#Long Range RFID Reader
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Long Range RFID Reader For Vehicle And Asset Tracking
A Long Range RFID Reader is a tool designed to examine RFID tags from prolonged distances, normally up to numerous meters. It is right for packages like automobile tracking, warehouse control and getting entry to manage. These readers offer excessive-velocity, correct information, seize and guide both passive and energetic RFID tag technology.
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Asset Tracking with RFID Long-Range Reader Technology

Fast-moving logistics operations and asset management depend on efficiency and precision. The RFID long range reader is one of the primary technological improvements enhancing these operational features. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) scanning devices differ from standard barcodes through their capability to detect many tags from extended distances, thus enhancing tracking systems. The long-distance readers prove ideal for massive operations such as warehouses, shipping yards, and transportation fleets because they eliminate both time-intensive manual scanning and human scanning inaccuracies.
How RFID Enhances Efficiency
Through RFID technology, organizations can conduct real-time asset tracking that enhances inventory precision, reduces labour costs, and stops asset loss or thievery. The long-range capabilities of RFID readers give them the ability to scan numerous tags at once, regardless of whether assets remain unmoving or move between locations. The automated data flow stream allows businesses to achieve rapid and well-informed choices through this system. RFID systems benefit from seamless connectivity to enterprise software that generates asset-based data, including usage records, tracking information, and maintenance tracking.
Power of RFID Solar Tag
The most remarkable advancement in RFID technology is the RFID solar tag which employs solar power for self-powered tracking operations in external and distant applications. The tags operate using solar power, which enables them to continue functioning longer, thus becoming suitable for difficult battery replacement environments. The tracking system finds practical applications by following shipping containers, mining sites, and construction site equipment. The solar power function allows continuous operation and data transfer without regular maintenance to reduce operational breakdowns and expenses.
Applications across Industries
The RFID technology finds broad implementation in logistics, agriculture, retail and construction fields. Minimal human involvement enables this technology to track vehicles along with livestock and inventory while monitoring equipment through its fields. RFID systems demonstrate versatility by allowing organizations to organize procedures more efficiently and minimize human mistakes, together with productivity increases in multiple operational settings.
Bottom Line
Incorporating solar-powered tags with RFID technology brings a revolutionary change to the innovative and sustainable tracking systems that industries need. Real-time control over business assets is possible due to these systems, which provide exceptional reliability and adaptability. Successful implementation of advanced RFID technology can be done using the innovative solutions offered by Eco Track Systems to address current logistical requirements. As a creative and environmentally conscious company specializing in asset management solutions Eco Track Systems delivers trusted solutions to customers working toward more innovative inventory management systems. For Any inquiry visit at https://www.etsrfid.com/contact-us/
0 notes
Text
The hotel management systems advantages
You may also efficiently manage the parking lot and system security with the help of the QR code-based parking Saudi. As more and more hotels transition to adopting small hotel management software in Saudi to manage operations, technology has completely changed the hospitality sector. https://www.prologicfirstss.com/blog-the-hotel-management-systems-advantages.html
#long range rfid reader price saudi#small hotel management software in saudi#best payroll software in Saudi Arabia
0 notes
Text
Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking Market : Key Trends, Regional Insights, and Strategical Forecast to 2032
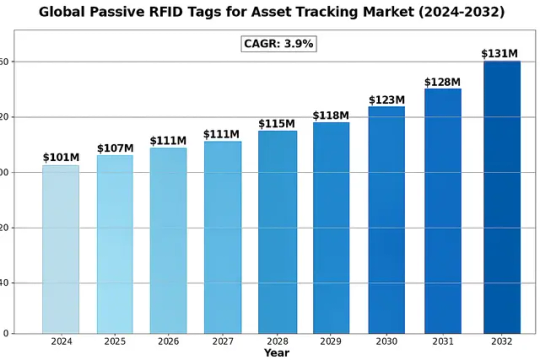
The global Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking Market was valued at 101 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 131 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period.
Passive RFID tags are wireless tracking devices that enable efficient asset management without requiring an internal power source. These tags operate by reflecting RF signals from readers, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term tracking with minimal maintenance. The technology is categorized into UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) and HF (High Frequency) variants, each offering distinct advantages in read range and data transfer speeds.
The market growth is driven by increasing adoption across retail, logistics, and manufacturing sectors where real-time asset visibility is critical. While cost-effectiveness remains a key advantage, emerging applications in healthcare and smart cities are creating new opportunities. However, challenges like signal interference in metal-rich environments persist. Leading players including Zebra Technologies and Avery Dennison are investing in advanced tag designs to overcome these limitations and expand market penetration.
Get Full Report with trend analysis, growth forecasts, and Future strategies : https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/passive-rfid-tags-for-asset-tracking-market/
Segment Analysis:
By Type
UHF Passive RFID Tags Lead the Market Owing to Long Read Range and Cost Efficiency
The market is segmented based on type into:
UHF (Ultra-High Frequency)
Subtypes: Gen 2 UHF tags, RAIN RFID, and others
HF (High Frequency)
Subtypes: NFC-enabled tags, ISO 15693 compliant, and others
By Application
Warehousing and Logistics Segment Dominates Due to Rising Automation in Supply Chain Management
The market is segmented based on application into:
Retail and Wholesale
Warehousing and Logistics
Industrial Manufacturing
Others
By Frequency Range
860-960 MHz Category Holds Major Share for Asset Tracking Applications
The market is segmented based on frequency range into:
Low Frequency (125-134 kHz)
High Frequency (13.56 MHz)
Ultra-High Frequency (860-960 MHz)
By Form Factor
On-Metal Tags Gain Traction for Industrial Asset Management Solutions
The market is segmented based on form factor into:
Label Tags
Card Tags
On-Metal Tags
Hard Tags
Regional Analysis: Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking Market
North America North America leads in passive RFID adoption, driven by advanced supply chain digitization and strong regulatory compliance mandates. The U.S. accounts for over 60% of the regional market, with extensive deployments in retail (e.g., Walmart’s RFID mandate) and logistics. The region’s mature IoT infrastructure and focus on real-time asset visibility fuel demand for UHF tags, particularly in cold chain monitoring and pharmaceutical tracking. Canada follows closely, with growing RFID use in oil & gas asset management and cross-border logistics. High-capacity logistics hubs and warehouse automation trends create sustained growth opportunities, though pricing pressures remain for high-volume adopters.
Europe Europe’s market is characterized by stringent data privacy regulations (GDPR) and emphasis on circular economy principles, driving RFID adoption for reusable asset tracking. Germany and the U.K. dominate, with manufacturing sectors leveraging Industry 4.0 integrations for tool tracking. The region shows strong preference for HF tags in embedded industrial applications, while retail adopts UHF labels. EU-wide initiatives like the Digital Product Passport proposal are expected to accelerate adoption. However, fragmentation in frequency regulations across countries complicates cross-border deployments, with ongoing harmonization efforts under ETSI standards.
Asia-Pacific As the fastest-growing regional market (5.2% CAGR), APAC benefits from manufacturing expansion and logistics modernization. China’s manufacturing sector consumes 40% of regional RFID tags for factory automation, while India’s retail sector shows surging adoption. Japan leads in RFID-embedded machinery parts, whereas Southeast Asia focuses on port logistics applications. Price sensitivity drives demand for low-cost UHF tags, with local manufacturers like Invengo gaining market share. However, inconsistent RFID infrastructure and spectrum allocation differences between countries create implementation hurdles for multinational corporations operating in the region.
South America Market growth is constrained by economic volatility but shows promise in mining equipment tracking (Chile, Peru) and agricultural asset management (Brazil). Brazil accounts for 55% of regional demand, with increasing RFID use in automotive parts logistics. The lack of standardized mandates and lower IoT maturity slows adoption compared to other regions. However, port modernization projects and growing cross-border trade are creating new opportunities for pallet and container tracking solutions. Local production remains limited, with most tags imported from North America or Asia.
Middle East & Africa The market is emerging, led by GCC countries’ logistics hubs and oilfield asset tracking requirements. UAE’s ports and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 projects drive adoption of durable RFID tags for harsh environments. Africa shows potential in pharmaceutical supply chains (supported by PEPFAR initiatives) and mining operations, though infrastructure constraints limit widespread use. The region demonstrates particular interest in metal-mountable UHF tags for industrial applications. While current market penetration remains low (under 15% of global share), strategic investments in smart cities and ports suggest long-term growth potential.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Emerging Industry 4.0 Applications to Unlock New Growth Potential
The convergence of passive RFID with Industry 4.0 technologies creates compelling new use cases. When integrated with AI-powered analytics platforms, RFID systems can enable predictive maintenance workflows by tracking tool usage patterns in manufacturing environments. Early implementations have demonstrated 25-40% reductions in equipment downtime. Similarly, combining RFID with blockchain solutions enhances supply chain provenance tracking – particularly valuable for pharmaceutical and luxury goods authentication.
