#10base2
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Difference between coax connectors and Network connectors?
Certainly, here are the key differences between coaxial connectors and network connectors:
Coaxial Connectors:

Physical Structure: Coaxial connectors are designed for coaxial cables, which consist of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, a conductive shield, and an outer insulating layer.
Applications: They are commonly used in cable television (CATV), satellite TV installations, broadband internet connections, and some older networking technologies like 10BASE2 Ethernet.
Transmission Medium: Coaxial cables use a single conductor to transmit data signals and are capable of supporting a wide range of frequencies, making them suitable for high-bandwidth applications.
Connector Types: Common coax connectors include F-type connectors, BNC connectors, and RCA connectors, each with its specific applications and characteristics.
Shielding: Coaxial cables offer excellent electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding due to the conductive shield surrounding the central conductor, which helps minimize signal loss and interference.
Network Connectors

Physical Structure: Network connectors are typically used for twisted pair Ethernet cables, which consist of multiple pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together.
Applications: They are primarily used in Ethernet networks for connecting computers, routers, switches, and other network devices in homes, offices, data centers, etc.
Transmission Medium: Twisted pair cables use multiple insulated copper wire pairs twisted together, providing good resistance to electromagnetic interference and crosstalk.
Connector Types: The most common network connector is the RJ45 connector, standardized for Ethernet connections. It has eight pins and is used for both Ethernet and telephone connections.
Speed and Standards: Network connectors are used in various Ethernet standards, including 10/100 Mbps Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps), 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps), and beyond, offering scalable speeds to meet different network requirements.
In summary, coaxial connectors are used for coaxial cable-based networks, offering high bandwidth and EMI shielding, while network connectors like RJ45 are specifically designed for Ethernet networks, providing flexibility and scalability in speed and standards.
0 notes
Photo
You want to set up the world's most complex active switching 10base2 network.
More modern same thing with moca.
No idea how the video switch does it's routing... but if it can handle the bandwidth, it would be pretty darn unique.


Why do I have 3 of these Knox 8x8′s, and a Knox Chameleon 48x48?
I don’t need 4 composite video routing switchers, and yet here we are…
25 notes
·
View notes
Photo

I remember wired this once...
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
I dreamed I was trying to set up a 10base2 ("thinnet") but sadly I woke up before I could get it working.
You always wake up before the good bit.
159 notes
·
View notes
Photo


3 notes
·
View notes
Text
you would definitely have a BNC port, but whether it would be used for 10base2 ethernet or video or radio frequency connections up to 2ghz/500v, I can't say
trans people get gender euphoria from wearing clothes or voice training, but as a trans robot i get gender euphoria from thinking about what kind of I/O ports i would have
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transceiver

The transceiver is a term that was utilized in electronic radio interchanges characterizing a unit that contains both a recipient and a transmitter. From the start long periods of radio, the collector and transmitter were independent units and remained so until around 1920. On a cell phone, the whole unit is a transceiver, for both sound and radio.
transceivers are called Medium Attachment Units (MAUs) in IEEE 802.3 archives and were broadly utilized in 10BASE2 and 10BASE5 Ethernet organizations. Fiber-optic gigabit, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, 40 Gigabit Ethernet, and 100 Gigabit Ethernet use transceivers known as GBIC, SFP, SFP+, QSFP, XFP, XAUI, CXP, and CFP. SFP transceivers (little structure factor pluggable) are modules that demonstration to associate the electrical hardware of the module with the optical or copper organization, generally utilized for both media transmission and information correspondences applications.
Read the full article here:
https://www.gbic-shop.de/blog/en/94-transceivers/258-why-transceivers-are-widely-used-in-communication.html
0 notes
Photo
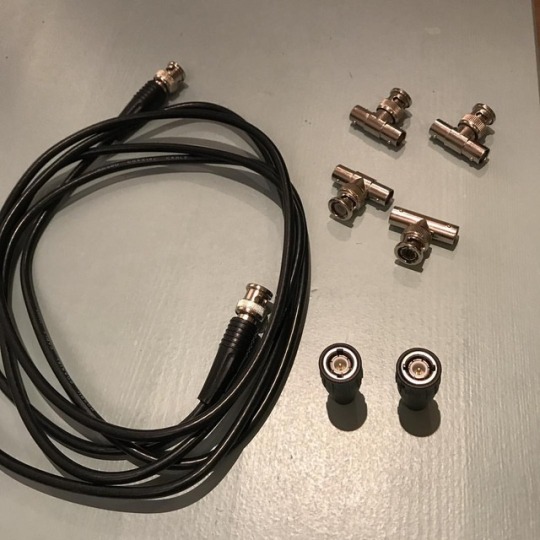

