Text
Matt Matthew Ginnow
#mattginnow
#Ginnow
On Monday, April 8, 2024, there’ll be a total solar eclipse – and it’ll be the last one to cross North America for 20 years. Make sure you’re tuned in to our live broadcast for this exciting event: there’ll be views from along the path of totality, special guests, and plenty of science.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Matthew Ginnow
#mattginnow
#Ginnow

Follow, follow the Sun / And which way the wind blows / When this day is done 🎶 Today, April 8, 2024, the last total solar eclipse until 2045 crossed North America.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
39K notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Matthew Ginnow
#mattginnow
#Ginnow

For Earth Day, we’re inviting you to take a moment to celebrate our wonderful water world, Earth. As far as we know, our Blue Marble is the only place in the universe with life, and that life depends on water. Snap a photo of yourself outside and tag it #GlobalSelfie – bonus points if your selfie features your favorite body of water! http://go.nasa.gov/3xFt0H0
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Matthew Ginnow
#mattginnow
#Ginnow

Setting Sail to Travel Through Space: 5 Things to Know about our New Mission
Our Advanced Composite Solar Sail System will launch aboard Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand no earlier than April 23, at 6 p.m. EDT. This mission will demonstrate the use of innovative materials and structures to deploy a next-generation solar sail from a CubeSat in low Earth orbit.
Here are five things to know about this upcoming mission:
1. Sailing on Sunshine
Solar sails use the pressure of sunlight for propulsion much like sailboats harness the wind, eliminating the need for rocket fuel after the spacecraft has launched. If all goes according to plan, this technology demonstration will help us test how the solar sail shape and design work in different orbits.
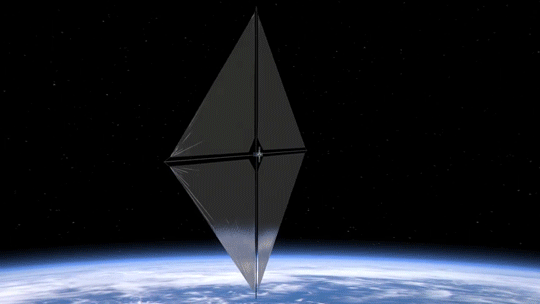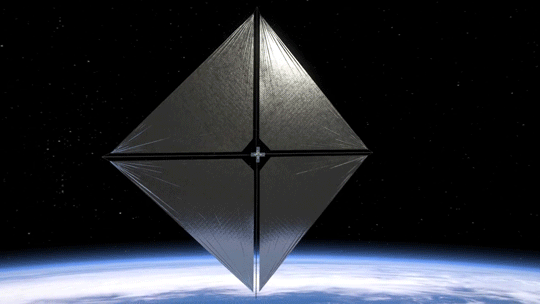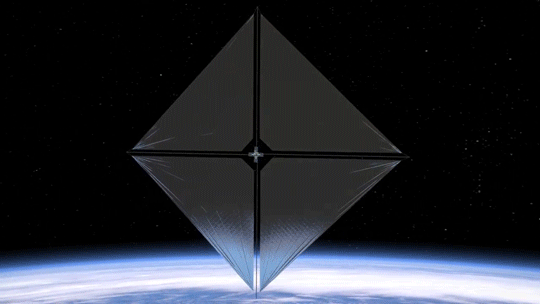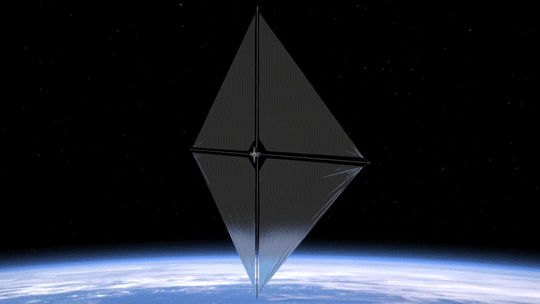
2. Small Package, Big Impact
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft is a CubeSat the size of a microwave, but when the package inside is fully unfurled, it will measure about 860 square feet (80 square meters) which is about the size of six parking spots. Once fully deployed, it will be the biggest, functional solar sail system – capable of controlled propulsion maneuvers – to be tested in space.

