#TDS threshold limit
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Interest from FDs, savings, or bonds? Learn how TDS applies to interest income, who deducts it, and when Form 15G/H can be used to avoid deduction. Get clarity on TDS and secure your refunds – read this complete guide now!
#TDS on interest#interest income tax#Form 15G#TDS threshold limit#interest tax rules#TDS refund#tax on FDs#income tax guide
0 notes
Text
Understanding Tax Refunds: JJ Tax made it easy
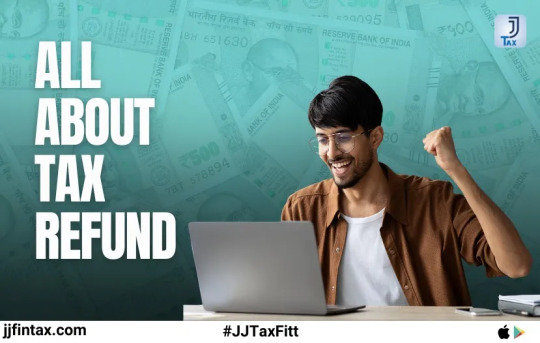
Handling tax refunds can seem overwhelming, but having a clear grasp of the process can make it straightforward. This newsletter aims to demystify tax refunds by covering key aspects: eligibility criteria, claiming procedures and tracking your refund status.
What is a Tax Refund?
A tax refund represents the amount returned to taxpayers who have overpaid their taxes over the fiscal year. This situation arises when the total tax deducted or paid exceeds the actual tax liability determined based on their income.
In India, tax payments are made through TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), advance tax, or self-assessment tax. When the total tax paid or deducted surpasses your tax liability as calculated in your Income Tax Return (ITR), the excess amount is refunded. This mechanism ensures taxpayers are reimbursed for any overpayments.
Who is Eligible for a Tax Refund?
Eligibility for a tax refund depends on various factors:
Excess Tax Payments If your TDS or advance tax payments exceed your tax liability, you’re eligible for a refund. This often applies to salaried employees, freelancers, and individuals with taxable investment income.
Claiming Deductions If you claim deductions under sections like 80C, 80D, etc., and these deductions lower your tax liability below the total tax paid, a refund may be due.
Filing an Income Tax Return Only those who file their Income Tax Return can claim a refund. The return must accurately reflect your income, deductions, and tax payments to establish if a refund is warranted.
Losses to Set Off If you have losses from previous years or the current year that can be carried forward and set off against current year income, you might be eligible for a refund if these losses reduce your tax liability.
Who is Not Eligible for a Tax Refund?
Certain situations or individuals may not qualify for a tax refund:
Income Below Taxable Threshold If your total income is below the taxable limit, a refund may not be applicable.
Salary Below Government Criteria Individuals earning below the minimum threshold specified by the Government of India may not qualify for a refund.
No Overpayment If your tax payments match your tax liability or you haven’t overpaid, a refund will not be available.
Non-Filers or Incorrect Filers Those who fail to file their Income Tax Return or file it incorrectly will not be eligible for a refund. Proper filing is essential for initiating the refund process.
Invalid Deductions Claims for deductions that do not meet tax regulations or lack valid documentation may result in a refund rejection.
Incorrect Bank Details If the bank account information provided in your ITR is incorrect or incomplete, the refund may not be processed.
How to Claim Your Tax Refund
Here’s a step-by-step guide to claiming your tax refund:
File Your Income Tax Return (ITR) Access the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal. Choose the correct ITR form based on your income sources and eligibility. Accurately complete all required details, including income, deductions, and tax payments.
Verify Your ITR Verify your ITR using Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or by sending a signed ITR-V to the Centralised Processing Centre (CPC). Verification must be completed within 120 days of filing your ITR.
ITR Processing The Income Tax Department will process your return, assess your tax liability, and determine the refund amount. This process can take a few weeks to several months.
Refund Issuance After processing, the refund will be credited directly to your bank account. Ensure your bank details are accurate and up-to-date in your ITR.
Update Bank Account Details (if needed) If your bank details change after filing your ITR, promptly update them on the e-filing portal to ensure correct refund crediting.
How to Check Your ITR Refund Status for FY 2024-2025
To check your refund status, follow these steps:
Visit the Income Tax E-Filing Portal Go to the official Income Tax Department e-filing website.
Access the 'Refund Status' Section Navigate to the ‘Refund Status’ page, typically under the ‘Services’ tab or a similar heading.
Enter Required Details Input your PAN (Permanent Account Number) and the assessment year for your filed return.
Review the Status The portal will show the status of your refund, including whether it has been processed, approved, or if further action is needed.
Track Refund Processing Keep an eye on any updates or notifications from the Income Tax Department regarding your refund.
Understanding the tax refund process can simplify the experience. By following these steps and staying informed about your eligibility, you can make sure that you have a smooth process and quickly receipt of any excess tax payments. For expert guidance and personalized assistance, consult with JJ Tax. Visit our website or contact us today to get the support you need for all your tax-related queries.
JJ Tax
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Common Tax Audit Challenges Faced by Delhi Businesses—and How to Overcome Them

For businesses in Delhi, undergoing a tax audit is a mandatory part of financial compliance once certain thresholds are crossed. While tax audits ensure transparency and adherence to Indian tax laws, they can also bring stress and confusion. Many companies encounter issues such as documentation gaps, deadline pressures, or tax calculation errors. In this blog, we break down the most common challenges in Tax Auditing in Delhi—and how businesses can overcome them with the right strategies.
Why Tax Audits Are Important
As per Section 44AB of the Income Tax Act, a tax audit is required if your turnover or professional receipts exceed the specified limits. Beyond legal compliance, a tax audit ensures that your financial records are accurate and up to date—helping avoid penalties, support funding, and protect your business reputation.
Top Tax Audit Challenges Faced by Businesses in Delhi
1. Incomplete or Inaccurate Records
Many businesses, especially MSMEs, struggle with maintaining organized books. Missing invoices, inconsistent ledgers, or outdated financial records make the audit process more difficult.
Solution: Use accounting software and establish monthly review routines to ensure all transactions are properly recorded.
2. GST and TDS Mismatches
Discrepancies between income reported in GST filings and books of accounts or errors in TDS deductions often result in audit red flags.
Solution: Perform monthly reconciliations of GST returns and TDS filings to match your books and rectify errors before the audit.
3. Lack of Understanding of Tax Sections
Misinterpretation of disallowance rules under Sections 40A(3), 43B, etc., may lead to incorrect reporting.
Solution: Consult professionals who specialize in Tax Auditing in Delhi to ensure each section is applied correctly.
4. Delays in Submitting Required Documents
Tax auditors require access to various documents—from bank statements to Form 26AS. Businesses often face delays due to poor organization.
Solution: Keep an audit checklist handy throughout the year and store key documents in a centralized system for quick access.
5. Missed Deadlines and Penalties
Failure to conduct and submit the tax audit report (Form 3CD) on time attracts penalties under Section 271B.
Solution: Engage with a chartered accountant early in the year to schedule audit timelines and avoid last-minute rushes.
Real-Life Scenario: How a Delhi Retailer Turned Around Audit Gaps
A retail business in Karol Bagh faced repeated delays due to TDS mismatches and missing GST input records. With help from Ruchi Anand and Associates, they implemented a digital record system and reconciled all tax accounts monthly. The next audit report was submitted on time with zero errors—earning them better creditworthiness from lenders.
How Professional Auditors Help Solve These Issues
Conduct pre-audit assessments
Provide document checklists
Reconcile inconsistencies in tax filings
Suggest internal process improvements
Ensure timely and accurate Form 3CD submission
FAQs
Q1: What if I fail to conduct a tax audit in time? You may be liable for a penalty of up to ₹1.5 lakh or 0.5% of turnover, whichever is lower, under Section 271B.
Q2: Can I request a tax audit even if I’m not legally required to do so? Yes. Many companies opt for voluntary audits to improve financial accuracy and investor confidence.
Q3: How long does a tax audit take to complete? Depending on the size of your business and quality of records, a tax audit typically takes 2–4 weeks.
Conclusion
While Tax Auditing in Delhi is a legal necessity for many businesses, it doesn’t have to be a stressful experience. By anticipating challenges and preparing ahead, you can make the audit process smooth and even beneficial. Partnering with a qualified audit firm ensures compliance, saves time, and prevents costly mistakes.
Need help with your upcoming tax audit? Trust Ruchi Anand and Associates to guide you through every step of the audit process—accurately and efficiently.
#Tax Auditing in Delhi#internal audit in india#usaid audit in india#income tax audit in india#due diligence services in india
0 notes
Text
Should NRIs File An Income Tax Return In India?

Many NRIs believe they are not required to file an income tax return in India—particularly when their income is either exempt, taxed at source through TDS, or falls below the basic exemption limit. However, this assumption can be risky. With advanced tracking systems like the Annual Information Statement (AIS) and the Compliance Management portal (CPC-CM), the Indian Income Tax Department now monitors financial transactions more closely than ever. Even if there’s no tax liability, non-filing can trigger notices, create compliance issues, and lead to unnecessary complications. This blog explores when and why NRIs should consider filing a return in India.
