#Agentic AI Artificial Intelligence Autonomous AI Smart Technology AI Revolution AI in Industries Future of AI AI Automation AI Assistants Se
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
AI That Knows What You Need Before You Do
Check out how Agentic AI tech is making waves across industries! 🚗💡 #AgenticAI #AI #TechInnovation #TechnologyTrends #AutonomousSystems #Tech Transformation
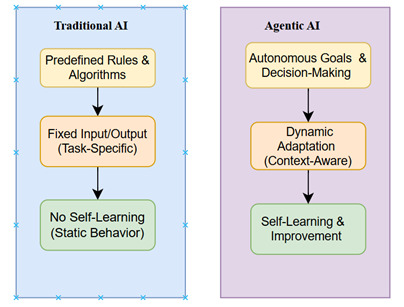
Suppose your coffee machine decides when you must have a caffeine boost—if it were up to me, I’d be the happiest person. So Meet Agentic AI, the smart technology that doesn’t wait for you to give it instructions. It says, “You don’t tell me what to do, I tell you what to do!” 😊 Unlike traditional AI assistant that responds to prompts, Agentic AI is A smart assistant that, along with responding…
View On WordPress
#Agentic AI#Agentic AI Artificial Intelligence Autonomous AI Smart Technology AI Revolution AI in Industries Future of AI AI Automation AI Assistants Se#AI Assistants#AI Automation#AI Decision-Making#AI in Finance#AI in Healthcare#AI in Industries#AI in Supply Chain#AI Innovations#AI Personalization#AI Revolution#Artificial Intelligence#Autonomous AI#Autonomous Systems#Future of AI#machine learning#Self-Driving Cars#Smart Technology#Tech Transformation#Technology Trends
1 note
·
View note
Text
End-to-End Automation Made Easy with Agentic AI Services
Introduction to Agentic AI Services
Welcome to the future, where automation isn’t just smart, it’s agentic. In a world increasingly run by artificial intelligence, Agentic AI services are leading a revolution in how businesses operate, scale, and serve customers. Please explain what agentic AI is and why it is increasingly becoming the preferred solution for companies globally.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to autonomous software agents capable of making decisions, adapting in real-time, and performing tasks with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional automation, these agents act independently, analyze complex situations, and take appropriate actions on their own.
Imagine empowering your AI with a driver's license and placing your trust in it not to crash.
The Rise of Agentic AI Services
From chatbots to workflow automation, businesses have dabbled in AI for years. However, agentic AI services redefine the industry by providing comprehensive automation across departments without the need for micromanagement.
Why now? Simple. The tech has caught up, and the demand for efficiency is skyrocketing.
Agentic AI vs Generative AI
Definitions and Core Differences:
Here’s a common confusion: agentic AI vs. generative AI. Let's clarify this matter.
Generative AI creates content—text, images, and code. Think ChatGPT or Midjourney.
Agentic AI takes actions—managing systems, making decisions, and executing strategies.
Both are smart. But one’s your brainstorming buddy, and the other’s your reliable project manager.
Use Cases of Agentic AI and Generative AI
Generative AI: content marketing, creative writing, art generation.
Agentic AI: Automating IT workflows, handling customer service, and managing operations.
Why Choose Agentic AI for Automation?
Agentic AI goes beyond mere thought. It acts—intelligently and autonomously.
Core Features of Agentic AI Services
Autonomous Decision-Making Capabilities:
Agentic systems don’t wait for you to press “Go.” They identify problems, analyze options, and move forward based on logic, context, and data.
Context Awareness and Adaptability:
These agents aren’t rigid bots. They’re adaptive—learning from their environment and changing behavior accordingly. That’s next-level intelligence.
Real-Time Learning and Optimization:
Imagine an employee who continuously learns, never sleeps, and consistently improves. That’s what you get with agentive AI.
Agentive AI in the Real World
Use of Agentive AI in Enterprise Solutions:
Whether you're running a global enterprise or a growing startup, agentive AI brings personalized, scalable solutions—cutting manual work and boosting performance.
Here are some examples of companies that provide Agentic AI services and their success stories:
Companies like UiPath, Replikant, and Adept AI are setting standards in agentic AI services, offering frameworks that empower autonomous agents across industries.
AI Agent Development Companies Driving Innovation
Top AI Agent Development Company Trends:
Modern AI agent development companies are blending machine learning, NLP, and decision science to craft next-gen solutions.
Custom Agentic AI Solution Development:
Need something specific? Custom-built Agentic AI solutions ensure your automation aligns perfectly with business goals.
Agentic AI in Sales and Marketing
Agentic AI Sales Automation:
Agentic AI in sales means leads get nurtured, follow-ups are instant, and deals close faster—all while your team focuses on strategy, not spreadsheets.
Boosting Customer Engagement and Conversion Rates:
Imagine a sales rep that knows every client’s preferences, history, and needs—available 24/7. That’s the power of agentic AI sales tools.
Agentic AI in Service and Support
Agentic Technology in Service Workflows:
Forget clunky ticket systems. Agentic technology in service allows real-time routing, prioritization, and resolution.
Using Agentic AI for Service Personalization:
Each customer feels heard. That’s because Agentic AI for service adapts its responses based on user sentiment, history, and intent.
Agentic AI Copilot for Customer Support Teams
Support teams love their Agentic AI copilot—an assistant that suggests solutions, flags issues, and learns from each interaction.
Vision AI Systems for Manufacturing
Vision AI solutions for manufacturing bring visual intelligence to production lines—detecting flaws, tracking components, and predicting failures before they happen.
AI Vision System in Quality Control and Efficiency
Say goodbye to human error. An AI vision system ensures consistent quality, optimized processes, and massive efficiency gains.
Benefits of End-to-End Automation with Agentic AI
Enhanced Productivity and Scalability:
From HR to logistics, end-to-end automation with Agentic AI services scales effortlessly—without expanding your workforce.
Cost Reduction and ROI
Fewer errors, faster workflows, and leaner teams = major cost savings. The ROI on Agentic AI solutions is evident.
Human-AI Collaboration
Humans plus agentive AI equals magic. It’s not about replacing jobs—it’s about upgrading them.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Privacy and Security:
With great power comes enormous responsibility. Protecting user data in Agentic AI services is non-negotiable.
Ethical Implications of Autonomous Agents
What happens when AI makes a disastrous decision? Designing ethical boundaries is key to responsible AI agent development.
Future of Agentic AI:
Trends to Watch
Expect smarter, more specialized agents. Integration with IoT, blockchain, and vision AI systems will reshape automation.
What’s Next for AI Agent Development Companies?
The competition is underway. Leading AI agent development companies are building the foundation for AI-driven enterprises of tomorrow.
Conclusion:
Agentic AI isn’t just another tech trend—it’s the future of intelligent automation. Whether you're running a sales team, a support desk, or a factory floor, Agentic AI services can simplify operations, boost efficiency, and unlock massive value.
FAQs:
1. What is the difference between agentic AI and generative AI? Agentic AI acts autonomously, while generative AI creates content. One type of AI makes decisions, while the other type creates content.
2. Can small businesses use agentic AI? Absolutely. Scalable solutions exist for companies of all sizes—from startups to enterprises.
3. How secure are Agentic AI services? With proper implementation, agentic AI can meet top-tier data security standards, including encryption and compliance protocols.
4. What industries benefit most from agentic AI solutions? Sales, customer service, manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare are seeing massive gains.
5. How do I choose the right AI agent development company? Search for experience, scalability, industry fit, and customization options in their portfolio.
#Agentic ai services#agentic ai#agentic ai vs generative ai#agentic ai companies#Agentic AI Solutions#Agentic AI in Sales#Agentic Technology in Service#Agentic AI Copilot#Agentic AI for Service
0 notes
Text
How AI Agent Development Is Revolutionizing Automation and Decision-Making
Artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept into a transformative force across industries. Among its most impactful innovations is AI agent development—an area that is revolutionizing automation and decision-making. AI agents are intelligent software systems capable of autonomously performing tasks, making decisions, and interacting with users or other systems. Their growing capabilities are reshaping how businesses operate, optimizing processes, and unlocking new levels of efficiency.

What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are software entities that use artificial intelligence to perceive their environment, process information, and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents can be:
Reactive Agents: Respond to stimuli in real-time without retaining past information.
Deliberative Agents: Use reasoning and planning to make informed decisions.
Learning Agents: Adapt and improve over time using machine learning techniques.
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS): A network of agents that collaborate to complete complex tasks.
From customer service chatbots to autonomous supply chain managers, AI agents are proving their versatility across industries.
How AI Agents Are Revolutionizing Automation
1. Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
AI agents automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex, strategic work. Businesses are leveraging AI-driven automation in areas such as:
Customer Support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants handle inquiries, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Management: AI agents optimize logistics, manage inventory, and predict demand fluctuations.