The healthcare sector presents particularly promising opportunities, with passive RFID enabling automated tracking of high-value medical equipment across hospital networks. Pilot programs show 80% reductions in equipment search times and 15% decreases in duplicate purchases. As healthcare systems prioritize operational efficiency, RFID adoption in this vertical is projected to grow at 7.2% CAGR through 2030.
➤ Recent advancements in chipless RFID technology promise to reduce tag costs below $0.01 per unit, potentially enabling item-level tagging for disposable consumer goods.
Additionally, the rise of smart city infrastructure creates new applications for passive RFID in municipal asset management, from tracking maintenance equipment to monitoring utility assets. These expanding use cases across emerging sectors position passive RFID for sustained long-term growth beyond traditional retail and logistics applications.
PASSIVE RFID TAGS FOR ASSET TRACKING MARKET TRENDS
Rising Adoption of IoT and Industry 4.0 Driving Market Expansion
The global Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the widespread adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 technologies. With the market valued at $101 million in 2024 and projected to reach $131 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 3.9%, organizations are increasingly leveraging passive RFID to enhance asset visibility and operational efficiency. These tags, which operate without internal batteries, rely on radio frequency signals from readers, making them cost-effective and low-maintenance. Industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and retail are deploying passive RFID solutions to streamline inventory management and reduce manual errors. The shift toward automation and real-time tracking in supply chains further underscores the importance of RFID technology.
Other Trends
Demand for UHF Passive RFID Tags
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) passive RFID tags are gaining traction due to their longer read ranges and faster data transmission compared to High-Frequency (HF) alternatives. These tags are particularly useful in large-scale warehousing and logistics applications where quick scanning of multiple assets is necessary. While HF tags retain dominance in applications requiring close-proximity tracking, such as retail item tagging, the flexibility and scalability of UHF tags are fueling their adoption. The ability to integrate these tags with cloud-based asset management systems further enhances their appeal, allowing businesses to monitor inventory levels in real time.
Technological Enhancements in Tag Durability and Readability
Manufacturers are focusing on improving the durability and readability of passive RFID tags to cater to harsh industrial environments. Advancements in materials and design have led to tags that withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, and chemical exposure—common challenges in sectors like oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, and automotive manufacturing. Additionally, innovations in anti-collision algorithms ensure reliable tag detection even in high-density deployments. This technological progress, combined with declining production costs, is making passive RFID solutions more accessible to small and medium enterprises, thereby expanding the market’s reach.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Key Industry Players
Innovation and Strategic Expansion Drive Competition in Passive RFID Asset Tracking
The global Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking market, valued at $101 million in 2024, is characterized by intense competition among established players and emerging innovators. While the market remains semi-consolidated, leadership positions are determined by technological advancements, geographic reach, and strategic partnerships. Zebra Technologies and Honeywell currently dominate the competitive landscape, collectively holding over 30% market share due to their comprehensive RFID solutions and strong foothold in North American and European markets.
Avery Dennison has emerged as a key disruptor through its recent investments in UHF RFID tags optimized for industrial environments. Their 2023 acquisition of Vestcom significantly strengthened their data intelligence capabilities in retail asset tracking. Similarly, Alien Technology has gained traction by focusing on high-memory passive tags for complex supply chain applications, particularly in Asia-Pacific markets where asset tracking demand grew by 28% last year.
Meanwhile, mid-sized players like Invengo and SATO are challenging incumbents through specialized solutions. Invengo’s temperature-resistant passive tags have become industry standards for cold chain logistics, while SATO’s partnership with NTT Data has expanded their reach in Japan’s manufacturing sector. These companies demonstrate how niche specialization combined with strategic alliances can effectively compete against larger corporations.
The competitive intensity is further heightened by China-based manufacturers such as Xindeco IOT and Tatwah Smartech, who leverage domestic production advantages to offer cost-competitive alternatives. While their global presence remains limited compared to Western counterparts, their 2023 combined revenue growth of 19% indicates rising influence in price-sensitive markets.
List of Key Passive RFID Tag Manufacturers Profiled
Zebra Technologies (U.S.)
Honeywell (U.S.)
SATO (Japan)
TSC Printronix Auto ID (Taiwan)
Avery Dennison (U.S.)
Beontag (Brazil)
Metalcraft (U.S.)
Alien Technology (U.S.)
MPI Label Systems (U.S.)
Invengo (China)
HID Global (U.S.)
GAO RFID (Canada)
The Tag Factory (U.K.)
Xindeco IOT (China)
Tatwah Smartech (China)
Hangzhou Century (China)
Learn more about Competitive Analysis, and Forecast of Global Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking Market : https://semiconductorinsight.com/download-sample-report/?product_id=103580
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
What is the current market size of Global Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking Market?
-> The global Passive RFID Tags for Asset Tracking Market was valued at 101 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 131 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period.
Which key companies operate in this market?
-> Major players include Zebra Technologies, Honeywell, Avery Dennison, Alien Technology, HID Global, and Invengo, collectively holding over 45% market share.
What are the key growth drivers?
-> Growth is driven by increasing adoption in logistics (35% of market), retail digitalization, and manufacturing automation, with UHF tags showing strongest demand at 62% market share.
Which region dominates the market?
-> North America currently leads with 38% market share, while Asia-Pacific is growing fastest at 5.2% CAGR due to manufacturing expansion in China and India.
What are the emerging trends?
-> Emerging trends include hybrid RFID solutions, environmentally sustainable tags, and integration with blockchain for supply chain transparency.
Browse Related Research Reports :
CONTACT US:
City vista, 203A, Fountain Road, Ashoka Nagar, Kharadi, Pune, Maharashtra 411014 +91 8087992013 [email protected]
0 notes
Text
RFID Definition 2025: How It Works & Why It Matters

In 2025, the RFID Definition remains the cornerstone of many modern industries: Radio-Frequency Identification is a wireless technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags store data that RFID readers can read or write. When an RFID tag passes near a compatible reader, the tag’s antenna picks up the reader’s radio waves, powering the tag (in passive systems) and sending back its unique ID. This simple mechanism fulfills the most fundamental RFID Definition, defining how items get recognized without physical contact or line-of-sight scanning.
As we dive deeper, you’ll discover how RFID Definition has evolved, how it works in real-world applications, and why this technology matters now more than ever.
What Is RFID? A 2025 Definition Explained
At its core, the RFID Definition describes a system comprising tags, readers, middleware, and back-end systems. In 2025, the definition has grown to include networked, cloud-enabled infrastructures. The tags contain tiny microchips connected to antennas, allowing them to receive and retransmit signals. Some tags are battery-powered (active), while others rely on the reader’s energy (passive). This ability to passively collect and transmit data wirelessly makes RFID a form of Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC), revolutionizing how businesses manage assets, inventory, and security.
How RFID Technology Works in 2025
Today’s RFID systems still operate on the same basic principle captured in the RFID Definition: a reader emits a radio signal; tags respond. However, in 2025, the technology supports multiple frequency ranges—Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF)—each suited to different use cases. LF works well with metal and liquids, HF is ideal for short-range secure applications like contactless payments, and UHF supports long-distance scans useful in logistics and warehousing.
RFID readers can be handheld, mounted on vehicles, or embedded in door frames and conveyor belts. When integrated with cloud software and analytics platforms, these readers feed real-time data into enterprise systems, enabling live tracking, predictive analytics, and automated workflows.
The Components of a Modern RFID System
RFID Tags: Small devices attached to objects that store and communicate data.
RFID Readers/Interrogators: Devices that send and receive radio waves to read or write tag data.
Antenna: Enables communication between the reader and tag.
Middleware: Software that filters and directs tag reads to the appropriate system.
Back-End Systems: Databases, ERP, and analytics platforms that store, process, and visualize data.
The RFID Definition includes this entire stack—from physical tags to cloud dashboards—demonstrating how diverse technologies combine to deliver seamless identification and automation.
Types of RFID: Active, Passive, and Semi‑Passive Tags
RFID systems in 2025 use three main tag types:
Passive Tags: No internal power source; powered by a reader’s electromagnetic field. They are small, cheap, and widely used for retail, inventory, and library tracking.
