#factory design pattern in java
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Hey people! As announced in my last post, my new post about the Abstract Factory Pattern is now happily available on my channel!😀
youtube
#java #javaprogramming #javatutorial #javaforbeginners #javaprojects #python #python3 #pythonprogramming #pythontutorial #pythonforbeginners #pythonprojects #programming #factory #abstractfactory #abstractfactorypattern #method #pattern #designpatterns #oop #objectorientedprogramming
#java#javaprogramming#java for beginners#100daysofcode#coding is fun#design patterns#python#python for beginners#coding#programming#software#technology#code#developer#python3#java online training#python programming#pythonprojects#abstract#factory#pattern#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide

That’s why we’ve created "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" to help you get fully prepared and stand out from the competition.
Java remains one of the most widely used programming languages across the tech industry. From building enterprise-grade applications to Android development and cloud-based systems, Java is a powerful, object-oriented language that has stood the test of time. As a result, Java continues to be a core requirement in thousands of job listings globally, and technical interviews often focus heavily on Java fundamentals, coding practices, and real-world problem-solving.
This guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of the most commonly asked Java interview questions, along with expert-level answers that explain not just the what, but the why—helping you build a strong conceptual foundation.
Why This Guide Matters
"Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" is designed to equip you with the most relevant, up-to-date, and frequently asked questions across various job roles and experience levels. Whether you're a fresher just entering the field or a seasoned Java developer with years of experience, the questions included in this guide cover all the core areas expected in a Java interview.
With structured answers, real-world examples, and technical explanations, this guide helps you understand each topic in depth—so you’re not just memorizing, but truly learning.
Key Topics Covered in This Guide
Here are the primary categories of Java interview questions and answers covered in this ultimate preparation guide:
1. Core Java Basics
These questions test your fundamental knowledge of Java, including syntax, control structures, and data types. Examples include:
What are the main features of Java?
What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?
Explain the concept of platform independence in Java.
2. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
As Java is built around the OOP paradigm, interviewers often assess your grasp of these principles:
What is encapsulation, and why is it important?
Explain inheritance with examples.
What is polymorphism, and how is it implemented in Java?
3. Exception Handling
Proper exception handling is critical in robust Java applications. Common questions include:
What is the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions?
How do try, catch, finally, and throw work together?
What is the purpose of custom exceptions?
4. Collections Framework
This is a favorite topic in Java interviews due to its practical importance:
What is the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList?
How does HashMap work internally?
What are the differences between Set, List, and Map?
5. Multithreading and Concurrency
Java supports concurrent programming, and questions in this category test your knowledge of threading concepts:
What is a thread in Java?
Explain the differences between Runnable and Thread.
How do you avoid thread-safety issues in Java applications?
6. Java 8 and Beyond
Modern Java versions introduced features like lambdas, streams, and functional programming:
What are lambda expressions?
How do you use the Stream API in Java 8?
What is the difference between Optional and null?
7. JVM Internals and Memory Management
Senior-level candidates are often expected to understand how Java works under the hood:
How does garbage collection work in Java?
What are the different memory areas in JVM?
How can memory leaks be detected and avoided?
8. Design Patterns and Best Practices
To demonstrate architectural thinking, candidates may be asked:
What is the Singleton pattern and how do you implement it?
Explain the Factory and Observer patterns.
What are SOLID principles in Java programming?
Sample Questions from the Guide
Here are a few samples from "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide":
1: What is the difference between ‘==’ and .equals() in Java? Ans: == checks reference equality, meaning whether two references point to the same object. .equals() checks logical equality, meaning whether two objects have the same value. For example, two different String objects with the same value will return true using .equals() but false using ==.
2: What is a HashMap, and how does it work internally? Ans: A HashMap stores key-value pairs. It uses a hash function to compute an index where the value should be stored in an array. If multiple keys hash to the same index, Java handles collisions using a linked list or a balanced tree (as of Java 8).
3: How does Java achieve platform independence? Ans: Java code is compiled into bytecode by the Java compiler. This bytecode is platform-independent and can be executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which is available on multiple operating systems.
How to Use This Guide for Effective Interview Prep
To get the most out of "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide", follow these steps:
Study the concepts – Don’t just read the answers; understand the reasoning behind them.
Practice coding – Use platforms like HackerRank, LeetCode, or Codeforces to apply Java in real coding problems.
Mock interviews – Simulate real interview scenarios with peers or mentors to practice verbalizing your thoughts.
Build small projects – Implement real-world solutions to solidify your understanding of Java concepts.
Keep learning – Stay up-to-date with Java updates and community discussions to stay ahead of the curve.
Conclusion
Preparation is key to succeeding in a Java interview, and "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" is your all-in-one resource for that journey. By mastering the topics covered in this guide, you'll gain the confidence and knowledge needed to impress your interviewers and secure your desired role in the tech industry.
0 notes
Text
java- single constructor Vs multiple constructors
❌ The Multiple Constructor Example
public class Human {
private String name;
private int limbs;
private String skinColor;
public Human(String name) {
this(name, 4, "Unknown"); // Magic numbers!
}
public Human(String name, int limbs) {
this(name, limbs, "Unknown");
}
Why this fails: Hidden assumptions (Why default limbs = 4?), duplicate validation (What if limbs < 0?), brittle maintenance (Adding bloodType breaks all constructors)
✅ The Single Constructor Solution
public class Human {
private final String name; // Required
private final int limbs; // Required
private final String skinColor; // Required
public Human(String name, int limbs, String skinColor) {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
if (limbs < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Limbs cannot be negative");
this.name = name;
this.limbs = limbs;
this.skinColor = skinColor;
}
}
benefits: No magic defaults -Forces explicit values, validation in one place - Fail fast principle, immutable by design - Thread-safe and predictable
Handling Optional Fields: The Builder Pattern For complex cases (like optional eyeColor), use a Builder:
Human britta = new Human.Builder("Britta", 4)
.skinColor("dark")
.eyeColor("blue")
.build();
Why Builders win: Clear defaults (`.skinColor("dark")` vs. constructor overloading), flexible (Add new fields without breaking changes), readable (Named parameters > positional args)
When Multiple Constructors Make Sense
Simple value objects (e.g., Point(x, y)), framework requirements (JPA/Hibernate no-arg constructor), most classes need just one constructor. Pair it with: factory methods for alternative creation logic and builders for optional parameters
This approach eliminates: hidden defaults, validation duplication and maintenance nightmares Do you prefer single or multiple constructors? Have you been bitten by constructor overload? Share your war stories in the comments!
#Java #CleanCode #OOP #SoftwareDevelopment #Programming
1 note
·
View note
Text
9 Key Benefits of the Java Best Practice Course on Coding Brushup
In today’s fast-paced software development world, writing code that just works isn't enough. Developers must write clean, scalable, and maintainable code to keep up with modern project demands. Whether you’re an aspiring full stack developer or an experienced backend engineer, mastering best practices in Java is a must. That’s exactly why the Java Best Practice Course on Coding Brushup is a game-changer.
Coding Brushup is a smart learning platform that delivers powerful, real-world programming content to help developers code more effectively. Its Java best practice course is specifically designed to take your Java programming course practice beyond syntax, teaching you how to write production-ready code like a professional.
Let’s dive into the 9 key benefits of this course and see how Coding Brushup can take your Java skills to the next level.
Master Clean Code Principles in Java
The first and most important benefit of the Java best practice course on Coding Brushup is its focus on writing clean code. You’ll learn the principles of writing readable, efficient, and modular Java code, which is vital for any long-term project success.
Clean code isn’t just about style; it’s about reducing bugs, improving maintainability, and making collaboration easier. Whether you're working solo or as part of a development team, Coding Brushup ensures your Java code meets industry standards.
Deep Dive into Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
The Java programming course practice on Coding Brushup gives you a solid grasp of core object-oriented programming concepts—encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
The course goes beyond definitions. You’ll work through practical Java examples that show how these principles are applied in real-world applications. This foundation is essential for building scalable software systems and is highly valued in full stack developer roles.
Learn Design Patterns the Right Way
One of the standout features of the Java course on Coding Brushup is the dedicated module on design patterns. Design patterns are time-tested solutions to common software problems, and knowing when and how to apply them is a hallmark of advanced developers.
From Singleton and Factory to Observer and Strategy, the Java best practice course teaches you when to use each pattern, with practical coding exercises and detailed explanations.
Emphasizes Error Handling and Debugging
Too often, developers overlook robust error handling until a bug appears in production. Coding Brushup teaches you how to handle exceptions in Java properly, log errors, and implement defensive programming strategies.
The course includes common error scenarios, how to debug effectively, and how to write code that fails gracefully—making your applications more resilient and reliable.
Boosts Job-Readiness for Full Stack Developer Roles
Whether you're aiming for your first job or leveling up in your career, the Java best practice course on Coding Brushup helps make you job-ready. Full stack developers are expected to have both frontend and backend skills, but backend logic—especially in Java—must be strong.
With Coding Brushup for Java, you’ll learn backend fundamentals, Java frameworks, and best practices that recruiters look for in a full stack developer. This gives you a competitive edge during interviews and on the job.
Enhances Your Java Programming Course Practice with Real Projects
Theory is only half the equation. The real learning happens when you build and practice. The Java course on Coding Brushup includes hands-on coding challenges and mini-projects to reinforce what you’ve learned.
You'll build applications like a user authentication system, online library manager, and inventory tracker—each aligned with real-world use cases. These projects strengthen your Java programming course practice and give you portfolio-ready work to show employers.
Covers the Latest Java Features (Java 17+)
Staying up to date with the latest Java versions is critical, especially for developers working in enterprise environments. Coding Brushup’s Java best practice course is regularly updated to include new language features, like:
Records
Switch expressions
Sealed classes
Text blocks
Pattern matching
By learning these features early, you keep your skills current and future-proof your career.
Teaches Testing and Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Writing tests is just as important as writing functional code. Coding Brushup includes a full module on unit testing with JUnit and how to implement test-driven development (TDD) in Java.
You’ll learn how to:
Write unit tests
Create mock objects
Set up automated test pipelines
Ensure code quality using coverage tools
These practices are essential for enterprise development and demonstrate a mature, professional coding style.
Gain Lifetime Access and Community Support
When you enroll in the Java best practice course on Coding Brushup, you get lifetime access to content. This means you can revisit lessons, download code snippets, and keep up with new modules at your pace.
More importantly, Coding Brushup offers a thriving community of developers. You can ask questions, share solutions, and collaborate with peers—all of which accelerate your learning journey.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Java Skills with Coding Brushup
If you’re serious about improving your coding standards, building scalable software, and growing as a full stack developer, the Java best practice course on Coding Brushup is the smart choice. It’s structured, practical, and aligned with what the industry demands.
Don’t just learn Java—master it the professional way with Coding Brushup.
Start your journey today at codingbrushup.com and experience the difference clean code, smart design, and real practice can make.
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Master Java Design Patterns with Confidence! This comprehensive eBook is your ultimate guide to mastering design patterns through an extensive collection of Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) designed for real-world success.Whether you're a student prepping for exams, a developer aiming to ace technical interviews, or a professional building scalable applications, this book has you covered. Dive into hundreds of carefully crafted MCQs covering Creational, Structural, and Behavioral patterns—Singleton, Factory, Adapter, Observer, and more. What sets this book apart? Every question comes with a detailed explanation and complete solution, breaking down complex concepts into clear, practical insights. Learn why a pattern works, how to apply it, and how to avoid common pitfalls, all while building expertise that translates directly to real-world coding challenges.Why Choose This Book?Extensive MCQs: Test and sharpen your knowledge with a wide range of questions.Diverse Question Types: Master patterns through concept-based, code-based, and scenario-based MCQs for a well-rounded learning experience.In-Depth Explanations: Gain a deep understanding of each pattern’s purpose and application.Real-World Focus: Learn to solve problems like a pro with patterns used in modern software development.Perfect for All Levels: From beginners to seasoned coders, grow your skills at your own pace.Get ready to code smarter, not harder. Whether you’re chasing certifications, career growth, or cleaner code, Java Design Patterns for Real-World Expertise is your key to unlocking mastery. Grab your copy now and start building solutions that stand out!Add to your book today and take the first step toward Java design pattern excellence! ASIN : B0F4Y467PL Language : English File size : 1.2 MB Text-to-Speech : Enabled Screen Reader : Supported Enhanced typesetting : Enabled X-Ray : Not Enabled Word Wise : Not Enabled Print length : 555 pages [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
Learning Design Patterns in Programming

