#Files with no machine-readable source
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Akihabara_Maids.JPG
#wikimedia commons#2000s#2006#Akihabara Station Electric Town entrance south front street#Maid café maids in promotional activities in Japan#Maids in Akihabara#Maid cafés in Akihabara#2006 in Akihabara#July 2006 in Tokyo#Photographs by Ricky G. Willems#Attribution only license#Media missing infobox template#Files in need of review (sources)#Files in need of review (sources)/Attribution#Files with no machine-readable author#Files with no machine-readable source
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Roads and Traveling

By JimChampion - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=135565344
Roads and pathways go back very far in human history, to about 10,000 BCE. Some of these might have started out as animal trails that were then used over and over, widening until they left their marks on the landscape, some were engineered and covered over by paving or logs. Some are blended with rivers to make travel faster and able to carry more and some were dictated by rulers of empires. Some are nothing more than sunken paths now, some are still in use.

By Adam37 - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=19961082
The oldest extant roads are sunken paths, many of which can be found in England as there is a tradition of maintaining public rights of way. Many of these paths connect farms to each other and also cross the country to reach important locations, such as temples and cities. One of the oldest of these is Harrow Way, or the Old Way, which connected what is now Seaton in Devon to Dover in Kent. The Old Way can be dated to somewhere between 600-450 BCE, but is believed to much older, going back into the Stone Age.

By John M, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=15868070
Roads that are paved with with wood can come in two types, corduroy roads that are made of logs laid across the roadway, especially across areas that tend to get extremely wet, like low lying areas and swamps. Plank roads are a newer take on that concept made with planks instead of whole logs. One of the oldest wood roads that still exists is the Corlea Trackway in Ireland, which dates to about 148 BCE and is the largest one found in Europe.

By Original creator: MossmapsCorrections according to Oxford Atlas of World History 2002, The Times Atlas of World History (1989), Philip's Atlas of World History (1999) by पाटलिपुत्र (talk) - This file was derived from: The Achaemenid Empire at its Greatest Extent.jpg, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73745174
Darius I (Darius the Great) of the Achaemenid empire, who reigned from 522-486 BCE had the Royal Road build during his reign. Some parts of it appear to follow that of the Assyrian kings, who reigned from the 21st-7th century BCE, beginning with a city-state and gradually expanding into an empire, based on the eastern parts of the roadway seeming to connect points that were important to them rather than taking the most direct or easiest path. Darius did improve the roads, though, which were later improved by the Romans. It was expected that mounted couriers were expected to traverse the 2,699 km (1,677 miles) journey from Susa to Sardis in 9 days, a trip that took 90 days by foot, or approximately 30 hours by vehicle today. It was primarily a 'post road', or one that was used to transport mail rather than the mass transportation of people and goods.

By No machine-readable author provided. Jan Kronsell assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=781888
In the Americas, many trails were blazed, or marked so that others could follow, quite early in history, possibly beginning by following ridge lines or large game animal paths, which followed dry ground through the forests between grazing lands and salt licks. One of the largest still extant of these trails is the Natchez Trace, or the Old Natchez Trace between Nashville, Tennessee and Natchez Mississippi and linking the Cumberland, Tennessee, and Mississippi Rivers, spanning 710 km (440 miles). Many of the trails were co-opted by European colonizers to explore and expand through the continent.

By Manco Capac - self-made from the images on this and this and this pages and mainly from the image in the book Inca Road System by John Hyslop., CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3878163
The Inca road system was the most vast and advanced transportation system in the Americas. It consisted of many paved roads, two major north-south routes with many branches cut into mountainous territory the Inca ruled over in the Andes, and around 39,900 km (24,800 miles) of roads. The best known part of this road system is the Trail to Machu Picchu. Parts of the road systems were built by cultures that lived in the areas before the Inca ruled over the area, especially the Wari culture, who lived there from about 500-1000 CE.

By DS28 - File:Roman Empire 125 general map.SVG, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=68002775
The Roman roads, perhaps the best known early roads, were built from about 300 BCE through the fall of the Western Roman Empire, about 400 CE. They were standardized, those standards laid down in the Law of the Twelve Tables from about 450 BCE, to 8 Roman feet (~2.37m) wide, double that around curves. In rural areas, the width was 12 Roman feet, allowing two standard width carts to pass by and allow for pedestrian traffic to continue on without interference. These tables also required private landowners to allow travelers to use their land if the roads were in disrepair, so durable roads became a very important consideration, as well as making them straight to use the least amount of materials. At its peak, the Roman roads consisted of at least 29 great military highways radiating from Rome, 327 great roads that connected provinces, and many smaller roads that comprised more than 400,000 km (260.000 miles), with over 80,500 km (50,000 miles) stone paved. Many of these are still used, being paved over with modern roads.


By Whole_world_-land_and_oceans_12000.jpg: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Centerderivative work: Splette (talk) - Whole_world-_land_and_oceans_12000.jpg, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=10449197 and By Nekitarc - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=43114716
In China, many roads were dedicated to trade routes like the Silk Road, which began in the Han Dynasty (207 BCE-220 CE). They focused primarily on the safety of the route to make it as lucrative as it could be, so major projects like extending the Great Wall of China, which was started during the 7th century BCE, were undertaken. The Silk Road shortened the Eurasian Steppe trail, which had been used for about 2000 years, from 10,000 km (6,200 miles) to 6,400 km (4,000 miles). Other roads in China that are worth noting are the Gallery Roads through remote mountains that are made of wooden planks secured to holes drilled into cliff sides in the Qin Mountains, which were built starting around the 4th century BCE and are still in use.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since I enjoy collecting things (big surprise) this year I've been working on collecting every Dreamcatcher music show performance in a quality that doesn't suck ass (aka not the seven pixels that YouTube compresses the official uploads down to). It went pretty well!
Pseudo research report under the cut (because I'm a massive nerd).
Scope
I started this project with the goal of collecting a full set of "music show performances". I didn't realise quite how ambiguous that definition is. After some deliberation I settled on the following as constituting "regular" performances:
Show Music Core
Inkigayo
The Show
Show Champion
M! Countdown
Music Bank
Simply K-Pop
Everything else I classified as misc. Most notably I left K-Force Special Show in the misc category despite there being quite a few performances on that show in the early days. This mostly came down to how I'm storing the files — I've organised the regular ones by era, but the K-Force Special Show performances frequently happened in between comebacks making them difficult to sort in that fashion. That and difficulties in ascertaining whether I do actually have all of them.
Methodology
The first step in collecting anything is finding out what you need to collect. I was surprised at how difficult it actually is to get a complete list of all of a group's music show performances. There are some fan sites which do a good job of presenting a lot of well categorised individual links to Dreamcatcher's appearances but I was hoping for something more "from the source" (aka the music shows themselves) and ideally machine readable to cross check that nothing is missing, since, for example, a collection of links to all official Inkigayo performance uploads is not a list of all Inkigayo performances (some never got official uploads). I ended up finding /r/kpop's music shows wiki fit my needs the most. The information is all in tables and sorted by music show and date which what I wanted.
Unfortunately, the main tables of /r/kpop's music show wikis only list debuts and comebacks, so I had to index and search all the individual pages to find what I was looking for. This involved spending a couple of afternoons opening up nearly 2,000 tabs of Reddit* and then downloading them using the SingleFile browser extension (Reddit rate limits you quite harshly and so I had to open a bunch of tabs, check they loaded, wait, and then repeat, which slowed it down a lot). While maybe a little overkill I did this for multiple reasons. Firstly, Reddit's search sucks, and I didn't trust it to find all instances of what I was looking for over so many pages. In contrast Everything's in-memory file content index beta is really good. But secondly, this is much more extensible, and now I can find any other group's performances as well (between 2017** and 2023).
*Reddit does not archive Simply K-Pop well at all (which caused some initial confusion), but the official Arirang website works fine as an alternative (albeit one that is somehow even slower than Reddit at opening new pages).
**Reddit's music show wiki pages start right before 2017. This is very convenient for a Dreamcatcher archivist, but, unfortunately for me, curiosity got the better of me and I did venture further out into the unknown. For 2014-2017 I have some scattered archives from various official websites, Twitter accounts, and Korean catch up services. I'm less confident in my music show data for this period in the general case but because the rough start and end dates for the two Minx promotion cycles are known I am confident enough that all the gaps I have in there are genuine gaps and that I'm not missing a performance date.
Once I had my wishlist I then had to go out and, you know, find them. And figure out what "best quality" actually means. I learned a lot about video encoding against my will. I also learned that HEVC is fucking haunted. When multiple sources were available I ranked them as follows:
2160p HEVC > 2160p h264 > 1080p HEVC (one weird edge case I didn't know what to do with) > 1080i h264 > 1080i MPEG2 > WEBDL (usually some kind of web livestream or online catch up service recording) > YouTube
Which I represented in my spreadsheet as:

This should be mostly uncontroversial, however, there is a slight complication in that the 4k broadcast copies are not all native 4k but often upscaled from the 1080 source (I can't find specifics on this as the information, if publicly accessible, would be in Korean, and there is only so much Google Translate can do, but the technical broadcasting details probably aren't public to the extend I am interested in regardless so I'm mostly basing this off information gleaned from secondary sources). As far as I can tell there exist two "grades" of upscales: one of which is upscaled by the network before being pushed out to a UHD channel, and one of which is upscaled by the end user by either recording a HD channel in 4k or running an existing recording through an upscaler. Traditionally upscales aren't very desirable due to providing no real material benefit you couldn't get from playing the 1080 copy on a 4k display yourself. Or, for people with an archival mindset like myself, because ones that actually look a bit crisper introduce "magic" pixels which may or may not have ever existed. See below for an example of this taken to the extreme (note the faces):

No one wants that, right? AND YET SOMEONE THOUGHT THAT WAS SUCH A BIG IMPROVEMENT THEY DELETED EVERYTHING ELSE, AND NOW IT REMAINS THE ONLY COPY I CAN FIND. Monsters!!! Anyway.
While upscales usually aren't desirable, I did come around to the idea that the network upscales deserve their place at the top of the list. There are a couple of points working in their favour: one is that they are, presumably, upscaled much more directly from the source, allowing them to avoid some of the data loss that being encoded into 1080i h264 and then upscaled would cause. The second is that quite a lot of them are encoded directly into HEVC, which makes the confetti and flashing lights look noticably smoother than the regular deinterlaced 1080i copies. Also, finally, as a touch of personal preference (especially in the case of 4k h264 where the second point doesn't apply), these do come pre-deinterlaced which is nicer for my chosen method of playback. Although some of those points apply to non network upscales too, the "impurity" of them far outweighs any benefit in my eyes, as I have more faith in whatever the network standard is than some random person on the internet trying to "fix" a file.
So how did I tell the difference? Also a frustratingly difficult problem, one which applies not just to spotting fake upscales but also to finding real TV recordings instead of lower quality catch up service clips. For the 1080 copies one of the biggest things was that the TV broadcast copies (unfortunately) always come through in 1080i. 1080p is suspicious. It means something has been touched (although sometimes in a way that is forgivable when nothing cleaner exists). File sizes are also a good sanity check. A single song in h264 should be in the 200-400MiB range, MPEG2 is 400MiB+. (For reference YouTube, and other inferior WEBDLs, usually come in at under 100MiB). This is a good reminder of why size does not always equal quality, because, in this scenario, worst to best is 100MiB < 450MiB < 250MiB.
On the 4k side: Music Bank, Show Music Core and Inkigayo are currently broadcast on UHD channels with a UHD variant of their channel names in the top right, which is a good indicator that something was recorded from a UHD source. (Although I've found 1080p copies recorded from UHD channels, so the presence of the logo doesn't mean no downscaling has occurred). Recent "4k" M! Countdown, Show Champion and The Show recordings, in comparison, appear identical in channel watermark to the 1080 copies. This and the fact that the only 4k copies I've found are from a source known to dabble in AI upscales means that I'm not going to trust these are genuine without further proof, and this was the main category of files which I decided against adding to my collection. (Note that The Show was in the past the only show that was broadcast in 4k, first on UMAX UHD and then on SBS F!L UHD, it is only recently that that seems to have stopped (or, no one has been recording it)). I paid less attention to the 4k file sizes than for 1080. 4k HEVC seems to come in pretty reliably at just under 1GiB, but 4k h264 is all over the place due to I think some differing quality profiles between uploaders (a range of 1GiB to nearly 3GiB). The latter is annoying because it means I can't figure out what the "true" recording should be, but I did develop an internal ranking of the trustworthiness of sources which was the tiebreaker when two differently sized 4k h264 recordings existed.
I prioritised collecting existing cuts where applicable (although many were not cut nearly as meticulously frame perfectly as I would like) but there were quite a few where I had to cut them out of full broadcast recordings myself. There were also instances where only the main performance was saved in 4k leaving interviews behind. In those cases I decided to keep the highest quality available for the bits in which it was and store the other segments separately.
Results
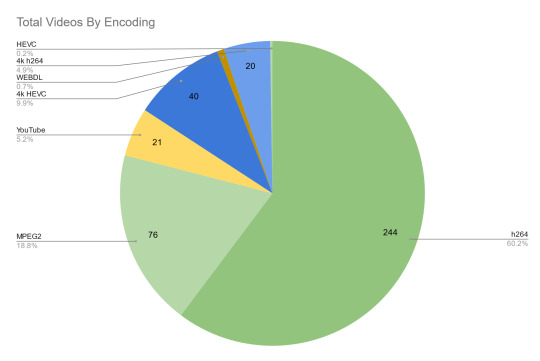
Alright, the fun stuff! I have successfully catalogued:
317 Dreamcatcher music show performances
34 Dreamcatcher miscellaneous appearances
46 Minx music show performances
16 Minx miscellaneous appearances
Those links go to mostly complete YouTube representations of what I found with exceptions listed in the descriptions of the playlists. You can also of course find a published version of my beautiful spreadsheet here. Finally, if you've made it this deep I would like to just quietly tell you I'm more than happy to share the originals, but please message me privately as I don't want to publicly host questionably copyrighted content on my good and morally upstanding posting images of dreamcatcher photobooks blog (for legal reasons the entire existence of this collection is a joke).
Honestly I'm pretty happy with the completeness of the collection after my first pass. The list of ones I would consider "missing" (aka not good enough quality) is:
It's almost all Simply K-Pop, which makes sense as it seems to not be archived with the same enthusiasm as the others. The missing M! Countdown, meanwhile, does kind of hurt, since it's ruining an otherwise perfect run. I'm out of ideas for now but am not going to give up on it forever, I have seen evidence that proper recordings exist, so I'm sure they have got to resurface eventually.
As can be seen in the breakdown for this section the percentage of MPEG2 recordings is also a pretty major victory, with the vast majority being h264:
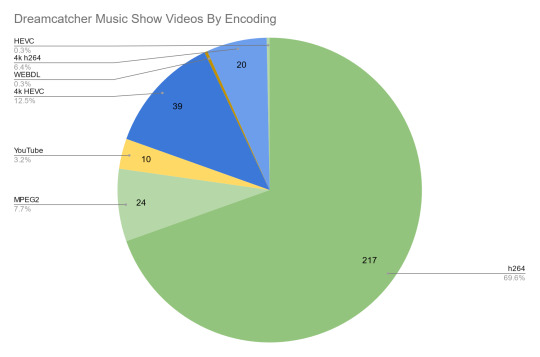
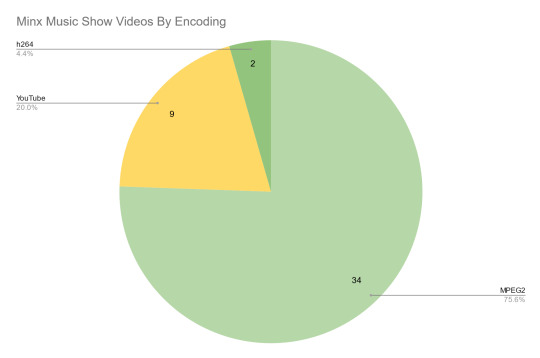
For Minx things look a bit worse:
But then again I hadn't been expecting much to begin with. To be honest, watching all of these to check quality did drive me a little insane. There is a reason I don't own Love Shake and Why Did You Come To My Home, and it's not purely the irresponsible financial decision, it's the thought of spending that much money on something I actually really don't like. Watching Minx performances is amusing for a little while, but man, am I glad Dreamcatcher exists instead.
It's also evident that people were holding to completely different standards even just a few years earlier, as this is where all those MPEG2s in the overall numbers are hiding:
Future Work
While I'm confident I've successfully catalogued the "music show performances" as defined in the scope, I know there is still much more to be discovered under Misc Appearances, as those were filled in not via a predefined wish list but just by what other recordings I happened across in my search for the original goal. The obvious next step would to be a little more systematic about finding out what I'm missing in that category by scouring some Dreamcatcher specific archives, but because I've already exhausted the full collections of my two main sources of recordings I'm not confident I would uncover many more performances outside of YouTube in that way, which isn't really that appealing.
I'm probably more likely going to do something about my performance outfit images collection which has been slowly but steadily increasing over the years. I'd like to put them into a proper searchable database alongside performance dates, which would have a similar effect of cataloguing the missing performances, but with the visual element that the spreadsheet lacks.
But then again, I also might not :)
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Python: Features and Where It's Used
Python is a versatile programming language that has gained significant popularity in recent times. It's known for its ease of use, readability, and adaptability, making it an excellent choice for both newcomers and experienced programmers. In this article, we'll delve into the specifics of what Python is and explore its various applications.
What is Python?
Python is an interpreted programming language that is high-level and serves multiple purposes. Created by Guido van Rossum and released in 1991, Python is designed to prioritize code readability and simplicity, with a clean and minimalistic syntax. It places emphasis on using proper indentation and whitespace, making it more convenient for programmers to write and comprehend code.
Key Traits of Python :
Simplicity and Readability: Python code is structured in a way that's easy to read and understand. This reduces the time and effort required for both creating and maintaining software.
Python code example: print("Hello, World!")
Versatility: Python is applicable across various domains, from web development and scientific computing to data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more.
Python code example: import numpy as np
Extensive Standard Library: Python offers an extensive collection of pre-built libraries and modules. These resources provide developers with ready-made tools and functions to tackle complex tasks efficiently.
Python code example: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Compatibility Across Platforms: Python is available on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This allows programmers to create and run code seamlessly across different platforms.
Strong Community Support: Python boasts an active community of developers who contribute to its growth and provide support through online forums, documentation, and open-source contributions. This community support makes Python an excellent choice for developers seeking assistance or collaboration.
Where is Python Utilized?