Active Tags: Battery-powered and capable of broadcasting signals over long distances (tens or hundreds of meters). They are used in asset tracking, vehicle management, and environmental sensing.
Semi‑Passive (Battery‑Assisted Passive or BAP) Tags: Battery-powered for internal electronics, but still rely on the reader’s energy to transmit. They offer better range and memory without the complexity of fully active tags.
These options embody the RFID Definition by showing how the same basic principle adapts to different performance needs.
Top Use Cases for RFID in 2025
Supply Chain & Warehousing: Pallets, cases, and individual items are tracked in real time, reducing shrinkage and boosting efficiency.
Retail: Smart shelves and returns processing use RFID to streamline stock management and improve customer experiences.
Healthcare: Hospitals use RFID to track equipment, patient wristbands, and medication carts to improve safety and compliance.
Manufacturing: Work-in-progress parts are tagged to support lean manufacturing and predictive maintenance.
Transportation & Logistics: Fleet management and toll collection rely on RFID for hands-free tracking and billing.
The ongoing relevance of RFID Definition is clear: it underpins these systems and services to enable identification, data capture, and operational improvements.
Why RFID Matters: Key Benefits Across Industries
Speed & Automation: Reading multiple tags in milliseconds without manual scanning.
Accuracy & Transparency: Reduces errors and improves insights into inventory and asset location.
Cost Savings: Decreases labor costs and loss from theft or misplacement.
Real-Time Visibility: Updates inventory systems instantly, supporting accurate planning.
Enhanced Security: Some RFID tags include encryption and authentication features to prevent counterfeiting or unauthorized reading.
The power of RFID lies in the broader RFID Definition—that it automates identification and data collection more efficiently than manual methods like barcodes.
RFID vs Other AIDC Technologies: What’s the Difference?
The term AIDC Technology refers to tools and systems that automatically identify objects and collect data without human input. RFID is one such technology. Others include barcodes, QR codes, biometrics, and optical character recognition (OCR). Compared to these, RFID stands out because:
No line of sight is needed.
Multiple tags can be read simultaneously.
It enables automatic, real-time updates.
It works in harsh environments.
RFID’s role within the spectrum of AIDC technologies makes it a versatile solution that complements, rather than replaces, other identification tools.
AIDC Technology: A Quick Overview
AIDC Technology refers to methods like RFID, barcodes, biometric scanners, and NFC that help businesses automatically capture data and identify items, people, or events. These systems reduce errors, speed up workflows, and provide accurate, real‑time information. RFID is a premier type of AIDC technology, offering speed, range, and automation unmatched by traditional scanning tools.
RFID Trends in 2025: What’s New and What’s Next
Sensor-Integrated Tags: Tags that monitor temperature, humidity, or physical shock—useful in pharmaceutical shipping, cold chains, and sensitive equipment.
Blockchain for Supply Chain: Secure, tamper‑proof transaction logs built on RFID data.
Edge & AI-Enabled Readers: Real-time analytics and anomaly detection performed locally at the reader.
Miniaturized Tags: Ultra‑small, printable tags for electronics, textiles, or delicate goods.
Sustainability: Recyclable or biodegradable tag materials to reduce electronic waste.
These future directions reinforce the RFID Definition as evolving to include advanced sensing, intelligence, and environmental responsibility.
Challenges and Limitations of RFID Technology
Cost: Tags, readers, and infrastructure can be expensive for smaller businesses.
Tag Collision: When many tags respond simultaneously, interference issues may occur.
Environmental Limitations: Metal and liquids can hamper radio waves; special tags or placement may be needed.
Security & Privacy: Without encryption, RFID data can be intercepted or spoofed.
Standardization: Despite widespread use, multiple frequency bands and regional regulations complicate deployment.
These challenges remind us that even though the RFID Definition appears simple, deploying a full system requires thoughtful planning and investment.
The Future of RFID and Its Business Impact
In 2025 and beyond, RFID will continue pushing forward in several key directions:
Greater IoT Integration: RFID readers embedded in smart environments for self‑automated reordering or reactively controlled workflows.
Advanced Analytics: AI-driven insights to optimize inventory, reduce waste, and boost supply chain resiliency.
Personalization: RFID-enabled experiences like smart dressing rooms, personalized museum guides, or contactless healthcare check-in.
Sustainability Goals: Using RFID to improve recycling, reduce loss, and promote circular economy initiatives.
These trends justify why the RFID Definition remains central to conversations about innovation and digitization.
Ready to Unlock the Power of RFID?
If you're interested in implementing RFID-based AIDC technology tailored to your business needs, don’t wait:
Book now AIDC Technologies to speak with an expert and explore custom RFID solutions that boost efficiency, accuracy, and growth.
#RFIDTechnology2025#SmartTrackingSolutions#RFIDBenefitsExplained#FutureOfRFID#InventoryAutomation2025
0 notes
Text
Mobile Document Reader Market: Industry Overview and Analysis 2025–2032

MARKET INSIGHTS
The global Mobile Document Reader Market size was valued at US$ 623.4 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 1.23 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast period 2025-2032.
Mobile document readers are portable devices or software applications designed to scan, authenticate, and process identity documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, and ID cards. These solutions incorporate advanced technologies including OCR (Optical Character Recognition), RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), and biometric verification to enhance security and streamline identity verification processes across multiple industries.
The market growth is driven by increasing security concerns, rising adoption of digital identity verification, and stringent government regulations for identity authentication. Key players such as Thales, IDEMIA, and Veridos (G&D) are expanding their product portfolios with AI-powered mobile readers capable of detecting sophisticated forgeries. The ID readers segment holds significant market share due to widespread deployment in border control and financial institutions.
MARKET DYNAMICS
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Demand for Secure Identity Verification to Accelerate Market Growth
The global surge in identity fraud cases is driving substantial demand for mobile document readers. With identity theft incidents increasing by over 35% annually across key regions, organizations are prioritizing advanced verification solutions. Mobile document readers provide real-time authentication of IDs, passports, and other critical documents through NFC and OCR technologies, significantly reducing fraud risks. Governments worldwide are mandating stricter identity verification protocols, particularly in aviation and financial sectors, creating sustained demand.
Digital Transformation in Border Control Creating Significant Market Opportunities
Border control agencies are undergoing massive digital transformations, with over 65 countries implementing e-gate systems requiring mobile document verification. The global biometric passport adoption rate now exceeds 85%, creating compatible infrastructure for mobile reader deployment. Recent technological advancements enable handheld devices to authenticate document security features like holograms, microprinting, and RFID chips with over 99% accuracy. Several international airports have already deployed mobile document readers for faster passenger processing, reducing wait times by an average of 40%.
Expansion of Mobile Banking Services Driving Financial Sector Adoption
The financial sector’s rapid shift toward digital onboarding is creating substantial growth avenues. Over 70% of global banks now offer mobile account opening services requiring robust identity verification. Mobile document readers enable customers to remotely verify identities by scanning government-issued IDs while detecting fraudulent alterations. This technology has reduced customer acquisition costs by approximately 30% while improving compliance with KYC regulations. Major financial institutions are increasingly integrating these solutions into their mobile apps following successful pilot programs showing over 90% fraud detection accuracy rates.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Implementation Costs Limiting Small Enterprise Adoption
While larger organizations are rapidly adopting mobile document readers, smaller enterprises face significant cost barriers. Enterprise-grade solutions with advanced verification capabilities typically require substantial upfront investments ranging from $5,000 to $20,000 per unit. Additional expenses for system integration, staff training, and software updates further strain budgets. Many SMBs consequently rely on manual verification methods despite higher long-term operational costs, creating a substantial adoption gap in the market.
Data Privacy Concerns Creating Regulatory Hurdles
Growing data privacy regulations worldwide pose complex compliance challenges for mobile document reader providers. The processing and storage of sensitive biometric and identity data must comply with increasingly stringent regional regulations that continue evolving. Recent legislative changes have increased certification requirements by over 40% in key markets, delaying product launches. Some organizations hesitate to adopt these solutions due to potential liabilities associated with data breaches involving personally identifiable information.