Finance & Accounting: Intelligent agents process transactions, detect fraud, and automate financial reporting.
2. Intelligent Decision-Making
Traditional automation follows predefined rules, but AI agents take it further by making data-driven decisions. By analyzing vast amounts of real-time data, AI agents:
Identify patterns and anomalies in financial markets.
Optimize energy usage in smart grids.
Provide personalized recommendations in e-commerce and healthcare.
3. Real-Time Adaptation and Learning
Unlike static automation tools, AI agents can learn and improve continuously. They refine their decision-making strategies based on new data, making them invaluable for:
Cybersecurity: AI-driven security agents detect and respond to threats dynamically.
Healthcare: AI models analyze patient data to suggest tailored treatments.
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving systems continuously adapt to road conditions.
The Future of AI Agent Development
As AI technology advances, AI agents will become even more sophisticated. Key trends shaping the future include:
Integration with IoT: AI agents will manage smart cities, homes, and industries more efficiently.
Advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI agents will better understand and generate human language, making interactions seamless.
Greater Autonomy: AI agents will make more complex decisions with minimal human intervention.
Conclusion
AI agent development is at the forefront of the automation revolution, driving efficiency, intelligence, and adaptability in decision-making. As businesses embrace AI-powered agents, they gain a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven world. Whether in customer service, healthcare, finance, or beyond, AI agents are shaping the future of automation and decision-making—ushering in an era of smarter, more autonomous systems.
0 notes
Text
AI Agent: Revolutionizing Automation and Intelligence
In an age where artificial intelligence (AI) continues to reshape industries, AI Agents are at the forefront of this technological revolution. These intelligent systems are making waves in automation, personalization, and decision-making processes across various sectors. Whether you're a business owner, tech enthusiast, or someone curious about the future of AI, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about AI Agents and how they're transforming our world.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI Agent is a program or system designed to perform tasks autonomously by mimicking human behavior, understanding context, and responding to real-time inputs. Think of it as a digital assistant with intelligence—capable of learning, reasoning, and adapting over time.
Some everyday examples include:
Chatbots that provide customer support.
Virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri.
Recommendation systems used by Netflix and Amazon. These agents can handle complex tasks and improve decision-making processes, offering a seamless experience.
How Does an AI Agent Work?
1. Perception
AI Agents begin by gathering data from their environment. This could include user queries, historical data, or real-time inputs like images and sounds. The use of machine learning algorithms allows them to process vast amounts of information efficiently.
2. Decision-Making
AI Agents analyze data using natural language processing (NLP), deep learning, and predictive analytics to make informed decisions. For instance, an AI Agent managing a smart home might decide when to turn lights on based on user habits.
3. Action Execution
Once a decision is made, the AI Agent executes the action—sending responses, triggering a task, or alerting users. This combination of automation and adaptability makes these systems invaluable in both personal and professional settings.
Key Applications of AI Agents
1. Customer Service
The role of AI-powered chatbots has become crucial in customer service. They handle queries, offer solutions, and guide users through troubleshooting—all while reducing response times.
Live Chat Integration: Platforms like Zendesk and Intercom use AI to assist customers in real time.
24/7 Availability: Unlike human agents, AI Agents never take a day off.
2. E-Commerce Personalization
In e-commerce, recommendation engines powered by AI Agents enhance user experience. These systems analyze shopping behaviors to suggest relevant products, increasing the chances of conversion.
3. Healthcare Assistance
AI Agents in healthcare have paved the way for virtual health assistants, aiding patients with reminders, basic diagnosis, and appointment scheduling. Examples include IBM’s Watson Health and Ada Health.
4. Smart Homes
Smart home devices rely heavily on AI Agents. From adjusting the thermostat to playing your favorite songs, these systems learn your habits and preferences to provide a customized experience.
5. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars are a prime example of how AI Agents work. They monitor surroundings, predict obstacles, and make real-time decisions to ensure passenger safety.
Benefits of Using AI Agents
1. Increased Efficiency
AI Agents streamline operations, saving time and resources. In industries like logistics and manufacturing, automation leads to faster production cycles.
2. Enhanced Personalization
By analyzing user behavior, AI Agents provide a tailored experience. For instance, music streaming services curate playlists based on your listening habits.
3. Cost Savings
Organizations can reduce operational costs significantly by replacing mundane tasks with AI-driven solutions.
4. Improved Scalability
AI Agents can handle multiple tasks simultaneously without compromising quality, making them an ideal choice for businesses looking to scale.
0 notes
Text

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a distant concept from science fiction—it’s at the forefront of a technological revolution that’s reshaping industries, societies, and even the way we think about the future. From enhancing our daily lives with virtual assistants to revolutionizing complex industries like healthcare, finance, and transportation, AI is ushering in a new era of innovation and efficiency.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the rise of AI, its transformative impact, and how it’s set to revolutionize the world as we know it.
What is the AI Revolution?
The AI revolution refers to the rapid advancement and integration of artificial intelligence technologies in nearly every aspect of life. AI encompasses machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, robotics, and other advanced systems designed to mimic human intelligence, enabling machines to learn from experience, solve complex problems, and perform tasks with increasing autonomy.
From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to self-driving cars, AI’s applications are growing rapidly. Its capabilities are becoming more sophisticated, allowing it to handle tasks that once required human intelligence, and in many cases, even surpassing human abilities in specific domains.
How AI is Transforming Industries
The AI revolution is transforming various sectors, bringing about unparalleled efficiency, innovation, and growth.
Healthcare: A New Era of Medicine AI’s impact on healthcare is profound. AI-driven tools and algorithms are helping doctors and healthcare providers improve patient care, speed up diagnoses, and even predict health issues before they arise. AI technologies are being used for:
Medical Imaging: AI can analyze medical images like X-rays and MRIs with remarkable accuracy, helping doctors detect diseases such as cancer earlier than ever before.
Personalized Medicine: AI helps in creating personalized treatment plans by analyzing patient data and predicting how they will respond to specific drugs.
Drug Discovery: Machine learning algorithms accelerate drug development by predicting how molecules will behave, shortening the time required to bring new drugs to market.
Finance: Revolutionizing Risk Management and Investment The finance industry has embraced AI to enhance decision-making, manage risks, and improve customer service. AI tools help in:
Fraud Detection: AI can detect unusual patterns in financial transactions, identifying potential fraud before it happens.
Algorithmic Trading: AI-driven trading platforms analyze vast amounts of market data in real time, helping traders make faster, more accurate decisions.
Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants offer personalized customer support, answering questions and handling routine transactions 24/7.
Transportation: The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles One of the most exciting aspects of the AI revolution is the development of autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars are already being tested and, in some places, used on roads today. AI algorithms enable these vehicles to make real-time decisions based on traffic conditions, road signs, and pedestrian movements. AI-powered systems also enhance:
Traffic Management: Smart cities use AI to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion, improving overall urban mobility.
Logistics and Delivery: AI is transforming the logistics sector by enabling autonomous delivery drones and trucks, streamlining supply chains and reducing human error.
Retail: Personalized Experiences and Smarter Shopping AI is helping retailers enhance the customer experience by offering personalized shopping journeys, optimizing inventory management, and improving marketing strategies. Key uses include:
Recommendation Engines: E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Netflix use AI to analyze user behavior and suggest products or content based on preferences.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-driven customer service agents can handle inquiries, solve problems, and guide shoppers through the purchasing process.
Inventory Management: AI analyzes purchasing patterns to predict stock needs, preventing overstocking or running out of products.
Education: Personalized Learning and Smarter Classrooms AI is also transforming the education sector by making learning more personalized and accessible:
Smart Tutors: AI-driven platforms can adapt to the learning pace and style of each student, offering personalized learning experiences and support.
Administrative Automation: AI can automate tasks such as grading, scheduling, and student feedback, allowing educators to focus more on teaching and less on administrative duties.
The Role of AI in Our Daily Lives
While AI has massive implications for industries, it’s also playing an increasingly important role in our everyday lives. Here’s how AI is impacting our day-to-day activities:
Virtual Assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant help us manage tasks, set reminders, and control smart devices in our homes with voice commands.
Entertainment: Platforms like Spotify and Netflix use AI to recommend music, movies, and TV shows based on our preferences and behaviors.
Smart Devices: AI powers everything from smart thermostats that learn our preferences to security cameras that can identify faces and detect unusual activity.
Social Media: AI algorithms are at the core of social media platforms, determining which posts we see in our feeds, identifying trends, and even filtering out harmful content.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the AI revolution offers immense potential, it also presents challenges that must be addressed:
Job Displacement: As AI automates more tasks, there are concerns about job losses, particularly in industries like manufacturing, customer service, and transportation. However, there is also potential for AI to create new jobs in emerging fields such as AI ethics, robotics, and data science.