Who is required to file an income tax return?
The Income Tax Department has laid down specific conditions under which filing becomes mandatory, regardless of whether tax is payable. These rules go beyond just income thresholds and extend to high-value transactions, TDS deductions, business turnover, and even claiming refunds. For NRIs, it’s particularly important to understand that certain types of income may still require filing, even if the total income appears exempt. Here’s a simplified breakdown of who must file a tax return under Indian law.
Anyone having an income of more than the maximum amount not chargeable to tax (basic exemption limit). Basic exemption limit is ignored for non-residents having income taxed at specified rates (e.g. LTCG on capital asset)
Anyone who incurs expenditure of more than Rs. 200,000 for foreign travel or Rs. 100,000 or more for electricity charges
Anyone who deposits cash of more than Rs. 1 crore in current account or Rs. 50L in one or more savings accounts
Anyone whose business sales turnover exceeds Rs.1 crore or gross receipts in the Profession exceeds Rs.50 Lakhs
Anyone whose TDS/TCS is Rs.25,000 or more (Rs.50,000 for resident senior citizen)
Any Ordinary Resident who owns or has beneficial interest in an asset or account out of India
Anyone who has sustained a loss that he wants to set off and/or carry forward to the next years,
Anyone who wants to claim a refund of TDS deducted on the interest income, even if it is below basic exemption limit
A company or a firm
Real examples of how filing is beneficial
While many NRIs assume they don’t need to file a tax return if there’s no taxable income, the reality is more nuanced. In several situations, filing a return can help NRIs recover excess TDS, remain compliant, or avoid unnecessary scrutiny from the Income Tax Department. Here are a few real-life examples that illustrate why filing is not just necessary in some cases, but also highly beneficial.
Zeeshan from Saudi Arabia has an NRO FD of Rs. 1,000,000 generating Rs. 100,000 as interest on which TDS of Rs. 31,200 is being deducted every year. Mr. Zeeshan is not required to file the income tax return as his income is less than 250,000. However, if he wants to claim the refund of tax, he would be required to file the tax return before due date. Owing to the ignorance of Income tax provisions, many NRIs like Mr. Zeeshan do not file tax return to claim the refund and end up paying more taxes every year in higher TDS rates.
If Mr. Praveen from USA has only short term capital gain on sale of equity Rs. 200,000, he would still be required to file the tax return as basic exemption is not allowed against STCG of equity to non-residents.
These examples underline a key point – Filing an ITR isn’t always about paying tax; it’s often about protecting your financial interests as an NRI. The following persons are thus recommended to file income tax return
Anyone who has entered into certain transactions during the year that have been reported to the income tax department under the Annual Information Statement (AIS).
Anyone who has made or entered into any large transactions, even if it resulted in generation of income that is exempt from income tax in India.
Why notices are sent – Even for exempt income
The Income Tax Department (ITD) in India is getting smarter every year and is using information technology to track major financial transactions. The ITD has been tracking and collecting all major financial information by requiring institutions to report such transactions. The objective is to restrict creation of black money and widen the tax base by identifying the potential taxpayer by examining their income, expenditure or investments patterns.
The Income Tax department includes all important high-value transactions in the Annual Information Statement (AIS), even if they result in exempt income. AIS is a comprehensive view of information for a taxpayer as submitted by various institutions. Taxpayers can provide feedback on information displayed in AIS and AIS will show both reported value and modified value (i.e. value after considering taxpayer feedback).
The Income Tax Department analyzes and compares the collected information with the income tax return filed by the taxpayer and if any discrepancy is found, notices are being issued.
Consequences of ignoring filing
Notices to NRIs even if income is exempt from tax:
Credits in the NRE accounts are being reported to the Income Tax department by the banks. While interest on NRE accounts is exempt from tax, if return is not filed and NRE interest is not reported as exempt income, the IT department has been issuing notices to NRIs asking them to explain the source of funds in the NRE accounts and why the income tax return is not filed.
Example:
Mr. Ravi, an OCI from the USA, transferred Rs. 20,000,000 from USA to India in the F.Y. 2021-22 and invested in NRE bank FDs. As NRE FD interest is exempt from tax, he did not file the tax return in India. However, the Income tax department received a detailed report that included credits in the NRE bank account during F.Y. 2021-22 and realized that no income tax return was filed. They may issue a notice asking to explain the source of funds credited in the NRE accounts. Practically, it is advisable for NRIs having significant NRE FDs to file income tax return and include all the exempt income to avoid or to have a base to reply to such notices.
What to do when you receive such notice?
It would be a mistake to ignore the notice as it would be kept open unless responded to. While the ITD may not follow up immediately, eventually, if not closed, it will be followed sooner or later and may be with harsh language and/or consequences. There are standard replies in a compliance module that needs to be selected from the drop-down menu. The person would need to select the reasons for non –filing (no taxable income or return under preparation) or provide details of return filed – date, acknowledgement number, circle/ward, city and mode of filing (electronic or physical).
Example:
Mr. Jaymit Shah, an NRI from Hong Kong, sold a residential property during 2024-25 for Rs. 10,000,000 resulting in a long-term capital gain of Rs. 2,000,000 and tax liability of Rs. 416,000. Mr. Shah did not have any other income during the year. He calculated and paid all the taxes of Rs. 416,000. However, he did not file a tax return. The Income Tax Officer (ITO) would know about the sale of immovable property and tax paid by Jaymit through CIB after about a year. As the income tax return had not been filed, ITO would not be able to compare the information with the return. ITO would issue a notice and follow up with Jaymit requiring him to file the tax return and may initiate proceedings as if the income has escaped assessment.
The Role of NRI Tax Consultants in India
Navigating tax compliance as an NRI can be complex, especially with evolving reporting systems like AIS and stricter scrutiny by the Income Tax Department. This is where NRI tax consultants India, like ExpertNRI, play a crucial role. From interpreting your AIS to determining whether a return is required, to accurately preparing your ITR, managing exempt income, and responding to notices – ExpertNRI simplifies every step. Their deep understanding of NRI-specific issues ensures you stay compliant while avoiding unnecessary penalties or missed refunds. More than just filing returns, ExpertNRI protects your financial interests in India, offering peace of mind and proactive tax strategy. With expert guidance, you’re never alone or unprepared – just compliant, informed, and well-represented.
Resource: Should NRIs File An Income Tax Return In India?
#BestFinancialAdvisorFirmsIndia#NRIInvestmentOpportunitiesInIndia#NRIWealthManagementServices#NRIRemittanceServices#NRIRepatriationServices#NRITaxConsultants#NRITaxServices#NRITaxPlanning#NRIComplianceServices#NRITransitionsServices#NRIReturningToIndia#NRIFinancialManagementServices#NROtoNREFundTransfer#NROAccountManagement#NREAccountManagement#FEMARegulationForNRIs#FEMACompliantInvestments#NRIInvestmentInRealEstate#GiftCityInvestmentIndia#NRIFinancialPartner#ExpertNRI#India
0 notes
Text
Key Parameters Analyzed in Chiller Water Testing: pH, Hardness, TDS & More
In modern HVAC systems, chillers play a vital role in maintaining optimal temperatures across commercial, industrial, and institutional buildings. To ensure these systems operate efficiently, Chiller Water Testing becomes essential. Proper analysis of water quality helps prevent corrosion, scaling, biofouling, and system inefficiencies. This blog explores the key parameters analyzed in chiller water testing—including pH, hardness, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), and more—highlighting their significance in protecting equipment and reducing energy consumption.
What is Chiller Water Testing?
Chiller Water Testing involves the chemical and microbiological analysis of water used in chiller systems. These systems rely on water to transfer heat away from a building or process. If the water quality is not properly maintained, it can degrade components like pipes, evaporators, condensers, and pumps—leading to increased energy usage, unplanned downtime, and high maintenance costs.
Routine testing ensures that water treatment programs are effective and the water chemistry is within the desired operating limits.
Why Is Chiller Water Testing Important?
Prevents Corrosion and Scaling: Testing helps identify corrosive or scale-forming tendencies.
Improves Energy Efficiency: Clean systems operate with less energy.
Extends Equipment Life: Controlling contaminants minimizes wear and tear.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Especially in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and healthcare.
Minimizes Downtime: Proactive testing helps detect issues before they become major problems.
Key Parameters in Chiller Water Testing
Let’s look at the most critical parameters commonly measured in chiller water testing labs:
1. pH Level
Target Range: 7.0 – 8.5 (depending on system requirements)
pH is one of the most important indicators of water chemistry. Water that is too acidic (low pH) can lead to metal corrosion, while alkaline water (high pH) can result in scaling and poor heat transfer.
Maintaining a neutral to slightly alkaline pH ensures minimal corrosion while avoiding mineral buildup.
2. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
Target Range: Below 1,000 ppm (for most chilled water systems)
TDS measures the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances in water. High TDS can:
Reduce heat exchange efficiency
Contribute to scaling
Lead to microbial growth
Regular monitoring ensures that the system remains within operational thresholds.