Technical Limitations in Document Recognition Accuracy
Despite significant advancements, mobile document readers still face challenges with certain document types. Handled documents with wear and tear show approximately 15% higher rejection rates compared to pristine specimens. Recognition accuracy for non-Latin character documents remains below 90% for some manufacturers, creating difficulties in multicultural environments. These technical limitations require ongoing R&D investments to address, particularly as counterfeiters develop more sophisticated fraudulent documents that test detection capabilities.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Emerging Smart City Infrastructure Creating New Use Cases
Global smart city initiatives present significant growth potential, with intelligent identity verification becoming integral to urban services. Pilot programs in several cities have successfully integrated mobile document readers with public transportation, healthcare access, and municipal services. These implementations have demonstrated efficiency improvements exceeding 30% in service delivery times while reducing identity fraud incidents by approximately 25%. As smart city investments are projected to grow significantly, demand for compatible mobile verification solutions will expand proportionally.
Advancements in AI Document Authentication Opening New Markets
Recent breakthroughs in artificial intelligence are enabling mobile document readers to analyze sophisticated security features previously undetectable by portable devices. New machine learning algorithms can authenticate documents by assessing over 200 security parameters with accuracy rates exceeding 98%. This technological leap is creating opportunities in high-security sectors like government facilities and critical infrastructure that previously required stationary verification equipment. Early adopters report reducing equipment costs by 60% while maintaining equivalent security standards.
Rental and Subscription Models Expanding Market Accessibility
Innovative business models are emerging to address cost barriers, particularly for intermittent users. Several leading providers now offer subscription-based services with pay-per-scan pricing starting under $1 per verification. This approach has shown particular success in the hospitality industry, where seasonal businesses need verification capabilities without substantial capital investments. Early data suggests these flexible models could expand the total addressable market by approximately 35% by making the technology accessible to smaller operators.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Increasing Document Standardization Complexity
The proliferation of new document formats and security features creates ongoing challenges for manufacturers. With over 70 countries implementing updated identity documents in the past five years, maintaining comprehensive verification databases requires continuous updates. Some jurisdictions issue multiple document versions simultaneously, while others incorporate unconventional security elements that standard readers struggle to authenticate. This variability forces manufacturers to dedicate approximately 25% of R&D budgets to ongoing database maintenance rather than innovation.
Intense Competition Driving Margin Pressures
The market’s rapid growth has attracted numerous competitors, including both established security firms and agile startups. This intense competition has reduced average selling prices by nearly 20% over three years while raising customer expectations for features and accuracy. Smaller players particularly struggle with profitability as they attempt to match the R&D capabilities of market leaders. The resulting consolidation trend has seen over 15 acquisitions in the sector during the past 24 months, reshaping the competitive landscape.
User Experience Expectations Outpacing Technology Development
End users increasingly demand seamless verification experiences comparable to consumer mobile applications, creating development challenges. Average acceptable verification times have decreased from 15 seconds to under 8 seconds in three years, requiring significant processing optimizations. Simultaneously, users expect flawless performance across diverse environmental conditions including low light and extreme angles. Meeting these expectations while maintaining security standards requires substantial engineering resources, with some manufacturers reporting development cycle increases exceeding 30%.
MOBILE DOCUMENT READER MARKET TRENDS
Rising Demand for Enhanced Security and Identity Verification to Drive Market Growth
The global Mobile Document Reader market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for secure identity verification across industries. With a projected market value of $79.4 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.4%, advancements in document authentication technologies are playing a pivotal role. Mobile document readers are increasingly being adopted in sectors such as security, banking, and travel due to their ability to rapidly verify IDs, passports, and other critical documents with high accuracy. The integration of AI-based optical character recognition (OCR) and machine learning has further enhanced their capability to detect fraudulent documents efficiently. This trend is particularly strong in regions with stringent security regulations, where manual verification is being replaced by automated systems to reduce human error and processing time.
Other Trends
Expansion of Mobile Check-In and Digital Border Control
The rise of mobile check-in systems in airlines and digital border control solutions is further fueling the adoption of mobile document readers. Airlines and airports worldwide are deploying these devices to streamline passenger verification processes, reducing wait times and improving operational efficiency. For instance, biometric-enabled document readers are increasingly being used at immigration checkpoints to authenticate passports and visas within seconds. Similarly, hotels and travel agencies are leveraging these devices to enhance guest onboarding, ensuring compliance with anti-fraud regulations while delivering a seamless customer experience.
Growing Adoption in Financial Institutions
Banks and financial services are rapidly integrating mobile document readers into their Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance workflows. With increasing regulatory scrutiny, financial institutions require reliable tools to verify customer identities and prevent fraudulent activities. Mobile document readers enable instant verification of government-issued IDs, reducing the risk of identity theft and improving compliance efficiency. Moreover, the shift toward digital banking has accelerated the demand for portable verification solutions that can be used both in-branch and remotely. Industry-leading players such as Thales and IDEMIA are developing advanced readers with NFC and RFID capabilities to cater to evolving banking needs.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Key Industry Players
Technology Leaders Accelerate Innovation to Capture Market Share in Mobile ID Verification
The global mobile document reader market exhibits a moderately fragmented competitive landscape, with established technology providers competing alongside specialized solution developers. Thales Group emerges as a dominant player, leveraging its biometric and identity verification expertise across aviation, government, and financial sectors worldwide. In 2024, Thales maintained approximately 18% market share in mobile ID reader solutions, supported by strategic acquisitions in digital identity technologies.
IDEMIA and Veridos (G&D) have solidified their positions through advanced passport reading technologies, collectively accounting for nearly 25% of the professional-grade mobile document verification market. Their growth stems from increasing demand for next-generation border control solutions and mobile police applications, particularly in Europe and North America.
The competitive intensity continues to rise as mid-sized players like Access IS and Regula Baltija expand their product lines with AI-powered document authentication features. These companies have successfully penetrated the hospitality and banking verticals by offering cost-effective, compact readers with high accuracy rates exceeding 98.5% for passport verification.
Meanwhile, Chinese manufacturers including China-Vision and Wintone are rapidly gaining traction in APAC markets through competitive pricing and localized solutions. Their success demonstrates how regional players can challenge global leaders by addressing specific compliance requirements and integration needs in emerging economies.
List of Key Mobile Document Reader Providers
Thales Group (France)
IDEMIA (France)
Veridos (G&D) (Germany)
ARH Inc. (Hungary)
Access IS (UK)
Regula Baltija (Latvia)
China-Vision (China)
Prehkeytec (Germany)
DILETTA (Italy)
Grabba (Australia)
BioID Technologies (Germany)
Wintone (China)
Segment Analysis:
By Type
ID Readers Segment Leads the Market with Expanding Use in Identity Verification and Security Applications
The market is segmented based on type into:
ID Readers
Passport Readers
By Application
Airlines and Airports Segment Dominates Due to Increasing Passenger Screening Requirements
The market is segmented based on application into:
Airlines and Airports
Security and Government
Hotels and Travel Agencies
Banks
Train and Bus Terminals
Others
By End User
Government Sector Accounts for Significant Share Due to Border Control and Law Enforcement Requirements
The market is segmented based on end user into:
Government Agencies
Transportation Hubs
Financial Institutions
Hospitality Industry
Corporate Enterprises
Regional Analysis: Mobile Document Reader Market
North America The North American market for mobile document readers is strongly driven by heightened security concerns and stringent regulatory requirements across airports, border control, and financial institutions. The U.S., accounting for the largest market share in the region, has seen increased adoption due to biometric identification mandates and NFC-enabled ID verification technologies. Key players like Thales and IDEMIA dominate this space, offering advanced solutions with AI-powered fraud detection. The market is further propelled by investments in smart city initiatives, with an estimated 35% of U.S. law enforcement agencies now deploying mobile document readers for field operations.
Europe Europe’s market is characterized by strict GDPR compliance requirements and standardized electronic identity (eID) programs. The EU’s emphasis on interoperable digital identity frameworks has accelerated demand for passport readers and secure authentication devices. Germany and France lead in adoption, particularly in banking and transportation sectors. The region shows strong preference for multimodal verification systems combining document scanning with facial recognition, with airports investing heavily in contactless passenger processing solutions. Regulatory pressure to combat identity fraud remains a persistent market driver.
Asia-Pacific As the fastest-growing regional market, Asia-Pacific benefits from rapid digital transformation and massive government ID programs. China’s ‘Internet+’ strategy and India’s Aadhaar system have created enormous demand for mobile verification tools. While cost sensitivity remains a factor, vendors are adapting with rugged, affordable solutions for high-volume applications. The region shows particular strength in mobile payment verification and hotel check-in systems, with Japan and South Korea leading in technological sophistication. Emerging smart airports across Southeast Asia are driving next-gen adoption.
