#Artificial Narrow Dynamic Intelligence
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Sexiest Podcast Character 2024 — Scripted Bracket — Round 1


Propaganda
Kayne (Malevolent):
He’s a god who acts like the main characters are his personal soap opera. His first appearance was playing the piano covered in blood after he had massacred an entire town. He just kinda shows up sometimes to cause chaos and is often munching on chips while he watches shit go down. Also he never wears shoes, for some reason
Literaly just a tumbr sexy man
black suit, no shoes, covered in blood, plays piano, quirky laugh
An eldritch god soaked in blood. He's Arthur Lester's number one cheer leader.
covered in blood, plays piano, silly laugh, very Will Wood coded
He's insane. He's so dynamic. Will Wood's The Normal Album in humanized eldritch god form. Always covered in blood. Need I say more?
ANDI (Marsfall):
Okay I didn't finish the podcast, but ANDI deserves all of the worlds.
#2024 Round 1#Kayne#ANDI#Malevolent#Marsfall#Kayne Malevolent#Artificial Narrow Dynamic Intelligence#Malevolent Podcast#ANDI Marsfall
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Human vs. AI: The Ultimate Comparison & Future Possibilities

The debate of Human Intelligence vs Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most important topics in today’s world. With AI advancing at an exponential rate, many wonder: Will AI surpass human intelligence? Can AI replace humans in creativity, emotions, and decision-making?
From self-driving cars to chatbots and even AI-generated art, artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming industries. But despite AI’s impressive capabilities, humans still have unique traits that make them irreplaceable in many aspects.
In this article, we will explore everything about Humans vs AI—how they differ, their strengths and weaknesses, and the possible future where both coexist.
What is Human Intelligence?
Human intelligence refers to the ability to think, learn, adapt, and make decisions based on emotions, logic, and experience. It is shaped by:
Cognitive Abilities: Problem-solving, creativity, critical thinking
Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and managing emotions
Adaptability: Learning from past experiences and adjusting to new situations
Consciousness & Self-Awareness: Understanding oneself and the impact of actions on others
Humans have common sense, emotions, and moral values, which help them make decisions in unpredictable environments.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is the simulation of human intelligence by machines. AI can process massive amounts of data and make decisions much faster than humans. The different types of AI include:
Narrow AI (Weak AI): AI specialized in specific tasks (e.g., voice assistants like Siri, Alexa)
General AI (Strong AI): AI with human-like reasoning and adaptability (not yet achieved)
Super AI: Hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in every aspect
AI works on algorithms, machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and neural networks to process information and improve over time.
Strengths & Weaknesses of Human Intelligence
Strengths of Humans
Creativity & Imagination: Humans can create original art, music, inventions, and solutions.
Emotional Understanding: Humans can relate to others through emotions, empathy, and social skills.
Problem-Solving: Humans can solve problems in unpredictable and unfamiliar environments.
Ethical Reasoning: Humans can make moral decisions based on personal beliefs and societal values.
Adaptability: Humans can learn from experience and change their approach dynamically.
Weaknesses of Humans
Limited Processing Power: Humans take time to analyze large amounts of data.
Subjective Thinking: Emotions can sometimes cloud judgment.
Fatigue & Errors: Humans get tired and make mistakes.
Memory Limitations: Humans forget information over time.
Strengths & Weaknesses of AI
Strengths of AI
Fast Data Processing: AI can analyze vast datasets in seconds.
Accuracy & Precision: AI minimizes errors in calculations and predictions.
Automation: AI can perform repetitive tasks efficiently.
No Fatigue: AI doesn’t get tired and works 24/7.
Pattern Recognition: AI detects trends and anomalies better than humans.
Weaknesses of AI
Lack of Creativity: AI cannot create something truly original.
No Emotions or Common Sense: AI cannot understand human feelings.
Dependency on Data: AI needs large datasets to function effectively.
Security & Ethical Risks: AI can be hacked or misused for harmful purposes.
Job Displacement: AI automation can replace human jobs.
How AI is Impacting Human Jobs?
AI is automating many industries, raising concerns about job security. Some professions being replaced or transformed by AI include:
Jobs AI is Replacing
Manufacturing: Robots handle repetitive production tasks.
Retail & Customer Service: AI chatbots assist customers.
Transportation: Self-driving cars and delivery drones.
Jobs AI Cannot Replace
Creative Professions: Artists, writers, filmmakers.
Healthcare & Therapy: Doctors, nurses, psychologists.
Leadership & Management: Decision-making roles that require intuition.
The future will require reskilling and upskilling for workers to adapt to AI-driven jobs.
Can AI Surpass Human Intelligence?
Currently, AI lacks self-awareness, emotions, and real-world adaptability. However, advancements in Quantum Computing, Neural Networks, and AI Ethics may bring AI closer to human-like intelligence.
Some experts believe AI could reach Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), where it can think and learn like a human. However, whether AI will truly replace humans is still debatable.
Future of AI & Human Collaboration
The future is not about AI replacing humans but about AI and humans working together. Possible future scenarios include:
AI-Augmented Workforce: AI assists humans in jobs, increasing efficiency.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI): AI could merge with human intelligence for enhanced cognition.
AI in Healthcare: AI helping doctors diagnose diseases more accurately.
Ethical AI Regulations: Governments enforcing AI laws to prevent misuse.
Rather than competing, humans and AI should collaborate to create a better future.
Conclusion
The battle between Human Intelligence vs AI is not about one replacing the other but about how they can complement each other. While AI excels in speed, accuracy, and automation, human intelligence remains unmatched in creativity, emotions, and moral judgment.
The future will not be AI vs Humans, but rather AI & Humans working together for a better society. By understanding AI’s capabilities and limitations, we can prepare for an AI-powered world while preserving what makes us uniquely human.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Digital Marketing: Exploring Emerging Trends and Strategies
In the dynamic world of digital marketing, being ahead of the curve is critical for efficiently reaching and engaging audiences in a continuously changing marketplace. As we look ahead, new technologies, changing customer behaviors, and inventive techniques are defining the future of digital marketing. Let's look at some developing trends and strategies that are likely to shape the future of this intriguing field.
Personalized Marketing
Personalization will continue to be a key component of successful digital marketing campaigns. Marketers can create highly personalized experiences tailored to individual interests and behaviors by leveraging massive volumes of data and advanced analytics. From personalized email campaigns to dynamic website content and targeted advertising, organizations will use personalization to increase customer engagement and conversions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming digital marketing by enabling automation, predictive analytics, and real-time personalization. AI-powered chatbots improve customer care, while predictive analytics help marketers anticipate consumer wants and optimize advertising. As AI evolves, its position in digital marketing will only grow, providing marketers with strong tools for streamlining operations and delivering more effective campaigns.
Voice search optimization
Voice search is growing increasingly popular as virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant gain traction. Optimizing content for voice search necessitates a shift in SEO tactics, with a focus on conversational keywords and brief, straightforward responses to frequent requests. Marketers must respond to this trend by optimizing content for voice inquiries to ensure exposure in voice search results.
Video Marketing Dominance
Video content continues to dominate digital platforms, catching the audience's attention and increasing interaction. Short-form videos on sites such as TikTok and Instagram Reels are especially popular with younger audiences. Live streaming is also growing in popularity, providing authentic and participatory experiences for viewers. Incorporating video into marketing efforts will be critical for organizations seeking to connect with viewers in meaningful ways.
Influencer Marketing Evolution
Influencer marketing is moving beyond traditional endorsements to prioritize authenticity, transparency, and long-term connections. Consumers demand authentic recommendations from relatable personalities; therefore, micro-influencers with narrow followings are becoming more popular. Brands will need to work strategically with influencers to develop authentic content that resonates with target audiences and is consistent with brand values.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are altering customer experiences by enabling marketers to provide immersive and interactive content. From virtual try-on experiences in the cosmetics business to virtual tours of real estate properties, AR and VR are transforming product presentation and narrative. As these technologies become more widely available, marketers will use AR and VR to increase engagement and drive conversions.
Sustainability and purpose-driven marketing
Consumers are increasingly drawn to brands that value sustainability and social responsibility. Purpose-driven marketing that supports environmental or social causes appeals to conscious consumers. To gain the trust and allegiance of socially conscious customers, brands must legitimately integrate sustainability into their marketing strategy, emphasizing transparency and accountability.
Conclusion
The future of digital marketing is dynamic and diverse, fueled by innovation, technology, and shifting customer behavior. By embracing emerging trends and implementing innovative methods, brands can navigate this changing landscape more effectively than ever before. As we move ahead, tailored experiences, AI-driven analytics, immersive content, and purpose-driven initiatives will shape the future of digital marketing, allowing organizations to make meaningful connections and generate long-term success in the digital age. Embrace these trends and methods to stay ahead in the fascinating journey of digital marketing transformation. If you want to become a digital marketing expert, then you can study Zoople Technologies three-month digital marketing course.
To read more content like this visit https://zoople.in/blog/
Visit our website https://zoople.in/
#artificial intelligence#python#kochi#kerala#seo#google#digital marketing#programming#machine learning#software engineering
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Agentic AI: The Next Evolution of Autonomous Business Systems
As markets evolve and competition intensifies across every industry, organizations are under immense pressure to find smarter, faster, and more adaptable solutions to stay ahead. One of the most promising developments in artificial intelligence is the rise of Agentic AI. Unlike traditional AI systems that operate under rigid instruction sets, Agentic AI exhibits autonomy, adaptability, and decision-making capabilities that mirror human-like behaviour. This transformative leap is poised to redefine how businesses operate, optimize, and scale.

