#CSF Advisers
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
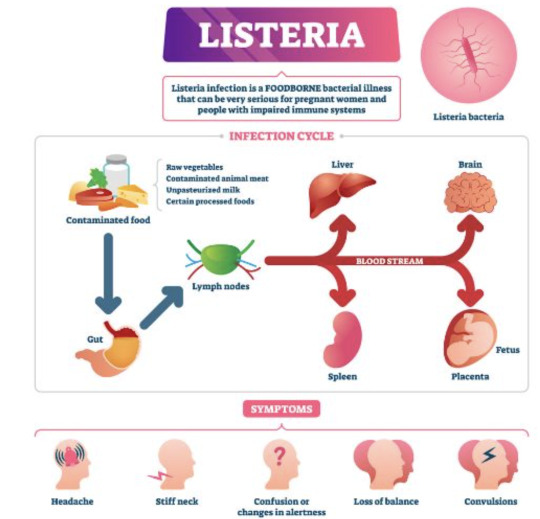
Listeria
For whatever reason it reminds me of Desperate Housewives and Wisteria lane. Or just Wisteria in general.

It's unfortunately it's anything but wistful or romantic.
This is inspired by the netflix series Poisoned. I hate that title but it's a great watch. I learned a lot from it. I highly recommend it particularly for medical students and residents etc.
So, listeria are gram positive rods (most bacilli are negative) making this relatively easier to remember (purple rods). Also catalase positive. IT's also a facultative anaerobe - so both cultures may be positive (aerobic and anaerobic bottles).

the species that is the culprit for major human pathogens is Listeria monocytogenes.
At increased risk groups (more likely to die of Listeriosis) - the immunocompromised and extremes of life, including the elderly, pregnant women and neonates. Immunocompromised: HIV, anyone on long term highish doses of steroids, leukaemia/oncology patients etc. Worryingly, incubation time is 3-90 days in these groups, so it's difficult to really trace or keep track of. Pregnant women are at 20x higher risk of acquiring the severe form.
Source: CDC

Hence why during pregnancy you're advised not to consume raw salads, fruits, cold cuts, soft cheeses, sprouts and smoked salmon or sushi, no mayo and no raw egg (definitely no raw milk) etc. Similarly, common recommendation is you serve none of these to children under the age of 1. It naturally lives in soil (hence avoidance of raw sprouts) and can live in animals. So it can frequently contaminate food.
Image Source: SA Health

As with COVID (I can't believe I'm using COVID as a measure of things), it can cause mild food borne illness (nausea, vomiting diarrhoea, myalgias, even fevers) to invasive disease causing sepsis and even meningitis or encephalitis. Incubation time is a few days in the mild form.
IMage source:
Death by Listeria when you have the severe form (Listeriosis) is 20%, astonishingly high given you have a 1% chance of dying from Salmonella.
It's a small risk but the issue is that complications and fatality if you do acquire is high. It's also highly preventable, but the challenge is food safety and avoiding certain foods as a consumer.
i.e. in pregnancy, most will have diarrhoeal illness that's mild. But in the subset that get invasive disease and really unwell, there's a 20% risk of miscarriage, risk of premature labour and risk of still birth at 3% in the US. In the states, pregnant women are also 10x more likely to get Listeria infection. That is, illness after exposure.
On the final note of prevention, also always properly refridgerate food to 4 degrees celsius and cook meat to 165 fahrenheit or 73 degrees celsius. As I've learned from the Poisoned documentary, you can ask restaurants to do this, ask them to use an internal thermometer to measure - as rare/medium rare etc have no meaning as it pertains to food safety. If they can't, order something else.

With meningoencephalitis, we just presume that Listeria is a possibility and treat empirically while awaiting investigations.
Investigations: - CSF (lumbar puncture) in event of signs of meningism or encephalitis (classic headache/fever/stiff neck/rash and/or acute confusion or seizure AND fevers) --> expect the classic features of bacterial meningiits and gram stain positive for purple rods - PCR - stool cultures have no value - blood cultures--> look for gram positive rods in the preliminary findings, expect a call from the lab Empirical therapy: - none in asymptomatic or mild disease. just monitoring until symptoms resolve and supportive care (fluids etc.) - Listeria is a notifiable disease to the health department in most Western countries that keep track of outbreaks. - in the US, standard treatment is ampicillin. - in Australia at least, standard therapy is IV benzylpenicillin, 2.4 g 4 hrly in meningitis or encephalitis and everyone is just started on this until bug identification/gram staining and sensitivities return. - in hypersensitivity, bactrim is used. - cephalosporins have no activity against them (or "inherently resistant), hence you can see IV ceftriaxone and benzylpen in the drug regimen for empirical therapy of meningitis - cef covers gram negatives, strep pneumo (most common cause of meningitis) and neisseria meningitidis - duration of therapy in severe disease: 3 weeks, 6 weeks if immunosuppressed
Really great summary here.
Random historical trivia
listeria is named for Dr. Joseph Lister, a British surgeon who introduced sterilisation of equipment and antiseptics to surgery, improve post op care and observed that microbes are the cause of cases of poor wound healing or post op infections. he also began to look at them under the microscope as an early pioneer of bacteriology.

Lister's father by the way, made compound microscopes for a living, so lister became proficient at using this and started publishing articles during medical school
this also led to a lot more research on inflammation and coagulation
weirder trivia: in his med school days, surgeons commonly did not wash hands between patients and some didn't even change gowns, glorifying how busy they where by how many stains were on it by the end of the day

so unsurprisingly his early battles to pioneer antiseptics and aseptic techqniues to prevent the transmission of infection in surgical patients were pretty uphill
Resources CDC guidelines WHO guidelines FDA Statpearls --> great at covering basic physiology and pathology etc. in a short form. Australian therapeutic guidelines - unfortunately not free.. so won't bother to link. If you work at any large-ish Australian hospital you'll have 'free' access. Wikipaedia US list of outbreaks CDC recommendations on foods to avoid vs okay to eat to avoid Listeria
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Billy Joel shares devastating diagnosis and cancels all tour dates through next year

LAS VEGAS, NEVADA – NOVEMBER 09: Billy Joel performs at Allegiant Stadium on November 09, 2024 in Las Vegas, Nevada.
The Piano Man is stepping back from the spotlight.
Billy Joel, 76, has officially canceled all upcoming tour dates following a recent medical diagnosis.
In a statement shared on social media Friday, the iconic Bronx-born singer revealed that he has been diagnosed with “normal pressure hydrocephalus”—a neurological condition caused by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain.

Joel’s condition has reportedly deteriorated following his recent concert engagements, resulting in complications affecting his hearing, vision, and balance — according to a detailed statement shared on his Instagram account.
Under the guidance of his medical team, the “Scenes From an Italian Restaurant” singer has been advised to cancel all performances for the duration of his recovery. He is currently undergoing a specialized course of physical therapy as part of his treatment regimen.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), the condition he is reportedly managing, is a rare neurological disorder impacting approximately 0.2% of individuals aged 70 to 80, and nearly 6% of those over 80.
The disorder arises when cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is not properly circulated or reabsorbed by the body, leading to a buildup that increases intracranial pressure. If left untreated, the continued accumulation of CSF can result in irreversible brain damage due to compression.
The symptoms of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) often resemble those seen in dementia, including gait disturbances (any deviation from a person’s normal walking pattern), cognitive impairments such as memory loss or mood changes, and involuntary leakage of urine.
Nonetheless, NPH is one of the few neurological conditions that can be reversible with appropriate treatment. So, despite the diagnosis, Joel’s condition does not necessarily mark a permanent retirement from performing.
His team told fans that Joel is “thankful for the excellent care he is receiving and is fully committed to prioritizing his health. He is grateful for the support from fans during this time and looks forward to the day when he can once again take the stage.”
“I’m sincerely sorry to disappoint our audience, and thank you for understanding,” Joel shared.
Those who purchased tickets for any of Joel’s canceled gigs, which include events in New York, New Orleans, Toronto, Santa Clara, California, Salt Lake City, Washington, DC, and Liverpool, will be reimbursed.
