#Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
new bucket list attempt everything on this list at least once
Master list of creative hobbies
Art creative hobbies
1. Botanical illustration
2. Architectural drawing
3. Urban sketching
4. Comic and manga illustration
5. Children’s book illustration
6. Digital art and design
7. Figure drawing
8. Fashion illustration
9. Mapmaking
10. Doodling and zentangle
11. Sticker making
12. Coloring books (for adults)
13. Paint by numbers
14. Diamond painting
DIY creative hobbies and crafts
15. Soap making
16. Resin molding
17. Button making
18. Candle making
19. Basket weaving
20. Terrazzo
21. Sand art bottles
22. String art
23. Perler beads
24. Seed beading
25. Wreath making
Industrial creative hobbies
26. Woodworking
27. Woodturning
28. Wood burning (pyrography)
29. Glass blowing
30. Glass etching
31. Stained glass art
32. Concrete molds
33. Jewelry making
34. Leather working
35. Metalworking and welding
36. Metal embossing
37. Mosaics
Sculpting and carving hobbies
38. Sculpting
39. Ice sculpting
40. Wood carving
41. Pottery
42. Soap carving
43. Sand sculptures and sandcastle building
Printmaking creative hobbies
44. Linocut printmaking
45. Woodcut printmaking
46. Screen printing
47. Rubber stamping
Needlecraft creative hobbies
48. Sewing
49. Cosplay
50. Embroidery
51. Cross-stitching
52. Crewel
53. Needle felting
54. Quilting
55. Crochet
56. Amigurumi
57. Knitting
58. Arm knitting
59. Needlepoint
Fiber arts hobbies
60. Visible mending
61. Macrame
62. Weaving
63. Rug tufting
64. Punch needle
65. Latch hook
66. Lace making
67. Dreamcatchers
Miniature creative hobbies
68. Model building
69. Painting miniatures
70. Dollhouses
71. Fairy gardens
72. Bonkei
73. Diorama making
74. Putz houses and nativity scenes
75. Lego MOC
Stationery and lettering hobbies
76. Calligraphy
77. Hand lettering
78. Art journaling
79. Bullet journaling
80. Card making
81. Scrapbooking
Papercraft creative hobbies
82. Origami
83. Papercraft modeling
84. Paper quilling
85. Collage art
86. Paper making
87. Bookbinding
88. Pop-up making
89. Paper mache
Digital creative hobbies
90. 3D printing
91. Stop motion animation
92. Graphic design
93. Photo manipulation
94. Game development
95. Raspberry Pi
Plant-related creative hobbies
96. Bonsai
97. Tree shaping (Pooktre)
98. Terrariums
99. Aquascaping
100. Flower pressing
101. Flower arranging
102. Topiary gardening
103. Seed art
104. Rock gardening
Other creative hobbies and crafts
105. Puzzles
106. Sudoku
107. Crossword puzzles
108. Writing
109. Learning a foreign language
110. Cooking
111. Music
112. Photography
113. Dancing
114. Sports
115. Improv
116. Nail art
117. Baking
118. Magic
119. Tarot cards
120. Card stacking
121. Collecting
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
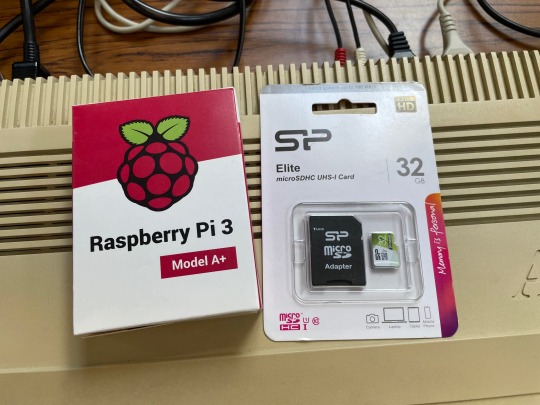

I've been waiting years to get my hands on a Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ so that I can try the PiStorm project in my Amiga 500
If you're not familiar, it allows for the Motorola 68000 CPU of an Amiga to be replaced with a Raspberry Pi that in turn emulates the original CPU in software.
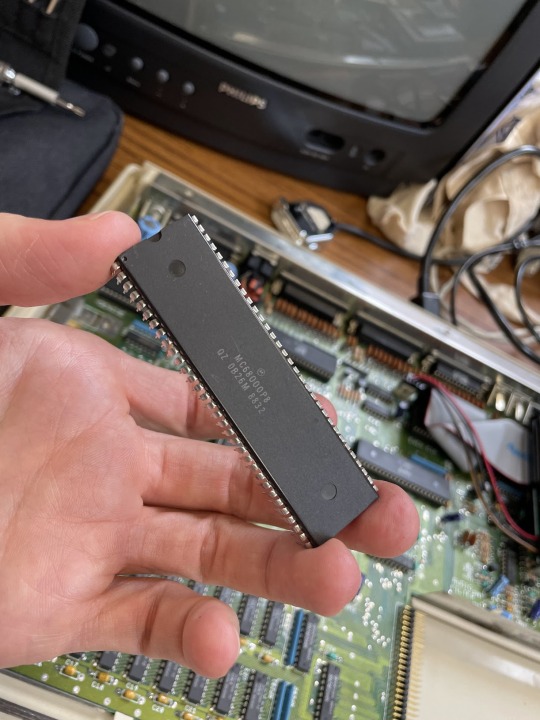


At a basic level this lets you upgrade the performance of the Amiga, as it's possible to run at much faster speeds than the original CPU. Very useful
However that's only the start of the feature set. You can also simulate additional memory, hard drive support, retargetable graphics (to output via the Pi's HDMI port), networking support, upgrading the native Kickstart ROM and more.
Essentially as the CPU socket has access to all the components of the Amiga, it has the capability to override and replace any of these native chips.
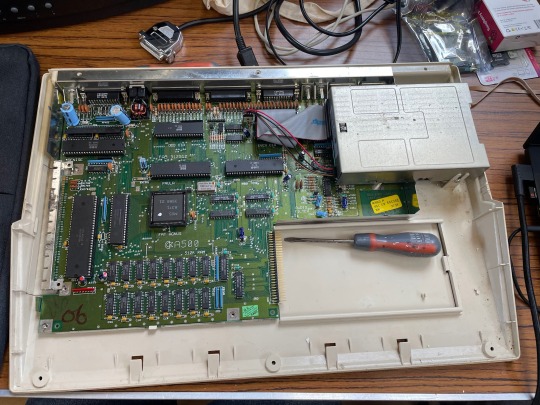
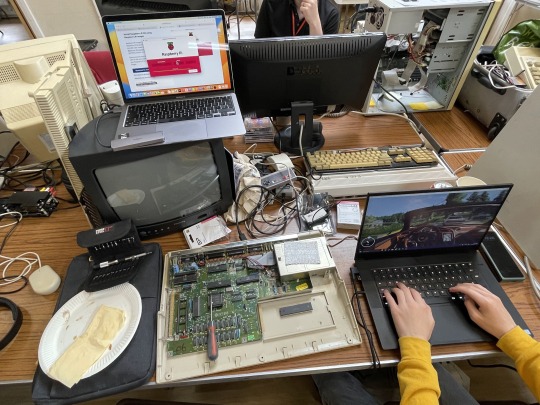


What better excuse and environment to perform the upgrade than the September 2023 SWAG meet up.
After cracking open my A500 for the first time I gently unseated the 68000 from it's socket and prepared to install the PiStorm. It was only then I realised I'd forgotten to bring the vital component, a small board that allows the Pi to connect to the 68000 socket! Oh well, an excuse to play some games instead!

Once I was back in my workshop at home I decided to finish the job. Thankfully with all the correct hardware at hand it was a quick and easy task to get it up and running.
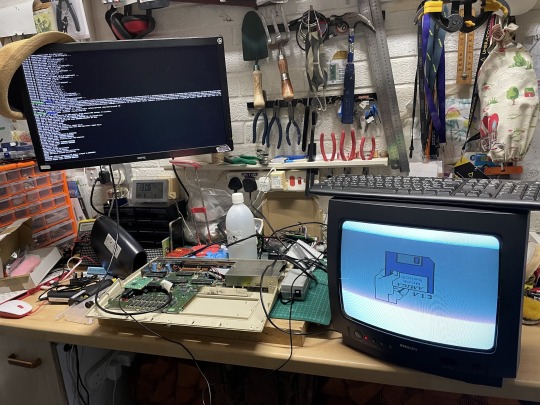
It was certainly quite a nice feeling the first time I started the emulator on the Pi and was rewarded by similar the familiar Kickstart 1.3 appear on the CRT monitor connected to the Amiga.
Seeing old and new hardware work in tandem always gives me a buzz
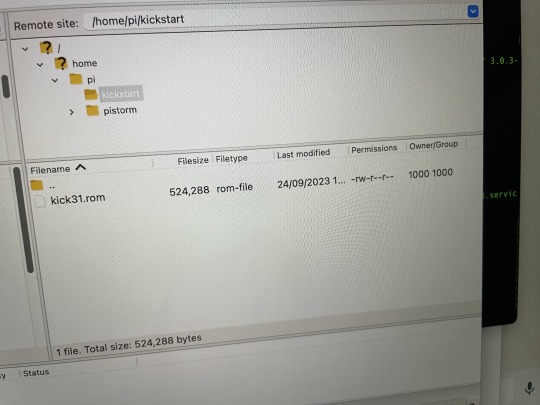

Finally I setup an FTP server on the Pi that enabled me to easily copy across a newer Kickstart version. After restarting the emulator on the Pi suddenly my A500 felt a lot newer.
Next on my list, to setup a virtual hard drive filled with classic games
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mythbusting Generative AI: The Ethical ChatGPT Is Out There
I've been hyperfixating learning a lot about Generative AI recently and here's what I've found - genAI doesn’t just apply to chatGPT or other large language models.
Small Language Models (specialised and more efficient versions of the large models)
are also generative
can perform in a similar way to large models for many writing and reasoning tasks
are community-trained on ethical data
and can run on your laptop.

"But isn't analytical AI good and generative AI bad?"
Fact: Generative AI creates stuff and is also used for analysis
In the past, before recent generative AI developments, most analytical AI relied on traditional machine learning models. But now the two are becoming more intertwined. Gen AI is being used to perform analytical tasks – they are no longer two distinct, separate categories. The models are being used synergistically.
For example, Oxford University in the UK is partnering with open.ai to use generative AI (ChatGPT-Edu) to support analytical work in areas like health research and climate change.

"But Generative AI stole fanfic. That makes any use of it inherently wrong."
Fact: there are Generative AI models developed on ethical data sets
Yes, many large language models scraped sites like AO3 without consent, incorporating these into their datasets to train on. That’s not okay.
But there are Small Language Models (compact, less powerful versions of LLMs) being developed which are built on transparent, opt-in, community-curated data sets – and that can still perform generative AI functions in the same way that the LLMS do (just not as powerfully). You can even build one yourself.

No it's actually really cool! Some real-life examples:
Dolly (Databricks): Trained on open, crowd-sourced instructions
RedPajama (Together.ai): Focused on creative-commons licensed and public domain data
There's a ton more examples here.
(A word of warning: there are some SLMs like Microsoft’s Phi-3 that have likely been trained on some of the datasets hosted on the platform huggingface (which include scraped web content like from AO3), and these big companies are being deliberately sketchy about where their datasets came from - so the key is to check the data set. All SLMs should be transparent about what datasets they’re using).
"But AI harms the environment, so any use is unethical."
Fact: There are small language models that don't use massive centralised data centres.
SLMs run on less energy, don’t require cloud servers or data centres, and can be used on laptops, phones, Raspberry Pi’s (basically running AI locally on your own device instead of relying on remote data centres)
If you're interested -
You can build your own SLM and even train it on your own data.

