Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
RS Puppis
RS Puppis RS Puppis as imaged by Hubble. Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Puppis Right ascension 08h 13m 04.21601s Declination −34° 34′ 42.7023″ Apparent magnitude (V) 6.5-7.6 Characteristics Spectral type G2Ib (G5-K7) U−B color index 1.2 B−V color index 1.5 Variable type Cepheid Variable Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) 24.60 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: -3.19 mas/yr Dec.: 2.33 mas/yr Parallax (π) 0.524 ± 0.022 mas Distance 1,910 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) -5.70 Details Mass 9.2 M☉ Radius 194 R☉ Luminosity 17,000 (15,000-30,000) L☉ Temperature 4,500-6,500 K Metallicity [Fe/H] 0.17 dex Age 28 Myr Other designations HD 68860, HIP 40233, SAO 198944, CD−34°4488 Database references SIMBAD data RS Puppis (or RS Pup) is a Cepheid variable star in the constellation of Puppis. It is one of the brightest known Cepheids in the Milky Way galaxy and has one of the longest periods of 41.4 days. Because it is located in a large nebula, astronomers using the ESO's New Technology Telescope at La Silla Observatory, Chile have been able to measure its distance in 2013 by strictly geometric analysis of light echoes from particles in the nebula, determining it to be 6500 ± 90 light years from Earth, the most accurate measurement achieved for any Cepheid as of early 2008. The accuracy of the new measurement is important because Cepheids serve as a marker for distances within the Milky Way galaxy and for nearby galaxies. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Text
Phi Velorum
Phi Velorum Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Vela Right ascension 09h 56m 51.742s Declination −54° 34′ 04.04″ Apparent magnitude (V) 3.52 Characteristics Spectral type B5 Ib U−B color index −0.62 B−V color index −0.08 Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) 14 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −13.08 ± 0.10 mas/yr Dec.: 3.55 ± 0.10 mas/yr Parallax (π) 2.05 ± 0.11 mas Distance 1,590 ± 90 ly (490 ± 30 pc) Absolute magnitude (MV) −5.34 Other designations Tseen Ke, HR 3940, HD 86440, SAO 237522, CP −53° 3075, FK5 375, GC 13711, CCDM 09569-5434, HIP 48774. "Tseen Ke" redirects here. Tseen Ke can also refer to Lambda Velorum. Phi Velorum (φ Vel, φ Velorum) is a star in the constellation Vela. It has the traditional name Tseen Ke, from Chinese 天紀 (Mandarin tiānjì) "star chart". (lit. "Record of Heaven"). Phi Velorum is a blue-white B-type supergiant with an apparent magnitude of +3.52. It is approximately 1590 light years from Earth. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Rigel
For other uses, see Rigel (disambiguation). Rigel Rigel in the constellation Orion Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Orion A Right ascension 05h 14m 32.27210s Declination −08° 12′ 05.8981″ Apparent magnitude (V) 0.13 (0.05 - 0.18) B Right ascension 05h 14m 32.049s Declination −08° 12′ 14.78″ Apparent magnitude (V) 6.67 Characteristics A Evolutionary stage Blue supergiant Spectral type B8 Ia U−B color index −0.66 B−V color index −0.03 Variable type Alpha Cygni B Evolutionary stage Spectroscopic binary Spectral type B9V + B9V U−B color index −0.66 B−V color index −0.03 Variable type Alpha Cygni Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) 7001178000000000000♠17.8±0.4 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: +1.31 mas/yr Dec.: +0.50 mas/yr Parallax (π) 3.78 ± 0.34 mas Distance 860 ± 80 ly (260 ± 20 pc) Absolute magnitude (MV) -7.84 Orbit Primary Ba Companion Bb Period (P) 9.860 days Eccentricity (e) 0.1 Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) 25.0 km/s Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) 32.6 km/s Details A Mass 23 M☉ Radius 7001789000000000000♠78.9±7.4 R☉ Luminosity (bolometric) 7000120000000000000♠1.20+0.25 −0.21×105 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 7000175000000000000♠1.75±0.10 cgs Temperature 7004121000000000000♠12100±150 K Metallicity [Fe/H] 3001400000000000000♠−0.06±0.10 dex Rotational velocity (v sin i) 7001250000000000000♠25±3 km/s Age 7000800000000000000♠8±1 Myr Ba Mass 3.84 M☉ Bb Mass 2.94 M☉ Other designations Rigel, Algebar, Elgebar, β Ori, 19 Ori, HD 34085, HR 1713, HIP 24436, SAO 131907 Database references SIMBAD data Rigel, also designated Beta Orionis (β Orionis, abbreviated Beta Ori, β Ori), is generally the seventh-brightest star in the night sky and the brightest star in the constellation of Orion—though there are times where it is outshone in the constellation by the variable Betelgeuse. With a visual magnitude of 0.13, it is a remote and luminous star some 863 light-years distant from Earth. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple or quadruple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a blue-white supergiant that is estimated to be anywhere from 120,000 to 279,000 times as luminous as the Sun, depending on method used to calculate its properties. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and swollen out to between 79 and 115 times the Sun's radius. It pulsates quasi-periodically and is classified as an Alpha Cygni variable. A companion, Rigel B, is 500 times fainter than the supergiant Rigel A and visible only with a telescope. Rigel B is itself a spectroscopic binary system, consisting of two main sequence blue-white stars of spectral type B9V that are estimated to be respectively 3.9 and 2.9 times as massive as the Sun. Rigel B also appears to have a very close visual companion Rigel C of almost identical appearance. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Kappa Crucis
κ Crucis The centre of NGC 4755, with κ Cru on the left Credit: NASA/ESA and Jesús Maíz Apellániz (Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, Spain) Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Crux Right ascension 12h 53m 48.91920s Declination −60° 22′ 34.4808″ Apparent magnitude (V) 5.98 Characteristics Spectral type B3Ia U−B color index −0.58 B−V color index +0.22 Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) -3.5 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −3.60 mas/yr Dec.: −1.89 mas/yr Parallax (π) -1.32 ± 0.57 mas Distance 2,600 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) −7.1 Details Mass 23.0 M☉ Luminosity 151,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 2.25 cgs Temperature 16,300 K Rotational velocity (v sin i) 70 km/s Other designations κ Cru, CD−59°4460, HD 111973, HIP 62931, HR 4890, SAO 252077, 2MASS J12534890-6022344 Database references SIMBAD data Kappa Crucis (κ Cru, HD 111973) is a spectroscopic binary star in the open cluster NGC 4755, which is also known as the Kappa Crucis Cluster or Jewel Box Cluster More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Kappa Cassiopeiae
κ Cassiopeiae Location of κ Cassiopeiae (circled) Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Cassiopeia Right ascension 00h 32m 59.991s Declination +62° 55′ 54.42″ Apparent magnitude (V) 4.16 Characteristics Spectral type BC0.7 Ia Apparent magnitude (U) 3.50 Apparent magnitude (B) 4.276 Apparent magnitude (J) 4.141 Apparent magnitude (H) 4.148 Apparent magnitude (K) 4.013 U−B color index -0.776 B−V color index +0.0869 J−H color index -0.0069 J−K color index +0.128 Variable type α Cyg Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) 0.30 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: 3.65 ± 0.17 mas/yr Dec.: –2.07 ± 0.16 mas/yr Parallax (π) 0.73 ± 0.17 mas Distance approx. 4,000 ly (approx. 1,400 pc) Absolute magnitude (MV) −7.00 Details Mass 33 M☉ Radius 33.0 R☉ Luminosity 302,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 2.75 cgs Temperature 23,500 K Rotational velocity (v sin i) 66 km/s Other designations 15 Cassiopeiae, HR 130, HD 2905, BD+62°102, FK5 16, HIP 2599, SAO 11256, GC 645 Database references SIMBAD data Kappa Cassiopeiae and its bow shock. Spitzer infrared image (NASA/JPL-Caltech) Kappa Cassiopeiae (κ Cas, κ Cassiopeiae) is a star in the constellation Cassiopeia. κ Cassiopeiae has an unusual spectrum that has anomalously weak nitrogen lines, taken as an actual nitrogen deficiency in the atmosphere. This is indicated by the modified letter C. It is also interpolated to BC0.7, being slightly hotter than a standard B1 star. It is assumed to be a mamber of the Cas OB14 stellar association at about 1,100 parsecs, while its distance found from the Hipparcos parallax is 1,369 parsecs. It is classified as an Alpha Cygni type variable star and its brightness varies by a few hundredths of a magnitude. Periods of two hours, nine days, and 2.65 days have been reported from observations at different times. It is a runaway star, moving at around 2.5 million mph relative to its neighbors (1,100 kilometers per second). Its magnetic field and wind of particles creates a visible bow shock 4 light-years ahead of it, colliding with the diffuse, and usually invisible, interstellar gas and dust. This is about the same distance that Earth is from Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to the Sun. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Text