What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to systems designed to act as autonomous agents capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and executing actions in pursuit of specific goals. These AI agents are not merely reactive; they are proactive, strategic, and capable of learning over time. While traditional AI relies on explicit programming to function within predefined parameters, Agentic AI systems exhibit goal-oriented behaviour and can operate independently with minimal human intervention.
Agentic AI is built upon advancements in several core areas of AI research:
Reinforcement Learning: Enables agents to learn optimal behaviours through trial and error.
Cognitive Architectures: Provides frameworks that mimic human decision-making processes.
Multi-Agent Systems: Facilitates collaboration and competition between multiple autonomous agents.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows agents to understand and communicate using human language.
Together, these technologies empower Agentic AI to engage in complex tasks such as strategic planning, resource allocation, customer interaction, and even creative problem-solving.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
Autonomy: Agentic AI systems operate independently, requiring minimal human oversight once objectives are defined.
Goal-Directed Behaviour: These systems pursue high-level objectives rather than executing narrow, task-specific instructions.
Adaptability: They adjust strategies and actions based on real-time data and evolving conditions.
Interactivity: Agentic AI can engage with users and systems through natural language and interfaces.
Self-Improvement: Through continuous learning and feedback, Agentic AI can enhance its performance over time.
Business Systems Powered by Agentic AI
Agentic AI is not just transforming individual workflows; it’s redefining entire business systems from the ground up. These agents are evolving from operational tools into dynamic components of enterprise architecture, capable of orchestrating complex interdependencies across departments.
1. Autonomous Business Operations
Agentic AI can manage end-to-end business processes with little to no human intervention. These agents are integrated into enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, turning them from static data repositories into proactive, decision-making ecosystems. For example, a procurement agent can dynamically renegotiate supplier contracts based on market fluctuations and risk analysis, while another manages compliance updates across jurisdictions.
2. Customer Experience Systems
By embedding agentic models within customer-facing systems, businesses can build AI-powered service layers that anticipate needs, resolve issues, and deliver personalized experiences. Unlike static chatbots or scripted IVRs, Agentic AI can traverse multiple customer touchpoints (email, chat, voice, social) and deliver consistent, context-aware support.
3. Sales and Marketing Platforms
Agentic AI enables continuous experimentation and optimization in marketing systems. These agents autonomously test messaging, allocate budgets across platforms, and modify content strategies based on user engagement and real-time analytics. In CRM systems, they identify upsell opportunities, draft personalized communications, and coordinate multi-channel campaigns, essentially becoming an autonomous marketing operations layer.
4. Finance and Risk Management
In finance departments, Agentic AI is reshaping systems like forecasting, budgeting, and compliance monitoring. Agents can generate real-time cash flow projections, detect anomalies in expense reports, or autonomously trigger fraud investigation protocols. As finance systems become more modular and API-driven, Agentic AI acts as the "glue" coordinating across them, making intelligent decisions without waiting on batch processes or human review.
5. Human Capital Systems
Talent management platforms infused with Agentic AI can manage workforce planning, skill development, and internal mobility. For example, an internal agent could monitor team workloads, project deadlines, and employee engagement metrics, and then recommend internal transfers or hiring actions. These agents don’t just automate HR tasks; they actively shape the workforce strategy.
The Strategic Layer: Agentic AI as Enterprise Orchestrator
Perhaps the most transformative potential lies in Agentic AI’s ability to operate as an orchestration layer across disparate business systems. Imagine a "Chief Operations Agent" that interfaces with finance, sales, HR, and logistics, balancing priorities, identifying cross-functional inefficiencies, and reallocating resources in real time.
Such a system could:
Adjust pricing models based on supply chain costs and customer demand.
Initiate hiring sprees based on projected sales pipeline activity.
Re-prioritize product development sprints based on customer feedback and competitor moves.
These agents don’t just automate; they synchronize and strategize, providing a layer of continuous enterprise optimization.
“Software is eating the world, but AI is going to eat software.” — Jensen Huang (CEO of NVIDIA)
The Benefits of Agentic AI in Business
The integration of Agentic AI into business systems offers a multitude of advantages:
Scalability: Agentic AI can manage increased workloads without proportional increases in cost or human resources.
Efficiency: By automating repetitive and complex tasks, businesses can redirect human talent to higher-value initiatives.
Resilience: These systems can quickly adapt to disruptions, making businesses more agile and robust.
Data Utilization: Agentic AI can analyze and act upon massive datasets far beyond human capabilities, uncovering hidden insights and opportunities.
Continuous Optimization: With the ability to learn and evolve, Agentic AI ensures that processes are constantly improving.
Comparison: Traditional AI vs. Agentic AI vs. Human Decision-Making
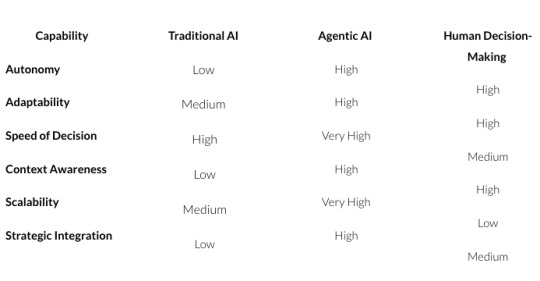
Challenges & Considerations
While the potential of Agentic AI is enormous, its adoption also presents challenges that businesses must navigate carefully:
Ethical Concerns: Autonomy raises questions about decision accountability, data use, and fairness.
Security Risks: Autonomous agents must be hardened against manipulation and breaches.
Integration Complexity: Replacing or augmenting legacy systems can be resource-intensive.
Governance and Control: Clear frameworks must define when and how AI agents act independently.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of strong internal governance, AI ethics frameworks, and next-generation IT infrastructure.
The Future of Agentic AI
The trajectory of Agentic AI suggests a future where businesses function as decentralized networks of intelligent agents collaborating in real time. Imagine a digital enterprise where finance, logistics, customer service, and strategy are orchestrated not by departments, but by autonomous agents that seamlessly integrate and adapt to changing circumstances.
We are likely to see the rise of meta-agents, which are AI systems that manage other agents, coordinate cross-domain workflows, and enforce organizational goals. These will serve as the AI equivalent of the executive suite, translating strategy into dynamic execution.
Additionally, the democratization of Agentic AI through low-code/no-code platforms will empower non-technical users to deploy and manage AI agents without technical barriers; further accelerating innovation across all levels of an organization.
We’re standing at the cusp of a new industrial revolution, one not powered by steam or silicon, but by intelligent autonomy. Agentic AI is more than just another technological advancement; it's a reimagining of how work gets done. As these systems become more capable, their role in business will shift from tool to collaborator and from support system to strategic partner.
Embracing Agentic AI requires more than investment. It demands systems thinking, executive sponsorship, and a willingness to challenge the status quo.
Learn more about DataPeak:
#factr#datapeak#saas#technology#agentic ai#artificial intelligence#machine learning#ai#ai-driven business solutions#machine learning for workflow#ai solutions for data driven decision making#ai business tools#ai agents#digital technology#digital trends#digitaltools#datadrivendecisions#data driven decision making#dataanalytics#ai platform for business process automation#ai for business efficiency#ai business solutions#ai driven business solutions#business#ai technology#techinnovation
0 notes
Text
Interactive Video Wall Industry: Transforming Digital Engagement Across Sectors
The Interactive Video Wall Industry is rapidly evolving into a cornerstone of digital communication and visualization. Valued at USD 5.6 billion in 2022, this industry is projected to reach USD 13.2 billion by 2030, growing at a robust CAGR of 11.2%. From retail showrooms and educational institutions to command centers and healthcare facilities, interactive video walls are reshaping how organizations deliver immersive and responsive experiences.
Industry Dynamics
A Shift Toward Experience-Driven Environments
The industry is moving from static signage to intelligent, real-time visual interfaces. Interactive video walls provide tactile and gesture-responsive surfaces, enabling dynamic content interaction. This has fueled adoption across industries where engagement and visibility are paramount.
Convergence of AI, IoT, and Big Data
Next-generation video walls are increasingly integrated with artificial intelligence and IoT devices. This allows businesses to display data-rich dashboards, environmental updates, or customer behavior analytics—all updated in real time. These capabilities position the interactive video wall industry at the center of smart workspace and city initiatives.
Digital Transformation in Control and Command Centers
Security, defense, utility, and traffic monitoring centers are deploying large-scale video walls for situational awareness and multi-source data visualization. Real-time control room operations now rely on unified visual intelligence delivered through high-resolution displays.
Growth of Hybrid and Remote Workplaces
With remote collaboration becoming mainstream, enterprises are investing in interactive displays for high-quality video conferencing and cross-regional collaboration. Touch-enabled video walls allow simultaneous engagement from multiple devices and sources.
Industry Applications
Retail: Enhances customer engagement with real-time promotions, product demos, and brand storytelling in flagship stores and malls.
Education: Enables active learning and group collaboration in digital classrooms, auditoriums, and virtual labs.
Healthcare: Supports surgical planning, telemedicine visualization, and patient education in modern medical centers.
Government & Defense: Powers mission-critical decisions in emergency operations, surveillance hubs, and border control.
Corporate Sector: Transforms meeting rooms and common areas into data-driven, presentation-friendly spaces.
Transportation: Improves traveler experience through flight/train information systems, digital signage, and wayfinding.
Competitive Landscape
The Interactive Video Wall Industry includes a mix of global tech innovators and display specialists. Major industry players include:
Samsung Electronics
LG Display
Barco NV
Planar Systems
NEC Display Solutions
Christie Digital Systems
ViewSonic Corporation
Delta Electronics
These companies compete through innovation in screen resolution (4K/8K), ultra-thin bezels, brightness control, and software features such as remote management, modular scalability, and AI-enhanced user interfaces.