Let's recap
Generative AI doesn't just include the big tools like chatGPT - it includes the Small Language Models that you can run ethically and locally
Some LLMs are trained on fanfic scraped from AO3 without consent. That's not okay
But ethical SLMs exist, which are developed on open, community-curated data that aims to avoid bias and misinformation - and you can even train your own models
These models can run on laptops and phones, using less energy
AI is a tool, it's up to humans to wield it responsibly

It means everything – and nothing
Everything – in the sense that it might remove some of the barriers and concerns people have which makes them reluctant to use AI. This may lead to more people using it - which will raise more questions on how to use it well.
It also means that nothing's changed – because even these ethical Small Language Models should be used in the same way as the other AI tools - ethically, transparently and responsibly.
So now what? Now, more than ever, we need to be having an open, respectful and curious discussion on how to use AI well in writing.
In the area of creative writing, it has the potential to be an awesome and insightful tool - a psychological mirror to analyse yourself through your stories, a narrative experimentation device (e.g. in the form of RPGs), to identify themes or emotional patterns in your fics and brainstorming when you get stuck -
but it also has capacity for great darkness too. It can steal your voice (and the voice of others), damage fandom community spirit, foster tech dependency and shortcut the whole creative process.

Just to add my two pence at the end - I don't think it has to be so all-or-nothing. AI shouldn't replace elements we love about fandom community; rather it can help fill the gaps and pick up the slack when people aren't available, or to help writers who, for whatever reason, struggle or don't have access to fan communities.
People who use AI as a tool are also part of fandom community. Let's keep talking about how to use AI well.
Feel free to push back on this, DM me or leave me an ask (the anon function is on for people who need it to be). You can also read more on my FAQ for an AI-using fanfic writer Master Post in which I reflect on AI transparency, ethics and something I call 'McWriting'.
#fandom#fanfiction#ethical ai#ai discourse#writing#writers#writing process#writing with ai#generative ai#my ai posts
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
FRISK FUN FACTS!
Last but not least, fun facts bout Friskyyy!
Birthday: 3. March
"I was born half an hour earlier than Chara, she almost got birthed on a different day. Would have been nice, to not share a birthday."
Favorite color: Red, Black, Yellow
"I wear a lot of red or black, but for different reasons~"
Liked food: Stollen, Kaiserschmarrn, Apfelstrudel, Burgers, anything Japanese
"Since I was born german, I can't help but like my roots, at least when it comes to food. But Japanese cuisines are just fantastic."
Absolute favorite food: Apple pie
"Toriel used to make them, my Toriel. We had an apple tree in our backyard, which she used for the pie. Even when using fire magic, the real magic was her pies."
Favorite music genres: Metal, Weirdcore, Guitar, 8-bit, Indi Rock, Glitch Hop, Horrorcore, Dark Ambient, Vaportrap
"Dee always said I had a strange taste in music, but at least we have a bit of them in common."
Favorite band (in Universe): End Strangers, Rse Dncrs, Phantoma, Calipso, Poison Jar
"I introduced Sans to End Strangers. I remember it like yesterday. We were sitting on the edge of a building, after a successful raid, the sun was setting, and he was exhausted. I pulled my phone out, and simply played it. It felt- it was beautiful. I miss those times... No... No they were awful. Maybe the moment was so nice because of the times surrounding it."
Favorite Songs (in Universe): Do it all again, Purgatory, Transcending Lines, Mourning every Summer Sunday, We are the coolest Loosers, Burned plastic flowers
"Do it all again was a fantastic end to Poison Jar's latest album. We both loved it a lot. Although Dee said it was a bit calmer than he anticipated. I liked it."
Favorite Icecream flavors: Black raspberry, Butterscotch, Blue moon, Dark Chocolate
"Sometimes I steal some strawberry from him. But he licks some of my Black raspberry from me as well."
Favorite hobby: Drawing, Crochet, Sewing, Baking, Programming
"Sans had to be my model for a lot of things. It was amazing to design him new clothes. At first, he protested severely, but he came around. I took some pictures, made it into my own little fashion magazine. We used to have more time together, chilling at a beach, and I used to draw him. It was a nice feeling, the wind, the sounds of the waves, but it also reminded me of how everything always changes, how quick the waves flushed back, how the wind picks up or calms down. How the sun slowly lowers on the horizon. I know we are both stuck living for an eternity, and that good and bad times come and go... But sometimes I wish I could stop time, and simply keep him close.
... Oh my, I rambled, didn't I? That wasn't my intention!"
Favorite book (in Universe): "Desert sand glass" by Jenna Wales
"It was... a fascinating book. It explored so many different concepts, and honestly I couldn't begin to comprehend what it is actually about. It was a strange but welcome journey..."
"There was a time when they were completely mesmerized with it, didn't even come to dinner."
"The food went cold unfortunately..."
"Even though you requested that I make ramen. It took ages too..."
"I'm sorry. I couldn't put it away. But the cold ramen were lovely as well."
Plays instrument: Piano, Electric Guitar/ Guitar
"Asgore had taught me piano, I picked up really quick, it took roughly 4 years. I had learned Guitar as a way to waste time, I had not much else to do in the time when Sans went to the army. That and learning how to fight as well, of course."
Best memory:
"Oh wow, okay, well my best memory was when Dee cooked for me, for the first time. It was... well, it wasn't very good at all."
"HEY I WAS STILL LEARNING!"
"Yes, I know. It's just, the fact that, despite your hate towards me at the time, you cared enough about me to cook for me, it... made the food more delicious."
"I-I didn't hate you THAT much..."
"Honey, you insulted me with every breath you made, not to mention you tried to kill me. Several times."
"Ouch... I forgot about that... Sorry."
"It's alright."
Worst memory:
"Can I skip this? I'd rather not answer, I hope you understand."
Favorite thing to wear:
"Oh, I have this beautiful golden dress. I only wear it to special occasions! Other than that, I honestly just steal Sansy's hoodies. Don't tell him~"
Since you skipped one, you have to answer this one!
Relationship to Sans:
"Cruel. We are just friends. Best friends, I would say....
If it were for me... I'd call us family, but then again, I don't think I deserve to call myself his..."
Random fun facts!
Frisk is genderfluid! But in more ways than you might think! Since their body is made from dust, and monsters being resonant with the emotions around and within them, Frisk had figured out how to manipulate the body that has been given to them to suit their current gender identity! ((I'm jealous))
Frisk's full name is Frisk Dreemurr, since they officially got adopted by the Dreemurrs!
Sans gave Frisk the nickname Bee, not only to get back at them for giving him the nickname Dee, but also because they have the tendency to call people 'Honey' and especially because of the following incident that happened shortly after leaving the anti-void for the first time!=
They were walking through the strange new world they had accidentally landed in, everything was much taller than them, but Frisk wanted to get a good view, so, they climbed on a nearby tree, it was gigantic, and looked at their surroundings, spotting a small village 'nearby' still a few kilometers away from them.
However, Dee screamed if they see anything and with that, surprising Frisk, who fell through the giant branches, into a big bee hive, they both crash to the ground. Frisk was covered in honey, and then they were chased by murderous bees. They escaped into water where frogs immediately tried to eat the swarms, turning into a battle field.
They luckily got out of there.
"But it was fucking hilarious. The shocked dumb expression you had was PRICELESS!"
"Thanks that you find our near deaths amusing."
Frisk's favorite tea flavor is golden flower, they like it with a tint of irony, reflecting back on the history they have with that flower.
They are also an excellent gardener, learning a lot from Asgore in the time they were with the Dreemurrs.
Currently, Frisk owns 430 different types of tea. They love to drink it in a special place, which only they and Dee have access to.
I hope you enjoyed this little information dump, if you got more questions about Frisk, leave a comment!
#red mass#undertale au#frisk#undertale au story#oc#FUN FACTS!#They also consume a ridiculous amount of anime#Their eye color is red btw#since you haven't seen it yet xdd
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Raspberry Pi Board: Revolutionizing Computing and Education

The Raspberry Pi board is a series of small, affordable single-board computers developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation, a UK-based charity focused on promoting computer science education and digital literacy. Since its launch in 2012, the Raspberry Pi has transformed from a niche educational tool into a versatile platform used in a wide range of applications, from DIY electronics projects to industrial automation.
A Brief History
The first Raspberry Pi, the Model B, was released in February 2012. Designed to promote basic computer science in schools and developing countries, it featured a 700 MHz ARM11 processor, 256 MB of RAM, and basic connectivity options. The success of the Model B led to a rapid expansion of the Raspberry Pi lineup, with various models offering improved performance, more memory, and enhanced connectivity.
Key Features and Models
Raspberry Pi 1 Model B (2012):
Processor: 700 MHz ARM11
Memory: 256 MB RAM
Ports: 2 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Storage: SD card slot
Raspberry Pi 2 Model B (2015):
Processor: 900 MHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A7
Memory: 1 GB RAM
Ports: 4 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Storage: MicroSD card slot
Raspberry Pi 3 Model B (2016):
Processor: 1.2 GHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A53
Memory: 1 GB RAM
Ports: 4 USB 2.0 ports, HDMI, Composite video, 3.5mm audio jack, Ethernet
Wireless: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B (2019):
Processor: 1.5 GHz quad-core ARM Cortex-A72
Memory: Options of 2 GB, 4 GB, and 8 GB RAM
Ports: 2 USB 3.0 ports, 2 USB 2.0 ports, 2 Micro HDMI ports, Ethernet, USB-C for power
Wireless: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Raspberry Pi Zero (2015) and Zero W (2017):
Processor: 1 GHz single-core ARM11
Memory: 512 MB RAM
Ports: Mini HDMI, Micro USB OTG, Micro USB for power, GPIO pins
Wireless (Zero W): Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Applications and Uses
The versatility of the Raspberry Pi has led to its adoption in numerous fields:
Education:
Coding and Programming: Used in schools and educational programs to teach students programming languages such as Python, Scratch, and Java.
Computer Science Concepts: Introduces concepts like hardware, software, and networking.
DIY Projects and Maker Community:
Home Automation: Controls smart home devices, including lights, thermostats, and security systems.
Media Centers: Powers home media centers using software like Kodi.
Retro Gaming: Emulates classic gaming consoles using software like RetroPie.
Industrial and Commercial Applications:
IoT Devices: Serves as a hub for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling data collection and remote control.
Automation and Control Systems: Used in factories and labs for monitoring and controlling equipment.
Research and Development:
Prototyping: Facilitates rapid prototyping of electronic devices and systems.
Data Collection: Gathers data from various sensors in environmental and scientific research.
Community and Ecosystem
The Raspberry Pi has cultivated a vibrant global community of developers, hobbyists, educators, and students. Online forums, tutorials, and community projects provide extensive support and resources for users at all skill levels. The Raspberry Pi Foundation also offers official accessories, including cases, cameras, and expansion boards, further enhancing the functionality of the Raspberry Pi.
Conclusion
The Raspberry Pi board has revolutionized the way people learn about and interact with technology. Its affordability, versatility, and extensive support network have made it an indispensable tool in education, DIY projects, and professional applications. As technology continues to evolve, the Raspberry Pi Foundation remains committed to expanding the capabilities and accessibility of this remarkable platform, ensuring that computing remains within reach for everyone.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Making your own Home Assistant (theorising)
Disclaimer: This is all theory and speculation. I have not tested anything or made my own home assistant yet, I just looked around for libraries and hardware that are likely compatible. I have not fully tested the compatibility or quality of these, this is simply the first iteration of an idea I have.
I just got news that Amazon Alexa has lost 10 billion dollars because their business model failed. This makes me happy, and has also made me realise that you can make your own home assistant.
Here are some of the links to things (I am aware that some are amazon, but it's the most global I could find. I encourage you to find other sellers, this is just what you should need. If you find anything cheaper or more local to where you are, go for it):
Hardware:
Raspberry Pi 4: https://www.canakit.com/raspberry-pi-4-2gb.html (RAM requirements may differ, I may do testing to see what comfortably runs)
8GB MicroSD: https://www.amazon.ca/Verbatim-Premium-microSDHC-Adapter-10-44081/dp/B00CBAUI40/ref=sr_1_3?crid=3CTN6X9TJXRR2&keywords=microsd%2Bcard%2B8gb&qid=1699209597&s=electronics&sprefix=microsd%2Bcard%2B8gb%2Celectronics%2C91&sr=1-3&th=1
Microphone: https://www.amazon.ca/SunFounder-Microphone-Raspberry-Recognition-Software/dp/B01KLRBHGM?th=1
Software:
Coqui STT: https://github.com/coqui-ai/STT
Coqui TTS: https://github.com/coqui-ai/TTS
If you have it set up correctly, you should be able to run both the STT and TTS in realtime (see https://github.com/coqui-ai/TTS/discussions/904).
After all of them are set up, the only thing to do is bridge it all together with software. There are bindings to Rust for both Coqui libraries (https://github.com/tazz4843/coqui-stt and https://github.com/rowan-sl/coqui-rs), and all that's left to do is implement parsing.
The libraries can also be swapped out for different ones if you like. If you can find and implement a DECtalk library that works for the Raspberry Pi, you can use that.
If I ever figure out how to manifest this idea, I will likely make the project modular so that you can use whatever library you want. You can even fork the project and include your own library of choice (if you can bind it to Rust).
Go FOSS!
#foss#open source#raspberry pi#technology#amazon#alexa#home assistant#coqui#rust#dectalk#programming#engineering#coding#software#software engineering#github#mozilla#hardware#computer engineering
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
27 czerwca 2025