HD 96919
For other stars with the Bayer designation Z or z Carinae, see z Carinae. V371 Carinae Location of V361 Carinae (circled) Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Carina Right ascension 11h 08m 33.99848s Declination −61° 56′ 49.8316″ Apparent magnitude (V) 5.19 (5.12 - 5.19) Characteristics Spectral type B9 Iae U−B color index −0.46 B−V color index +0.23 Variable type α Cyg Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −22.4 ± 2 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −5.78 mas/yr Dec.: 1.74 mas/yr Parallax (π) 0.23 ± 0.25 mas Distance 1,920 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) −7.0 Details Mass 23 M☉ Radius 141 R☉ Luminosity 105,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 1.50 cgs Temperature 12,500 K Rotational velocity (v sin i) 60 km/s Other designations z2 Carinae, V371 Carinae, 261 G. Carinae, CD−61°2941, CPD−61°2075, CPC 20.1 3080, FK5 2891, GC 15331, GCRV 6856, GSC 08962-02640, HD 96919, HIC 54461, HIP 54461, HR 4338, PPM 358516, SAO 251286 Database references SIMBAD data HD 96919, also known by its Bayer designation of z2 Carinae and the variable star designation of V371 Carinae, is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Carina. It lies near the Carina Nebula and at a comparable distance. V371 Car is an α Cyg variable, erratically pulsating and changing brightness by a few hundredths of a magnitude. Periods of 10 - 80 days have been identified. It shows unusual emission lines in its spectrum, and high-velocity absorption (HVA) events, temporary spectral features that are thought to indicate localised regions of enhanced mass loss. HD 96919 is a B9 supergiant, possibly located 6,000 light years from Earth. It is considered to be a post red supergiant star, either evolving towards a Wolf-Rayet star or on a blue loop before returning to a cooler temperature. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Text
Nu Cephei
Nu Cephei Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Cepheus Right ascension 21h 45m 26.925s Declination +61° 07′ 14.90″ Apparent magnitude (V) 4.289 (4.25 - 4.35) Characteristics Spectral type A2Iab Apparent magnitude (U) 4.94 Apparent magnitude (B) 4.81 Apparent magnitude (J) 3.14 Apparent magnitude (K) 2.85 U−B color index +0.119 B−V color index +0.518 Variable type Alpha Cygni Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −25.90 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −3.74 ± 0.13 mas/yr Dec.: −2.10 ± 0.12 mas/yr Parallax (π) 0.48 ± 0.14 mas Distance 1,450 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) −6.82 Details Mass 16.5 M☉ Radius 137 R☉ Luminosity 102,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 1.35 cgs Temperature 8,800 K Rotational velocity (v sin i) 15 km/s Age 8 Myr Other designations 10 Cephei, HD 207260, HR 8334, SAO 19624, FK5 1572, BD+60°2288, HIP 107418 Database references SIMBAD data Nu Cephei (ν Cephei) is a class A2, fourth-magnitude supergiant star in the constellation Cepheus. It is a white pulsating α Cygni variable star located about 4,700 light-years from Earth. ν Cephei is a member of the Cepheus OB2 stellar association, which includes stars such as μ Cephei and VV Cephei. It began life as an approximately 20 M☉ star around eight million years ago. It has now exhausted its core hydrogen and expanded and cooled into a supergiant. Elemental abundance analyes indicate that it has not yet spent time as a red supergiant, which would have brought about convection of fusion products to the surface in a Dredge-up. ν Cephei is currently about 15 times as massive as the sun, 190 times as large, and 100,000 times as luminous. Its large size and luminosity cause it to be somewhat unstable and produce irregular pulsations. This is a common feature of class A and B supergiants, which are grouped as α Cygni variable stars. The brightness changes by at most a tenth of a magnitude. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Mu Lyrae
