#PDCA Cycle Software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Optimize Continuous Improvement with PDCA Cycle Software

Discover how PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle software by Performance Storyboard empowers quality and process improvement teams. Our intuitive platform supports structured problem-solving, real-time tracking, and visual workflow tools perfect for lean manufacturing, engineering, and quality assurance professionals aiming for operational excellence.
Read more- https://performance-storyboard.com/pdca/
0 notes
Text
CMMI and ISO 27001 Mapping
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) and ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System) are two different frameworks, each with its own focus and purpose. While they address related areas of business operations, they are not directly comparable or mappable to each other. However, organizations can leverage both frameworks to enhance their overall cybersecurity and process maturity. Here's an overview of each framework and how they can be related:
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration):
CMMI is a framework for process improvement that focuses on the maturity and capability of an organization's processes across various domains, including software development, systems engineering, and project management. It provides a structured approach to assessing and improving an organization's processes, emphasizing efficiency, consistency, and quality.
CMMI maturity levels range from Level 1 (Initial) to Level 5 (Optimizing), with each level representing a higher degree of process maturity and capability. Organizations use CMMI to assess their current process maturity, identify areas for improvement, and implement best practices to reach higher maturity levels.
ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System):
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for information security management. It provides a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks within an organization. ISO 27001 aims to establish a robust Information Security Management System (ISMS) that protects sensitive information, ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and complies with legal and regulatory requirements.
ISO 27001 specifies a set of requirements that organizations must meet to establish and maintain an ISMS effectively. It includes processes for risk assessment, risk treatment, security controls, and continuous improvement of information security practices.
Relation between CMMI and ISO 27001:
While CMMI and ISO 27001 are distinct frameworks, they can complement each other in enhancing an organization's overall cybersecurity and process maturity. Here's how they can be related:
Process Improvement: CMMI focuses on process improvement across various domains, including software development and project management. An organization can apply CMMI practices to enhance the maturity of its software development processes, which is particularly relevant for security-related processes.
Integration: Organizations can integrate information security practices from ISO 27001 into their existing CMMI-based processes. For example, security requirements, risk assessments, and security controls can be incorporated into project management and software development processes.
Risk Management: Both CMMI and ISO 27001 emphasize risk management. ISO 27001 provides a structured approach to information security risk management, which can align with the broader risk management practices encouraged by CMMI.
Continuous Improvement: Both frameworks promote continuous improvement. ISO 27001's PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle aligns with the principles of process improvement in CMMI. Organizations can use the feedback and data collected from ISO 27001 audits and risk assessments to drive improvements in their CMMI processes.
Compliance: ISO 27001 helps organizations comply with information security-related legal and regulatory requirements. Compliance with these requirements can be integrated into CMMI processes to ensure that security considerations are consistently addressed.
In summary, while CMMI and ISO 27001 are not directly mappable, they can work together to enhance an organization's overall process maturity and information security posture. Organizations looking to strengthen both process efficiency and cybersecurity can benefit from a strategic integration of these two frameworks, tailoring their implementation to meet their specific needs and objectives.
0 notes
Text
How to Maintain a Quality Assurance System?

A quality assurance system aims to help companies establish effective management of their manufacturing and delivery of products and services. It is designed and focused on customer satisfaction. The following blog will discuss how effective small and medium companies can be when they implement and maintain a productive quality assurance (QA) system.
1. Regular Monitoring and Audits
Internal Audits: Conduct routine audits to ensure compliance with the QA system and identify areas for improvement.
Surveillance Audits: If ISO certified, work with the certification body for periodic surveillance audits to maintain certification.
Performance Metrics: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) regularly to measure the effectiveness of the QA system.
2. Update Policies and Procedures
Periodic Review: Regularly review quality manuals, policies, and procedures to ensure they remain relevant.
Change Management: Update the system in response to organizational changes, such as new processes, technology, or regulations.
3. Employee Training and Awareness
Continuous Training: Offer ongoing training for staff on QA principles, standards, and their specific roles in maintaining quality.
Awareness Programs: Reinforce the importance of quality assurance through workshops, team meetings, and communication channels.
4. Customer Feedback Integration
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish channels for customers to provide feedback on products or services.
Issue Resolution: Address complaints and suggestions promptly and use them as opportunities for improvement.
5. Risk Management
Risk Assessment: Regularly identify and assess risks that could impact quality.
Preventive Actions: Implement proactive measures to mitigate risks before they result in quality issues.
6. Documentation and Record Keeping
Accurate Records: Maintain up-to-date records of quality checks, audits, corrective actions, and customer feedback.
Documentation Control: Ensure all documents are properly stored, easily accessible, and version controlled.
7. Continuous Improvement
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA): Use the PDCA cycle to drive continuous improvements in the QA system.