3. Water Hardness
Measured as: Calcium and Magnesium (in ppm or grains/gallon)
Hard water contains high levels of calcium and magnesium ions, which cause scale formation on heat exchanger surfaces. This buildup acts as an insulator, reducing heat transfer and increasing energy consumption.
A water softening system or chemical treatment can help reduce hardness levels, and testing confirms its effectiveness.
4. Alkalinity
Target Range: 50 – 150 ppm (as CaCO₃)
Alkalinity measures the water’s ability to neutralize acids. Excessive alkalinity can increase the risk of scale formation and raise the pH beyond the acceptable limit. Too low, and it may lead to corrosion due to poor buffering capacity.
Balancing alkalinity is key to maintaining system stability.
5. Conductivity
Unit: µS/cm (microsiemens per centimeter)
Conductivity is an indirect measure of TDS. High conductivity suggests elevated mineral content and potential for scaling or biofilm formation. It’s often used as a quick field parameter to monitor water quality.
6. Chloride and Sulfate Levels
Chloride: Corrosive to stainless steel and copper alloys Sulfate: Can cause scale in combination with calcium
These anions can significantly impact corrosion rates. Elevated levels, especially in combination with low pH, can lead to pitting corrosion, which is highly destructive to metal surfaces.
7. Microbiological Activity
Tests include:
Total Bacterial Count
Presence of Legionella
Algae and Slime-forming Organisms
Bacterial growth in chiller systems can cause biofouling, reduce flow efficiency, and lead to health risks. This is particularly important in hospital HVAC systems and food-grade environments.
8. Inhibitor Concentration
Water in closed-loop systems is often treated with corrosion and scale inhibitors. Chiller water testing ensures these chemicals remain in effective concentration ranges. Too little leads to corrosion; too much may increase operational cost without added benefit.
9. Silica
Range: Less than 20 ppm (ideal)
Silica can precipitate onto heat exchanger surfaces, forming hard and glassy deposits that are difficult to remove. Silica scale dramatically lowers heat transfer efficiency and may damage system components.
10. Iron and Manganese
Iron and manganese levels can indicate ongoing corrosion inside the system. Excess levels also contribute to staining, scaling, and bacterial growth. Their presence in high amounts calls for immediate corrective action.
How Often Should Chiller Water Be Tested?
Weekly or Monthly: For routine monitoring of pH, conductivity, TDS, and inhibitor levels.
Quarterly or Bi-Annually: For a full spectrum analysis including microbiological testing.
After Maintenance or Refills: Immediately test after adding water or performing system maintenance.
Choosing a Chiller Water Testing Lab
A certified and experienced water testing laboratory will offer:
Testing as per ASHRAE, AHRI, and IS standards
On-site sample collection and fast turnaround times
Expert interpretation and treatment recommendations
Detailed reporting on all physical, chemical, and microbial parameters
In commercial and industrial setups, these insights help facilities management teams make informed decisions to optimize HVAC performance and extend system life.
Conclusion
Chiller Water Testing is not just a routine maintenance task—it’s an essential part of preserving your HVAC investment. By closely monitoring parameters such as pH, TDS, hardness, conductivity, and microbiological activity, facility managers can prevent corrosion, improve system efficiency, and reduce operational costs.
For long-term sustainability, partner with an accredited chiller water testing lab that uses advanced analytical techniques and complies with international guidelines. Regular testing and corrective treatment will ensure your system continues to run smoothly—without unnecessary downtime or energy waste.
#chiller water testing#water testing#water testing lab#testing lab near me#testing lab in delhi#water testing laboratory#testing lab#testing labs
0 notes
Text
Top Regulatory Requirements New Businesses Cannot Ignore

A new business is an adventure that is very thrilling, yet it is accompanied by numerous legal and regulatory compliance requirements that should be fulfilled to allow successful operations without encountering hefty penalties.
Are you looking for the best Legal Compliance for a New Business? If yes, look no further than Corporate Clairvoyants is your one-stop shop when it comes to helping startups understand the messy world of compliance. The following is an exhaustive list of the best regulatory requirements every business startup ought to consider-
1. Business Registration and Licensing
Make sure your business is duly registered and that you possess all licenses before starting your business.
Company Registration- Use the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) to determine the proper company registration (e.g., Private Limited Company, Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), etc.).
GST Registration- This is an obligatory requirement in case your turnover sum is 20 lakh (in the case of special category states, it is 10 lakh) annually, following the Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017. This is a registration that enables you to charge tax to clients and be able to receive tax credit on the tax paid on business purchases.
Trade License- It is required to obtain a trade license offered by local municipalities to conduct legal activity in their region.
Industry-Specific License- There may be further licenses that will be needed since most businesses have specific licenses needed, such as FSSAI in the case of food businesses and a Drug License in the case of pharmaceuticals.
2. Intellectual Property Defense
Protect your innovations and brand-
Trademark Registration: This protects against abuse of your brand name, logo, and slogans.
Patent Filing: Grants rights to your inventions or distinct procedures.
Copyrights: It defends things that are original, such as software, designs, and marketing material.
The Design Registration: Protects the special visual appearance of your goods.
3. Compliance with Employment and Labor Laws: Employment and labor law compliance
Just and right treatment of your employees-
Employment Contracts- Employment, job roles, and duties should be clearly defined in terms of employment.
Minimum Wages Act- Comply with the stipulated minimum wage standards.
Provident Fund (PF) and Employees State Insurance (ESI)- Get registered and contribute accordingly by the existing thresholds.
Shops and Establishments Act: Adhere to the work, rest, and overtime guidelines.
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013: Where 10 or more employees are working, form an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) that can deal with cases of harassment at the workplace.
4. Tax Compliance
Keep current with the tax liability-
Income Tax, 1961- Annual returns must be filed, and Tax Deducted at Source (TDS), wherever necessary, will be deducted.
GST Compliance- Maintain the required records and file GST regularly (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-9).
Advance Tax Payments- You can pay taxes beforehand in case your tax burden is higher than 10000 rupees in the financial year.
Tax Audits- File any tax audit in case your turnover exceeds the stipulated limits.
5. Data Security and Protection
As everything becomes more digitalized, the need to provide customer data security is the priority-
Data Privacy Laws- Adhere to the Information Technology Act,2000, and the prospective Personal Data Protection Bill.
Privacy Policy- A well-written policy should explain the method of collection, storage, and usage of customer data.
Cybersecurity- Take measures such as ensuring a strong security protocol is applied to data to prevent its abuse.
6. Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Depending on your industry and business, you may also need to consider-
Environmental Clearances- For any business that may harm the environment, including a manufacturing unit.
Industry-Specific Regulations- Businesses need to remain aware of industry regulations (e.g., healthcare, finance, food preparation).
7. Regular Compliance Audits
It is important to conduct regular reviews and updates of your compliance status-
Internal Audits- Conduct an internal audit periodically to confirm compliance with all the regulatory requirements.
Record Keeping- Have clear financial records, contracts, employee records, and compliance records on file.
Legal Counsel- Seek legal advice to support compliance with complicated regulatory issues and limit the exposure to risks.
Conclusion
Starting any business is tough, and figuring out the regulatory environment can be tough. And that's exactly what Corporate Clairvoyants will help you with when it comes to the business side of things. Aside from helping new businesses get started, we offer enough corporate services that make compliance safe and easy, so you can focus your attention on being exponential. If you are searching forward to a Corporate Lawyer, we are here to assist you.
If you'd like to get in touch with any one of the Corporate Clairvoyants team members or just to learn more about us, visit Corporate Clairvoyants Corporate Services.
0 notes
Text
Top Compliance Services in India Every Startup Should Know
Starting a business is exciting, but keeping it legally compliant is where many startups stumble. Compliance services in India are essential for ensuring your company meets all the legal, regulatory, and tax requirements right from the beginning. Without the right support, startups risk fines, penalties, or even shutdowns due to non-compliance. In this blog, we’ll explore the top compliance services every startup in India must know to stay legally strong and future-ready.

1. Business Registration Services – Your First Legal Step
The foundation of a compliant business begins with proper registration. Choosing the right business structure is crucial—whether it's a Private Limited Company, LLP, or One Person Company.
Business registration services help you:
Choose the right entity type (Pvt Ltd, LLP, OPC)
Obtain a Certificate of Incorporation (COI)
Get a PAN, TAN, and DIN
Apply for GST registration, if applicable
With experienced professionals handling your registration, the process becomes smooth, error-free, and fast—saving time and ensuring legal accuracy. It's not just about paperwork; it's about creating a strong legal identity for your startup that aligns with your business goals.
2. GST Registration and Return Filing
If your startup is involved in selling goods or services and your turnover crosses the prescribed threshold, GST registration is mandatory. Post-registration, monthly or quarterly GST return filings become essential.
Compliance services ensure:
Accurate GST registration
Filing of monthly/quarterly GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and annual returns
GST reconciliation and audit readiness
Avoidance of late fees and penalties
Timely GST compliance builds credibility and allows businesses to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC), which reduces the cost burden.