#cleanup time! Goodbye #10base2 #cables #ancienthistory #ethernet
0 notes
Text
The New Basis of Industrial Connectivity and Networking Solutions
With the Industrial Internet of Things fast becoming the norm in industries, converging IT and OT technologies securely—a cornerstone of the IIoT—is still the Achilles heel for many companies. Thus, choosing the right industrial network solutions for your operation, and this cannot be repeated often enough, is essential. At the same time, this is easier said than done. Too often, this arduous task befalls an IT engineer with little experience of OT protocols and automation systems, or, on the flip side, an OT engineer with no knowledge of enterprise IT networking. In this article, we take a closer look at how new technologies are shaping the role of industrial connectivity and networking solutions in your IIoT applications.
Industrial Connectivity Needs—Now and in the Future
Connecting your previously unconnected industrial devices and assets is the first step to enabling IIoT applications. Accomplishing this task requires a thorough assessment of the types of OT assets you need to connect as well as the specific connectivity requirements, such as connecting OT assets to a local network or a cloud server. Since OT assets in industrial applications mainly use serial or I/O communication interfaces, choosing the right serial and I/O connectivity solutions is essential to enable industrial connectivity. Moreover, you need to keep in mind additional considerations, such as cybersecurity and large-scale device management, when connecting OT assets to remote or cloud servers.
Besides enabling connectivity for previously unconnected OT assets, connecting all of these field devices also requires building a network that can support information flows among multiple interconnected devices, systems, and even remote sites.
Suitable Solutions
With more than thirty years of experience in helping customers overcome industrial connectivity and networking challenges, we have identified several key criteria for selecting the most suitable solutions for industrial automation applications. Download our E-book where you can find considerations for each specific connectivity and networking solution you are looking for.
Before we come to the comparison between inline couplers and keystone jacks, let’s have a brief overview of these two jacks. A small device for connecting two ethernet cables to make a longer cable, usually called an inline coupler or RJ45 coupler. Inline couplers do not provide any amplification or signal boost, and can cause attenuation and signal degradation unless they are of high quality. There are cat5e and cat6 RJ45 inline couplers available on the market.
People who have electrical cable installation experience know clearly what is a keystone jack. A keystone jack is a female connector for mounting a variety of low-voltage electrical jacks or optical connectors into a keystone wall plate, faceplate, surface-mount box or patch panel. A keystone plug is a matching male connector, usually attached to the end of a cable or cord. Traditional keystone jack needs a punch-down tool to help finish cable installation, but this toolless STP keystone jack is different. With the snap-fit cap design, conductors can be terminated simultaneously when the cap is pressed into place, allowing for a simple installation without the need for a punch-down tool.
The eight-position modular plug uses insulation displacement contacts that terminate the conductors and provide the contact interface surface for the mating jack contacts. These plugs are crimp-terminated onto cordage or cable. With these new technologies, we are witnessing the conversion of many commercial building devices and systems from analog, to digital, and now IP-addressable. The resulting migration of these devices and systems to four-twisted-pair cabling represents an additional class of equipment looking to be served by versions of communication cabling.
A network wall plate is a cabling fixture attached to a wall in a work area for connecting computers to the network. Also called a faceplate. Wall Plates can have RJ-45 jacks for 10BaseT networks (which resemble household RJ-11 telephone wall jacks), BNC jacks for 10Base2 networks, or SC jacks for networks that use fiber-optic cabling. The back end of the connector joins a horizontal cable that runs inside the wall or through a false ceiling or floor to a patch panel in the wiring closet for that floor. Computers are then connected to the wall plate by a short unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable called a drop cable. Wallplates typically come in mono-port, dual-port, and quad-port configurations.
0 notes
Text
five paragraphs explaining 10base2/10base5 technologies. uh, this stuff was updated for 2015? ..... are there places seriously still using this stuff and that’s why it’s on tests? mark my fucking worms, i hope not
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Estrela
Na topologia de rede designada por rede em estrela, toda a informação deve passar obrigatoriamente por uma estação central inteligente, que deve conectar cada estação da rede e distribuir o tráfego para que uma estação não receba, indevidamente, dados destinados às outras. É neste aspecto que esta topologia difere da topologia barramento: uma rede local que use um hub não é considerada como estrela, pois o tráfego que entra pela porta do hub é destinado a todas as outras portas. Porém, uma rede que usa switches, apenas os dados destinados àquele nó são enviados a ele. Portanto, ao se medir o desempenho por meio da resiliência, é possível obter, com uma topologia em estrela, melhor desempenho que aquele obtido com uma topologia em barramento.