Benchmarking: Compare your QA practices with industry standards or competitors to identify opportunities for enhancement.
Root Cause Analysis: Investigate recurring issues and implement corrective and preventive actions.
8. Management Commitment
Leadership Involvement: Ensure that senior management is actively involved in and committed to the QA system.
Resource Allocation: Provide adequate resources, including budget, personnel, and technology, to maintain quality.
9. Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Regular Updates: Stay informed about changes to relevant industry standards or regulations.
Third-Party Reviews: Engage external experts to verify compliance if necessary.
10. Technology Utilization
Quality Management Software: Use software tools to automate quality checks, data collection, and reporting.
Data Analytics: Leverage analytics to identify trends and improve decision-making.
Key Focus Areas for Maintenance
Preventing non-conformities through proactive measures.
Fostering a culture of quality among employees.
Aligning the QA system with organizational goals and customer expectations.
To learn more about a quality assurance system, you will need to contact certified ISO consultancy centres. Before appointing anyone, you must conduct a background check to verify and learn more about their prices and availability.
Also Read: How to Obtain an ISO 27001 Certification in Australia For Small and Medium Companies?
0 notes
Text
Deming's Principles for PDCA Cycle Include: A Guide to Continuous Improvement in Software Testing Service

Deming's principles for PDCA cycle include a set of guidelines that emphasize continuous improvement in processes. PDCA, which stands for Plan-Do-Check-Act, is a four-step model for driving quality improvement. Originating from W. Edwards Deming, a renowned quality management expert, this methodology is widely used in various industries, including software testing service.
Plan: The first step focuses on identifying and understanding the problem. In software testing service, this involves gathering requirements, setting objectives, and designing a strategy for testing that aligns with the project’s goals.
Do: The second step emphasizes execution. In the context of software testing service, this involves running the tests as planned, executing the test cases, and gathering data to assess the software’s performance and functionality.
Check: Here, the results are analyzed to check for deviations or areas of improvement. In software testing, this step ensures that the results meet the expected quality standards and helps detect bugs or issues that need attention.
Act: Based on the analysis, improvements are made. If issues are identified in the previous steps, actions are taken to correct them, refining the testing process to ensure future quality.
By incorporating Deming's principles for PDCA cycle include, software testing service can significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and quality of their testing efforts. It promotes an iterative approach where feedback is constantly used to optimize processes, ensuring the delivery of high-quality software.
0 notes
Text
Top Continuous Process Improvement Methods to Boost Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to enhance operational efficiency and reduce waste. Continuous process improvement (CPI) is a systematic approach that focuses on refining processes to achieve better performance. Here, we explore some of the top continuous process improvement methods that can significantly boost efficiency in your organization.

1. Lean Management
Lean management is a methodology that emphasizes minimizing waste without sacrificing productivity. The core principles of lean involve identifying value from the customer's perspective and eliminating any non-value-adding activities. By streamlining processes, organizations can improve workflow, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Key tools in lean management include value stream mapping, 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), and Kaizen (continuous improvement).
2. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that aims to improve quality by identifying and eliminating defects in processes. By applying statistical methods and quality management techniques, organizations can achieve significant improvements in process efficiency. The Six Sigma methodology follows the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework, which guides teams through a structured process to identify root causes of issues and implement effective solutions. This method is particularly beneficial in manufacturing and service industries.
3. Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is an organization-wide approach to improving quality and performance. TQM focuses on continuous improvement, employee involvement, and customer satisfaction. By fostering a culture of quality, organizations can enhance processes at every level. Key principles of TQM include leadership commitment, customer focus, and data-driven decision-making. TQM encourages collaboration and empowers employees to take ownership of quality improvements.
4. Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) involves rethinking and redesigning existing processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical performance measures. Unlike incremental improvements, BPR aims for radical change by analyzing workflows and eliminating unnecessary steps. This method is particularly effective for organizations facing significant challenges or needing to adapt to changing market conditions. Successful BPR initiatives require strong leadership and a willingness to embrace change.
5. Agile Methodology
Originally developed for software development, Agile methodology has found its way into various industries as a process improvement method. Agile emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. By breaking projects into smaller, manageable increments (sprints), teams can adapt quickly to changes and continuously improve their processes. Agile fosters a culture of experimentation and learning, allowing organizations to respond effectively to market demands.
6. Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
The PDCA cycle is a simple yet powerful continuous improvement tool that helps organizations systematically test changes and refine processes. The four stages—Plan, Do, Check, and Act—provide a framework for problem-solving and process optimization. Organizations can use the PDCA cycle to implement small changes, monitor their effectiveness, and make necessary adjustments. This iterative approach ensures continuous learning and improvement over time.
7. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing an organization's processes and performance metrics to industry best practices. By identifying gaps and opportunities for improvement, organizations can adopt strategies that lead to enhanced efficiency. Benchmarking can be internal (comparing departments within the same organization) or external (comparing with competitors or industry leaders). This method encourages organizations to strive for excellence by learning from others.
youtube
Conclusion
Implementing continuous process improvement methods is essential for organizations seeking to enhance efficiency and stay competitive. By adopting lean management, Six Sigma, TQM, BPR, Agile, the PDCA cycle, and benchmarking, businesses can create a culture of continuous improvement. These methods not only boost operational efficiency but also lead to higher customer satisfaction and long-term success.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Invoice Process Work - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
Maintaining ISO 45001 Certification: Continuous Improvement Strategies

Introduction
Brief overview of ISO 45001 certification and its importance for occupational health and safety.
Highlight the significance of continuous improvement in maintaining the certification.
State the purpose of the blog: to discuss strategies for continuous improvement and maintaining ISO 45001 Certification in Dubai, UAE.
1. Understanding the Importance of Continuous Improvement
Explanation: Discuss why continuous improvement is crucial for sustaining ISO 45001 certification.
Benefits: Improved safety performance, compliance with evolving regulations, enhanced employee morale, and reduced incidents.
2. Conduct Regular Internal Audits
Challenge: Ensuring ongoing compliance with ISO 45001 standards.
Solution: Schedule regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of your Occupational Health and Safety Management System (OHSMS).
Provide tips for conducting thorough and effective audits.
Emphasize the importance of identifying non-conformities and areas for improvement.
3. Implement a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
Challenge: Establishing a systematic approach to continuous improvement.
Solution: Use the PDCA cycle to guide your improvement efforts.
Plan: Identify opportunities for improvement and develop action plans.
Do: Implement the action plans.
Check: Monitor and measure the effectiveness of the implemented actions.
Act: Make necessary adjustments and standardize successful improvements.
4. Engage and Train Employees
Challenge: Ensuring employee involvement and understanding of OHSMS.
Solution: Provide regular training and development programs.
Highlight the importance of employee engagement in identifying hazards and suggesting improvements.
Share success stories of how employee involvement has led to significant safety improvements.
5. Monitor and Analyze Safety Performance Data
Challenge: Keeping track of safety performance and identifying trends.
Solution: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) for health and safety.
Use data analysis tools to monitor trends and identify areas needing attention.
Share examples of effective KPIs and how they can drive improvement.
6. Management Review and Commitment
Challenge: Maintaining top management commitment to OHSMS.
Solution: Conduct regular management reviews to assess the performance of the OHSMS.
Discuss the outcomes of these reviews and how they lead to strategic decisions for improvement.
Highlight the role of leadership in driving a culture of continuous improvement.
7. Foster a Culture of Safety
Challenge: Creating an organizational culture that prioritizes health and safety.
Solution: Promote a safety-first mindset throughout the organization.
Share best practices for fostering a culture of safety, such as recognition programs, open communication channels, and leadership by example.
8. Use Technology and Innovation
Challenge: Keeping up with technological advancements and leveraging them for safety improvements.
Solution: Implement digital tools and technologies for safety management.
Discuss examples of technologies such as safety management software, IoT devices, and data analytics.
Explain how these technologies can streamline processes and enhance safety performance.
9. Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes
Challenge: Adapting to changes in regulations and standards.
Solution: Regularly review and update your OHSMS to comply with new regulations.
Provide resources for staying informed about regulatory changes.
Highlight the importance of proactive compliance to avoid penalties and ensure worker safety.
Conclusion
Recap the key strategies discussed in the blog.
Reinforce the importance of continuous improvement for maintaining ISO 45001 Certification in Dubai, UAE.
Encourage readers to implement these strategies to achieve sustained compliance and improved safety performance.
Call to Action
Invite readers to share their own strategies and experiences with maintaining ISO 45001 certification.
Provide contact information or links for readers seeking professional assistance or more information about ISO 45001 certification.
This outline will help you create a comprehensive and informative blog post that offers valuable insights and practical strategies for maintaining ISO 45001 Certification in Dubai, UAE through continuous improvement.
0 notes
Text
ISO Training
Introduction:
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) training stands as a cornerstone for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency and ensure quality standards. Whether in manufacturing, services, or software development, adherence to ISO norms not only streamlines processes but also fosters credibility in the market. In this article, we delve into the significance of ISO training, its benefits, and how organizations can leverage it to stay competitive in today's dynamic business landscape.
Understanding ISO Standards:
ISO standards serve as a benchmark for quality, safety, and efficiency across various industries. From ISO 9001 for quality management to ISO 14001 for environmental management, these standards provide a framework for organizations to optimize their processes and meet customer expectations consistently.