Bias and Fairness: AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If the data is biased, the AI may perpetuate or even amplify these biases. Addressing bias in AI systems is a critical issue for ensuring fairness and equality.
Privacy Concerns: As AI gathers and analyzes vast amounts of personal data, ensuring privacy and data protection will be key to maintaining trust in AI systems.
The Future of AI: What Lies Ahead?
The potential of AI is limitless. As AI systems continue to improve and learn, they will become more intelligent, capable, and integrated into every aspect of our lives. Here are a few areas where AI will continue to evolve:
AI in Creativity: AI-generated art, music, and even writing are on the rise, raising questions about the role of AI in creative fields. Will AI become a true creative partner, or will it remain a tool for human expression?
AI and Ethics: As AI becomes more integrated into society, establishing ethical guidelines for its use will become more important. Governments, businesses, and technologists must work together to ensure AI is used for the benefit of all.
General AI: While we currently have narrow AI (AI designed for specific tasks), there’s ongoing research into general AI, which would be capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can do. While this remains a distant goal, it could revolutionize everything from healthcare to problem-solving at a global scale.
Conclusion: Embracing the AI Revolution
AI is no longer the technology of the future—it’s the driving force of today’s technological revolution. Its impact spans every industry, enhancing efficiency, innovation, and personal experiences. As we continue to embrace the AI revolution, it’s crucial to balance innovation with ethics, ensuring that these advancements benefit society as a whole. The AI revolution is just beginning, and we’re only scratching the surface of its transformative potential.
Are you ready to be part of the AI revolution? The future is smarter, faster, and more connected than ever before. Let’s harness the power of AI to shape a brighter tomorrow LEARN MORE
#ArtificialIntelligence#AIRevolution#MachineLearning#AIinHealthcare#AIinFinance#AIinEducation#Automation#FutureOfAI#AIinBusiness#AIApplications#TechInnovation#AIandTechnology#AIandEthics#SmartTechnology#DigitalTransformation
1 note
·
View note
Text
Efficiency meets Brilliance: The Future of Car Wash Equipment
Introduction:
The car wash industry is on the cusp of a technological revolution, where efficiency meets brilliance to redefine the way we clean and care for our vehicles. The future of car wash equipment promises a seamless fusion of innovation, environmental responsibility, and exceptional performance. In this blog, we will delve into the exciting advancements that will shape the future of car wash equipment.
Automated Car Wash Systems: Precision Redefined
The future of car wash equipment lies in automated systems that push the boundaries of precision cleaning. Smart sensor technology will enable these systems to identify the exact dimensions and contours of each vehicle, providing customized wash programs tailored to its specific needs. This level of detail ensures a flawless and efficient clean, leaving no area untouched.
AI-Powered Cleaning Algorithms: Smart and Adaptive Solutions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in the future of car wash equipment. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms will optimize cleaning processes, learning from each vehicle's unique features and applying that knowledge to deliver smarter and more adaptive cleaning solutions.
Waterless and Eco-Friendly Solutions: Green Innovations
Environmental responsibility will be a driving force in the future of car wash equipment. Waterless and eco-friendly cleaning solutions will take center stage, minimizing water consumption and reducing the environmental impact of car washing. Biodegradable cleaning agents and advanced encapsulation technologies will become standard, ensuring a sparkling clean finish without harming the planet.
Autonomous Car Wash Vehicles: Mobility Redefined
Imagine your car being washed while you relax or work from the comfort of your home or office. Autonomous car wash vehicles equipped with advanced robotics and cleaning systems will revolutionize the car wash experience. These mobile units will travel to the customer's location, providing a convenient and time-saving service.
Nanotechnology and Ceramic Coatings: The Ultimate Protection
Nanotechnology will lead to advancements in car care, with self-healing coatings and protective layers that go beyond the traditional wax and sealants. Ceramic coatings infused with nanomaterials will provide long-lasting protection against environmental contaminants, UV rays, and scratches, keeping vehicles in pristine condition for extended periods.
Sustainable Infrastructure: Energy Efficiency and Water Recycling
Car wash facilities of the future will embrace sustainable infrastructure to reduce their carbon footprint. Energy-efficient systems powered by renewable sources will be employed to minimize energy consumption. Additionally, water recycling and treatment technologies will be integrated into car wash operations, preserving precious resources and promoting eco-friendly practices.
Conclusion:
The future of car wash equipment is a convergence of efficiency and brilliance. Through automation, AI-powered algorithms, eco-friendly solutions, and innovative technologies, car wash equipment will deliver unparalleled precision, convenience, and environmental responsibility. From custom-tailored wash programs to autonomous mobile units and advanced ceramic coatings, the future promises an extraordinary car wash experience that exceeds expectations. As we embrace these innovations, we move toward a greener, smarter, and more sustainable approach to car washing, ensuring that our vehicles stay brilliantly clean while caring for the planet.
0 notes
Text
AI Is Not Blue-Sky Thinking, It Is Common Sense

Artificial Intelligence refers to the ability of smart devices to use the available information sources to take decisions that mimic human behaviour. Termed as AI, artificial intelligence has been developed over the last five decades and is no longer just a blue-sky concept. We interact with AI every day as they route our phone calls, answer our questions, approve credit card transactions and help interpret medical results. There are now numerous branches to artificial intelligence a few key areas are: natural language processing, pattern recognition (including audio and visual recognition), agents, intelligent tutoring Interfaces, machine consciousness, computational creativity, robo-ethics. Here, we describe how it is changing various industries and how you can quickly leverage AI implementation.
AI in the Industry
AI is already producing improvements across most industries, especially ones that require work with the help of machines. Currently, we employ AI in several industries, such as controlling industrial robots, performing sensing, medical diagnosis, online ordering (food or shopping) and electronic trading tools to name just a few. This means that AI is changing the way most industries and organisations are planning their future strategies.
If we focus on an early adopter of AI then aviation has been a leading force. Starting with basic AI in the form of training simulators and autopilots later development of altitude monitoring and realignment for too steep banking help improve safety. The autopilot has grown up over the years. Changing from fixed pre-planned route profiles to using machine learning (ML) to create a more adaptive and resilient system. ML processes thousands of hours of real flight data and builds a library of scenarios that enable it to be more responsive in challenging situations. Maybe one day we won’t just have autonomous cars, we will have fully automated AI co-piloted planes.
Computer scientists are using AI all the time to resolve simple to complex problems, such as creating optimal timesharing resource management, automatic data storage and employ interactive interpreters. Intelligent tutoring systems are being developed and enhanced with the use of AI. DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) already employs AI-based systems to train Navy recruits to develop complex technical skills in the shortest possible time.
Touted by various thought leaders to be the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Al capabilities under development are limitless. Neuro technological brain enhancements, genetic editing and early detection of some cancers. Technology giants are using it as virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa. Whilst the financial sector has been using it to provide investment advice to customers. Big Data, the world’s newest most valuable resource, is enabling ML to create, test and train the AI. Companies that deploy AI will gather more data and from its continual learning will improve their algorithms and develop responsive solutions ahead of their rivals.
How to Leverage AI
Regardless of the industry in which you work, it is always possible to leverage AI to improve your current working practices. Understanding that AI is all about leveraging machine learning, based on volume data and human language processing, then coming up with adaptive computing to constantly improve the functional performance.
You do not have to worry about specific technology, as you should look to improve customer interactions and implement tools that can enhance performance. Here are a few important steps that you can take to ensure that AI is quickly leveraged in your business model:
Customise for the Client
The AI tools can be employed in your business to customise the client experience. This is possible by using AI to collect data, run an algorithm to find out their needs and then employ a service filter to provide each customer with a customised service structure.
Process Efficiency
You can improve the daily business functions as AI algorithms can analyse the data and come up with excellent suggestions for improving the current operations. AI tools can improve the workflow, find out problems in the current supply chain, and ensure that business costs are minimised as much as possible.
Chatbots
Another way to ensure that you can improve business, is to improve the way your business deals with its customers. This is possible to implementing chatbots to empower your business. They can communicate with your customers and learn by interacting with them. They can identify context and emotions and produce interactive replies.
Marketing
Marketing is enhanced with AI tools. Use them to gather detailed information about your possible market segments and then allow the tools to come up with the optimal strategy to target these segments. AI algorithms can quickly process demographic information, and help you create the best advertisement campaigns.
The summary is clear, AI is here to stay and will only develop further over the years to come. The key is how you identify ways of employing it to better your business and your customer’s experience.