3. Second NASA Solar Sail in Space
If successful, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System will be the second NASA solar sail to deploy in space, and not only will it be much larger, but this system will also test navigation capabilities to change the spacecraft’s orbit. This will help us gather data for future missions with even larger sails.

4. BOOM: Stronger, Lighter Booms
Just like a sailboat mast supports its cloth sails, a solar sail has support beams called booms that provide structure. The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System mission’s primary objective is to deploy a new type of boom. These booms are made from flexible polymer and carbon fiber materials that are stiffer and 75% lighter than previous boom designs. They can also be flattened and rolled like a tape measure. Two booms spanning the diagonal of the square (23 feet or about 7 meters in length) could be rolled up and fit into the palm of your hand!

5. It’s a bird...it’s a plane...it’s our solar sail!
About one to two months after launch, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft will deploy its booms and unfurl its solar sail. Because of its large size and reflective material, the spacecraft may be visible from Earth with the naked eye if the lighting conditions and orientation are just right!
To learn more about this mission that will inform future space travel and expand our understanding of our Sun and solar system, visit https://www.nasa.gov/mission/acs3/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Webb Captures New Views Of The Horsehead Nebula
0 notes
Video
youtube
Tour the Crab Nebula Matt GinnowMatthew Ginnow #mattginnow#matthewginnow
0 notes
Video
youtube
Take a Tour of Cassiopeia A
0 notes
Video
Matt Ginnow
Matthew Ginnow #mattginnow
#matthewginnow
youtube
The Search For Elusive Planets is Over | Space Documentary | 3 Decades o…
1 note
·
View note
Photo
Matt Ginnow
Matthew Ginnow #mattginnow
#matthewginnow

Matthew Ginnow by Matthew Ginnow
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Our Webb Space Telescope’s New Look at an Exploded Star on This Week @NA...
0 notes
Video
youtube
The Search For Elusive Planets is Over | Space Documentary | 3 Decades o...
1 note
·
View note
Text
Matt Ginnow, Matthew Ginnow, #mattginnow, #matthewginnow
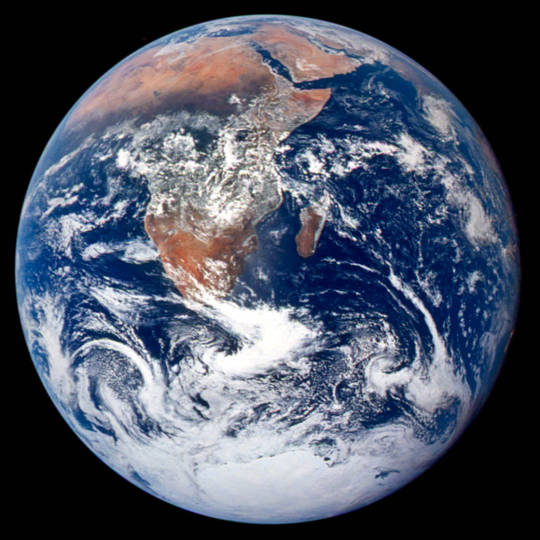