Importance of ISO Training:
ISO training equips employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain ISO standards effectively. Through comprehensive training programs, individuals gain insights into the principles of quality management, risk assessment, and continuous improvement. This knowledge empowers them to contribute proactively to the organization's adherence to ISO norms.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency:
One of the primary objectives of iso training is to streamline operations. By standardizing processes and identifying areas for improvement, organizations can minimize waste, reduce errors, and enhance overall efficiency. Employees trained in ISO methodologies become adept at identifying bottlenecks and implementing corrective actions, leading to smoother workflows and higher productivity.
Ensuring Consistent Quality:
Consistency in quality is vital for building customer trust and loyalty. ISO training instills a culture of quality consciousness within the organization, where every employee understands their role in maintaining and improving product or service quality. By adhering to ISO standards, businesses can deliver consistent results, meet regulatory requirements, and surpass customer expectations.
Driving Continuous Improvement:
ISO training encourages a mindset of continuous improvement. By embracing principles such as the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, organizations can systematically identify areas for enhancement, implement changes, and monitor the results. This iterative process fosters innovation, agility, and adaptability, enabling businesses to stay ahead of the curve in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Conclusion:
In today's competitive landscape, organizations cannot afford to overlook the importance of ISO training. By investing in comprehensive training programs, businesses can optimize their operations, ensure consistent quality, and drive continuous improvement. Ultimately, ISO training not only enhances efficiency and effectiveness but also reinforces the foundation for long-term success and sustainability.
0 notes
Text
Drive Continuous Improvement with PDCA Cycle Software from Performance Storyboard
Unlock operational excellence with the PDCA Cycle Software by Performance Storyboard, a powerful tool built for continuous improvement teams. This user-friendly solution enables organizations to plan strategically, execute with focus, check results accurately, and act for long-term success. Whether you're managing quality control or enhancing workflows, this software turns every cycle into measurable progress.
Key Features: ✔ Intuitive Plan-Do-Check-Act framework ✔ Real-time performance tracking ✔ Visual progress dashboards & KPIs ✔ Seamless team collaboration ✔ Integration with existing management systems
Ideal for sectors like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, Performance Storyboard’s PDCA tool empowers your team to make smarter decisions, faster. Start optimizing your process today!
Learn more: https://performance-storyboard.com/pdca/
0 notes
Text
How long does it take to obtain ISO 45001 certification in India?

ISO 45001 Certification in India offers organizations an internationally recognized framework to ensure that their workplaces are safe and free of hazards. If you manage an industrial unit, a construction company, or even a corporate office, ISO 45001 Certification in India can significantly improve your credibility as a business, reduce the risk of accidents, and enhance the well-being of employees.
What is ISO 45001 Certification?
ISO 45001 is an international standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) created through ISO, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It replaces OHSAS 18001 and is focused on proactive risk reduction, innovation, and continuous improvement.
Why ISO 45001 Certification is Important in India
The growing industrial sector in India and the large workforce create particular issues for work-related security. Here’s the reason why ISO 45001 Certification in India is crucial:
Legal Conformity: Helps organizations meet international and national occupational safety standards.
Safeguarding Employees Reducing workplace accidents and risks.
Reputation Management Improves your organization’s credibility with partners, clients and other stakeholders.
Cost Efficiency It reduces time spent on downtime and compensation claims.
Global Recognition: It facilitates business transactions with foreign partners and clients.
Key Benefits of ISO 45001 Certification
Better risk management and identification of hazards.
Improved morale and engagement of employees.
Improved compliance with the regulatory system.
Improved operational efficiency.
Competitive advantage both in international and domestic markets.
ISO 45001 Certification Process in India
Gap Analysis: Evaluate existing systems against ISO 45001 Certification in India standards.
Plan: Develop an implementation plan and assign responsibilities.
Education: Educate employees and managers on the standards’ requirements.
Mandatory documentation Documents include OH&S policies, objectives, or risk evaluations.
Implementation: Integrate ISO 45001 Certification in India practices into everyday activities.
Internal Audit: Perform audits to uncover any inconsistencies.
Managerial Review Check the results of audits and take corrective steps.
Certificate Audit: A certified body examines your OHSMS for conformity.
Who Should Get ISO 45001 Certified?
ISO 45001 Certification in India is suitable for businesses that are of any size and in all sectors, including:
Manufacturing Industries
Construction Companies
IT & Software Firms
Healthcare Institutions
Educational Organizations
Why Choose Factocert for ISO 45001 Certification in India?
Factocert is among India’s most reputable ISO certification firms and provides complete assistance for ISO 45001 Certification in India implementation and certification. This is what makes us stand out:
Highly experienced consultants with specific expertise in their field.
Complete training and support for documentation.
Timely and cost-effective service delivery.