For more details visit: Incepteo.com
#bespoke software development#custom software development#web application development#mobile app development
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding the 4 Types of Artificial Intelligence: Gartner Report 2018

Artificial Intelligence, with a vast ocean of various evolutionary innovations, has marked a new epoch in the enterprise industry worldwide. There is seldom any aspect of life that has not interspersed with the tech-revolutions brought by AI. Moving away from human lives in general, Artificial Intelligence is taking the world of business beyond boundaries, providing it with far more depth and reach.
Different AI technologies are giving ways to tech strategic planners for redrawing long-term and short-term product strategies. AI is anticipated to be more pervasive in the forthcoming years. In the future, enterprises are expected to leverage AI for multiple goals spanning different industries, domains, and technologies.
Recently, Gartner’s forecast of AI enterprise levels has broken down Artificial Intelligence into four major project types including, decision support/augmentation, agents, decision automation, and smart products. In the following content, let’s put a spotlight on these four project types that will have AI functioning as the fulcrum. Take a look:
Decision Support Augmentation
Breaking out the international enterprise value derived from Artificial Intelligence type, decision support/augmentation is expected to represent almost 36% of the worldwide AI-derived enterprise values in the year 2017. By the year 2030, decision support/ augmentation is expected to surpass every other type of AI initiative in order to account for around 44% of the international AI-derived enterprise values.
The usage of DNNs in decision support/augmentation improves AI systems that are developed on conventional statistical and analytics techniques. These are capable enough to enhance the quality of different business decisions. DNNs would let organizations perform pattern recognition and data mining across various datasets. These tools can also classify complicated inputs which feed conventional programming systems.
These programming systems can offer insights, predict events, provide personalization, and make probabilistic recommendations at a more spectacular scale than any other conventional technologies. These systems have an influence on the capacity of different companies for automating decisions and interacting processes. This new kind of automation can minimize risks and expenses in leaps and bounds. These can also enable increased revenues via an upgraded segmentation, micro-targeting, marketing, and selling.
Agents
Agents generally, count on voices or texts to interact with users in a natural language. Agents have mainly gained their pride of place by Microsoft’s Cortana and Amazon’s Alexa. These are apparently ubiquitous in text messaging applications. They can transform the spoken words into messages, capturing several other attributes from the speech of the users. Capturing words or even intents are just a part of the issue.
These days, consumer service apps still need manual coding for dealing with a better extraction of intent, which is possible with the previous systems. Upon being implemented properly, the automated systems can handle different steps of a consumer interaction impeccably. These systems can capture the nature of an issue and identify different information. It owns the capacity of examining probable resolutions sans engaging a human assistant.
An agent can connect to a human assistant to address complicated issues in one step. These systems can drive consistent results in some domains. This apart, it can deal with different languages as well. Different cultures, as well as languages, might materially impact a decision tree though.
The virtual agents can allow different corporate hubs to minimize labor expenses as they take over various simple requests. The virtual employee assistants or virtual agents can aid in scheduling, calendaring and several other administrative tasks like feeding up the workers’ time for a higher value-added work or minimizing the requirement of human assistance.
The virtual agents are capable of accounting for almost forty percent of the international AI-oriented business values in the year 2017. It’s a matter of anticipation that by the year 2030 numerous other types of AI will grow and add to business values.
Decision Automation
Decision automation system relies on Artificial Intelligence to optimize business procedures or automate tasks. They are effective in accomplishing different tasks such as translating voice to messages and vice versa, classifying different data contents, and processing hand-written images or forms.
The statistical process is capable of automating routing or recommending next steps dependent on heuristics, which enhance over time with experience. The importance of decision automation is paramount, especially when there is enough ambiguity and non-quantitative objects are engaged.
The rule-based repetitive procedures with a structured data could be addressed by a lot more simple RPA or Robotic Process Automation. As ambiguity and unstructured data are the staples of today’s corporate industry or decision automation. As it grows, it ensures to bring tremendous enterprise values to different companies.
At present, decision automation can account for only two percent of the international AI-oriented enterprise values in the year 2017. But, this ratio is expected to increase to some extent by the year 2030.
Smart Products
Smart products can account for almost eighteen percent of the international AI-oriented enterprise values in the year 2017. However, it would shrink to almost thirteen percent by the year 2030 because several other DNN-driven system types grow smart products in their contribution to enterprise values.
Smart products own AI-embedded in them, generally in the shape of cloud systems, which can implement data about the users’ overall performance from different interactions and systems. They can learn about their users and their overall performances to hyper-personalize their experience and drive more engagements.
A smart products’ subset is embedded with AI, which uses a sophisticated model for moving in and interacting with a robot’s environ. Some examples include factory robots and autonomous vehicles that can eliminate the necessities of putting human beings at risk in a difficult environment. A few humanoid robots have recently come into being that can interact via emotion, body language or speech and classify different tones of voice.
Final Words
Almost every discovery of Artificial Intelligence comes with its own unique trademark. Each of them emphasizes accomplishing that ultimate goal – to transform human lives. The influences of AI have percolated down to the world of enterprise worldwide. Looking at the monumental proliferation of AI, we can state that the day is not far when Artificial Intelligence would emerge as a springboard for upward enterprise mobility.
Aarsh, Co- Founder & COO, Gravitas AI
www.gravitas.bot
0 notes
Text
Tech Development, Investments and NFT to Drive Crypto Adoption in 2020
Tech Development, Investments and NFT to Drive Crypto Adoption in 2020:

As the end of the year draws closer, discussing what the future holds for the crypto industry becomes increasingly relevant. In particular, how global financial and technological trends will affect the adoption of cryptocurrencies in the coming year.
Despite the critics, the number of industry experts and crypto enthusiasts who foresee a promising future for cryptocurrencies has been on the rise. Institutional investors are now paying more attention to crypto-related projects and products, and universities have even started to offer courses on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
Now, talks of how emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things can influence crypto have emerged, with possibilities for new applications coming to the fore. Furthermore, a global trend toward a cashless society is set to have a real impact on how privacy and freedom are perceived. Could cryptocurrencies provide a much-needed solution as early as 2020?
Increased use of AI and the IoT
No matter the industry, experts are more than willing to proclaim that artificial intelligence is the next big thing in their industry. The ubiquity of datasets, not to mention machine learning and high-performance scalable computing, are truly propelling the world into an age of AI. Many even consider the technology to be a sure sign of the incoming fourth Industrial Revolution.
However, despite the fast rise of AI technology, few practical applications are being discovered at present. A report called “The State of AI 2019” shows that projects associating themselves with the AI buzzword receive up to 50% more funding. This overwhelming hype around AI has led to a scenario where real applications are outnumbered by projects that only claim to be AI-related.
The good news is that the crypto industry has various applications where AI can be used to make cryptocurrencies attractive to the mainstream public. For instance, efficiently optimizing energy consumption during the mining process. For the most part, the energy it takes to mine Bitcoin has been a concern, and certain programs can reduce the energy costs. This provides increased profit margins to miners, who reduce transaction fees as a result.
Once implemented, AI can potentially compute the probability of a particular node’s performance and recommend methods that can be used to enable faster and cheaper transactions on the blockchain. Furthermore, when combined with IoT tech, different nodes will be able to communicate autonomously, achieving an increase in efficiency in terms of consensus protocols on the blockchain.
Al, IoT and blockchain can be used to make electronic devices completely autonomous, so that instead of using credit cards, these devices can be programmed to use cryptocurrencies to transact with one another.
On the subject, Cointelegraph reached out to Dominik Shiener, the founder of Iota — a cryptocurrency project that seeks to integrate cryptocurrencies to IoT. Shiener said that he believes autonomy should be the ultimate technological goal:
“The ultimate vision of all these technological advances is it to move from automation towards autonomy, and turn machines into autonomous economic agents. By simply giving a machine a wallet and way to verify, receive and send payments, we are creating an entire new Machine Economy where machines provide services and data to each other.”
Shiener also added that by combining IoT, AI and DLT, new and groundbreaking applications will become available, and as such, “we move away from today’s centralized networks with single points of failure, towards ‘Smart Decentralization’ where our networks are decentralized, resilient, secure, and smart.”
Institutional investors’ increased interest in crypto
Another trend that will likely take cryptocurrencies to the mainstream in 2020 is the increased interest in crypto-related projects from institutional investors.
A survey by Fidelity investment reveals that out of 441 United States-based institutional investors, 47% “appreciate that digital assets are an innovative technology play.”
The survey also showed that more than 70% of respondents view digital assets favorably, and four in 10 respondents said that they are open to future investments in digital assets.
What’s even more interesting is the fact that 22% of institutional investors already own digital assets. Basically, interest in cryptocurrencies or digital assets has matured from a reserve group of early adopters to financial advisors, traditional hedge funds, and family offices taking a keen interest in the industry.