3. ROC Filing Services in India �� Stay Company Law Compliant
Every registered company must comply with the Registrar of Companies (ROC) by filing annual returns, financial statements, and event-based forms like director changes or share allotments. ROC filing services in India help startups meet these requirements on time and accurately.
Key ROC compliance services include:
Filing of MCA annual returns (Form AOC-4 & MGT-7)
Director KYC and DIN updates
Form PAS-3 for share allotment
Form DIR-12 for director appointments/resignations
Non-compliance leads to penalties or disqualification of directors, which can severely impact operations and credibility. Partnering with a compliance service provider ensures your startup remains in good standing with the MCA.
4. Income Tax Filing and TDS Compliance
Beyond GST and ROC, startups also need to manage income tax filings—especially if they’re making profits or paying salaries and vendor fees. TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) compliance is essential if your company deducts taxes on payments made.
Key income tax services include:
Filing of ITR for the company or LLP
Advance tax calculations and payments
TDS returns and compliance (Form 24Q, 26Q)
Issuance of TDS certificates (Form 16/16A)
Timely income tax filing helps avoid notices, penalties, and legal hassles.
5. MSME Registration and Startup India Recognition
For eligible businesses, registering under MSME and Startup India can unlock a range of benefits such as tax exemptions, subsidies, and access to government tenders.
Services include:
Udyam Registration (MSME)
DPIIT Startup India Certificate
Assistance in availing benefits under government schemes
Trademark and IP support for brand protection
These services boost your brand's legal status and improve funding and partnership opportunities.
6. Labour Law & Payroll Compliance
As your startup grows and you hire employees, adhering to labour laws becomes critical. Labour compliance services help you manage PF, ESI, bonus, gratuity, and professional tax obligations seamlessly.
Payroll and labour compliance services include:
PF and ESI registration and returns
Salary structuring in accordance with labour laws
Maintaining statutory registers and records
Grievance handling and compliance audits
These ensure a legally safe workplace for your employees while avoiding disputes or penalties from labour departments.
7. Startup Compliance Solutions – One-Stop Legal Partner
Startups often struggle to juggle multiple legal tasks. That’s where startup compliance solutions come in — a bundled service that covers all major regulatory needs from registration to tax filing.
Benefits of opting for startup compliance packages:
One dashboard for all filings and renewals
Dedicated compliance advisor
Timely alerts for upcoming deadlines
Lower overall cost compared to individual services
This ensures that startups remain legally strong while focusing more on growth, innovation, and market reach.
8. Trademark Registration & IP Protection
Your business identity—name, logo, and slogan—must be protected from being misused. Trademark registration offers you legal ownership and helps in brand-building.
Services include:
Trademark search
TM filing and tracking
Response to objections (if any)
Copyright and patent advisory
IP compliance is not just a legal task but a strategic move to safeguard your brand identity.
Final Thoughts
For any startup in India, legal compliance isn’t just a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing responsibility. From choosing the right business structure to managing taxes and filings, a trusted compliance partner like Compliance Sarathi can make the journey smooth, affordable, and secure. By leveraging professional startup compliance solutions, your business can avoid legal risks, attract investors, and grow with confidence.
If you're looking for reliable ROC filing services in India or end-to-end compliance management, visit ComplianceSarathi.in — your legal journey starts here.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Set Up Alerts for Stock Price Movements?

Staying on top of market fluctuations is essential for every investor, whether you're a beginner or a seasoned trader. But monitoring the market every second of the day? That’s not realistic. That’s why learning how to set up alerts for stock price movements is a game-changer—it helps you track important price changes without constantly watching your screen.
In this guide, we’ll show you the best tools and methods to set up price alerts so you never miss an opportunity to buy, sell, or react quickly to stock changes.
Why Set Up Stock Price Alerts?
Stock prices can swing dramatically in minutes. With alerts in place, you can:
React quickly to market shifts
Lock in profits when a target price is hit
Limit losses with early sell notifications
Stay informed on your watchlist stocks
Setting alerts empowers you to trade smarter, not harder.
How to Set Up Alerts for Stock Price Movements
There are several platforms and apps that let you set up real-time price alerts easily. Let’s look at the most popular methods:
1. Using Brokerage Platforms
Most online brokers offer built-in alert tools:
✅ Example Platforms:
Robinhood
Fidelity
TD Ameritrade
E*TRADE
How to Set It Up:
Search for the stock you're interested in
Click on "Set Alert" or "Price Notification"
Choose your target price (e.g., "Alert me when Apple hits $200")
Select how you want to be notified (push, email, SMS)
2. Mobile Apps & Financial Tools
Several standalone apps offer advanced alert options—even if you don't use their brokerage services.
📱 Popular Apps:
Yahoo Finance
TradingView
Stocktwits
Webull
These apps offer more customizations, including:
Alerts for percentage changes
Alerts for volume spikes
Alerts for news events tied to the stock
3. Google Alerts (for News-Based Triggers)
While not price-specific, Google Alerts can help you track news that may affect stock prices.
How to Use:
Go to Google Alerts
Type in the company name (e.g., “Tesla stock news”)
Set notification frequency (daily, real-time, etc.)
This can complement price alerts by giving you early warning on potential catalysts.
Pro Tips for Setting Up Effective Alerts
To make the most of your alerts, consider the following:
Set realistic price targets based on past performance or resistance levels
Use both upper and lower thresholds to cover upside and downside risk
Avoid alert overload—only monitor stocks you’re actively interested in
Pair alerts with technical analysis for better trade timing
➡️ For a step-by-step walkthrough of different platforms and alert customization tips, check out this helpful guide: How to Set Up Alerts for Stock Price Movements?
Best Practices for Stock Alert Management
To avoid missing opportunities or becoming overwhelmed:
Review your alerts weekly to ensure they’re still relevant
Turn off alerts for stocks you no longer follow
Use multiple apps or platforms for backup notifications
Track triggered alerts in a journal or spreadsheet for reference
Final Thoughts
Knowing how to set up alerts for stock price movements can dramatically improve your reaction time and trading decisions. Whether you’re waiting for the right buying opportunity or protecting your gains, automated alerts keep you informed and in control—without the stress of constantly monitoring the market.
0 notes
Text
Nuclear Backscattering-Inspired Molecular Scattering Coefficient (MSC) for Reverse Engineering of Ice-Oil Interfacial Biosurfactants
Renato F. Silva
Abstract
This study introduces a novel physics-inspired approach for designing biosurfactants tailored for oil remediation in icy environments, drawing from Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy (RBS). We define a Molecular Scattering Coefficient (MSC) that quantifies surfactant penetration efficiency at oil-ice interfaces by translating nuclear scattering parameters to molecular dynamics. Combining coarse-grained and all-atom simulations, NSGA-III multi-objective optimization, and cryogenic validation, we engineered three biosurfactants with >40% interfacial tension reduction at -10°C and >80% biodegradation within 28 days. Additionally, preliminary metrics for ice-oil separation and viscosity reduction are discussed. Our environmental efficiency index (Φ) integrates MSC, insertion energy (ΔGinsert), and biodegradability probability (Pbio) into a unified optimization framework. This work contributes a foundational strategy for sustainable surfactant design through interdisciplinary modeling.
Keywords: biosurfactants, oil-ice interface, molecular scattering coefficient, reverse engineering, cryogenic remediation
1. Introduction
The accelerating frequency of Arctic oil spills (increase of over 300% since 2020; see [Ref. X]) demands urgent solutions for efficient cold-environment remediation. Conventional biosurfactants fail below 5°C due to:
Reduced molecular mobility
Increased oil viscosity
Limited biodegradation kinetics
Poor interfacial reorganization
Current approaches lack predictive frameworks for molecular design under cryogenic conditions. We address this gap through a radical transposition of Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy (RBS) principles to molecular interfaces. RBS quantifies material composition through particle scattering angles (θ) and energy loss (ΔE)—concepts we adapt to surfactant penetration dynamics. While this analogy involves scale differences (nuclear vs. molecular), it provides a useful abstraction for quantifying interfacial behaviors in cold systems.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1 Molecular Scattering Coefficient (MSC)
We define MSC as a quantum analog to nuclear backscattering cross-sections:MSC=∫0zc∂θ(z)∂zexp(−ΔG(z)kBT)dz
Where:
$\theta(z)$: Mean penetration angle relative to ice lattice normal (in radians)
$\Delta G(z)$: Free energy profile from umbrella sampling (in kJ/mol)
$z_c$: Critical depth (1.5 nm, justified via density gradient thresholds in Supplementary §S2)
$k_B T$: Thermal energy (in kJ/mol)
MSC units: rad·nm⁻¹
A first-principles derivation based on interface thermodynamics and angular diffusion is provided in Supplementary §S1.