◢ #unknownews ◣
Zapraszam do lektury dzisiejszego newslettera.
Sponsorem tego wydania newslettera jest firma Hostinger — najszybciej rozwijająca się firma hostingowa na świecie, obsługująca już ponad 3.5 miliona użytkowników z całego świata. W ofercie firmy poza klasycznym hostingiem współdzielonym znajdziesz także wysokowydajne serwery VPS działające na procesorach AMD EPYC, z wbudowaną ochroną Anty-DDoS, z łączem symetrycznym 1000 Mb/s, łatwym skalowaniem zasobów i wieloma lokalizacjami datacenter do wyboru. W ofercie znajdziesz cztery modele serwerów VPS, które obecnie przecenione są do 67%, ale korzystając z kodu "JAKUB" (możesz wpisać go w koszyku), możesz zaoszczędzić jeszcze więcej.
1) Jak może wyglądać test rekrutacyjny do CIA dla początkujących? (film, 20m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kLntZF5oD8g INFO: Autor filmu postanowił zmierzyć się z testem, który rzekomo przypomina pierwszy etap rekrutacji do CIA. Test koncentruje się na logicznym myśleniu, analizie informacji i szybkości działania z mocnym naciskiem na techniki OSINT. Choć to tylko nieoficjalna wersja testu, materiał daje dobry wgląd w to, jak mogą wyglądać takie zadania sprawdzające zdolność logicznego rozumowania kandydatów do wywiadu. Film dla fanów OSINT i cybersecurity.
2) Stan jakości kodu generowanego przez AI w 2025 roku - raport od Qodo https://www.qodo.ai/reports/state-of-ai-code-quality/ INFO: "Sztuczna inteligencja generuje straszny kod! Tego się nawet czytać nie da!" to stwierdzenie powtarzane niczym mantra przez programistów, którzy... nie za często z AI korzystają. ;) Linkuję do badania z udziałem 609 programistów, którzy w większości codziennie lub wiele razy dziennie korzystają ze sztucznej inteligencji w swojej pracy. Jak oceniają pracę z AI? Czy ich produktywność spadła, czy wzrosła? Czy jakość tworzonego w projektach kodu polepszyła się? Ciekawe badanie. Jest sporo narzekania, ale i sporo imponujących efektów osiągniętych dzięki AI.
3) Dlaczego Raspberry Pi 4 może być za wolne jako serwer? https://ergaster.org/posts/2025/06/24-why-restore-raspi-slow/ INFO: Autor wpadł na pomysł, aby przenieść wszystkie usługi ze swojego serwera VPS na domowe Raspberry Pi 4 z 8 GB RAM-u i dyskiem NVMe podpiętym przez USB3, co wydaje się całkiem mocną konfiguracją. Migracja miała być przeprowadzona poprzez wykonanie kopii bezpieczeństwa serwera do usługi S3 i późniejsze odtworzenie tej kopii na malince. Jak się jednak okazało, prędkość odtwarzania wynosiła 13 B/s (tak, bajtów). Skąd tak wolne działanie urządzenia? Co było wąskim gardłem? Czy chodziło o sieć, dysk twardy, procesor, czy może jeszcze coś innego? Autor przeprowadza śledztwo w tej sprawie.
4) Dlaczego argumentacja punkt po punkcie może być szkodliwa w dyskusjach technicznych https://www.seangoedecke.com/point-by-point-considered-harmful/?= INFO: Przekonujący się wzajemnie do swoich racji pracownicy techniczni prowadzą rozmowę w bardzo specyficzny sposób. Rozbijają omawiany problem na listę argumentów, a później przechodzą kolejno przez listę, omawiając każdy jej punkt, jakby był oddzielnym problemem do rozwiązania, zamiast traktować problem jako całość. Autor przekonuje jednak, że w sytuacjach spornych takie podejście może prowadzić do bezowocnych debat i częstych frustracji, a bardziej efektywne jest skupienie się na głównym przesłaniu i pytaniu, co naprawdę blokuje drugą stronę. Artykuł dostarcza praktycznych wskazówek, jak skuteczniej dyskutować i unikać pułapek wspomnianego 'technicznego ping-ponga', który niczego nie rozwiązuje.
5) Darmowy kurs OWASP Top 10 z praktycznymi labami (3 h+ filmów i laby) https://owasp.10minuteshack.com/pl/ INFO: Szkolenie wprowadza uczestnika w tematykę bezpieczeństwa aplikacji webowych w oparciu o OWASP Top 10 i łączy teorię z praktyką (laby wykonane na podatnej aplikacji Juice Shop). Kurs trwa ok. 3–4 godziny i nie wymaga doświadczenia programistycznego, a jego celem jest nauczenie wykrywania i naprawiania realnych podatności. Materiały wideo są po polsku, a całość dostępna jest za darmo – wystarczy podać e-mail, żeby uzyskać dostęp. Do kursu dodano także bonusowy rozdział dotyczący bezpiecznego zastosowania sztucznej inteligencji w projektach.
6) Darmowy dostęp do ChatGPT, Claude i innych modeli w chmurze (film, 15m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vSWr9ew9opc INFO: LM Arena to platforma umożliwiająca darmowe testowanie i porównywanie wyników z wielu modeli językowych (a jest ich do wyboru całkiem sporo). Film pokazuje, jak korzystać ze wszystkich funkcji serwisu: testowanie modeli na ślepo, bezpośrednie porównania odpowiedzi, aktualizowany ranking modeli czy możliwość czatowania bezpośrednio z konkretnym LLM-em. Dodatkowo omawiany jest model "Flux Context" służący do generowania obrazów AI, który zachowuje kontekst zdjęcia, modyfikując jedynie wskazane elementy.
7) Wydajne i solidne serwery VPS do zastosowań profesjonalnych i hobbystycznych [sponsorowane] https://www.hostg.xyz/SHHdB INFO: Jeśli szukasz serwera do hostowania swoich projektów, czy strony firmowej, czy nawet startupu, to ta oferta jest dla Ciebie. Skorzystaj z ograniczonej czasowo promocji i kup serwer VPS do 67% taniej. Pamiętaj, że z kodem "JAKUB" zyskasz dodatkowe 10% zniżki.
8) Jak działają "residential proxy" i dlaczego stały się fundamentem cyberprzestępczości? https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/security/news/cybercrime-and-digital-threats/the-rise-of-residential-proxies-and-its-impact-on-cyber-risk-exposure-management INFO: Prywatni użytkownicy internetu coraz częściej udostępniają swoje łącze internetowe w zamian za różne benefity (najczęściej finansowe). Prowadzi to do sytuacji, w której dowolna osoba może kupić dostęp do serwera proxy postawionego na takim łączu, co chętnie wykorzystują przestępcy do ukrycia swojego prawdziwego adresu IP. Przepuszczanie ruchu przez "domowe" łącza pozwala także omijać liczne zabezpieczenia, których nie da się obejść korzystając z VPN-ów czy komercyjnych serwerów. To zjawisko tworzy niemały problem dla branży cybersecurity, bo jak odciąć ataki wykonywane z domowych sieci?
9) Jak pojedynczy błąd sparaliżował Google Cloud i pół internetu https://blog.bytebytego.com/how-the-google-cloud-outage-crashed INFO: 12 czerwca 2025 platforma Google Cloud zaliczyła globalną awarię, która sparaliżowała działanie takich serwisów jak Gmail, Spotify, Discord, GitLab czy Cloudflare. Artykuł omawia, co od strony technicznej było przyczyną tej sytuacji, dlaczego awaria się rozprzestrzeniała i jak ostatecznie Google sobie z nią poradziło. Błąd dość szybko usunięto, ale pokazał on w ciekawy sposób skalę zależności między komponentami w infrastrukturze chmurowej.
10) Dlaczego warto budować zespoły dla „normalnych” inżynierów? https://charity.wtf/2025/06/19/in-praise-of-normal-engineers/ INFO: W sieci popularny jest mit "10x engineer", czyli takiego superproduktywnego gościa, który pracuje szybciej, dokładniej i sprawniej od innych członków zespołu. Tylko czy zespoły w firmie powinny być budowane z myślą o takich właśnie pracownikach? Autor rozprawia się z mitem "10x inżyniera", pokazując, że nawet jeśli istnieją w firmie jednostki wyjątkowo produktywne, to nie mają one większego znaczenia bez dobrze funkcjonującego zespołu. Podkreśla, że największą wartość dla organizacji przynosi tworzenie środowisk, w których przeciętni, ale solidni inżynierowie mogą efektywnie pracować i rozwijać się. Według autora, długofalowy sukces firmy zbudowany jest nie na pojedynczych geniuszach, a na tych zupełnie "normalnych" pracownikach.
11) Przyszłość ekonomii twórców 2025 – raport od Epidemic Sound https://downloads.ctfassets.net/js6ap5wzepad/6fum3OU3owMjSM9fgCGUCu/e975f6e9492c10554b37f015a4f58584/The_Future_of_the_Creator_Economy_Report_2025_Epidemic_Sound.pdf INFO: Raport omawia obecny stan, jak i przewidywania dotyczące branży twórców internetowych w 2025 roku. Na czym i ile zarabiają, ile źródeł dochodów posiadają, jak wykorzystują w swojej pracy AI i wiele innych. To, co mnie zaskoczyło w raporcie, to procent twórców zajmujących się tworzeniem treści pełnoetatowo oraz platforma, na której chcą się w większości najmocniej skupić w tym roku.
12) Tworzenie skutecznych promptów do AI, użytecznych przy programowaniu https://addyo.substack.com/p/the-prompt-engineering-playbook-for INFO: Sposób, w jaki komunikujesz się z asystentem AI, bezpośrednio wpływa na jakość otrzymywanych odpowiedzi i generowanego kodu. Ten poradnik wyjaśnia, jak tworzyć skuteczne prompty poprzez dodanie kontekstu, definiowanie celu, dzielenie zadań na mniejsze kroki oraz stosowanie ról i przykładów wejścia/wyjścia. Autor porównuje dobre i złe prompty, pokazując, jak można lepiej prowadzić rozmowę z AI.
13) Czym jest "levered beta" i dlaczego tego potrzebujesz, tworząc startup? https://textql.notion.site/levered-beta-is-all-you-need-20ba769a508880388186ef0c2fa11389 INFO: Stwórz dopracowany projekt, np. SaaS, przetestuj go dobrze i zdobądź klientów? Niekoniecznie. W branży AI coraz częściej wygrywają firmy, które stawiają na skrajnie szybkie wejście na rynek, szeroką dystrybucję tego, co tworzą, a nie na dopracowywanie swoich produktów do perfekcji. Wykorzystują one trend rynkowy, a nie przewagę technologiczną. Ciekawe i lekko kontrowersyjne podejście do tworzenia produktów.
14) Lista 9 pytań, które warto zadać, gdy zauważysz spadek wydajności pracownika https://newsletter.canopy.is/p/9-questions-to-ask-when-you-start?= INFO: Czasem pierwsze oznaki spadku wydajności są subtelne i łatwo je przeoczyć. Ktoś staje się mniej zaangażowany, popełnia drobne błędy, a czasami zachowuje się inaczej niż zwykle. Autorka podpowiada, jak w takiej sytuacji zareagować z empatią i skutecznie zacząć rozmowę, która pozwoli zrozumieć kontekst i wspólnie poszukać jakiegoś rozwiązania. Omawia 9 konkretnych pytań, które pomagają rozpocząć taką trudną rozmowę, ale bez oceniania i bez naruszania prywatności drugiej osoby.