For instance, JP Morgan issued its customers the JPM Coin as a newly released cryptocurrency aimed at facilitating international money transfers among its institutional clients.
Furthermore, Morgan Creek Digital Assets (an asset management firm) partnered with two pension funds that have a combined $5.1 billion in assets under management. Through the partnership, Morgan Creek Digital Assets reportedly raised $40 million that will go into a venture fund that invests in Bitcoin and other blockchain-related companies.
Another study conducted in the last quarter of 2018 by the Global Custodian and BitGo states that 94% of financial endowments have been making investments in crypto-related projects.
The report further showed that only 7% of the endowments “anticipate a decrease in their allocation in the next 12 months” and that the rest were optimistic about increasing their allocation. What’s most fascinating is that despite the heavy regulatory pressure and volatility that the cryptocurrency industry has been facing, these institutional investors and endowment fund managers are hardly showing any signs of stepping away.
Because a crypto-asset fund needs to exhibit sufficient capital flow, not to mention liquidity, the increased interest from financial endowments is a clear indicator that the crypto industry is growing. The University of Michigan, for instance, has planned this year to increase its stake in the crypto fund managed by Andreessen Horowitz.
Other top-ranking universities whose endowments have shown interest in cryptocurrencies include Havard and Yale. In 2019, Harvard, together with two pension plans in Virginia have bought about 95.8 million tokens of Blockstack, a digital rights protection platform, valued at about $11.5 million at the time. Furthermore, Blockstack’s token sale managed to make history by being the first token sale to get qualified by the SEC.
For Yale, in particular, the move to invest in crypto seems to have been inspired by a study conducted by Yale economists (Aleh Tsyvinski and Yukun Liu). In their study, the Yale economists reported that although cryptocurrencies demonstrate a lot of volatility, they also show a return that is higher than the risk implied by volatility.
Increased microchipping and use of cashless systems globally
All over the world, the movement toward a global cashless society is picking up speed. From Africa to Europe to Asia and America, there is no shortage of countries that are replacing banknotes for the convenience of electronic or plastic money.
In places such as Sweden, the move toward a cashless society has been so efficient that cash in circulation in the country has dropped to just 1% of GDP. Furthermore, Swedish legislation has made it possible for various retailers to refuse cash payments altogether.
Related: Crypto Vs. Cash: Which Countries Expect to Go Digital Soon?
To keep up with the changes, the Swedish central bank has set up plans to issue a digital version of its national fiat currency dubbed ‘e-krona.’ Add that to the increased popularity for microchipping among the Swedes and, in a few years, experts predict that the country could be among the first in the world to go completely cashless, bringing about several major advantages.
Swedes who make cashless payments with microchip implants report that they can pay for train tickets, eat at restaurants, and even open office doors without the inconvenience of pulling out their wallets, phones or keys. However, the price for this level of convenience is the threat of surveillance and safety of personal information.
Although electronic payment methods might offer convenience, a detailed record of the user’s purchases, location and time are recorded. This data can be sold and marketed by a user’s payment provider, retailers, and payment processors.
In China, the ubiquity of digital payments has become so instrumental that the country’s social credit system has been built around it. So far, cash payments in China have been reduced from 96% in 2012 to 15% as of 2019.
As countries further embrace the cashless movement, people will gradually lose the ability to transact value without the involvement of third parties or government entities. A cashless society might enable governments to better protect their people from crime, but it comes at the cost of each citizen’s data privacy and autonomy. On the subject, Cointelegraph spoke with Ray Wang, founder, chairman and analyst at Constellation Research, who said:
“This is the paradox. The companies contending to win our trust to manage our digital identities all seem to have complementary (or competing) business models that breach that trust by selling our data.”
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin could provide a hedge against the cashless movement, allowing people to transact value without the involvement of third parties or the government. Although not as private as cash payments in terms of user data, Bitcoin payments — much like cash payments — are decentralized and do not require a third party, thanks to the blockchain. Therefore, as societies go cashless, the demand for alternative payment methods such as what Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer will be in demand.
Furthermore, with increased global economic uncertainty (keeping in mind that fiat currencies are affected by government policies), cryptocurrencies will likely provide a hedge against negative interest rates.
2020 and ahead
Even though global trends can highlight significant changes that are yet to come, the future remains highly unpredictable, and what happens in 2020 and beyond is anyone’s guess.
The rise of key Industry 4.0 technologies like AI, IoT and blockchain can shift the scales of power quickly and in directions previously unexpected. As much as the increased interest in blockchain technology is worth considering as a telltale sign of what the future has to offer, one still has to take multiple other factors into account before concluding with a definitive answer on whether crypto will go mainstream.
Hopefully, with the increasing flow of institutional capital, not to mention the influence of the trends mentioned above, the industry will be legitimized in the eyes of the mainstream public.
0 notes
Link

As the end of the year draws closer, discussing what the future holds for the crypto industry becomes increasingly relevant. In particular, how global financial and technological trends will affect the adoption of cryptocurrencies in the coming year.
Despite the critics, the number of industry experts and crypto enthusiasts who foresee a promising future for cryptocurrencies has been on the rise. Institutional investors are now paying more attention to crypto-related projects and products, and universities have even started to offer courses on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
Now, talks of how emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things can influence crypto have emerged, with possibilities for new applications coming to the fore. Furthermore, a global trend toward a cashless society is set to have a real impact on how privacy and freedom are perceived. Could cryptocurrencies provide a much-needed solution as early as 2020?
Increased use of AI and the IoT
No matter the industry, experts are more than willing to proclaim that artificial intelligence is the next big thing in their industry. The ubiquity of datasets, not to mention machine learning and high-performance scalable computing, are truly propelling the world into an age of AI. Many even consider the technology to be a sure sign of the incoming fourth Industrial Revolution.
However, despite the fast rise of AI technology, few practical applications are being discovered at present. A report called “The State of AI 2019” shows that projects associating themselves with the AI buzzword receive up to 50% more funding. This overwhelming hype around AI has led to a scenario where real applications are outnumbered by projects that only claim to be AI-related.
The good news is that the crypto industry has various applications where AI can be used to make cryptocurrencies attractive to the mainstream public. For instance, efficiently optimizing energy consumption during the mining process. For the most part, the energy it takes to mine Bitcoin has been a concern, and certain programs can reduce the energy costs. This provides increased profit margins to miners, who reduce transaction fees as a result.
Once implemented, AI can potentially compute the probability of a particular node’s performance and recommend methods that can be used to enable faster and cheaper transactions on the blockchain. Furthermore, when combined with IoT tech, different nodes will be able to communicate autonomously, achieving an increase in efficiency in terms of consensus protocols on the blockchain.
Al, IoT and blockchain can be used to make electronic devices completely autonomous, so that instead of using credit cards, these devices can be programmed to use cryptocurrencies to transact with one another.
On the subject, Cointelegraph reached out to Dominik Shiener, the founder of Iota — a cryptocurrency project that seeks to integrate cryptocurrencies to IoT. Shiener said that he believes autonomy should be the ultimate technological goal:
“The ultimate vision of all these technological advances is it to move from automation towards autonomy, and turn machines into autonomous economic agents. By simply giving a machine a wallet and way to verify, receive and send payments, we are creating an entire new Machine Economy where machines provide services and data to each other.”
Shiener also added that by combining IoT, AI and DLT, new and groundbreaking applications will become available, and as such, “we move away from today’s centralized networks with single points of failure, towards ‘Smart Decentralization’ where our networks are decentralized, resilient, secure, and smart.”
Institutional investors’ increased interest in crypto
Another trend that will likely take cryptocurrencies to the mainstream in 2020 is the increased interest in crypto-related projects from institutional investors.
A survey by Fidelity investment reveals that out of 441 United States-based institutional investors, 47% “appreciate that digital assets are an innovative technology play.”
The survey also showed that more than 70% of respondents view digital assets favorably, and four in 10 respondents said that they are open to future investments in digital assets.
What’s even more interesting is the fact that 22% of institutional investors already own digital assets. Basically, interest in cryptocurrencies or digital assets has matured from a reserve group of early adopters to financial advisors, traditional hedge funds, and family offices taking a keen interest in the industry.
For instance, JP Morgan issued its customers the JPM Coin as a newly released cryptocurrency aimed at facilitating international money transfers among its institutional clients.
Furthermore, Morgan Creek Digital Assets (an asset management firm) partnered with two pension funds that have a combined $5.1 billion in assets under management. Through the partnership, Morgan Creek Digital Assets reportedly raised $40 million that will go into a venture fund that invests in Bitcoin and other blockchain-related companies.
Another study conducted in the last quarter of 2018 by the Global Custodian and BitGo states that 94% of financial endowments have been making investments in crypto-related projects.