Stay informed! Receive breaking news blasts directly to your inbox for free. Subscribe here. https://www.oann.com/alerts
0 notes
Text
Drug Monograph FOR SERIOUS INFECTIONS ONLY Drug Monograph: Vancomycin Drug Name -- Vancocin (brand), Vancomycin HCL -- oral (generic) This is a time-dependent bactericidal antibiotic, which inhibits cell wall synthesis (Levinson, 2009). Glycopeptides VA Class - AM900 CAS Number 1404-93-9 Therapeutic Category -- a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic Pharmacology Vancomycin is not too well-absorbed from the GI tract after oral administration (Levinson 2009). When given parenterally, it penetrates the bile, pleural, pericardial, synovial and ascitic fluids. It is excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration (Levison). When taken orally, Vancomycin is not absorbed in the intestines so that it can stop the growth of a severe intestinal condition known as Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (Medicine Net, 2012). When vancomycin is given by mouth, it is not absorbed by the body but remains in the intestines. This is to allow it to stop the growth of the Clostridium difficile bacteria. Vancomycin is intended as treatment only for bacterial infections of the intestines. It is not effective for other bacterial infections or infections caused by viruses. Its overuse can decrease its effectiveness (Medicine Net). Indications Vancomycin is intended for the treatment of serious or severe bacterial infections caused by susceptible strains of methicillin-resistant staphylococci (PDR, 2012, Drug.com, 2012). It is indicated for use by patients who are allergic to penicillin and cannot or fail to respond to other drugs. It is for infections caused by Vancomycin-susceptible organisms resistant to other anti-microbials. It is indicated as initial therapy when methicillin-resistant staphylococci infection is suspected. It is also effective in the treatment of staphylococcal endocarditis. It has been successfully used in combination with either rifampin or an aminoglycoside or both for early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis, caused by S. epidermidis or diphtheroid. Its parenteral form may be administered orally in treating antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis caused by C. difficile and for staphylococcal enterocolitis (PDR, Drug.com). Vancomycin is the drug of choice against serious infection and endocarditis caused by Methicillin-resistant S. aureaus, Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, B-Hemolytic streptococci, Corynebacterium group JK, Viridans streptococci and enterococci (Levinson, 2009). It has been used as an alternative drug for pneumococcal meningitis caused by strains with reduced penicillin sensitivity. But its erratic penetration into the CSF and reported clinical failures make it not advisable for use alone to treat pneumococcal meningitis. Dosages For Adults The usual is 500 mg by IV every 6 hours or 1 g by IV every 12 hours (PDR, 2012). It should be administered no more than at 10 mg per minute or at least 60 minutes, whichever is longer. For those with renal impairment, the initial dose is not less than 15 mg per kg. The daily dosage is about 15 times the GFR in ML per minute. For elderly patients, the dose should be reduced. The initial dose for anephric patients is 15 mg/kg then 1.9 mg/kg/24 hours. The dose for those with marked renal impairment is 250-1,000 mg once every several days and for those with anuria, 1,000 mg every 7-10 days. For PO administration, divided doses of 500-2,000 mg/day should be given for 7-10 days or a maximum dose of 2,000 mg/day. The doses may be diluted in 1 oz of water or administered through an NG tube (PDR). Vancomycin is taken orally usually 4 times a day for 7-10 days according to the doctor's instructions (Medicine Net, 2012). He determines the dosage according to the medical condition and the patient's response to treatment. Cholestyramine and colestipol can lessen the effects of Vancomycin when they are taken at the same time. If they have to be taken, they should be given at least 3-4 hours from Vancomycin. Vancomycin works best when kept at a constant level at the intestines. Medication should be continued until the prescribed amount is completed even if symptoms have disappeared. Re-infection can occur if the medication is stopped before completion. If the condition persists after 7 days or gets worse, the doctor should be informed (Medicine Net). For Pediatric Patients The usual does for all pediatric patients is 10 mg/kg by IV every six hours (PDR, 2012). The initial for newborns is 15 mg/kg, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for the first week of life. This is continued every 8 hours until their first month of age. Vancomycin should be given for at least 60 minutes. The initial dosage for pediatrics with renal impairment is not less than 15 mg/kg per day or 15 times the GFR in mL/min. Premature infants should have longer dosing intervals. PO administration should be 40 mg/kg/day in 3-4 divided doses for 7-10 days. The maximum is 2,000 mg/day, which may be diluted in 1 oz of water or administered through an NG tube (PDR). Contraindications Vancomycin is contraindicated to patients with hypersensitivity to vancomycin (Drug.com, 2012). Commercially prepared frozen Vancomycyn Hydrochloride injections in 5% dextrose may also be contraindicated to those with known allergic reaction to corn or corn products (Drug.com). Drug-Drug Interactions The patient should inform the doctor or pharmacist of all prescription and non-prescription or herbal products currently used (Medicine Net, 2012; Levinson, 2012). Aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, other antibiotics, and live bacterial vaccines are special mentions. If treatment requires anesthesia, the doctor or dentist should be told if the patient has been using Vancomycin. Although most antibiotics do not significantly affect hormonal birth control medications, they may decrease the effectiveness of these hormone medications and cause pregnancy (Medicine Net). Current or sequential systemic or topical use of neurotoxic or nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully monitored (PDR, 2012). Periodic leukocyte count monitoring with drugs, which may cause neutropenia, should be performed. Serial monitoring of renal function and particular care after dosing should also be done to minimize the risk of nephrotoxicity with concomitant aminoglycoside (PDR). Other Precautions and Potential Adverse Effects A patient's medical history should be revealed before Vancomycin is administed (Medicine Net, 2012). Elderly patients should be able to eliminate the drug from their bodies when needed. Otherwise, it should be administered to them with caution for possible sensitivity to its effects. It should be used on pregnant women only when clearly needed. Risks and benefits should be discussed with the doctor. Vancomycin does not pass on to breast milk and is thus not harmful to nursing infants. But the doctor must still be consulted on its effect on breastfeeding (Medicine Net). Vancomycin may cause hypotension and cardiac arrest, though rarely, by rapid bolus administration (PDR, 2012). Ototoxicity has been reported and calls for caution for those with underlying hearing loss. Prolonged use can lead to an overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. Safety and efficacy of administration through the intraperitoneal and intrathecal routes have not been confirmed. Use via the intraperitoneal route during dialysis has been reported to lead to a syndrome of chemical peritonitis (PDR). Look-alike/Sound-alike Drugs and Prescription Refill Requirements Vancomycin is 6th in the list of top 10 medications involved in drug errors (Medscape Pharmacists, 2007). These medications are the most commonly mis-used or mishandled some way by healthcare professionals, based on the database of the U.S. Pharmacopoeia. Liquid dose concentrations increase the risk of medication errors. There has been confusion over mL and tsp errors, which leads to overdose or under-dose of up to 5 times if undetected. Reconstituting antibiotics can also be risky as when the antibiotic powder is mixed with alcohol instead of distilled water (Medscape Pharmacists). Vancomycin was also one of the 10 most frequently reported drugs with the highest adverse drug reactions by the Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Program for 2003-2004 (Bebout, 2004). Half of all the 360 drugs were anti-infective (Bebout). # BIBLIOGRAPHY Bebout, K. (2004). Adverse drug reporting program update and recent drug safety warnings. P & T. News: the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/pharmacy/PTNews/2004/december.html Drug.com (2010). Vancomycin Hydrochlorde. Drugs.com. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.drugs.com/monograph/vancomycin-hydrochloride.html Harrison's Practice (2012). Vancomycin. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.harrisonspractice.com/practice/ub/view/DrugMonographs/156696/all/Vancomycin Levison, M.E. (2009). Vancomycin. The Merck Manual: Merck Sharp & Dohme. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.merckmanuals.com/professionals/infections_diseases/bacteria_and_antibackterial_drugs/vancomycin.html Medicine Net (2011). Vancomycin. Medicine Net. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.medicinenet.com/vancomycin-oral/article.htm Medscape Pharmacists (2007). The top 10 drug errors and how to prevent them. Medscape Education: Medscape LLC. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/556487 PDR (2012). Vancomycin HCL. Physician's Desk Reference: PDR Network LLC. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.pdr.net/drugpages/concisemonograph.aspx?concise=688 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Any project is completed as a result of a combination of various activities, some of which often happen unexpectedly, sometimes in defiance of a project plan. Regardless of their nature, projects are fulfilled in a constantly changing environment, so, during a project, different events can occur, influencing the final result. Taking the high possibility of changes into consideration, it is advisable to understand which factors are more critical to the project success so that to make an attempt to manage risks connected with their possible changes. According to Amberg et al. (2005) the critical success factors (CSF) approach in the context of the project management has been first established by Rockart (1979), which defined CSF as “the limited number of areas in which results, if they are satisfactory, will ensure successful competitive performance for the organization” (Rockart, 1979, cited in Amberg et al., 2005, p.1). In spite of the fact that initially Rockart used the CSF concept regarding to the Information System projects, Amberg et al. (2005) emphasise that it can be used in different industrial areas what is confirmed by a number of studies, carried out during 30 years after the first introduction of the CSF term. In this paper I briefly review some referred journal articles which deal with the identifying of variables influencing the success of project implementation according to various CSF approaches. In the centre of my investigation’s attention there are research papers, which describe multidimensional, multiobservational approaches to assess project success, which are specifically “designed to capture the “real world” experiences of project managers with a view to determining the extent to which those involved in the management of projects actually make use of the methods and techniques that are available and how effective the methods and techniques used are felt to be” (White & Fortune, 2002, p.1). Thus, the review will help me to understand commonalities and differences in the CSF definition, including in respect of contract and in-house projects. Search strategy To find referred article for reviewing I used Google services – classical Google search engine1 and Google Scholar2. At first, I used a word-combination “project success factors” directly in search box in Google and browsed among the relevant materials, picking out mostly articles or papers of researchers and experts in Project Management area. I looked through references given by authors and selected titles of academic journal articles, which were mentioned more often or seemed to me more appropriate to the objective of my review. As a consequence of this selection the initial list of articles for reviewing has been composed. Then I used Google Scholar to seek whether the previously chosen article has been cited in other relevant articles and made a final choose of four articles for reviewing. I was guided by the following criteria: 1. An article should make a significant contribution to the body of knowledge in the Project Management area, representing a new approach or generic ideas, so that it enables to serve as a basis for other researches. 2. It is desirable that the Project Critical Success Factors approach or approaches described in the article are related or can be applied to different types of projects, including contract and in-house projects. 3. The chosen articles should reveal a development of the Project Management theory and practical methods regarding the Project Critical Success Factors area. As a result I’ve chosen two descriptions of researches in specific approaches to the project success factors, which are widely used now in other researches; and two descriptions of researches aimed to make an overview of current practices and generic models of defining the project success and managing the project effectiveness Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Planning And Establishing Of Schools
Raghav Foundation is a pioneer in setting up K-12 schools with exclusive services and is the best New school opening consultancy in India.
Establishment of schools requires educational field specialists. Raghav Foundation is a pioneer in setting up K-12 schools and is the best new school opening consultancy in India, who have the required experience, a keen understanding of the logistics process, the ability to gauge probable hurdles, and the capability to map the growth plan.

What we consider before planning & establishment of school?