Ways NASA Studies the Ocean
We live on a water planet. The ocean covers a huge part of the Earth's surface – earning it the name Blue Marble.
The ocean is one of Earth’s largest ecosystems and helps moderate Earth’s climate. NASA scientists spend a lot of time studying the ocean and how it is changing as Earth’s climate changes.
In the last few years, NASA has launched an array of missions dedicated to studying this precious part of our planet, with more to come. For World Oceans Month, which starts in June, here are new ways NASA studies the ocean.
youtube
1. Seeing the colors of the ocean 🎨
A new NASA mission called PACE will see Earth’s oceans in more color than ever before. The color of the ocean is determined by the interaction of sunlight with substances or particles present in seawater.
Scheduled to launch in 2024, PACE will help scientists assess ocean health by measuring the distribution of phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will also continue measuring key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate.
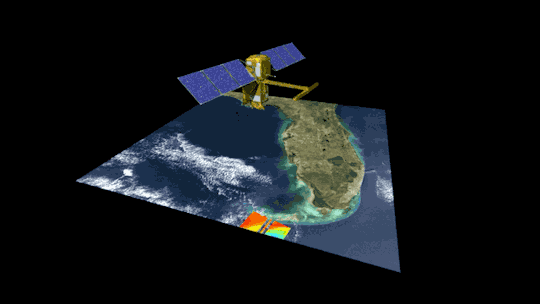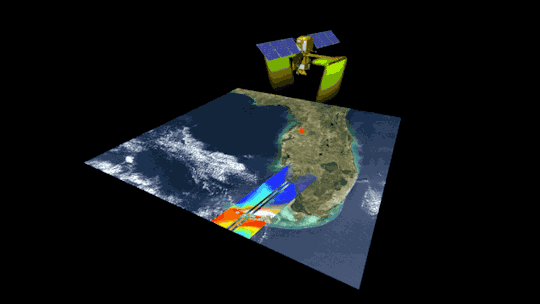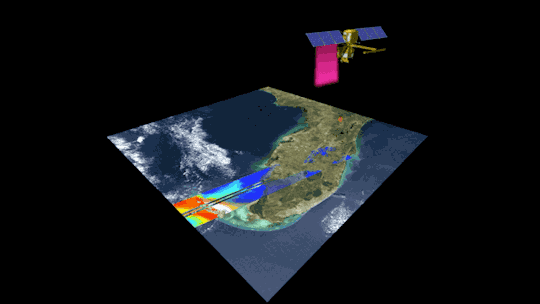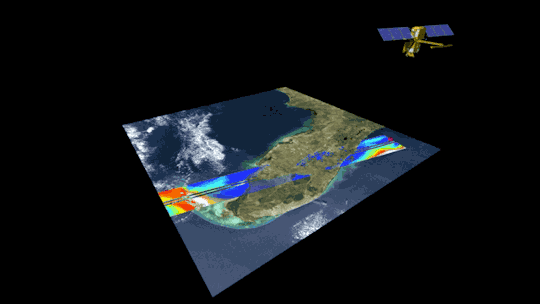