2.2 Environmental Efficiency Index (Φ)
To reflect molecular performance and sustainability, we define a revised Φ function:Φ(R,X)=MSC(R,X)⋅Pbio(R,X)∣ΔGinsert(R,X)∣
Subject to constraints:
$|\Delta G_{\text{insert}}| \leq 80,\text{kJ/mol}$
$P_{\text{bio}} \geq 0.75$
$\Delta H_{\text{mic}}(-10^\circ \text{C}) < 20,\text{kJ/mol}$ (empirical threshold derived from cryo-micellization studies [Ref. Y])
3. Methods
3.1 Computational Pipeline
graph TD A[Coarse-Grained Screening] --> B[All-Atom MD] B --> C[ΔG_insert Calculation] C --> D[MSC Evaluation] D --> E[QSAR Biodegradability] E --> F[NSGA-III Optimization] F --> G[Top Candidates]
Simulation Details:
Force Fields: CHARMM36 for surfactants, TIP4P/Ice for water. Validation against experimental interfacial tensions is provided in Supplementary §S3.
Temperatures: -10°C, 0°C, 10°C
Software: GROMACS 2024.1, PLUMED 2.8
Sampling: 3,000 ns aggregate sampling across 6 replicas. Convergence metrics in Supplementary §S4.
3.2 Experimental Validation
Interfacial tension: Cryo-ellipsometry (Krüss ESA, -10°C)
Biodegradation: Modified OECD 301F at 5°C (limitations in Arctic microbial modeling acknowledged)
Benchmarks: Rhamnolipids, Triton X-100, and Petrozyme™
4. Results
4.1 MSC Correlates with Interfacial Activity
Figure 1: Correlation (R²=0.89; 95% CI indicated) between MSC and experimental interfacial tension reduction at -10°C. BS-03 achieves leading performance, exceeding Petrozyme™.
4.2 Optimized Biosurfactants
Table 1: Performance of engineered biosurfactantsCompoundMSCΔGinsert (kJ/mol)PbioΦΔγ (%)BS-010.17 ± 0.0263.4 ± 1.20.82 ± 0.030.2242.3 ± 1.1BS-020.15 ± 0.0158.9 ± 0.90.87 ± 0.020.2246.1 ± 0.9BS-030.23 ± 0.0371.2 ± 1.50.79 ± 0.030.2648.7 ± 1.2Rhamnolipid0.08 ± 0.0192.5 ± 2.10.68 ± 0.040.0618.4 ± 0.8
4.3 Structural Insights
Figure 2: BS-03 at oil-ice interface (-10°C) showing:
Alkyl chain (C16) penetration into quasi-liquid layer
Glucosyl headgroup H-bonding with ice lattice
Low-energy conformation (ΔG = -12.3 kJ/mol)
SAXS/SANS profiles for BS-01 and BS-02 are included in Supplementary §S5.
5. Discussion
5.1 The MSC Paradigm
MSC demonstrates utility in predicting surfactant efficiency. The metric translates:
Scattering angle → Molecular orientation
Energy loss → Free energy barriers
Depth profiling → Penetration dynamics
BS-03's high MSC correlates with top performance. Simulated energy minima suggest this value approaches theoretical optimum for branched amphiphiles in quasi-liquid layers (Supplementary §S6).
5.2 Cold-Adaptation Mechanisms
Optimized surfactants share key features:
Branched alkyl chains: Prevent crystallization at -10°C
Glycosyl headgroups: Form ice-mimetic H-bond networks
Kinked spacers: Enhance conformational flexibility
graph LR A[Branched Chains] --> B[Prevent Crystallization] C[Glycosyl Heads] --> D[Ice Lattice Matching] E[Kinked Spacers] --> F[Conformational Flexibility]
5.3 Environmental and Deployment Implications
The revised Φ index enabled simultaneous optimization of:
Performance (MSC)
Energy efficiency (ΔGinsert)
Sustainability (Pbio)
BS-01 to BS-03 achieved complete mineralization within 28 days. Arctic deployment feasibility, including sea ice mobility and biosurfactant delivery methods, is discussed in Supplementary §S7.
6. Conclusion
We present a physics-driven framework for biosurfactant design:
MSC: First nuclear physics-derived metric for molecular interfacial efficiency
Φ index: Multi-objective sustainability-oriented optimization
Cryogenic validation: Benchmarking at -10°C under field-relevant conditions
Limitations include sensitivity of MSC to ice facet geometry and limited microbial modeling. Despite these, our approach achieves leading cold-environment remediation performance, surpassing commercial benchmarks.
References
Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces (Academic Press, 2011)
Gudina, E. J. et al. Bioresour. Technol. 191, 205-213 (2015)
Ziegler, J. et al. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 249, 584-604 (2006)
Sakai, Y. et al. Langmuir 36, 11561-11569 (2020)
Myers, D. Surfactant Science and Technology (Wiley, 2020)
CHARMM36 Validation. Proteins 82, 1165 (2014)
NSGA-III. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 18, 694 (2014)
Cryogenic MD. J. Chem. Phys. 153, 204101 (2020)
0 notes
Text
Don't Owe Tax? Why You Still Need to File a Nil ITR

If your income falls below the taxable limit, you might think filing an Income Tax Return (ITR) is unnecessary. However, submitting a Nil ITR can actually save you money and simplify various financial and legal processes.
What Exactly is a Nil ITR?
A Nil ITR is an income tax return filed when your total income for the financial year doesn’t exceed the basic exemption limit set by the tax authorities, meaning you have no tax liability.
Why File a Nil ITR? It’s More Beneficial Than You Think!
Even if you don’t owe any tax, filing a Nil ITR offers several advantages:
Reclaim Your Money:
If Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) has been withheld from your income (like interest from bank deposits or payments for freelance work), and your total income is below the taxable threshold, filing a Nil ITR is your ticket to getting that surplus TDS back.
Essential for Applications:
Need a passport? A Nil ITR often serves as valid address proof.
Applying for a visa? It’s frequently required to demonstrate your financial standing.
Seeking a loan? Even without a tax liability, a Nil ITR provides crucial evidence of your income for financial institutions.
Carry Forward Losses:
If you’ve incurred stock market losses, filing an ITR (even a Nil one) is essential to carry forward these losses. This allows you to offset them against future capital gains, potentially saving you money down the line.
Mandatory for Certain Situations:
Foreign Assets: If you own any assets outside of India, filing an ITR is mandatory, regardless of your income level.
High-Value Transactions: You must file an ITR if you’ve:
Deposited over ₹1 crore in current accounts.
Incurred significant expenses on foreign travel.
Paid substantial electricity bills.
Maintain Financial Records: A Nil ITR helps you keep a clear record of your financial transactions, which can be invaluable for future reference and compliance.
Utilize Tax Rebates: Even if your income is below the taxable limit due to available rebates (like up to ₹12,500 under the old tax regime or ₹25,000 under the new regime), filing an ITR is still necessary to claim these benefits and ensure proper tax documentation.
Key Deadlines to Remember
The deadline for filing a Nil ITR generally aligns with that of a regular return. For the fiscal year 2024-25, the deadline for non-audit cases has been extended to September 15, 2025. The good news is that unlike regular returns, no late fees apply for belated Nil ITRs, giving you a bit more breathing room.
Basic Exemption Limits (Quick Reference)
Old Tax Regime:
Below 60 years: Up to ₹2,50,000
Between 60 and 80 years: Up to ₹3,00,000
Above 80 years: Up to ₹5,00,000
New Tax Regime:
Uniform exemption limit of ₹3,00,000 for all individuals.
The Bottom Line
While a Nil ITR indicates no tax liability, the act of filing it goes beyond mere obligation. It’s a proactive step that can save you money by allowing you to claim refunds, and it provides essential documentation for various financial and legal processes. Understanding these aspects is crucial for everyone, whether you’re new to tax filing or a seasoned taxpayer.
Do you have any specific questions about filing a Nil ITR, or would you like to know more about a particular benefit?
0 notes
Text
Benefits of Filing ITR Even If You’re Not Mandated To

Many individuals in India believe that if their income is below the taxable threshold, they are exempt from filing Income Tax Returns (ITR). While it's true that ITR filing is not legally mandatory for everyone, voluntarily filing your ITR can offer a wide range of long-term financial and legal benefits. Whether you're a student, homemaker, senior citizen, or a freelancer with minimal income, submitting an ITR can be a smart financial move.
In this article, we explore the key benefits of ITR filing, even when you're not required to by law.
1. Claim Tax Refunds
One of the most direct benefits of ITR filing is the ability to claim a refund on taxes already deducted. If your employer or bank has deducted TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) on salary or interest income, but your total income is below the taxable limit, filing an ITR allows you to claim that money back.
Example:
If your annual income is ₹2.4 lakhs but your bank deducted TDS on fixed deposit interest, filing ITR is the only way to get that refund.
2. Smooth Visa Processing
Planning to travel abroad for work, education, or leisure? Many foreign embassies—especially those of the US, UK, Canada, and Schengen countries—ask for your ITR documents during visa interviews as proof of financial stability. Even a nil return helps build your financial credibility in such cases.