Location planning
Advise and Guidance on statutory approvals liaison and compliances with the architect and the client to ensure that the final design incorporates the vision of the client
Classroom Design
Surveying of the area in which the school is proposed to be located
Technology implementation guidance
Marketing and branding of school
Study of Return on Investment (ROI)
Guidance regarding society registration and all other procedures for obtaining registrations and permissions
School Affiliations (CBSE & ICSE school)
Staffing, positioning and teacher's training
Identification of Critical Success Factors (CSFs) and Unique Selling Points (USPs)
Curriculum design
Academic planning
Plan & design map for new school
Business positioning and many more
0 notes
Text
Popular Sleep Medications Could Hinder Brain's Natural Waste-Clearing Process

The Complex Relationship Between Sleep Aids and Brain Health
An estimated 70 million people worldwide face persistent sleep issues. Chronic sleep deprivation significantly elevates the risk of numerous health concerns, including cognitive decline and dementia. Now, groundbreaking research has illuminated the mechanisms through which sleep facilitates the brain’s “waste” removal system, highlighting potential concerns about commonly prescribed sleep medications.
Understanding Sleep and the Brain’s Glymphatic System
Recent research, utilizing a mouse model, offers the first detailed description of how synchronized oscillations during sleep power the brain’s glymphatic system. This system is responsible for removing waste products linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Scientists discovered that these oscillations involve coordinated activity of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, cerebral blood flow, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). During non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep, slow oscillations in norepinephrine levels drive rhythmic fluctuations in blood vessel diameter, creating a pumping effect that facilitates the flow of CSF and clears unwanted molecules from brain tissue.
According to Dr. Maiken Nedergaard, a leading researcher in the study, this waste-clearing process is vital for maintaining brain health. “Sleep is crucial as it gives the brain time to perform housekeeping tasks such as waste removal. On the contrary, sleep aids block the neuromodulators that drive this system, preventing the brain from properly preparing for a new day,” Nedergaard explained.
Potential Risks of Sleep Aids on Brain Function
The study also revealed that zolpidem, a commonly prescribed sleep aid marketed under the name Ambien, might suppress the essential oscillations required for the glymphatic system’s function. Researchers observed that zolpidem disrupted norepinephrine’s rhythmic activity, thereby inhibiting the brain’s ability to effectively clear waste during sleep.
Dr. Natalie Hauglund, the study’s first author, emphasized caution in the use of sleep aids. “While sleep aids may help induce sleep, our findings indicate that this sleep might lack the restorative benefits of natural, deep sleep. These medications should be used sparingly and as a last resort,” she advised.
Sleep and Cognitive Decline: A Growing Concern
The importance of addressing all factors contributing to cognitive decline is underscored by recent estimates suggesting that dementia risk among Americans over age 55 has more than doubled. Despite recommendations for adults to get at least seven hours of quality sleep nightly, data from 2022 shows that 39% of U.S. adults over age 45 report insufficient sleep, raising concerns about long-term brain health.
“Sleep allows the brain to go offline, shut down processing of the external world, and focus on maintenance tasks like immune surveillance and waste removal,” Hauglund explained. “Lack of sleep is strongly associated with cognitive impairment and disease development.”
Differing Opinions in the Medical Community
Not all experts agree on the implications of these findings. Dr. Clifford Segil, a neurologist at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in California, expressed skepticism.
“It is unlikely that the benefits of improved sleep from medications like zolpidem are outweighed by potential adverse effects on REM sleep and brain function,” Segil stated. “For elderly patients struggling with insomnia, the immediate benefits of sleep often outweigh theoretical risks.”
Dr. Peter G. Polos, a sleep medicine specialist, found the study intriguing but urged caution in interpreting its results. “While the interaction between the glymphatic system and various brain transmitters is fascinating, this research is based on animal models. Extrapolating these findings to humans requires further investigation,” Polos said. He also called for more advanced imaging studies to assess the effects of sleep aids on human glymphatic function.
The Path Forward: Prioritizing Sleep and Brain Health
The intricate relationship between sleep, brain health, and overall well-being cannot be overstated. This research underscores the critical role of restorative sleep in maintaining cognitive function and highlights the need for careful evaluation of sleep aids. While sleep medications can provide short-term relief for insomnia, their potential long-term impact on brain health warrants further study.
As researchers continue to explore these connections, the importance of prioritizing natural, high-quality sleep becomes increasingly clear. Individuals experiencing chronic sleep issues are encouraged to consult healthcare providers to develop strategies that promote healthy sleep patterns without reliance on medications.
By understanding and respecting the brain’s natural processes, we can take significant steps toward safeguarding cognitive health and overall wellness.
#Alzheimer's / Dementia#Neurology / Neuroscience#Sleep / Sleep Disorders#InsomniaDrugs#Health#Health News
1 note
·
View note
Link
2020 Yale-G’s Monthly Clinical Updates According to www.uptodate.com
(As of 2020-11-12, updated in Yale-G’s 6th-Ed Kindle Version; will be emailed to buyers of Ed6 paper books)
Chapter 1: Infectious Diseases
Special Viruses: Coronaviruses
Coronaviruses are important human and animal pathogens, accounting for 5-10% community-acquired URIs in adults and probably also playing a role in severe LRIs, particularly in immunocompromised patients and primarily in the winter. Virology: Medium-sized enveloped positive-stranded RNA viruses as a family within the Nidovirales order, further classified into four genera (alpha, beta, gamma, delta), encoding 4-5 structural proteins, S, M, N, HE, and E; severe types: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV, which causes COVID-19). Routes of transmission: Similar to that of rhinoviruses, via direct contact with infected secretions or large aerosol droplets. Immunity develops soon after infection but wanes gradually over time. Reinfection is common. Clinical manifestations: 1. Coronaviruses mostly cause respiratory symptoms (nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, and cough) and influenza-like symptoms (fever, headache). 2. Severe types (2019-nCoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV): Typically with pneumonia–fever, cough, dyspnea, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, and sometimes enterocolitis (diarrhea), particularly in immunocompromised hosts (HIV+, elders, children). 3. Most community-acquired coronavirus infections are diagnosed clinically, although RT-PCR applied to respiratory secretions is the diagnostic test of choice.
Treatment: 1. Mainly consists of ensuring appropriate infection control and supportive care for sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. 2. In study: Chloroquine showed activity against the SARS-CoV, HCoV-229E, and HCoV-OC43 and remdesivir against 2019-nCoV. Dexamethasone may have clinical benefit.
Prevention: 1. For most coronaviruses: The same as for rhinovirus infections, which consist of handwashing and the careful disposal of materials infected with nasal sec retions. 2. For novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV: (1) Preventing exposure by diligent hand washing, respiratory hygiene, and avoiding close contact with live or dead animals and ill individuals. (2) Infection control for suspected or confirmed cases: Wear a medical mask to contain their respiratory secretions and seek medical attention; standard contact and airborne precautions, with eye protection.
Hepatitis A: HAV vaccine is newly recommended to adults at increased risk for HAV infection (substance use treatment centers, group homes, and day care facilities for disabled persons), and to all children and adolescents aged 2 to 18 years who have not previously received HAV vaccine.
Hepatitis C: 8-week glecaprevir-pibrentasvir is recommended for chronic HCV infection in treatment-naive patients. In addition to the new broad one-time HCV screening (17-79 y/a), a repeated screening in individuals with ongoing risk factors is suggested.
New: Lefamulin is active against many common community-acquired pneumonia pathogens, including S. pneumoniae, Hib, M. catarrhalis, S. aureus, and atypical pathogens.
New: Cefiderocol is a novel parenteral cephalosporin that has activity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria, including carbapenemase-producing organisms and Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant to other beta-lactams. It’s reserved for infections for which there are no alternative options.
New: Novel macrolide fidaxomicin is reserved for treating the second or greater recurrence of C. difficile infection in children. Vitamin C is not beneficial in adults with sepsis and ARDS.
Chapter 2: CVD
AF: Catheter ablation is recommended to some drug-refractory, paroxysmal AF to decrease symptom burden. In study: Renal nerve denervation has been proposed as an adjunctive therapy to catheter ablation in hypertensive patients with AF. Alcohol abstinence lowers the risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation among regular drinkers.
VF: For nonshockable rhythms, epinephrine is given as soon as feasible during CPR, while for shockable rhythms epinephrine is given after initial defibrillation attempts are unsuccessful. Avoid vasopressin use.
All patients with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) should receive a P2Y12 inhibitor. For patients undergoing an invasive approach, either prasugrel or ticagrelor has been preferred to clopidogrel. Long-term antithrombotic therapy in patients with stable CAD and AF has newly been modified as either anticoagulant (AC) monotherapy or AC plus a single antiplatelet agent.
Long-term antithrombotic therapy (rivaroxaban +/- aspirin) is recommended for patients with AF and stable CAD. Ticagrelor plus aspirin is recommended for some patients with CAD and diabetes.
VTE (venous thromboembolism): LMW heparin or oral anticoagulant edoxaban is the first-line anticoagulants in patients with cancer-associated VTE.
Dosing of warfarin for VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing total hip or total knee arthroplasty should continue to target an INR of 2.5.
Chapter 3: Resp. Disorders
Asthma: Benralizumab is an IL-5 receptor antibody that is used as add-on therapy for patients with severe asthma and high blood eosinophil counts.
Recombinant GM-CSF is still reserved for patients who cannot undergo, or who have failed, whole lung lavage.
Pulmonary embolism (PE): PE response teams (PERT, with specialists from vascular surgery, critical care, interventional radiology, emergency medicine, cardiac surgery, and cardiology) are being increasingly used in management of patients with intermediate and high-risk PE.
