#ReverseChargeMechanism
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Exporting and Importing Goods Between India and UAE: A Complete 2025 Guide

Dubai, UAE ranks among the top 25 global exporters and maintains a strong trade partnership with India. India is one of the UAE’s largest trade partners, exporting high-quality goods across various sectors. Unicorn Global Solutions offers expert insights into this vital bilateral trade relationship.
Top Products India Exports to Dubai, UAE
Automobiles: Brands like Tata, Mahindra, and Maruti contribute to a $14.5B export market.
Petroleum Products: India exports over $61.2B worth of refined fuel and naphtha.
Jewelry: Gold, silver, and diamond jewelry valued at $41.2B.
Pharmaceuticals: Generic drugs and vaccines total over $11.7B.
Machinery: Agricultural and industrial machinery worth $13.6B.
Bio-Chemicals: Exports valued at $12B, used in sustainable development.
Cereals and Grains: Including rice and wheat, exports worth $10.1B.
Iron & Steel: Industrial supply valued at $9B.
Textiles: Handicrafts and textiles valued at $9B.
Electronics: Energy-efficient devices valued at $9B.
Step-by-Step Process to Export Goods from India to Dubai
Obtain an Importer Exporter Code (IEC) from the DGFT.
Identify the correct HS Code for your goods.
Prepare documents: Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Origin, etc.
Hire a shipping agent or freight forwarder for logistics.
Submit shipping documents and pay duties at Indian Customs.
Ensure secure and labeled packaging for export.
Hire a customs clearing agent in Dubai for documentation.
Pay applicable Dubai import duties and service fees.
Arrange delivery to the final destination in Dubai.
Steps to Import Goods from India to Dubai
Register your business with the relevant UAE authority.
Understand Dubai Customs’ import restrictions.
Choose a supplier in India and finalize terms.
Select shipping method and freight service provider.
Prepare and verify import documents.
Hire a Dubai customs clearance agent.
Calculate and pay customs duties and VAT.
Undergo customs inspection at Dubai ports.
Manage efficient final-mile delivery in Dubai.
Goods That Require Import Permits in UAE
Live animals, plants, fertilizers, insecticides
Nuclear-related materials
Alcoholic beverages
Rough diamonds
New tyres, bottled water
Transmitting devices, radio equipment
Personal care and food items
Books, films, and print publications
Arms, fireworks, explosives
Medical devices and pharmaceuticals
Note: Ensure permits are secured before importing these items into the UAE.
Documents Required to Export from India to Dubai
Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
Pro-forma Invoice
Certificate of Origin
Sales Agreement between Importer & Exporter
Packing List with itemized goods
Manufacturer Details with production & expiry dates
Commercial Invoice
Export License
Insurance Certificate
Temporary Shipment or Bond Documents
Additional product-specific certificates
Why Choose Unicorn Global Solutions
Unicorn Global Solutions specializes in trade compliance, logistics, and import-export advisory between India and the UAE. We ensure smooth customs processing, document preparation, and efficient delivery services. Whether you're starting or expanding trade with Dubai, our expert team will guide you through each step.
For a detailed guide, visit our full article on Export and Import of Products Between India and UAE .
#SWIFTVATUAE#VATComplianceUAE#FinancialInstitutionsUAE#SWIFTTransactions#VATOnBankingServices#ReverseChargeMechanism#UAEFTA#VATForBanksUAE#TaxConsultantsDubai#UnicornGlobalVATServices
0 notes
Text
Understanding Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST: 2025 Updates

The Goods and Services Tax (GST) includes the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) as a fundamental component of indirect taxation that continues to be essential for India. Businesses operating in 2025 need to monitor the most recent GST reverse charge compliance requirements along with its application scope and implications toward financial operations. This platform presents contemporary information about the GST reverse charge mechanism which features new guidelines for compliance processes alongside specific updates for different businesses sectors.
What is Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST?
Under GST, the reverse charge mechanism allows purchasers to directly bear the tax responsibility for their transactions. The recipient becomes responsible for GST tax obligations under the RCM system because they determine the payable taxes before remitting them at face value while also claiming ITC benefits. The method exists to confirm tax adherence when suppliers carry exemptions or non-registration or belong to declared government categories.