All over the country, including major cities such as Bangalore, Mumbai, Delhi and Chennai.
Contact us now to begin with your ISO 45001 certification journey!
Implementation of ISO standard involves, the utilization of a very efficient methodology “Plan do check act” that is the PDCA cycle, each clause in every part of the organization. ISO 45001 Certification in India certification in India involves all these factors to be more productive. ISO 45001 cost in India is very competitive and to know more contact us at [email protected]. And to know how to get ISO 45001 certification in India
For More Information Visit ISO 45001 Certification in India
0 notes
Text
What is Software Quality Assurance?
Software quality assurance (SQA) generally refers to the process of assuring that the end product performs as intended and as supposed to. It is an ongoing process that takes place before, during, and after the software development cycle.
SQA identifies all the potential failures and catches all the shortcomings as well as deficiencies before it backfires the financial loss. According to The Cost of Poor Software Quality in the US: A 2020 Report, the total Cost of Poor Software Quality in the US is $2.08 trillion, accounting for a 14% rise compared to 2018 statistics.
In order to ensure Software Quality Assurance processes and procedures are up to certified standards, Software Quality Assurance often combines with international standards, such as ISO (The International Organization for Standardization), CMMI model, TMM, etc.
Trong phương pháp đảm bảo chất lượng, chu trình PDCA được áp dụng như một mô hình quy trình được xác định rõ ràng, do Tiến sĩ William Edwards Deming phát triển vào những năm 1950 nhằm cải tiến liên tục sản phẩm một cách hiệu quả.
Làm thế nào để đảm bảo chất lượng phần mềm “đúng cách”?
This four-step approach iteratively detects the problem when the software is not functioning properly or delivering the desired results. PDCA comes in as an analysis tool to explore and discover the rooted issues while finding possible solutions to resolve and improve such. The 4 stages of PDCA are:
Plan Establishing the project’s objectives and goals is the very first step in kick-starting this cycle. From here, define success metrics and the processes (supporting methods) to achieve these goals.
Do At this stage, we execute our plan, implement it and collect data for later analysis of the next stage.
Check Here we evaluate the results of the implemented plan and certain that our set out goals and objectives have been reached. Coming up with a checklist of revision to refine and striving to meet the defined goals.
Act This step closes the circle. Reflected on whether the improvements and changes that have been made were our predefined goals or not. If not, continue the cycle by carrying out a new task of improvement with another plan. Repeat the cycle over and over again until we achieve our goals.
An organization needs to have a decent Software Testing And Quality Assurance process in place to monitor the consistency of the production process. Many companies have pursued the help of third-party software testing and quality assurance service providers, fully outsourcing to concentrate on the coding itself. SHIFT ASIS is a leading Software Quality Assurance company providing the best test automation, system testing, and other testing solutions as required. For inquiries and questions on our services, contact our support team for assistance.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Maintain a Quality Assurance System?

A quality assurance system aims to help companies establish effective management of their manufacturing and delivery of products and services. It is designed and focused on customer satisfaction. The following blog will discuss how effective small and medium companies can be when they implement and maintain a productive quality assurance (QA) system.
1. Regular Monitoring and Audits
Internal Audits: Conduct routine audits to ensure compliance with the QA system and identify areas for improvement.
Surveillance Audits: If ISO certified, work with the certification body for periodic surveillance audits to maintain certification.
Performance Metrics: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) regularly to measure the effectiveness of the QA system.
2. Update Policies and Procedures
Periodic Review: Regularly review quality manuals, policies, and procedures to ensure they remain relevant.
Change Management: Update the system in response to organizational changes, such as new processes, technology, or regulations.
3. Employee Training and Awareness
Continuous Training: Offer ongoing training for staff on QA principles, standards, and their specific roles in maintaining quality.
Awareness Programs: Reinforce the importance of quality assurance through workshops, team meetings, and communication channels.
4. Customer Feedback Integration
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish channels for customers to provide feedback on products or services.
Issue Resolution: Address complaints and suggestions promptly and use them as opportunities for improvement.
5. Risk Management
Risk Assessment: Regularly identify and assess risks that could impact quality.
Preventive Actions: Implement proactive measures to mitigate risks before they result in quality issues.
6. Documentation and Record Keeping
Accurate Records: Maintain up-to-date records of quality checks, audits, corrective actions, and customer feedback.
Documentation Control: Ensure all documents are properly stored, easily accessible, and version controlled.
7. Continuous Improvement
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA): Use the PDCA cycle to drive continuous improvements in the QA system.
Benchmarking: Compare your QA practices with industry standards or competitors to identify opportunities for enhancement.
Root Cause Analysis: Investigate recurring issues and implement corrective and preventive actions.
8. Management Commitment
Leadership Involvement: Ensure that senior management is actively involved in and committed to the QA system.