2. Surveying surface water around the globe 💧
The SWOT satellite, launched in late 2022, is studying Earth’s freshwater – from oceans and coasts to rivers, lakes and more – to create the first global survey of Earth’s surface water.
SWOT is able to measure the elevation of water, observing how major bodies of water are changing and detecting ocean features. The data SWOT collects will help scientists assess water resources, track regional sea level changes, monitor changing coastlines, and observe small ocean currents and eddies.
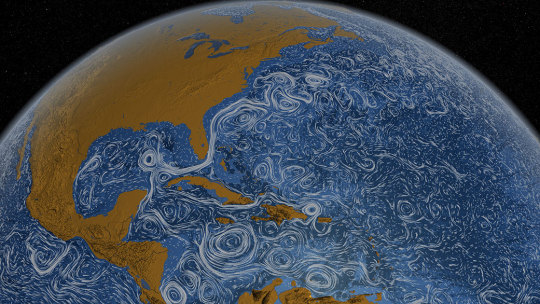
3. Setting sail to understand interactions between the ocean and atmosphere 🚢
With research aircraft, a research ship, and autonomous ocean instruments like gliders, NASA’s S-MODE mission is setting sail to study Earth’s oceans up close. Their goal? To understand ocean whirlpools, eddies and currents.
These swirling ocean features drive the give-and-take of nutrients and energy between the ocean and atmosphere and, ultimately, help shape Earth’s climate.
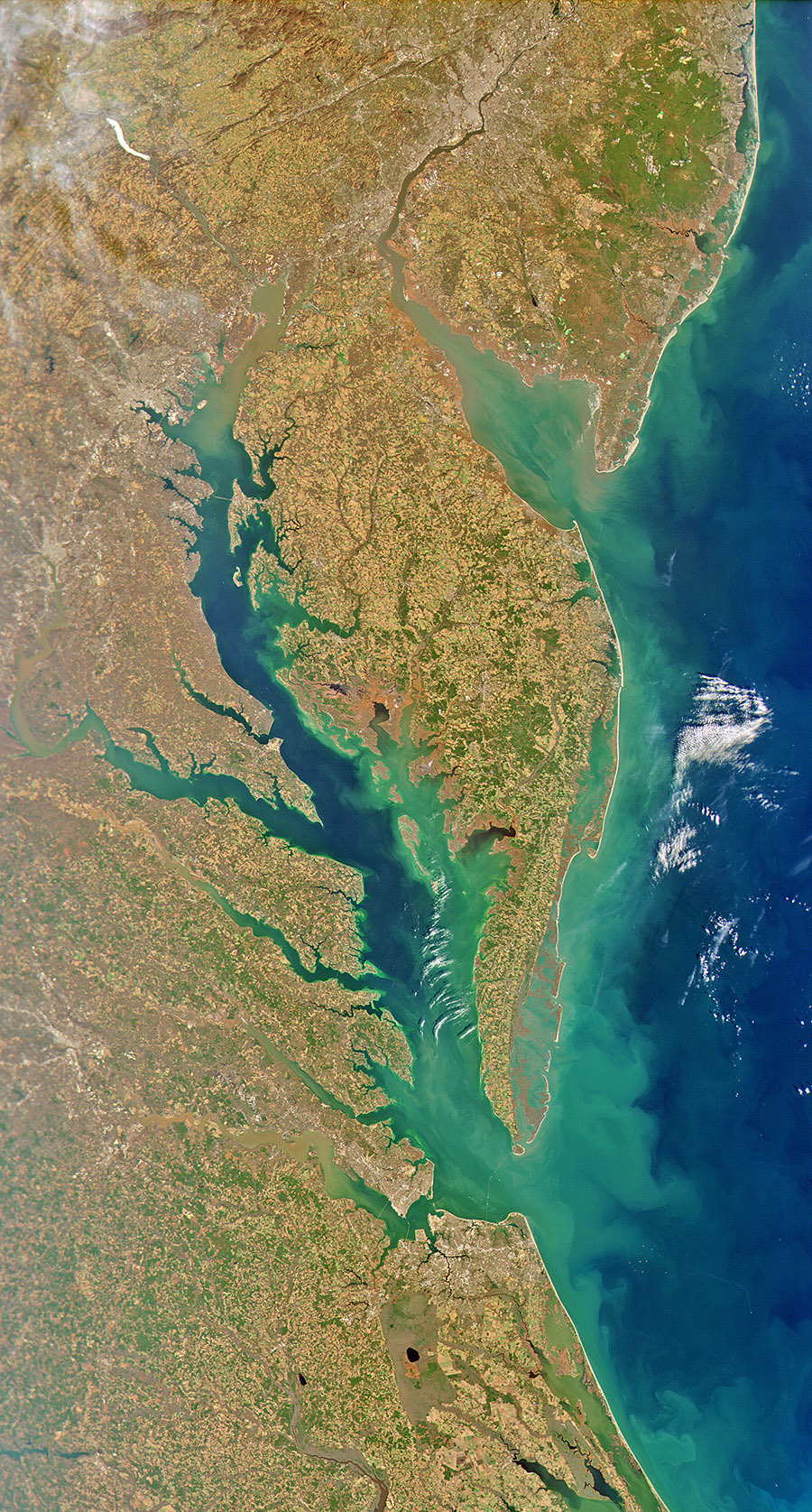