Strategic Moves:
Partnerships with AV integrators
Acquisitions of touch tech and signage software firms
Expansions into emerging markets
Development of energy-efficient, ultra-narrow bezel displays
Regional Highlights
North America leads due to enterprise innovation and control room integration.
Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid adoption in smart cities, retail, and education.
Europe shows consistent demand driven by infrastructure modernization and public transit systems.
Future Outlook
As demand for smarter, more interactive environments grows, the Interactive Video Wall Industry is poised for exponential expansion. Investments in AR/VR integration, seamless multi-display interfaces, and AI-powered content delivery will drive future innovation. This sector will continue to redefine how institutions visualize, collaborate, and communicate information.
Trending Report Highlights
Discover other fast-evolving sectors aligned with visual and collaborative tech:
Automotive Manufacturing Equipment Market
Mid High Level Precision GP Market
RF Chip Inductor Market
Zoom Lens Market
Frame Grabber Market
0 notes
Text
Soaring from the Ground: How Flight Simulators Redefine Aviation Access
A teenage aviation enthusiast once sat in front of a basic joystick and computer screen, dreaming of piloting a commercial jet. Decades ago, such experiences were limited to crude visuals and minimal realism. Today, that same dream is being fulfilled with astonishing precision through the Flight Simulator, which now offers hyper-realistic environments, advanced controls, and real-time flight dynamics. This article examines how flight simulation has become a powerful tool in aviation education, training, and recreation, reshaping how people learn, experience, and interact with the skies.
THE TRANSFORMATION OF SIMULATION TECHNOLOGY
Early simulators served basic instructional purposes with limited features. Over time, the Flight Simulator has evolved into a dynamic, highly detailed system used by hobbyists, flight schools, and aviation professionals. What began as a mechanical setup with minimal interactivity has now become an advanced system driven by real-world weather data, global airport databases, and high-resolution terrain modeling. Flight simulation bridges the gap between theoretical aviation knowledge and hands-on experience, enabling users to practice essential skills in a risk-free environment that still mimics real-world conditions.
ENHANCING PILOT TRAINING WITH REALISTIC SCENARIOS
Flight simulation plays a vital role in preparing new and seasoned pilots for actual flight conditions. The Flight Simulator offers access to realistic cockpit layouts, navigational systems, and flight controls that replicate specific aircraft models. This enables aspiring pilots to develop situational awareness and muscle memory without leaving the ground. Instructors can simulate a wide range of emergency scenarios, such as engine failure or sudden weather changes, helping students practice their responses without danger. Such immersive training prepares aviators for complex, real-life challenges before ever taking off.
IMMERSIVE TECHNOLOGY FOR ENTHUSIASTS AND GAMERS
As the aviation community expands, so too does the appeal of flight simulation for non-professionals. Many hobbyists invest in premium home rigs, enjoying the experience of international flights, night landings, or navigating storms. For these individuals, the Flight Simulator is not just a game it’s a gateway to understanding aviation mechanics and appreciating aircraft design. With features like 360-degree visual fields, VR integration, and real-time air traffic emulation, simulators bring the thrill of flying to desktops and living rooms, transforming casual interest into immersive participation.
FLIGHT SIMULATION IN STEM EDUCATION AND CAREER PREPARATION
The educational benefits of simulation have expanded far beyond flight schools. Increasingly, the Flight Simulator is used in STEM classrooms and aerospace programs to teach students about aerodynamics, physics, and weather systems. Interactive lessons involving aircraft operation, instrument panels, and flight planning enhance comprehension and critical thinking. Simulators offer students a hands-on experience that textbooks alone cannot provide. As a result, they are not only fostering interest in aviation careers but also cultivating transferable skills like decision-making, precision, and spatial reasoning that apply across scientific and technical disciplines.
ADVANCEMENTS THAT PUSH SIMULATION INTO THE FUTURE
Flight simulation technology continues to evolve rapidly, incorporating artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and ultra-realistic rendering engines. Developers are integrating advanced avionics systems and predictive weather modeling into the Flight Simulator to further narrow the gap between simulated and real-world aviation. Future versions may use augmented reality and haptic feedback to simulate cockpit vibrations and airflow dynamics. These innovations will enable deeper levels of realism and interactivity, making simulators even more effective for both professional training and enthusiast engagement in the years ahead.
ACCESSIBILITY AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS FOR TRAINING PROGRAMS
A full-scale aircraft is costly to operate and maintain, making real-world flight hours expensive. For aviation schools and individual learners, the Flight Simulator offers a more affordable training path. Simulators allow repeated practice of maneuvers, landings, and takeoffs without incurring fuel or maintenance costs. They also allow instructors to guide students in specific areas of weakness by replaying challenging scenarios. This targeted approach leads to more efficient learning outcomes and supports the development of safer, more confident pilots who are better prepared for certification exams.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Future of AI: Harnessing Multimodal Control Strategies for Autonomous Systems
The landscape of artificial intelligence is undergoing a profound transformation. Gone are the days when AI was confined to narrow, siloed tasks. Today, enterprises are embracing multimodal, agentic AI systems that integrate diverse data types, execute complex workflows autonomously, and adapt dynamically to evolving business needs. At the heart of this transformation are large language models (LLMs) and multimodal foundation architectures, which are not only transforming industries but redefining what it means for software to be truly intelligent.
For AI practitioners, software architects, and CTOs, especially those considering a Agentic AI course in Mumbai or a Generative AI course in Mumbai, the challenge is no longer about building isolated models but orchestrating resilient, autonomous agents that can process text, images, audio, and video in real time, make context-aware decisions, and recover gracefully from failures. This article explores the convergence of Agentic and Generative AI in software, the latest tools and deployment strategies, and the critical role of software engineering best practices in ensuring reliability, security, and compliance.
Evolution of Agentic and Generative AI in Software
The journey from rule-based systems to today’s agentic AI is a story of increasing complexity and autonomy. Early AI models were narrowly focused, requiring manual input and strict rules. The advent of machine learning brought about predictive models, but these still relied heavily on human oversight. The real breakthrough came with the rise of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal architectures, which enabled AI to process and generate content across text, images, audio, and video.
Agentic AI represents the next evolutionary step. These systems are designed to act autonomously, making decisions, executing workflows, and even self-improving without constant human intervention. They leverage multimodal data to understand context, anticipate trends, and optimize strategies in real time. This shift is not just technical; it is fundamentally changing how businesses operate, enabling hyper-intelligent workflows that drive innovation and competitive advantage.
Generative AI, meanwhile, has moved beyond simple text generation to become a core component of multimodal systems. Today’s generative models can create content, synthesize information, and even simulate complex scenarios, making them indispensable for tasks like personalized marketing, fraud detection, and supply chain optimization. For professionals in Mumbai, enrolling in a Generative AI course in Mumbai can provide hands-on experience with these cutting-edge technologies.
Key Trends in Agentic and Generative AI
Unified Multimodal Foundation Models: These architectures enable seamless integration of multiple data types, improving performance and scalability. Enterprises can now deploy a single model for a wide range of use cases, from customer support to creative content generation.
Agentic AI Orchestration: Platforms like Jeda.ai are integrating multiple LLMs into visual workspaces, allowing businesses to leverage the strengths of different models for parallel task execution. This approach enhances efficiency and enables more sophisticated, context-aware decision-making.
MLOps for Generative Models: As generative AI becomes more central to business operations, robust MLOps pipelines are essential for managing model training, deployment, monitoring, and retraining. Tools like MLflow, Kubeflow, and custom orchestration layers are now standard for enterprise AI teams. For those new to the field, Agentic AI courses for beginners offer a structured introduction to these concepts and the practical skills needed to implement them.
Latest Frameworks, Tools, and Deployment Strategies
The rapid maturation of multimodal AI has given rise to a new generation of frameworks and tools designed to orchestrate complex AI workflows. Leading the charge are unified multimodal foundation models such as OpenAI’s GPT-4o, Google’s Gemini, and Meta’s LLaMA 3. These models can process and generate text, images, audio, and video, reducing the need for separate, specialized models and streamlining deployment across industries.
Key Deployment Strategies
Hybrid Cloud and Edge Architectures: To support real-time, multimodal processing, enterprises are adopting hybrid architectures that combine cloud scalability with edge computing for low-latency inference.
Containerization and Kubernetes: Containerized deployment using Kubernetes ensures portability, scalability, and resilience for AI workloads.
API-first Design: Exposing AI capabilities via well-defined APIs enables seamless integration with existing business systems and third-party applications. For professionals seeking to upskill, a Agentic AI course in Mumbai can provide practical training in these deployment strategies.
Advanced Tactics for Scalable, Reliable AI Systems
Building resilient, autonomous AI systems requires more than just advanced models. It demands a holistic approach to system design, deployment, and operations.
Resilience and Fault Tolerance
Redundancy and Failover: Deploying multiple instances of critical AI components ensures continuous operation even in the event of hardware or software failures.
Self-Healing Mechanisms: Autonomous agents must be able to detect and recover from errors, whether caused by data drift, model degradation, or external disruptions.
Graceful Degradation: When faced with unexpected inputs or system failures, AI systems should degrade gracefully, providing partial results or fallback mechanisms rather than failing outright.
Scalability
Horizontal Scaling: Distributing AI workloads across multiple nodes enables efficient scaling to meet fluctuating demand.
Asynchronous Processing: Leveraging event-driven architectures and message queues allows for efficient handling of high-throughput, multimodal data streams.
Security and Compliance
Data Privacy and Anonymization: Multimodal AI systems often process sensitive data, necessitating robust privacy controls and anonymization techniques.
Model Explainability and Auditability: Enterprises must ensure that AI decisions can be explained and audited, particularly in regulated industries.
For beginners, Agentic AI courses for beginners often include modules on these advanced tactics, providing a solid foundation for real-world deployment.