Design patterns are reusable solutions to common software design problems. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, learning design patterns can greatly improve your ability to write clean, scalable, and maintainable code. This post introduces the concept of design patterns, why they're important, and how you can start using them effectively in your projects.
What Are Design Patterns?
A design pattern is a proven way to solve a specific problem in software design. These patterns are not code snippets but templates or best practices that guide developers in structuring their programs.
Why Use Design Patterns?
Code Reusability: Promotes the use of reusable solutions.
Scalability: Makes it easier to scale applications.
Maintainability: Leads to cleaner and more organized code.
Team Collaboration: Helps teams follow a shared vocabulary and approach.
Problem Solving: Speeds up decision-making by providing tried-and-tested approaches.
Categories of Design Patterns
Creational Patterns: Focus on object creation mechanisms (e.g., Singleton, Factory).
Structural Patterns: Deal with object composition (e.g., Adapter, Decorator).
Behavioral Patterns: Manage communication and behavior (e.g., Observer, Strategy).
Common Design Patterns Explained
1. Singleton Pattern
Ensures a class has only one instance and provides a global access point to it.// Singleton in Java public class Database { private static Database instance; private Database() {} public static Database getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new Database(); } return instance; } }
2. Factory Pattern
Creates objects without exposing the instantiation logic to the client.// Factory Example in Python class ShapeFactory: def get_shape(self, type): if type == 'circle': return Circle() elif type == 'square': return Square()
3. Observer Pattern
Defines a one-to-many dependency so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified.
4. Strategy Pattern
Allows algorithms to be selected at runtime by defining a family of interchangeable behaviors.
5. Decorator Pattern
Adds new functionality to objects dynamically without changing their structure.
Best Practices for Learning Design Patterns
Start with the basics: Singleton, Factory, and Observer.
Understand the problem each pattern solves.
Use real-world examples to grasp each pattern.
Refactor your existing code using design patterns where applicable.
Don't force patterns—use them where they naturally fit.
Resources for Learning
Refactoring Guru – Visual and code-based examples.
SourceMaking – Classic explanations.
Java Design Patterns GitHub Repo
Book: Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software by the "Gang of Four".
Conclusion
Design patterns are a powerful tool for developers at all levels. They provide a structured approach to solving common programming problems and help build applications that are easier to manage and extend. Start small, practice often, and soon you'll be writing better code with confidence.
0 notes
Text
AI Code Generator : The Best Free AI Code Generators