Although high-sensitivity D-dimer testing is preferred, protocols that use D-dimer levels adjusted for pretest probability may be an alternative to unadjusted D-dimer in patients with a low pretest probability for PE.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Newly approved capmatinib is for advanced NSCLC associated with a MET mutation, and selpercatinib for those with advanced RET fusion-positive. Atezolizumab was newly approved for PD-L1 high NSCLC.
Circulating tumor DNA tests for cancers such as NSCLC are increasingly used as “liquid biopsy”. Due to its limited sensitivity, NSCLC patients who test (-) for the biomarkers should undergo tissue biopsy.
Cystic Fibrosis (CF): Tx: CFTR modulator therapy (elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor) is recommended for patients ≥12 years with the F508del variant.
Vitamin E acetate has been implicated in the development of electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use associated lung injury.
Chapter 4: Digestive and Nutritional Disorders
Comparison of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC):
Common: They are two major types of chronic cholestatic liver disease, with fatigue, pruritus, obstructive jaundice, similar biochemical tests of copper metabolism, overlapped histology (which is not diagnostic), destructive cholangitis, and both ultimately result in cirrhosis and hepatic failure. (1) PBC: Mainly in middle-aged women, with keratoconjunctivitis sicca, hyperpigmentation, and high titer of antimitochondrial Ab (which is negative for PSC). (2) PSC: Primarily in middle-aged men, with chronic ulcerative colitis (80%), irregular intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts, and anti-centromere Ab (+).
CRC: Patients with colorectal adenomas at high risk for subsequent colorectal cancer (CRC) (≥3 adenomas, villous type with high-grade dysplasia, or ≥10 mm in diameter) are advised short follow-up intervals for CRC surveillance. Pembrolizumab was approved for the first-line treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic DNA mismatch repair (dMMR) CRC.
UC and CRC: Patients with extensive colitis (not proctitis or left-sided colitis) have increased CRC risk.
Eradication of H. pylori: adding bismuth to clarithromycin-based triple therapy for patients with risk factors for macrolide resistance.
Thromboelastography and rotational thromboelastometry are bedside tests recommended for patients with cirrhosis and bleeding.
Pancreatic cancer: Screening for patients at risk for hereditary pancreatic cancer (PC): Individuals with mutations in the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene and one first-degree relative with PC can be screened with endoscopic ultrasound and/or MRI/magnetic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Olaparib is recommended for BRCA-mutated advanced pancreatic cancer after 16 weeks of initial platinum-containing therapy.
HCC (unresectable): New first-line therapy is a TKI (sorafenib or sunitinib) or immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, +/- doxorubicin. Monitor kidney toxicity for these drugs.
UC: Ustekinumab (-umab) anti-interleukin 12/23 antibody, is newly approved for the treatment of UC.
Crohn disease: The combination of partial enteral nutrition with the specific Crohn disease exclusion diet is a valuable alternative to exclusive enteral nutrition for induction of remission.
Obesity: Lorcaserin, a 5HT2C agonist that can reduce food intake, has been discontinued in the treatment of obesity due to increased malignancies (including colorectal, pancreatic, and lung cancers).
Diet and cancer deaths: A low-fat diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and grains experienced fewer deaths resulted from many types of cancer.
Note that H2-blockers (-tidines) are no longer recommended due to the associated carcinogenic N-nitrosodimethylamine.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST):
GIST is a rare type of tumor that occurs in the GI tract, mostly in the stomach (50%) or small intestine. As a sarcoma, it’s the #1 common in the GI tract. It is considered to grow from specialized cells in the GI tract called interstitial cells of Cajal, associated with high rates of malignant transformation.
Clinical features and diagnosis: Most GISTs are asymptomatic. Nausea, early satiety, bloating, weight loss, and signs of anemia may develop, depending on the location, size, and pattern of growth of the tumor. They are best diagnosed by CT scan and mostly positive staining for CD117 (C-Kit), CD34, and/or DOG-1.
Treatment: Approaches include resection of primary low-risk tumors, resection of high-risk primary or metastatic tumors with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib for 12 months, or if the tumor is unresectable, neoadjuvant imatinib followed by resection. Radiofrequency ablation has shown to be effective when surgery is not suitable. Newer therapies of ipilimumab, nivolumab, and endoscopic ultrasound alcohol ablation have shown promising results. Avapritinib or ripretinib (new TKI) is recommended for advanced unresectable or metastatic GIST with PDGFRA mutations.
Anal Cancer:
Anal cancer is uncommon and more similar to a genital cancer than it is to a GI malignancy by etiology. By histology, it is divided into SCC (#1 common) and adenocarcinoma. Anal cancer (particularly SCC among women) has increased fast over the last 30 years and may surpass cervical cancer to become the leading HPV-linked cancer in older women. A higher incidence has been associated with HPV/HIV infection, multiple sexual partners, genital warts, receptive anal intercourse, and cigarette smoking. SCCs that arise in the rectum are treated as anal canal SCCs.
Clinical features and diagnosis: 1. Bleeding (#1) and itching (often mistaken as hemorrhoids). Later on, patients may develop focal pain or pressure, unusual discharges, and lump near the anus, and changes in bowel habits. 2. Diagnosis is made by a routine digital rectal exam, anoscopy/proctoscopy plus biopsy, +/- endorectal ultrasound.
Treatment: Anal cancer is primarily treated with a combination of radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery—especially for patients failing the above therapy or for true perianal skin cancers.
Chapter 5: Endocrinology
Diabetes (DM): Liraglutide can be added as a second agent for type-2 DM patients who fail monotherapy with metformin or as a third agent for those who fail combination therapy with metformin and insulin. Metformin is suggested to prevent type 2 DM in high-risk patients in whom lifestyle interventions fail to improve glycemic indices. Metabolic (bariatric) surgery improves glucose control in obese patients with type 2 DM and also reduce diabetes-related complications, such as CVD. Teprotumumab, an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor, can be used for Graves’ orbitopathy if corticosteroids are not effective. Subclinical hypothyroidism should not be routinely treated (with T4) in older adults with TSH <10 mU/L.
Chapter 6: Hematology & Immunology
Anticoagulants: Apixaban is preferred to warfarin for atrial fibrillation with osteoporosis because it lowers the risk of fracture. Rivaroxaban is inferior to warfarin for antiphospholipid syndrome.
Cancer-associated VTE: LMW heparin or oral edoxaban is the first-line anticoagulant prophylaxis.
NH-Lymphoma Tx: New suggestion is four cycles of R(rituximab)-CHOP for limited stage (stage I or II) diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (DLBCL) without adverse features. New suggestions: selinexor is for patients with ≥2 relapses of DLBCL, and tafasitamab plus lenalidomide is for patients with r/r DLBCL who are not eligible for autologous HCT.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T (NK) immunotherapy is newly suggested for refractory lymphoid malignancies, with less toxicity than CAR-T therapy. Polatuzumab + bendamustine + rituximab (PBR) is an alternative to CAR-T, allogeneic HCT, etc. for multiply relapsed diffuse large B-C NHL.
Refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma (r/r cHL) is responsive to immune checkpoint inhibition with pembrolizumab or nivolumab, including those previously treated with brentuximab vedotin or autologous transplantation.
Mantle cell lymphoma: Induction therapy is bendamustine + rituximab or other conventional chemoimmunotherapy rather than more intensive approaches. CAR-T cell therapy is for refractory mantle cell lymphoma.
AML: Gilteritinib is a new alternative to intensive chemotherapy for patients with FLT3-mutated r/r AML.
Oral decitabine plus cedazuridine is suggested for MDS and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia.
Multiple myeloma (MM): Levofloxacin prophylaxis is suggested for patients with newly diagnosed MM during the first three months of treatment. For relapsed MM: Three-drug regimens (daratumumab, carfilzomib, and dexamethasone) are newly recommended.
Transplantation: As the transplant waitlist continues to grow, there may be an increasing need of HIV-positive to HIV-positive transplants.
Porphyria: Porphyria is a group of disorders (mostly inherited) caused by an overaccumulation of porphyrin, which results in hemoglobin and neurovisceral dysfunctions, and skin lesions. Clinical types, features, and diagnosis: I. Acute porphyrias: 1. Acute intermittent porphyria: Increased porphobilinogen (PBG) causes attacks of abdominal pain (90%), neurologic dysfunction (tetraparesis, limb pain and weakness), psychosis, and constipation, but no rash. Discolored urine is common. 2. ALA (aminolevulinic acid) dehydratase deficiency porphyria (Doss porphyria): Sensorimotor neuropathy and cutaneous photosensitivity. 3. Hereditary coproporphyria: Abdominal pain, constipation, neuropathies, and skin rash. 4. Variegate porphyria: Cutaneous photosensitivity and neuropathies. II. Chronic porphyrias: 1. Erythropoietic porphyria: Deficient uroporphyrinogen III synthase leads to cutaneous photosensitivity characterized by blisters, erosions, and scarring of light-exposed skin. Hemolytic anemia, splenomegaly, and osseous fragility may occur. 2. Cutaneous porphyrias–porphyria cutanea tarda: Skin fragility, photosensitivity, and blistering; the liver and nervous system may or may not be involved. III. Lab diagnosis: Significantly increased ALA and PBG levels in urine have 100% specificity for most acute porphyrias. Normal PBG levels in urine can exclude acute porphyria. Treatment: 1. Acute episodes: Parenteral narcotics are indicated for pain relief. Hemin (plasma-derived intravenous heme) is the definitive treatment and mainstay of management. 2. Avoidance of sunlight is the key in treating cutaneous porphyrias. Afamelanotide may permit increased duration of sun exposure in patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Chapter 7: Renal & UG
Membranous nephropathy (MN): Rituximab is a first-line therapy in patients with high or moderate risk of progressive disease and requiring immunosuppressive therapy.