Due to its versatility, Python is utilized in various domains and industries. Some key areas where Python is widely applied include:
Web Development: Python is highly suitable for web development tasks. It offers powerful frameworks like Django and Flask, simplifying the process of building robust web applications. The simplicity and readability of Python code enable developers to create clean and maintainable web applications efficiently.
Data Science and Machine Learning: Python has become the go-to language for data scientists and machine learning practitioners. Its extensive libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and SciPy, along with specialized libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch, facilitate a seamless workflow for data analysis, modeling, and implementing machine learning algorithms.
Scientific Computing: Python is extensively used in scientific computing and research due to its rich scientific libraries and tools. Libraries like SciPy, Matplotlib, and NumPy enable efficient handling of scientific data, visualization, and numerical computations, making Python indispensable for scientists and researchers.
Automation and Scripting: Python's simplicity and versatility make it a preferred language for automating repetitive tasks and writing scripts. Its comprehensive standard library empowers developers to automate various processes within the operating system, network operations, and file manipulation, making it popular among system administrators and DevOps professionals.
Game Development: Python's ease of use and availability of libraries like Pygame make it an excellent choice for game development. Developers can create interactive and engaging games efficiently, and the language's simplicity allows for quick prototyping and development cycles.
Internet of Things (IoT): Python's lightweight nature and compatibility with microcontrollers make it suitable for developing applications for the Internet of Things. Libraries like Circuit Python enable developers to work with sensors, create interactive hardware projects, and connect devices to the internet.
Python's versatility and simplicity have made it one of the most widely used programming languages across diverse domains. Its clean syntax, extensive libraries, and cross-platform compatibility make it a powerful tool for developers. Whether for web development, data science, automation, or game development, Python proves to be an excellent choice for programmers seeking efficiency and user-friendliness. If you're considering learning a programming language or expanding your skills, Python is undoubtedly worth exploring.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text


EMail Me: [email protected]
Exploring EX4 and MQ4 Decompiler Tool 2024:
Understanding EX4 Files:
EX4 files are compiled binaries utilized within the MetaTrader 4 (MT4) trading platform. They encapsulate trading strategies, expert advisors, and indicators in a format that the platform can efficiently execute. These files are not designed for human readability, as they are in a machine code format, optimized for rapid and efficient execution within the MT4 environment.
Defining MQ4 Files:
MQ4 files represent the editable source code written in the MQL4 programming language. These files are human-readable and provide the blueprint for trading algorithms and indicators. They allow traders and developers to modify, enhance, and customize trading strategies to meet specific requirements or preferences, offering flexibility and control over the trading process.
Advantages of Converting EX4 to MQ4
Converting EX4 files back into the MQ4 format offers several practical benefits:
Customization and Personalization: Enables users to tailor and modify trading strategies or indicators to better fit their unique trading styles and needs. Customizations might include tweaking parameters, adding new features, or integrating with other systems.
Performance Optimization: Provides an opportunity to refine and enhance the code for improved efficiency and performance. By optimizing the MQ4 code, traders can achieve faster execution times and potentially better trading results.
Educational Insights: Allows for a deeper understanding of the underlying logic and mechanics of trading algorithms. By examining and studying the MQ4 code, users can gain valuable knowledge and insights into how specific trading strategies operate.
#ex4 to mq4#ex4 to mq4 decompiler#ex4 to mq4 converter online#ex5 to mq5#ex4 to mq4 decompiler online free
1 note
·
View note
Text
What’s Hot in Open Source? 10 Projects Everyone’s Talking About.
Let’s be honest: Open source is no longer just a corner of the internet for hardcore hackers and hoodie-wearing devs in dark rooms.
In 2025, open source is culture. It’s powering your apps, building your AI, running your code — and shaping the future of the web.