Resource Allocation: Provide adequate resources, including budget, personnel, and technology, to maintain quality.
9. Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Regular Updates: Stay informed about changes to relevant industry standards or regulations.
Third-Party Reviews: Engage external experts to verify compliance if necessary.
10. Technology Utilization
Quality Management Software: Use software tools to automate quality checks, data collection, and reporting.
Data Analytics: Leverage analytics to identify trends and improve decision-making.
Key Focus Areas for Maintenance
Preventing non-conformities through proactive measures.
Fostering a culture of quality among employees.
Aligning the QA system with organizational goals and customer expectations.
To learn more about a quality assurance system, you will need to contact certified ISO consultancy centres. Before appointing anyone, you must conduct a background check to verify and learn more about their prices and availability.
Also Read: How to Optimise the Benefits of The ISO 22301 Certification
0 notes
Text
Understanding Deming Principles for PDCA Cycle in Software Testing Services

In the realm of software testing services, maintaining high quality and continuous improvement is essential for delivering reliable products. One framework that has proven effective in ensuring this is the PDCA cycle, which stands for Plan, Do, Check, Act. The cycle emphasizes iterative improvement and is strongly influenced by the Deming principles, a set of guidelines created by W. Edwards Deming to foster better processes and quality control.
The Deming principles for PDCA cycle include focusing on customer satisfaction, empowering employees, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. These principles encourage organizations to build a testing process that not only identifies defects but also refines and enhances the overall development process. By incorporating these principles into software testing, businesses can streamline their workflows and ensure higher quality products.
In the "Plan" phase, testing teams identify requirements, set clear goals, and define the criteria for success. The "Do" phase involves executing the test cases based on the previously defined plan. During the "Check" phase, results are evaluated to identify discrepancies and areas for improvement. Finally, in the "Act" phase, corrective actions are implemented to refine the process, ensuring that future testing cycles are even more efficient.
By applying Deming's principles to the PDCA cycle, software testing services can continuously evolve, ensuring that each iteration brings products closer to perfection. This approach not only optimizes the testing process but also boosts overall software quality, making it a valuable strategy for any organization focused on delivering reliable software solutions.
0 notes
Text
How to Build a Culture of Continuous Process Improvement in Your Organization
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, fostering a culture of continuous process improvement (CPI) is essential for organizations aiming to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and adapt to evolving market demands. Establishing this culture requires a strategic approach that engages employees at all levels and integrates improvement practices into the organization’s daily operations. Here’s how you can build a culture of continuous process improvement in your organization.

1. Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Start by clearly defining the goals and objectives of your continuous process improvement initiatives. What specific areas do you want to improve? Whether it’s reducing lead times, enhancing product quality, or increasing customer satisfaction, having clear goals provides direction and purpose. Communicate these goals to all employees to ensure everyone understands the importance of their contributions to the improvement process.
2. Engage Leadership Support
For continuous process improvement to thrive, it’s crucial to have strong support from leadership. Leaders should champion CPI initiatives and demonstrate commitment by actively participating in improvement efforts. This involves not only providing resources but also modeling the behaviors and attitudes that promote a culture of improvement. When employees see their leaders prioritizing CPI, they are more likely to embrace these practices themselves.
3. Encourage Employee Involvement
Empower your employees by involving them in the improvement process. Encourage them to identify inefficiencies and suggest solutions based on their firsthand experiences. Create an open environment where employees feel safe to share their ideas and feedback. Regularly hold brainstorming sessions, workshops, or team meetings to discuss potential improvements and celebrate contributions.
4. Provide Training and Resources
Invest in training programs to equip employees with the skills and knowledge they need to participate in continuous process improvement. Training can cover methodologies like Lean, Six Sigma, or Kaizen, which provide structured approaches to identify and eliminate waste. Additionally, ensure that employees have access to the necessary tools and resources that support their improvement efforts, such as software for tracking progress and metrics.
5. Implement a Systematic Approach
Develop a systematic approach to continuous process improvement. This may include implementing a formal framework or methodology that guides improvement initiatives. For example, the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle encourages teams to plan improvements, implement changes, check the results, and take action based on what they learn. A structured approach helps ensure consistency and provides a roadmap for teams to follow.
6. Celebrate Successes and Learn from Failures
Recognizing and celebrating achievements is vital for sustaining motivation and engagement. Share success stories within the organization to highlight the impact of continuous process improvement. Conversely, it’s important to foster a mindset that views failures as learning opportunities rather than setbacks. Encourage teams to analyze what went wrong, adapt their strategies, and move forward with renewed determination.