3. Serves as Income Proof for Loan Applications
When applying for loans—whether for a home, car, or education—banks and financial institutions often request ITRs for the past 2–3 years as proof of income. Even if you’re self-employed or a freelancer with irregular income, consistent ITR filing shows financial discipline and makes loan approvals smoother.
4. Helps Build a Financial Record
Just like a credit report, your ITR filings create a financial footprint. A history of filed returns shows consistency and transparency, which can be advantageous in future financial dealings, including investments, insurance, and property transactions.
5. Carry Forward Losses
If you have incurred a capital loss (e.g., from stock trading or property), filing your ITR—whether mandatory or not—allows you to carry forward these losses to offset them against future gains. This can significantly reduce your tax liability in subsequent years.
6. Avoid Notices from the IT Department
Even if your income is non-taxable, high-value transactions like large deposits, property purchases, or mutual fund investments can attract attention from the Income Tax Department. Filing a return proactively explains your income source and avoids unnecessary scrutiny or future notices.
7. Faster Processing of TDS and Income Reconciliation
When you file an ITR, you can easily reconcile your income with Form 26AS and AIS (Annual Information Statement). This ensures that the TDS deducted matches your income records and helps resolve discrepancies without future complications.
8. Eligibility for Government Tenders and Contracts
For professionals and small business owners, ITR filing is often a pre-requisite for applying to government contracts, tenders, or startup incentives. It acts as proof of business activity and financial compliance.
9. Facilitates Higher Insurance Coverage
Many life insurance companies now request ITR documents before issuing high-value policies (typically above ₹50 lakhs). It acts as a proxy for your income and helps underwriters assess your risk profile.
Final Thoughts
Even if your annual income is below the taxable limit, ITR filing offers a host of advantages that go far beyond tax compliance. From building a strong financial record to unlocking refunds and enabling credit access, the benefits are both immediate and long-term. With the process becoming increasingly digital and user-friendly, there’s really no reason not to file your return—even if you're not mandated to.
Start building your financial credibility today—file your ITR and stay ahead of the curve.
0 notes
Text
TDS Return Filing Madhapur | Tirumalesh & Co
TDS in India: Understanding Tax Deducted at Source and Its Functioning
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a crucial mechanism in India’s tax collection system. It ensures steady revenue for the government and promotes transparency in transactions. In this comprehensive guide, we will decode what TDS is, how it works, its importance, and offer practical insights into compliance.

What is TDS? Meaning and Definition
TDS, or Tax Deducted at Source, is a system introduced by the Government of India to collect tax at the point where an income is generated, rather than at a later date. Under this system, a prescribed percentage of the payment is deducted by the payer while making specific payments such as salary, interest, commission, rent, professional fees, etc. The deducted amount is then remitted to the government on behalf of the receiver. Income Tax Filing Madhapur Hyderabad
This process is governed mainly by the provisions laid out in the Income Tax Act, 1961. The person who deducts TDS is called the diductor, and the person whose payment is deducted is termed the deducted.
How Does TDS Work? The Step-by-Step Process
Understanding how the TDS system operates is key to ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how TDS works in India: Best Ca Firms In Madhapur
1. Transaction Execution
When a payment is made that falls under the TDS provisions—such as salary, rent, contractual payments, or professional fees—the person responsible for making the payment (the deductor) checks if the payment amount exceeds the threshold limit specified under the Income Tax Act.
2. Rate Applicability
Each category of payment has its own TDS rate, defined by the government. For example, salaries may have a different TDS rate than commission or professional fees. TDS Return Filing Madhapur
3. Deduction of Tax
Before making the payment, the deductor deducts the TDS at the applicable rate.
4. Deposit with the Government
The deducted TDS amount is deposited to the Central Government’s account, using prescribed challans, generally within a stipulated period from the deduction date.
5. Filing of TDS Returns
The deductor is required to file quarterly TDS returns, mentioning details of the deductions and the beneficiaries.
6. Issuance of TDS Certificate
After depositing the TDS, the deductor issues a TDS certificate (such as Form 16 for salaries or Form 16A for other payments) to the deductee. The deductee can use these documents to claim tax credits while filing annual income tax returns.
Major Payments Subject to TDS
To streamline tax collection, the government requires TDS deduction for a broad range of payments. Some of the most common income streams where TDS is applicable include:
- Salaries
- Interest from banks and other financial institutions
- Payments to contractors and sub-contractors
- Rent payments
- Professional and technical fees
- Commission and brokerage
- Royalty payments
- Dividend payouts
Every payment type is regulated by a specific provision with a threshold limit and rate, periodically updated by the government in the Union Budget.
Importance and Benefits of TDS
1. Assured Collection of Revenue
TDS provides the government with a regular and steady source of revenue, reducing the chances of tax evasion.
2. Easy Compliance
Both individuals and businesses can comply easily with TDS obligations using digital platforms such as the TRACES portal and e-payment systems.
3. Wider Tax Net
By collecting tax at the source, the government ensures that taxpayers across various segments are brought into the tax net, enhancing overall compliance.
4. Tax Credit to Taxpayers
The deductee receives tax credit for the TDS, which can be adjusted against their total tax liability while filing income tax returns.
TDS Rates and Thresholds: A Snapshot
The rates at which TDS is deducted vary based on the nature of the transaction and the legal status of the deductee (individual, HUF, company, etc.). For instance:
| Nature of Payment | Threshold Limit | TDS Rate |
|----------------------------------|------------------------|----------------------|
| Salary | As per income slab | As per slab |
| Interest on securities | ₹5,000 | 10% |
| Dividend | ₹5,000 | 10% |
| Rent (Land/Building/Furniture) | ₹2,40,000 | 10% (individual) |
| Professional Fees | ₹30,000 | 10% |
| Contractor Payments | ₹30,000/₹1,00,000 | 1%/2% |
| Commission/Brokerage | ₹15,000 | 5% |
Note: TDS rates and thresholds are subject to change as per government notifications.
Consequences of TDS Non-Compliance
Non-compliance in TDS, such as failure to deduct or deposit the tax or not filing TDS returns, can result in:
- Interest for late deduction or deposit
- Penalty for failure to deduct or deposit
- Disallowance of the expenditure under certain circumstances
- Prosecution in extreme cases
It is therefore crucial for payers and receivers to stay updated with current TDS rules and deadlines.
How to Claim TDS Refunds
If excess TDS has been deducted, the deductee can claim a refund by filing their income tax return. After a review by the Income Tax Department, the excess amount (if any) is refunded to the taxpayer’s bank account.
Filing TDS Returns: An Overview
The deductor must electronically file TDS returns every quarter using the appropriate forms (such as Form 24Q for salary, 26Q for other payments to residents, and 27Q for payments to non-residents). Correct filing ensures timely credit of TDS to the deductee and avoids penalties.
Conclusion: The Centrality of TDS in India’s Tax System
TDS is the backbone of India’s contemporary taxation system. Practicing timely and accurate TDS deduction, deposit, and reporting reduces the burden at the end of the financial year, promotes a culture of tax compliance, and helps in nation-building. Both deductors and deductees benefit from understanding and adhering to TDS provisions, ensuring smooth, penalty-free financial operations.
For updated TDS rates, due dates, and compliance procedures, it is advisable to regularly consult the official Income Tax Department website or seek professional advice.
Tirumalesh & Co | Chartered Accountants offers expert Best CA Firms In Madhapur Get accurate, timely solutions from trusted professionals near you.
Call/What’s App – +91 84998 05550.
Location: https://bit.ly/42ljdS4
Visit link: https://www.catirumalesh.in/
#Income Tax Filing Madhapur Hyderabad#Best Ca Firms In Madhapur#TDS Return Filing Madhapur#Company Registration Madhapur#ROC Compliance Services Hyderabad#Professional Tax Filing Madhapur#Company Audit Services Near Me
0 notes
Text
Income Tax Audit in India: Why It Matters for Your Business

If your business or professional income has crossed certain thresholds, chances are you're required to go through an Income Tax Audit in India. This isn’t just about following rules—it’s about ensuring your financial records are clear, transparent, and in full compliance with the Income Tax Act. Audits serve as a checkpoint to verify that the information submitted in your tax returns matches your actual financial activities.
What Is an Income Tax Audit?
An income tax audit is a detailed examination of your financial accounts by a Chartered Accountant (CA). The goal is to confirm that all income, deductions, and other relevant details are correctly reported in your income tax return. The audit must be completed and submitted in a specific format as per Section 44AB of the Income Tax Act.
Who Needs a Tax Audit?
Not every taxpayer in India is required to undergo a tax audit. Here's when it becomes mandatory:
Businesses with annual turnover exceeding ₹1 crore (₹10 crore if 95% or more transactions are digital)
Professionals with gross receipts over ₹50 lakh
Individuals or firms using presumptive taxation schemes under Sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE who report lower profits than prescribed and have income above the exemption limit
Benefits of an Income Tax Audit
Ensures accuracy in income declaration
Minimizes the risk of tax penalties or scrutiny
Enhances credibility with financial institutions
Encourages systematic bookkeeping and compliance
Helps in faster and smoother tax assessments
Documents Required for Tax Audit
To complete the audit process efficiently, you’ll need to provide:
Complete financial statements (P&L, Balance Sheet)
Ledger accounts and journals
Cash flow details and bank statements
Fixed assets records and depreciation schedule
TDS statements and challans
Previous tax audit reports (if any)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Who can perform an income tax audit? Only a qualified Chartered Accountant (CA) registered with ICAI can conduct an audit under Section 44AB.