15) Czy teraz jest najlepszy moment, aby nauczyć się programowania? https://substack.com/home/post/p-165655726 INFO: Sporo się teraz mówi o tym, że programiści stracą pracę, a AI zajmie ich miejsce. Autor tego artykułu ma odmienne zdanie. Podkreśla, że aktualne czasy — ze względu na dostępność narzędzi i demokratyzację technologii — sprzyjają osobom chcącym rozwijać się w programowaniu. Nawet niezależni twórcy mają dziś większe możliwości przebicia się niż kiedykolwiek wcześniej.
16) Jak korzystam z terminala? - zaawansowany workflow z tmux, zsh i nvim https://jyn.dev/how-i-use-my-terminal/ INFO: Autor pokazuje konfigurację swojego terminala, w której całość pracy (od SSH, przez wyszukiwanie plików, po otwieranie ich w podzielonym edytorze) dzieje się z użyciem tmuxa i tylko z poziomu terminala. Interfejsy takie jak ripgrep, zoxide, własne skrypty w Perlu i niestandardowe skróty klawiszowe pozwalają zrealizować funkcje znane z nowoczesnych IDE, ale w tym minimalistycznym środowisku tekstowym. Całość opiera się na sprytnym rozszerzeniu możliwości tmuxa.
17) Jak Cloudflare zablokowało rekordowy atak DDoS o mocy 7,3 Tbps https://blog.cloudflare.com/defending-the-internet-how-cloudflare-blocked-a-monumental-7-3-tbps-ddos/ INFO: W maju 2025 Cloudflare powstrzymało ponad 7,3 Tbps ataku, który w zaledwie 45 sekund wygenerował ponad 37 TB danych i uderzył w klienta korzystającego z usługi Magic Transit. Atak był wielowektorowy, dominowały w nim zalewy pakietami UDP, ale pojawiły się także mniej popularne techniki (od QOTD, czy Echo po RIPv1). Artykuł szczegółowo omawia mechanizmy obronne Cloudflare oraz podpowiada, jak nie stać się przypadkiem pośrednikiem realizacji takich ataków.
18) Które umiejętności zyskają na wartości w erze AI? https://80000hours.org/agi/guide/skills-ai-makes-valuable/ INFO: Artykuł wyjaśnia, dlaczego automatyzacja wcale nie musi prowadzić do masowej utraty miejsc pracy, a wręcz może zwiększyć zapotrzebowanie na niektóre umiejętności – zwłaszcza te trudne do zautomatyzowania, te, które uzupełniają się z AI lub takie, których efekty można łatwo skalować. Autor wymienia konkretne kategorie kompetencji, które najprawdopodobniej zyskają na znaczeniu w nadchodzących latach i które warto zdobywać. Sporo przemyśleń na temat tego, jak nie stracić pracy w tych zmieniających się czasach i utrzymać dobrą pozycję na rynku pracy.
19) Trzy podatności SSRF w Azure DevOps - jak zostały odnalezione https://binsec.no/posts/2025/01/finding-ssrfs-in-devops INFO: Autorzy artykułu odnaleźli trzy podatności typu SSRF (Server-Side Request Forgery) w Azure DevOps i pokazali, jak można je wykorzystać, m.in. za pomocą DNS rebindingu i CRLF injection. Główny wektor ataku opiera się na słabej walidacji parametrów używanych w jednym z endpointów w API, co umożliwia wysyłanie żądań do dowolnych adresów, także z uprawnieniami ARM (Azure Resource Manager). Dobra lektura dla pentesterów i fanów cyberbezpieczeństwa.
20) Raycast trafia na Windowsa - pierwsze spojrzenie (film, 7m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YKARc05qixw INFO: Jeden z najpopularniejszych launcherów aplikacji na macOS (nie licząc Spotlighta oczywiście) trafia na Windowsa. Obecnie dostępny jest jedynie w wersji beta, ale prezentuje się znakomicie. Używam go na Macu od lat i mocno wpłynął on na wzrost mojej produktywności. Aplikacja pozwala szybko uruchamiać aplikacje, przeszukiwać pliki, zarządzać schowkiem, wykonywać obliczenia matematyczne, przeliczać waluty, integrować się z AI i wiele innych. Jeśli jesteś użytkownikiem Windowsa i jeszcze nigdy nie pracowałeś z launcherem tego typu, to zacznij od Raycasta.
21) Oferta Mikrusa dla posiadaczy "uczelnianych" maili https://edu.mikr.us/ INFO: Jeśli jesteś studentem i masz uczelniany adres mailowy (np. kończący się na .edu.pl), możesz bez żadnych formalności i zobowiązań odebrać paczkę kursów online. W skład paczki wchodzi 5 kursów online (przetwarzanie danych tekstowych w terminalu, podstawy wyrażeń regularnych, praca z curl, debugowanie aplikacji webowych i podstawy Javy) o łącznej wartości ponad 190 zł.
22) Oszuści wstrzykują fałszywe numery telefonów do wyników wyszukiwania https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/news/2025/06/scammers-hijack-websites-of-bank-of-america-netflix-microsoft-and-more-to-insert-fake-phone-number INFO: Scamerzy wykorzystują reklamy sponsorowane w Google, aby przekierowywać użytkowników na prawdziwe strony znanych marek (np. Netflix, Apple czy PayPal), ale z podmienionym numerem telefonu na taki, który prowadzi do fałszywej infolinii. W jaki sposób oszustom udaje się umieścić na prawdziwych stronach swoje numery telefonów? Okazuje się, że technika ataku jest niezwykle prosta. Więcej o tym w artykule.
23) State of Devs 2025 - część pierwsza wyników nowego badania https://2025.stateofdevs.com/en-US INFO: W tym roku badanie koncentruje się nie tylko na technologiach, ale także na zdrowiu, hobby programistów, temacie wypalenia zawodowego, dyskryminacji w pracy i innych aspektach pracy programisty. W badaniu wzięło udział 8717 osób. Nie wiem, kiedy opublikowana zostanie druga część wyników, ale już teraz można zapoznać się z tym, co udało się opublikować twórcom.
24) Lista 12 pojęć z inżynierii oprogramowania, które warto znać https://strategizeyourcareer.com/p/the-12-practical-software-engineering-concepts INFO: Zbiór 12 pojęć, takich jak "yak shaving", "scope creep" czy "shotgun debugging", pokazuje, jak często używane terminy w środowisku technicznym mogą usprawniać komunikację, ale też prowadzić do pewnych nieporozumień. Dla każdego pojęcia autor podaje wyjaśnienie i uzasadnia, dlaczego warto znać jego znaczenie nie tylko w kontekście pisania kodu, ale też przy współpracy w zespole. Niektóre z pojęć są zabawne, ale i tak warto je znać, aby zrozumieć pewne zjawiska występujące w branży IT.
25) Lista 600+ realnych wdrożeń gen AI z podziałem na branże i zastosowania https://cloud.google.com/transform/101-real-world-generative-ai-use-cases-from-industry-leaders INFO: Firma Google od pewnego czasu kolekcjonuje przykłady wykorzystania generatywnej sztucznej inteligencji w różnych branżach i obszarach działania. Ostatnio zaktualizowali swoją listę o 280 nowych wpisów. Warto rzucić okiem, aby zobaczyć, jak firmy wdrażają u siebie sztuczną inteligencję i do czego naprawdę jej używają.
26) Jak zintegrować Home Assistant, AdGuard Home i tani smart plug, by ograniczyć social media https://www.romanklasen.com/blog/beating-brainrot-by-button/ INFO: Autor opisuje, jak wykorzystał wspomniane w tytule narzędzia, aby tymczasowo odblokowywać social media w domu, ale tylko na określony czas. Skrypt oparty na automatyzacjach Home Assistanta i API AdGuard pozwala na dynamiczne zarządzanie filtrami DNS przy pomocy fizycznego przycisku. Ciekawe podejście do walki z rozpraszaczami bez całkowitego odcinania internetu. Nawet jeśli nie masz problemu z nadużywaniem social mediów (albo przynajmniej tak uważasz), to i tak warto rzucić okiem na to rozwiązanie jako na przykład ciekawej implementacji automatyzacji w domu.
27) o3-pro już dostępny – czy warto czekać 20 minut na odpowiedź? https://thezvi.substack.com/p/o3-turns-pro INFO: o3-pro to nowa, bardziej zaawansowana wersja modelu o3 od OpenAI, dostępna w ramach subskrypcji ChatGPT Pro i przez API. Według twórców model oferuje dokładniejsze odpowiedzi kosztem znacznie dłuższego czasu oczekiwania (nawet 15–25 minut). Choć model rzeczywiście lepiej radzi sobie m.in. z zadaniami naukowymi i wykazuje mniejszą skłonność do halucynacji, użytkownicy są podzieleni co do tego, czy zyski rekompensują koszty i spowolnienie pracy. Jak nowy model wypada w oficjalnych testach? Więcej w artykule.
28) Agent AI odbierający telefon i robiący notatki – jak go zbudować krok po kroku (film, 24m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xL4HRNX15Xk INFO: Autor filmu pokazuje, jak stworzyć agenta AI, który będzie za Ciebie odbierał telefony, gdy jesteś niedostępny, a następnie przeprowadzi rozmowę z dzwoniącym, zrobi z niej notatki, a na koniec prześle wszystko na wybrany przez Ciebie kanał komunikacji (np. zapisze je w Google Sheets). Projekt oparty jest o integrację platform takich jak ElevenLabs, Twilio i N8N. Użyteczna wiedza, nawet jeżeli nie planujesz robić takiego automatu odbierającego telefony, ale chcesz nauczyć się, jak tworzyć voicebota, który będzie w stanie rozmawiać z użytkownikiem.
29) Modem analogowy bez linii telefonicznej w 2025 roku? (film, 16m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lw4W5S7YRm8 INFO: Autor filmu podjął się wyzwania, aby podłączyć stary, analogowy modem telefoniczny do internetu, ale nie korzystając przy tym z linii telefonicznej i nie ponosząc żadnych opłat za to połączenie. Brzmi to kuriozalnie, ale jednak udało mu się to zrobić za pomocą Raspberry Pi i projektu DreamPi. Film omawia także historyczny kontekst dostępu dial-up w Polsce (numer 0202122 od TPSA), a następnie pokazuje krok po kroku, jak uruchomić własną "symulowaną" centralę telefoniczną i umożliwić połączenie nawet z komputerem z Windows 98 SE. Ciekawe nie tylko dla fanów retro, ale i dla tych, których interesuje nietypowe łączenie technologii oldschoolowej i tej nowoczesnej.
30) Agent AI bez kodowania z użyciem N8N + Groq (film, 14m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LakMi3njfi8 INFO: Autor pokazuje krok po kroku, jak w kilkanaście minut stworzyć własnego agenta AI, który potrafi z nami rozmawiać, wykonywać obliczenia i wysyłać maile. Wykorzystano tutaj narzędzie no-code N8N oraz model językowy LLama-4 hostowany na platformie Groq (aby było szybko i tanio). Film wyjaśnia, jak ustawić logikę działania agenta, dodać integracje (z Gmail oraz kalkulatorem), zdefiniować komunikat systemowy oraz jak bezpiecznie udostępnić agenta publicznie. Dobry materiał na szybki start z tematyką AI agentów.