Diabetes Insipidus (DI): Arginine-stimulated plasma copeptin assays are newly used to diagnose central DI and primary polydipsia, often alleviating the need for water restriction, hypertonic saline, and exogenous desmopressin.
Prostate cancer: Enzalutamide (new androgen blocker) is available for metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer. Cabazitaxel, despite its great toxicity, is suggested as third-line agent for metastatic prostate cancer. Either early salvage RT or adjuvant RT is acceptable after radical prostatectomy for high-risk disease.
UG cancers: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab is suggested in metastatic renal cell carcinoma for long-term survival.
Enfortumab vedotin is suggested in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Maintenance avelumab is recommended with other chemotherapy in advanced urothelial bladder cancer. Pyelocalyceal mitomycin is suggested for low-grade upper tract urothelial carcinomas.
Chapter 8: Rheumatology
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (upadacitinib, filgotinib) are new options for active, resistant RA and ankylosing spondylitis.
Graves’ orbitopathy: new therapy–teprotumumab, an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor.
Chapter 9: Neurology & Special Senses
Epilepsy: Cenobamate, a novel tetrazole alkyl carbamate derivative that inhibits Na-channels, provides a new treatment option for patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. A benzodiazepine plus either fosphenytoin, valproate, or levetiracetam is recommended as the initial treatment of generalized convulsive status epilepticus.
Migraine: Lasmiditan is a selective 5H1F receptor agonist that lacks vasoconstrictor activity, new therapy for patients with relative contraindications to triptans due to cardiovascular risk factors.
Stroke: New recommendation for cerebellar hemorrhages >3 cm in diameter is surgical evacuation. TBI: Antifibrolytic agent tranexamic acid is newly recommended for moderate and severe acute traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Ofatumumab is a new agent that may delay progression of MS.
Chapter 10: Dermatology
Minocycline foam is a new topical drug option for moderate to severe acne vulgaris.
Melanloma: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in metastatic melanoma has confirmed long-term survival. With sun-protective behavior, melanoma incidence is decreasing.
New: Tazemetostat is suggested in patients with locally advanced or metastatic epithelioid sarcoma (rare and aggressive) ineligible for complete surgical resection.
Psoriasis: New therapies for severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a TNF-alpha inhibitor (infliximab or adalimumab, golimumab) or IL-inhibitor (etanercept or ustekinumab) is effective. Ixekizumab is a newly approved monoclonal antibody against IL-17A. Clinical data support vigilance for signs of symptoms of malignancy in patients with psoriasis.
Chapter 11: GYH
Breast cancer: Although combined CDK 4/6 and aromatase inhibition is an effective strategy in older adults with advanced receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, toxicities (myelosuppression, diarrhea, and increased creatinine) should be carefully monitored. SC trastuzumab and pertuzumab is newly recommended for HER2-positive breast cancer.
Whole breast irradiation is suggested for most early-stage breast cancers treated with lumpectomy. Accelerated partial breast irradiation can be an alternative for women ≥50 years old with small (≤2 cm), hormone receptor-positive, node-negative tumors.
Endocrine therapy is recommended for breast cancer prevention in high-risk postmenopausal women.
Uterine fibroids: Elagolix (oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist) in combination with estradiol and norethindrone is for treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) due to uterine fibroids.
Chapter 12: OB
Table 12-6: Active labor can start after OS > 4cm, and 6cm is relatively more acceptable but not a strict number.
Table 12-7: Preeclampsia is a multisystem progressive disorder characterized by the new onset of hypertension and proteinuria, or of hypertension and significant end-organ dysfunction with or without proteinuria, in the last half of pregnancy or postpartum. Once a diagnosis of preeclampsia is established, testing for proteinuria is no longerdiagnostic or prognostic. “proteinuria>5g/24hours” may only indicate the severity.
Mole: For partial moles, obtain a confirmatory hCG level one month after normalization; for complete moles, reduce monitoring from 6 to 3 months post-normalization.
Chapter 14: EM
SHOCK RESUSCITATION
Emergency treatment—critical care!
“A-B-C”: Breathing: …In mechanically ventilated adults with critical illness in ICU, intermittent sedative-analgesic medications (morphine, propofol, midazolam) are recommended.
Chapter 15: Surgery
Surgery and Geriatrics: Hemiarthroplasty is a suitable option for patients who sustain a displaced femoral neck fracture.
Chapter 16: Psychiatry
Depression: Both short-term and maintenance therapies with esketamine are beneficial for treatment-resistant depression.
Schizophrenia: Long-term antipsychotics may decrease long-term suicide mortality.
Narcolepsy: Pitolisant is a novel oral histamine H3 receptor inverse agonist used in narcolepsy patients with poor response or tolerate to other medications. Oxybate salts, a lower sodium mixed-salt formulation of gamma hydroxybutyrate is for treatment of narcolepsy with cataplexy.
Chapter 17: Last Chapter
PEARLS—Table 17-9: Important Immunization Schedules for All (2020, USA)
Vaccine Birth 2M 4M 6M 12-15M 2Y 4-6Y 11-12Y Sum
HAV 1st 2nd (2-18Y) 2 doses
HBV 1st 2nd 3rd (6-12M) 3 doses
DTaP 1st 2nd 3rd 4th (15-18M) 5th + Td per 10Y
IPV 1st 2nd 3rd (6-18M) 4th 4 doses
Rotavirus 1st 2nd 2 doses
Hib 1st 2nd (3rd) (3-4th) 3-4 doses
MMR 1st 2nd 2 doses
Varicella 1st 2nd + Shingles at 60Y
Influenza 1st (IIV: 6-12Y; LAIV: >2Y (2nd dose) 1-2 doses annually
PCV 1st 2nd 3rd 4th PCV13+PPSV at 65Y
MCV (Men A, B) 1st Booster at 16Y
HPV 9-12Y starting: <15Y: 2 doses (0, 6-12M); >15Y or immunosuppression: 3 doses (0, 2, 6M).
Chapter 17 HYQ answer 22: No routine prostate cancer screening (including PSA) is recommended and answer “G” is still correct–PSA
screening among healthy men is not routinely done but should be indicated in a patient with two risk factors.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reflect on the assessment and intervention that you implemented with your client. You need to reflect on the feedback received from your supervisors and how will this change the intervention you will provide next week.
08/03/2023
Nompumelelo Mtshali.
I have been in the placement for the past 2 weeks. During these weeks I was able to assess 3 patients. My first patient was Mr M, a 24-year-old. He was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease stage 5. From my observations and assessments with him, I found that he had decreased physical endurance, and decreased muscle strength of both his lower limbs and presented with oedema of both his lower limbs which limited his range of motion. I used lecture notes, a website and a video from youtube to guide my assessment with him. According to OAT.COM, it is advised that OTs should focus on improving physical activity, and improving psychological functioning as patients with this diagnosis show a lot of anxiety and depression symptoms. It is important that as OTs, we also facilitate independence in ADLs, IADLs and Work. In my first with Meluleki, I treated oedema but elevated his legs with a blanket, which was one of the treatment principles from the lecture notes. In the following session, I planned to do a treatment session using an IADL activity( Home Management) unfortunately he was transferred to another hospital. However, I did share with my supervisor the activity I had planned for him. I received great feedback from her but she did say I should incorporate more principles of the AFR I used, in this case, it was the Biomechical AFR however the session was well planned.
My second patient, Ms B was diagnosed with Hydrocephalus. I only conducted assessments with her. My assessment was guided by research from the American Association of Neurological Surgeons that shared that hydrocephalus occurs when a stroke or injury damages the brain and brain matter shrinks. The brain may shrink in older patients or those with Alzheimer's disease, and CSF volume increases to fill the extra space. In these instances, the ventricles are enlarged, but the pressure usually is normal. From this information, I assessed my patient more like a stroke patient as she presented similarly to them. I followed the principles of assessments from the lecture notes for CVA. Ms Baartman is the patient, I did my assessment findings on for the previous week. From the feedback from the supervisor, I did well on the assessment findings but I need to use more OT jargon when reporting, be specific on muscles and joints being assessed and focus on the format of assessments.
My third patient, Mr N has a left neck femur fracture, and pressure sore on his feet. I assessed his ROM, Muscle strength, and endurance and observed for any impaired psychological components as he is old. From his first assessment, I found that he did have limitations in his range of motion of the lower limb, he has muscle stiffness in his upper and lower limbs, and he complained of pain. So from the first assessment, I planned to continue with assessments on 08/03/23. In the assessment, I was aiming to assess his ADLs( Bed mobility- moving from supine to long sitting than too short sitting). The assessment was conducted in the presents of Physio students and the supervisor, from it, the client requires maximal assistance with bed mobility and transfers. I continued with the treatment of wheelchair transfer and wheelchair education with the patient. From the treatment, I had to use principles used for dementia patients. I can't have a feedback session with the supervisor due to time.
As much as I had to work with 3 patients, the week was very stressful which raised my anxiety levels to their maximum. However, I believe I will have the confidence and ability to plan and execute better and more relevant treatment sessions with the use of correct AFRs Principles and other treatment principles for my patients. I will be using feedback and more resource to execute such sessions.