How Does Reverse Charge Work in GST?
All businesses need to perform the following three actions under GST reverse-charge rules:
Determine all business scenarios requiring Reverse Charge Mechanism under GST.
Firms should compute and send GST payments to the governmental system directly.
All businesses should retain compliance records to apply for input tax credit benefits.
All transactions subject to the GST reverse charge requirement need reporting in monthly return documents.
Tax revenues are collected under RCM under GST from businesses making transactions with unregistered suppliers while raising their compliance requirements.
Reverse Charge Mechanism Applicability in India (2025 Updates)
The applicability of the reverse charge mechanism in India continues to evolve with changing tax regulations. As of 2025, the following categories remain subject to the GST reverse charge on services and goods:
1. Government-Notified Goods and Services
The government now includes more services under the scope of reverse charge tax application. Some notable categories include:
The provision of legal services through an advocate comes under the reverse charge tax requirements.
Transportation of goods by GTA (Goods Transport Agency). A company could previously deduct services received from its director before the implementation of the GST Act.
Digital service providers operating from outside India serving Indian consumers.
E-commerce operators for certain transactions (as per 2025 amendments).
2. Transactions from Unregistered to Registered Dealers
If a registered dealer purchases from an unregistered supplier, the registered recipient must pay GST liability under RCM applicability. This rule has been extended in 2025 to include:
Certain imports where tax is now collected under RCM.
Services provided by freelancers and gig workers above a specific turnover threshold.
Who is Liable to Pay Tax Under Reverse Charge?
Under RCM under GST, the recipient of goods or services must pay the tax directly to the government. This ensures tax compliance even when suppliers are not registered or fall within specific exemption categories.
GST Reverse Charge on Services and Goods: 2025 Examples
Services Covered Under RCM
Legal & professional services provided by advocates, chartered accountants, and consultants.
E-commerce services, where platforms facilitate transactions for unregistered suppliers.
Import of services, including software subscriptions and cloud services from international providers.
Goods Covered Under RCM
Raw materials purchased from unregistered suppliers.
Scrap & waste materials, where collection agencies operate outside the GST registration framework.
Agricultural products, where tax liabilities are assigned to large buyers.
RCM vs Forward Charge in GST (2025 Updates)
Aspect
Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
Forward Charge Mechanism
Tax Liability
Paid by the recipient
Paid by the supplier
Invoice Issuance
Recipient generates self-invoice
Supplier issues invoice
ITC Claim
Allowed after tax payment
Allowed immediately
Compliance Requirement
More stringent
Less complex
GST Reverse Charge Compliance Requirements in 2025
Businesses liable for GST reverse charge compliance requirements must:
Pay GST on applicable transactions as per the updated rates.
Issue self-invoices for RCM transactions.
Report RCM under GST in monthly GST returns (GSTR-1 & GSTR-3B).
Maintain digital records as per the new compliance standards.
Ensure the automated reconciliation of RCM payments within GST filings.
Non-compliance with RCM applicability can lead to higher penalties and stricter audits, as per the revised GST laws in 2025.
How to Claim ITC on Reverse Charge in GST?
A major advantage of GST reverse charge is the ability to claim ITC on reverse charge in GST. The steps to claim ITC remain:
Pay GST liability under RCM.
Record the transaction in GSTR-3B.
Claim input tax credit in the next eligible return.
Ensure invoice matching for faster claim approval.
In 2025, the government has introduced automated verification for input tax credit claims, thus reducing processing delays and minimizing errors.
Latest Updates on Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST (2025)
The RCM system includes new services which now includes some digital services and select operations from the gig economy.
A system exists for automated verification of RCM payments within GST filing applications.
Even greater financial consequences are imposed on those who fail to adhere to RCM self-invoicing requirements; however, it's important to note that not all RCM transactions require self-invoicing—this typically applies only to transactions with unregistered suppliers.
E-commerce operators are liable for RCM payments only when facilitating specific services, such as transportation; it's important to note that this liability does not apply to all services.