Developers often struggle with writing repetitive code, debugging complex logic, and keeping up with evolving programming languages. Free AI code generator tools have revolutionized coding by automating code generation, reducing development time, and improving efficiency. If you are looking for an AI-powered code generator that is free, efficient, and reliable, this guide will help you explore the best options available.
What is an AI Code Generator?
An AI code generator is a tool that uses artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to generate, optimize, and suggest code snippets for developers. These tools are designed to understand programming syntax, context, and best practices to help developers write efficient and error-free code.
How Does an AI Code Generator Work?
AI-powered code generators use advanced natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning techniques to analyze input prompts and generate code snippets in various programming languages. These tools are trained on vast datasets, making them capable of writing code based on a given requirement or fixing issues in existing code.
Note: Do checkout our Ai Agents blog for a better understanding of how AI Code generation works.
The working mechanism of AI code generators involves:
Understanding Natural Language Input: Developers provide input in plain English, such as "Write a Python function to calculate factorial."
Processing via AI Models: The tool processes the input using deep learning models trained on vast code repositories.
Code Generation: The AI produces a syntactically correct and optimized code snippet based on best practices.
Syntax Checking & Debugging: Many AI tools perform additional checks to eliminate syntax errors before suggesting code.
Customization & Learning: Some AI models improve with use, learning from the developer’s coding style to generate better suggestions over time.
For instance, if a developer inputs a natural language prompt such as "write a Python function to sort a list of numbers," the AI code generator can instantly provide a working code snippet. This eliminates the need to manually write repetitive functions and allows developers to focus on more complex problem-solving.
For a better understanding, take a look at Keploy UTGen as an example, it’s based on Meta's research, TestGen-LLM top level architecture.
Benefits of Using a Free AI Code Generator
1. Increased Productivity
AI code generators save time by providing instant code suggestions, automating repetitive tasks, and reducing manual coding efforts. This allows developers to focus on high-level logic rather than syntax errors.
2. Error Reduction
By leveraging AI-driven suggestions, developers can minimize syntax errors and logical mistakes, improving the overall code quality. AI tools often analyze patterns in previous code and suggest improvements, leading to better optimization and fewer runtime errors.
3. Support for Multiple Languages
Most AI code generators support various programming languages, including JavaScript, Python, Java, C++, C#, and more. This makes them versatile tools that can be used across different projects and tech stacks.
4. Learning and Skill Enhancement
Beginner programmers can use AI-generated code snippets to understand coding patterns and best practices. These tools provide an interactive way to learn new programming languages by breaking down complex problems into smaller, more understandable solutions.
5. Cost-Efficiency
Since many AI code generator free tools are available, developers can use them without any investment, making them accessible to students, freelancers, and professionals. Premium versions offer additional features, but free versions are often sufficient for most coding needs.
Best Free AI Code Generators Available Today
1. GitHub Copilot

Merits: 1. Context-Aware Suggestions – Provides highly relevant code completions based on the code you’re writing. 2. Multi-Language Support – Supports JavaScript, Python, Go, TypeScript, Ruby, and many other languages. 3. Seamless IDE Integration – Works directly within popular IDEs, reducing the need to switch between windows. 4. Speeds Up Development – Helps write repetitive code faster, improving developer productivity.
Demerits: 1. Limited Free Usage – While it offers a free trial, full functionality requires a paid subscription. 2. Occasional Inaccuracies – May generate incorrect or insecure code that needs human review. 3. Not Ideal for Beginners – Requires programming knowledge to validate suggestions properly.
2. Keploy

Merits:
Automates Test Case Generation – Eliminates the need for manually writing test cases, saving time and effort.
Captures API Calls and Responses – Helps in end-to-end testing by logging real-world API interactions.
Reduces Bugs and Improves Code Quality – Helps maintain application stability by catching errors early.
Open-Source and Developer-Friendly – Keploy is an open source software which means that developers can contribute to and customize Keploy as per their needs. You can contribute to it too at the Keploy Github.
Keploy VS Code Extension: AI-Powered Test Automation Inside Your Editor
The Keploy VS Code Extension is an AI-driven tool that automates test case generation directly within Visual Studio Code. Instead of manually writing test cases, Keploy records real API interactions and automatically generates test cases, making it easier for developers to validate their applications.

Key Features of Keploy’s VS Code Extension
1. Automated Test Case Generation
Works seamlessly with REST APIs, gRPC, and GraphQL.
Saves hours of testing effort and reduces human error.
2. One-Click Test Execution
Create tests with a single click inside VS Code.
Eliminates the hassle of running test suites from the command line.
Integrates with Jest, Mocha, and other testing frameworks.
3. Record and Replay Mechanism
Keploy records API requests and responses during runtime.
It can replay these requests to check if the application behaves consistently over time.
Ensures API backward compatibility - no breaking changes go unnoticed.
4. Customizable Test Cases
Developers can modify AI-generated test cases inside VS Code.
Allows tweaking of request parameters, headers, and expected responses.
Ensures flexibility while maintaining high test coverage.
How to Install Keploy in VS Code?
Open VS Code and go to the Extensions Marketplace.
Search for “Keploy” and click Install.
Open your backend project and ensure Keploy is configured correctly.
Use Keploy commands to record, replay, and validate API calls.
OpenAI Codex
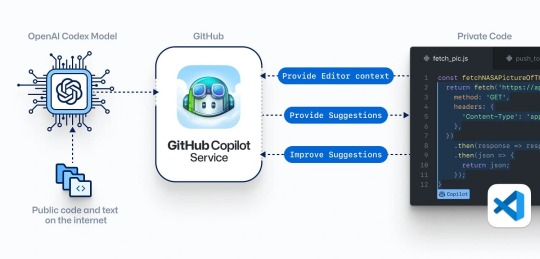
Merits: 1. Highly Versatile – Can generate code snippets, complete functions, and even translate between programming languages. 2. Natural Language Understanding – Developers can describe functionality in plain English, and Codex will generate the corresponding code. 3. Custom Integration – Available via OpenAI’s API, allowing developers to build their own AI-powered applications.
Demerits: 1. No Dedicated UI – Unlike Copilot, Codex does not have a built-in interface and requires API integration. 2. Limited Free Access – OpenAI provides limited free-tier API usage before requiring a paid plan. 3. Quality Varies – While impressive, the generated code may require refinement or debugging.
3. Tabnine

Merits: 1. Privacy-Focused – Unlike Copilot, which sends data to the cloud, Tabnine offers an on-device AI model for improved privacy. 2. Supports Many IDEs – Works with VS Code, IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, WebStorm, and other popular development environments. 3. Lightweight and Fast – Consumes fewer resources compared to other AI coding tools.
Demerits: 1. Limited Free Features – The free version provides only basic code completions, with advanced AI features requiring a subscription. 2. Less Contextual Awareness – Suggestions are less context-aware compared to GitHub Copilot. 3. May Struggle with Complex Code – Works well for simple autocompletions but is less capable of generating complex code snippets.
4. CodeT5