7. Measure and Monitor Progress
To maintain a culture of continuous process improvement, establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that allow you to measure progress. Regularly monitor these metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of your improvement initiatives. Use data-driven insights to make informed decisions and adjustments to your strategies. Transparency in sharing results with the team fosters accountability and reinforces the importance of their contributions.
8. Embed CPI into the Organization’s DNA
Finally, for continuous process improvement to become ingrained in your organization’s culture, it should be woven into everyday practices. Encourage teams to integrate improvement discussions into regular meetings, performance evaluations, and project planning sessions. By making CPI a fundamental aspect of your organizational identity, you’ll ensure that it remains a priority even as business needs evolve.
youtube
Conclusion
Building a culture of continuous process improvement is a journey that requires commitment and collaboration from all levels of the organization. By defining clear goals, engaging leadership, empowering employees, providing training, and implementing a systematic approach, you can create an environment that embraces improvement. Ultimately, a culture of continuous process improvement will lead to increased efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and sustained organizational growth. Start your journey today and watch your organization thrive!
SITES WE SUPPORT
Invoice Process Work - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
1 note
·
View note
Text
Risk-Based Thinking in the Airline industry — It’s about time.
The airline industry statistically has one of the best safest records. AS9100 defines the framework for a quality management system for aerospace parts manufacturers across the globe. Over the past decade there have been several airline accidents however, that have brought the safety of airlines to the forefront. In a most recent case of the Boeing 737-max a software glitch was identified as the cause. As investigations proceed the general consensus is that this glitch should have been previously identified.
Risk generally is associated with ‘uncertainty’ or ‘negativity’. This changed with ISO 9001:2015 and the onset of risk-based thinking that now asks companies to consider the opportunities for improvement that may arise out of taking a ‘calculated’ risk. Further in AS9100, that is built on ISO 9001, there are requirements for consideration of strategic risks and operational risks and the need to take action to address each. The impact of coronavirus or a similar pandemic is a great example of a strategic risk that can affect business continuity.
Risk-based thinking in the AS9100 standard promotes customer focus within an organization. While risk-based thinking has been inherent in previous versions of the standard with preventive action, the new standards address risk at each stage of the PDCA cycle thus enabling the entire As9100 management system at each stage as a preventive tool.
The aerospace and automotive industry are leaders in the implementation of Failure mode and effects Analysis (FMEA) and the Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle (PDCA) of process management. Originally adopted by the military in the 1950’s, FMEA later was embraced by the auto and aerospace industries. The FMEA process identifies risks that can then be addressed using mistake proofing and problem solving with a team approach. FMEA can be used for either product or process. When used properly it can be a very effective at addressing risks. FMEA is a great core tool that can be applied to address the AS9100 clause 8.1.1 operational risk requirements.
AS9100 asks top management to take accountability for the quality of products and services produced by their organization; keeping a customer focus at the core of all they do. The influence of end users, customers and the companies marketing department on the product’s design needs to be constantly reviewed. At each stage of the requirements gathering, design & development and manufacturing stages of the AS9100 system there are potential risks. As such doing a single FMEA may not be sufficient but may require a review of the FMEA at periodic intervals as a change in inputs to the process/product may change the associated risks or identify new ones.
Management wants to encourage continuous improvement and innovative recommendations by all stakeholders, but changes must be reviewed. Whenever a change is made to a AS9100 certified product or service, that change should follow the PDCA Cycle approach, the same way it was done when the product was first introduced. This will reduce the number of recalls, and the risk of injuries to end users of the products.
A single non-conforming product that goes out of the organization into the market results in an intangible loss for no value can be put on the loss of reputation. It only takes a single incident! Starting with risk appreciation at the Plan stage of the PDCA cycle and then throughout the rest of the cycle, with a focus on customer satisfaction, will help the aerospace industry improve by preventing non-conformities before they occur as well as hopefully, improve their As9100 certified products
0 notes
Text
Best Practices for Business Analysts in an Agile World!!
A Business Analyst works as a bridge between stakeholders and the developing team in Tech startups in India. His main job is to take requirements from the stakeholders and develop user stories. He then sits with the developers to implement that user story correctly. After that, he documents all the requirements and tests all the implemented business processes.
A Business Analyst should use the following practices for agile software development.
1. Iterative Method
In agile iterative software development companies, big projects are broken down into smaller parts and continuous tests are done in repetitive cycles. In this way, agile teams get an idea of new features that need to be added to the final product and contribute toward more flexible product development.
The most prominent iterative methods are :
SCRUM (Systematic Customer Resolution Unravelling Meeting)
DSDM (Dynamic system development method) and
FDD (Feature-driven development)
Each iteration is given a fixed length of time known as a timebox. A single timebox usually lasts 2–4 weeks.