A topologia em estrela é caracterizada por um elemento central que "gerencia" o fluxo de dados da rede, estando diretamente conectado (ponto-a-ponto) a cada nó, daí surgiu a designação "Estrela". As informações trafegam na rede de um host para o outro. Toda informação enviada de um nó para outro é enviada primeiro ao dispositivo que fica no centro da estrela, portanto os dados não passam por todos os hosts. O concentrador encarrega-se de encaminhar o sinal especificamente para as estações solicitadas, economizando tempo. Existem também redes estrela com conexão passiva (similar ao barramento), na qual o elemento central nada mais é do que uma peça mecânica que atrela os "braços" entre si, não interferindo no sinal que flui por todos os nós, da mesma forma que o faria em redes com topologia barramento. Mas este tipo de conexão passiva é mais comum em redes ponto-a-ponto lineares, sendo muito pouco utilizado já que os dispositivos concentradores (HUBs, Multiportas, Pontes e outros) não apresentam um custo tão elevado se levarmos em consideração as vantagens que são oferecidas.As redes em estrela, que são as mais comuns hoje em dia, utilizam cabos de par trançado e uma switch como ponto central da rede. O hub se encarrega de retransmitir todos os dados para todas as estações, mas com a vantagem de tornar mais fácil a localização dos problemas, já que se um dos cabos, uma das portas do hub ou uma das placas de rede estiver com problemas, apenas o PC ligado ao componente defeituoso ficará fora da rede, ao contrário do que ocorre nas redes 10Base2, onde um mau contato em qualquer um dos conectores derruba a rede inteira.
0 notes
Photo

انواع کابل شبکه
Networking cables، به صورت کلی، براساس نحوه عملکرد و ابعاد، از نازک تا ضخیم، تولید و عرضه شدهاند به طوری که هرکدام از آنها را در شرایط خاص میتوان استفاده کرد و از مزایای آنها بهره برد.
از جمله مدلهای بسیار پرکاربرد میتوان به Networking cables با استانداردها و نامهای 10BASE2، 10BASE5 و 10BASE35 اشاره کرد که هرکدام از آنها، ویژگیهای کاملا منحصر به فردی را به کاربران میدهند که برای استفاده حد��کثری، باید به این استانداردها و براساس تجهیزات مورد استفاده در شبکه، توجه کرد.
از جمله مهمترین تفاوتهایی که در این کابلهای شبکه باید به آن اشاره کرد، مسافت قابل انتقال سیگنال است به طوری که کابلهای شبکه 10BASE2، نهایتا تا 185 متر، کابلهای شبکه 10BASE5 تا 500 متر، و کابلهای 10BASE35 تا 3600 متر میتوانند اطلاعات را انتقال دهند.
0 notes
Text
The function of Wanli HUB, what will it bring to you with the 8-in-1 port?
A hub is a device that connects multiple Ethernet twisted pairs or optical fibers together under the same physical medium. The hub is the physical layer operating in the OSI model. It can be regarded as a multi-port repeater, if it detects a collision, it will submit a blocking signal. The hub usually attaches a BNCand/orAUI adapter to connect to a traditional 10BASE2 or 10BASE5 network.