Merits: 1. Open Source – Fully open-source, allowing developers to customize and fine-tune the model as needed. 2. Supports Multiple Programming Languages – Works with Java, Python, JavaScript, and more. 3. Good for Research and Customization – Useful for AI researchers and developers who want to explore AI-assisted coding.
Demerits: 1. Requires Setup – Unlike plug-and-play tools, users need to install and configure the model themselves. 2. Not as Advanced as Copilot – CodeT5’s code suggestions may not be as refined or context-aware as GitHub Copilot. 3. Higher Learning Curve – Requires knowledge of machine learning frameworks to make full use of its capabilities.
How to Choose the Right AI Code Generator?
With multiple AI code generators available, choosing the right one can be challenging. Here are some key factors to consider:
Programming Language Support: Ensure the AI code generator supports the languages you use.
Integration with IDEs: Tools like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine integrate well with popular IDEs like Visual Studio Code, JetBrains, and Sublime Text.
Accuracy and Context Understanding: The AI should generate relevant and correct code snippets based on natural language prompts.
Pricing and Free Plans: Many tools offer free versions with limited features. Choose based on your requirements and upgrade if needed.
Community Support & Documentation: A well-documented tool with active community support can be more beneficial in the long run.
Future of Software Engineering With AI Code Generators
AI code generators are not just improving - they are reshaping the entire landscape of software development. As artificial intelligence continues to advance, we are moving towards a future where AI-driven coding tools will be deeply integrated into every stage of the development lifecycle, from writing and debugging to testing and deployment.
Smarter and More Context-Aware AI
One of the biggest advancements in AI-driven code generation is the increasing ability of models to understand context and intent. Current AI tools already analyze surrounding code to generate relevant suggestions, but future versions will go beyond syntax and logic. They will be able to:
Understand business logic: AI tools will generate code not just based on syntax but also on the specific goals of an application.
Refactor code intelligently: AI will help developers optimize existing code, improving readability, efficiency, and maintainability.
Predict and suggest architecture patterns: Instead of just generating snippets, AI will recommend best practices for entire projects.
AI-Generated Full Applications
Today’s AI tools generate snippets or assist in code completion, but the future will bring the capability to build entire applications from high-level specifications. Developers may only need to provide a rough outline or describe an application in natural language, and AI will generate everything from the front-end UI to the back-end logic and database schema.
We tried making a fullstack CRUD application we talked about in our React Testing Blog. The results were good but without human insights this would’nt be as good as it should have been. Hence, human oversight will still be required for fine-tuning, debugging, and security considerations, AI-generated applications could significantly reduce development time and lower the barrier to entry for new programmers.
AI and the Role of Software Engineers
With AI becoming more capable, does that mean developers will become obsolete? Not at all. Instead, the role of software engineers will shift:
From writing boilerplate code to designing high-level logic
From debugging syntax errors to fine-tuning AI-generated code
From manual testing to overseeing AI-driven testing automation
Developers will need to learn how to collaborate with AI, treating it as a tool that enhances their capabilities rather than replacing them. Those who can leverage AI effectively will be more productive, allowing them to focus on creativity, architecture, and problem-solving.
Ethical and Security Considerations
As AI-generated code becomes more prevalent, concerns around security vulnerabilities, biases in AI models, and intellectual property ownership will need to be addressed. AI tools must be trained responsibly to ensure they produce secure, ethical, and unbiased code.
In the coming years, we can expect industry-wide standards and regulations to govern AI-generated code, ensuring it aligns with best security practices and legal compliance.
Conclusion
AI-powered code generation tools are transforming software development by improving productivity and reducing coding errors. If you are looking for a free AI code generator, tools like GitHub Copilot, OpenAI Codex, and Tabnine are excellent choices. By leveraging these tools, developers can speed up their workflows, enhance code quality, and focus on more complex problem-solving tasks.
Whether you're a beginner learning to code or an experienced developer looking to streamline your workflow, AI code generators can help you achieve faster, more efficient, and error-free coding. Start exploring free AI code generators today and take your programming skills to the next level!
FAQs
1. Are free AI code generators as effective as paid ones?
Free AI code generators provide significant assistance, but paid versions often offer more features, better context understanding, and enhanced accuracy.
2. Can AI code generators replace human developers?
No, AI code generators assist developers by automating repetitive tasks but lack human creativity, critical thinking, and deep problem-solving abilities.
3. What are the best free AI code generators?
Several AI-powered code generators are available for free, including:
GitHub Copilot – Provides real-time code suggestions based on OpenAI Codex.
Keploy – Specializes in AI-powered test case generation for software testing.
OpenAI Codex – Generates code from natural language inputs and supports multiple languages.
Tabnine – AI-powered autocompletion tool that integrates with various IDEs.
CodeT5 – Open-source AI model developed by Salesforce for code generation.
Each tool has unique strengths, so choosing the right one depends on your specific needs.
4. How secure is the code generated by AI?
AI-generated code should always be reviewed for security vulnerabilities and best practices before deployment.
5. Can AI code generators be used for learning programming?
Yes, beginners can use AI-generated code snippets to understand coding patterns, syntax, and best practices.
0 notes
Text
Discuss common design patterns and their implementation in Java.