Ethical Considerations in AI Deployment
As AI systems become more autonomous and pervasive, ethical considerations become paramount. Key challenges include:
Bias and Fairness: Ensuring that AI models are fair and unbiased is crucial for maintaining trust and avoiding discrimination.
Transparency and Explainability: Providing clear explanations for AI-driven decisions is essential for accountability and compliance.
Data Privacy: Protecting user data and ensuring privacy is a critical ethical concern in AI deployment.
For professionals in Mumbai, a Generative AI course in Mumbai may include case studies and discussions on these ethical issues, helping learners navigate the complexities of responsible AI deployment.
The Role of Software Engineering Best Practices
Software engineering principles are the bedrock of reliable AI systems. Without them, even the most advanced models can falter.
Code Quality and Maintainability
Modular Design: Breaking down AI systems into reusable, modular components simplifies maintenance and enables incremental improvements.
Automated Testing: Comprehensive test suites, including unit, integration, and end-to-end tests, are essential for catching regressions and ensuring system stability.
DevOps and CI/CD
Continuous Integration and Delivery: Automating the build, test, and deployment pipeline accelerates innovation and reduces the risk of human error.
Infrastructure as Code: Managing infrastructure programmatically ensures consistency and repeatability across environments.
Monitoring and Observability
Real-Time Monitoring: Tracking system health, performance, and data quality in real time enables proactive issue resolution.
Logging and Tracing: Detailed logs and distributed tracing help diagnose complex, multimodal workflows.
For those considering an Agentic AI course in Mumbai, these best practices are often a core focus, ensuring that graduates are equipped to build robust, scalable AI solutions.
Cross-Functional Collaboration for AI Success
The complexity of modern AI systems demands close collaboration between data scientists, software engineers, and business stakeholders.
Breaking Down Silos
Shared Goals and Metrics: Aligning technical and business objectives ensures that AI initiatives deliver real value.
Cross-Functional Teams: Embedding data scientists within engineering teams fosters a culture of collaboration and rapid iteration.
Communication and Documentation
Clear Documentation: Well-documented APIs, data schemas, and deployment processes reduce friction and accelerate onboarding.
Regular Reviews: Frequent code and design reviews help catch issues early and promote knowledge sharing.
For beginners, Agentic AI courses for beginners often emphasize the importance of teamwork and communication in successful AI projects.
Measuring Success: Analytics and Monitoring
The true measure of AI success lies in its impact on business outcomes.
Key Metrics
Accuracy and Performance: Model accuracy, inference speed, and resource utilization are critical for assessing technical performance.
Business Impact: Metrics such as customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and revenue growth reflect the real-world value of AI deployments.
User Engagement: For customer-facing AI, engagement metrics like session duration and task completion rates provide insights into user experience.
Continuous Improvement
Feedback Loops: Collecting feedback from end users and monitoring system behavior enables continuous refinement of AI models and workflows.
A/B Testing: Comparing different model versions or deployment strategies helps identify the most effective approaches.
For professionals in Mumbai, a Generative AI course in Mumbai may include hands-on projects focused on analytics and monitoring, providing practical experience with these critical aspects of AI deployment.
Case Study: Jeda.ai – Orchestrating Multimodal AI at Scale
Jeda.ai is a leading innovator in the field of multimodal, agentic AI. Their platform integrates multiple LLMs, including GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, LLaMA 3, and o1, into a unified visual workspace, enabling businesses to execute complex, AI-driven workflows with unprecedented efficiency and autonomy.
Technical Challenges
Data Integration: Jeda.ai needed to seamlessly process and analyze text, images, audio, and video from diverse sources.
Orchestration Complexity: Managing multiple LLMs and ensuring smooth handoffs between models required sophisticated orchestration logic.
Scalability: The platform had to support high-throughput, real-time processing for enterprise clients.
Solutions and Innovations
Unified Data Pipeline: Jeda.ai developed a robust data pipeline capable of ingesting and preprocessing multimodal data in real time.
Multi-LLM Orchestration: The platform’s orchestration engine dynamically routes tasks to the most appropriate LLM based on context, data type, and performance requirements.
Autonomous Workflow Execution: Jeda.ai’s agents can execute entire workflows autonomously, from data ingestion to decision-making and output generation.
Business Outcomes
Operational Efficiency: Clients report significant improvements in workflow automation and operational efficiency.
Enhanced Decision-Making: The platform’s context-aware agents enable more accurate, data-driven decisions.
Scalability and Reliability: Jeda.ai’s architecture ensures high availability and resilience, even under heavy load.
Lessons Learned
Embrace Modularity: Breaking down complex workflows into modular components simplifies development and maintenance.
Invest in Observability: Comprehensive monitoring and logging are essential for diagnosing issues in multimodal, agentic systems.
Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration: Close collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and business stakeholders accelerates innovation and ensures alignment with business goals.
For those interested in mastering these techniques, a Agentic AI course in Mumbai can provide valuable insights and practical experience.
Additional Case Studies: Multimodal AI in Diverse Industries
Healthcare
Personalized Medicine: Multimodal AI can analyze patient data, including medical images and genomic information, to provide personalized treatment plans.
Diagnostic Assistance: AI systems can assist in diagnosing diseases by analyzing symptoms, medical histories, and imaging data.
Finance
Risk Management: Multimodal AI helps in risk assessment by analyzing financial data, news, and market trends to predict potential risks.
Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots can provide personalized customer support by understanding voice, text, and visual inputs.
For professionals seeking to specialize, a Generative AI course in Mumbai may offer industry-specific case studies and hands-on projects.
Actionable Tips and Lessons Learned
Start Small, Scale Fast: Begin with a focused proof of concept, then expand to more complex workflows as confidence and expertise grow.
Prioritize Resilience: Design systems with redundancy, self-healing, and graceful degradation in mind.
Leverage Unified Models: Use multimodal foundation models to streamline deployment and improve performance.
Invest in MLOps: Robust MLOps pipelines are critical for managing the lifecycle of generative and agentic AI models.
Monitor and Iterate: Continuously monitor system performance and user feedback, and iterate based on real-world insights.
Collaborate Across Teams: Break down silos and foster a culture of collaboration between technical and business teams.
For beginners, Agentic AI courses for beginners often include practical exercises based on these tips, helping learners build confidence and competence.
Conclusion
The era of autonomous, multimodal AI is upon us. Enterprises that embrace agentic and generative AI will unlock new levels of resilience, efficiency, and innovation. By leveraging the latest frameworks, adopting software engineering best practices, and fostering cross-functional collaboration, AI teams can build systems that not only process and generate content across multiple modalities but also adapt, recover, and thrive in dynamic, real-world environments.
For AI practitioners and technology leaders, especially those considering a Agentic AI course in Mumbai or a Generative AI course in Mumbai, the path forward is clear: invest in multimodal control strategies, prioritize resilience and scalability, and never stop learning from real-world deployments. For beginners, Agentic AI courses for beginners provide a structured entry point into this exciting field, equipping learners with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the future of AI.
0 notes
Text
Why Adaptive AI Development Is Crucial for Scalable Innovation?
In today’s fast-evolving digital world, businesses and organizations are under increasing pressure to innovate rapidly while maintaining efficiency and relevance. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a pivotal tool in this race, but traditional AI models—once trained—often lack the flexibility to evolve with shifting demands.

This is where adaptive AI development becomes not just beneficial, but essential. By embracing adaptability, organizations can unlock scalable innovation, continuously improve performance, and stay ahead of the competition.
What Is Adaptive AI?
Adaptive AI refers to systems that can learn and adjust in real time or near-real time based on new data and evolving environments. Unlike static AI models, which require complete retraining for updates, adaptive AI uses continuous learning, feedback loops, and context-aware algorithms to dynamically refine their behavior.
This capability allows adaptive AI to:
Respond to changing user behavior
Improve predictions and decisions over time
Mitigate risks by learning from failures
Scale across different use cases without redesigning the core model
The Need for Scalability in Innovation
Scalable innovation means the ability to grow, iterate, and expand ideas or solutions across an organization without hitting performance or cost bottlenecks. For innovation to scale effectively, technology must be:
Flexible to different contexts
Efficient in resource utilization
Reliable under increasing complexity
Quick to adapt to unforeseen challenges
Traditional AI often falls short on these fronts because it’s built for specific, narrow tasks. In contrast, adaptive AI aligns perfectly with the ethos of scalability.
How Adaptive AI Enables Scalable Innovation
1. Accelerates Time-to-Value
With adaptive AI, models can be deployed quickly and improve continuously without needing massive reengineering. This fast feedback cycle accelerates experimentation and innovation while reducing development overhead.
2. Supports Personalization at Scale
Consumer preferences shift constantly. Adaptive AI enables hyper-personalized experiences by learning from user interactions in real-time, allowing businesses to tailor products, services, and recommendations on the fly.
3. Reduces Operational Friction
As businesses scale, so do their data pipelines, customer bases, and operational challenges. Adaptive AI systems can autonomously detect anomalies, correct course, and optimize workflows, thus reducing the burden on human teams.
4. Enhances Decision-Making
Scalable innovation depends on making fast, data-driven decisions. Adaptive AI provides contextual insights that evolve with changing business landscapes, offering decision-makers more reliable, up-to-date intelligence.
5. Enables Continuous Learning
Static models degrade over time. Adaptive AI maintains performance by learning continuously, which means businesses can innovate without pausing to “retrain” their intelligence infrastructure.
Real-World Applications
Healthcare: Adaptive AI in diagnostics can evolve with new medical research, patient data, and treatment protocols.
Finance: Fraud detection systems that learn from new attack vectors can provide real-time protection.
Retail: AI models that adapt to seasonal trends, local preferences, and inventory shifts enable smarter demand forecasting.