South America The South American market presents a mixed adoption landscape, with Brazil and Argentina showing the most progress in mobile document reader deployment. Financial institutions are primary adopters, implementing solutions for anti-money laundering compliance. Challenges include inconsistent regulatory frameworks and infrastructure limitations in rural areas. However, the growing tourism industry and need for improved border security are creating opportunities, particularly for portable passport verification systems at major entry points. Economic volatility continues to impact investment cycles in the region.
Middle East & Africa This emerging market is witnessing strategic deployments centered around major transportation hubs and financial centers. The UAE leads in adoption, particularly for airport security and hotel guest verification systems. Smart city initiatives in Saudi Arabia and digital transformation programs in South Africa are creating new demand vectors. While the market remains cost-conscious, there’s growing recognition of mobile readers as force multipliers for security personnel. Challenges include limited technical expertise in some areas and the need for solutions that can operate effectively in extreme environmental conditions.
Report Scope
This market research report provides a comprehensive analysis of the global and regional Mobile Document Reader markets, covering the forecast period 2024–2032. It offers detailed insights into market dynamics, technological advancements, competitive landscape, and key trends shaping the industry.
Key focus areas of the report include:
Market Size & Forecast: Historical data and future projections for revenue, unit shipments, and market value across major regions and segments. The Global Mobile Document Reader market was valued at USD 55.4 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 79.4 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.4%.
Segmentation Analysis: Detailed breakdown by product type (ID Readers, Passport Readers) and application (Airlines, Security, Hospitality, Banking, etc.) to identify high-growth segments.
Regional Outlook: Insights into market performance across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa, with country-level analysis of key markets.
Competitive Landscape: Profiles of leading players including Thales, IDEMIA, Regula Baltija, and others, covering their market share, product portfolios, and strategic initiatives.
Technology Trends & Innovation: Analysis of OCR advancements, biometric integration, AI-powered verification, and mobile scanning technologies.
Market Drivers & Restraints: Evaluation of security concerns, regulatory compliance needs, and digital transformation trends versus cost sensitivity.
Stakeholder Analysis: Strategic insights for hardware providers, software developers, system integrators, and end-user industries.
Related Reports:https://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/inductive-proximity-switches-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/cellular-iot-module-chipset-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/sine-wave-inverter-market-shifts-in.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/pilot-air-control-valves-market-cost.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/video-multiplexer-market-role-in.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/semiconductor-packaging-capillary.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/screw-in-circuit-board-connector-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/wafer-carrier-tray-market-integration.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/digital-display-potentiometer-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/glass-encapsulated-ntc-thermistor.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/shafted-hall-effect-sensors-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/point-of-load-power-chip-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/x-ray-grating-market-key-players-and.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/picmg-single-board-computer-market.htmlhttps://semiconductorblogs21.blogspot.com/2025/06/lighting-control-dimming-panel-market.html
0 notes
Text

Discover advanced UHF RFID readers in Jaipur from Sarthi Systems. Offering high-performance, long-range RFID solutions for inventory management, access control, and asset tracking. Trusted by industries for reliable and efficient identification technology. Contact Sarthi Systems today for customized RFID solutions tailored to your needs.
0 notes
Text
Tripod Turnstile: Secure & Efficient Access Control Solution
Tripod turnstiles are a widely used access control solution found in various public and private facilities, offering a reliable way to manage pedestrian traffic. With their compact design, durable structure, and efficient operation, tripod turnstiles are perfect for locations that require regulated entry without compromising on security or user convenience.
What is a Tripod Turnstile?
A tripod turnstile is a waist-high mechanical gate featuring three rotating arms spaced at 120 degrees apart. These arms allow one person to pass at a time and are commonly installed at entry and exit points in places like offices, metro stations, stadiums, and gyms. Operated either manually or electronically, tripod turnstiles can be integrated with access control systems such as RFID cards, biometric readers, or QR code scanners.
Key Benefits of Tripod Turnstiles
1. Controlled Access: Tripod turnstiles are designed to restrict unauthorized entry by allowing only one person through at a time. They can be linked with ID systems to ensure only registered users are granted access.
2. High Durability: Made from stainless steel or powder-coated metal, tripod turnstiles are built to withstand heavy usage and tough environmental conditions, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
3. Space-Efficient Design: Their slim, compact structure takes up minimal space while effectively guiding pedestrian flow. This makes them ideal for areas with limited room.
4. Cost-Effective Security: Compared to full-height turnstiles or more advanced systems, tripod turnstiles offer an affordable yet efficient security option that still maintains a professional appearance.
5. Integration-Friendly: Tripod turnstiles can be seamlessly integrated with a range of security and access control technologies, including fingerprint scanners, facial recognition systems, and ticketing software.
Common Applications
Corporate Offices: To regulate staff and visitor entry.
Public Transport Hubs: For managing passenger flow at metro or bus stations.
Sports Stadiums & Event Venues: To control crowd movement and ticket validation.
Gyms & Fitness Centers: For secure member access.
Educational Institutions: To monitor student and staff attendance.
Conclusion
Tripod Turnstile are a smart investment for any facility seeking a practical, secure, and efficient way to manage pedestrian access. With their sturdy design, ease of integration, and reliable performance, they offer long-term value and enhanced control in high-traffic environments. Whether for security, access regulation, or crowd management, tripod turnstiles provide a streamlined solution that balances safety with convenience.
0 notes
Text

RFID vs. NFC: Key Differences Explained
1. Technology Basics
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification): Uses wireless radio waves to identify and track objects (tags) via a reader, working over long ranges (up to 100m).
NFC (Near Field Communication): A subset of high-frequency RFID (13.56 MHz), but designed for ultra-short-range communication (≤10 cm).
2. Key Differences

3. Practical Applications
RFID: Warehouse logistics, toll collection, animal tracking.
NFC: Contactless payments (Apple Pay), keyless entry, file sharing.
TL;DR: NFC is a specialized, short-range form of RFID with two-way communication. RFID excels in tracking, while NFC dominates secure, close-range interactions.
0 notes
Text
Revolutionising Inventory Control: The Unparalleled Efficiency of a Mobile RFID Reader
The Potential of a Mobile RFID Reader
In a world of hyper-efficiency, companies cannot waste time on slow, inaccurate inventory management systems. That's where the mobile RFID reader comes in, an industry-altering device that has the potential to transform the way businesses monitor assets, optimise supply chains, and improve operational precision. Mobile RFID readers differ from standard barcode scanners as they don't require line-of-sight scanning, allowing fast data capture even in dense environments. Whether managing inventory in vast warehouses or tracking high-value equipment in the field, the mobile RFID reader is becoming an indispensable tool across industries.
This article delves into the unparalleled advantages of mobile RFID readers, the industries leveraging this cutting-edge technology, and key considerations for adopting the right system for your business.
Beyond Barcodes: Why a Mobile RFID Reader is a Game Changer
1. Speed and Efficiency Like Never Before
Traditional barcode scanning involves scanning each item physically—a painstaking process when dealing with thousands of SKUs. However, a mobile RFID reader can read multiple tags simultaneously, significantly processing time. Consider a warehouse staff scanning a whole pallet of items in seconds rather than minutes. That's the time-saving boost RFID technology provides.
2. Accuracy That Redefines Inventory Management
Problems in inventory tracking result in lost stock, shipment errors, and lost sales. Using a handheld RFID reader, the accuracy of the data goes through the roof with manual input excluded and automated scan keeping the records updated in real-time. The accuracy is gold in businesses where mishandling can cost fortunes, such as in pharma or aeronautics.
3. Long-Range and Bulk Scanning Capability
Unlike barcode scanners that require close-range scanning, RFID technology enables workers to capture data from several meters away. A mobile RFID reader can scan entire warehouse sections without requiring direct visibility, ensuring seamless asset tracking without disrupting operations.
4. Enhanced Security and Loss Prevention
Theft and lost stock cost companies billions every year. RFID tracking can instantly inform organisations when any unauthorised movement is detected, thereby minimising shrinkage and enhancing overall security. A mobile RFID reader provides real-time notifications as assets are moved, helping companies have better control over resources.
Industries Served by Mobile RFID Readers
1. Warehousing & Logistics: Optimizing Supply Chains
Warehouses are implementing mobile RFID readers to speed up inventory audits, streamline stock rotation, and automate reordering. RFID technology removes human error in monitoring incoming and outgoing shipments, cutting inefficiency from global supply chains.