31) Zarządzanie dużymi zmianami w kodzie dzięki stacked diffs https://devszczepaniak.pl/stacked-diffs/ INFO: Artykuł omawia, czym jest "Stacked Diffs" i jak ta technika ułatwia pracę z dużymi zmianami w kodzie, dzieląc je na mniejsze części. Jest to podejście do pracy z gitem, dzięki któremu proces code review nie blokuje pracy, a samo review przebiega znacznie szybciej i pozwala przeanalizować zmiany bardziej wnikliwie. Autor pokazuje na przykładach, jak można podzielić większe zadania na mniejsze. Jeśli nigdy wcześniej nie słyszałeś o pracy w takim trybie, to koniecznie zapoznaj się z artykułem.
32) Dlaczego inżynierowie nie cierpią swoich menedżerów (i co z tym zrobić) https://terriblesoftware.org/2025/06/24/why-engineers-hate-their-managers-and-what-to-do-about-it/ INFO: Autor, który sam przeszedł drogę od programisty do menedżera, opisuje najczęstsze zachowania menedżerów, które naprawdę wkurzają inżynierów — od przerywania im w środku pracy, przez brak zrozumienia technicznych wyzwań, aż po zabieranie należnych im zasług. Zamiast jednak tylko wskazywać błędy, pokazuje również, co robią najlepsi liderzy, aby praca z nimi była lepsza. Ciekawa lektura zarówno dla menedżerów, jak i ich podwładnych.
33) Pierwsze kroki z mikrokontrolerami na przykładzie PicoBricks (film, 21m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sd42q3OaOrE INFO: Ten film to ciekawe wprowadzenie do świata mikrokontrolerów, od prostych układów logicznych po współczesne "płytki rozwojowe". Pokazane są podstawy programowania i pracy z zestawem PicoBricks, w tym budowa prostych układów, takich jak migająca dioda czy automatyczny przełącznik zmierzchowy. Całość odbywa się zupełnie bez potrzeby lutowania, co sprawia, że poradnik jest przyjazny dla początkujących. Całkiem dobre wprowadzenie dla osób, które do tej pory nie miały styczności z programowaniem mikrokontrolerów.
34) LLM-y nie halucynują — po prostu robią, co do nich należy https://blog.scottlogic.com/2024/09/10/llms-dont-hallucinate.html INFO: Mówi się, że modele językowe często halucynują, czyli zwracają odpowiedzi, które albo nie mają sensu (np. wymyślone fakty), albo są po prostu błędne. Autor tego artykułu analizuje ten popularny termin zwany halucynacją i tłumaczy, że używanie go jest błędem, jeśli chodzi o naturę działania tego procesu. Autor pokazuje, że błędne lub zmyślone odpowiedzi nie są anomalią, lecz normalnym efektem predykcyjnego działania modelu, który nie posiada intencji, wiedzy ani inteligencji, a jedynie przewiduje najbardziej prawdopodobne kolejne słowa. Ciekawe rozważania na temat tego, jak działają modele językowe.
35) Hurl - narzędzie CLI do testowania zapytań HTTP w formacie tekstowym https://github.com/Orange-OpenSource/hurl INFO: Aplikacja pozwala tworzyć uproszczone zapytania HTTP zapisane w formacie tekstowym, w których można łączyć żądania, przechwytywać i wykorzystywać dane oraz walidować odpowiedzi. Wspiera REST, SOAP, GraphQL oraz inne protokoły oparte na JSON/XML. Umożliwia też testowanie szybkości odpowiedzi i generowanie raportów. Narzędzie działa w oparciu o CURL-a i świetnie sprawdza się zarówno lokalnie, jak i w pipeline w ramach CI/CD.
36) Microsoftowy edytor tekstu Edit dostępny na Linuksa https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2025/06/microsoft-edit-text-editor-ubuntu INFO: Edit to nowy, open-source’owy edytor tekstu Microsoftu działający w terminalu, zbudowany w Rust i zaprojektowany jako prosty odpowiednik klasycznego edytora znanego jeszcze z czasów MS-DOS. Działa na Linuksie, macOS i Windowsie, oferując intuicyjny interfejs TUI (nie trzeba uczyć się komend jak w VIM), znajome skróty klawiszowe (inspirowane VSCode), szybkie działanie i podstawowe funkcje edycyjne. Choć nie zastąpi zaawansowanych narzędzi typu Vim czy Nano, może być lekką alternatywą dla prostych zadań tekstowych, zwłaszcza dla bardzo początkujących użytkowników.
== LINKI TYLKO DLA PATRONÓW ==
37) Pełen kurs animacji webowej – biblioteka GSAP i projekt z React i Tailwind (film, 2h i 28min) https://uw7.org/un_5785b1409065e INFO: Ponad dwugodzinny kurs, w którym krok po kroku tworzony jest animowany landing page oparty o React, TailwindCSS i bibliotekę GSAP. Autor nie pokazuje najprostszych animacji, a skupia się na bardziej zaawansowanych przykładach, które prezentują się naprawdę efektownie. Materiał dla bardziej zaawansowanych frontendowców.
38) Nagranie z mojego wystąpienia na temat automatyzacji newslettera (spotkanie w ramach One Man Army AI) https://uw7.org/un_6a8c281f44ac6 INFO: kilka dni temu byłem gościem zaproszonym na spotkanie w ramach szkolenia "One Man Army", gdzie prowadzący uczą kursantów automatyzacji zadań i pracy ze sztuczną inteligencją. Przedstawiłem, z jakich automatyzacji ja korzystam i skupiłem się przede wszystkim na metodach wyszukiwania ciekawych treści w internecie, co szczególnie przydaje mi się przy redagowaniu tego newslettera. Nagranie dostępne jest tylko dla kursantów wspomnianego szkolenia oraz dla moich patronów. Aby zobaczyć nagranie, musisz mieć dostęp do "Skarbca patrona". Jeśli go nie masz, to na Patronite znajdziesz informację, jak go zdobyć.
0 notes
Text
Game Anywhere: Mastering Steam Link on Raspberry Pi in Minutes Setting up Steam Link on your Raspberry Pi allows you to stream games from your gaming PC to any TV or monitor in your house. This budget-friendly solution transforms your Raspberry Pi into a powerful game streaming device. In this comprehensive guide, I'll walk you through the entire installation and optimization process. What You'll Need A Raspberry Pi (Pi 4 or Pi 5 recommended for best performance) Raspberry Pi OS installed Gaming PC with Steam installed Strong network connection (wired Ethernet recommended) Game controller (optional but recommended) Installation Steps 1. Update Your Raspberry Pi OS Before installing Steam Link, ensure your system is up to date by running these commands in the terminal: sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade 2. Install Steam Link Install the Steam Link application and its dependencies: sudo apt install steamlink Once installed, you can launch Steam Link from the terminal with: steamlink Pairing Your Raspberry Pi with Your Gaming PC 1. Enable Remote Play on Your Gaming PC First, you need to configure your gaming PC to allow remote connections: Open Steam on your PC Navigate to Settings > Remote Play Make sure the "Enable Remote Play" option is checked 2. Connect via Steam Link On your Raspberry Pi: Launch Steam Link by typing steamlink in the terminal Select Get Started when prompted The app will scan your network for PCs with Steam running Select your PC from the detected list, or choose Other Computer to manually enter the hostname or IP address 3. Enter the Pairing PIN When prompted, you'll see a PIN displayed on your Raspberry Pi screen: Enter this PIN in the Steam application on your PC Look for the prompt under Remote Play > Pair Steam Link Once paired successfully, you'll be able to access your Steam library on the Raspberry Pi Performance Optimization Tips Network Optimization For the best streaming experience: Use a wired connection: Connect both your Raspberry Pi and gaming PC to your router via Ethernet cables If using Wi-Fi, ensure you're connected to a 5GHz network for reduced latency Position your devices close to your router for optimal signal strength Resolution and Refresh Rate Settings Different Raspberry Pi models support various resolution and refresh rate combinations: Raspberry Pi 5: Supports up to 4K@60Hz or 1080p@240Hz Raspberry Pi 4: Can handle 1080p@120Hz/144Hz with optimized settings To adjust streaming quality: Launch Steam Link on your Pi Navigate to Settings Select Streaming quality options Adjust based on your network capabilities and Pi model Controller Setup For the best experience: Connect your game controllers directly to the Raspberry Pi before launching Steam Link Most USB controllers and Bluetooth controllers are compatible Xbox and PlayStation controllers typically work with minimal configuration Setting Up Autostart To launch Steam Link automatically when your Raspberry Pi boots: Edit the autostart file: sudo nano /etc/xdg/labwc/autostart Add the following line: steamlink Save and exit (Ctrl+X, Y, Enter) Troubleshooting Common Issues Streaming Lag or Stuttering If you experience performance issues: Reduce the streaming resolution and quality in Steam Link settings Close background applications on both your PC and Raspberry Pi Ensure both devices are on the same network Check for network congestion from other devices Controller Not Recognized If your controller isn't working: Connect it before launching Steam Link Test the controller using jstest to verify it's functioning Try connecting directly to a USB port on the Pi rather than through a hub Conclusion Setting up Steam Link on your Raspberry Pi creates an affordable and versatile game streaming solution. With proper optimization, you can enjoy your entire Steam library on any screen in your home.
The Raspberry Pi 5 offers the best performance with support for higher resolutions and refresh rates, but even the Pi 4 provides an excellent streaming experience when properly configured. Remember that a stable network connection is crucial for smooth gameplay, so prioritize a wired connection whenever possible. With these tips and instructions, you'll be streaming your favorite Steam games to your Raspberry Pi in no time.
0 notes
Text