Best part? It’s being built by regular people with laptops, passion, and late-night coffee habits.
If you want to see where the tech world is heading, look at what the open source community is obsessed with right now.
Here are 10 of the most talked-about, starred, cloned, and loved open source projects — and why they're getting so much hype.
🥁 1. Bun – JavaScript, But Supercharged Node js walked so Bun could absolutely sprint.
What’s the buzz?
A lightning-fast JavaScript runtime
All-in-one: package manager, bundler, test runner
Built from the ground up for performance and simplicity
If you’ve ever felt like your JS tooling was slow, clunky, or too scattered — Bun is your new favorite toy.
⚙️ 2. Zig – The “C Replacement” That’s Actually Enjoyable Zig is becoming the language for devs who want control without chaos.
Why it’s trending:
Safer and more readable than C
Zero hidden behaviors
Cross-compilation is dead simple
More and more projects (like Bun) are using Zig under the hood — and developers are falling hard for its no-nonsense elegance.
🧠 3. Open Interpreter – Your Terminal Just Got a Brain Imagine asking your computer to "rename all these files, zip them, and move them to Dropbox" — and it actually does it.
That’s Open Interpreter.
Why devs love it:
Natural language meets command line
Executes code, automates tasks, writes scripts
Feels like pair programming with ChatGPT — but local
Total game changer for productivity nerds, automators, and CLI lovers.
🤖 4. Auto-GPT – The Rise of Autonomous AI Agents Remember when AI just answered questions? Now it thinks ahead.
Auto-GPT is an experiment gone viral — and it’s only growing.
Why it matters:
Gives large language models goals — not just prompts
Executes tasks, adjusts plans, loops intelligently
Wildly unpredictable, but wildly powerful
This is the stuff of future startups. And yes, it’s still open source.
🧵 5. Tauri – Finally, a Desktop App Framework That Isn’t Bloated Electron apps are powerful… and heavy. Tauri is the fix.
What devs are saying:
Uses Rust for secure, fast backends
Integrates with your favorite front-end frameworks
Tiny file sizes, way faster load times
From indie devs to full-stack teams, everyone’s jumping on board.
🔗 6. LangChain – The Toolkit for Building Smart, Context-Aware Apps Want to build your own AI assistant, chatbot, or tool that thinks? LangChain is your new best friend.
Why it’s still dominating:
Lets you chain LLMs, tools, and logic together
Powers everything from research agents to customer support
Works across GPT-4, Claude, Mistral, and more
It’s basically the foundation of any next-gen AI app in 2025.
🧩 7. Nix / NixOS – The Package Manager That’s Finally Cool Nix has been around for a while — but now? It’s having a full-blown renaissance.
Why developers are obsessed:
Perfectly reproducible dev environments
Declarative system configs
No more “it works on my machine” drama
If you’ve ever nuked your setup with one bad install, Nix is a lifesaver.
🧬 8. DuckDB – The SQLite of Analytics Say hello to the tiny, blazing-fast SQL engine built for serious data work.
Why it’s trending:
Runs analytics queries locally — with insane speed
Perfect for devs, data scientists, and anyone working with big CSVs
Doesn’t need servers or setup — just works
It’s like having a personal warehouse engine in your laptop.
🕹️ 9. Godot – The Free Game Engine That’s Beating the Big Guys Indie game devs are rallying behind Godot — and for good reason.
Why it’s blowing up:
Fully open source, no licensing mess
Lightweight, cross-platform, and beginner-friendly
A true alternative to Unity (especially after the pricing drama)
It’s not just for games — people are building apps, tools, and even UI frameworks with it.
🔐 10. Turbopack – The Successor to Webpack (But Not Painful) Built by the Vercel team, Turbopack is a next-gen bundler that makes building modern web apps feel sane again.
What makes it great:
Insanely fast
Designed for React, Next js, and modern workflows
Incremental, efficient, and easy to plug in
If you’re tired of waiting for your site to build — this is your upgrade.
🎯 Final Thought: Open Source Is Where the Future Happens First All of these projects have one thing in common: They’re made by real people who just want better tools.
Not billion-dollar budgets. Not boardrooms. Just brilliant builders sharing code, learning in public, and pushing tech forward.
If you’re watching these projects, you’re not just following trends — You’re watching the next wave of innovation unfold in real time.
💬 Want to get involved? Star a repo. File an issue. Share something cool. Open source isn’t just code — it’s community.
And it’s never been a better time to join in.
0 notes
Text
Why AI-Readable Healthcare Websites Are Now Non-Negotiable

Platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity are no longer experimental tools — they’ve become central to how people search for medical answers. If your healthcare website isn’t built for AI readability, you’re effectively invisible on the modern web.
Today, when users ask AI platforms about symptoms, treatments, or providers, only well-structured, high-trust content is pulled into the answers. That’s why making your site AI-readable isn’t optional. It’s essential.
AI readability website goes beyond traditional SEO. It’s not just about keywords or backlinks. It’s about structure, semantics, and clarity. According to BrightEdge, over 40% of all browsing sessions now include some form of AI summarization. That figure is only growing.
Structure Is Everything
Don’t build random pages around keyword volume. Create a strategic content architecture with topical clusters. Link your main service pages to supporting content — like treatment options, doctor bios, FAQs, and care instructions — to build topical authority. Tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider can help you map and optimize these internal links effectively.
If you’re, say, a top dental clinic for implants in Dubai, your implant page should connect to content about implant types, procedures, before-and-after care, and patient stories. That’s how you signal relevance and depth to AI crawlers.
Semantic HTML and Schema: Speak Machine
Ditch the endless <div>s. Use semantic HTML tags like <article>, <section>, <main>, and <header> to give your pages logical meaning.
Add rich schema markup — not just for search engines, but for AI systems. Use schema.org types like MedicalWebPage, LocalBusiness, MedicalCondition, and Person for doctors. Mark up your FAQs, reviews, and breadcrumbs. Enable Speakable schema for voice assistants. This helps AI models parse and present your content more accurately.
Let AI Bots Crawl Your Site
Allow access to GPTBot, GeminiBot, and similar AI crawlers in your robots.txt file. Create an AI-friendly sitemap. Remove outdated, low-quality, or duplicate content. Simplify metadata. Avoid script-heavy pages that slow down parsing.
Clear Answers, Medical Accuracy
Start with direct answers. Don’t bury definitions under fluff. Use credible sources like PubMed or Mayo Clinic to back your claims. Use clear, plain English alongside clinical terms like “leiomyoma” or “embolization” to guide both humans and machines.
Meet Patients Where They Search
AI-driven discovery happens on more than just Google now. Your content must perform across voice search, smart assistants, chatbots, and summarizers. That means structured data, clean HTML, and no PDFs or image-heavy pages that models can’t read.
Need help?
At Harvee Health, we specialize in building healthcare websites that aren’t just SEO-ready — they’re AI-optimized. From schema to strategy, our expert team ensures your content performs where modern patients are searching.
0 notes
Text
DICS: Best Python Training in Laxmi Nagar