Reference list
Lecture notes for CVA by Mrs Nadioo
Lecture notes endurance, oedema, ROM by Mr Mpanza
Lecture notes muscle strength by Mrs Tupuae
youtube
0 notes
Text
Potential hidden cause of dementia detected
Researchers say these findings, published in the peer-reviewed journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research and Clinical Interventions, may point the way to a cure. “Many of these patients experience cognitive, behavioral and personality changes so severe that they are arrested or placed in nursing homes,” said Wouter Schievink, MD, director of the Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak and Microvascular Neurosurgery Program and professor of Neurosurgery at Cedars-Sinai. “If they have behavioral-variant frontotemporal dementia with an unknown cause, then no treatment is available. But our study shows that patients with cerebrospinal fluid leaks can be cured if we can find the source of the leak.” Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates in and around the brain and spinal cord to help cushion them from injury. When this fluid leaks into the body, the brain can sag, causing dementia symptoms. Schievink said many patients with brain sagging — which can be detected through MRI — go undiagnosed, and he advises clinicians to take a second look at patients with telltale symptoms. “A knowledgeable radiologist, neurosurgeon or neurologist should check the patient’s MRI again to make sure there is no evidence for brain sagging,” Schievink said. Clinicians can also ask about a history of severe headaches that improve when the patient lies down, significant sleepiness even after adequate nighttime sleep, and whether the patient has ever been diagnosed with a Chiari brain malformation, a condition in which brain tissue extends into the spinal canal. Brain sagging, Schievink said, is often mistaken for a Chiari malformation. Even when brain sagging is detected, the source of a CSF leak can be difficult to locate. When the fluid leaks through a tear or cyst in the surrounding membrane, it is visible on CT myelogram imaging with the aid of contrast medium. Schievink and his team recently discovered an additional cause of CSF leak: the CSF-venous fistula. In these cases, the fluid leaks into a vein, making it difficult to see on a routine CT myelogram. To detect these leaks, technicians must use a specialized CT scan and observe the contrast medium in motion as it flows through the cerebrospinal fluid. In this study, investigators used this imaging technique on 21 patients with brain sagging and symptoms of bvFTD, and they discovered CSF-venous fistulas in nine of those patients. All nine patients had their fistulas surgically closed, and their brain sagging and accompanying symptoms were completely reversed. “This is a rapidly evolving field of study, and advances in imaging technology have greatly improved our ability to detect sources of CSF leak, especially CSF-venous fistula,” said Keith L. Black, MD, chair of the department of Neurosurgery and the Ruth and Lawrence Harvey Chair in Neuroscience at Cedars-Sinai. “This specialized imaging is not widely available, and this study suggests the need for further research to improve detection and cure rates for patients.” The remaining 12 study participants, whose leaks could not be identified, were treated with nontargeted therapies designed to relieve brain sagging, such as implantable systems for infusing the patient with CSF. However, only three of these patients experienced relief from their symptoms. “Great efforts need to be made to improve the detection rate of CSF leak in these patients,” Schievink said. “We have developed nontargeted treatments for patients where no leak can be detected, but as our study shows, these treatments are much less effective than targeted, surgical correction of the leak.”
0 notes
Text
Uvular injury after double lumen tube insertion: A rare cause of persistent postoperative sore throat by Deepti Ahuja in International Journal of Clinical Images and Medical Reviews
Letter to Editor
Postoperative sore throat (POST) is a common complaint with an incidence of 24-100% 1 that occurs following placement of airway devices in patients administered general anaesthesia. POST results in discomfort, patient dissatisfaction after surgery and leads to delay in patient’s return to normal routine activities. Severe, persistent and unresolving POST may be attributed to uvula injury. We report uvular injury in a patient inspite of uneventful placement and removal of double lumen tube (DLT). A 58-year-old male (Weight-75 kilograms, Height-172 cm, BMI-25), case of left lower lobe carcinoid tumour was posted for left lower lobe sleeve lobectomy. On preanaesthetic checkup, according to American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status (ASAPS) classification system, patient belonged to ASAPS I.
The patient was fasted according to standard ASA fasting guidelines. We planned combined general anaesthesia and thoracic epidural as the anaesthetic and analgesic technique. After shifting the patient to operating room, peripheral intravenous access was obtained and all standard monitoring devices including electrocardiography, noninvasive blood pressure, and pulse oximetry were attached. After positioning patient in left lateral decubitus, painting and draping, using 18-gauge Touhy needle, T6– T7 epidural space was identified at 7.5 cm mark using loss of resistance (LOR) technique and catheter threaded upto 13 cm mark. After securing catheter and confirming negative aspiration of blood or CSF, 3 ml of 2% lignocaine with 1 in 200000-unit adrenaline was given as test dose. The patient was turned supine, preoxygenation with 100% oxygen was done. The patient was premedicated with Inj Fentanyl 160 micrograms. General anaesthesia was induced using titrated doses of Inj Propofol. Adequate bag and mask ventilation were ensured and Inj atracurium 0.5 mg/kg was administered. After completion of 3 minutes, tracheal intubation was done with direct laryngoscope (Macintosh #4) and 39 Fr Robertshaw’s left sided DLT was placed. The correct position of tube was checked by auscultation and further confirmed by fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Left radial artery was cannulated. Total duration of one lung ventilation (OLV) was 4 hours 20 minutes. The overall period of OLV was uneventful as there were no episodes of desaturation and hemodynamic instability. After completion of surgical procedure, patient was turned supine, thorough suction from both lumens of DLT was done. DLT was removed and I-gel no 4 was placed.
After return of spontaneous respiratory efforts, patient was reversed and extubated. He was shited to intensive care unit (ICU) for further observation. Few hours later, he complained of foreign body sensation in throat and as if something was stuck in throat. The foreign body moved backwards during inspiration and aggravated airway obstruction. We considered it most probably as airway mucous secretions that would have accumulated due to failure to cough them out effectively. Steam inhalation, saline nebulization and chest physiotherapy was done and patient was encouraged to cough out secretions in throat. However, few hours later he again reported same complaints as there was no improvement with measures taken by us. Hence, we decided to go for inspection of his pharynx and found an elongated, swollen, inflamed uvula was noted (Figure 1). We diagnosed as uvula injury caused by impingement of DLT. We reassured him and advised not to strain further as it would further aggravate uvular injury. He made complete recovery over a period of 5 days. Uvula injury after placement of endotracheal intubation 2 and laryngeal mask airway 3 has been reported earlier. The compression of uvula between hard palate and airway device has been reported as causative factor. Excessive compression can cause mechanical interruption of blood supply and result in uvular necrosis. Proper positioning of DLT to one side of midline can avoid this complication.
To conclude, uvular injury should always be kept as differential diagnosis in patient with severe persistent sore throat particularly if associated with foreign body like sensation. Careful and thorough examination of oropharynx should be done to confirm diagnosis. Though condition responds well to conservative management but reassurance addressing the cause and expected duration is must to reduce distress experienced by patient.
For more details: https://ijcimr.org/editorial-board/
#Postoperative sore throat#Anesthesiologists physical status#POST#DLT#ASA#double lumen tube#sleeve lobectomy#OLV#intensive care unit#ICU#hemodynamic#Deepti Ahuja#ijcimr
0 notes
Text
Drug Monograph FOR SERIOUS INFECTIONS ONLY Drug Monograph: Vancomycin Drug Name -- Vancocin (brand), Vancomycin HCL -- oral (generic) This is a time-dependent bactericidal antibiotic, which inhibits cell wall synthesis (Levinson, 2009). Glycopeptides VA Class - AM900 CAS Number 1404-93-9 Therapeutic Category -- a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic Pharmacology Vancomycin is not too well-absorbed from the GI tract after oral administration (Levinson 2009). When given parenterally, it penetrates the bile, pleural, pericardial, synovial and ascitic fluids. It is excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration (Levison). When taken orally, Vancomycin is not absorbed in the intestines so that it can stop the growth of a severe intestinal condition known as Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (Medicine Net, 2012). When vancomycin is given by mouth, it is not absorbed by the body but remains in the intestines. This is to allow it to stop the growth of the Clostridium difficile bacteria. Vancomycin is intended as treatment only for bacterial infections of the intestines. It is not effective for other bacterial infections or infections caused by viruses. Its overuse can decrease its effectiveness (Medicine Net). Indications Vancomycin is intended for the treatment of serious or severe bacterial infections caused by susceptible strains of methicillin-resistant staphylococci (PDR, 2012, Drug.com, 2012). It is indicated for use by patients who are allergic to penicillin and cannot or fail to respond to other drugs. It is for infections caused by Vancomycin-susceptible organisms resistant to other anti-microbials. It is indicated as initial therapy when methicillin-resistant staphylococci infection is suspected. It is also effective in the treatment of staphylococcal endocarditis. It has been successfully used in combination with either rifampin or an aminoglycoside or both for early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis, caused by S. epidermidis or diphtheroid. Its parenteral form may be administered orally in treating antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis caused by C. difficile and for staphylococcal enterocolitis (PDR, Drug.com). Vancomycin is the drug of choice against serious infection and endocarditis caused by Methicillin-resistant S. aureaus, Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, B-Hemolytic streptococci, Corynebacterium group JK, Viridans streptococci and enterococci (Levinson, 2009). It has been used as an alternative drug for pneumococcal meningitis caused by strains with reduced penicillin sensitivity. But its erratic penetration into the CSF and reported clinical failures make it not advisable for use alone to treat pneumococcal meningitis. Dosages For Adults The usual is 500 mg by IV every 6 hours or 1 g by IV every 12 hours (PDR, 2012). It should be administered no more than at 10 mg per minute or at least 60 minutes, whichever is longer. For those with renal impairment, the initial dose is not less than 15 mg per kg. The daily dosage is about 15 times the GFR in ML