The report further showed that only 7% of the endowments “anticipate a decrease in their allocation in the next 12 months” and that the rest were optimistic about increasing their allocation. What’s most fascinating is that despite the heavy regulatory pressure and volatility that the cryptocurrency industry has been facing, these institutional investors and endowment fund managers are hardly showing any signs of stepping away.
Because a crypto-asset fund needs to exhibit sufficient capital flow, not to mention liquidity, the increased interest from financial endowments is a clear indicator that the crypto industry is growing. The University of Michigan, for instance, has planned this year to increase its stake in the crypto fund managed by Andreessen Horowitz.
Other top-ranking universities whose endowments have shown interest in cryptocurrencies include Havard and Yale. In 2019, Harvard, together with two pension plans in Virginia have bought about 95.8 million tokens of Blockstack, a digital rights protection platform, valued at about $11.5 million at the time. Furthermore, Blockstack’s token sale managed to make history by being the first token sale to get qualified by the SEC.
For Yale, in particular, the move to invest in crypto seems to have been inspired by a study conducted by Yale economists (Aleh Tsyvinski and Yukun Liu). In their study, the Yale economists reported that although cryptocurrencies demonstrate a lot of volatility, they also show a return that is higher than the risk implied by volatility.
Increased microchipping and use of cashless systems globally
All over the world, the movement toward a global cashless society is picking up speed. From Africa to Europe to Asia and America, there is no shortage of countries that are replacing banknotes for the convenience of electronic or plastic money.
In places such as Sweden, the move toward a cashless society has been so efficient that cash in circulation in the country has dropped to just 1% of GDP. Furthermore, Swedish legislation has made it possible for various retailers to refuse cash payments altogether.
Related: Crypto Vs. Cash: Which Countries Expect to Go Digital Soon?
To keep up with the changes, the Swedish central bank has set up plans to issue a digital version of its national fiat currency dubbed ‘e-krona.’ Add that to the increased popularity for microchipping among the Swedes and, in a few years, experts predict that the country could be among the first in the world to go completely cashless, bringing about several major advantages.
Swedes who make cashless payments with microchip implants report that they can pay for train tickets, eat at restaurants, and even open office doors without the inconvenience of pulling out their wallets, phones or keys. However, the price for this level of convenience is the threat of surveillance and safety of personal information.
Although electronic payment methods might offer convenience, a detailed record of the user’s purchases, location and time are recorded. This data can be sold and marketed by a user’s payment provider, retailers, and payment processors.
In China, the ubiquity of digital payments has become so instrumental that the country’s social credit system has been built around it. So far, cash payments in China have been reduced from 96% in 2012 to 15% as of 2019.
As countries further embrace the cashless movement, people will gradually lose the ability to transact value without the involvement of third parties or government entities. A cashless society might enable governments to better protect their people from crime, but it comes at the cost of each citizen’s data privacy and autonomy. On the subject, Cointelegraph spoke with Ray Wang, founder, chairman and analyst at Constellation Research, who said:
“This is the paradox. The companies contending to win our trust to manage our digital identities all seem to have complementary (or competing) business models that breach that trust by selling our data.”
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin could provide a hedge against the cashless movement, allowing people to transact value without the involvement of third parties or the government. Although not as private as cash payments in terms of user data, Bitcoin payments — much like cash payments — are decentralized and do not require a third party, thanks to the blockchain. Therefore, as societies go cashless, the demand for alternative payment methods such as what Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer will be in demand.
Furthermore, with increased global economic uncertainty (keeping in mind that fiat currencies are affected by government policies), cryptocurrencies will likely provide a hedge against negative interest rates.
2020 and ahead
Even though global trends can highlight significant changes that are yet to come, the future remains highly unpredictable, and what happens in 2020 and beyond is anyone’s guess.
The rise of key Industry 4.0 technologies like AI, IoT and blockchain can shift the scales of power quickly and in directions previously unexpected. As much as the increased interest in blockchain technology is worth considering as a telltale sign of what the future has to offer, one still has to take multiple other factors into account before concluding with a definitive answer on whether crypto will go mainstream.
Hopefully, with the increasing flow of institutional capital, not to mention the influence of the trends mentioned above, the industry will be legitimized in the eyes of the mainstream public.
0 notes
Text
Tech Development, Investments and NFT to Drive Crypto Adoption in 2020

As the end of the year draws closer, discussing what the future holds for the crypto industry becomes increasingly relevant. In particular, how global financial and technological trends will affect the adoption of cryptocurrencies in the coming year.
Despite the critics, the number of industry experts and crypto enthusiasts who foresee a promising future for cryptocurrencies has been on the rise. Institutional investors are now paying more attention to crypto-related projects and products, and universities have even started to offer courses on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
Now, talks of how emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things can influence crypto have emerged, with possibilities for new applications coming to the fore. Furthermore, a global trend toward a cashless society is set to have a real impact on how privacy and freedom are perceived. Could cryptocurrencies provide a much-needed solution as early as 2020?
Increased use of AI and the IoT
No matter the industry, experts are more than willing to proclaim that artificial intelligence is the next big thing in their industry. The ubiquity of datasets, not to mention machine learning and high-performance scalable computing, are truly propelling the world into an age of AI. Many even consider the technology to be a sure sign of the incoming fourth Industrial Revolution.
However, despite the fast rise of AI technology, few practical applications are being discovered at present. A report called “The State of AI 2019” shows that projects associating themselves with the AI buzzword receive up to 50% more funding. This overwhelming hype around AI has led to a scenario where real applications are outnumbered by projects that only claim to be AI-related.
The good news is that the crypto industry has various applications where AI can be used to make cryptocurrencies attractive to the mainstream public. For instance, efficiently optimizing energy consumption during the mining process. For the most part, the energy it takes to mine Bitcoin has been a concern, and certain programs can reduce the energy costs. This provides increased profit margins to miners, who reduce transaction fees as a result.
Once implemented, AI can potentially compute the probability of a particular node’s performance and recommend methods that can be used to enable faster and cheaper transactions on the blockchain. Furthermore, when combined with IoT tech, different nodes will be able to communicate autonomously, achieving an increase in efficiency in terms of consensus protocols on the blockchain.
Al, IoT and blockchain can be used to make electronic devices completely autonomous, so that instead of using credit cards, these devices can be programmed to use cryptocurrencies to transact with one another.
On the subject, Cointelegraph reached out to Dominik Shiener, the founder of Iota — a cryptocurrency project that seeks to integrate cryptocurrencies to IoT. Shiener said that he believes autonomy should be the ultimate technological goal:
“The ultimate vision of all these technological advances is it to move from automation towards autonomy, and turn machines into autonomous economic agents. By simply giving a machine a wallet and way to verify, receive and send payments, we are creating an entire new Machine Economy where machines provide services and data to each other.”
Shiener also added that by combining IoT, AI and DLT, new and groundbreaking applications will become available, and as such, “we move away from today’s centralized networks with single points of failure, towards ‘Smart Decentralization’ where our networks are decentralized, resilient, secure, and smart.”
Institutional investors’ increased interest in crypto
Another trend that will likely take cryptocurrencies to the mainstream in 2020 is the increased interest in crypto-related projects from institutional investors.
A survey by Fidelity investment reveals that out of 441 United States-based institutional investors, 47% “appreciate that digital assets are an innovative technology play.”
The survey also showed that more than 70% of respondents view digital assets favorably, and four in 10 respondents said that they are open to future investments in digital assets.
What’s even more interesting is the fact that 22% of institutional investors already own digital assets. Basically, interest in cryptocurrencies or digital assets has matured from a reserve group of early adopters to financial advisors, traditional hedge funds, and family offices taking a keen interest in the industry.
For instance, JP Morgan issued its customers the JPM Coin as a newly released cryptocurrency aimed at facilitating international money transfers among its institutional clients.
Furthermore, Morgan Creek Digital Assets (an asset management firm) partnered with two pension funds that have a combined $5.1 billion in assets under management. Through the partnership, Morgan Creek Digital Assets reportedly raised $40 million that will go into a venture fund that invests in Bitcoin and other blockchain-related companies.
Another study conducted in the last quarter of 2018 by the Global Custodian and BitGo states that 94% of financial endowments have been making investments in crypto-related projects.
The report further showed that only 7% of the endowments “anticipate a decrease in their allocation in the next 12 months” and that the rest were optimistic about increasing their allocation. What’s most fascinating is that despite the heavy regulatory pressure and volatility that the cryptocurrency industry has been facing, these institutional investors and endowment fund managers are hardly showing any signs of stepping away.
Because a crypto-asset fund needs to exhibit sufficient capital flow, not to mention liquidity, the increased interest from financial endowments is a clear indicator that the crypto industry is growing. The University of Michigan, for instance, has planned this year to increase its stake in the crypto fund managed by Andreessen Horowitz.