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance powered by adaptive AI minimizes downtime by adjusting to machinery behavior.
Key Considerations for Adoption
Despite its advantages, adopting adaptive AI requires careful planning:
Ethical Oversight: Systems that learn autonomously must be monitored to avoid bias or unintended consequences.
Robust Infrastructure: Continuous learning requires access to real-time data, scalable compute, and secure environments.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Adaptive AI thrives when data scientists, engineers, and business leaders align on goals and metrics.
Conclusion
As innovation becomes the currency of modern enterprise success, the ability to scale intelligently and responsibly is more important than ever. Adaptive AI offers a blueprint for building systems that don’t just solve today’s problems but evolve to meet tomorrow’s challenges. It’s not just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic imperative for any organization looking to lead in the age of intelligent transformation.
0 notes
Text
Reasons To Study Supply Chain Management In France
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is nowadays a very essential activity in most industries in the modern globalized and connected world. Whether it is an e-commerce giant or a pharmaceutical company, the efficiency of supply chain processes directly influences the performance, profitability, and customer satisfaction of a company. Consequently, a degree in Supply Chain Management is a wise option for students who plan to establish a dynamic and future-enabled career.
In the case of international education in SCM, France has cut a niche as one of the leading countries that international students from all over the world would like to attend. France has a strong industrial tradition, globally recognized business schools and a strategic location on the European business market, combining academic and professional possibilities in this domain uniquely.
Today and in this blog, we are going to discuss the best reasons to study Supply Chain Management in France and why it may be the launching pad to your successful international career.
1. Home to Top-Ranked Business and Engineering Schools
France boasts a prestigious lineup of globally recognized institutions offering specialized programs in Supply Chain Management. Schools like:
HEC Paris
ESCP Business School
NEOMA Business School
KEDGE Business School
Skema Business School
EDHEC Business School
They are ranked among the top business schools worldwide. These institutions offer MSc, MBA, and Master’s programs in Supply Chain, Logistics, and Operations Management with a focus on both theoretical knowledge and practical industry applications.
Most of these programs are taught in English, making them accessible to international students.
2. Industry-Focused Curriculum with Internships
The fact that the study of SCM in France offers a practical and industry-based curriculum is one of the most alluring aspects. The courses are developed with the help of industry professionals and are constantly improved according to the latest market trends and technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, and Big Data in logistics.
Mandatory internships, industry projects, case studies, and company visits give students practical experience and thus allow them to narrow the gap between academic study and practice.
3. Strategic Location in the Heart of Europe
The geographical location of France in the heart of Europe is a great strength for supply chain professionals. France has a very good transport and logistics infrastructure with substantial ports such as Le Havre and Marseille, a high-speed rail network, and a high-speed road network, which makes it a logistics platform used by companies with operations in Europe.
Such a strategic position makes students familiar with cross-border logistics activities and European Union supply chain behaviors, which is a significant advantage to any individual seeking employment in multinational settings.
4. Thriving Job Market with Global Opportunities
France is home to many multinational corporations and logistics giants such as:
L'Oréal
Airbus
Schneider Electric
CMA CGM
Renault
Michelin
Decathlon
Bolloré Logistics
These companies offer excellent career opportunities in procurement, logistics, transportation, and supply chain analytics. After completing a degree in France, students can tap into a wide network of recruiters and alumni working across Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
Additionally, international students in France can stay up to two years after graduation to seek employment under the “APS” (Autorisation Provisoire de Séjour) visa, which enhances the return on educational investment.
5. Focus on Sustainability and Green Supply Chains
France is one of the global promoters of sustainability and climate action and this is evident in the approach of Supply Chain Management teaching and practice in the country. The students get acquainted with the notion of green logistics, carbon footprint calculation, and the circular supply chain.
Such an environmentally-friendly mindset renders the graduates of French establishments extremely attractive in the eyes of corporations devoted to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) objectives.
6. Affordable Tuition and Cost of Living
France also has low tuition fees compared to other countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom or Australia, in particular in their public universities and Grandes Écoles. Even the privately owned institutions are fairly priced, taking into account the international accolades of their courses.
As well, the French government provides international students with a housing subsidy (CAF - Caisse d'Allocations Familiales), which makes the cost of living much cheaper. Students equally enjoy subsidized transport, student food, and medical services.
7. English-Taught Programs with French Language Support
A large number of the SCM programs in France are conducted in English, but this is not a limiting factor since non-French speakers can understand the course. Meanwhile, the universities provide classes in French to the international students as a means of assimilation with the local culture and employment market.
English and French are a massive benefit in the worldwide employment market, and being a bilingual speaker can give an upper hand in getting a job in Europe, Africa, and certain areas of Canada.
8. Vibrant Student Life and Cultural Exposure
And it is not only academics when studying in France, but it is also about living French French-rich lifestyle, art, cuisine, and history. Cities such as Paris, Lyon, Bordeaux, or Lille are full of museums, music festivals, sports events, and international communities that make student life there unforgettable.
The experience of this culture develops interpersonal skills, cross-cultural knowledge, and international networking – key qualities of the future leaders of supply chains.
9. Research and Innovation in Logistics and SCM
France has been a centre of innovation and research in the field of digitization of supply chain, automation of warehouses, and predictive analytics. Research institutions, tech startups, and industry actors in France partner with the French institutions to undertake advanced projects.
Students get a chance to engage in research, publish articles, and acquire experience in the innovative supply chain strategies, which enables them to have a competitive advantage in the job market.
10. Strong Alumni Networks and Career Services
The French business and engineering schools' networks are well spread globally. Such networks tend to offer mentorship, internship opportunities, job referrals and business partners.
In addition, the majority of institutions have career services, CV workshops, interview training, and job fairs where students can meet the leading recruiters in the industry of logistics and consulting as well as retail and manufacturing.
11. Gateway to the European Union and Global Mobility
A French institutional degree is very respected in Europe and abroad. Being an EU member, France provides the students with opportunities to access any of the job markets within the European Economic Area (EEA) without the need for individual work permits.
Such mobility benefit is especially useful when one is targeting a career with multinational corporations or consulting firms that work with international clients.
12. High Return on Investment (ROI)
With affordable education, government subsidies, and a favorable job market, students studying SCM in France often enjoy a high return on investment. Many graduates go on to secure roles with competitive salaries in procurement, logistics planning, operations, and consulting within months of graduation.
Starting salaries in SCM roles in France typically range from €35,000 to €50,000 per year, with rapid career progression possible based on experience and specialization.
Conclusion
France is a good place to study Supply Chain Management when you are an international student who is interested in getting a high-quality education, practical experience, and international employment. Whether it is the best-ranked schools and the possibility to learn by doing or an impressive presence in the industry and cultural diversity, France has it all to make a future supply chain professional flourish.
France may be your best springboard in case you intend to pursue a career in logistics, procurement, or operations. Its academic quality, low cost, and global perspective and orientation place it among the most desirable places to study a Supply Chain Management course.
Looking to Study Supply Chain Management in France?
At Cliftons Study Abroad, we offer expert guidance on choosing the right university, preparing your application, securing scholarships, and navigating the visa process. Our counselors are here to support you at every step of your journey.
Book a free consultation today and take the first step toward a successful global career in Supply Chain Management!
#study abroad#study in uk#study abroad consultants#study in germany#study in australia#study in ireland#study blog
0 notes
Text
Sexiest Podcast Character 2024 — Scripted Redemption Bracket — Round 2


Propaganda
ANDI (Marsfall):
Okay I didn't finish the podcast, but ANDI deserves all of the worlds.
The Obituary Writer (Death by Dying):
canonically good looking, but also a cringefail loser wet cat of a man who fails to do ninja stealth rolls and has a facial expression like he's a murderer. loves his best friend so very very much (give it up for important platonic relationships!) and is totally fine and coping well with the events of the podcast, no need to worry :)
Additional propaganda below the cut:
The Obituary Writer (Death by Dying):
#OK THIS ISNT FAIR#You cant put the baby boy bi goth against a raging lesbian??? [In reference to Madge Stallion]
#OBITUARY WRITER PLEASE PLEASE PLEASE #he is sooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo shdjdjdjdjwjwjejsjdjdushbwbsbdjdjsjwhsbbdjdjdjd #<- sorry for bad keyboard smash on my phone
#i can't believe o.w is losing #the only thing we know about his physical description is that he's beautiful #he's even bisexual #he lives in a pinterest board home with his best friend's heart in a strawberry jar on his shelf
#O.W.sweep :[
#hey guys. why the fuck is my wife losing?? #he is the most perfect man ever if your into pathetic bisexuals
#2024 Round 2#ANDI#The Obituary Writer#Marsfall#Death by Dying#ANDI Marsfall#Artificial Narrow Dynamic Intelligence#DbD
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rise of Agentic AI: Future Business Technology Leader
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a catchword—it's rapidly transforming into a powerful business enabler. One of the most exciting developments in this domain is Agentic AI. Unlike traditional AI, which typically follows human commands, Agentic AI operates with a level of autonomy, problem-solving ability, and decision-making that makes it more like a proactive "agent" than a simple tool.
In this article, we will explore what Agentic AI is, why it matters, and how it is poised to become a future leader in business technology.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that can independently analyze situations, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. Rather than waiting for humans to issue every command, Agentic AI operates with:
Autonomy: It acts independently within defined boundaries.
Goal-Oriented Behavior: It works toward achieving objectives.
Continuous Learning: It adapts and refines its strategies over time.
Decision-Making Capability: It assesses risks, evaluates options, and selects optimal courses of action.
Unlike narrow AI, which is programmed for a single task, Agentic AI exhibits a higher level of reasoning and contextual understanding, making it more valuable in complex business environments.