per minute. For elderly patients, the dose should be reduced. The initial dose for anephric patients is 15 mg/kg then 1.9 mg/kg/24 hours. The dose for those with marked renal impairment is 250-1,000 mg once every several days and for those with anuria, 1,000 mg every 7-10 days. For PO administration, divided doses of 500-2,000 mg/day should be given for 7-10 days or a maximum dose of 2,000 mg/day. The doses may be diluted in 1 oz of water or administered through an NG tube (PDR). Vancomycin is taken orally usually 4 times a day for 7-10 days according to the doctor's instructions (Medicine Net, 2012). He determines the dosage according to the medical condition and the patient's response to treatment. Cholestyramine and colestipol can lessen the effects of Vancomycin when they are taken at the same time. If they have to be taken, they should be given at least 3-4 hours from Vancomycin. Vancomycin works best when kept at a constant level at the intestines. Medication should be continued until the prescribed amount is completed even if symptoms have disappeared. Re-infection can occur if the medication is stopped before completion. If the condition persists after 7 days or gets worse, the doctor should be informed (Medicine Net). For Pediatric Patients The usual does for all pediatric patients is 10 mg/kg by IV every six hours (PDR, 2012). The initial for newborns is 15 mg/kg, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for the first week of life. This is continued every 8 hours until their first month of age. Vancomycin should be given for at least 60 minutes. The initial dosage for pediatrics with renal impairment is not less than 15 mg/kg per day or 15 times the GFR in mL/min. Premature infants should have longer dosing intervals. PO administration should be 40 mg/kg/day in 3-4 divided doses for 7-10 days. The maximum is 2,000 mg/day, which may be diluted in 1 oz of water or administered through an NG tube (PDR). Contraindications Vancomycin is contraindicated to patients with hypersensitivity to vancomycin (Drug.com, 2012). Commercially prepared frozen Vancomycyn Hydrochloride injections in 5% dextrose may also be contraindicated to those with known allergic reaction to corn or corn products (Drug.com). Drug-Drug Interactions The patient should inform the doctor or pharmacist of all prescription and non-prescription or herbal products currently used (Medicine Net, 2012; Levinson, 2012). Aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, other antibiotics, and live bacterial vaccines are special mentions. If treatment requires anesthesia, the doctor or dentist should be told if the patient has been using Vancomycin. Although most antibiotics do not significantly affect hormonal birth control medications, they may decrease the effectiveness of these hormone medications and cause pregnancy (Medicine Net). Current or sequential systemic or topical use of neurotoxic or nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully monitored (PDR, 2012). Periodic leukocyte count monitoring with drugs, which may cause neutropenia, should be performed. Serial monitoring of renal function and particular care after dosing should also be done to minimize the risk of nephrotoxicity with concomitant aminoglycoside (PDR). Other Precautions and Potential Adverse Effects A patient's medical history should be revealed before Vancomycin is administed (Medicine Net, 2012). Elderly patients should be able to eliminate the drug from their bodies when needed. Otherwise, it should be administered to them with caution for possible sensitivity to its effects. It should be used on pregnant women only when clearly needed. Risks and benefits should be discussed with the doctor. Vancomycin does not pass on to breast milk and is thus not harmful to nursing infants. But the doctor must still be consulted on its effect on breastfeeding (Medicine Net). Vancomycin may cause hypotension and cardiac arrest, though rarely, by rapid bolus administration (PDR, 2012). Ototoxicity has been reported and calls for caution for those with underlying hearing loss. Prolonged use can lead to an overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. Safety and efficacy of administration through the intraperitoneal and intrathecal routes have not been confirmed. Use via the intraperitoneal route during dialysis has been reported to lead to a syndrome of chemical peritonitis (PDR). Look-alike/Sound-alike Drugs and Prescription Refill Requirements Vancomycin is 6th in the list of top 10 medications involved in drug errors (Medscape Pharmacists, 2007). These medications are the most commonly mis-used or mishandled some way by healthcare professionals, based on the database of the U.S. Pharmacopoeia. Liquid dose concentrations increase the risk of medication errors. There has been confusion over mL and tsp errors, which leads to overdose or under-dose of up to 5 times if undetected. Reconstituting antibiotics can also be risky as when the antibiotic powder is mixed with alcohol instead of distilled water (Medscape Pharmacists). Vancomycin was also one of the 10 most frequently reported drugs with the highest adverse drug reactions by the Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Program for 2003-2004 (Bebout, 2004). Half of all the 360 drugs were anti-infective (Bebout). # BIBLIOGRAPHY Bebout, K. (2004). Adverse drug reporting program update and recent drug safety warnings. P & T. News: the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/pharmacy/PTNews/2004/december.html Drug.com (2010). Vancomycin Hydrochlorde. Drugs.com. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.drugs.com/monograph/vancomycin-hydrochloride.html Harrison's Practice (2012). Vancomycin. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.harrisonspractice.com/practice/ub/view/DrugMonographs/156696/all/Vancomycin Levison, M.E. (2009). Vancomycin. The Merck Manual: Merck Sharp & Dohme. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.merckmanuals.com/professionals/infections_diseases/bacteria_and_antibackterial_drugs/vancomycin.html Medicine Net (2011). Vancomycin. Medicine Net. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.medicinenet.com/vancomycin-oral/article.htm Medscape Pharmacists (2007). The top 10 drug errors and how to prevent them. Medscape Education: Medscape LLC. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/556487 PDR (2012). Vancomycin HCL. Physician's Desk Reference: PDR Network LLC. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.pdr.net/drugpages/concisemonograph.aspx?concise=688 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Planning And Establishing Of Schools
Raghav Foundation is a pioneer in setting up K-12 schools with exclusive services and is the best New school opening consultancy in India.
Establishing a school requires educational field specialists. Raghav Foundation is a pioneer in setting up K-12 schools and is the best new school opening consultancy in India, who have the required experience, a keen understanding of the logistics process, the ability to gauge probable hurdles, and the capability to map the growth plan.

What we consider before planning & establishment of school?
Location planning
Advise and Guidance on statutory approvals liaison and compliances with the architect and the client to ensure that the final design incorporates the vision of the client
Classroom Design
Surveying of the area in which the school is proposed to be located
Technology implementation guidance
Marketing and branding of school
Study of Return on Investment (ROI)
Guidance regarding society registration and all other procedures for obtaining registrations and permissions
School Affiliations (CBSE & ICSE school)
Staffing, positioning and teacher's training
Identification of Critical Success Factors (CSFs) and Unique Selling Points (USPs)
Curriculum design
Academic planning
Plan & design map for new school
Business positioning and many more
Read More: https://raghavfoundation.org.in/new-school-opening-consultancy/
0 notes
Text
The game changer
My doctor called that afternoon like he promised.
He had spoken to my neurologist and reviewed the images with her. They were 95% sure my leak is at the T1-T2 level of my spine. They could see a calcification on the front side of my disc between T1 and T2 that is piercing my dura mater and creating a hole to allow CSF to leave the enclosed space its supposed to be in.
And although I was so happy to be certain I definitely have a CSF leak, my treatment options became horribly limited.
Initially, my doctors had thought my leak was higher up in my spine in my neck. This would have allowed a neurosurgeon or a spine surgeon to operate through the front of my neck. The surgeon could reach the calcification easily from the front to remove it, as well as repair the hole in my dura mater with stitches. And although I didn’t want surgery, it seemed like a relatively manageable surgery.
Unfortunately, this was now not the case.
Because my leak is lower, at T1/T2, the leak site is behind my sternum. A surgeon cannot access the front of my spine through my sternum. Not to mention my heart and major blood vessels there as well. Now, you may be wondering, “why can’t a surgeon go through her back?” Well, because my leak is at the front of my spine, a surgeon would have to make an incision in my back, cut the vertebra, and manipulate my spinal cord to reach the front of my spine where the leak is. And not many surgeons are going to want to manipulate the spinal cord of an otherwise healthy 27 year old woman. The risk outweighs the benefit at this point.
My doctor informed us of this reality, and then began offering his other treatments. He can do a targeted blood patch, targeted fibrin glue, or targeted DuraSeal.
He advised us that my leak may complicate 2 out of those 3 options. When my CSF leaks out of the dura mater, it creates a large pool at the leak site. My doctor explained the blood patch and fibrin glue as this: blood and fibrin are not very viscous. CSF is extremely watery. If he were to inject blood or fibrin into that pool of CSF to try and get it to stick to my dura mater, it would be like injecting paint into water. The paint would quickly dissipate and may never find where it’s supposed to go. He therefore would have a hard time recommending those treatments.
He informed us he is trialing a third option. There is a medical glue called DuraSeal that is typically used on top of sutures for cranial and spinal surgeries. My doctor has started injecting DuraSeal at leak sites because it is more viscous and has a higher probability of sticking when a CSF pool is present. The only caveat is he’s only tried this in 2 other patients.
He could only give us his success rate on 2 other patients, and they had only received their treatment 2 months ahead of me. So, the long term results of this treatment are not available. However, what choices did I really have? We knew a surgeon would not operate on me until we tried less invasive treatments. And we knew before the myelogram that blood patches and fibrin glue have a less than 25% chance of working when a leak is caused by a calcification. Therefore, we were left with the DuraSeal option.
When we expressed our choice to my doctor, he then informed us that he would like to do another myelogram to confirm my leak site. He explained that he was only 95% sure of my leak being at T1-T2, and if he’s going to be sticking a needle to my spine, he wanted to be 100% certain that’s where the leak is.
This myelogram would be a little different than the one I just had, and he would be willing to squeeze me in that Monday since he knew we traveled from out of town to Jacksonville. We accepted. We immediately booked an Airbnb to stay in for the weekend since the hotel room was beginning to feel claustrophobic and cramped.