2. Healthcare: Ensuring Patient Safety & Compliance
Hospitals and drug manufacturers use RFID readers to monitor medical supplies, equipment, and patient records. A portable RFID reader increases compliance with regulations, avoids the dispensing of expired drugs, and maintains critical equipment at hand when required.
3. Retail: Transforming Checkout & Inventory Management
RFID is being used by retailers to streamline inventory replenishment, lower checkout times, and improve customer experiences. Consider entering a store, grabbing goods, and exiting while an RFID system makes the payment for you. The mobile RFID reader is a stepping stone to a future without cashiers.
4. Manufacturing: Real-Time Tracking of Production Processes
Manufacturers use RFID to track raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished goods in real-time. An RFID reader on the mobile device provides real-time visibility into supply chains to avoid production delays and save operational waste.
5. Aviation & Defense: Location of High-Value Equipment
In asset-critical industries, RFID is essential. Air carriers and military contractors use wireless RFID readers to monitor everything from aircraft parts to military equipment for compliance, security, and better operations.
Picking the right mobile RFID reader for your enterprise
1. Think about scanning range requirements
Some companies need short-range RFID solutions, while others need long-read ranges of meters. Decide if your operations call for a mobile RFID reader with UHF (Ultra High Frequency) capability for far-distance scanning.
2. Evaluate Compatibility with Existing Systems
Acquiring an RFID reader should not result in the need to rebuild your entire IT infrastructure. Ensure your mobile RFID reader integrates well with your enterprise resource planning (ERP) or warehouse management systems (WMS).
3. Assess Battery Life and Portability
As mobility is paramount, choose a portable RFID reader with extended battery life and ergonomic design. Field service and warehousing teams need lightweight, rugged devices that withstand harsh work conditions.
4. Security and Data Encryption Features
As security concerns over data increase, opt for an RFID reader with effective encryption and authentication measures. Compromised RFID would mean the vulnerability of sensitive corporate data, rendering security an essential non-negotiable aspect.
5. IoT and AI Convergence for Future-Proofing
Top enterprises are converging RFID technology with IoT and AI. An RFID reader on the go linked with AI-based analytics can offer forecasted insights, automate decisions, and streamline operations workflows.
Challenges and Considerations in RFID Implementation
1. Upfront Expenses and ROI Calculation
Initial investment in readers, tags, and infrastructure is needed to implement RFID technology. However, long-term gains in efficiency, lower labour, and increased accuracy make the cost worthwhile.
2. Signal Interference in Special Environments
Substances like metal or liquid may impact RFID operation. Companies with high signal interference environments should conduct real-world tests on mobile RFID readers before large-scale deployment.
3. Regulatory Standards Compliance
Varying RFID regulations exist across different industries and regions. Make sure your mobile RFID reader meets compliance standards to prevent legal issues.
Conclusion: The Future of Asset Management with Mobile RFID Readers
As technologies advance, companies that adopt the latest technologies have a clear edge. The mobile RFID reader is no longer a luxury but a requirement for companies that want to attain real-time visibility, operational efficiency, and better inventory management. Across warehousing and healthcare, manufacturing, and defence, RFID technology is transforming asset tracking on an unprecedented scale.
Purchasing a mobile RFID reader isn't simply about improving workflow—it's about future-proofing your company for the digital era. Whether you need to reduce errors, streamline processes, or improve security, implementing RFID technology will keep you one step ahead of the competition in a rapidly automating world.
0 notes
Text
Long Range RFID Reader For Asset Tracking Solutions
Long Range RFID Reader are superior devices designed to read tags from prolonged distances, frequently several meters to tens of meters. They permit efficient tracking, inventory management, and access management in industries like logistics, manufacturing and protection. These readers help high-frequency and extremely-excessive-frequency tags for dependable, speedy data seizure.
0 notes
Text
Industry trend|ZiPIoT: The first innovative application of RFID in DNA management, with huge potential market space
Today, as the wave of digital transformation sweeps the world, Guangzhou ZiPIoT Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "ZiPIoT") has become a bright new star in the field of the Internet of Things with its profound technical accumulation and innovation capabilities. As a high-tech enterprise, a Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Little Giants registered enterprise and the drafting unit of the Shenzhen RFID Archives Management System Standard, ZiPIoT has always adhered to the core concept of "simple, practical, and bringing value to customers", and is committed to providing efficient and intelligent solutions to global users through the deep integration of the Internet of Things, automation and intelligent technologies. Recently, the AIoT Star Chart Research Institute research team had an in-depth dialogue with Liu Lang, general manager of ZiPIoT, and learned about the company's recent development and future plans.
Deeply cultivating the industry, technology-driven innovation
ZiPIoT was established in 2019. Its predecessor was Guangzhou Youchang Information Technology Co., Ltd. Since 2014, it has been deeply engaged in the field of RFID Internet of Things and smart cities. The company started from system integration and gradually extended downward to hardware production, forming a complete industrial chain from system to hardware. This unique business model enables ZiPIoT to provide highly customized solutions according to the needs of different industries. At present, the company has more than 50 patents and software copyrights with independent intellectual property rights, covering RFID reading and writing equipment, smart terminals, system platforms and other fields, and its technical strength and innovation capabilities are highly recognized.

In high-demand scenarios such as aviation, forensics, and archive management, ZiPIoT pioneered RFID innovative applications and launched solutions such as passport cabinet management system, smart tool cabinet, and archive luminous label, realizing the digitalization, automation and intelligence of item management. For example, its passport cabinet management system has completely changed the traditional mode of people managing things through electronic label technology, reduced the manual handover link, greatly improved the tool turnover rate and management efficiency, and provided new ideas for the digital transformation of the industry. In the field of public security, the innovative application of DNA sample management system has solved the long-standing problems of difficult sample search and chaotic management. In this field, only one prefecture-level city corresponds to the use of millions of RFID tags, and the potential market space is huge.
Full industrial chain layout, building an intelligent ecosystem
ZiPIoT not only provides complete system platform construction and software development services, but also independently develops a full range of intelligent products, covering self-service equipment, RFID electronic tags, antennas, handheld devices, readers, etc. Its 16-channel reader module, as an industry benchmark product, has high performance, high compatibility and excellent stability. It can be widely used in complex scenarios such as warehousing, logistics, and production line management. The maximum reading distance is 15 meters, and its comprehensive performance is in the leading position in the industry.

The company has also launched hardware products such as passport cabinets, filing cabinets, tool cabinets, smart charging cabinets, and miniaturized automatic cabinets. The products adopt a differentiated strategy. For example, the filing cabinet uses patented technology to store 70% more files than other friendly companies. Combined with integrated desktop readers, ultra-high frequency handheld data terminals and other equipment, it has formed an end-to-end solution covering all scenarios. Whether it is government agencies, enterprises and institutions, or industrial manufacturing, medical health and other fields, ZiPIoT can provide customized services to meet the diverse needs of customers.
Looking to the future, ZiPIoT will continue to take "making business simpler, easier, more automated and intelligent" as its mission, deeply cultivate the fields of RFID Internet of Things and smart cities, and promote the deep integration of technology and scenarios. The company plans to further expand its product line, optimize its service system, provide more efficient and smarter solutions for global users, and help various industries achieve digital transformation and intelligent upgrading.
This paper is from Ulink Media, Shenzhen, China, the organizer of IOTE EXPO (IoT Expo in China)
0 notes
Text
Reliable Hand Held Terminal (HHT) Solutions in Dubai & UAE

At Forte Tech, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge Hand Held Terminal Solutions across Dubai and UAE, tailored to meet the evolving needs of modern enterprises. Whether you're in retail, logistics, warehousing, or field operations, our advanced HHT Solutions streamline your business processes, increase productivity, and reduce operational costs.
What is a Hand Held Terminal (HHT)?
A HHT is a compact, mobile computing device used to collect, access, and manage data on the go. Integrated with barcode scanners, RFID readers, and wireless connectivity, Hand Held Terminals allow seamless data capturing and syncing with backend systems. These devices are crucial in real-time inventory management, order processing, and asset tracking.
Our Comprehensive Solutions
As a trusted provider of Hand Held Terminal Solutions, We offers a full range of services, from hardware supply to customized this Software development. We understand that each business has unique needs, and we tailor our HHT Solutions in Dubai to align perfectly with your workflow and goals.
Key Features of Our HHT Solutions:
Rugged Design: Built for durability in tough environments like warehouses and outdoor operations.
Real-time Sync: Instantly connect with ERP, WMS, or POS systems.