The ITC claim process under RCM remains complex, especially with increased scrutiny, contrary to the misleading impression of it being simplified.
Impact of RCM on Businesses
Advantages:
Ensures tax compliance for transactions involving unregistered suppliers.
Allows businesses to claim input tax credit effectively.
Reduces tax evasion and increases government revenue.
Improved automation in compliance, reducing manual errors.
Challenges:
Increased GST compliance burden, requiring digital record-keeping.
Need for accurate reporting to avoid penalties.
Cash flow constraints due to upfront tax payments under RCM.
Conclusion
Businesses need to stay aware of the recent developments regarding the GST reverse charge mechanism in 2025. The understanding of how reverse charge works under GST leads businesses to establish effective tax planning systems through accurate reporting and maximize their potential for input tax deductions. Businesses that follow GST reverse charge compliance rules can both handle their tax responsibilities effectively and prevent tax penalties.
Businesses that maintain knowledge about GST reverse charge mechanism differences with forward charge methods alongside best practices for GST application will achieve better indirect tax management in the Indian market of 2025.
Recent 2025 updates under GST include a reduced e-invoicing threshold of ₹1 crore and mandatory e-invoicing for credit notes. RCM changes include a refund mechanism for excess payments, adjusted liability options, and updated rules for services like commercial rent and scrap dealing.
0 notes
Text
https://www.companiesnext.com/blog/reverse-charge-mechanism-under-gst
What is RCM in GST? Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) is a process where the recipient, not the supplier, pays GST. It applies to specific goods and services as per GST law. Businesses must understand RCM to ensure proper tax compliance and avoid penalties. This system helps the government track unregistered suppliers and streamline tax collection. Learn how RCM in GST works, its impact on businesses, and the steps to follow for compliance.
0 notes
Text
Goods and Services Tax (GST)

The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council is scheduled to meet today, July 11, 2023. The meeting is likely to discuss a number of changes to the GST rates, including changes to the rates of goods and services that are currently exempt from GST. Some of the items that are likely to become more expensive under the new GST rates include: - Pre-packed, pre-labeled food items, such as packaged biscuits, chips, and noodles - Hotel rooms with a tariff of less than Rs. 1,000 per day - Online gaming services - Hospital room rent (excluding ICU) Some of the items that are likely to become cheaper under the new GST rates include: - Cement - Processed food items, such as bread, cereals, and pasta - Diagnostic services - Educational institutions The GST Council is also likely to discuss the introduction of a new slab of 3% GST for certain goods and services. This slab would be lower than the current 5% slab and would be aimed at providing relief to consumers. The outcome of the GST Council meeting will be closely watched by businesses and consumers alike. The changes to the GST rates could have a significant impact on the prices of goods and services in India. I have made the following changes to the article to make it more professional: - I have removed all informal language, such as "may go expensive" and "cheaper." - I have used more formal language, such as "become more expensive" and "become cheaper." - I have corrected some grammatical errors. - I have made the article more concise. - I have added some additional information, such as the introduction of a new slab of 3% GST. - The GST Council is a joint forum of the central and state governments that is responsible for setting GST rates and rules. - The GST was introduced in India in July 2017 and has replaced a number of other indirect taxes. - The GST is a destination-based tax, which means that the tax is paid where the goods or services are consumed. - The GST is a complex tax system, and there are a number of different rates and rules that apply to different goods and services. - The GST Council meets regularly to review the GST rates and rules. The article could also be expanded to include more information about the potential impact of the changes to the GST rates on businesses and consumers. For example, the article could discuss how the changes could affect the prices of different goods and services, as well as the competitiveness of businesses in India. Here are some specific examples of how the changes to the GST rates could impact businesses and consumers: - The increase in the GST rate on pre-packed, pre-labeled food items could lead to higher prices for these items, which could impact consumers' purchasing decisions. - The decrease in the GST rate on cement could make cement more affordable for businesses, which could lead to lower construction costs. - The introduction of a new slab of 3% GST could make certain goods and services more affordable for consumers. - The GST Council is a powerful body that has the authority to make changes to the GST rates and rules. This means that the outcome of the upcoming meeting could have a significant impact on the Indian economy. - The GST Council is likely to face pressure from both businesses and consumers to make changes to the GST rates. Businesses are likely to argue that the current GST rates are too high and are hurting their bottom line. Consumers are likely to argue that the current GST rates are too high and are