In today’s technology-driven world, programming is no longer a skill reserved for computer scientists alone—it’s a must-have for anyone aiming to thrive in the digital age. Among all programming languages, Python stands out as one of the most powerful, beginner-friendly, and versatile languages in the tech ecosystem. Whether you want to build websites, automate tasks, analyze data, or dive into artificial intelligence, Python is the perfect starting point. And if you're located in East Delhi, you’re in luck—because the best Python institute in Laxmi Nagar is right around the corner, ready to launch your career to new heights.
Why Python?
Before diving into where to learn Python, it’s important to understand why this language is so crucial. Python is open-source, easy to learn, and boasts a massive community that continuously contributes libraries and frameworks. It’s the backbone of some of the world’s most in-demand fields like data science, machine learning, and web development. Its clear syntax and readability make it ideal for beginners, yet powerful enough for seasoned professionals.
Discover the Best Python Institute in Laxmi Nagar
When it comes to learning Python, the quality of your institute makes all the difference. In Laxmi Nagar—a well-known education hub in Delhi—you’ll find several training centers. But only a few can truly deliver the quality, depth, and practical exposure you need to succeed. That’s where the best Python institute in Laxmi Nagar sets itself apart.
This institute offers a structured, industry-oriented curriculum that goes beyond textbook theory. You’ll get hands-on experience with real-time projects, one-on-one mentorship, and personalized career guidance. Whether you're a student, working professional, or aspiring freelancer, the institute’s flexible class schedules, online and offline learning options, and lifetime access to course materials ensure that you never fall behind.
The Best Python Course in Laxmi Nagar
What makes this course the best Python course in Laxmi Nagar? It's the perfect blend of fundamental and advanced concepts taught by certified, experienced trainers. The course begins with the basics of Python programming, including variables, data types, control structures, and functions. It then moves into more complex areas like object-oriented programming, file handling, modules, and exception handling.
But it doesn’t stop there. The course also covers essential libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and frameworks like Django or Flask—giving you a well-rounded skill set that today’s employers value. By the end of the course, you'll be fully equipped to build applications, automate repetitive tasks, analyze data, and even crack job interviews.
Your Career Starts Here
Choosing the right training can transform your life. With an affordable fee structure, live project training, internship opportunities, and 100% placement assistance, the best Python course in Laxmi Nagar is an investment in your future. Don't settle for average—choose excellence, choose success.
Whether you’re starting from scratch or looking to enhance your existing skills, the best Python institute in Laxmi Nagar is your gateway to a successful tech career. Enroll today and take the first step toward becoming a Python pro!
#PythonCourse#DICSLaxmiNagar#BestPythonInstitute#PythonTraining#LearnPython#PythonInLaxmiNagar#BestPythonCourse#CodingInLaxmiNagar#PythonForBeginners#DICSInstitute
0 notes
Text
wait a second. the gpl requires you to a) license derivative works the same, and b) share source code when distributing. if you distribute an interpreted language like javascript with no build step and don't minify... you are, inherently, distributing the source, right? there's nothing that says you need to link a public git repository or whatever. so if you just, like, email someone a zip, or publish to npm...
okay, let's see:
The “source code” for a work means the preferred form of the work for making modifications to it. “Object code” means any non-source form of a work. The “Corresponding Source” for a work in object code form means all the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to control those activities.
You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License, in one of these ways...
I guess it hinges upon whether what you are distributing is the "preferred form of the work for making modifications to it." do things like linter config files count as things that must be distributed?
(I guess in the case of a web extension, which is most likely what I would be using gpl code in thanks to the xkit projects, this is all irrelevant. while an xpi file is in fact a zip archive of the potentially entirely unmodified source of your extension, suggesting the recipient rename the .xpi to .zip if they want to extract it and read the source is almost certainly too arcane to count.)
0 notes
Text

1. „Suche“:
Please search for a machine-readable version of the text titled: [insert title]
I am looking for a publicly accessible, full or partial version of the text that is:
Machine-readable (i.e. not image-only scans, not rendered via JavaScript, and not embedded in inaccessible frames),
Hosted on a reliable platform (e.g. Wikisource, Aozora Bunko, Japanese Text Initiative, archive.org),
Preferably includes chapter or section divisions to facilitate reference,
If possible, includes metadata about the manuscript base or edition (e.g. Karasumaru-bon, Kōshōji-bon),
Available in either the original Japanese or in a parallel translation (indicate if you prefer one).
If multiple versions are available, please compare and recommend the one most suited for close reading or term-based search. Include direct links and note any technical limitations (e.g. missing OCR, access restrictions).
2. „Deep Research“:
Now that we have identified a suitable version of [title], please search it for the following: Term(s) / Topic(s): [insert keywords or themes, e.g. 「言の葉」, impermanence, Yoshitsune]
Please proceed as follows:
Confirm that the text is technically accessible and searchable.
Search the text thoroughly for occurrences of the specified term(s) or theme(s).
For each occurrence, provide:
The exact location (e.g. chapter or passage number),
A full quotation of the relevant passage,
A brief summary or paraphrase of its meaning and significance in context.
If the term appears repeatedly, note any variation in usage, tone, or function.
If the source is unexpectedly unreadable or incomplete, explain why and suggest a workaround (e.g. alternative editions, downloadable files, or parallel texts).
0 notes
Text

