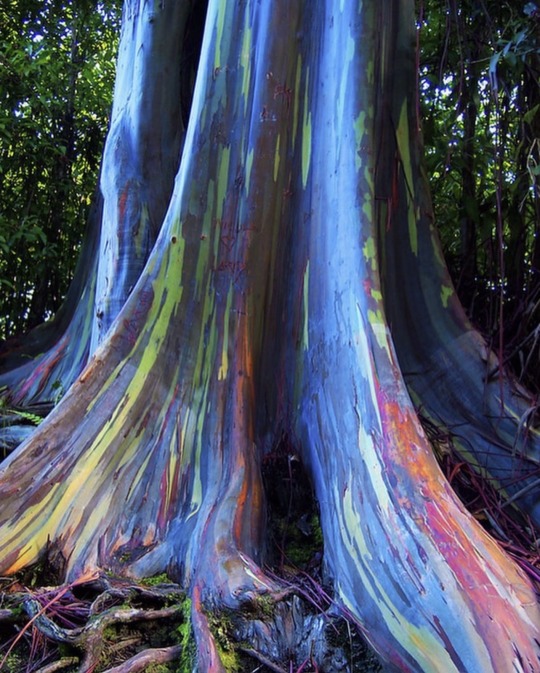
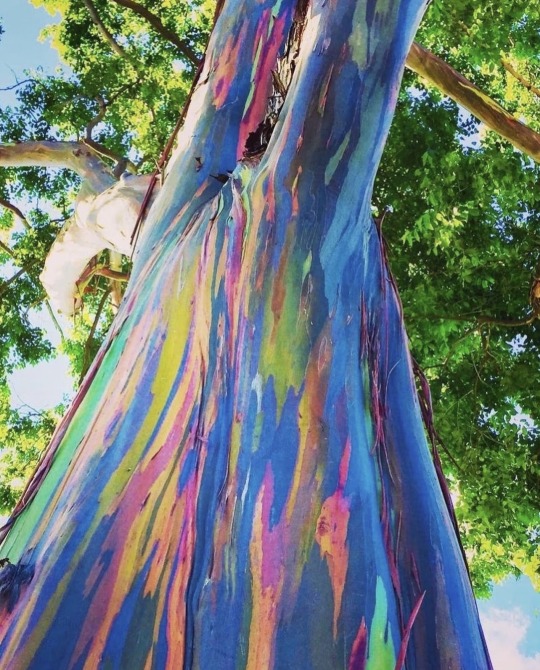
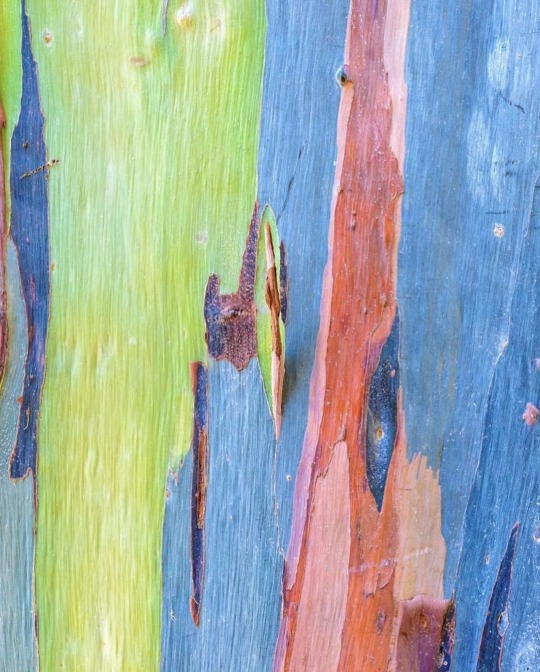






Rainbow Eucalyptus trees get their colorful appearance when they shed their bark, starting with bright green patches that gradually transform into orange, maroon, and blue hues
36K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Lana at her apartment in 2008, photo by Caroline Grant
70K notes
·
View notes
Text
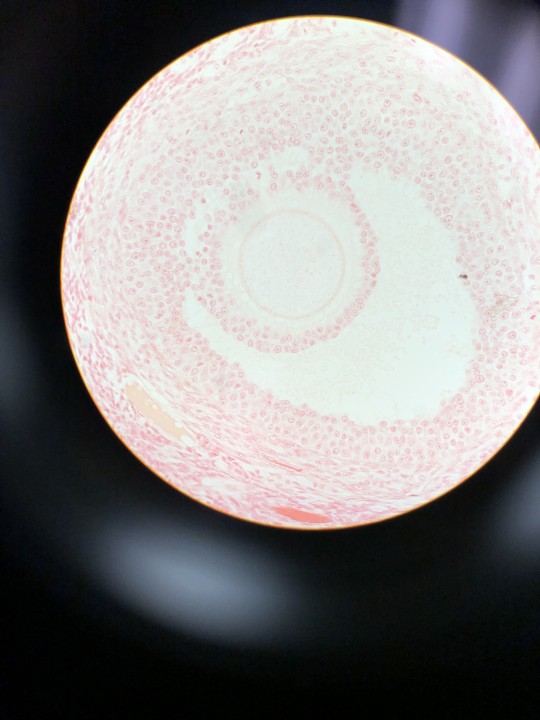
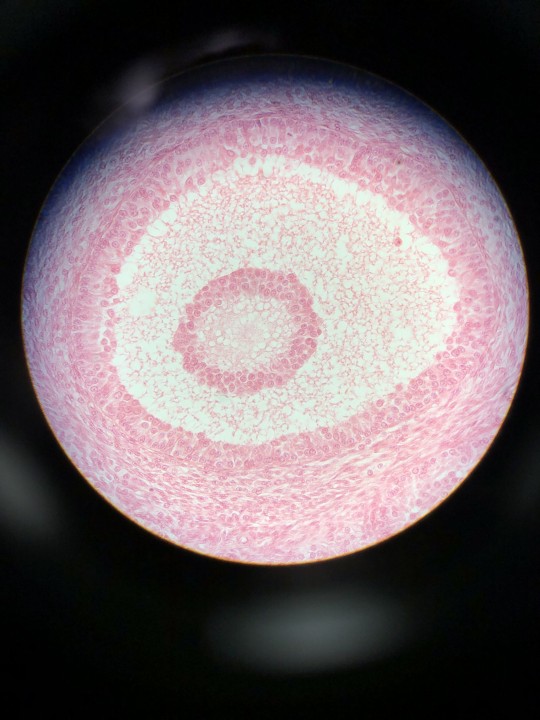
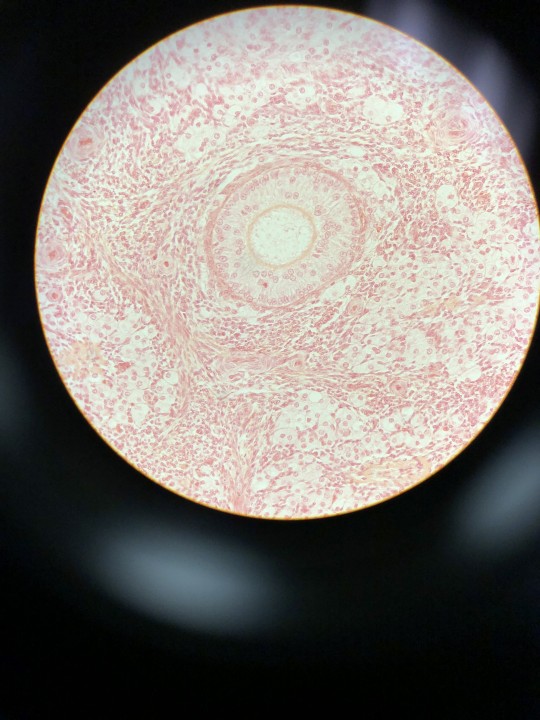



Pretty sure I haven't posted these yet... 🤨
1-3.) Graafian follicles in ovary
4.) Corpus luteum in ovary
5.) Fallopian tube ampulla
6.) Testis