Other top-ranking universities whose endowments have shown interest in cryptocurrencies include Havard and Yale. In 2019, Harvard, together with two pension plans in Virginia have bought about 95.8 million tokens of Blockstack, a digital rights protection platform, valued at about $11.5 million at the time. Furthermore, Blockstack’s token sale managed to make history by being the first token sale to get qualified by the SEC.
For Yale, in particular, the move to invest in crypto seems to have been inspired by a study conducted by Yale economists (Aleh Tsyvinski and Yukun Liu). In their study, the Yale economists reported that although cryptocurrencies demonstrate a lot of volatility, they also show a return that is higher than the risk implied by volatility.
Increased microchipping and use of cashless systems globally
All over the world, the movement toward a global cashless society is picking up speed. From Africa to Europe to Asia and America, there is no shortage of countries that are replacing banknotes for the convenience of electronic or plastic money.
In places such as Sweden, the move toward a cashless society has been so efficient that cash in circulation in the country has dropped to just 1% of GDP. Furthermore, Swedish legislation has made it possible for various retailers to refuse cash payments altogether.
Related: Crypto Vs. Cash: Which Countries Expect to Go Digital Soon?
To keep up with the changes, the Swedish central bank has set up plans to issue a digital version of its national fiat currency dubbed ‘e-krona.’ Add that to the increased popularity for microchipping among the Swedes and, in a few years, experts predict that the country could be among the first in the world to go completely cashless, bringing about several major advantages.
Swedes who make cashless payments with microchip implants report that they can pay for train tickets, eat at restaurants, and even open office doors without the inconvenience of pulling out their wallets, phones or keys. However, the price for this level of convenience is the threat of surveillance and safety of personal information.
Although electronic payment methods might offer convenience, a detailed record of the user’s purchases, location and time are recorded. This data can be sold and marketed by a user’s payment provider, retailers, and payment processors.
In China, the ubiquity of digital payments has become so instrumental that the country’s social credit system has been built around it. So far, cash payments in China have been reduced from 96% in 2012 to 15% as of 2019.
As countries further embrace the cashless movement, people will gradually lose the ability to transact value without the involvement of third parties or government entities. A cashless society might enable governments to better protect their people from crime, but it comes at the cost of each citizen’s data privacy and autonomy. On the subject, Cointelegraph spoke with Ray Wang, founder, chairman and analyst at Constellation Research, who said:
“This is the paradox. The companies contending to win our trust to manage our digital identities all seem to have complementary (or competing) business models that breach that trust by selling our data.”
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin could provide a hedge against the cashless movement, allowing people to transact value without the involvement of third parties or the government. Although not as private as cash payments in terms of user data, Bitcoin payments — much like cash payments — are decentralized and do not require a third party, thanks to the blockchain. Therefore, as societies go cashless, the demand for alternative payment methods such as what Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies offer will be in demand.
Furthermore, with increased global economic uncertainty (keeping in mind that fiat currencies are affected by government policies), cryptocurrencies will likely provide a hedge against negative interest rates.
2020 and ahead
Even though global trends can highlight significant changes that are yet to come, the future remains highly unpredictable, and what happens in 2020 and beyond is anyone’s guess.
The rise of key Industry 4.0 technologies like AI, IoT and blockchain can shift the scales of power quickly and in directions previously unexpected. As much as the increased interest in blockchain technology is worth considering as a telltale sign of what the future has to offer, one still has to take multiple other factors into account before concluding with a definitive answer on whether crypto will go mainstream.
Hopefully, with the increasing flow of institutional capital, not to mention the influence of the trends mentioned above, the industry will be legitimized in the eyes of the mainstream public.

0 notes
Text
Adapt or die: How to cope when the bots take your job
Visit Now - http://zeroviral.com/adapt-or-die-how-to-cope-when-the-bots-take-your-job/
Adapt or die: How to cope when the bots take your job
Image copyright Getty Images
Image caption Will smart virtual assistants take our jobs or make them more fulfilling?
Reports that robots, automation and artificial intelligence are going to put millions of us out of work may sound troubling, but should we believe them? That largely depends on whether we’re technology optimists or pessimists. In our Future of Work series we look at how jobs might change in the future.
The Snewing family lived in 62 Falkner Street, Liverpool, for more than four decades. They were saddlers working in the late 19th and early 20th Centuries. And while the horse-drawn economy dominated, they enjoyed a brisk trade.
But then, as the BBC2 series A House Through Time relates, along came the motor car.
Rival saddlery businesses saw the lie of the land and turned to making leather footballs, handbags and luggage instead. The Snewings sadly carried on regardless and eventually went out of business.
That, in a nutshell, is the challenge we face when new technologies come along. Adapt or die.
But it is the pace of technological change that is unprecedented in the modern era and which poses the greatest challenge for jobs.
Image copyright Getty Images
Image caption Ford’s Model-T motorcar symbolised the death-knell for the horse-drawn economy
Image copyright Getty Images
Image caption Saddlers didn’t disappear completely as engines replaced horses, but businesses had to adapt
These days algorithms dictate the automated trading of trillions of dollars’ worth of assets in the financial markets. Artificially intelligent chatbots are taking over from humans in calls centres. And soon, planes and cars could be operating autonomously, putting in jeopardy the livelihoods of those who drive professionally.
Robots have been doing the repetitive drudge work in our factories for decades. But now they can flip burgers, flick away unripe tomatoes on a high-speed sorting machine using image recognition, lay bricks, even co-operate to open doors and escape.
Giant 3D printers can make houses out of concrete in a fraction of the time humans can.
The International Federation of Robotics says in manufacturing there are now 74 robot units per 10,000 employees on average, compared to 66 units in 2015. The highest growth rate is in Asia, China in particular.
And software automation, informed by machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) , will have a profound effect on our workplaces and the jobs we do.
“AI is a big threat to low-skilled jobs, no question,” says Bernard Louvat, general manager of digital customer engagement solutions at tech firm Nuance.
Image copyright Getty Images
Image caption Will robots really be able to help around the house or care for the elderly?
“I don’t think we’re ready to handle this problem yet.”
He thinks clever chatbots will replace most call centre staff within 10 years.
“A virtual assistant can handle 60%-80% of all customer conversations now without any need for a human agent to intervene – five years ago it would have been 25%-30%,” he says.
“Chatbots are certainly eliminating jobs – we need fewer and fewer human agents each year. The ones that are left will be highly skilled super-agents looking after the most complicated cases.”
Click here for more Future of Work stories
Research firm Gartner predicts that by 2020, 85% of questions will be answered by virtual assistants.
When you think that a huge telecoms company like AT&T employs around 100,000 call centre agents to look after its 120 million customers, that’s a lot of jobs that could disappear pretty quickly.
But the cost-savings are too big for large corporations to ignore. And they say customer satisfaction increases as these chatbots learn from the millions of previous customer conversations and become smarter.
Image copyright Getty Images
Image caption Some experts fear that self-replicating AI could run out of control
Consultancy Accenture says 81% of executives it interviewed think that within two years AI will be working next to humans in their organisation as “a co-worker, collaborator and trusted adviser”.
A recent report by the McKinsey Global Institute – Jobs Lost, Jobs Gained: Workforce Transitions in a Time of Automation – concluded that nearly two thirds of all jobs could have a significant chunk – at least 30% – of their activities automated by 2030.
That could affect 800 million roles, it said.
But McKinsey also acknowledged that this new technology “will also create new occupations that do not exist today, much as technologies in the past have done”.
Could the saddler of the past ever have imagined the roles of car mechanic, smartphone app developer or drone pilot?
The Industrial Revolution from the late 17th Century onwards saw mechanisation sweep through many industries. Farming in particular, which accounted for around 50% of all jobs across Europe, saw that percentage dwindle to less than 5% now.
Image copyright duncan1890
Image caption The mechanisation of farming saw many agricultural jobs move to other sectors
Such upheaval was undoubtedly painful for those unable to adapt, but new types of employment came along eventually.
More recently, there have seismic changes to the global economy over the last 30 years – the digital transformation, the rise of the internet, globalisation – but figures from the World Bank show that global unemployment as a percentage of total labour force has actually fallen from 6.1% in 1991 to 5.8% in 2017, despite the population rising from 5.4 billion to 7.6 billion over the same period.
Robotic process automation – RPA – will remove the need for staff to do boring, repetitive, rules-based activities, such as inputting data or handling payroll, tech optimists say.
“This is an evolution of work – the type of work we do will change,” says Ian Barkin, co-founder of Symphony Ventures, an RPA specialist with clients such as Lloyds Banking Group and US payroll giant ADP.