Time to hurry up and wait again for another test.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Drug Monograph FOR SERIOUS INFECTIONS ONLY Drug Monograph: Vancomycin Drug Name -- Vancocin (brand), Vancomycin HCL -- oral (generic) This is a time-dependent bactericidal antibiotic, which inhibits cell wall synthesis (Levinson, 2009). Glycopeptides VA Class - AM900 CAS Number 1404-93-9 Therapeutic Category -- a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic Pharmacology Vancomycin is not too well-absorbed from the GI tract after oral administration (Levinson 2009). When given parenterally, it penetrates the bile, pleural, pericardial, synovial and ascitic fluids. It is excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration (Levison). When taken orally, Vancomycin is not absorbed in the intestines so that it can stop the growth of a severe intestinal condition known as Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (Medicine Net, 2012). When vancomycin is given by mouth, it is not absorbed by the body but remains in the intestines. This is to allow it to stop the growth of the Clostridium difficile bacteria. Vancomycin is intended as treatment only for bacterial infections of the intestines. It is not effective for other bacterial infections or infections caused by viruses. Its overuse can decrease its effectiveness (Medicine Net). Indications Vancomycin is intended for the treatment of serious or severe bacterial infections caused by susceptible strains of methicillin-resistant staphylococci (PDR, 2012, Drug.com, 2012). It is indicated for use by patients who are allergic to penicillin and cannot or fail to respond to other drugs. It is for infections caused by Vancomycin-susceptible organisms resistant to other anti-microbials. It is indicated as initial therapy when methicillin-resistant staphylococci infection is suspected. It is also effective in the treatment of staphylococcal endocarditis. It has been successfully used in combination with either rifampin or an aminoglycoside or both for early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis, caused by S. epidermidis or diphtheroid. Its parenteral form may be administered orally in treating antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis caused by C. difficile and for staphylococcal enterocolitis (PDR, Drug.com). Vancomycin is the drug of choice against serious infection and endocarditis caused by Methicillin-resistant S. aureaus, Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, B-Hemolytic streptococci, Corynebacterium group JK, Viridans streptococci and enterococci (Levinson, 2009). It has been used as an alternative drug for pneumococcal meningitis caused by strains with reduced penicillin sensitivity. But its erratic penetration into the CSF and reported clinical failures make it not advisable for use alone to treat pneumococcal meningitis. Dosages For Adults The usual is 500 mg by IV every 6 hours or 1 g by IV every 12 hours (PDR, 2012). It should be administered no more than at 10 mg per minute or at least 60 minutes, whichever is longer. For those with renal impairment, the initial dose is not less than 15 mg per kg. The daily dosage is about 15 times the GFR in ML per minute. For elderly patients, the dose should be reduced. The initial dose for anephric patients is 15 mg/kg then 1.9 mg/kg/24 hours. The dose for those with marked renal impairment is 250-1,000 mg once every several days and for those with anuria, 1,000 mg every 7-10 days. For PO administration, divided doses of 500-2,000 mg/day should be given for 7-10 days or a maximum dose of 2,000 mg/day. The doses may be diluted in 1 oz of water or administered through an NG tube (PDR). Vancomycin is taken orally usually 4 times a day for 7-10 days according to the doctor's instructions (Medicine Net, 2012). He determines the dosage according to the medical condition and the patient's response to treatment. Cholestyramine and colestipol can lessen the effects of Vancomycin when they are taken at the same time. If they have to be taken, they should be given at least 3-4 hours from Vancomycin. Vancomycin works best when kept at a constant level at the intestines. Medication should be continued until the prescribed amount is completed even if symptoms have disappeared. Re-infection can occur if the medication is stopped before completion. If the condition persists after 7 days or gets worse, the doctor should be informed (Medicine Net). For Pediatric Patients The usual does for all pediatric patients is 10 mg/kg by IV every six hours (PDR, 2012). The initial for newborns is 15 mg/kg, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for the first week of life. This is continued every 8 hours until their first month of age. Vancomycin should be given for at least 60 minutes. The initial dosage for pediatrics with renal impairment is not less than 15 mg/kg per day or 15 times the GFR in mL/min. Premature infants should have longer dosing intervals. PO administration should be 40 mg/kg/day in 3-4 divided doses for 7-10 days. The maximum is 2,000 mg/day, which may be diluted in 1 oz of water or administered through an NG tube (PDR). Contraindications Vancomycin is contraindicated to patients with hypersensitivity to vancomycin (Drug.com, 2012). Commercially prepared frozen Vancomycyn Hydrochloride injections in 5% dextrose may also be contraindicated to those with known allergic reaction to corn or corn products (Drug.com). Drug-Drug Interactions The patient should inform the doctor or pharmacist of all prescription and non-prescription or herbal products currently used (Medicine Net, 2012; Levinson, 2012). Aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, other antibiotics, and live bacterial vaccines are special mentions. If treatment requires anesthesia, the doctor or dentist should be told if the patient has been using Vancomycin. Although most antibiotics do not significantly affect hormonal birth control medications, they may decrease the effectiveness of these hormone medications and cause pregnancy (Medicine Net). Current or sequential systemic or topical use of neurotoxic or nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully monitored (PDR, 2012). Periodic leukocyte count monitoring with drugs, which may cause neutropenia, should be performed. Serial monitoring of renal function and particular care after dosing should also be done to minimize the risk of nephrotoxicity with concomitant aminoglycoside (PDR). Other Precautions and Potential Adverse Effects A patient's medical history should be revealed before Vancomycin is administed (Medicine Net, 2012). Elderly patients should be able to eliminate the drug from their bodies when needed. Otherwise, it should be administered to them with caution for possible sensitivity to its effects. It should be used on pregnant women only when clearly needed. Risks and benefits should be discussed with the doctor. Vancomycin does not pass on to breast milk and is thus not harmful to nursing infants. But the doctor must still be consulted on its effect on breastfeeding (Medicine Net). Vancomycin may cause hypotension and cardiac arrest, though rarely, by rapid bolus administration (PDR, 2012). Ototoxicity has been reported and calls for caution for those with underlying hearing loss. Prolonged use can lead to an overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. Safety and efficacy of administration through the intraperitoneal and intrathecal routes have not been confirmed. Use via the intraperitoneal route during dialysis has been reported to lead to a syndrome of chemical peritonitis (PDR). Look-alike/Sound-alike Drugs and Prescription Refill Requirements Vancomycin is 6th in the list of top 10 medications involved in drug errors (Medscape Pharmacists, 2007). These medications are the most commonly mis-used or mishandled some way by healthcare professionals, based on the database of the U.S. Pharmacopoeia. Liquid dose concentrations increase the risk of medication errors. There has been confusion over mL and tsp errors, which leads to overdose or under-dose of up to 5 times if undetected. Reconstituting antibiotics can also be risky as when the antibiotic powder is mixed with alcohol instead of distilled water (Medscape Pharmacists). Vancomycin was also one of the 10 most frequently reported drugs with the highest adverse drug reactions by the Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting Program for 2003-2004 (Bebout, 2004). Half of all the 360 drugs were anti-infective (Bebout). # BIBLIOGRAPHY Bebout, K. (2004). Adverse drug reporting program update and recent drug safety warnings. P & T. News: the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/pharmacy/PTNews/2004/december.html Drug.com (2010). Vancomycin Hydrochlorde. Drugs.com. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.drugs.com/monograph/vancomycin-hydrochloride.html Harrison's Practice (2012). Vancomycin. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.harrisonspractice.com/practice/ub/view/DrugMonographs/156696/all/Vancomycin Levison, M.E. (2009). Vancomycin. The Merck Manual: Merck Sharp & Dohme. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.merckmanuals.com/professionals/infections_diseases/bacteria_and_antibackterial_drugs/vancomycin.html Medicine Net (2011). Vancomycin. Medicine Net. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.medicinenet.com/vancomycin-oral/article.htm Medscape Pharmacists (2007). The top 10 drug errors and how to prevent them. Medscape Education: Medscape LLC. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/556487 PDR (2012). Vancomycin HCL. Physician's Desk Reference: PDR Network LLC. Retrieved on April 20, 2012 from http://www.pdr.net/drugpages/concisemonograph.aspx?concise=688 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Raghav Foundation is a pioneer in setting up K-12 schools with exclusive services and is the best New school opening consultancy in India.
Establishing a school requires educational field specialists. Raghav Foundation is a pioneer in setting up K-12 schools and is the best new school opening consultancy in India, who have the required experience, a keen understanding of the logistics process, the ability to gauge probable hurdles, and the capability to map the growth plan.

What we consider before planning & establishment of school?
Location planning
Advise and Guidance on statutory approvals liaison and compliances with the architect and the client to ensure that the final design incorporates the vision of the client
Classroom Design
Surveying of the area in which the school is proposed to be located
Technology implementation guidance
Marketing and branding of school
Study of Return on Investment (ROI)
Guidance regarding society registration and all other procedures for obtaining registrations and permissions
School Affiliations (CBSE & ICSE school)
Staffing, positioning and teacher's training
Identification of Critical Success Factors (CSFs) and Unique Selling Points (USPs)
Curriculum design
Academic planning
Plan & design map for new school
Business positioning and many more
Raghav Foundation is unique New School Establishment consultant in India. We plan, design & implement ideas as per the requirements of the clients
0 notes
Text

Cahya Mata Sarawak Bhd is a public limited company in which ordinary shareholders and savings institutions hold shares. Last month, following whistleblower complaints about insider dealing and conflicts of interest the Board of Directors suspended the Deputy Chairman Abu Bekir Taib and Chief Communications Officer, the Australian national Karl Vink.
The whistleblowing information had triggered a formal investigation within the company, resulting in a Board of Inquiry report which has now been widely leaked and viewed by Sarawak Report.
That report provides compelling evidence that the pair had conspired to use their positions in the company to pressure CMSB to hand a large data handling contract to a little known technology outfit named Vienna Advantage Asia, in which they secretly held controlling interests through a company named Silver Lining Systems Sdn Bhd. It has emerged that the son of the Chairman of CMSB, Abdul Rashid Manaf, also has shares in the same company (see below).
The pair also arranged for the outsourcing of CMSB private cloud to a supposed third party named CSF Advisers. Yet it has emerged that CSF Advisers were also secretly managed by the same Silver Lining Systems which they owned.
0 notes