Since the hub will regenerate or amplify any digital signal received, and then submit it from all ports of the hub, this will cause a great chance of collision between the signals, and the signal may also be eavesdropped, and this means all connected to the hub The devices belong to the same collision domain name and broadcast domain name, so most hubs have been replaced by switches.

HUB hub function The main function of the HUB hub is to regenerate, reshape, and amplify the received signal to expand the transmission distance of the network while concentrating all nodes on the node centered on it. It works on the first layer of the OSI (Open System Interconnection Reference Model) reference model, the "physical layer".
0 notes
Text
TP線(ケーブル)て言うよね!? 10BASE2とか10BASE5とかも通じない時代。。
TP線(ケーブル)て言うよね!? 10BASE2とか10BASE5とかも通じない時代。。 #LAN #TPケーブル #ブログ更新:
システム関係の仕事してると、ときどきあるノスタルジアトーク。 普通に使ってた「TP線」てことばの意味を説明しても、イマドキ世代には響かなかったw
TPケーブル
ツイストペアケーブルってわざわざ言うってことは、そーじゃないヤツがいたんだよ。 「同軸ケーブル」ってね。テレビのアンテナ接続線みたいなの。
規格品でさあ。リピーターが必要とかって話も。。 自分も聞いただけで、TP線か光ファイバーしか扱ったことないけど。。
ツイストペアケーブルと同軸ケーブル
ネットワーク関係の資格の勉強でもしない限り出てこない話なのか。 てか、もはや無線LANが普通になっちゃ��て、オフィスじゃケーブル自体見ないって!?
昔は、それぞれのパソコンにLANケーブルを挿してたんだよ。
さらに昔は、もっと大きなコネクターだった。
ツイストペアケーブルは、いわゆるLANケーブルってやつ。TPケーブル。てーぴーせん、…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Parte de un cable Top- Descripcion
Cable de par trenzado sin apantallar / Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
El cable par trenzado es un tipo de cable eléctrico que se usa en telecomunicaciones básicamente por su capacidad para cancelar las interferencias o la diafonía con cables cercanos. Se explica de qué forma funciona el cable par trenzado, qué es, sus aplicaciones, partes, estructuras y más. Los cables de RF son un tipo de cable coaxial que se usa para enviar señales de frecuencia de radio.
Composición de los cables coaxiales
Estos frecuentemente se usan para enviar información de video a un aparato de TV. Se refiere exactamente al conector que se une al cable telefónico y tiene 6 situaciones con cuatro contactos centrales por los cuatro hilos del cable telefónico, aunque normalmente se utilizan sólo dos (los 2 centrales).
¿Cuál es la fibra óptica?

El roentgenio (anteriormente llamado Ununumio o Ununio, Uuu) es un elemento químico del grupo 11 de la tabla periódica cuyo símbolo es Rg y su número atómico es 111. También tenía asignado el nombre de plutirio con el símbolo Pl al no ser oficial.
Conector para cable coaxial
Elgrosor del cable coaxialva desde 5mm los más finos hasta media pulgada los más gruesos.
Estos de forma frecuente se emplean para enviar información de video a un aparato de TV.
El cable coaxial se ha diseñado para transportar señales de alta frecuencia y para protegerlas frente a las interferencias electromagnéticas de fuentes externas.
Imaginar un mundo sin cables eléctricos es misión imposible, puesto que actualmente la electricidad es el tipo de energía más empleado en la vida rutinaria.
Existen múltiples géneros de cable coaxial, cada uno con un diámetro y también impedancia diferentes.