Comparison of Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto for IIoT and Edge Computing
In industrial IoT (IIoT) and edge computing scenarios, Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto Project each have unique advantages. Below is a detailed comparison and recommendations for these three systems:
1. Ubuntu (ARM)
Advantages
Ready-to-use: Provides official ARM images (e.g., Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS) supporting hardware like Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson, requiring no complex configuration.
Cloud-native support: Built-in tools like MicroK8s, Docker, and Kubernetes, ideal for edge-cloud collaboration.
Long-term support (LTS): 5 years of security updates, meeting industrial stability requirements.
Rich software ecosystem: Access to AI/ML tools (e.g., TensorFlow Lite) and databases (e.g., PostgreSQL ARM-optimized) via APT and Snap Store.
Use Cases
Rapid prototyping: Quick deployment of Python/Node.js applications on edge gateways.
AI edge inference: Running computer vision models (e.g., ROS 2 + Ubuntu) on Jetson devices.
Lightweight K8s clusters: Edge nodes managed by MicroK8s.
Limitations
Higher resource usage (minimum ~512MB RAM), unsuitable for ultra-low-power devices.
2. Debian (ARM)
Advantages
Exceptional stability: Packages undergo rigorous testing, ideal for 24/7 industrial operation.
Lightweight: Minimal installation requires only 128MB RAM; GUI-free versions available.
Long-term support: Up to 10+ years of security updates via Debian LTS (with commercial support).
Hardware compatibility: Supports older or niche ARM chips (e.g., TI Sitara series).
Use Cases
Industrial controllers: PLCs, HMIs, and other devices requiring deterministic responses.
Network edge devices: Firewalls, protocol gateways (e.g., Modbus-to-MQTT).
Critical systems (medical/transport): Compliance with IEC 62304/DO-178C certifications.
Limitations
Older software versions (e.g., default GCC version); newer features require backports.
3. Yocto Project
Advantages
Full customization: Tailor everything from kernel to user space, generating minimal images (<50MB possible).
Real-time extensions: Supports Xenomai/Preempt-RT patches for μs-level latency.
Cross-platform portability: Single recipe set adapts to multiple hardware platforms (e.g., NXP i.MX6 → i.MX8).
Security design: Built-in industrial-grade features like SELinux and dm-verity.
Use Cases
Custom industrial devices: Requires specific kernel configurations or proprietary drivers (e.g., CAN-FD bus support).
High real-time systems: Robotic motion control, CNC machines.
Resource-constrained terminals: Sensor nodes running lightweight stacks (e.g., Zephyr+FreeRTOS hybrid deployment).
Limitations
Steep learning curve (BitBake syntax required); longer development cycles.
4. Comparison Summary
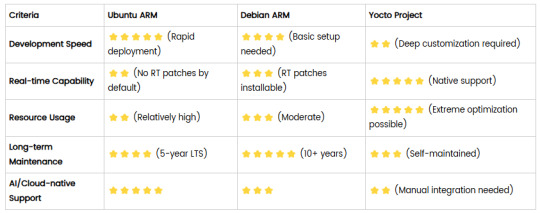
5. Selection Recommendations
Choose Ubuntu ARM: For rapid deployment of edge AI applications (e.g., vision detection on Jetson) or deep integration with public clouds (e.g., AWS IoT Greengrass).
Choose Debian ARM: For mission-critical industrial equipment (e.g., substation monitoring) where stability outweighs feature novelty.
Choose Yocto Project: For custom hardware development (e.g., proprietary industrial boards) or strict real-time/safety certification (e.g., ISO 13849) requirements.
6. Hybrid Architecture Example
Smart factory edge node:
Real-time control layer: RTOS built with Yocto (controlling robotic arms)
Data processing layer: Debian running OPC UA servers
Cloud connectivity layer: Ubuntu Server managing K8s edge clusters
Combining these systems based on specific needs can maximize the efficiency of IIoT edge computing.
0 notes
Text
Affordable Robotics: Finding the Best Price Robotic Kit
Robotics is an exciting and rapidly evolving field, offering opportunities for learning, experimentation, and innovation. Whether you're a student, a hobbyist, or an aspiring engineer, investing in a Best Price Robotic Kit can be the perfect way to enter the world of robotics without breaking the bank. These kits provide affordable solutions while ensuring quality and functionality, making them accessible to both beginners and experienced users.Get more news about Best Price Robotic Kit,you can vist our website!
Key Features of a Best Price Robotic Kit A well-rounded robotic kit should include essential components to facilitate learning and project development. Some key features to consider include:
Microcontroller or Development Board – Most robotic kits come with microcontrollers like Arduino or Raspberry Pi, which serve as the brain of the robot.
Sensors and Actuators – Sensors like ultrasonic, infrared, or motion detectors enhance the functionality of the robot, while actuators such as motors and servos allow movement.
Wireless Connectivity – Some kits include Bluetooth or Wi-Fi modules for remote control and programming convenience.
Easy Assembly – A user-friendly design with clear instructions ensures seamless construction and programming.
Benefits of Using a Budget-Friendly Robotic Kit 1. Cost-Effective Learning Many educational and DIY robotic kits are designed to be affordable while providing fundamental learning experiences in programming and engineering. These kits allow individuals to build hands-on projects without spending excessive amounts on high-end models.
2. Ideal for Beginners A best-price robotic kit often includes simple, easy-to-follow instructions, making it perfect for those new to robotics. Users can learn coding basics, mechanical design, and sensor integration through practical experimentation.
3. Encourages Creativity and Innovation Even within budget constraints, affordable robotic kits provide ample room for customization and creativity. Users can enhance and modify their robots by adding new components or integrating advanced programming features.
Applications of a Best Price Robotic Kit These budget-friendly robotic kits serve various purposes, including:
STEM Education – Schools and universities use robotic kits to teach programming, electronics, and engineering concepts interactively.
Personal Projects – Hobbyists enjoy building robots for automation, remote control, or interactive tasks.
Prototyping and Research – Aspiring engineers and researchers leverage robotic kits for developing functional prototypes and testing robotic applications.
How to Choose the Right Robotic Kit When selecting a robotic kit, consider the following factors:
Purpose: Determine if the kit is meant for education, hobby use, or professional development.
Expandability: Look for a kit with components that can be upgraded and modified as you advance.
Compatibility: Ensure the kit is compatible with common programming platforms and software like Python, C++, or Arduino IDE.
User Support: Some kits offer online tutorials, community forums, and technical support for troubleshooting and guidance.
Conclusion A Best Price Robotic Kit is a fantastic investment for those eager to explore robotics while keeping costs low. Whether you’re a beginner looking for hands-on learning or an enthusiast aiming to create innovative projects, these kits offer an affordable yet powerful solution for robotic development. By choosing the right kit with essential features, you can embark on a rewarding journey of programming, design, and automation without exceeding your budget.
0 notes
Text
Features of the Linux Operating System
The Linux operating system is one of the most popular and influential open-source platforms in the computing world today. Developed originally by Linus Torvalds in 1991, Linux has evolved from a modest personal project into a powerful, flexible, and secure operating system used across various devices and environments—from smartphones and personal computers to servers, supercomputers, and embedded systems. Its widespread adoption and strong community support stem from a range of compelling features. This essay explores the key features of Linux that make it a preferred choice among developers, system administrators, and enterprises.
1. Open Source and Free
One of the most significant features of Linux is that it is open source and free to use. The Linux kernel and most distributions (or "distros") are released under the GNU General Public License (GPL), which allows users to freely access, modify, and distribute the source code. This openness fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation. Users and developers can customize the operating system according to their needs, fix bugs, or even develop their own versions of the OS.
This model contrasts with proprietary systems like Microsoft Windows or macOS, where source code is closed, and licensing fees are required. With Linux, individuals, educational institutions, startups, and large enterprises can benefit from a cost-effective, highly customizable operating system without recurring software licensing costs.
2. Multiuser Capability
Linux is a true multiuser operating system. This means that multiple users can access the system's resources—such as memory, CPU, and storage—at the same time without interfering with each other. Each user has a separate account with specific permissions and access controls. The system's security and file permission structures ensure that one user's data is isolated from another's, making it ideal for shared environments like servers and academic labs.
This feature is particularly valuable in enterprise and hosting environments, where multiple clients or departments may share a single server.
3. Multitasking
Linux supports robust multitasking, allowing multiple processes to run simultaneously without affecting each other. It can handle several applications at once—like editing documents, browsing the web, downloading files, and compiling code—without slowing down. The system's kernel efficiently manages CPU time and prioritizes tasks to ensure smooth operation even under heavy load.
This makes Linux suitable for both everyday use and high-performance environments, such as data centers and cloud computing platforms.
4. Portability
Linux is highly portable, meaning it can run on a wide variety of hardware platforms. Whether it's a personal computer, a mobile device, a mainframe, or an embedded system, there's likely a Linux version available for it. Its architecture-neutral design allows the Linux kernel to be compiled for nearly any processor, making it a dominant force in diverse computing ecosystems.
For example, Android, the most widely used mobile OS, is based on the Linux kernel. Linux is also the go-to choice for Raspberry Pi and other development boards used in robotics, automation, and IoT projects.
5. Stability and Reliability
Linux is known for its stability and reliability. Systems running Linux can operate for years without needing a reboot. Many servers running on Linux have uptimes that span months or even years. The system doesn’t slow down over time due to memory leaks or fragmentation as is common with some other operating systems.
Because of this stability, Linux is widely used for mission-critical applications such as web servers, financial systems, and government infrastructure. Downtime in such systems can lead to significant losses, and Linux helps minimize that risk.
6. Security
Security is a key feature of Linux. It uses a permission-based structure, where each file and process has an associated owner and set of permissions (read, write, execute). This ensures that unauthorized users cannot access or modify files they do not own. Additionally, Linux supports user roles, firewalls (like iptables and nftables), and strong authentication methods.
Since Linux is open source, vulnerabilities can be quickly identified and patched by the global community. Linux distributions frequently release security updates, and administrators can automate patch management using package managers. Advanced security features like SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) provide mandatory access controls and fine-grained security policies.
7. Flexibility and Customization
One of Linux’s most praised attributes is its flexibility. Users can choose from numerous distributions such as Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, Arch Linux, and CentOS, each tailored for different purposes. Whether you need a minimal install for a lightweight IoT device or a full-featured desktop environment, Linux offers something for everyone.
Additionally, users can choose from different desktop environments (e.g., GNOME, KDE, Xfce) and window managers, tweak kernel settings, or even build a Linux system from scratch using tools like Linux From Scratch (LFS).
This level of customization is unparalleled and allows for an efficient system setup optimized for specific use cases.
8. Command Line Interface (CLI)
Linux boasts a powerful command-line interface, which provides users with complete control over the system. While graphical interfaces are available and user-friendly, the CLI is preferred by system administrators, developers, and power users for its speed, efficiency, and scripting capabilities.
The shell (like Bash, Zsh, or Fish) allows users to automate tasks, manage system processes, install software, and configure system settings. Bash scripting is a powerful tool for creating automated workflows, monitoring systems, and managing large-scale infrastructure.
9. Software Package Management
Linux uses package management systems to simplify software installation, updates, and removal. Each distribution has its own package manager (e.g., APT for Debian-based systems, YUM/DNF for Red Hat-based systems, Pacman for Arch Linux). These tools handle dependencies, download necessary files, and keep the system up to date.
Additionally, universal package formats like Snap, Flatpak, and AppImage offer cross-distribution compatibility and sandboxing, improving both convenience and security.
10. Community Support and Documentation
Linux has a vibrant global community of users, developers, and enthusiasts who contribute to its growth. Online forums, wikis, IRC channels, mailing lists, and websites like Stack Overflow and Reddit provide support and troubleshooting help. Most distributions maintain extensive documentation, making it easy for users to learn and resolve issues on their own.
This culture of collaboration not only makes Linux accessible to beginners but also ensures that it continually evolves in response to user needs.
11. Efficient Resource Usage
Linux is highly efficient in managing system resources. It can run on both high-end servers and low-spec hardware with minimal RAM and processing power. This makes it an excellent choice for reviving older computers or running headless servers where performance and efficiency are key.
Moreover, Linux does not require frequent reboots, uses less disk space, and has fewer background processes, reducing overhead and maximizing performance.
12. Support for Programming and Development
Linux is a developer-friendly operating system. It comes preloaded with essential programming tools such as GCC (GNU Compiler Collection), make, gdb, and numerous text editors like Vim, Nano, and Emacs. It also supports modern development environments and languages like Python, Java, C++, Node.js, Ruby, and Rust.
Because of its open nature and access to core components, Linux is often the platform of choice for software development, web development, DevOps, and system programming.
13. Networking and Server Capabilities
Linux is exceptionally strong in networking and server management. It includes built-in tools for configuring networks, monitoring traffic, and managing users and services. Common servers—such as Apache, Nginx, MySQL, Samba, FTP, and SSH—run seamlessly on Linux.
Its performance, security, and reliability make it the most popular operating system for web hosting, cloud computing, and container orchestration tools like Docker and Kubernetes.
Conclusion
Linux is not just an operating system; it's a robust ecosystem shaped by community, transparency, and freedom. Its features—ranging from open-source access and strong security to multitasking, resource efficiency, and rich customization—make it a powerful tool for a wide range of applications. Whether you're a home user, a developer, a systems administrator, or an enterprise, Linux offers a stable, secure, and scalable platform to build upon.
As technology continues to advance and the demand for open, secure, and high-performance systems grows, Linux’s relevance is only set to increase. Its adaptability, community-driven development, and strong foundation ensure that it will remain a cornerstone of modern computing for years to come.
0 notes
Text
Elmalo, let's commit to that direction. We'll start with a robust Sensor Fusion Layer Prototype that forms the nervous system of Iron Spine, enabling tangible, live data connectivity from the field into the AI's processing core. Below is a detailed technical blueprint that outlines the approach, components, and future integrability with your Empathic AI Core.
1. Hardware Selection
Edge Devices:
Primary Platform: NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier or Nano for on-site processing. Their GPU acceleration is perfect for real-time preprocessing and running early fusion algorithms.
Supplementary Controllers: Raspberry Pi Compute Modules or Arduino-based microcontrollers to gather data from specific sensors when cost or miniaturization is critical.
Sensor Modalities:
Environmental Sensors: Radiation detectors, pressure sensors, temperature/humidity sensors—critical for extreme environments (space, deep sea, underground).
Motion & Optical Sensors: Insect-inspired motion sensors, high-resolution cameras, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) to capture detailed movement and orientation.
Acoustic & RF Sensors: Microphones, sonar, and RF sensors for detecting vibrational, audio, or electromagnetic signals.
2. Software Stack and Data Flow Pipeline
Data Ingestion:
Frameworks: Utilize Apache Kafka or Apache NiFi to build a robust, scalable data pipeline that can handle streaming sensor data in real time.
Protocol: MQTT or LoRaWAN can serve as the communication backbone in environments where connectivity is intermittent or bandwidth-constrained.
Data Preprocessing & Filtering:
Edge Analytics: Develop tailored algorithms that run on your edge devices—leveraging NVIDIA’s TensorRT for accelerated inference—to filter raw inputs and perform preliminary sensor fusion.
Fusion Algorithms: Employ Kalman or Particle Filters to synthesize multiple sensor streams into actionable readings.
Data Abstraction Layer:
API Endpoints: Create modular interfaces that transform fused sensor data into abstracted, standardized feeds for higher-level consumption by the AI core later.
Middleware: Consider microservices that handle data routing, error correction, and redundancy mechanisms to ensure data integrity under harsh conditions.
3. Infrastructure Deployment Map
4. Future Hooks for Empathic AI Core Integration
API-Driven Design: The sensor fusion module will produce standardized, real-time data feeds. These endpoints will act as the bridge to plug in your Empathic AI Core whenever you’re ready to evolve the “soul” of Iron Spine.
Modular Data Abstraction: Build abstraction layers that allow easy mapping of raw sensor data into higher-level representations—ideal for feeding into predictive, decision-making models later.
Feedback Mechanisms: Implement logging and event-based triggers from the sensor fusion system to continuously improve both hardware and AI components based on real-world performance and environmental nuance.
5. Roadmap and Next Steps
Design & Prototype:
Define the hardware specifications for edge devices and sensor modules.
Develop a small-scale sensor hub integrating a few key sensor types (e.g., motion + environmental).
Data Pipeline Setup:
Set up your data ingestion framework (e.g., Apache Kafka cluster).
Prototype and evaluate basic preprocessing and fusion algorithms on your chosen edge device.
Field Testing:
Deploy the prototype in a controlled environment similar to your target extremes (e.g., a pressure chamber, simulated low-gravity environment).
Refine data accuracy and real-time performance based on initial feedback.
Integration Preparation:
Build standardized API interfaces for future connection with the Empathic AI Core.
Document system architecture to ensure a smooth handoff between the hardware-first and AI-core teams.
Elmalo, this blueprint establishes a tangible, modular system that grounds Iron Spine in reality. It not only demonstrates your vision but also builds the foundational “nervous system” that your emergent, empathic AI will later use to perceive and interact with its environment.
Does this detailed roadmap align with your vision? Would you like to dive further into any individual section—perhaps starting with hardware specifications, software configuration, or the integration strategy for the future AI core?
0 notes
Text