Mu Lyrae Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Lyra Right ascension 118h 24m 13.78580s Declination +39° 30′ 26.0562″ Apparent magnitude (V) 5.12 Characteristics Spectral type A0IV Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) -24.0 ± 2 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: -21.14 ± 0.15 mas/yr Dec.: -4.91 ± 0.17 mas/yr Parallax (π) 7.43 ± 0.16 mas Distance 439 ± 9 ly (135 ± 3 pc) Details Luminosity 125 L☉ Temperature 8190 K Other designations 2 Lyr, HD 169702, HIP 90191, HR 6903, SAO 66943. Mu Lyrae (μ Lyr, μ Lyrae) is a star in the constellation Lyra. It has the traditional name Alathfar, from the Arabic الأظفر al-’uz̧fur "the talons (of the swooping eagle)", a name it shares with Eta Lyrae (though the latter is typically spelled Aladfar in English). Mu Lyrae has apparent magnitude 5.12 and belongs to the spectral class A0IV. Located around 439 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 125 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 8190 K. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Upsilon Sagittarii
Upsilon Sagittarii Location of υ Sgr (circled) Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Sagittarius Right ascension 19h 21m 43.62284s Declination −15° 57′ 18.0625″ Apparent magnitude (V) 4.61 Characteristics Spectral type A2 Ia + B2 Vpe U−B color index −0.53 B−V color index +0.10 Variable type PV Tel (β Lyr?) Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) 8.9 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: 1.34 mas/yr Dec.: −6.25 mas/yr Parallax (π) 1.83 ± 0.23 mas Distance approx. 1,800 ly (approx. 550 pc) Absolute magnitude (MV) ~−6 Orbit Primary υ Sgr1 Companion υ Sgr2 Period (P) 137.9 days Semi-major axis (a) 270.8 R☉ Eccentricity (e) 0 Inclination (i) 50° Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) 49.6 km/s Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) 29.7 km/s Details Mass 2.5 + 4 M☉ Radius 50 R☉ Luminosity 39,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 2.5 cgs Temperature 12,300 K Metallicity [Fe/H] −0.2 dex Age 52 Myr Other designations υ Sagittarii, υ Sgr, Upsilon Sgr, 46 Sagittarii, BD−16°5283, FK5 727, GC 26697, HD 181615, HD 181616, HIP 95176, HR 7342, PPM 235885, SAO 162518 Database references SIMBAD data Upsilon Sagittarii (Upsilon Sgr, υ Sagittarii, υ Sgr) is a spectroscopic binary star system in the constellation Sagittarius. Upsilon Sagittarii is the prototypical hydrogen-deficient binary (HdB), and one of only four such systems known. The unusual spectrum of hydrogen-deficient binaries has made stellar classification of Upsilon Sagittarii difficult. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Deneb
For the Deneb processor core, see Phenom II. For the Italian steamship, see SS Deneb. For the star known as Deneb Kaitos, see Beta Ceti. Not to be confused with Denebola, a star in the constellation Leo. Deneb Cygnus, the constellation in which Deneb is located. Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Cygnus Right ascension 20h 41m 25.9s Declination +45° 16′ 49″ Apparent magnitude (V) 1.25 (1.21 - 1.29) Characteristics Spectral type A2 Ia U−B color index −0.23 B−V color index +0.09 Variable type Alpha Cyg Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −4.5 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: 1.99 mas/yr Dec.: 1.95 mas/yr Parallax (π) 2.29 ± 0.32 mas Distance 802 ± 66 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) −8.38 Details Mass 19 ± 4 M☉ Radius 203 ± 17 R☉ Luminosity 196,000 ± 32,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 1.10 ± 0.05 cgs Temperature 8,525 ± 75 K Metallicity [Fe/H] -0.25 dex Rotational velocity (v sin i) 20 ± 2 km/s Other designations α Cygni, Alpha Cyg, 50 Cyg, Arided, Aridif, Gallina, Arrioph, HR 7924, BD +44°3541, HD 197345, SAO 49941, FK5 777, HIP 102098. Database references SIMBAD data Deneb (/ˈdɛnɛb/), also designated Alpha Cygni (α Cygni, abbreviated Alpha Cyg, α Cyg), is the brightest star in the constellation of Cygnus. It is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and forms the 'head' of the Northern Cross. It is the 19th brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent magnitude of 1.25. A blue-white supergiant, Deneb is also one of the most luminous stars. However, its exact distance (and hence luminosity) has been difficult to calculate; it is estimated to be somewhere between 55,000 and 196,000 times as luminous as the Sun. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Text