Personally, I'd love to go into histology but I can never identify the cells in the tissues/purpose of specific tissues :p
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
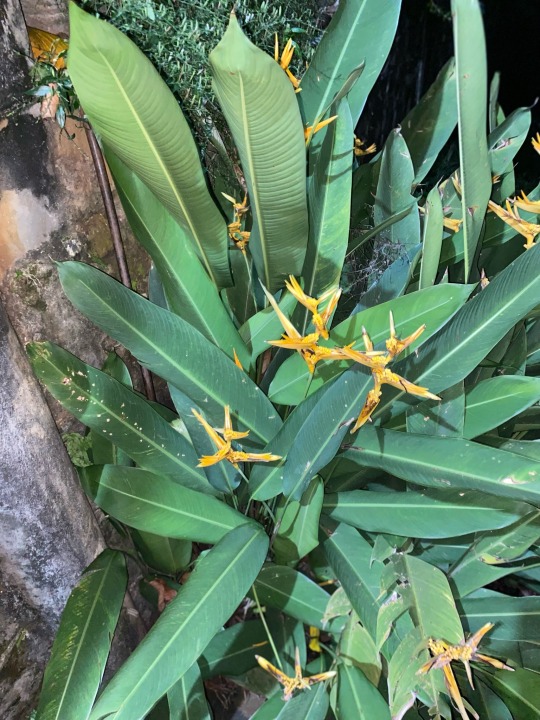
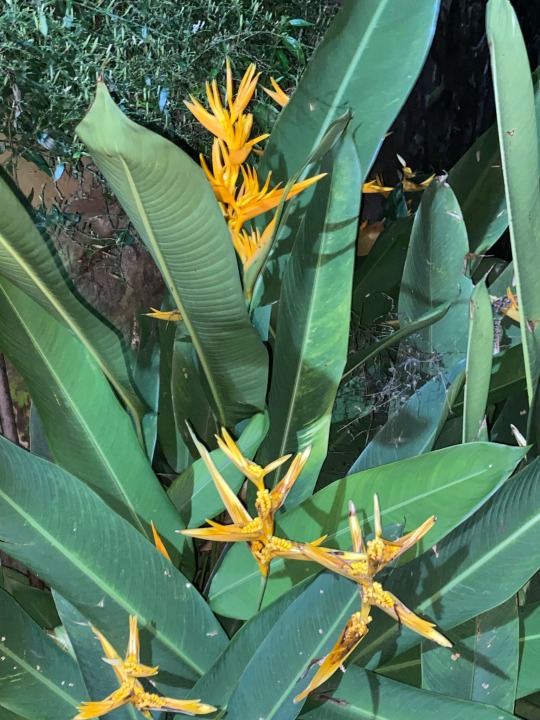
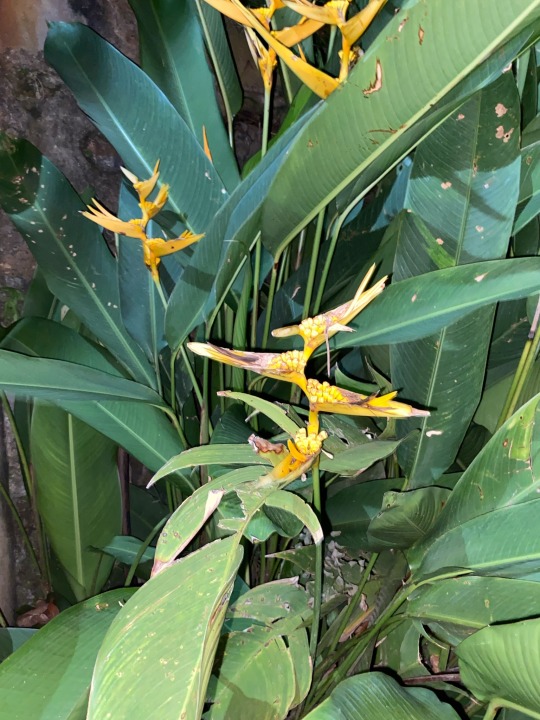



As we know this is Marantaceae
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Howl truly is the man of all time. He’s a playboy. He’s a malewife. He fell in love with a ninety year old woman. He’s a rugby player. He smells like hyacinths. He’s not a natural blond. When dying his hair went slightly wrong, he filled his home with slime. He has a PhD. He’s a wizard. He found a way to another universe and he told absolutely nobody about it. He makes video games about the magical universe for his nephews. He can’t play the guitar. He always takes a guitar with him when he’s trying to seduce a woman. He’s a self-proclaimed coward. He got drunk to trick himself into doing something dangerous. He overcharges for his services to rich people. He undercharges for his services to poor people. A woman invaded his home and declared herself his cleaning lady and he just let her stay. He loves spiders. He lies about his surname to everyone, including royalty. The true spelling of his first name is Howell, but we don’t find out until halfway through the book because the POV character thinks it’s spelled Howl. He’s even Welsh.