Why is Agentic AI a Game Changer?
As businesses face increasing complexity, competition, and data overload, Agentic AI offers solutions that go beyond simple automation. Here’s why it’s revolutionary:
Proactive Problem Solving
Agentic AI doesn't just respond; it anticipates. For example, in supply chain management, it can foresee disruptions and reroute logistics accordingly before any human intervention is needed.
Enhanced Decision Support
Agentic AI evaluates multiple data sources in real-time to provide businesses with the best possible recommendations. Leaders can make informed decisions faster, reducing risks and seizing opportunities.
Operational Efficiency
By automating complex processes that require adaptive thinking, businesses can significantly cut costs, reduce errors, and optimize resources.
Scalability
Agentic AI can handle increasing complexity as businesses grow. Whether managing thousands of customer interactions or optimizing global logistics, its capability scales without proportionally increasing costs.
Continuous Improvement
With advanced machine learning algorithms, Agentic AI systems continuously improve themselves, refining their understanding and making better decisions over time.
Real-World Applications of Agentic AI
Many industries are already exploring or deploying Agentic AI to solve complex challenges. Here are some notable examples:
Healthcare
Personalized treatment planning
Predictive diagnostics
Autonomous medical data analysis
Finance
Automated investment advisory
Fraud detection and prevention
Intelligent risk management
Retail
Dynamic pricing models
Inventory management
Personalized customer experience
Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance
Autonomous quality control
Supply chain optimization
Customer Service
AI-powered virtual assistants
Multi-language support bots
Sentiment analysis for better customer interaction
The Technology Behind Agentic AI
Agentic AI relies on a combination of cutting-edge technologies to achieve its capabilities:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): To understand and process human language.
Machine Learning (ML): For continuous learning and improvement.
Deep Learning: For complex pattern recognition.
Reinforcement Learning: To learn optimal actions based on feedback.
Data Integration Platforms: To merge and analyze diverse data sources.
Knowledge Graphs: To create contextual understanding of data relationships.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential, Agentic AI also presents several challenges:
Data Privacy: Handling sensitive data responsibly.
Bias & Fairness: Avoiding the replication of existing biases.
Transparency: Ensuring decisions are explainable.
Accountability: Defining responsibility for AI-driven actions.
Businesses adopting Agentic AI must develop strong governance frameworks to address these concerns proactively.
The Future of Agentic AI in Business
Agentic AI will not replace human leadership; instead, it will augment it. By handling repetitive, data-heavy, and complex decision-making tasks, it frees up human leaders to focus on strategy, creativity, and innovation.
Key trends to watch:
Widespread adoption in SMBs, not just large enterprises
Seamless integration with IoT and edge computing
Democratization through AI-as-a-Service platforms
Stronger focus on AI ethics and governance
Collaboration between humans and AI agents Visit: livosotech.com
Final Thoughts
The rise of Agentic AI signals a significant shift in how businesses operate and compete. By enabling machines to act with greater autonomy, companies can unlock unprecedented efficiency, adaptability, and innovation.
For forward-thinking business leaders, investing in Agentic AI isn't just an option—it’s rapidly becoming a necessity to stay competitive in the digital era.
👉 The future belongs to those who embrace the power of intelligent autonomy.
SEO Keywords you can target for better ranking:
Agentic AI
Future of AI in business
AI business technology
Autonomous AI systems
AI-powered decision making
Business automation with AI
Intelligent automation
Future technology trends
If you want, I can also prepare:
Meta title & meta description for SEO
A catchy blog banner title
Social media captions to promote this blog
#logistics company in Bhubaneswar#top 10 logistics companies in Bhubaneswar#logistic companies in Bhubaneswar#logistic company jobs in Bhubaneswar#logistics company job in Bhubaneswar#logistics company jobs in Bhubaneswar
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unlocking Audience Engagement With Branching
Branching storylines are transforming the way films truly engage their audiences. Instead of passively watching, viewers get to influence the direction of the story, crafting a unique experience each time. For filmmakers — whether you’re part of a small indie group fueled by creativity or working at a major studio equipped with abundant resources — this trend is impossible to overlook in 2025. Interactive storytelling has evolved from a mere experiment into a full-fledged movement, encouraging creators to reconsider how they connect with and captivate their viewers. If you’ve imagined a more dynamic, collaborative relationship with your audience, now is the moment to stay ahead.
The Evolution of Interactive Storytelling
Not long ago, few in the film industry would have predicted giving viewers control over story outcomes. Today, the technology makes that feel seamless. Anyone who watched “Black Mirror: Bandersnatch” on Netflix remembers the choice-driven moments — select your path and watch what happens next. Streaming platforms have since embraced the format, releasing more choose-your-own-adventure films and interactive shorts. The message is clear: audiences no longer follow a fixed path. Filmmakers integrate decision points directly into their narratives. Each choice alters a character’s fate or shifts the atmosphere, making every viewing experience distinctive. The traditional divide between filmmaker and viewer narrows — storytelling becomes an immersive journey rather than a predetermined script. Budgets don’t need to be sci-fi level, just an openness to ditch linear storytelling.
AI: Driving Richer, More Complex Narratives
What truly unlocked this potential isn’t just specialized platforms or coding — it’s artificial intelligence. In 2025, nearly no one starts writing from scratch anymore. Creators toss ideas to tailored AI systems, which then generate story branches, alternative scenes, or even completely different endings on the fly. Ask for an “act two twist that heightens drama” and receive multiple well-crafted proposals instantly. AI doesn’t replace creativity; it removes tedious tasks, helping teams brainstorm and adapt faster. Editing and rewriting become less daunting. Smaller indie groups—without expansive writing teams—now have the capability to construct intricate story webs, explore various pathways, and deliver highly personalized narratives far more efficiently.
Technological Foundations Empowering Production Freedom
Keeping track of all narrative threads used to be a huge challenge. Now, dedicated tools exist just for filmmakers building interactive stories. Specialized scriptwriting software lets you visualize the entire branching flow, preventing any storyline from dropping off prematurely. Visual storymapping applications streamline logic checks and inspire creativity. Combine that with cutting-edge production methods like virtual sets and real-time rendering, and suddenly testing new ideas becomes cost-effective and fast. Extended reality (XR) technology also plays a big role—allowing creators to build, merge, and tweak environments on-demand without juggling dozens of physical locations. XR enhances immersion across genres—from sci-fi epics to intimate dramas—regardless of budget constraints.
Bridging Indie and Studio Efforts: A Level Playing Field
By 2025, branching storylines are no longer exclusive to blockbuster franchises or large game developers. Major studios view them as powerful tools for standing out and gaining deeper insights into audience preferences. Branching narratives combine brand building, engagement, and storytelling into one package. Meanwhile, indie filmmakers see branching as an opportunity to differentiate themselves and take creative risks without relying on extensive VFX or large casts. Smaller teams focus on compelling stories where each choice deepens rather than broadens the plot. Viewers are motivated to return and explore, giving films extended visibility with minimal added marketing. Analytics now reveal which paths resonate the most, helping directors and marketers understand what emotions and story arcs truly connect.
Getting Started with Branching Stories in 2025
Both beginners and veterans need a thoughtful strategy to create successful branching narratives. The key isn’t packing in countless small decisions but designing meaningful, coherent branches that genuinely impact the story. Here’s the recommended approach:
Build a compelling core narrative. Every pathway should have stakes — filler choices won’t hold interest no matter what.
Maintain consistent character logic. Even with multiple endings, audiences notice if motivations feel off. Plan where and why characters act differently based on choices.
Design modularly. Segment scenes so they slot neatly into different branches. Label everything clearly to avoid confusion as complexity grows.
Prioritize the viewer experience. Introduce decision points thoughtfully. Overloading with choices can confuse, while too few makes interactivity seem superficial. Subtle effects or sound cues can highlight major decisions without breaking immersion.
Collaborate with diverse expertise. Partnering with game designers or interactive writers brings fresh insights, especially on pacing and interface design.
Leverage analytics. Monitor where viewers engage, revisit, or drop off. Use these insights to refine your story and enhance future projects.
Preserve emotional impact. Regardless of genre or outcome, ensure each branch delivers genuine feeling—not just alternate plot points.
Successful teams usually start with a few meaningful decisions rather than a flood of options. Simplicity paired with flexibility is crucial. Developing content for platforms built with interactivity in mind also greatly improves the experience versus bending standard streaming solutions to fit. Plus, sustainability has become central across industries, so focusing on digital-first workflows can reduce resource use while unlocking new creative possibilities.
Looking forward, projects blending film, gaming, and interactive art will increasingly blur boundaries. As software capabilities grow and AI advances, nearly every filmmaker will be able to explore choice-driven storytelling. The next game-changing work could come from an indie release or a big-budget hit. Ultimately, audiences crave engagement — to feel immersed, to care, and to put their personal stamp on the story. For creators ready to experiment, collaborate, and reimagine film’s potential, an exciting, open future awaits with endless new voices and ideas.
#BranchingNarratives #InteractiveStorytelling #FutureOfFilm #AIinCinema #IndieFilmmaking
Explore new storytelling techniques for your next project: https://www.kvibe.com
0 notes
Text
Top Industries That Benefit from Boutique Search Firm Expertise
Hiring the right talent can prove an arduous task for companies in various industries in this competitive market. This is where boutique agencies come into play, offering a narrow scope of search and recruitment as per niche sectors and business needs. The myriad recruitment agencies function differently from boutique search agencies, so the latter will provide you with a more personal and hands-on approach in finding the best-fit candidate for your organization, requiring less time and energy.
Let us go through some top industries that gain great value from working with the boutique search firm.