The Agile team implements the PDCA cycle on each iteration separately in the following manner:
P (Plan) — Iteration Planning
D (Design) — Iteration Execution
C (Check) — Iteration Review
A (Adjust) — Iteration Retrospect
A backlog is maintained for future reference after each iteration cycle. The iterations are repeated with improvements learned after each cycle until a fully functional software is ready to hit the market.
2. Regular Day Meetings
Regular small day meetings should be a practice in the successful development of software. The business analyst should know the day-to-day problems coming in the way of the team while developing the project. He then can find a way to solve the problems by connecting with stakeholders and team for the smooth development.
3. Professional Tools Usage in Project Management
Using project management tools in an agile environment helps the team to better structure their workflows and improve team collaboration. For proper documentation and management of team meetings professional project management software can greatly reduce the effort to manage your tasks.
Many Benefits to use project management tools are as follows:
1. Through this it’s very easy to delegate the tasks to team members with a proper timeline in an effective way.
2. It’s very easy to collaborate with all team members for the latest update on the project.
3. It helps to plan and schedule every task very effectively.
One such tool that you can easily use is Jira. It’s a comprehensive software, with the most intelligent features and provides a smart overall coverage to all agile project management needs.

0 notes
Text
What is quality assurance and why is it important?
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) is a type of process that ensures methods, activities, engineering processes of software, and work items are monitored and comply with the defined standards. These standards are globally set and defined by the international private ad governmental organization. The SQA standards are one or a combination of ISO 9000, CMMI, ISO 15504 and some others.
Quality Assurance (QA) is any systematic process of determining whether a product or service meets specified requirements.
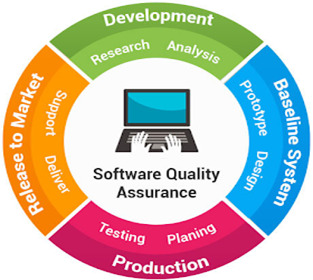
Elements of Software Quality Assurance:
There are 10 essential elements of SQA which are enlisted below for your reference:
1. Software Testing for Quality Control
2. Software Engineering Standards
3. Technical Reviews & Adults
4. Error collection & analysis
5. Change Management
6. Educational Programs
7. Vendor Management
8. Security Management
9. Risk Management
10. Safety
Software Quality Assurance Techniques:
There are several techniques for SQA. Auditing is the major technique that is widely used by professionals. These techniques and others such as Quality Assurance Course Certification, QA Specialists courses, IT training courses, QA manual testing, QA Automation Testing, and Software Quality Assurance. Skylineittech is a well-reputed training institute in the US that is well-known for QA Automation Testing, Software Quality Assurance and Quality Assurance training,
There are many techniques for Software Quality Assurance as follows:
1. Auditing
2. Reviewing
3. Simulation
4. Standardization
5. Static Analysis
6. Code Inspection
7. Design Inspection
8. Functional Testing
9. Standardization
10. Static Analysis
11. Walkthroughs
12. Path Testing
13. Stress Testing
14. Six Sigma
Software development methodologies have been developed gradually that depends on SQA, which includes Waterfall, Agile and Scrum. Each process focuses to enhance work efficiency.
Waterfall: This is a linear approach to software development. It is a sequential process that usually includes gathering requirements, formalization of a design, implementation of code, and code testing.
Agile: It is a method for software development where each step in the process is approached as a sprint. It is quite adaptive yet less predictive.
Scrum: This is a combination of processes in which developers are divided into teams to handle specific tasks and these tasks are divided into several sprints.
Importance of Quality Assurance:
The question that arises, why is Software Quality Assurance is important? Makes us answer this question.
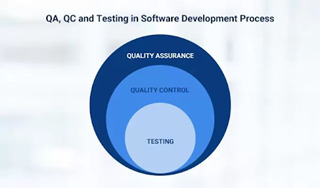
The importance of the SQA could easily be understood as follows:
· Saves finances
· Surety of Security
· Customer Satisfaction
· Maintains the product quality
· Maintains standards and reputation
SQA systematically determines patterns and the actions needed to improve development cycles. Quality assurance has a defined cycle called the PDCA cycle or also known as the Deming cycle. There are 4 phases of this cycle as follows:
Plan: The Company must plan and establish the needed process about the objectives and develop strategies needed to provide top-quality products.
Do: At this phase, it is time to apply the devised plan and build testing of processes. At this stage, strategies improve efficiency.
Check: Monitoring of processes, modify the functions check whether it meets the pre-set goals.
Act: At this stage, the necessary actions are implemented to determine that if a product or service is performing as intended or programmed.
Hopefully, the afore-mentioned information must have cleared any confusion about what is quality assurance and why is it important? Quality assurance is the need of the day and it will remain so in the coming future.
#Quality Assurance (AQ) training course online#Quality Assurance course#Quality Assurance course certification#IT training course#Quality Assurance testing course
0 notes