4. Building ocean satellites the size of a shoebox 📦
NASA’s HawkEye instrument collects ocean color data and captures gorgeous images of Earth from its orbit just over 355 miles (575 kilometers) above Earth’s surface. It’s also aboard a tiny satellite measuring just 10cm x 10 cm x 30 cm – about the size of a shoebox!

5. Designing new missions to study Earth’s oceans! 🌊
NASA is currently designing a new space-based instrument called GLIMR that will help scientists observe and monitor oceans throughout the Gulf of Mexico, the southeastern U.S. coastline and the Amazon River plume that stretches to the Atlantic Ocean. GLIMR will also provide important information about oil spills, harmful algae blooms, water quality and more to local agencies.
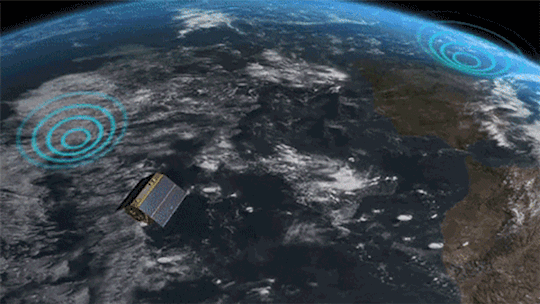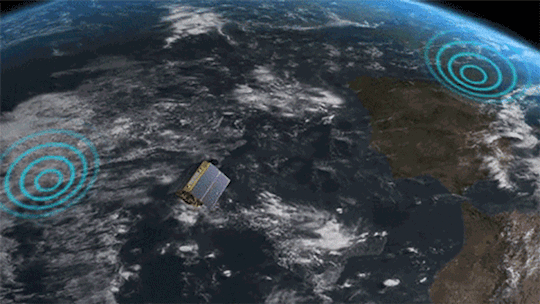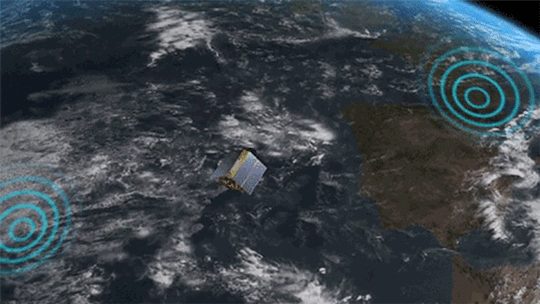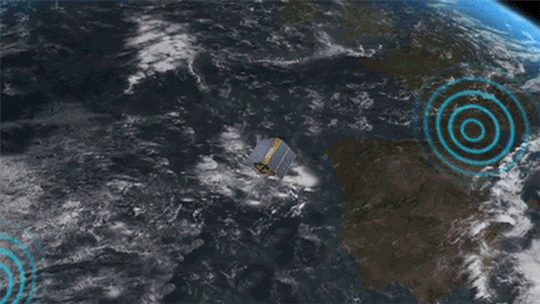
6. Taking the ocean to new heights ⬆️
The U.S.-European Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is helping researchers measure the height of the ocean - a key component in understanding how Earth’s climate is changing.
This mission, which launched in 2020, has a serious job to do. It’s not only helping meteorologists improve their weather forecasts, but it’s helping researchers understand how climate change is changing Earth’s coastlines in real time.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Ginnow, Matthew Ginnow, #mattginnow, #matthewginnow

Of course Saturn brought its ring light.
On June 25, 2023, our James Webb Space Telescope made its first near-infrared observations of Saturn. The planet itself appears extremely dark at this infrared wavelength, since methane gas absorbs almost all the sunlight falling on the atmosphere. The icy rings, however, stay relatively bright, leading to Saturn’s unusual appearance in this image.
This new image of Saturn clearly shows details within the planet’s ring system, several of the planet’s moons (Dione, Enceladus, and Tethys), and even Saturn’s atmosphere in surprising and unexpected detail.
These observations from Webb are just a hint at what this observatory will add to Saturn’s story in the coming years as the science team delves deep into the data to prepare peer-reviewed results.
Download the full-resolution image, both labeled and unlabeled, from the Space Telescope Science Institute.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Ginnow, Matthew Ginnow, #mattginnow, #matthewginnow

Space Craft! Make NASA-Inspired Creations for World Embroidery Day
It’s time to get crafty with some needle and thread. At NASA, we hope to inspire art of all kinds. To highlight #WorldEmbroideryDay on July 30, we want to know: does our imagery inspire you? Show us your art and we may feature it on social media.
How?
Search for a NASA image that inspires you. Here are a few places to get you started: Hubble, James Webb Space Telescope, Ocean Color, Landsat and Earth Observatory
Create. Over the years, we've seen a growing number of embroidered pieces that showcase our organization's research, especially with needlepoint.
Share your creation, along with the image it was inspired by, on social media using the hashtag #NASAEmbroidery. We will share selected pieces on July 30 for World Embroidery Day
Why?