Technology and the IT Sector
Technology is one of the fastest-growing and dynamic industries globally. Hence, there has always been an increasing demand for professionals highly skilled in software development, cybersecurity, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. In-depth research has to be done to screen for candidates with these technical skills and having cultural fit and adaptability.
In the tech recruitment business, a boutique search firm will usually have a greater understanding of the intricacies of the tech industry, emerging trends, and the skills in demand at any given time. This particular firm uses their contacts in the industry strategically with their special sourcing techniques to identify candidates who seem good on paper but are in fact long-term candidates for the forward-looking tech companies.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Another industry sufficiently impacted by strict consideration of end-user or professional expertise is Healthcare and Life Sciences. Whether it's hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, or biotechs, the right hiring decisions can make a difference for patient care, research, and regulatory environments.
A boutique search firm in healthcare recruitment provides certain insight into medical roles, clinical functions, and health leadership. They know certifications, licenses, and the regulatory environment that govern health hiring. The expertise of such agencies makes sure that healthcare organizations find candidates with technical know-how as well as interpersonal skills.
Financial Services and Banking
Within the financial services the banking, investment firms, and insurance companies-there is a need for recruitment allies who appreciate the utmost regulation and complexity of the industry. Candidates, having the right technical skills in compliance, risk management, and financial analysis, must uphold high standards in ethics and integrity.
Boutique search firms specializing in finance and banking bring mass experience and relationships with top professionals. They are proficient at finding candidates who can meet the onerous requirements of the industry while adding value to the growth and stability of the company. Their more contoured approach ensures the engagement of senior executives and specialists who embrace key strategic initiatives.
Hospitality and Leisure
The hospitality industry- and hotels, resorts, and luxury services- expects leadership that affords extraordinary experiences to guests and operations at the highest levels. It is also about knowing who you are hiring, the culture, brand values, and, unmistakably, the guest-first approach.
Boutique search firms dedicated to hospitality recruitment bring a nuanced understanding of the sector’s unique challenges. They identify leaders with a proven track record in guest services, revenue management, and team leadership. By focusing on quality over quantity, these firms help hospitality companies attract visionary executives who elevate the brand and enhance guest satisfaction.
Creative and Marketing Industries
Marketing, advertising, and creative fields define themselves through continual innovation, requiring a touch of creative genius that truly bonds with their audience. With every setting being unique and brand-oriented, it is tough to find talent that mixes creative and strategic thinking in equal parts.
Boutique search firms dealing with creative recruitment offer search services with true customization for positions such as brand managers, creative directors, digital marketers, and content strategists. Firms acknowledge that creative roles change over time and look for candidates who meld artistical perspective with real business impact. With this hand-holding approach, companies land candidates who dare to push boundaries but also get the job done.
Manufacturing and Industrial
Manufacturing and industrial companies are unique: they face challenges that usually arise in recruitment due to the specificity of technical roles and evolution of industry standards. Candidates for such positions are required to have particular technical skills in engineering, production management, quality control, and supply chain logistics.
Boutique search firms focusing on manufacturing and industrial matters offer custom-tailored executive search solutions to meet the technical requirements. They consult all about industry certifications, safety, and organizational workflows in detail, thus their suggested candidates are not just qualified to the technical standards but fit into an organizational culture of efficiency and safety as well.
Legal and Compliance
The legal department demands precision, trustworthiness, and in-depth knowledge of regulations and laws. Whether the firms are looking for corporate lawyers, compliance officers, or legal consultants, the talent required remains highly specialized.
A boutique search firm specializing in legal recruitment understands the intricacies of the market and the need for confidentiality in this field. They maintain excellent relationships with legal professionals, aware of the differences between specializations. They offer an invaluable service in being able to discreetly link firms with candidates who possess the right skills and professional values in sectors where reputation truly counts.
Nonprofit and Social Impact Organizations
Nonprofit and social enterprises hire for a variety of needs that often mush together passion and professional skills. Such organizations seek leaders and staff who are mission-driven and have strong fundraising, program management, and community engagement skills.
Using these boutique search firms for the nonprofit sector means having recruitment strategies tailored to the specific needs of organizations that embody social impact. They help find candidates whose expertise and actual heart for the cause ensure their lasting success and meaningful impact on nonprofit organizations.
Why Choose a Boutique Search Firm?
The consistent advantage in choosing a boutique search firm across all these sectors is the personalized attention and deep sector expertise these firms offer. Such programs work closely with clients to understand their unique challenges, culture, and goals. That close collaboration results in the best match to a candidate, speedier hiring, and lowered turnover.
Big recruitment agencies sometimes adopt a more general approach, while boutique search firms like Alliance Recruitment Agency take an extremely consultative and collaborative process, always assuring that the candidates and clients are in sync with one another for cultivating a successful working relationship over time. Contact us now.
#BoutiqueSearchFirm#ExecutiveSearch#ConstructExecutiveSearch#ConstructionRecruitment#ConstructionExecutiveSearch#LeadershipSearch#ConstructionHiring#ConstructionLeadership#TalentAcquisition#RecruitmentExperts
0 notes
Text
How to Choose a Modern Transport Management System (TMS): A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, as the demand for faster, efficient, and cost-friendly delivery grows, selecting the right Transport Management System (TMS) has become a crucial decision for any businesses dealing with moving goods. Logistics leaders would relate with the challenge of striking the right balance between flexibility, scalability and cost efficiency. In this blog, we’ll detail the evaluation criteria before onboarding a modern TMS and how it can empower businesses in the pharmaceuticals, e-commerce, automotive, chemical, retail, parcel/post and FMCG sectors to find a TMS best suited for your unique needs.
What is a TMS?
A Transportation Management System Software (TMS) is a solution that serves as a centralized platform, enabling businesses to manage routes, carriers, freight costs, and delivery schedules efficiently. Over the years, modern technologies have significantly evolved a transport software’s capabilities. Early systems focused on basic freight management but lacked integration and automation. Today’s TMS platforms leverage cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT), enhancing predictive analytics, real-time fleet monitoring, scalability and seamless integration, with some next-gen softwares offering autonomous decision making. These advancements have transformed TMS into a dynamic tool capable of addressing complex logistics challenges, and even removing manual decision making from the process.
The Detailed Checklist
If you are on the lookout for a TMS, you know that selecting the right transport software can be challenging as different solutions often emphasize distinct value propositions. This makes it difficult to pinpoint the best fit for your business. For instance, some might prioritize cost reduction / integration capabilities / multi-modal transportation support, while others focus on real-time tracking, analytics or autonomous decision making. Given this diversity, businesses must adopt a structured evaluation paradigm to ensure their chosen TMS aligns with their operational needs. Let’s delve into how you can navigate the crowded TMS market confidently and select a solution that maximizes efficiency and ROI.
1. Define Your Needs and Objectives:
Before you start evaluating TMS solutions, take a step back and define your specific needs and objectives. Ask yourself:
What are your current pain points in transportation management?
- High costs
- Lack of visibility
- Inefficient/manual order management
- Issue with software provider
What are your key performance indicators (KPIs) for transportation software?
- On-time delivery rate
- Transportation cost per unit
- Accurate capacity and route planning
What are your future growth plans and how will they impact your needs?
- Can the software handle peak festival season rush?
- Can the system scale seamlessly to double or triple the normal load as your business expands?
What specific functionalities are crucial for your business?
- Reducing long term costs
- Risk free deliveries
- Freight management and auditing
- Real-time tracking
- Agility and customizability on the TMS provider’s part
- Data encryption and compliance
What is your budget?
Documenting your needs and objectives will help you narrow down your options and ensure you select a TMS that addresses your unique requirements.
2. Evaluate Important Functionalities:
A modern TMS should offer a comprehensive suite of functionalities, including:
Route Optimization: The ability to plan and optimize routes based on factors like distance, traffic, and delivery windows.
Freight Management: Features for automating and managing freight rates, carrier selection, and shipment tracking.
Order Management: Seamless integration with your order management system to streamline order processing and fulfillment.
Real-Time Tracking and Visibility: End-to-end visibility into your shipments, with real-time tracking and alerts.
Freight Auditing and Payment: Automated freight auditing and payment processing to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Analytics and Reporting: Robust reporting capabilities to track KPIs, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Carrier Management: Tools for managing carrier relationships, contracts, and performance.
Mobile Friendliness: Mobile apps for drivers and other stakeholders to access information and update shipment status.
Autonomous Decision Making: How much is the system confidently capable of making important decisions without human intervention 99% of the time.
3. Consider Integration Capabilities:
A TMS should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, such as your ERP, WMS, and e-commerce platform. Evaluate:
- API availability and ease of integration
- Pre-built integrations with commonly used systems
- Data exchange compliance, capabilities and compatibility
4. Assess Scalability and Flexibility:
Choose a TMS that can scale with your business and adapt to your evolving needs. Consider:
Cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions — Leverage cloud solutions for superior scalability and adaptability.
Customization options to tailor the system to your specific workflows.
5. Evaluate Vendor Reputation and Support:
Select a reputable vendor with a proven track record and excellent customer support. Consider:
- Vendor experience and industry expertise
- Customer reviews and testimonials
- Availability of training and support resources
- Support and uptime service level agreements
6. Prioritize User Experience:
A user-friendly TMS will increase adoption and efficiency. Consider:
- Intuitive interface and easy navigation
- Mobile-friendly design
- Training and onboarding resources
7. Security and Compliance:
Ensure the TMS meets your security and compliance requirements. Consider:
- Data security measures and encryption
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards
- Data privacy policies
Although these are key considerations anyone looking for a TMS should evaluate, the approach is slightly nuanced between those new to the technology and those looking to replace an existing system. Summarizing the key differences below :

By carefully evaluating your needs and considering the factors outlined, you can select a TMS that empowers your business to achieve its logistics goals.