V533 Carinae
For Y Carinae, see Y Carinae. V533 Carinae Location of V533 Carinae (circled) Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Carina Right ascension 11h 12m 36.01358s Declination −60° 19′ 03.4516″ Apparent magnitude (V) 4.59 Characteristics Evolutionary stage Blue supergiant Spectral type A5Iae: U−B color index +0.08 B−V color index +0.52 Variable type α Cyg Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −8.40 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −5.68 mas/yr Dec.: 2.15 mas/yr Parallax (π) −0.02 ± 0.30 mas Distance 12,700 ly (3,900 pc) Absolute magnitude (MV) −7.9 Details Mass 17 M☉ Radius 141.5 R☉ Luminosity 96,000 L☉ Temperature 8,330 K Rotational velocity (v sin i) 34 km/s Other designations V533 Carinae, y Carinae, HR 4352, HD 97534, CD−59°3611, HIP 54751, SAO 251316, GC 15415, CCDM J11126-6019 Database references SIMBAD data V533 Carinae (V533 Car, y Car, y Carinae) is a white A-type supergiant variable star with a mean apparent magnitude of +4.59 in the constellation Carina. It is over 10,000 light years from Earth. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Text
V399 Carinae
V399 Carinae Location of V399 Carinae (circled) Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Carina Right ascension 10h 27m 24.47114s Declination −57° 38′ 19.6958″ Apparent magnitude (V) +4.69 Characteristics Spectral type A5Iae U−B color index +0.22 B−V color index +0.46 Variable type SRd? Astrometry Proper motion (μ) RA: −6.51 ± 0.29 mas/yr Dec.: 3.82 ± 0.26 mas/yr Parallax (π) 0.06 ± 0.28 mas Distance 2,308 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) −8.8 Details Luminosity 305,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 1.00 cgs Temperature 8,000 K Age 12 Myr Other designations P Carinae, 195 G. Carinae, HR 4110, HD 90772, CP−57°3256, HIP 51192, SAO 238077, GC 14373, IC 2581 1 Database references SIMBAD data V399 Carinae (V399 Car, P Carinae, P Car, 195 G. Carinae) is a variable star in the constellation Carina. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

49 Cancri
Redirect to: List of stars in Cancer More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Text
HR Carinae
HR Car Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Carina Right ascension 10h 22m 53.84074s Declination −59° 37′ 28.3774″ Apparent magnitude (V) 8.42 (6.95 - 8.80) Characteristics Spectral type LBV U−B color index −0.22 B−V color index +0.92 Variable type LBV Astrometry Proper motion (μ) RA: -6.87 mas/yr Dec.: +2.33 mas/yr Parallax (π) 1.69 ± 0.82 mas Distance 5.4k pc Absolute magnitude (MV) -8.4 Orbit Period (P) 4557.5 ± 21.0 days Semi-major axis (a) 3.324 ± 0.026" (18 AU) Eccentricity (e) 0.4 ± 0.2 Inclination (i) 119.2 ± 0.7° Details Mass 25- 40 M☉ Radius 220 (100 - 350) R☉ Luminosity 416,000-790,000 L☉ Temperature 7,900-21,900 K Rotational velocity (v sin i) 150 km/s Other designations HR Car, HD 90177, HIP 50843, SAO 238005, CD-59 3044, GC 14276, MWC 202, AAVSO 1019-59 Database references SIMBAD data HR Carinae is a luminous blue variable star located in the constellation Carina. It is surrounded by a vast nebula of ejected nuclear-processed material because this star has a multiple shell expanding atmosphere. This star is among the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. It has very broad emission wings on the Balmer lines, reminiscent from the broad lines observed in the spectra of O and Wolf–Rayet stars. A distance of 5 kpc and a bolometric magnitude of -9.4 put HR Car among the most luminous stars of the galaxy. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo
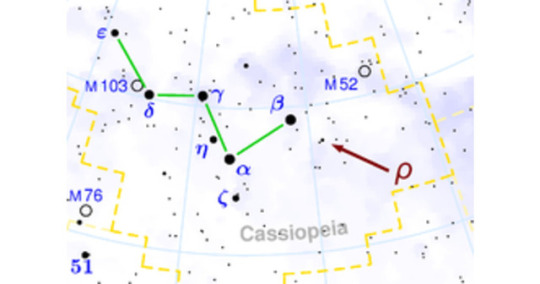
Rho Cassiopeiae