Introduction
Overview of design patterns in software development.
Why design patterns are crucial for writing scalable, maintainable, and reusable code.
Categories of design patterns:
Creational — Object creation mechanisms.
Structural — Class and object composition.
Behavioral — Communication between objects.
1. Creational Design Patterns
1.1 Singleton Pattern
Ensures that only one instance of a class is created.
Used for logging, database connections, and configuration management.
Implementation:javapublic class Singleton { private static Singleton instance; private Singleton() {} // Private constructor public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new Singleton(); } return instance; } }
✅ Use Case: Database connection manager.
1.2 Factory Pattern
Provides an interface for creating objects without specifying their exact class.
Implementation:javainterface Shape { void draw(); }class Circle implements Shape { public void draw() { System.out.println("Drawing Circle"); } }class Square implements Shape { public void draw() { System.out.println("Drawing Square"); } }class ShapeFactory { public static Shape getShape(String type) { if (type.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")) return new Circle(); if (type.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")) return new Square(); return null; } }// Usage Shape shape = ShapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE"); shape.draw();
✅ Use Case: UI component creation (e.g., buttons, text fields).
1.3 Builder Pattern
Used for constructing complex objects step by step.
Implementation:javaclass Car { private String engine; private int wheels; public static class Builder { private String engine; private int wheels; public Builder setEngine(String engine) { this.engine = engine; return this; } public Builder setWheels(int wheels) { this.wheels = wheels; return this; } public Car build() { return new Car(this); } } private Car(Builder builder) { this.engine = builder.engine; this.wheels = builder.wheels; } }// Usage Car car = new Car.Builder().setEngine("V8").setWheels(4).build();
✅ Use Case: Configuring objects with multiple optional parameters (e.g., HTTP requests).
2. Structural Design Patterns
2.1 Adapter Pattern
Allows incompatible interfaces to work together.
Implementation:javainterface MediaPlayer { void play(String audioType); }class MP3Player implements MediaPlayer { public void play(String audioType) { System.out.println("Playing MP3 file"); } }class MP4Player { void playMP4() { System.out.println("Playing MP4 file"); } }class MediaAdapter implements MediaPlayer { private MP4Player mp4Player; public MediaAdapter() { mp4Player = new MP4Player(); } public void play(String audioType) { if (audioType.equalsIgnoreCase("MP4")) { mp4Player.playMP4(); } } }// Usage MediaPlayer player = new MediaAdapter(); player.play("MP4");
✅ Use Case: Integrating third-party libraries.
2.2 Decorator Pattern
Dynamically adds behavior to objects.
Implementation:javainterface Coffee { String getDescription(); double cost(); }class SimpleCoffee implements Coffee { public String getDescription() { return "Simple Coffee"; } public double cost() { return 5.0; } }class MilkDecorator implements Coffee { private Coffee coffee; public MilkDecorator(Coffee coffee) { this.coffee = coffee; } public String getDescription() { return coffee.getDescription() + ", Milk"; } public double cost() { return coffee.cost() + 1.5; } }// Usage Coffee coffee = new MilkDecorator(new SimpleCoffee()); System.out.println(coffee.getDescription() + " - $" + coffee.cost());
✅ Use Case: Adding toppings to a coffee order in an online coffee shop.
3. Behavioral Design Patterns
3.1 Observer Pattern
Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects.
Implementation:javaimport java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;interface Observer { void update(String message); }class Subscriber implements Observer { private String name; public Subscriber(String name) { this.name = name; } public void update(String message) { System.out.println(name + " received: " + message); } }class Publisher { private List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<>(); public void addObserver(Observer observer) { observers.add(observer); } public void notifyObservers(String message) { for (Observer observer : observers) { observer.update(message); } } }// Usage Publisher newsPublisher = new Publisher(); Observer user1 = new Subscriber("Alice"); Observer user2 = new Subscriber("Bob");newsPublisher.addObserver(user1); newsPublisher.addObserver(user2);newsPublisher.notifyObservers("New article published!");
✅ Use Case: Event-driven notifications (e.g., stock market updates, messaging apps).
3.2 Strategy Pattern
Defines a family of algorithms, encapsulates them, and makes them interchangeable.
Implementation:javainterface PaymentStrategy { void pay(int amount); }class CreditCardPayment implements PaymentStrategy { public void pay(int amount) { System.out.println("Paid $" + amount + " using Credit Card."); } }class PayPalPayment implements PaymentStrategy { public void pay(int amount) { System.out.println("Paid $" + amount + " using PayPal."); } }class PaymentContext { private PaymentStrategy strategy; public void setPaymentStrategy(PaymentStrategy strategy) { this.strategy = strategy; } public void pay(int amount) { strategy.pay(amount); } }// Usage PaymentContext context = new PaymentContext(); context.setPaymentStrategy(new PayPalPayment()); context.pay(100);
✅ Use Case: Payment gateway selection (Credit Card, PayPal, etc.).
Conclusion
Design patterns enhance code reusability, scalability, and maintainability.
Each pattern solves a specific design problem efficiently.
Choosing the right pattern is key to writing better Java applications.
🔹 Next Steps:
Explore Java Design Pattern Libraries like Spring Framework.
Implement patterns in real-world projects.
Experiment with combining multiple patterns.
0 notes
Text
Tips for Cracking Your First Job Interview as a Developer
Getting your first job as a developer can be both exciting and nerve-wracking. "Tips for Cracking Your First Job Interview as a Developer" are invaluable to help you navigate the process with confidence. Whether you’re a fresher or someone transitioning into the tech industry, mastering the art of interviews is crucial for starting your career in programming.
How to Crack Technical Interview for Freshers
Freshers often find technical interviews intimidating, but preparation is the key to overcoming anxiety. Here's a step-by-step guide: 1. Research About the Company
Before walking into any interview, research the company thoroughly. Understand its mission, values, and recent projects. Tailor your responses to show how you align with the company’s goals and culture. Look up their tech stack and current openings to see how you can fit into their team. 2. Understand the Job Description
Carefully read the job description to identify the skills and tools the company is looking for. Make a checklist and match it with your own skills to prepare better. Highlight the technical and soft skills that align with the job role. Understanding the role’s key responsibilities helps you frame answers that showcase your strengths. 3. Understand the Basics of Coding and Programming
Companies want to see that you have a strong foundation in coding. Brush up on:
Data structures (e.g., arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues)
Algorithms (sorting, searching, recursion)
Problem-solving skills
Programming languages such as Python, Java, or C++
Object-oriented programming principles
4. Collect the Best Resources for Learning
Gather reliable resources like online tutorials, books, and platforms. For example:
"Cracking the Coding Interview" by Gayle Laakmann McDowell
Platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, and Codewars
5. Work on Real-World Projects
Practical experience matters. Build projects like:
A personal portfolio website showcasing your skills.
A task management app with frontend, backend, and database integration.
Contributions to open-source projects on GitHub to build credibility.
6. Stay Updated on Industry Trends
Keep an eye on emerging technologies like cloud computing, AI, and blockchain. Understanding how these trends impact software development will set you apart from other candidates.
How to Clear Any Technical Interview
Clearing a technical interview is about more than just knowing how to code. You need to demonstrate your problem-solving approach, communication skills, and technical proficiency. 1. Do Mock Interviews
Participate in mock interview sessions with peers or mentors to simulate real-life scenarios. These sessions help you identify gaps in your knowledge and improve your communication. Use platforms like Pramp and Interviewing.io for structured mock interviews. 2. Work on Software Design Skills
If you’re aiming for roles like "Software Developer" or "Software Engineer," learn the basics of system design. Familiarize yourself with:
Design patterns (Singleton, Observer, Factory)
Database design principles
Microservices architecture
3. Write Clean Code
Employers value developers who write clean, maintainable code. Follow principles like
DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself)
KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid)
SOLID principles for object-oriented programming
Maintain proper code commenting and documentation 4. Test Your Code
Testing is critical in software development. Be prepared to explain how you would
Identify edge cases
Write unit tests using frameworks like JUnit or PyTest
Debug common issues effectively 5. Listen to Every Detail
Pay close attention to the questions and requirements provided during the interview. Sometimes, small details can make a significant difference in how you approach a problem. 6. Prepare for Behavioral Questions
Coding interviews aren’t just about technical skills. Be ready to answer questions like:
"Describe a time you faced a challenging project and how you handled it.
"How do you approach working with a team that has conflicting ideas?"
Use the STAR (Situation, Task, Action, Result) method to structure your responses.
Coding Interviews: Everything You Need to Prepare
If you're wondering how to approach coding interviews everything you need to prepare follow these actionable tips: 1. Practice Coding Questions
Spend time on platforms like LeetCode, HackerRank, and Codewars to get familiar with common "coding interview" questions. These questions often involve problem-solving under time constraints and test your logical thinking. 2. Try to Get Coding Certificates
Certification in programming languages or frameworks can enhance your resume. Look for certifications in Python, Java, or full-stack development with AI technologies such as NodeJS, DotNet Core, Angular, and ReactJS. 3. Good Communication Skills and Body Language
Your communication and body language can impact how interviewers perceive you. Maintain eye contact, speak clearly, and show enthusiasm for the role.
4. Self-Introduction and Formal Attire
Prepare a concise self-introduction highlighting your key skills and projects. Dress professionally to make a positive impression. 5. Stay Calm Under Pressure
Many interviews include challenging questions to test how you handle stress. Take a deep breath, think through your answer, and stay composed.
Company Interview Preparation
Preparing for specific companies can give you an edge. Each organization’s interview process varies, so tailor your strategy accordingly. 1. Optimize LinkedIn
Keep your LinkedIn profile updated. Connect with professionals from your target company to understand their culture and technical expectations. Post projects or achievements regularly to showcase your expertise. 2. Learn from Past Candidates
Look up company-specific interview questions on platforms like GeeksforGeeks or Glassdoor. Understanding the interview pattern and commonly asked questions can help you strategize better. 3. Freelancing as Practice
While learning, explore freelancing platforms like
Toptal
We Work Remotely
FlexJobs
Freelancing allows you to apply your skills in real-world scenarios and builds confidence.
Tips to Crack Your First Technical Interview
Your first technical interview is a significant milestone. Here are practical tips to ace it:
1. Speak Your Thoughts
When solving a problem, explain your thought process aloud. For example:
"First, I’d identify the constraints of the problem."
"Next, I’d choose the most efficient data structure to solve it." This approach showcases your problem-solving skills and logical thinking.
2. Leverage Online Resources
Use coding platforms and resources like:
Cracking the Coding Interview (book)
AlgoExpert (for algorithm prep)
Mock interviews on Pramp or Interviewing.io
3. Company-Specific Preparation
Research company’s tools and frameworks. Prepare accordingly to show how your skills align with their requirements.
4. Practice Real-Time Scenarios
Prepare for real-world scenarios where you may have to:
Debug an existing codebase
Build a feature from scratch
Optimize an algorithm for better performance
FAQs
What are the most common interview questions for developers?
Expect questions on data structures, algorithms, and coding problems. Behavioral questions like "Describe a challenging project" are also common. 2. Should I focus only on technical skills?
No, soft skills like communication and problem-solving are equally important. 3. How can I improve my coding skills?
Practice consistently on platforms like LeetCode and build real-world projects.
4. What tools should I learn as a Full Stack Developer?
Focus on tools like GitHub, Visual Studio Code, Node.js, ReactJS, MongoDB, and Docker to enhance your development skills.
5. How can I stand out during a technical interview?
Show a clear understanding of the problem
Communicate your solution effectively
Ask clarifying questions
Discuss alternative approaches if applicable
Conclusion
The article "Tips for Cracking Your First Job Interview as a Developer" provides actionable advice to help you prepare for and excel in coding interviews. These tips emphasize the importance of preparation, from mastering coding fundamentals to acing mock interviews and practicing system design. If you're ready to scale your career and become a skilled developer, consider enrolling in the "Full Stack Developer - MERN Stack Master's Program" at TechEntry. This program equips you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in roles requiring expertise in Python, NodeJS, DotNet Core, Angular, and ReactJS. Got questions about "Tips for Cracking Your First Job Interview as a Developer" or our programs? Leave a comment below, and our experts will respond promptly. Start your journey to success with TechEntry today!
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Single Most Important Thing You Need To Know About JAVA DEVELOPMENT
Java, a versatile and widely-used programming language, has stood the test of time as a cornerstone of software development. Since its introduction in 1995, it has been adopted for various purposes, from building web applications to creating robust enterprise systems. For developers diving into Java or seeking to refine their expertise, it’s easy to get lost in the vast ecosystem. Frameworks, libraries, and tools abound, and opinions on the “most important thing” vary. However, at its core, the single most crucial aspect of Java development is understanding and applying object-oriented programming (OOP) principles effectively.
Why Object-Oriented Programming is Essential in Java
Java is inherently an object-oriented programming language. The language’s design, libraries, and frameworks are deeply intertwined with OOP principles. Understanding these principles goes beyond academic knowledge; they’re the foundation of writing efficient, maintainable, and scalable Java applications. Let’s delve into what makes OOP principles the heart of Java development:
1. Encapsulation: Protecting Your Data
Encapsulation refers to bundling data (fields) and methods that operate on the data into a single unit or class. It also means restricting direct access to some of the object’s components, which helps maintain control over the internal state of the object.
Example:

Encapsulation ensures the balance field is not directly accessible, allowing controlled modifications only through the provided methods.
2. Inheritance: Building on Existing Code
Inheritance allows developers to create new classes based on existing ones, promoting code reuse and reducing redundancy.
Example:

Inheritance simplifies code and fosters a hierarchical structure, but overuse can lead to complex dependencies. Striking the right balance is key.
3. Polymorphism: Writing Flexible Code
Polymorphism enables a single interface to represent different data types. It promotes flexibility and scalability in applications.
Example:

Polymorphism ensures the application can accommodate new types with minimal changes, enhancing its adaptability.
4. Abstraction: Simplifying Complex Systems
Abstraction focuses on exposing only the necessary details while hiding the implementation complexities. In Java, abstraction is achieved through abstract classes and interfaces.
Example:

Abstraction helps in managing complexity by defining clear boundaries and responsibilities within the code.
How Mastering OOP Enhances Java Development
Improves Code Maintainability
When your code adheres to OOP principles, it’s easier to debug, extend, and maintain. Encapsulation ensures that changes in one part of the application don’t inadvertently affect other parts.
Enables Scalability
Well-structured object-oriented applications are inherently scalable. As your application grows, new features can be added with minimal disruption to existing code.
Fosters Reusability
Inheritance and abstraction promote code reuse, reducing development time and effort.
Enhances Collaboration
Object-oriented designs are intuitive and modular, making it easier for teams to collaborate. Developers can work on different classes or modules simultaneously without conflict.
Practical Steps to Master OOP in Java
Understand the Basics: Start with the fundamental concepts of OOP, including classes, objects, and methods.
Practice: Build small projects to reinforce your understanding of encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
Read Code: Study well-written open-source Java projects to see how OOP principles are applied in real-world scenarios.
Learn Design Patterns: Patterns like Singleton, Factory, and Observer are built on OOP principles and provide solutions to common design problems.
Refactor Your Code: Regularly refactor to improve your application’s adherence to OOP principles.
Beyond OOP: Integrating Modern Java Practices
While mastering OOP is the single most important thing for Java developers, the language and its ecosystem have evolved. To remain competitive, developers should also embrace:
Functional Programming: Modern Java versions (starting with Java 8) support functional programming paradigms through features like lambdas and streams.
Microservices Architecture: Java frameworks like Spring Boot facilitate the development of microservices, a popular approach in modern application development.
Performance Optimization: Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and optimizing garbage collection, threading, and memory usage are critical for high-performance applications.
Testing and Automation: Tools like JUnit and Mockito enable robust unit testing, ensuring code reliability.
Continuous Learning: The Java ecosystem is vast and ever-evolving. Staying updated with new versions, frameworks, and tools is essential.
Conclusion
Java’s success lies in its simplicity and power, underpinned by object-oriented principles. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced developer, understanding and applying OOP effectively is the most critical skill you can cultivate in Java development. By mastering these principles and embracing modern practices, you’ll be equipped to build robust, scalable, and maintainable applications that stand the test of time.
0 notes
Text
Key Concepts to Review Before Your Java Interview
youtube
Java interviews can be both challenging and rewarding, often acting as a gateway to exciting roles in software development. Whether you're applying for an entry-level position or an advanced role, being well-prepared with core concepts is essential. In this guide, we’ll cover key topics to review before your Java interview, ensuring you're confident and ready to impress. Additionally, don't forget to check out this detailed video guide to strengthen your preparation with visual explanations and code demonstrations.
1. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts
Java is known for its robust implementation of OOP principles. Before your interview, make sure to have a firm grasp on:
Classes and Objects: Understand how to create and use objects.
Inheritance: Review how subclasses inherit from superclasses, and when to use inheritance.
Polymorphism: Know the difference between compile-time (method overloading) and runtime polymorphism (method overriding).
Abstraction and Encapsulation: Be prepared to explain how and why they are used in Java.
Interview Tip: Be ready to provide examples of how you’ve used these concepts in your projects or coding exercises.
2. Core Java Concepts
In addition to OOP, there are foundational Java topics you need to master:
Data Types and Variables: Understand primitive types (int, double, char, etc.) and how they differ from non-primitive types.
Control Structures: Revise loops (for, while, do-while), conditional statements (if-else, switch-case), and how they control program flow.
Exception Handling: Know how try, catch, finally, and custom exceptions are used to manage errors in Java.
Collections Framework: Familiarize yourself with classes such as ArrayList, HashSet, HashMap, and their interfaces (List, Set, Map).
Interview Tip: Be prepared to discuss the time and space complexities of different collection types.
3. Java Memory Management
Understanding how Java manages memory can set you apart from other candidates:
Heap vs. Stack Memory: Explain the difference and how Java allocates memory.
Garbage Collection: Understand how it works and how to manage memory leaks.
Memory Leaks: Be prepared to discuss common scenarios where memory leaks may occur and how to avoid them.
Interview Tip: You may be asked how to optimize code for better memory management or to explain how Java’s finalize() method works.
4. Multithreading and Concurrency
With modern applications requiring multi-threading for efficient performance, expect questions on:
Threads and the Runnable Interface: Know how to create and run threads.
Thread Lifecycle: Be aware of thread states and what happens during transitions (e.g., from NEW to RUNNABLE).
Synchronization and Deadlocks: Understand how to use synchronized methods and blocks to manage concurrent access, and how deadlocks occur.
Concurrency Utilities: Review tools like ExecutorService, CountDownLatch, and Semaphore.
Interview Tip: Practice writing simple programs demonstrating thread synchronization and handling race conditions.
5. Java 8 Features and Beyond
Many companies expect candidates to be familiar with Java’s evolution, especially from Java 8 onward:
Lambda Expressions: Know how to write concise code with functional programming.
Streams API: Understand how to use streams for data manipulation and processing.
Optional Class: Learn to use Optional for handling null checks effectively.
Date and Time API: Review java.time package for managing date and time operations.
Interview Tip: Be prepared to solve coding problems using Java 8 features to show you’re up-to-date with recent enhancements.
6. Design Patterns
Java interviews often include questions on how to write clean, efficient, and scalable code:
Singleton Pattern: Know how to implement and when to use it.
Factory Pattern: Understand the basics of creating objects without specifying their exact class.
Observer Pattern: Be familiar with the publish-subscribe mechanism.
Decorator and Strategy Patterns: Understand their practical uses.
Interview Tip: Have examples ready that demonstrate how you’ve used these patterns in your projects.
7. Commonly Asked Coding Problems
Prepare by solving coding problems related to:
String Manipulations: Reverse a string, find duplicates, and check for anagrams.
Array Operations: Find the largest/smallest element, rotate arrays, or merge two sorted arrays.
Linked List Questions: Implement basic operations such as reversal, detecting cycles, and finding the middle element.
Sorting and Searching Algorithms: Review quicksort, mergesort, and binary search implementations.
Interview Tip: Practice on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank to improve your problem-solving skills under time constraints.
Final Preparation Tips
Mock Interviews: Conduct practice interviews with peers or mentors.
Review Your Code: Ensure your past projects and code snippets are polished and ready to discuss.
Brush Up on Basics: Don’t forget to revise simple concepts, as interviews can include questions on any level of difficulty.
For more in-depth preparation, watch this helpful video that provides practical examples and coding tips to boost your confidence.
With these concepts in mind, you'll be well-equipped to handle any Java interview with poise. Good luck!
0 notes
Text