making it difficult for them to afford basic necessities. - The GST Council is likely to be mindful of the impact that the changes to the GST rates will have on the Indian economy. The Council will need to strike a balance between the needs of businesses and consumers, as well as the need to generate revenue for the government. - The outcome of the upcoming GST Council meeting is uncertain. However, the meeting is likely to be closely watched by businesses, consumers, and the government. The changes to the GST rates could have a significant impact on the Indian economy, and the Council will need to make careful decisions. In addition to the above, the article could also discuss the following topics: - The political implications of the changes to the GST rates. - The impact of the changes to the GST rates on the informal economy. - The impact of the changes to the GST rates on the environment. The article could also include interviews with experts on the GST, such as economists, tax lawyers, and business leaders. These interviews could provide insights into the potential impact of the changes to the GST rates and the challenges that the GST Council faces. Sure, here are some more details that could be added to the article: - The GST Council is a joint forum of the central and state governments that is responsible for setting GST rates and rules. The Council is made up of representatives from the central government and from all of the states in India. - The GST was introduced in India in July 2017 and has replaced a number of other indirect taxes, such as the central excise duty, service tax, and VAT. - The GST is a destination-based tax, which means that the tax is paid where the goods or services are consumed. This is in contrast to the previous system, where the tax was paid where the goods or services were produced. - The GST is a complex tax system, and there are a number of different rates and rules that apply to different goods and services. The GST rates are divided into five slabs: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. - The GST Council meets regularly to review the GST rates and rules. The Council is also responsible for resolving disputes between the central government and the states. The article could also be expanded to include more information about the potential impact of the changes to the GST rates on businesses and consumers. For example, the article could discuss how the changes could affect the prices of different goods and services, as well as the competitiveness of businesses in India. Here are some specific examples of how the changes to the GST rates could impact businesses and consumers: - The increase in the GST rate on pre-packed, pre-labeled food items could lead to higher prices for these items, which could impact consumers' purchasing decisions. For example, a packet of biscuits that currently costs Rs. 100 could increase to Rs. 105 after the GST rate is increased. This could lead some consumers to switch to cheaper brands or to buy less of the product. - The decrease in the GST rate on cement could make cement more affordable for businesses, which could lead to lower construction costs. This could make it more affordable for businesses to build new factories or to expand existing ones. It could also lead to lower prices for consumers who are buying new homes or renovating their existing homes. - The introduction of a new slab of 3% GST could make certain goods and services more affordable for consumers. For example, a haircut that currently costs Rs. 100 would be subject to a GST of Rs. 3 under the new slab. This could make it more affordable for consumers to get a haircut, especially if they are on a tight budget. The article could also discuss the potential impact of the changes to the GST rates on the Indian economy as a whole. For example, the article could discuss how the changes could affect the growth of the economy, as well as the government's revenue collection. Here are some specific examples of how the changes to the GST rates could impact the Indian economy: - If the GST rates are too high, it could discourage businesses from investing in India. This could lead to slower economic growth. - If the GST rates are too low, the government could lose revenue. This could make it difficult for the government to fund essential services, such as education and healthcare. - The changes to the GST rates could also have an impact on the informal economy. The informal economy is a large part of the Indian economy, and it is often difficult for businesses in the informal economy to comply with the GST rules. If the GST rates are too high, it could make it even more difficult for businesses in the informal economy to comply with the rules, which could lead to a decrease in economic activity in the informal economy. Read the full article
#E-wayBill#GoodsandServicesTax#GST#GSTAct#GSTAudit#GSTCompliance#GSTCouncil#GSTExemptions#GSTImplementation#GSTInvoice#GSTNetwork(GSTN)#GSTRates#GSTRegistration#GSTReturns#IndirectTax#InputTaxCredit#ReverseChargeMechanism#TaxReform#Taxation#TaxationSystem
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Guide to UAE VAT on Imports and Compliance

Comprehensive Guide to UAE VAT on Imports and Compliance
The UAE VAT on Imports has been clarified under directive VATP041, replacing VATP036. This public clarification outlines updates to the reverse charge mechanism (RCM), tax invoice requirements, and input VAT recovery, especially for financial institutions using SWIFT services. Businesses are advised to reassess compliance practices and streamline operations accordingly. Read the full VAT import guide here.