49K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Different Types of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue can be classified into several types based on its structure and function. Here are some of the different kinds of epithelial tissue:
Simple Squamous Epithelium:
Features a single layer of flattened cells.
Found in areas where diffusion and filtration occur, such as the lining of blood vessels (endothelium) and air sacs of the lungs (alveoli).
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium:
Consists of a single layer of cube-shaped cells.
Found in areas involved in secretion and absorption, such as kidney tubules and glands.
Simple Columnar Epithelium:
Composed of a single layer of column-shaped cells.
May contain specialized cells, such as goblet cells that secrete mucus.
Found in the lining of the digestive tract, where it aids in absorption and secretion.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium:
Appears stratified but is actually a single layer of cells of varying heights.
Often contains cilia and goblet cells.
Found in the respiratory tract, where it helps in moving mucus and trapping foreign particles.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium:
Comprises multiple layers of flattened cells.
Provides protection against abrasion and forms the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) and lines the oral cavity, esophagus, vagina, and anal canal.
Transitional Epithelium:
Features multiple layers of cells that change shape when stretched.
Found in organs that undergo stretching, such as the urinary bladder, allowing it to accommodate varying volumes of fluid.
Stratified Cuboidal and Stratified Columnar Epithelium:
Less common types of epithelium.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium consists of two or more layers of cuboidal cells and is found in some ducts.
Stratified columnar epithelium consists of two or more layers of columnar cells and can be found in certain parts of the male urethra and large ducts of some glands.
These are just a few examples of the diverse epithelial tissues in the body. Each type is specialized for specific functions and locations within various organs and tissues.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Epithelium
Normal epithelium by systems… (summary of Wheater’s)
Linings
Endothelium - simple squamous
Mesothelium - simple squamous
Skin
Epidermis - stratified squamous (mostly keratinising)
Respiratory
Nose - pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Sinus - pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Epiglottis - stratified squamous
Respiratory tract - pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Alveoli - simple squamous
Breast
Breast - compound glandular.