Explore essential design patterns commonly used in Java development to build flexible, maintainable, and efficient software! This infographic provides a visual guide to the most popular design patterns grouped into three main categories: Creational, Structural, and Behavioral patterns. Each section explains how the patterns work, where they’re typically applied, and the benefits they bring to Java applications. Perfect for Java developers of all levels, this guide will help you understand key concepts like Singleton, Factory, Observer, and Decorator patterns, among others. Boost your Java skills by mastering these core design patterns!
0 notes
Text
ALL ABOUT DESIGN PATTERN
A design pattern [1,2] is a specific method to solve a specific object-oriented software problem, realizing a more simple and convenient reuse of successful designs and architectures. Design patterns are widely used in the modern software industry to reuse best practices and improve the quality of software systems [3]. Nowadays, software engineers have a greet tendency to use design patterns (DPs) because they are considered to have an important role in software engineering in the sense that they can make the understanding of nonentities easier [4]. When a software is conducted, it needs to be carefully architected and designed to get benefitted from the inherent features of software quality [5].
Software design patterns have a considerable impact on the software development life cycle [6]. According to Dave Cohen a developer who find design pattern intriguing, the applicability at the third level (feature) is the “sweet spot.” They shine at encapsulating business logic, memory management, server calls, and much more [7]. Creational Design Pattern is an unlimited scope to recreate Geographical Area Objects without restrictions, developers would use different types of creational design patterns to cook an object in an orderly and sophisticated manner [8]. Structural design patterns focus on organizing classes and objects [9] to form larger, more flexible software structures. These patterns facilitates the composition of objects and define relationships between them to achieve system structural integrity. By emphasizing object composition, inheritance, and interface implementation, structural patterns promote code reusability, and maintainability, and scalability [10]. Multiple research papers involving Behavioral design pattern [11] which have been proven of how have it became an important form in addressing major societal challenges.
Recent studies on design patterns 202-2024 underscore their significant role in enhancing software quality, adaptability, and performance. For instance, a systematic review highlights how design patterns can improve code readability, maintainability, and reusability, which are crucial for larger, object-oriented systems [12]. This is especially relevant in modern domains like microservices and machine learning applications, where modularity and scalability are essential. Research indicates that design patterns offer effective architectural solutions, particularly in complex systems with high performance and reliability demands. For example, in microservice-based architectures, design patterns support optimal resource use and scalability by structuring system components to handle increasing workloads efficiently [13].
To discover more about design pattern, here are some sites for you to learn them:
References:
Naghdipour, A., Hasheminejad, S., Keyvanpour, M.R. DPSA. A Brief Review for Design Pattern Selection Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2021 26th International Computer Conference: Computer Society of Iran (CSICC), Tehran, Iran, 3–4 March 2021; pp. 1–14. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9420629
Ohstuki, M.; Kakeshita, T. Generating Relationship between Design Pattern and Source Code. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Prague, Czech Republic, 23–25 April 2021; pp. 288–293. https://www.scitepress.org/PublishedPapers/2021/104725/104725.pdf
Wang, L., Song, T., Song, H., & Zhang, S. (2022). Research on Design Pattern Detection Method Based on UML Model with Extended Image Information and Deep Learning. Applied Sciences, 12(17), 8718. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178718
Yarahmadi, H.; Hasheminejad, S. Design pattern detection approaches: A systematic review of the literature. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5789–5846. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10462-020-09834-5
Rana, M.E, Saleh, O.S. Chapter 15 - High assurance software architecture and design. In Emerging Methodologies and Applications in Modelling, System Assurances, Academic Press, 2022, Pages 271-285, ISBN 9780323902403. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323902403000151
Barmaki, R., Hasheminejad,S., Naghdipour, A. (2023). Software design pattern selection approaches: A systematic literature review.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366827284_Software_design_pattern_selection_approaches_A_systematic_literature_review
Cohen D. (2021). INTRODUCTION TO DESIGN PATTERNS: WHY THEY'RE WORTH LEARNING. Tech Design Patterns. https://www.scraggo.com/design-patterns-intro/
Okeyo, B. (2024). Creational Design Pattern. https://www.billyokeyo.com/posts/creational-design-pattern/
Ngaogate W. (2023). Applying the Flyweight Design Pattern to Android Application Development. ASEAN Journal of Scientific and Technological Reports 26(2):49-57. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369544605_Applying_the_Flyweight_Design_Pattern_to_Android_Application_Development
Aratchige, R.M, Guratne, M. Kariyawasam, K. Weerasinghe, P.N. (2024). An Overview of Structural Design Patterns in Object-Oriented Software Engineering. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/377969013_An_Overview_of_Structural_Design_Patterns_in_Object-Oriented_Software_Engineering
Khadilkar, P.R, Cash, P. (2020). Understanding behavioral design: barriers and enablers. Journal of Engineering Design. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09544828.2020.1836611#d1e126
Software-Engineering design patterns for machine learning applications. (2022). IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9734272
Meijer, W., Trubiani, C., & Aleti, A. (2024). Experimental evaluation of architectural software performance design patterns in microservices. Journal of Systems and Software, 218, 112183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2024.112183
A song about Design Pattern:
0 notes
Text
Effective Tips for Java Developers to Prepare for Interviews
Introduction
Interview preparation is crucial for Java developers aiming to land their dream job. With Java being one of the most widely used programming languages, employers expect candidates to be skilled in both technical and non-technical areas. This guide outlines essential tips and strategies to help you prepare effectively for your Java development interviews. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, being ready for the variety of questions that may come up will give you the confidence to ace the interview.
Java interviews often focus on core programming concepts, problem-solving skills, and your ability to handle real-world development challenges. Effective job preparation for Java also requires you to prepare for behavioral questions to showcase your teamwork and communication skills.