Bring your imagination to life and hone your tech skills with Heartening Raspberry Pi projects that are more practical than theoretical. Raspberry Pi projects. No matter if you have interest in electronics, IoT, robotics, or automation-these projects prove to be suitable for Computer Science, Electronics, as well as Electrical engineering students. Construct authentic solutions for the world, improve your CV, and remain in front of the competition in technology!
Types of Raspberry Pi Projects for Engineering Students Raspberry Pi is truly the breakthrough invention that will take up engineering students building ground breaking yet real-time applications. Some of the most common types of Raspberry Pi projects are:
1. Through Internet of Things (IoT) projects, sensors and devices can be connected to the internet for making advanced homes, weather stations, or health monitoring systems.
2. Automate anything from lights and appliances to security systems with Raspberry Pi and Python.
3. Using motor drivers and Raspberry Pi, a robotic project would control robots that may be line followers or robotic arms.
4. AI and ML projects simulate basic image recognition, voice assistants, or face detection modelling in Python and TensorFlow Lite.
5. Networking is where mini-servers, VPNs, or network scanners can be made using Raspberry Pi.
6. Projects of Media and Entertainment create smart mirrors and media centers and also game emulators for some fun and learning.
7. Educational projects will create learning kits for kids, digital notice boards, or interactive classroom tools.
It is the best medium for undergraduate students who are interested in practical study in the domains of computer science, electrical, electronics, electronic systems, and telecommunications engineering.
#RaspberryPi#EngineeringProjects#IoTProjects#Automation#RoboticsWithPi#AIProjects#PythonProjects#FinalYearProjects#CSEProjects#EEEProjects#EmbeddedSystems#StudentInnovators#TakeoffEduGroup#Takeoffprojects
0 notes
Video
youtube
The GPRS-Based Smart Medicine Reminder is a microcontroller-based health monitoring system designed to assist individuals—especially the elderly, patients, and busy professionals—in remembering their medication schedules. This intelligent system combines the functionality of an RTC (Real-Time Clock), Arduino, GSM/GPRS Module, and Voice Playback to deliver timely medicine reminders using audio alerts, SMS notifications, and automated voice calls. This innovative solution ensures that a user never misses a dose by triggering alerts at pre-set times throughout the day. The system is designed to be user-friendly, reliable, and portable, making it suitable for home or clinical environments.***********************************************************If You Want To Purchase the Full Working Project KITMail Us: [email protected] Name Along With You-Tube Video LinkWe are Located at Telangana, Hyderabad, Boduppal. Project Changes also Made according to Student Requirementshttp://svsembedded.com/ https://www.svskits.in/ http://svsembedded.in/ http://www.svskit.com/M1: 91 9491535690 M2: 91 7842358459 We Will Send Working Model Project KIT through DTDC / DHL / Blue Dart We Will Provide Project Soft Data through Google Drive1. Project Abstract / Synopsis 2. Project Related Datasheets of Each Component3. Project Sample Report / Documentation4. Project Kit Circuit / Schematic Diagram 5. Project Kit Working Software Code6. Project Related Software Compilers7. Project Related Sample PPT’s8. Project Kit Photos9. Project Kit Working Video linksLatest Projects with Year Wise YouTube video Links152 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2024.php133 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2023.php157 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2022.php135 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2021.php 151 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2020.php103 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2019.php61 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2018.php171 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2017.php170 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2016.php67 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2015.php55 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2014.php43 Projects https://svsembedded.com/ieee_2013.php1600 Projects https://www.svskit.com/2025/01/1500-f...***********************************************************1. Smart Medicine Reminder Box | e-pill Medication Reminders,2. MeDuino - Automatic Medicine Reminder. Arduino diy,3. Medicine Reminder using Arduino by Saddam Khan,4. Smart Medicine Box,5. Arduino Uno based Medicine reminder project,6. Pill Reminder with Arduino version,7. Automatic patient medicine reminder system || Best project center in Bangalore,8. Automatic Pill Reminder Using Arduino uno,9. Raspberry Pi Based Speaking Medication Reminder Project,10. IoT Based Smart Medicine Box,11. Medicine Reminder simulation on proteus,12. Automatic Medicine Reminder with date using Arduino,13. Medicine reminder,14. Smart Medicine Pill Reminder IOT Project using Aurdino,15. Medicine Reminder Box Using Arduino,16. Smart Medicine Dispenser,17. Medicine reminder/Alarm using Arduino,18. MedBox: Smart Medication Box with Arduino - self test,19. Medicine Reminder System | Smart Medicine Pill Reminder Project,20. Medicine reminder using Arduino,21. Best Medicine Reminder DIY,22. Explanation of our Medicine Reminder Project,23. SmartSF Smart Pill Box,24. Medication Reminder using PIC Microcontroller,25. Medicine Reminder Using Home Made Arduino,26. Medicine Reminder System Using Microcontroller,27. ANDROID APP BASED SMART MEDICATION REMINDER SYSTEM,28. IOT Based Medicine Reminder System with Email Alert,29. Simulation: Photoresistor-based Smart Pill Dispenser | Schematic Diagram, Arduino Code
0 notes
Text
raspberry pi pc
Yes, a Raspberry Pi would indeed work much better than an Arduino for implementing a system where two "computers" are communicating and learning from each other. The Raspberry Pi is a full-fledged single-board computer (SBC), which means it has far greater processing power, memory, and capabilities compared to an Arduino. This makes it much more suitable for complex tasks like data processing, machine learning, and communication between two devices.
Key Differences Between Arduino and Raspberry Pi for This Task:
1. Processing Power:
Arduino: Limited to simple microcontroller tasks (e.g., simple sensors, I/O operations, small control tasks). It has very little computational power and memory (e.g., 2 KB of RAM, 32 KB of flash memory).
Raspberry Pi: Has a powerful CPU, much more memory (e.g., 4 GB or 8 GB of RAM on newer models), and can run a full Linux-based operating system (e.g., Raspberry Pi OS). This makes it suitable for tasks like running machine learning models, more complex algorithms, and networking tasks.
2. Communication:
Arduino: Can communicate using simple protocols like Serial, I2C, or SPI, which are ideal for small-scale, low-speed communication between devices.
Raspberry Pi: Has multiple communication options including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, along with more advanced serial protocols. It can communicate over a local network or even the internet, making it ideal for real-time communication between two "computers."
3. Storage and Software:
Arduino: Does not have a storage system other than its limited onboard memory (though you can use SD cards for small amounts of storage). The code running on an Arduino is typically bare-metal (no operating system), and it can only run a single program at a time.
Raspberry Pi: Has access to a large amount of storage (via microSD card or external storage), and runs a full operating system, allowing you to install software libraries, run multiple processes simultaneously, and use advanced tools and frameworks for communication and learning (e.g., TensorFlow, OpenCV, etc.).
4. Machine Learning and Data Processing:
Arduino: You can implement simple algorithms (like decision trees or basic pattern recognition), but it’s not suited for real-time machine learning or complex data analysis.
Raspberry Pi: Can run machine learning models, handle large datasets, and run frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, etc. This makes it much more capable of "learning" from data, making decisions, and adapting based on feedback.
5. How a Raspberry Pi PC System Could Work Better
Given that Raspberry Pi is a full-fledged computer, you can implement the original idea of two computers communicating and learning from each other in a much more robust way. Here’s how you can achieve that:
Hardware Setup for Raspberry Pi PCs:
Two Raspberry Pi boards (e.g., Raspberry Pi 4, Raspberry Pi 3, or even Raspberry Pi Zero for smaller setups).
Display, keyboard, and mouse for local interaction, or run everything remotely via SSH (headless).
Networking: Use Wi-Fi or Ethernet to connect the two Raspberry Pi boards and enable communication.
Optional: Camera, microphone, sensors, or other input/output devices for more advanced interaction and learning tasks.
Communication Between Raspberry Pi PCs:
You can use several methods for communication between the two Raspberry Pi boards:
TCP/IP Communication: Set up a client-server model, where one Raspberry Pi acts as the server and the other as the client. They can communicate over a local network using sockets.
MQTT: A lightweight messaging protocol suitable for device-to-device communication, commonly used in IoT.
HTTP/REST APIs: You can use a web framework (e.g., Flask, FastAPI) to create APIs on each Raspberry Pi, allowing them to communicate via HTTP requests and responses.
WebSocket: For real-time bidirectional communication, you can use WebSockets.
Software/Frameworks for Machine Learning:
You can install frameworks like TensorFlow, Keras, or scikit-learn on the Raspberry Pi to allow for more advanced learning tasks.
Use Python as the programming language to communicate between the two Pi boards and implement machine learning algorithms.