Öland_Gettlinge.jpg
#wikimedia commons#2000s#2005#Gettlinge gravfält#Archaeological monuments in Sweden with known IDs#Archaeological monuments in Sweden with UUIDs#Assumed own work#Files with no machine-readable source#License migration redundant#GFDL#CC-BY-SA-3.0-migrated#Self-published work
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Python Training in Chandigarh: Unlocking a Future in Programming
In today’s fast-paced digital world, programming has become a core skill across numerous industries. Among all programming languages, Python stands out due to its simplicity, versatility, and powerful capabilities. As a result, Python training has become one of the most sought-after courses for students, professionals, and aspiring developers. In Chandigarh, a city known for its educational institutions and growing IT ecosystem, Python training opens up exciting career opportunities for learners of all levels.
Why Learn Python?
Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language that emphasizes code readability with its clear syntax. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. Python has grown rapidly in popularity, currently ranking as one of the top programming languages worldwide.
Some of the key reasons to learn Python include:
Ease of learning: Python has a gentle learning curve, making it ideal for beginners.
Versatility: It’s used in web development, data science, artificial intelligence, automation, game development, and more.
Strong community support: Python has a vast library ecosystem and an active community that contributes to open-source tools and frameworks.
High demand: From startups to tech giants like Google, Facebook, and Netflix, Python developers are in high demand globally.
The Growing Demand for Python in India
India's digital transformation has resulted in a booming demand for skilled programmers. Python, being at the center of technologies like machine learning, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, is a critical skill in the current job market. According to recent job market surveys, Python is consistently among the top 3 most requested skills in software development roles.
Industries such as finance, healthcare, education, and e-commerce in India are actively seeking professionals with Python expertise. As the use of big data and automation expands, the demand for Python-trained professionals is expected to rise even more.
Why Choose Chandigarh for Python Training?
Chandigarh, the capital of Punjab and Haryana, is emerging as a technology hub in North India. Known for its well-planned infrastructure and high quality of life, the city is home to several IT companies, startups, and training institutes.
Key reasons to choose Chandigarh for Python training:
High-quality education centers: Chandigarh hosts some of the best training institutes offering Python courses with practical, project-based learning.
Affordable living: Compared to metropolitan cities, Chandigarh offers cost-effective training and living expenses.
Growing IT ecosystem: With IT parks and emerging startups, the city offers internship and job opportunities for learners.
Peaceful environment: The city’s clean and organized environment enhances the learning experience.
What to Expect from a Python Training Program in Chandigarh?
Python training programs in Chandigarh cater to both beginners and advanced learners. Whether you are a student, fresher, or working professional looking to upskill, you can find a suitable course.
Course Structure
Most Python training programs include:
Introduction to Python: Basics of syntax, variables, data types, and control structures.
Functions and Modules: Writing reusable code using functions and importing modules.
Object-Oriented Programming: Concepts such as classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism.
File Handling: Reading from and writing to files.
Error Handling: Managing exceptions and debugging.
Libraries and Frameworks: Use of popular libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and frameworks like Flask or Django.
Database Integration: Connecting Python applications with databases like MySQL or SQLite.
Project Work: Real-world projects that test your understanding and give hands-on experience.
Modes of Training
Institutes offer various modes of learning:
Classroom training: Traditional in-person classes with face-to-face interaction.
Online training: Live or recorded sessions accessible from home.
Weekend batches: Ideal for working professionals.
Fast-track courses: For learners who want to complete the course in a shorter time.
Certifications and Placement Support
Most reputed institutes provide certification upon course completion, which can be a great addition to your resume. Some also offer:
Resume-building assistance
Mock interviews
Placement support or job referrals
Internship opportunities with IT firms in Chandigarh
Career Opportunities After Python Training
After completing Python training, learners can pursue various career paths, such as:
Python Developer: Focused on building software applications using Python.
Web Developer: Using frameworks like Django or Flask to build web applications.
Data Analyst: Analyzing data using Pandas, NumPy, and data visualization tools.
Machine Learning Engineer: Building intelligent systems using libraries like Scikit-learn and TensorFlow.
Automation Engineer: Writing scripts for process automation in business and IT environments.
Backend Developer: Creating server-side logic for mobile and web applications.
Top Institutes for Python Training in Chandigarh
While there are many training providers, here are a few well-regarded Python training institutes in Chandigarh (as of recent trends):
CBitss Technologies
ThinkNEXT Technologies
Webtech Learning
Infowiz Software Solutions
Netmax Technologies
Each of these institutes offers various Python courses, including beginner and advanced levels, along with certification and placement support.
Tips for Choosing the Right Python Course
Check the syllabus: Ensure it covers both basics and advanced topics relevant to your goals.
Trainer experience: Look for instructors with industry experience.
Hands-on projects: Courses should include real-world projects for practical exposure.
Student reviews: Read testimonials and online reviews to gauge course quality.
Demo classes: Attend a trial session if available before enrolling.
Conclusion
Python training in Chandigarh offers a gateway to exciting and diverse career opportunities in the tech industry. Whether you aim to become a developer, data analyst, or machine learning expert, Python is a foundational skill that can set you apart in the competitive job market. With its growing tech scene, quality institutes, and supportive learning environment, Chandigarh is an ideal location to begin or advance your Python programming journey.
Investing in Python training today can pave the way for a dynamic career tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Roadmap to Web Development – Coding Brushup
In today's digital world, web development is more than just writing code—it's about creating fast, user-friendly, and secure applications that solve real-world problems. Whether you're a beginner trying to understand where to start or an experienced developer brushing up on your skills, this ultimate roadmap will guide you through everything you need to know. This blog also offers a coding brushup for Java programming, shares Java coding best practices, and outlines what it takes to become a proficient Java full stack developer.

Why Web Development Is More Relevant Than Ever
The demand for web developers continues to soar as businesses shift their presence online. According to recent industry data, the global software development market is expected to reach $1.4 trillion by 2027. A well-defined roadmap is crucial to navigate this fast-growing field effectively, especially if you're aiming for a career as a Java full stack developer.
Phase 1: The Basics – Understanding Web Development
Web development is broadly divided into three categories:
Frontend Development: What users interact with directly.
Backend Development: The server-side logic that powers applications.
Full Stack Development: A combination of both frontend and backend skills.
To start your journey, get a solid grasp of:
HTML – Structure of the web
CSS – Styling and responsiveness
JavaScript – Interactivity and functionality
These are essential even if you're focusing on Java full stack development, as modern developers are expected to understand how frontend and backend integrate.
Phase 2: Dive Deeper – Backend Development with Java
Java remains one of the most robust and secure languages for backend development. It’s widely used in enterprise-level applications, making it an essential skill for aspiring Java full stack developers.
Why Choose Java?
Platform independence via the JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
Strong memory management
Rich APIs and open-source libraries
Large and active community
Scalable and secure
If you're doing a coding brushup for Java programming, focus on mastering the core concepts:
OOP (Object-Oriented Programming)
Exception Handling
Multithreading
Collections Framework
File I/O
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Java Coding Best Practices for Web Development
To write efficient and maintainable code, follow these Java coding best practices:
Use meaningful variable names: Improves readability and maintainability.
Follow design patterns: Apply Singleton, Factory, and MVC to structure your application.
Avoid hardcoding: Always use constants or configuration files.
Use Java Streams and Lambda expressions: They improve performance and readability.
Write unit tests: Use JUnit and Mockito for test-driven development.
Handle exceptions properly: Always use specific catch blocks and avoid empty catch statements.
Optimize database access: Use ORM tools like Hibernate to manage database operations.
Keep methods short and focused: One method should serve one purpose.
Use dependency injection: Leverage frameworks like Spring to decouple components.
Document your code: JavaDoc is essential for long-term project scalability.
A coding brushup for Java programming should reinforce these principles to ensure code quality and performance.
Phase 3: Frameworks and Tools for Java Full Stack Developers
As a full stack developer, you'll need to work with various tools and frameworks. Here’s what your tech stack might include:
Frontend:
HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript
React.js or Angular: Popular JavaScript frameworks
Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS: For responsive design
Backend:
Java with Spring Boot: Most preferred for building REST APIs
Hibernate: ORM tool to manage database operations
Maven/Gradle: For project management and builds
Database:
MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB
Version Control:
Git & GitHub
DevOps (Optional for advanced full stack developers):
Docker
Jenkins
Kubernetes
AWS or Azure
Learning to integrate these tools efficiently is key to becoming a competent Java full stack developer.
Phase 4: Projects & Portfolio – Putting Knowledge Into Practice
Practical experience is critical. Try building projects that demonstrate both frontend and backend integration.
Project Ideas:
Online Bookstore
Job Portal
E-commerce Website
Blog Platform with User Authentication
Incorporate Java coding best practices into every project. Use GitHub to showcase your code and document the learning process. This builds credibility and demonstrates your expertise.
Phase 5: Stay Updated & Continue Your Coding Brushup
Technology evolves rapidly. A coding brushup for Java programming should be a recurring part of your development cycle. Here’s how to stay sharp:
Follow Java-related GitHub repositories and blogs.
Contribute to open-source Java projects.
Take part in coding challenges on platforms like HackerRank or LeetCode.
Subscribe to newsletters like JavaWorld, InfoQ, or Baeldung.
By doing so, you’ll stay in sync with the latest in the Java full stack developer world.
Conclusion
Web development is a constantly evolving field that offers tremendous career opportunities. Whether you're looking to enter the tech industry or grow as a seasoned developer, following a structured roadmap can make your journey smoother and more impactful. Java remains a cornerstone in backend development, and by following Java coding best practices, engaging in regular coding brushup for Java programming, and mastering both frontend and backend skills, you can carve your path as a successful Java full stack developer.
Start today. Keep coding. Stay curious.
0 notes
Text
Ultimate Guide to Python Compiler