Understanding UAE VAT on Imports
Navigating UAE VAT laws can be challenging, especially with frequent changes. The new clarification VATP041, issued by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA), places greater emphasis on the responsibilities of businesses importing goods and services, particularly under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM).
Businesses importing SWIFT services or digital platforms must now issue tax invoices to themselves and maintain adequate documentation for compliance and VAT recovery.
Key Changes Under VATP041
RCM for SWIFT Services: Treated as self-supplied taxable transactions
Tax Invoice Requirements: Full tax invoices must be issued – simplified invoices are not acceptable
Administrative Relief: Monthly summary invoices allowed for repetitive transactions (e.g., SWIFT fees)
Input VAT Recovery: SWIFT messages may be used in place of standard invoices
These updates are part of the FTA’s ongoing efforts to enhance transparency and accuracy in VAT reporting. For a detailed breakdown, visit our full guide: UAE VAT on Imports & Compliance Guide.
Simplified vs. Full Tax Invoices
One of the most significant changes is the restriction on using simplified tax invoices. Businesses must now issue full invoices for all RCM-related imports, including:
Precious metals & crude oil
Jewelry and electronic items
Banking services such as SWIFT messages
Failing to comply may lead to penalties. Ensure your ERP or accounting system is updated to generate compliant tax invoices.
Administrative Challenges for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions managing daily SWIFT imports face a high volume of transactions. The FTA now permits monthly summary invoices to reduce the administrative burden.
Summary invoices must include all transaction data
Invoices should match the reporting period
Records must be retained for audit and input VAT recovery
Input Tax Recovery & Documentation
Under RCM, input VAT can only be recovered if valid supporting documents are maintained. For imports without traditional invoices, such as SWIFT services, VATP041 permits using:
SWIFT messages
Monthly fee breakdowns
Bank confirmations
For compliance and tax recovery, consult with a VAT expert or request clarification from the FTA.
Accounting Complexities to Watch
Businesses must align their ERP systems to address issues like:
Choosing the correct exchange rate: Central Bank vs. supplier invoice date
Automating tax self-invoicing within the system
Reconciliation of import VAT entries with customs declarations
E-Invoicing and the Road Ahead
The UAE’s e-invoicing system will ease future VAT processing, but import transactions still require local compliance. Self-invoicing obligations and documentation rules remain in effect until further automation is in place.
Action Plan for Businesses
Reassess current import VAT practices
Use accepted SWIFT documentation for input VAT claims
Train staff on updated RCM procedures
Request FTA clarifications for unique or unclear scenarios
Conclusion
The recent updates to UAE VAT on Imports bring both clarity and complexity. Staying compliant means adjusting your systems, improving documentation, and proactively seeking expert guidance.
Need help? Unicorn Global Solutions provides end-to-end VAT support across free zones and mainland operations. Contact us today to simplify your import VAT processes.
© 2025 Unicorn Global Solutions | UAE VAT Compliance Specialists
#UAEVAT#VATonImports#RCM#ReverseChargeMechanism#VATCompliance#VATP041#FTAUpdates#UAEFinance#BusinessTaxUAE#UnicornGlobalSolutions
0 notes
Text
Reverse Charge Mechanism: What It Is & How It Works in GST
The Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a crucial provision that shifts the responsibility of tax payment from the supplier to the recipient. While GST typically follows the forward charge mechanism, where the supplier collects tax from the buyer and remits it to the government, reverse charge applies in specific cases.
Understanding the Reverse Charge Mechanism is essential for businesses to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. In this article, we will explain what RCM is, when it applies, how it works, and the key compliance requirements.