Raspberry Pi can interact with real-world data (e.g., sensors, cameras, etc.) and learn from it by running algorithms like reinforcement learning, supervised learning, or unsupervised learning.
6. Example Use Case: Two Raspberry Pi PCs Learning from Each Other
Here’s an example scenario where two Raspberry Pi boards communicate and learn from each other using TCP/IP communication and basic machine learning (e.g., reinforcement learning).
Raspberry Pi 1 (PC1): This board makes a decision based on its current state (e.g., it guesses a number or makes a recommendation).
Raspberry Pi 2 (PC2): This board evaluates the decision made by PC1 and sends feedback. PC2 might "reward" or "punish" PC1 based on whether the decision was correct (e.g., in a game or optimization problem).
Feedback Loop: PC1 uses the feedback from PC2 to adjust its behavior and improve its future decisions.
Example Architecture:
PC1 (Raspberry Pi 1):
Makes a guess (e.g., guesses a number or makes a recommendation).
Sends the guess to PC2 via TCP/IP.
Receives feedback from PC2 about the quality of the guess.
Updates its model/behavior based on the feedback.
PC2 (Raspberry Pi 2):
Receives the guess or recommendation from PC1.
Evaluates the guess (e.g., checks if it’s close to the correct answer).
Sends feedback to PC1 (e.g., positive or negative reinforcement).
Basic Python Code for TCP Communication:
On both Raspberry Pis, you can use Python’s socket library to establish a client-server communication:
PC1 (Server) Code:
import socket import random # Create a TCP/IP socket server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) server_socket.bind(('0.0.0.0', 65432)) # Bind to any address, port 65432 server_socket.listen(1) print("PC1: Waiting for connection...") connection, client_address = server_socket.accept() print("PC1: Connected to PC2") while True: # Simulate a decision (e.g., guessing a number) guess = random.randint(1, 100) print(f"PC1: Guessing number {guess}") # Send the guess to PC2 connection.sendall(str(guess).encode()) # Wait for feedback from PC2 feedback = connection.recv(1024).decode() print(f"PC1: Received feedback: {feedback}") # Adjust behavior based on feedback (simple learning mechanism) if feedback == "correct": print("PC1: Correct guess!") else: print("PC1: Incorrect guess, trying again.") # Wait before making another guess time.sleep(2)
PC2 (Client) Code:
import socket # Create a TCP/IP socket client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) client_socket.connect(('PC1_IP_ADDRESS', 65432)) # Connect to PC1 while True: # Receive the guess from PC1 guess = int(client_socket.recv(1024).decode()) print(f"PC2: Received guess {guess}") # Evaluate the guess (simple decision: correct if guess is 50) if guess == 50: feedback = "correct" else: feedback = "incorrect" # Send feedback to PC1 client_socket.sendall(feedback.encode()) print(f"PC2: Sent feedback: {feedback}")
7. Expanding This System
Advanced Communication: If you're looking for real-time interaction, you can explore using WebSockets or MQTT for more efficient, bidirectional communication.
Machine Learning: You can train models on both Raspberry Pi devices, where one device sends data to the other for training, and they both improve over time.
Distributed Systems: With two Raspberry Pis, you can build a distributed system where each Pi runs part of the computation, and they collaborate to solve more complex tasks.
Conclusion:
Raspberry Pi is definitely a better choice for the task of two computers communicating and learning from each other, as it offers the computational power, memory, and flexibility needed for machine learning, real-time communication, and more advanced systems. The Arduino is more suitable for simple tasks and small embedded systems, whereas the Raspberry Pi can handle much more complex processing, communication, and learning systems.
If you want to build a more advanced learning system, I would recommend using Raspberry Pi boards. Would you like to dive deeper into a specific part of the setup or need help with more advanced machine learning on Raspberry Pi?
Creating a Raspberry Pi-based PC involves setting up a Raspberry Pi board to function as a full desktop computer, capable of running an operating system, connecting to the internet, and supporting peripherals like a keyboard, mouse, and display. Unlike an Arduino, which is used for embedded systems, a Raspberry Pi is a full-fledged computer, making it much easier to set up as a personal computer.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to turn a Raspberry Pi into a fully functional PC.
What You Need:
Raspberry Pi Board (e.g., Raspberry Pi 4, Raspberry Pi 3, or Raspberry Pi Zero)
MicroSD Card (at least 8 GB, recommended 16 GB or more) for the operating system
Power Supply (5V 3A USB-C for Raspberry Pi 4, or appropriate power for other models)
HDMI Cable and a Display (HDMI-compatible monitor or TV)
Keyboard and Mouse (USB or Bluetooth, depending on your preference)
Internet connection (Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi)
USB storage (optional, for additional storage)
MicroSD card reader (for flashing the operating system)
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Prepare the MicroSD Card with Raspberry Pi OS
First, you'll need to install the operating system on your MicroSD card. The most common and recommended OS for Raspberry Pi is Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian).
Download Raspberry Pi Imager: Visit Raspberry Pi’s official website and download the Raspberry Pi Imager for your computer (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
Install Raspberry Pi OS:
Open the Raspberry Pi Imager, select "Choose OS", and select Raspberry Pi OS (32-bit) (recommended for most users).
Select your MicroSD card as the target.
Click Write to flash the OS onto the SD card.
Enable SSH or Wi-Fi (Optional): If you plan to use the Raspberry Pi headlessly (without a monitor, keyboard, or mouse), you can enable SSH or configure Wi-Fi before inserting the SD card into the Pi:
After flashing, insert the SD card into your computer.
Open the boot partition and create an empty file named "ssh" (no extension) to enable SSH.
For Wi-Fi, create a file called wpa_supplicant.conf with your Wi-Fi credentials: country=US ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev update_config=1 network={ ssid="Your_SSID" psk="Your_Password" }
2. Set Up the Raspberry Pi
Insert the SD card into the Raspberry Pi.
Connect your HDMI cable from the Raspberry Pi to the monitor.
Plug in your keyboard and mouse via the USB ports.
Connect the power supply to the Raspberry Pi.
3. First Boot and Raspberry Pi OS Setup
When you power on the Raspberry Pi, it should boot into Raspberry Pi OS.
Follow the on-screen instructions to:
Set up your language, timezone, and keyboard layout.
Set up your Wi-Fi connection (if not already done).
Update the system by running sudo apt update and sudo apt upgrade in the terminal.
4. Install Additional Software
Once your Raspberry Pi is running, you can install additional software based on your needs. For example:
Web Browsing: The default browser is Chromium, but you can install others like Firefox.
Office Suite: Install LibreOffice for document editing, spreadsheets, and presentations.
Command: sudo apt install libreoffice
Development Tools: If you want to use the Pi for programming, you can install IDEs like Thonny (for Python) or Visual Studio Code.
Command: sudo apt install code
Media Software: You can use VLC for media playback or Kodi for a home theater system.
5. Optimize Your Setup
To make your Raspberry Pi run smoothly and feel more like a desktop PC:
Increase Memory Allocation: If you're using a Raspberry Pi 4, you can allocate more memory to the GPU via sudo raspi-config.
Enable Auto-Login: To skip the login screen on boot, you can configure auto-login:
Run sudo raspi-config.
Select Boot Options → Desktop/CLI → Desktop Autologin.
Configure Performance Settings: You can tweak performance settings like CPU overclocking or enabling hardware acceleration for graphics in the Raspberry Pi configuration tool (raspi-config).
6. Optional: Adding a Large Storage Device
If the 8 GB or 16 GB of storage on the SD card isn’t enough, you can plug in a USB hard drive or USB flash drive to expand your storage. You can also configure the Raspberry Pi to boot from a USB drive (for faster performance compared to an SD card).
7. Set Up Remote Access (Optional)
If you prefer to control the Raspberry Pi from another computer:
SSH: You can access the Raspberry Pi's terminal remotely via SSH (if enabled during setup). To connect, use a tool like PuTTY (Windows) or the terminal (Linux/macOS):
Command: ssh pi@<raspberrypi-ip-address>
VNC: You can use VNC for remote desktop access.
Enable VNC using sudo raspi-config.
Download and install RealVNC on your computer to access the Raspberry Pi’s graphical desktop remotely.
8. Using Your Raspberry Pi as a Full PC
Once you’ve completed the setup, your Raspberry Pi will be ready to use like a regular desktop computer. You can:
Surf the web, check emails, and use social media with browsers like Chromium or Firefox.
Write documents, create spreadsheets, and presentations using LibreOffice.
Code in multiple languages (Python, Java, C++, etc.).
Play media files with VLC or stream content using Kodi.
9. Advanced Uses: Building a Raspberry Pi "Server"
If you want your Raspberry Pi to act as a server or take on additional tasks, you can configure it for various roles:
Home Automation: Set up a Home Assistant or OpenHAB server for smart home automation.
Web Server: You can install Apache or Nginx and run a web server.
Command: sudo apt install apache2
Cloud Server: Set up Nextcloud or ownCloud to create your own cloud storage.
Conclusion
Creating a Raspberry Pi PC is a great way to repurpose the Raspberry Pi as a low-cost, energy-efficient desktop computer. Whether you're using it for everyday tasks like browsing, programming, or media consumption, or even more advanced tasks like running servers or learning about Linux, the Raspberry Pi is incredibly versatile.
If you need help with specific configurations, software installation, or troubleshooting, feel free to ask!
0 notes