El cable coaxial no es habitualmente perjudicado por interferencias externas, y es capaz de conseguir grandes velocidades de transmisión de datos a grandes distancias. Por esa razón, se emplea en redes de comunicación de banda ancha (CATV) y cables de banda base (Ethernet). Vamos a hablarte de los tipos deconectores coaxialesque existen para dicho género de cable. Un profundo análisis sobre lasopciones disponiblesparabanda base para banda ancha.
PARTES DE UN CABLE
Imaginar un mundo sin cables eléctricos es misión imposible, en tanto que hoy día la electricidad es el tipo de energía más empleado en la vida cotidiana. Este invento cambió el mundo por completo, mejorando el bienestar de cada humano.
¿Cuándo fue creado el cable coaxial?
youtube
RG-6/U es un tipo común de cable coaxial utilizado en una amplia variedad de aplicaciones residenciales y comerciales. En la práctica, el término RG-6 se utiliza generalmente para referirse a los cables coaxiales con un conductor central 18 de AWG y 75 ohmios de impedancia característica.
Empleados en las redes de transmisión de datos como Ethernet en sus viejas versiones 10BASE2 y 10BASE5. En las redes telefónicas interurbanas y en los cables submarinos. Son conectores hechos para cables de un mayor blindaje, que puede abarcar velocidades mayores y tramos más largos. Haydos clases de cables coaxialesque se emplean en este tipo de conectores, una es la de cable de50 ohmsque se utiliza en general par transmisión digital, y la otra es la de cable de75 ohmsmás utilizada en transmisión equivalentes. Se trata de un conector de plástico similar al conector del cable telefónico.
0 notes
Text
Networking - Ethernet

Ethernet adalah sistem jaringan yang dibuat dan dipatenkan perusahaan Xerox. Ethernet merupakan implementasi metoda CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) yang dikembangkan tahun 1960 pada proyek wireless ALOHA di Hawaii University diatas kabel coaxial. Standarisasi sistem ethernet dilakukan sejak tahun 1978 oleh IEEE. Kecepatan transmisi data di ethernet sampai saat ini adalah 10 sampai 100 Mbps. Saat in yang umum ada dipasaran adalah ethernet berkecepatan 10 Mbps yang biasa disebut seri 10Base. Ada bermacam-macam jenis 10Base diantaranya adalah: 10Base5, 10Base2, 10BaseT, dan 10BaseF yang akan diterangkan lebih lanjut kemudian. Pada metoda CSMA/CD, sebuah host komputer yang akan mengirim data ke jaringan pertama-tama memastikan bahwa jaringan sedang tidak dipakai untuk transfer dari dan oleh host komputer lainnya. Jika pada tahap pengecekan ditemukan transmisi data lain dan terjadi tabrakan (collision), maka host komputer tersebut diharuskan mengulang permohonan (request) pengiriman pada selang waktu berikutnya yang dilakukan secara acak (random). Dengan demikian maka jaringan efektif bisa digunakan secara bergantian. Untuk menentukan pada posisi mana sebuah host komputer berada, maka tiap-tiap perangkat ethernet diberikan alamat (address) sepanjang 48 bit yang unik (hanya satu di dunia). Informasi alamat disimpan dalam chip yang biasanya nampak pada saat komputer di start dalam urutan angka berbasis 16.

Contoh ethernet address 48 bit angka agar mudah dimengerti dikelompokkan masing-masing 8 bit untuk menyetakan bilangan berbasis 16 seperti contoh di atas (00 40 05 61 20 e6), 3 angka didepan adalah kode perusahaan pembuat chip tersebut. Chip diatas dibuat oleh ANI Communications Inc. Untuk informasi lebih lengkap lainnya dapat diperoleh di http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.html