GIT & its parts
Oral cavity - stratified squamous
Epiglottis - stratified squamous
Oesophagus - stratified squamous
Liver - glandular
Gallbladder - simple columnar
Pancreas - glandular ( exocrine, endocrine)
Stomach - simple glandular
Brunner’s glands - compound glandular
Colon - simple glandular
Anus - stratified squamous
Large ducts of exocrine glands - stratified cuboidal
Small ducts of exocrine glands - simple cuboidal
Renal & Urinary
Bowman’s capsule - simple squamous
Renal collecting tubules - simple cuboidal
Renal collecting ducts - simple columnar
Loop of Henle - simple squamous
Renal pelvis - transitional
Urters - transitional
Bladder - transitional
Urethra - transitional
Reproductive Systems
Prostate - compound glandular
Rete testis - simple cuboidal
Glans penis - stratified squamous
Ovary surface - simple cuboidal
Fallopian tubes - simple ciliated columnar
Endocervix - simple columnar
Cervix, vagina, vulva - stratified squamous
Endocrine & Glandy stuff
Adrenal - glandular
Anterior pituitary - glandular
Eccrine sweat glands - simple glandular
Sebaceous sweat glands - compound glandular
Thyroid - glandular
Salivary glands - glandular (compound glandular is small salivary glands)
Special Senses
Cornea - stratified sqamous
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

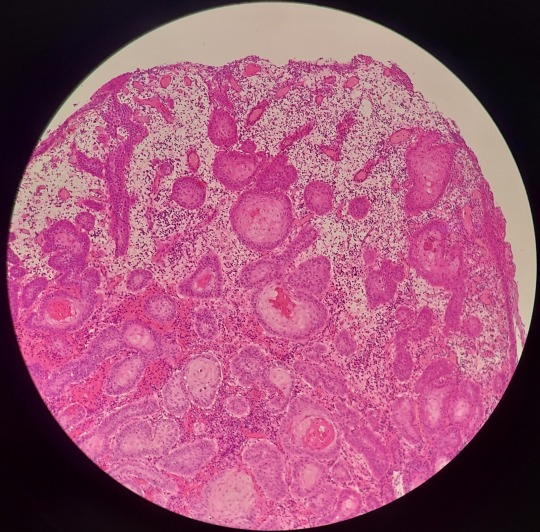
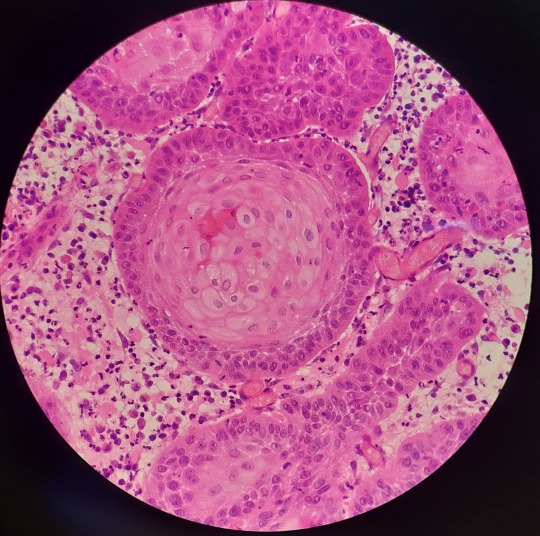
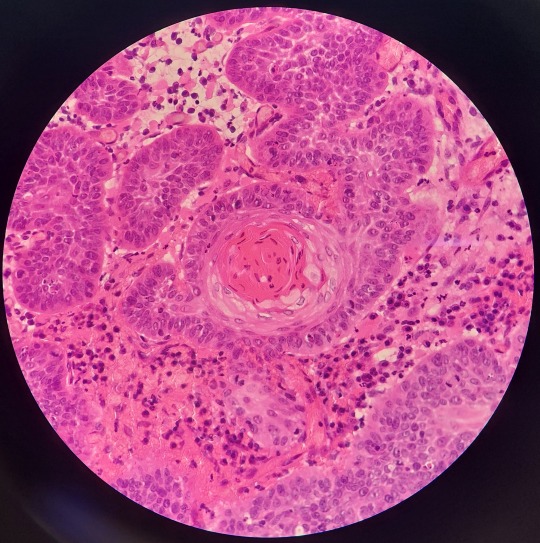
Work has had a few squamous cell carcinomas come in recently and I wanted to share just how pretty these can look, even when they are inflamed like this one is.
This invasive neoplasm typically consists of islands and trabeculae of keratinising (keratin-producing) stratified squamous epithelium. They can range from well differentiated like in this case, to more poorly differentiated and difficult to diagnose. The presence of keratin pearls (pictured in the top left and bottom right photos) is a huge help in diagnosing these neoplasms.
238 notes
·
View notes