User-Friendly Interface: Simplified UI to ensure ease of use for field workers and warehouse staff.
Long Battery Life: Ensures full-day usage with minimal downtime.
Scalable Software: Our Hand Held Terminal Software is scalable and can be customized to fit various industries.
Why Choose Forte Tech for HHT Solutions in UAE?
Our team brings years of experience in deploying HHT Solutions with a focus on reliability, functionality, and integration. We pride ourselves on understanding your business operations and delivering solutions that improve efficiency at every level.
Industry Applications:
Retail & Point-of-Sale: Stock management, price checks, and digital ordering.
Logistics & Warehousing: Real-time inventory updates, pick and pack operations.
Field Services: Mobile data entry, order tracking, digital signatures.
Healthcare: Patient data access, medication tracking, and record management.
Customized Hand Held Terminal Software Development
We don’t just provide devices — we build intelligent Hand Held Terminal Software tailored to your workflows. Our developers design intuitive, responsive apps for Android and Windows-based terminals that integrate with your existing ERP or WMS platforms, including Dynamics 365, SAP, Oracle, and more.
From barcode scanning to location tracking and cloud data sync, our software ensures your team can perform critical tasks quickly and accurately.
Forte Tech – Your Partner for HHT Solutions in Dubai
As a leading name in HHT Solution providers, We ensures your handheld terminals are configured, secured, and ready to perform. From initial consultation and device selection to software deployment and ongoing support, we offer end-to-end Hand Held Terminal Solutions in UAE.
We are also partners with global hardware manufacturers like Zebra, Honeywell, and Datalogic, bringing you the most reliable and rugged devices available in the market today.
Benefits of Choosing us:
Local support team
Fast deployment and training
Custom integrations with existing business systems
Reliable post-sale support and AMC options
Competitive pricing on both hardware and software
Get Started with us Today
Looking for a reliable provider of HHT Solutions in UAE? Contact Forte Tech today for a free consultation and discover how our Hand Held Terminal Solutions in Dubai can revolutionize the way your business operates. Whether you need just the hardware, customized software, or a full-service deployment, we’ve got you covered.
Let us help you improve your operations, reduce manual errors, and boost efficiency with our reliable Hand Held Terminal Software and HHT Solutions.
0 notes
Text
Chipless RFID Market Research Report, Demand and Future Trends Till 2037
The chipless RFID market is on a rapid expansion trajectory. By the close of the forecast period in 2037, global revenues are projected to reach approximately USD 12.7 billion, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.8% from 2025 through 2037. This strong upward curve is underpinned by escalating adoption across diverse end-use sectors, economies of scale in tag production, and ongoing breakthroughs in printing-based identification technologies.
While exact figures for the 2025 baseline vary by source, most industry estimates place the market at just over USD 2.5 billion in that year, implying a near five-fold increase over the dozen-year span.
Chipless RFID Industry Demand
Chipless RFID refers to radio-frequency identification systems that encode data directly into the physical geometry or dielectric properties of inexpensive, printed substrates—eliminating the need for silicon chips. These tags can be mass-produced via roll-to-roll printing or laser-etching on plastics and papers, and are read by specialized readers that detect variations in backscatter or resonance patterns.
Cost-Effectiveness: Without the cost of a silicon IC, chipless tags can be manufactured for mere fractions of a cent apiece, making them ideal for low-margin items and disposable applications.
Ease of Administration: The simple physical encoding allows straightforward bulk production and integration into existing packaging or documents without altering form-factors.
Long Shelf Life and Durability: Chipless tags lack moving parts or sensitive semiconductors, granting them exceptional stability in harsh environments, over long storage periods, and across a wide temperature range.
Sustainability Angle: Many chipless substrates are based on recyclable or bio-derived materials, aligning with growing regulatory and corporate sustainability mandates.
Chipless RFID Market: Growth Drivers & Key Restraint
Growth Drivers –
Advances in Printable Electronics: Continued improvements in conductive inks, laser-etch technologies, and high-resolution printing have expanded the data capacity and read reliability of chipless tags, opening new use cases beyond basic inventory tracking.
Surge in Asset Tracking & Serialization Needs: Industries such as pharmaceuticals (driven by stringent anti-counterfeiting regulations and the prevalence of chronic diseases requiring precise drug supply-chain oversight) and fresh perishables logistics increasingly demand granular, tamper-proof item-level monitoring—a sweet spot for ultra-low-cost, disposable tags.
Outsourcing & Contract Manufacturing Trends: As more original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and consumer-packaged goods companies shift production to third-party contractors in emerging economies, the need for standardized, easy-to-apply chipless labels has skyrocketed, simplifying quality control across geographically dispersed facilities.
Restraint –
Limited Read Range & Data Density Compared to Chipped RFID: Despite rapid progress, chipless RFID currently offers shorter read distances (often under 1 meter) and lower payload capacities than traditional silicon-based tags, which can hinder adoption in applications demanding long-range or high-security data exchange.
Request Report Sample@ https://www.kennethresearch.com/sample-request-10352550
Chipless RFID Market: Segment Analysis
Segment Analysis by Product Type (Tags, Readers:) –
Tags: Accounting for the majority of units shipped, printed chipless tags see robust demand due to their minimal unit cost, ease of integration into packaging lines, and disposability. Volumes are highest in sectors requiring item-level serialization—particularly pharmaceuticals and fast-moving consumer goods—while maturity in printing processes continues to drive down per-tag expenses.
Readers: The reader market, though smaller in unit count, has experienced steady growth as enterprises deploy fixed and handheld scanners tailored for chipless frequencies. Investment in multi-mode readers (capable of handling both chipless and chipped RFID) is a notable trend, enhancing flexibility but adding to device complexity and cost.
Segment Analysis by Application (Smart Cards, Smart Tickets)–
Smart Cards: Chipless solutions in secure credentialing leverage custom resonance patterns to store small payloads (e.g., authentication tokens), appealing where near-field reads suffice and chip-based cards are deemed excessive. Adoption is nascent but growing in campus access, event accreditation, and limited-run loyalty programs.
Smart Tickets: For transport and venue control, single-use chipless tickets allow for instant distribution and sustainable disposal, while delivering reliable near-field reads at turnstile access points. Pilot programs in metropolitan metro systems and large-scale festivals are validating the value proposition.
Segment Analysis by End‑User –
Retail: Item-level tagging for loss prevention, streamlined checkout, and demand forecasting constitutes the largest application slice, especially in apparel and small electronics.
Healthcare: From surgical kit tracking to specimen monitoring and pharmaceutical authentication, healthcare providers prize chipless RFID for sterile-environment compatibility and waste reduction.
Logistics & Transportation: Pallet and package routing in last-mile delivery leverages chipless labels to reduce per-unit tagging costs, particularly for low-value parcels.
BFSI (Banking, Financial Services & Insurance): The segment is experimenting with chipless-based access credentials and paper-based document tracking—still an emerging frontier but one likely to benefit from enhanced anti-fraud measures.
Chipless RFID Market: Regional Insights
North America: The United States is spearheading reader installations and pilot rollouts market thrives on substantial backing from major retail chains and pharmaceutical corporations. Regulatory encouragement around anti-counterfeit measures (e.g., FDA’s DSCSA) further accelerates uptake. Canada’s focus on cold-chain visibility in food and vaccine distribution also fuels growth.
Europe: Stringent environmental directives (e.g., EU Packaging Waste Regulation) and robust recycling targets position chipless tags—often recyclable with primary packaging—favorably. Key driver segments include luxury goods authentication in Western Europe and parcel tracking in Eastern European e-commerce corridors.
Asia-Pacific (APAC): Fastest-growing region by percentage, APAC benefits from large-scale contract manufacturing hubs in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Government initiatives supporting “Industry 4.0” smart factories, coupled with booming e-commerce logistics networks, underlie strong demand.
Access our detailed report at: https://www.kennethresearch.com/report-details/chipless-rfid-market/10352550
Key Suppliers Shaping the Chipless RFID Arena
Distinguished vendors in this space include Impinj Inc., Alien Technology and NXP Semiconductors. hardware specialists such as Zebra Technologies, Honeywell International, and SATO Holdings; large-scale technology providers like Samsung SDS, Siemens AG, Toshiba Tec, and Fujitsu; and niche innovators including Identiv Inc., Avery Dennison, Thinfilm Electronics (Smartrac), GAO RFID, and Wiliot. Tertium Technology, RFID4U, Securitag Assembly Group (SAG), Tego Inc., and RFID Global Solution represent the leading vendors shaping the chipless RFID landscape, each bringing distinct strengths in materials science, reader hardware, software integration, and global distribution networks.