When diving into the world of Python programming, understanding how Python code is executed is crucial for anyone looking to develop, test, or optimize their applications. This process involves using a Python compiler, a vital tool for transforming human-readable Python code into machine-readable instructions. But what exactly is a Python compiler, how does it work, and why is it so important? This guide will break it all down for you in detail, covering everything from the basic principles to advanced usage.
What is a Python Compiler?
A Python compiler is a software tool that translates Python code (written in a human-readable form) into machine code or bytecode that the computer can execute. Unlike languages like C or Java, Python is primarily an interpreted language, which means the code is executed line by line by an interpreter. However, Python compilers and interpreters often work together to convert the source code into something that can run on your system.
Difference Between Compiler and Interpreter
Before we delve deeper into Python compilers, it’s important to understand the distinction between a compiler and an interpreter. A compiler translates the entire source code into a machine-readable format at once, before execution begins. Once compiled, the program can be executed multiple times without needing to recompile.
On the other hand, an interpreter processes the source code line by line, converting each line into machine code and executing it immediately. Python, as a high-level language, uses both techniques: it compiles the Python code into an intermediate form (called bytecode) and then interprets that bytecode.
How Does the Python Compiler Work?
The Python compiler is an essential part of the Python runtime environment. When you write Python code, it first undergoes a compilation process before execution. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works:
1. Source Code Parsing
The process starts when the Python source code (.py file) is written. The Python interpreter reads this code, parsing it into a data structure called an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST). The AST is a hierarchical tree-like representation of the Python code, breaking it down into different components like variables, functions, loops, and classes.
2. Compilation to Bytecode
After parsing the source code, the Python interpreter uses a compiler to convert the AST into bytecode. This bytecode is a lower-level representation of the source code that is platform-independent, meaning it can run on any machine that has a Python interpreter. Bytecode is not human-readable and acts as an intermediate step between the high-level source code and the machine code that runs on the hardware.
The bytecode generated is saved in .pyc (Python Compiled) files, which are stored in a special directory named __pycache__. When you run a Python program, if a compiled .pyc file is already available, Python uses it to speed up the startup process. If not, it re-compiles the source code.
3. Execution by the Python Virtual Machine (PVM)
After the bytecode is generated, it is sent to the Python Virtual Machine (PVM), which executes the bytecode instructions. The PVM is an interpreter that reads and runs the bytecode, line by line. It communicates with the operating system to perform tasks such as memory allocation, input/output operations, and managing hardware resources.
This combination of bytecode compilation and interpretation is what allows Python to run efficiently on various platforms, without needing separate versions of the program for different operating systems.
Why is a Python Compiler Important?
Using a Python compiler offers several benefits to developers and users alike. Here are a few reasons why a Python compiler is so important in the programming ecosystem:
1. Portability
Since Python compiles to bytecode, it’s not tied to a specific operating system or hardware. This allows Python programs to run on different platforms without modification, making it an ideal language for cross-platform development. Once the code is compiled into bytecode, the same .pyc file can be executed on any machine that has a compatible Python interpreter installed.
2. Faster Execution
Although Python is an interpreted language, compiling Python code to bytecode allows for faster execution compared to direct interpretation. Bytecode is more efficient for the interpreter to execute, reducing the overhead of processing the raw source code each time the program runs. It also helps improve performance for larger and more complex applications.
3. Error Detection
By using a Python compiler, errors in the code can be detected earlier in the development process. The compilation step checks for syntax and other issues, alerting the developer before the program is even executed. This reduces the chances of runtime errors, making the development process smoother and more reliable.
4. Optimizations
Some compilers provide optimizations during the compilation process, which can improve the overall performance of the Python program. Although Python is a high-level language, there are still opportunities to make certain parts of the program run faster. These optimizations can include techniques like constant folding, loop unrolling, and more.
Types of Python Compilers
While the official Python implementation, CPython, uses a standard Python compiler to generate bytecode, there are alternative compilers and implementations available. Here are a few examples:
1. CPython
CPython is the most commonly used Python implementation. It is the default compiler for Python, written in C, and is the reference implementation for the language. When you install Python from the official website, you’re installing CPython. This compiler converts Python code into bytecode and then uses the PVM to execute it.
2. PyPy
PyPy is an alternative implementation of Python that features a Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler. JIT compilers generate machine code at runtime, which can significantly speed up execution. PyPy is especially useful for long-running Python applications that require high performance. It is highly compatible with CPython, meaning most Python code runs without modification on PyPy.
3. Cython
Cython is a superset of Python that allows you to write Python code that is compiled into C code. Cython enables Python programs to achieve performance close to that of C while retaining Python’s simplicity. It is commonly used when optimizing computationally intensive parts of a Python program.
4. Jython
Jython is a Python compiler written in Java that allows Python code to be compiled into Java bytecode. This enables Python programs to run on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), making it easier to integrate with Java libraries and tools.
5. IronPython
IronPython is an implementation of Python for the .NET framework. It compiles Python code into .NET Intermediate Language (IL), enabling it to run on the .NET runtime. IronPython allows Python developers to access .NET libraries and integrate with other .NET languages.
Python Compiler vs. Interpreter: What’s the Difference?
While both compilers and interpreters serve the same fundamental purpose—turning source code into machine-executable code—there are distinct differences between them. Here are the key differences:
Compilation Process
Compiler: Translates the entire source code into machine code before execution. Once compiled, the program can be executed multiple times without recompilation.
Interpreter: Translates and executes source code line by line. No separate executable file is created; execution happens on the fly.
Execution Speed
Compiler: Generally faster during execution, as the code is already compiled into machine code.
Interpreter: Slower, as each line is parsed and executed individually.
Error Detection
Compiler: Detects syntax and other errors before the program starts executing. All errors must be fixed before running the program.
Interpreter: Detects errors as the code is executed. Errors can happen at any point during execution.
Conclusion
The Python compiler plays a crucial role in the Python programming language by converting source code into machine-readable bytecode. Whether you’re using the default CPython implementation, exploring the performance improvements with PyPy, or enhancing Python with Cython, understanding how compilers work is essential for optimizing and running Python code effectively.
The compilation process, which includes parsing, bytecode generation, and execution, offers various benefits like portability, faster execution, error detection, and optimizations. By choosing the right compiler and understanding how they operate, you can significantly improve both the performance and efficiency of your Python applications.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of how Python compilers work, you’re equipped with the knowledge to leverage them in your development workflow, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned developer.
0 notes
Text
10 Key Benefits of Using Python Programming