Rho Cassiopeiae Location of Rho Cassiopeiae in the Cassiopeia constellation. Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Cassiopeia Right ascension 23h 54m 23.0s Declination +57° 29′ 58″ Apparent magnitude (V) 4.1 to 6.2 Characteristics Spectral type G2Iae (F8pIa-K0pIa-0) U−B color index 1.15 B−V color index 1.26 Variable type SRd Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −47 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −4.54 mas/yr Dec.: −3.45 mas/yr Parallax (π) 0.28 ± 0.58 mas Distance 2,500 pc Absolute magnitude (MV) –9.5 Details Mass 14-30 M☉ Radius 400-500 R☉ Luminosity ~500,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 0.1 cgs Temperature 5777-7200 K Metallicity [Fe/H] 0.3 dex Rotational velocity (v sin i) 25 km/s Other designations 7 Cassiopeiae, HR 9045, BD+56°3111, HD 224014, SAO 35879, FK5 899, HIP 117863, GC 33160 Database references SIMBAD data Rho Cassiopeiae (/ˌroʊ kæsiəˈpiː.iː/; ρ Cas, ρ Cassiopeiae) is a yellow hypergiant star in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is about 8,200 light-years (2,500 pc) from Earth, yet can still be seen by the naked eye as it is 500,000 times brighter than the Sun. On average it has an absolute magnitude of −9.5, making it visually one of the brightest stars known. Its diameter measures 450 times that of the Sun, approximately 630,000,000 kilometers, or about twice the size of the Earth's orbit. Rho Cassiopeiae is a single star, and is categorized as a semiregular variable. As a yellow hypergiant, it is one of the rarest types of stars. Only around a dozen are known in the Milky Way, but it is not the only one in its constellation which also contains V509 Cassiopeiae. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

HR 5171
HR 5171 Combined optical and infrared image Credit: ESO/Digitized Sky Survey 2 Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 Constellation Centaurus A Right ascension 13h 47m 10.875s Declination −62° 35′ 23.06″ Apparent magnitude (V) 6.1 - 7.5 B Right ascension 13h 47m 10.224s Declination −62° 35′ 17.40″ Apparent magnitude (V) 9.83 Characteristics A Spectral type K0 0-Ia B−V color index +2.499 Variable type EB + SDOR? B Spectral type B0 Ibp B−V color index +0.39 Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −38.20 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −2.94 mas/yr Dec.: −-2.54 mas/yr Parallax (π) 1.35 ± 1.59 mas Distance 11,700 ly (3,600 pc) Absolute magnitude (MV) −9.2 + −5.8 Orbit Primary Aa Companion Ab Period (P) 1,304 ± 6 days Semi-major axis (a) ~2,000 R☉ Eccentricity (e) 0 Inclination (i) >60° Details Aa Mass 60 - 74 M☉ Radius 1,315 ± 260 R☉ Luminosity 500,000 - 1,000,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 0 cgs Temperature 5,000 K Ab Mass 3 - 6 M☉ Radius 312 - 401 R☉ Temperature 4,800 - 5,200 K Age 3.5 Myr B Luminosity 316,000 L☉ Surface gravity (log g) 3.0 - 3.5 cgs Temperature 26,000 K Age 4 Myr Other designations V766 Cen, HR 5171, HD 119796, HIP 67261, SAO 252448, CD−61°3988, WDS J13472-6235, AAVSO 1340-62 Database references SIMBAD data HR 5171, also known as HD 119796 and V766 Centauri, is a triple star system in the constellation Centaurus, around 12,000 light years from Earth. It contains the largest known yellow hypergiant star which is also an eclipsing binary. More details Android, Windows
0 notes
Photo

Pistol Star
Pistol Star False-color image of the Pistol Star and Pistol Nebula Credit: HST NICMOS Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 Constellation Sagittarius Right ascension 17h 46m 15.3s Declination −28° 50′ 04″ Apparent magnitude (V) >28 Characteristics Spectral type LBV Apparent magnitude (J) 11.828 Apparent magnitude (H) 8.920 Apparent magnitude (K) 7.291 Variable type cLBV Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) +130 km/s Distance 8,000 pc Details Mass 27.5 M☉ Radius 306 R☉ Luminosity 1,600,000 L☉ Temperature 11,800 K Metallicity [Fe/H] 0.1 dex Age ~4×106 years Other designations V4647 Sgr, qF 134, 2MASS J17461524-2850035 Database references SIMBAD data The Pistol Star is a blue hypergiant and is one of the most luminous known stars in the Milky Way. It is one of many massive young stars in the Quintuplet cluster in the Galactic Center region. The star owes its name to the shape of the Pistol Nebula, which it illuminates. It is located approximately 25,000 light years from Earth in the direction of Sagittarius. It would be visible to the naked eye as a fourth magnitude star if it were not for the interstellar dust that completely hides it from view in visible light. More details Android, Windows
0 notes