Daftar vendor terkenal chip ethernet Dengan berdasarkan address ehternet, maka setiap protokol komunikasi (TCP/IP, IPX, AppleTalk, dll.) berusaha memanfaatkan untuk informasi masing-masing host komputer di jaringan. 10Base5 Sistem 10Base5 menggunakan kabel coaxial berdiameter 0,5 inch (10 mm) sebagai media penghubung berbentuk bus. Biasanya kabelnya berwarna kuning dan pada kedua ujung kebelnya diberi konsentrator sehingga mempunyai resistansi sebesar 50 ohm. Jika menggunakan 10Base5, satu segmen jaringan bisa sepanjang maksimal 500 m, bahkan jika dipasang penghubung (repeater) sebuah jaringan bisa mencapai panjang maksimum 2,5 km.
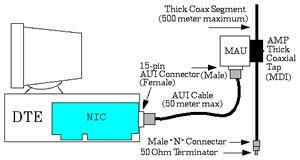
Jaringan dengan media 10Base5 Antara NIC (Network Interface Card) yang ada di komputer (DTE, Data Terminal Equipment) dengan media transmisi bus (kabel coaxial)-nya diperlukan sebuah transceiver (MAU, Medium Attachment Unit). Antar MAU dibuat jarak minimal 2,5 m, dan setiap segment hanya mampu menampung sebanyak 100 unit. Konektor yang dipakai adalah konektor 15 pin.
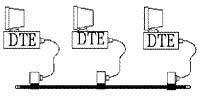
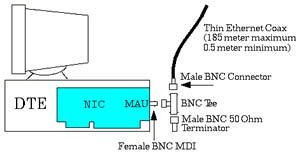
Struktur 10Base5 10Base2 Seperti pada jaringan 10Base5, 10Base2 mempunyai struktur jaringan berbentuk bus. Hanya saja kabel yang digunakan lebih kecil, berdiameter 5 mm dengan jenis twisted pair. Tidak diperlukan MAU kerena MAU telah ada didalam NIC-nya sehingga bisa menjadi lebih ekonomis. Karenanya jaringan ini dikenal juga dengan sebutan CheaperNet.
Jaringan dengan media 10Base2 Dibandingkan dengan jaringan 10Base5, panjang maksimal sebuah segmennya menjadi lebih pendek, sekitar 185 m, dan bisa disambbung sampai 5 segmen menjadi sekitar 925 m. Sebuah segmen hanya mampu menampung tidak lebih dari 30 unit komputer saja. Pada jaringan ini pun diperlukan konsentrator yang membuat ujung-ujung media transmisi busnya menjadi beresistansi 50 ohm. Untuk jenis konektor dipakai jenis BNC.
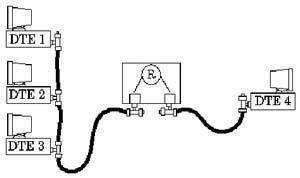
Struktur 10Base2 10BaseT Berbeda dengan 2 jenis jaringan diatas, 10BaseT berstruktur bintang (star). Tidak diperlukan MAU kerena sudah termasuk didalam NIC-nya. Sebagai pengganti konsentrator dan repeater diperlukan hub karena jaringan berbentuk star. Panjang sebuah segmen jaringan maksimal 100 m, dan setiap hub bisa dihubungkan untuk memperpanjang jaringan sampai 4 unit sehingga maksimal komputer tersambung bisa mencapai 1024 unit.

Jaringan dengan media 10BaseT
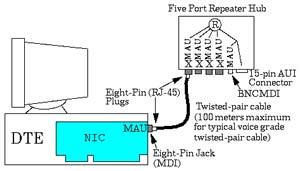
Struktur 10BaseT Menggunakan konektor modular jack RJ-45 dan kabel jenis UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) seperti kabel telepon di rumah-rumah. Saat ini kabel UTP yang banyak digunakan adalah jenis kategori 5 karena bisa mencapai kecepatan transmisi 100 Mbps.

Jenis kabel UTP dan aplikasinya.

Contoh perangkat 10base5 10base2 10baseT 10BaseF Bentuk jaringan 10BaseF sama dengan 10BaseT yakni berbentuk star. Karena menggunakan serat optik (fiber optic) untuk media transmisinya, maka panjang jarak antara NIC dan konsentratornya menjadi lebih panjang sampai 20 kali (2000 m). Demikian pula dengan panjang total jaringannya. Pada 10BaseF, untuk transmisi output (TX) dan input (RX) menggunakan kabel/media yang berbeda.
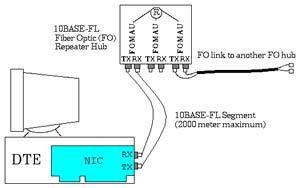
Struktur 10BaseF Fast Ethernet (100BaseT series) Selain jenis NIC yang telah diterangkan di atas, jenis ethernet chip lainnya adalah seri 100Base. Seri 100Base mempunyai beragam jenis berdasarkan metode akses datanya diantaranya adalah: 100Base-T4, 100Base-TX, dan 100Base-FX. Kecepatan transmisi seri 100Base bisa melebihi kecepatan chip pendahulunya (seri 10Base) antara 2-20 kali (20-200 Mbps). Ini dibuat untuk menyaingi jenis LAN berkecepatan tinggi lainnya seperti: FDDI, 100VGAnyLAN dan lain sebagainya. Read the full article
0 notes