It is interesting to note that today Python is among the most widely used programming languages globally. However, the language must be so because of one good reason: simplicity, versatility, and powerful features. It is useful from web development and data science all the way through artificial intelligence. Whether you have just started learning programming or you have been doing it for some time, Python provides some really good advantages, which make it a very popular programming language for programmers.
1. Very Easy to Read and Learn
Python is often recommended for beginners because of the higher level of readability and user-friendly syntax. Coding becomes very intuitive and keeps the learning curve short since it's plain English-like; even the most complex works can be done in far fewer lines of code than most other programming languages.
2. Open Source and Free
Python is totally free to use, distribute and modify. Since it's open-source, a big community of developers is involved in supporting the language; they are in the process of constantly improving and expanding its usefulness. This ensures that you obtain up-to-date versions of the language and are aware of latest trends and tools used across the globe.
3 Extensive Libraries and Frameworks
Libraries like NumPy, pandas, Matplotlib, TensorFlow, and Django are examples of Python's most significant assets-the rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. These libraries equip programmers with the ready-to-use tools for data analysis, machine learning, web development, and many others.
4. Independent of Platform
Being a cross-platform language, Python allows the code-written on one operating system to be run on another without any changes. Therefore, the time it takes to develop and deploy applications is lesser and easier to develop in multi-platform environments.
5. Highly Versatile
Python can be applied in a variety of almost any domain for development; including web development, desktop applications, automation, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT). Flexibility is the best asset of Python to possess where creating nearly anything using one language becomes practical.
6. Strong Community Support
The potential that Python provides exists with solid backing from a very large and active global community. If you have a problem or want guidance on a library, you'll always find available forums, tutorials, and documentation. Websites like Stack Overflow and GitHub have enough resources for Python.
7. Ideal for Automation
Such tasks as emailing, sorting files, and web scraping can very aptly be carried out using Python. The scripting capabilities are such that writing an automation script becomes very easy and efficient.
8. Excellent for Data Science and AI
Python is the best-performing language for data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence applications. With up-to-date libraries like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and Keras, Python offers intelligent modeling and big data analysis tools.
9. Easy to Integrate with Other Languages
Python makes it very easy for one to integrate with other
such as C, C++, and Java. It, therefore, becomes perfect for projects where the intense optimization of performance must be handled or the integration of legacy systems needed.
10. Career Paths
The demand for python development has hit a high note. Companies, ranging from tech startups to multinational corporations, are running a search to find professionals who possess such skills. One of the emerging fields applications of python is found in artificial intelligence and data science, making it a skill for the future.
Conclusion
Python is more than just an easy programming language-it is a strong and powerful tool utilized in many ways across industries. Its simplicity, flexibility, and strong support by community make it one of the best choices for new learners and the most experienced developers alike. Whether you wish to automate tasks, build websites, or dive into data science, Python gives you the tools to succeed.
Location: Bopal & Iskcon-Ambli in Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Visit Our Website: http://tccicomputercoaching.com/
#computer classes near me#Programming Classes in Bopal Ahmedabad – TCCI#Python Training Course in Bopal Ahmedabad#Software Training Institute in Iskcon Ahmedabad#TCCI - Tririd Computer Coaching Institute
0 notes
Text
Best Python Training Institute in Kerala: A Roadmap to Building a Successful Tech Career
Python has taken the tech world by storm. Its simplicity, readability, and versatility make it one of the most sought-after programming languages today. From web development and automation to data science and artificial intelligence, Python plays a central role across various domains. For aspiring developers and working professionals alike, mastering Python is no longer optional—it’s essential.
If you’re in Kerala and planning to begin or upskill your programming journey, finding the Best Python Training Institute in Kerala can be the stepping stone to your success. This guide explores the importance of Python, what a high-quality training program should include, and why Zoople Technologies stands out as a top choice.
Why Python is a Must-Learn Language in 2025
1. Beginner-Friendly Yet Powerful
Python’s syntax is intuitive and close to natural English, making it ideal for beginners. At the same time, it is robust enough to power applications used by giants like Google, Netflix, and NASA.
2. Wide Range of Applications
Python is widely used in:
Web development (using frameworks like Django and Flask)
Data science and analytics
Machine learning and AI
Game development
Internet of Things (IoT)
Scripting and automation
This versatility ensures that learning Python opens doors to various career paths.
3. High Market Demand
Companies across the globe are hiring Python developers for diverse roles. In India, especially in Kerala’s growing IT hubs like Kochi, Trivandrum, and Calicut, Python-skilled professionals are in strong demand.
4. Thriving Community and Resources
Python boasts a massive global community. Learners can access an abundance of tutorials, open-source projects, and peer support forums to accelerate their growth.
What Should You Expect from the Best Python Training Institute in Kerala?
To ensure your time, money, and effort are well invested, here’s what the Best Python Training Institute in Kerala should offer:
1. Comprehensive Curriculum
A top-tier training program should cover:
Core concepts: Variables, data types, operators, control structures
Functions and object-oriented programming
Error handling and file operations
Python libraries: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib
Web frameworks: Django and Flask
Real-world project development
Basics of APIs, version control (Git), and deployment techniques
2. Hands-On Learning
Theory alone won’t make you job-ready. Look for institutes that emphasize:
Live coding sessions
Real-time project implementation
Capstone projects
Coding challenges and assessments
3. Qualified and Experienced Trainers
Learning under experienced mentors can fast-track your understanding and confidence. Trainers should:
Have industry experience
Offer personalized mentorship
Be updated with current tech trends
4. Flexible Learning Modes
The institute should cater to diverse learners—students, professionals, and career switchers—offering:
Online and offline batches
Weekday and weekend classes
Access to recorded sessions
5. Certification and Placement Support
A recognized certificate from a reputed institute adds value to your resume. Placement assistance, resume building, and interview prep are key offerings of a leading training institute.
Career Prospects After Learning Python
Python’s wide application spectrum means you can pursue multiple in-demand roles such as:
Python Developer
Full Stack Web Developer
Data Analyst
Machine Learning Engineer
Backend Developer
Automation Tester
Kerala’s tech ecosystem is expanding rapidly, especially in cities like Kochi, Technopark Trivandrum, and Kozhikode Cyberpark. Companies here are constantly scouting for skilled Python professionals. Additionally, with remote work opportunities increasing, Kerala-based professionals can now work for global companies from the comfort of their hometown.
Why Kerala is an Ideal Destination for Python Training
Kerala, known for its high literacy rate and educational infrastructure, is quickly transforming into a technological education hub. Here’s why Choosing The Best Python Training Institute in Kerala makes sense:
Growing IT Hubs: Cities like Kochi and Trivandrum are witnessing exponential growth in IT infrastructure.
Affordable Education: High-quality education at lower costs compared to metros like Bangalore or Hyderabad.
Excellent Connectivity: With a strong internet presence and robust digital infrastructure, learners in Kerala can easily access online resources and hybrid learning options.
Supportive Government Policies: The Kerala Startup Mission and other government initiatives are pushing tech education and employment aggressively.
Whether you're a student or a working professional, Kerala offers the right ecosystem to build and grow your tech skills.
Zoople Technologies – The Best Python Training Institute in Kerala
When it comes to high-quality, job-oriented training, Zoople Technologies stands out as the Best Python Training Institute in Kerala. With a proven track record of creating skilled developers and a student-first approach, Zoople has emerged as a trusted name in the tech training landscape.
Why Zoople Technologies?
Industry-Relevant Curriculum: Zoople’s course content is designed by experienced developers and is regularly updated to match industry trends.
Project-Based Learning: Students work on live projects that mimic real-world challenges, giving them hands-on experience that employers value.
Experienced Trainers: The instructors are not just teachers—they are professionals who bring industry insights directly into the classroom.
Flexible Batches: Whether you’re a student or a working professional, Zoople offers batch timings that suit your schedule, including online options.
Placement Support: Zoople has a dedicated placement team that assists students with job applications, interview preparation, and resume building.
Supportive Learning Environment: With one-on-one mentoring, practical labs, and open forums, Zoople ensures every student gets the attention they need to succeed.
Zoople Technologies has earned its reputation by consistently producing industry-ready professionals who land jobs in top companies across India and abroad.
Final Thoughts
In the world of programming, Python is your gateway language—and choosing the Best Python Training Institute in Kerala is the first step toward a rewarding tech career. Kerala offers the right environment to learn and grow, and Zoople Technologies provides the quality, support, and expertise needed to turn your ambition into a profession.
If you're serious about a future in tech and want to learn from the best, Zoople Technologies is where your journey should begin.
0 notes