NASA imagery has many functions. From studying distant galaxies to tracking ocean health, our scientists use these images to not only monitor our home planet, but better understand life beyond our solar system.
Embroidery is an ancient craft that has experienced a revival over the years. It involves decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Have you recently taken up embroidery? What images are you inspired by? We’d love to see it.
Image Resources for #NASAEmbroidery Inspiration
NASA Images
Hubble Image Gallery
NASA’s Ocean Color Image Gallery
James Webb Space Telescope
Landsat Image Gallery
Create and Share Your #NASAEmbroidery
Take a picture of your piece and upload it to Twitter, Instagram, Tumblr or Facebook. Make sure you use the hashtag #NASAEmbroidery so we know that you are taking part in the event and make sure that your privacy permissions allow us to view your post.
If the piece catches our eye, we may share your work on NASA’s main social media accounts as well as theme-related ones. We may also feature your art in a NASA Flickr gallery and our Tumblr pages. We’ll contact you directly to grant us permission to feature your work. You can follow @NASA on Twitter, Instagram and Facebook for embroidery creations, which will be featured from July 30-Aug. 1
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
Matt Ginnow, Matthew Ginnow, #mattginnow, #matthewginnow
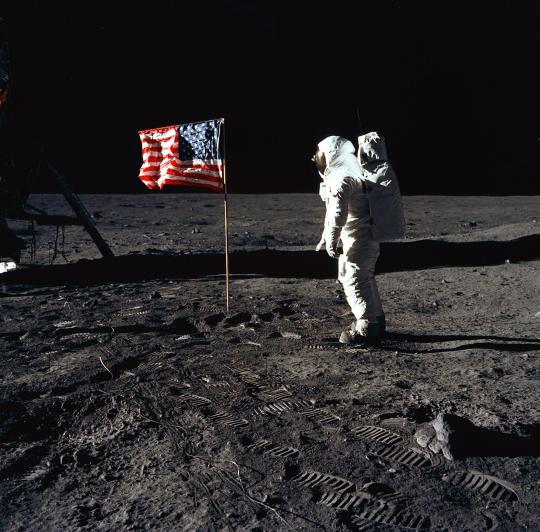

54 Years Ago: Apollo 11 Crew Walks on the Moon via NASA https://ift.tt/y2FoDE9
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Matt Ginnow, Matthew Ginnow, #mattginnow, #matthewginnow

The James Webb Space Telescope has just completed a successful first year of science. Let’s celebrate by seeing the birth of Sun-like stars in this brand-new image from the Webb telescope!
This is a small star-forming region in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. At 390 light-years away, it's the closest star-forming region to Earth. There are around 50 young stars here, all of them similar in mass to the Sun, or smaller. The darkest areas are the densest, where thick dust cocoons still-forming protostars. Huge red bipolar jets of molecular hydrogen dominate the image, appearing horizontally across the upper third and vertically on the right. These occur when a star first bursts through its natal envelope of cosmic dust, shooting out a pair of opposing jets into space like a newborn first stretching her arms out into the world. In contrast, the star S1 has carved out a glowing cave of dust in the lower half of the image. It is the only star in the image that is significantly more massive than the Sun.
Thanks to Webb’s sensitive instruments, we get to witness moments like this at the beginning of a star’s life. One year in, Webb’s science mission is only just getting started. The second year of observations has already been selected, with plans to build on an exciting first year that exceeded expectations. Here’s to many more years of scientific discovery with Webb.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI)
12K notes
·
View notes