Conclusion
In summary, selecting a modern Transportation Management System requires a structured evaluation process to meet your business requirements.. Businesses must define their unique needs, assess functionalities like visibility and system autonomy, prioritize integration capabilities, consider vendor support and security compliance.
Libera AI-powered autonomous TMS ensures you delegate your transportation to AI. With features like automated checks, AI-powered transporter selection, dynamic routing, live tracking and autonomous decision-making capabilities, it addresses complex logistics challenges while eliminating manual inefficiencies..
Ultimately, no matter the system you decide to opt for, ask yourself one thing -
“Is this going to transform my current transportation process for the better?”
0 notes
Text
What Is Artificial Intelligence? A Beginner’s Guide with Examples
Artificial Intelligence refers to the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence. These systems can perform tasks that typically require human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, understanding language, and visual perception.
AI is a branch of computer science that encompasses subfields like machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), and robotics. In simple terms, AI makes it possible for machines to think and act like humans sometimes even better.
Today, many individuals are exploring AI through self-paced learning, hands-on projects, and enrolling in a structured artificial intelligence to gain a solid foundation. These courses often introduce the basics of algorithms, data handling, and model training perfect for beginners.
Types of AI: Narrow, General, and Super AI
AI can be classified into three categories:
Narrow AI (Weak AI): This type is designed to perform a specific task. Examples include Google Maps, spam filters, and facial recognition systems. Narrow AI is the most commonly used form in today’s world.
General AI (Strong AI): This version of AI would have the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human can do. It remains largely theoretical at this point.
Super AI: This would surpass human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and emotional understanding. While still a concept, many researchers are working toward this vision.
As this field grows rapidly, more professionals are seeking guidance through an AI course in Coimbatore to better understand the practical differences between these types and how to work with them responsibly.
How AI Works: Key Technologies Behind the Magic
AI systems function through a mix of data, algorithms, and computational power. Here are some core technologies behind AI:
1. Machine Learning (ML):
ML allows systems to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. Algorithms process huge amounts of data to detect patterns and make predictions.
2. Deep Learning:
This is a subfield of ML that uses neural networks with multiple layers. It’s especially useful in tasks like image recognition and speech processing.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Chatbots and voice assistants rely heavily on NLP.
4. Computer Vision:
Used for interpreting images and video, this is applied in facial recognition, autonomous driving, and medical diagnostics.
Understanding how these technologies work is essential for anyone aiming to apply AI in real-life scenarios. A well-structured artificial intelligence institute in coimbatore often covers these technologies, providing real-world projects to enhance learning.
Real-World Applications of AI
AI is not just a buzzword, it's actively shaping industries. Here are some examples that highlight its impact:
1. Healthcare:
AI assists in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. AI-powered tools can detect conditions like cancer from X-rays with high accuracy.
2. Retail:
From personalized recommendations to inventory management and dynamic pricing, AI is revolutionizing customer experience and operational efficiency.
3. Finance:
AI is used in fraud detection, algorithmic trading, credit scoring, and customer service via chatbots.
4. Transportation:
Self-driving cars, route optimization, and smart traffic signals are examples of AI in action.
5. Education:
AI personalizes learning paths, automates grading, and powers virtual tutors that adapt to student needs.
To understand how to build such systems or use them efficiently, beginners are encouraged to join an artificial intelligence course in Datamites that includes case studies and hands-on applications.
Advantages and Limitations of AI
✅ Advantages:
Efficiency: AI automates repetitive tasks, saving time and cost.
Accuracy: AI can reduce human error, especially in data-heavy environments.
24/7 Availability: AI systems don’t need breaks, making them ideal for customer service and monitoring tasks.
Data-Driven Decisions: AI can analyze large datasets quickly, helping businesses make smarter decisions.
❌ Limitations:
Data Dependency: AI systems require vast, high-quality data for effective learning.
Bias and Fairness: Poorly trained models may reflect biases in the data.
Lack of Creativity: AI lacks true creative thought, relying on existing data patterns.
High Initial Cost: Implementation can be expensive for small businesses.
These limitations are precisely why ethical AI practices and proper training are essential. Many artificial intelligence modules now include topics on fairness, transparency, and data ethics to help learners use AI responsibly.
Artificial Intelligence Course Introduction
youtube
Getting Started with Learning AI
If you're inspired to begin your AI journey, here are some beginner-friendly tips:
Start with the Basics: Learn about Python, data structures, and basic statistics.
Practice with Projects: Work on small projects like spam classifiers, movie recommendations, or chatbot development.
Understand the Mathematics: Linear algebra, calculus, and probability theory are fundamental.
Follow AI News: Stay updated with the latest developments through blogs, research papers, and webinars.
Enroll in an Artificial Intelligence Course: Choose a beginner-friendly program that includes theoretical concepts, practical exercises, and industry use-cases.
A good artificial intelligence will also offer quizzes, real-time assignments, and expert guidance to reinforce your learning. Whether you're from a technical background or not, structured learning can help you gain confidence and clarity.
Future Scope of AI
AI is expected to play a central role in the future of technology. With advancements in quantum computing, 5G, and edge computing, AI systems will become even more powerful and responsive.
Jobs in AI are expanding in areas such as:
AI Research
Machine Learning Engineering
Data Science
AI Product Management
Robotics and Automation
Preparing for these roles requires a solid understanding of AI principles, which can be gained from a focused artificial intelligence tailored to modern industry needs.
Artificial Intelligence is no longer just a futuristic idea, it's a reality shaping industries, jobs, and our everyday lives. Whether you’re a student exploring your interests or a working professional looking to upskill, now is the best time to dive into AI.
By understanding the basics, exploring real-world examples, and enrolling in a practical artificial intelligence, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a part of the AI revolution. The future belongs to those who understand how to use technology, not just consume it.
0 notes
Text
What the NASDAQ 100 index Reveals About Sector Rotation and Market Sentiment
The NASDAQ 100 index represents one of the most influential benchmarks within global equity markets. Comprising 100 of the largest non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq exchange, the index serves as a focal point for analyzing high-growth, innovation-led sectors including technology, healthcare, consumer services, and digital communications.
Due to its concentration in forward-looking industries, the index functions as a real-time indicator of sentiment shifts, sector momentum, and broader market alignment. From daily market movement to quarterly trend analysis, the NASDAQ 100 index offers critical insight into how dynamic business models are evolving across global economies.
Composition and Strategic Focus
The NASDAQ 100 index includes a wide range of market leaders across cloud computing, semiconductors, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and digital infrastructure. It excludes financial firms, which distinguishes it from broader indices and reinforces its emphasis on companies driven by innovation and scalability.
This composition creates a technology-forward structure, enabling the index to reflect the behavior of sectors that respond quickly to economic changes, regulatory updates, and consumer demand shifts. The companies within this index often pioneer solutions that are embedded in enterprise systems, communication networks, and digital ecosystems worldwide.
Market Responsiveness and Sentiment Signals
The NASDAQ 100 index is known for its responsiveness to macroeconomic updates and corporate developments. Data points such as labor market trends, inflation readings, and manufacturing activity often trigger immediate price responses in the index due to the growth-centric nature of its components.
When positive sentiment builds around future-focused industries, the index tends to rise quickly, reflecting momentum in sectors like software, cybersecurity, biotech, and digital commerce. Conversely, caution or economic tightening tends to produce early pullbacks in these same areas, often signaling broader equity adjustments.
This responsiveness positions the index as a reliable barometer for interpreting real-time market mood.
Sector Rotation and Leadership Patterns
Observing sector leadership within the NASDAQ 100 index helps to identify when market participants are rotating between growth and defensive themes. During periods of expansion, technology and consumer innovation often dominate, while in more uncertain phases, rotation may shift toward stability-focused names or out of the index altogether.
Volume trends and breadth indicators within the index offer further clarity. Strong performance across a wide range of constituents suggests healthy momentum, while narrow gains among a few top names may highlight fragility or over-reliance on individual stock performance.
Understanding these internal movements allows for better interpretation of where market focus is consolidating or dispersing.
Global Influence and Operational Scale
The companies within the NASDAQ 100 index operate across international markets, offering services and solutions to businesses, governments, and consumers globally. Their exposure to global trade, cross-border regulation, and regional demand cycles means the index reacts not only to domestic signals but also to international developments.
This global footprint reinforces the index’s relevance in reflecting real-time market dynamics. Events such as foreign policy shifts, economic realignments, or technological regulation abroad can quickly influence pricing and positioning within the index.
It also emphasizes the agility and competitive scale of these companies, which frequently adjust to evolving global conditions faster than more traditional sectors.
Technical Patterns and Index Behavior
Technical analysis is commonly applied to the NASDAQ 100 index to assess trend strength, consolidation zones, and potential reversals. Chart watchers monitor levels such as long-term moving averages, trendlines, and breakout zones to determine the market’s directional bias.
When the index sustains movement above key technical thresholds with increasing volume, it often reflects confidence in sector performance. On the other hand, fading momentum or breakdowns below support levels may indicate caution, rotation, or reevaluation of near-term growth potential.
Gap analysis, particularly between previous closing levels and pre-market futures pricing, also provides insight into overnight sentiment shifts and anticipated open direction.
Innovation as a Defining Characteristic
A consistent theme among the constituents of the NASDAQ 100 index is their leadership in innovation. These companies are deeply involved in developing or delivering next-generation technologies that shape how business is conducted and how consumers interact with digital platforms.
From advanced microchips and AI models to virtual infrastructure and integrated healthcare platforms, these firms are central to ongoing digital transformation. Their activity defines product cycles, shifts enterprise strategies, and influences capital allocation across industries.
As a result, the index is often viewed as a signal of where the global economy may be heading in terms of technological maturity and productivity trends.
0 notes