Image copyright Polycom
Image caption Polycom boss Mary McDowell thinks new technologies will make us more productive
“RPA doesn’t have to lead to a culling of staff, it can empower them and unleash their creativity. It’s freeing them from doing the unproductive stuff.”
Mary McDowell, chief executive of video-conferencing provider Polycom, envisages a time where AI will effectively run virtual meetings for us, using facial recognition to identify who’s speaking and calling up relevant documents and statistics to support points being made.
“The management of sound and video will be so much better,” she says. “Participants will feel like they’re actually present and augmented reality will help us collaborate and annotate documents much more productively.
“Meetings will be about the ideas, not the mechanics. Without technical barriers we can focus on the work at hand, whether that’s providing telemedicine or distance learning services.”
But even the optimists admit that as low-skilled jobs disappear, people will need to learn new skills to compensate.
“This calls on us all to focus on up-skilling,” says Mr Barkin. “There’s an urgent need for education reform – people need to learn design thinking, creativity, analytics, programming.
Research by job site Indeed finds that in the last three years demand from UK employers for AI specialists has almost tripled.
“Technology can lead to job reductions, but it doesn’t have to. This could be a huge good news story,” concludes Mr Barkin.
Just don’t carry on making saddles when the car is driving down the street towards you.
In the rest of this series we will look at the new types of job that could emerge in the age of robots, AI and automation.
Follow Matthew on Twitter.
0 notes
Photo

How Blockchain Revol
How Blockchain Revolution is Going to Make Global Economy More Fair: Federico Pistono Interview Federico Pistono is a charismatic writer entrepreneur researcher angel investor TV presenter and public speaker who routinely tours around the world lecturing on exponential technologies and their economic impact on society. In 2012 Pistono wrote the book "Robots Will Steal Your Job But That's OK: How to Survive the Economic Collapse and be Happy" which became an international success. Recently he published another book Startup Zero to help his compatriots Italians get a better understanding of the startup culture. In addition Federico has more than a decade of professional experience in different fields that vary from IT Management and human machine interaction to screenwriting and directing. We speak with Federico Pistono about his views on how Blockchain could really change the current global economic model that is unfair how close we came to the AI ruling the world and how could we find our place in the emerging paradigm. CG: How did you get involved in the fintech industry? FP: Computers always fascinated me and systems in general and just learning new things.I have a background in mathematics and computer science so that was double spending and operating research data structures algorithms. Those were things that really interested me at the mathematical level. To then think that those principles could be applied for social change it was kind of a love at first sight of blending these things together. I started programming when I was 12 or 13 and got into Blockchain around 2011 when I read the Bitcoin whitepaper written by Satoshi. At the time I was very interested in the Byzantine generals problem. Then I was one of the first people to get into Ethereum and from then on it just grew more and more. Now I am leading the Blockchain theme at Hyperloop Transportation Technologies which is this new tech thats essentially a supersonic speed travel on a train. So you have an evacuated tube you got a tube you suck out the air you put a capsule inside with about 30 people and then you have got magnetic levitation-passive magnetic levitation its called Indutrack. And you can just move this thing at super high speed- supersonic so more than 1200 km/h. CG: What would you say about the relationship between AI and Blockchain? FP: Regarding AI and Blockchain I would say one of the biggest issues probably is how we decide to structure the algorithm and the incentive mechanisms that we put into the system because in the end you get your reward. AIs today and probably for the foreseeable future are not really intelligent in any sort. They perform narrow tasks and they optimize for specific things that we tell them to do and so we dont know really know how to give them the right constraints. If we just say hey make profit and do this they may find all sorts of ways around to perform that task very well to optimize for that factor. Now we have a system where there is a huge centralization of power centralization of capital centralization of risk and in particular the big players are de-risking everything by hedging the risk on the small guys particularly in developing countries. I think every time that you have a shift in technology or dramatic shift you have the ability to change things by creating a new incentive structure by changing the rules of the game. Right now that is that moment that seismic event that can change the incentive structure and the mechanisms underneath. The Blockchain is a way to do it distributively securely and I think we can do great things but they dont come by themselves we have to actively pursue a specific goal and to agree on how to design these new systems. CG: Are we ready for above-mentioned inventions or do we have to evolve further? FP: I think currently we are not ready for this change. Well first of all the technology isnt ready. We havent figured out still so many things about Blockchain systems. We are still in the very very early stage of the protocols and of the mechanisms that we are building. I mean we dont know how to scale we dont know how to do it securely we dont know how to do it fast enough. We really dont have the game theory behind it; we dont know how all these things are going to be put together. We dont have the social infrastructure and the technological infrastructure. But its a feedback loop its a system of systems so by interacting with the system by allowing ourselves to make mistakes and to do it faster and faster we create resilience in the network. Where a single entity might die or go bust the overall network captures some of that value and then you can increase the value again again and again. Hopefully we can find something thats not just resilient but its anti-fragile so that by stressing the system it becomes stronger- something like your body. When you go to the gym and you do exercise you actually stress your muscles and you break them apart and because you break them apart they become stronger afterwards so thats an anti-fragile system. We should do that for the economic system and also for decision-making and everything. Since we know that we are going to make mistakes- we should design a system that gets better as we make more mistakes because we learn from them instead of just repeating the same shit over and over and not learning from it which is mostly what has been happening recently. CG: Tell us about your books FP: I wrote a few books. First one is called Robots Will Steal Your Job But Thats OK. I wrote it six years ago. Kind of unsuspected time I was told I was a charlatan I didnt have a PhD in economics I wasnt a professor from MIT or Oxford I should just stick to my computer science and not talk about these things how little do you know. Then two to three years later professors from MIT and Oxford have written the papers that say exactly the same things with exactly the same numbers but using different methodologies so they were kind of validating everything that I was saying. Thus I went from a charlatan to an oracle. It was kind of weird but you know same stuff just has caused different reactions from people. Then I wrote another book a fiction book this time called Tale of Two Futures. Its a short sci-fi. It shows two different paths we can take. One where things have taken the decentralized open source model and a more sensible approach on how to use technology to better society and the other is this hyper-capitalistic narrowly focused mindless repetitive work that leads to a dystopian society. The third book I wrote was a book for Italians about how to build startups because in Italy no one knows how to build startups. Very few people know and the few people who do they leave the country and go elsewhere and they never tell anyone back in town. Now they call startups everything like if a pizzeria were a startup. No thats not a startup- a startup is something else! So I wrote this most recent book thats called Startup Zero.0. To kind of give the idea that we are not even step one we are at step zero we should get the basics first and understand them. So I have been doing that a lot of that. I also have a TV show in Italy on national TV its called Codice La vita è digitale it means Code Life is Digital. We have had about two or three mln people watching it every week. First it was just about Blockchain and Bitcoin. We went to BitFury China Japan we interviewed Roger Ver; we had a bunch of people there. I think it was very well done the episode on Blockchain. We did one on IoT smart cities the cognitive revolution artificial intelligence robotics synthetic biology genetic engineering. We are bringing these emerging technologies to the wider audience. Also I am an angel investor. I invest in about 20 companies so far- mostly in Blockchain but also I am moving to the medical sector things that I think will help humanity in one way or another. I try to give my contribution in some way. Now I am spending most of my time doing Hyperloop. CG: What does that mean Blockchain Revolution? How will it change the globe? FP: I think one of the biggest opportunities we have is to use autonomous agents to automate all things that should be automated particularly in bureaucracy and in how systems interoperate. There is no reason why I should go ask a person to verify my identity or to stamp something and wait for months for a paper to come back or fax it somewhere I mean some places still need a fax machine. A lot of this stuff is because you dont trust the computer to verify that transaction or that information that is being conveyed. Now the Blockchain can solve that. Not only can it solve it but it can solve it systematically securely and for anybody. Also its censorship resistant not just the government censoring information but also a company not releasing some of the data that maybe you should own. For example from all the social networks the only one that gives you the contacts is LinkedIn. Everyone else doesnt allow you to export the contacts. They are your contacts! Why shouldnt you be allowed to have your own contacts and information about them? Its crazy but this happens! Think about all the corruption that happens throughout the world- trillions of dollar worth of value and hundreds of millions of people in distress who can be forced into doing things because they have no legal recourse. The Blockchain can help all these people. Before it helps the First World it can help the long tail of the supply chain thats now being held hostage by the owners of capital who have an unfair advantage in that game. They can be less efficient than them but still win just because they have access to cheap capital. That is really unfair. All the risk is on these people who have no power no legal recourse and their lives are miserable because the game is tilted. The game is unfair. Blockchain can allow for that to change but we need to actively pursue that goal because it will not come automatically by itself. I think thats a moral responsibility that we have. I think we have to step up and take that responsibility. Follow us on Facebook
http://ift.tt/2A4OePm
0 notes