Q2: What’s the filing deadline? Tax audit reports must usually be filed by 30th September of the relevant assessment year unless otherwise notified.
Q3: What if I miss the audit deadline? A penalty may be imposed—0.5% of your turnover or ₹1,50,000, whichever is less, unless there’s a reasonable cause.
Q4: Is digital submission mandatory? Yes, tax audit reports must be submitted online with the digital signature of the auditing CA.
Conclusion
Understanding the rules and relevance of Income Tax Audit in India can help avoid legal trouble and financial misreporting. It’s a proactive way to ensure your business stays tax-compliant, well-documented, and audit-ready. Engaging a trusted CA and keeping your books in order can turn the tax audit from a stressful event into a routine business responsibility.
#Income Tax Audit#Tax Audit India#Section 44AB#Chartered Accountant#Income Tax Compliance#Tax Audit Rules#Business Audit#Professional Audit
1 note
·
View note
Text
Do NRIs Need To File Income Tax Returns In India?

Understanding The Rules, Case Studies, And Updated Deadlines
For many Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), submitting income tax returns in India might seem optional or even pointless – particularly when their income falls below the basic exemption threshold. Nevertheless, the Income Tax Act has clear rules that require return filing, and not adhering to these can result in lost refunds, penalties, or interest charges. In this blog, we explore the rules, exemptions, deadlines, filing methods, and practical examples that NRIs need to be aware of.
Who should file an ITR in India? A checklist for NRI investors
The following individuals are required to file an Income Tax Return (ITR) in India.
Anyone whose income surpasses the non-taxable threshold of Rs. 250,000 (However, this basic exemption does not apply to NRIs when their income is taxed at special rates, like Long-Term or Short-Term Capital Gains on equity or equity mutual funds)
Expenditures exceeding ₹2,00,000 on foreign travel, electricity bills over ₹1,00,000, or deposits exceeding ₹1 crore in a current account or ₹50 lakh in savings accounts
Business turnover that exceeds ₹1 crore or gross professional receipts that surpass ₹50 lakh
TDS/TCS of ₹25,000 or more (₹50,000 for resident senior citizens)
Any ordinary resident who possesses or has a beneficial interest in an asset or account located outside India
Anyone who has incurred a loss that they wish to set off and/or carry forward to subsequent years
Anyone seeking to claim a refund of TDS deducted on interest income, even if it falls below the basic exemption limit
All companies and firms, regardless of their income levels
Anyone who has engaged in specific transactions during the year that have been reported to the income tax department via the Annual Information Statement (AIS)
Anyone who has conducted any significant transactions, even if they resulted in income that is exempt from income tax in India
Real-Life Examples Every NRI Should Learn From
Example 1: Mr. A, a non-resident living in Saudi Arabia
Mr. A holds an NRO Fixed Deposit of ₹1,50,000, which generates ₹10,000 in interest annually and Tax is deducted (TDS) of ₹3,120 is deducted. As his total income is under ₹2,50,000, he is not obligated to file an ITR. However, if wants to claim the refund of tax deducted, he must submit his return by the due date. Many NRIs, like Mr. A, often miss filing returns due to lack of awareness, resulting in lost refunds and the burden of high TDS rates.
Example 2: Mr. B, a non resident living in the USA
Mr. B realized a short-term capital gain (STCG) of ₹2,00,000 from selling equity. While this amount is below the exemption threshold, NRIs are not eligible for the basic exemption on income that is charged at specified rate (STCG from equity is taxed at 20%). Mr. B is required to file an ITR, even if his income is below ₹2,50,000, and he is also required to pay tax of Rs. 41,600 (@20.8% including surcharge on STCG of 200,000) because the special tax rate provisions take precedence over the basic exemption for non-residents.
Income tax filing for NRIs: Physical, electronic & verification options
Physical: Only individuals residing in the country who are over 80 years old and using ITR-1 or ITR-4 forms are permitted to submit manual returns.
Electronic: All individuals under 80 years of age are required to file their returns electronically. All NRIs are also required to file their income tax returns electronically.
Income tax portal: You can download the JSON file for AIS Utility from the income tax portal. This file can then be imported into the AIS utility or income tax software, allowing for a pre-filled income tax return to be generated based on the JSON file. The taxpayer will need to review and adjust the figures as necessary before filing the tax return.
Verification: After filing, ITRs must be verified using a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC), Aadhaar OTP, or Electronic Verification Code (EVC) via Bank account, Demat account, or Net banking. Alternatively, the acknowledgement (ITR-V) can be printed, signed manually, and sent to the CPC – Bengaluru within 30 days of filing the return.
Due date of filing income tax return
For most NRIs, the standard deadline for filing income tax returns in India is July 31 of the relevant assessment year. However, for the financial year 2024-25 (assessment year 2025-26), the due date has been extended to September 15, 2025, owing to delays in updating tax forms and system infrastructure.
For individuals or Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) with income from business or profession where accounts are subject to audit, the filing deadline is October 31, 2025. If the taxpayer is also required to furnish a transfer pricing report, the deadline extends further to November 30, 2025.
Note: To carry forward any loss or to revise a return, the return must be filed within the prescribed due date. Filing beyond the deadline may lead to penalties and loss of certain benefits.
What if you miss the deadline?
Although income tax returns are ideally required to be filed by the due date, the law permits NRIs to file a belated return or a revised return up to by December 31. For the financial year 2024-25 (AY 2025-26), delayed return can be filed by December 31, 2025.
If the original return is not filed by the due date, it can still be submitted as a belated return by December 31. However, this attracts late filing fees and interest, and certain benefits – such as the ability to carry forward business or capital losses – will be forfeited.
If the original return was filed on time but contains errors, a revised return may be submitted by December 31. While interest at 1% per month may apply, no late filing fee is charged for revised returns.
Late filing fees for belated returns:
1,000 – if total income is below Rs. 5,00,000
5,000 – if total income exceeds Rs. 5,00,000
Note: Both belated and revised returns are subject to interest under Section 234A at 1% per month from the due date until the actual date of filing. Timely filing is crucial to avoid penalties and preserve tax benefits.
Why ExpertNRI recommends filing – Even when not mandatory
Drawing from extensive experience with NRIs in over 80 countries, ExpertNRI highly advises filing income tax returns in several important situations:
to obtain TDS refunds,
to adhere to foreign asset reporting obligations,
to carry forward business or capital losses,
to keep a clean and consistent financial record in India,
to report significant transactions shown in the Annual Information Statement (AIS), and
to prevent possible scrutiny or income tax notices based on the Specified Financial Transactions (SFT) or AIS transactions (e.g. new NRE FD).
Many NRIs fail to recognize the importance of timely and precise tax filing, particularly when their income seems to fall below the threshold. With ExpertNRI, you can receive clear, practical, and tailored guidance, ensuring compliance and peace of mind throughout your NRI financial journey.
Ultimately, while NRIs may not always be legally required to file income tax returns in India, doing so is often the smarter, more strategic choice – especially when viewed through the lens of long-term financial planning. Regular and timely ITR filing ensures compliance, minimizes future tax complications, and builds a credible financial history in India. This not only helps avoid penalties or missed refunds but also strengthens your position when making high-value investments, repatriating funds, or applying for financial products like loans or credit in India. For those exploring NRI investment opportunities in India, consistent tax compliance becomes a vital pillar of a secure, transparent, and opportunity-ready financial journey.
Resource: Read more
#BestFinancialAdvisorFirmsIndia#NRIInvestmentOpportunitiesInIndia#NRIWealthManagementServices#NRIRemittanceServices#NRIRepatriationServices#NRITaxConsultants#NRITaxServices#NRITaxPlanning#NRIComplianceServices#NRITransitionsServices#NRIReturningToIndia#NRIFinancialManagementServices#NROtoNREFundTransfer#NROAccountManagement#NREAccountManagement#FEMARegulationForNRIs#FEMACompliantInvestments#NRIInvestmentInRealEstate#GiftCityInvestmentIndia#NRIFinancialPartner#ExpertNRI#India
0 notes
Text
Gold Selling Regulations in Mohali: Legal Requirements and Documentation

Understanding the legal structure in Mohali is very important when selling gold. The city has very specific regulations that protect both buyers and sellers in precious metal transactions. These laws promote transparency and also stop illegal activities in the gold trade.
Many in the community who sell old gold in Mohali do not know the proper legal processes. This gap in knowledge results in issues with tax authorities or regulatory bodies. Compliance will protect your interests and ensure that your transaction goes smoothly.
The Mohali Admin has established extensive rules governing gold sales. These regulations are in accordance with national policies but also take into account the local market conditions. By familiarizing yourself with these requirements, you will be able to sell gold in Mohali legally and safely.