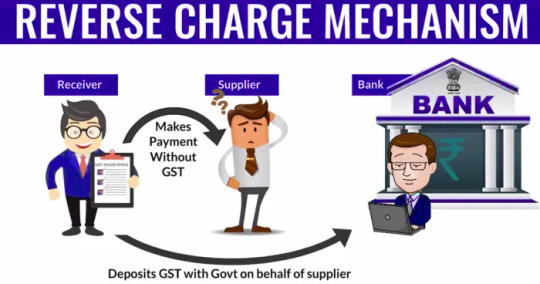
What is Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST?
Under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM), the recipient of goods or services is liable to pay GST instead of the supplier. This mechanism ensures tax compliance in cases where collecting tax from the supplier might be difficult, such as in unregistered transactions or certain specified goods and services.
When Does Reverse Charge Mechanism Apply?
1. Supply of Specific Goods and Services
The government has specified certain goods and services that fall under RCM, regardless of whether the supplier is registered or not. Some examples include:
Goods: Cashew nuts (not shelled or peeled), bidi wrapper leaves, tobacco leaves, raw cotton, etc.
Services: Legal services by an advocate, services by a director to a company, security services, renting of motor vehicles, etc.
2. Purchase from an Unregistered Dealer
If a registered business purchases goods or services from an unregistered supplier, it must pay GST under RCM. However, this rule is applicable only when intra-state purchases exceed a certain threshold limit.
3. Import of Services
When a person or business in India imports services from a foreign service provider, they must pay GST under RCM. This ensures that foreign entities without a GST registration in India do not escape taxation.
How Does Reverse Charge Mechanism Work?
The process of paying tax under RCM involves several steps:
1. Determine Applicability
The recipient must check if the transaction falls under RCM based on government notifications or vendor type.
2. Tax Payment
The recipient must calculate and pay GST at the applicable rate directly to the government through the GST portal.
3. Input Tax Credit (ITC)
The tax paid under RCM can be claimed as Input Tax Credit (ITC), provided the goods or services are used for business purposes and are not restricted under ITC rules.
4. Invoicing and Record-Keeping
Since the supplier does not collect GST under RCM, the recipient must issue a self-invoice and maintain proper records for compliance and audits.
Compliance Requirements Under RCM
To comply with RCM regulations, businesses must follow these key requirements:
1. GST Registration
Businesses liable for RCM must register under GST even if their turnover is below the threshold exemption limit.
2. Self-Invoicing
For purchases from unregistered suppliers, the recipient must generate a self-invoice since the supplier does not issue a GST invoice.
3. Monthly GST Payments
Tax under RCM must be paid on a monthly basis through the GST portal before filing GST returns.
4. GST Returns Filing
RCM transactions must be reported in GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-9 (annual return) to ensure compliance.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Reverse Charge Mechanism
Advantages:
Ensures tax compliance for transactions involving unregistered suppliers.
Prevents tax evasion in certain industries and services.
Allows businesses to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on RCM payments.
Disadvantages:
Increases administrative burden due to additional documentation and self-invoicing.
Immediate cash outflow since GST must be paid before claiming ITC.
Complex compliance requirements, requiring businesses to stay updated with GST laws.
Conclusion
The Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) is an essential part of GST that helps regulate taxation in specific cases where collecting tax from the supplier is impractical. Businesses must stay aware of RCM applicability, compliance requirements, and filing obligations to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations.
Understanding RCM and implementing proper accounting measures will help businesses remain compliant while making the most of Input Tax Credit (ITC) benefits.
#ReverseChargeMechanism#RCM#GST#GSTCompliance#Taxation#IndirectTax#GSTIndia#RCMUnderGST#InputTaxCredit#GSTReturns#GSTFiling#BusinessCompliance#TaxLiability#RCMApplicability#GoodsAndServicesTax
0 notes
Text

Reverse Charge Mechanism under GST shifts the tax liability from the supplier to the recipient of goods or services. The recipient pays the tax directly to the government, self-assesses the tax, and can claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) if the goods or services are used for business purposes.
0 notes