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to identify and track objects. Unlike traditional barcode technology, RFID does not require a line of sight for scanning. This system consists of tags with microchips that store information and antennas to transmit data wirelessly to RFID readers. RFID vs. NFC: RFID is a broad technology used for long-range identification and tracking, ideal for asset management in extensive operations like warehouses. NFC is a branch of RFID designed for short-range (up to a few centimeters) communication, which suits secure, fast data exchanges such as digital payments. Moreover NFC tags can be read from compatible smartphones. NFC Use Cases: NFC tags enable wireless data transfer and interaction with a simple tap. They can be used for cashless payments, digital keys, device pairing, marketing, and event access. Industrial RFID/NFC Applications:Asset Tracking: Monitor tools and machinery with NFC tags.Safety Protocol Enforcement: Check safety measures with NFC checkpoints.Quality Control: NFC for instant quality checks on production lines.Workforce Time Management: Simplify clocking in and out using NFC.Supply Chain Oversight: Track products from production to delivery.Medical RFID/ NFC Applications:Patient Identification: NFC cards for quick access to medical records.Medication Authentication: Verify drug authenticity and manage dosages.Medical Equipment Management: Inventory and maintenance tracking.NTAG213 NFC Cards Specs:Chip: NTAG213, NFC Forum Type 2 Tag compliant.Memory: 144 bytes, suitable for URLs/text.Frequency: 13.56 MHz for quick, reliable scans. Blank Printable RFID/NFC Card with 144 bytes user memory. Rewritable NTAG213 chip. Universally compatible with all NFC Phones and Readers. Standard CR80(credit card) size - 85.6 mm x 54 mm. Rounded Corner. Semi-flexible rigid PVC.Durable, Waterproof, Withstands bending/flexing. All cards come with 100% Quality Assurance & are Performance Tested. [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
RFID Definition vs Barcode Codes: What’s the Difference?

1. Introduction: Understanding RFID vs Barcode Codes in 2025
In the fast-paced world of business and technology, tracking and identification systems have become more crucial than ever. As companies aim to improve efficiency, cut down on errors, and enhance visibility across operations, the debate between RFID vs Barcode Codes has become a hot topic in 2025. Each technology offers unique advantages and use cases. At the heart of helping businesses navigate this decision is AIDC Technologies India, a trusted leader in automation, tracking, and smart labeling solutions. With years of industry expertise, AIDC simplifies the complexity of choosing the right tracking system by offering practical solutions customized to different business needs.
2. What Is RFID? AIDC’s Modern Take on RFID Technology
To understand how RFID works, we first need to look at the RFID Definition. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, a wireless technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects without the need for physical contact or line-of-sight. It uses tags embedded with a small chip and antenna, which can store data and communicate with RFID readers.
AIDC Technologies India provides end-to-end RFID solutions—from RFID printers and tags to integrated software that allows seamless tracking in real time. RFID is especially useful in environments that demand high speed and accuracy, such as logistics, supply chain, healthcare, and manufacturing. AIDC helps businesses not only implement RFID technology but also understand how it can be customized for their operations.
3. What Are Barcode Codes? AIDC’s Breakdown of Traditional Tracking
Barcode codes are a familiar sight in our daily lives. From supermarket billing counters to warehouse shelves, barcodes are used to identify items quickly and accurately. They consist of lines and numbers that are read by a barcode scanner. This system is cost-effective, simple, and widely adopted across industries.
AIDC Technologies India offers a wide range of barcode printers and scanners tailored to business environments—from compact desktop printers to heavy-duty industrial models. For many small and mid-sized businesses, barcodes remain the preferred choice due to their affordability and ease of implementation. While barcodes require manual scanning and line-of-sight, their simplicity makes them highly reliable for inventory management, point-of-sale, and labeling.
4. RFID vs Barcode Codes: AIDC’s Feature-by-Feature Comparison
The real difference between RFID vs Barcode Codes comes down to how they collect and manage data. Barcodes are scanned one at a time, while RFID tags can be read in bulk from a distance. Barcodes need clear visibility, while RFID tags can be hidden inside packaging or attached to non-visible surfaces. In terms of data capacity, RFID tags can store more information than a typical barcode.
From a cost perspective, barcodes are cheaper to print and maintain, making them ideal for businesses with tight budgets. RFID, although more expensive initially, offers long-term savings by speeding up operations and reducing human errors.
AIDC Technologies India helps businesses make informed choices by evaluating their needs, infrastructure, and scale of operations. They also offer hybrid systems where both technologies work together to maximize tracking efficiency.
5. Where RFID Works Best – AIDC’s Real-World Industry Use Cases
RFID technology shines in environments that require fast, automated, and high-volume item tracking. In large warehouses, for example, RFID readers can scan hundreds of items simultaneously without needing to point at each label. In healthcare, RFID is used to track patient files, equipment, and even medication batches for safety and compliance. In retail, RFID is used to manage stock levels, prevent theft, and speed up the checkout process.
With AIDC’s smart RFID integration, businesses gain real-time visibility and insights into their operations. The company's RFID solutions are designed for scalability, meaning businesses can start small and expand as they grow. Knowing the RFID Definition is not enough; understanding how it fits into your workflow is where AIDC Technologies India truly adds value.
6. Where Barcode Codes Still Lead – AIDC’s Value-Based Approach
Despite the advancements of RFID, barcode technology continues to play a key role in many sectors. Barcodes are easier and cheaper to print and require no special infrastructure to scan. For example, retail billing systems, inventory labeling, and library management still rely heavily on barcodes. Their widespread use and standardization make them convenient for day-to-day tracking.
AIDC Technologies India ensures that businesses using barcode systems continue to receive efficient, up-to-date solutions. They provide top-quality barcode printers, handheld scanners, and label supplies, along with software that simplifies inventory and asset management. For businesses that don’t require real-time tracking or automation, barcodes remain a practical and dependable choice.
7. How AIDC Combines RFID and Barcode Systems for Complete Solutions
One of the biggest advantages of working with AIDC Technologies India is their ability to provide integrated solutions. Many businesses benefit from a system that combines both RFID and barcode technologies. For example, an item can have a barcode label for quick visual scanning and an RFID tag for automated tracking in storage or transit.
This dual setup allows for flexibility, redundancy, and greater control. AIDC’s hybrid solutions are widely used in retail chains, logistics networks, and warehouses across India. They design systems that are easy to manage, cost-effective, and tailored to your operational goals. Whether it's understanding the RFID Definition or knowing when to use a barcode, AIDC simplifies it all for their clients.
8. Choosing Between RFID and Barcode: AIDC’s Custom Consultation Process
Selecting the right tracking method isn’t just about technology—it’s about business fit. AIDC Technologies India follows a consultative approach. Their team evaluates your business model, the type of products you handle, budget constraints, and operational challenges. Based on this, they recommend the best-fit solution—be it RFID, barcode, or a combination of both.
AIDC also provides implementation support, staff training, and maintenance services. Their solutions are not just off-the-shelf—they are customized for performance, scalability, and user-friendliness.
9. RFID and Barcode Trends in India: What’s Ahead in 2025
As we move further into a digital economy, both RFID and barcode technologies are evolving. RFID is becoming more affordable and is being adopted in smart city projects, automated toll systems, and advanced logistics. Barcodes, on the other hand, are being integrated with mobile apps, QR codes, and cloud-based inventory systems.
AIDC Technologies India continues to lead this transformation by bringing the latest advancements in tracking technologies to Indian businesses. Their mission is to make smart tracking accessible, affordable, and impactful for companies of all sizes.
10. Conclusion: Let AIDC India Help You Decide What’s Best
Understanding the difference between RFID vs Barcode Codes is just the beginning. The real challenge is selecting and implementing the system that matches your goals. Whether you're leaning toward cost-effective barcode labels or want to explore automation through RFID, AIDC Technologies India is your go-to expert. With a focus on innovation, customization, and support, AIDC empowers businesses to track smarter and grow faster.
Need help choosing between RFID and barcode solutions? Contact AIDC Technologies India for a free consultation. Let us guide you with the right tools to improve your tracking, visibility, and business performance in 2025.
#RFIDvsBarcode2025#SmartInventoryTracking#RFIDDefinitionExplained#BarcodeTechnologyComparison#RFIDvsBarcodeDifferences
0 notes