Identity Documentation Requirements
Every gold transaction in Mohali requires sellers to present proper identification. Government-issued photo identification is the foundation of legal compliance.
Aadhaar cards serve as primary identification for most transactions. Voters' identity cards, driving licences, and passports are equally acceptable alternatives.
PAN cards become mandatory for transactions exceeding ₹50,000 in value. This threshold applies to single transactions or multiple sales to the same buyer within a financial year.
Address proof accompanies identity verification in many cases. Utility bills, bank statements, or rental agreements establish your current residence status.
Old gold buyers in Mohali must maintain detailed records of all seller identifications. They photocopy these documents and store them for regulatory inspections.
Transaction Value Thresholds
Different transaction amounts trigger varying documentation requirements. Understanding these thresholds helps you prepare appropriate paperwork.
Sales below ₹50,000 require only basic identity verification. Sellers provide photo IDs, and buyers record the transaction details.
Transactions between ₹50,000 and ₹2 lakhs require additional documentation. At this level, PAN card submission becomes mandatory.
Sales exceeding ₹2 lakhs trigger reporting requirements to government authorities. Buyers must report these transactions to prevent money laundering.
Form 26QB requires filing for cash payments above ₹2 lakhs. This form details the transaction and both parties' information.
Tax Implications for Sellers
Capital gains tax applies to profits from gold sales in Mohali. The calculation depends on how long you owned the gold before selling.
Short-term capital gains apply to gold held for less than three years. These gains are taxed at your regular income tax slab rates.
Long-term capital gains affect gold held for three years or more. The tax rate is 20% with indexation benefits or 10% without indexation.
Purchase receipts and proof of acquisition date determine your capital gains calculation. Maintain these documents from your original gold purchases.
TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) applies to certain high-value transactions. Buyers deduct tax at source when purchasing gold above specified limits.
Business Licensing for Buyers
Gold-buying businesses in Mohali must obtain proper licences before operating. The Municipal Corporation issues trade licences for these establishments.
Shop and Establishment Act registration applies to all commercial gold buyers. This registration ensures compliance with labour and business laws.
GST registration becomes mandatory for buyers with annual turnover above ₹20 lakhs. Many established buyers register voluntarily for credibility.
Police verification forms part of the licensing process. Authorities conduct background checks on business owners and key employees.
State excise department clearances may apply depending on business structure and location.
Record Keeping Obligations
Both buyers and sellers benefit from maintaining comprehensive transaction records. These documents serve multiple legal and financial purposes.
Purchase invoices from your original gold acquisitions establish a cost basis for tax calculations. Store these safely throughout your ownership period.
Transaction receipts from gold sales provide proof of income reporting. They should include detailed breakdowns of weight, purity, and pricing.
Bank statements showing payment receipts help track financial flows. Electronic transfers create clear audit trails for large transactions.
Photography of items before sale provides additional documentation. Images help resolve disputes and support insurance claims.
Compliance Verification Process
Legitimate buyers in Mohali follow standard compliance verification procedures. Understanding these processes helps you identify professional operations.
KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures involve identity verification and address confirmation. Buyers collect and verify all required documents before transactions.
Digital documentation systems help buyers maintain accurate records. Many use computerised systems to track transactions and generate reports.
Regular compliance audits ensure buyers follow all applicable regulations. Government authorities conduct periodic inspections of licensed businesses.
Avoiding Legal Complications
Proper preparation prevents legal issues when you sell gold jewelry or other precious items. Following established procedures protects your interests.
Always deal with licensed, established buyers in Mohali. Check their credentials and verify their business registrations before transactions.
Maintain all required documentation throughout the selling process. Complete paperwork reduces complications and ensures smooth transactions.
When you sell gold for significant amounts, consider consulting with tax professionals. They provide guidance on reporting requirements and tax optimisation.
Selling gold for cash legally requires adherence to all applicable regulations and documentation requirements.
Professional Guidance Benefits
Working with experienced, compliant buyers simplifies the legal aspects of gold sales. They handle most documentation requirements and ensure regulatory compliance.
Choose buyers who explain their legal procedures clearly. Professional operations welcome questions about their compliance processes.
Research "sell gold near me in Mohali" options prioritising legal compliance and competitive pricing. Ready to sell gold in Mohali with complete legal compliance? Contact Jewel House for expert guidance on all regulatory requirements. Our experienced team ensures your gold transactions meet all legal standards whilst maximising your returns through transparent, compliant processes.
#jewel house#sell gold#cash for gold#gold buyer#sell gold near me in Mohali#sell gold in Mohali#gold near me in Mohali#sell gold mohali#mohali#cash for gold in mohali#gold buyer in mohali
0 notes
Text
Key Legal and Strategic Considerations After Company Registration in Mumbai (2025 Edition)
So, your company is officially registered in Mumbai — congratulations! But the journey doesn’t end there. Post-incorporation compliance and strategic planning are critical to ensuring your business operates smoothly, legally, and profitably.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of what to focus on after registration to build a strong legal and operational foundation.
1. 📂 Opening a Business Bank Account
Why it matters:
Keeps your personal and business finances separate.
Mandatory for statutory payments like GST, TDS, etc.
Helps maintain accounting accuracy and transparency.
Documents Required:
Certificate of Incorporation
PAN Card of the company
Memorandum & Articles of Association
KYC of directors
Board resolution authorizing account opening
Choose from leading banks company registration in Mumbai such as HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, or State Bank of India, depending on your preference for digital services or in-branch support.
2. 🧾 Apply for GST Registration
If your annual turnover exceeds:
₹40 lakh for goods
₹20 lakh for services
Then GST registration is mandatory. Even if your turnover is below the threshold, voluntary registration may be beneficial to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) and build business credibility.
Documents Needed:
PAN, Aadhaar
Company incorporation documents
Bank account proof
Office address proof
DSC & Authorized Signatory authorization
Apply on the GST portal.
3. 🧑💼 Appoint a Chartered Accountant or Company Secretary
You’ll need professional help for:
Filing statutory returns (ROC filings)
Annual financial statements
Audits (if applicable)
Advisory on tax saving and compliance
Engaging a Mumbai-based professional ensures faster response times and better understanding of local jurisdiction.
4. 📊 Set Up Bookkeeping & Accounting Systems
Good accounting is the backbone of legal and financial health.
Options:
Use accounting software: Tally, Zoho Books, QuickBooks India
Hire in-house accountant
Outsource to a CA firm
Make sure to track:
Sales and purchase invoices
Employee payroll
Tax payments (GST, TDS)
Reimbursements and petty cash
5. 🧑💻 Employment & Labor Law Compliance
If hiring employees, you must:
Register for EPFO & ESIC (mandatory if you have more than 10 employees)
Issue employment letters
Maintain salary registers and employee records
Follow Shops & Establishments Act, Maharashtra
Also ensure:
Gratuity and Provident Fund contributions
Compliance with sexual harassment laws (PoSH Act)
6. 📆 Mandatory Annual ROC Filings
Every company registered under the Companies Act must file annual returns with the Registrar of Companies (ROC), Mumbai.
Key filings:
MGT-7 – Annual Return
AOC-4 – Financial Statements
DIR-3 KYC – Director KYC filing
Due Dates:
30 days from AGM for AOC-4
60 days from AGM for MGT-7
30th September or 31st December for DIR-3 KYC
7. 📢 Brand & Trademark Protection
Your brand is your identity — protect it.
Register your company’s name/logo as a trademark under the Trademarks Act, 1999.
Filing can be done online via the IP India website.
Prevents others from copying or misusing your brand.
8. 💼 Build Business Credit & Apply for MSME Benefits
Once operational:
Apply for Udyam Registration (MSME Certificate)
Helps access government tenders, subsidies, and collateral-free loans.
Additionally, register on:
GeM (Government eMarketplace)
Startup India (if eligible)
9. 🧮 Conduct Board Meetings & Maintain Registers
As a private limited company, you are required to:
Hold first board meeting within 30 days of incorporation
Maintain statutory registers like:
Register of Directors
Register of Shareholders
Register of Charges (if any loan is taken)
10. 🗂️ Other Registrations (If Applicable)
Import Export Code (IEC): If you're in export/import
FSSAI License: For food businesses
Shop and Establishment License: Mandatory for businesses operating in Mumbai
Professional Tax Registration: Required in Maharashtra for employees and professionals
🚀 Strategic Advice for New Business Owners in Mumbai
Network Constantly: Attend local startup meetups, chamber of commerce events.
Stay Tax-Aware: Keep up with tax reforms through platforms like Taxmann, CAClubIndia.
Focus on Digital Presence: Build a website, register on Google My Business, start social media branding.
Stay Organized: Set up reminders for statutory compliance deadlines.
🏁 Conclusion
Company registration in Mumbai is just the beginning. The real work starts post-registration — with regulatory, operational, and strategic actions that shape your business’s future.
By staying compliant and focusing on sound financial and operational practices, you lay the foundation for long-term success and scalability.
0 notes