Section 1: Strengthen Your Core Java Concepts
The foundation of any Java interview is your knowledge of core concepts. Employers will test your understanding of Java fundamentals, so it’s essential to master these key topics:
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts: Understand principles like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
Exception Handling: Learn how Java manages errors and how to handle exceptions effectively.
Collections Framework: Familiarize yourself with collections such as Lists, Sets, and Maps.
Multithreading and Concurrency: Understand thread management, synchronization, and how Java handles parallel processes.
Generics and Serialization: These advanced topics are crucial for building scalable and efficient applications.
In addition, you should review Data Structures and Algorithms. Employers commonly ask questions related to arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, hash maps, and more. It's essential to understand the time complexity of different operations and how to optimize code.
Section 2: Practice Coding Challenges
Practicing coding challenges is one of the best ways to prepare for technical interviews. There are many platforms where you can practice coding problems, including:
LeetCode
HackerRank
CodeChef
Focus on problems that involve array manipulation, string handling, sorting, and searching algorithms. Be sure to also work on recursion and dynamic programming, as these concepts are frequently tested.
Setting a daily practice routine will help you stay consistent. Try to solve coding problems regularly to sharpen your problem-solving skills and improve your speed.
Section 3: Revise Object-Oriented Design Principles
Java is an object-oriented programming language, so you'll need to demonstrate a strong understanding of OOP design principles. Key principles to focus on include:
SOLID Principles: Learn how to write clean, maintainable, and scalable code using these design principles.
Design Patterns: Study commonly used design patterns like Singleton, Factory, Observer, and Strategy. These are often used in Java applications to solve recurring design problems.
Be prepared to solve common design problems and explain how OOP principles apply to real-world scenarios. Understanding UML diagrams and how to design software systems is also essential.
Section 4: Focus on Java Frameworks and Libraries
Many Java applications are built using popular frameworks and libraries. Familiarize yourself with frameworks like:
Spring: Used for building enterprise-level applications with dependency injection.
Hibernate: An ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework used for managing database interactions.
JavaFX: For building graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
Understand how to use dependency injection in Spring, manage database operations with ORM, and apply basic MVC (Model-View-Controller) concepts in Java applications.
Section 5: Prepare for System Design and Architecture Questions
System design and architecture questions test your ability to build large-scale applications. Key topics to cover include:
RESTful APIs and Microservices: Understand how to design and implement RESTful web services.
Scalability, Load Balancing, and Caching: Learn how to build systems that can handle high traffic and optimize performance.
Database Design and Optimization: Be familiar with both SQL and NoSQL databases and understand when to use each.
Distributed Systems and Cloud Services: Know how to design systems that run on distributed networks and use cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud.
Section 6: Brush Up on Java Build Tools and DevOps Knowledge
Many modern Java projects use build tools and DevOps practices. Familiarize yourself with:
Maven and Gradle: These are essential tools for managing project dependencies and automating builds.
Version Control (Git): Understand how to use Git for source control and collaborative development.
CI/CD Pipelines: Learn how to set up Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines for automating testing and deployment.
You should also understand the basics of containerization with Docker and orchestration with Kubernetes. These tools are commonly used in DevOps environments to deploy Java applications efficiently.
Section 7: Prepare for Behavioral Interview Questions
In addition to technical skills, employers want to know how well you work with others. Be ready for behavioral questions such as:
Examples of past projects and challenges you've faced.
How you handle teamwork, deadlines, and problem-solving.
Your approach to time management and personal development.
Use the STAR technique (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to structure your answers. This approach helps you provide clear, concise, and impactful responses.
Section 8: Mock Interviews and Communication Skills
Mock interviews are a great way to practice for the real thing. They simulate the interview environment and help you get comfortable with both technical and non-technical questions.
Practice live coding interviews to simulate the pressure of solving problems in front of an interviewer.
Role-play technical and HR rounds to practice answering behavioral questions and explaining your thought process.
During coding interviews, focus on communication. Explain your thought process as you solve problems and discuss any alternative solutions or optimizations you can think of.
Conclusion
Preparing for a Java development interview requires a combination of technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and communication abilities. By consistently practicing coding challenges, mastering core Java concepts, and understanding system design principles, you'll be well-prepared for any interview.
Remember, preparation doesn't stop at technical skills. Make sure you also work on your behavioral interview responses and communication skills to leave a lasting impression on your potential employer. Keep learning and stay updated with the latest Java technologies and trends.
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Roadmap to Web Development – Coding Brushup
In today's digital world, web development is more than just writing code—it's about creating fast, user-friendly, and secure applications that solve real-world problems. Whether you're a beginner trying to understand where to start or an experienced developer brushing up on your skills, this ultimate roadmap will guide you through everything you need to know. This blog also offers a coding brushup for Java programming, shares Java coding best practices, and outlines what it takes to become a proficient Java full stack developer.

Why Web Development Is More Relevant Than Ever
The demand for web developers continues to soar as businesses shift their presence online. According to recent industry data, the global software development market is expected to reach $1.4 trillion by 2027. A well-defined roadmap is crucial to navigate this fast-growing field effectively, especially if you're aiming for a career as a Java full stack developer.
Phase 1: The Basics – Understanding Web Development
Web development is broadly divided into three categories:
Frontend Development: What users interact with directly.
Backend Development: The server-side logic that powers applications.
Full Stack Development: A combination of both frontend and backend skills.
To start your journey, get a solid grasp of:
HTML – Structure of the web
CSS – Styling and responsiveness
JavaScript – Interactivity and functionality
These are essential even if you're focusing on Java full stack development, as modern developers are expected to understand how frontend and backend integrate.
Phase 2: Dive Deeper – Backend Development with Java
Java remains one of the most robust and secure languages for backend development. It’s widely used in enterprise-level applications, making it an essential skill for aspiring Java full stack developers.
Why Choose Java?
Platform independence via the JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
Strong memory management
Rich APIs and open-source libraries
Large and active community
Scalable and secure
If you're doing a coding brushup for Java programming, focus on mastering the core concepts:
OOP (Object-Oriented Programming)
Exception Handling
Multithreading
Collections Framework
File I/O
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Java Coding Best Practices for Web Development
To write efficient and maintainable code, follow these Java coding best practices:
Use meaningful variable names: Improves readability and maintainability.
Follow design patterns: Apply Singleton, Factory, and MVC to structure your application.
Avoid hardcoding: Always use constants or configuration files.
Use Java Streams and Lambda expressions: They improve performance and readability.
Write unit tests: Use JUnit and Mockito for test-driven development.
Handle exceptions properly: Always use specific catch blocks and avoid empty catch statements.
Optimize database access: Use ORM tools like Hibernate to manage database operations.
Keep methods short and focused: One method should serve one purpose.
Use dependency injection: Leverage frameworks like Spring to decouple components.
Document your code: JavaDoc is essential for long-term project scalability.
A coding brushup for Java programming should reinforce these principles to ensure code quality and performance.
Phase 3: Frameworks and Tools for Java Full Stack Developers
As a full stack developer, you'll need to work with various tools and frameworks. Here’s what your tech stack might include:
Frontend:
HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript
React.js or Angular: Popular JavaScript frameworks
Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS: For responsive design
Backend:
Java with Spring Boot: Most preferred for building REST APIs
Hibernate: ORM tool to manage database operations
Maven/Gradle: For project management and builds
Database:
MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB
Version Control:
Git & GitHub
DevOps (Optional for advanced full stack developers):
Docker
Jenkins
Kubernetes
AWS or Azure
Learning to integrate these tools efficiently is key to becoming a competent Java full stack developer.
Phase 4: Projects & Portfolio – Putting Knowledge Into Practice
Practical experience is critical. Try building projects that demonstrate both frontend and backend integration.
Project Ideas:
Online Bookstore
Job Portal
E-commerce Website
Blog Platform with User Authentication
Incorporate Java coding best practices into every project. Use GitHub to showcase your code and document the learning process. This builds credibility and demonstrates your expertise.
Phase 5: Stay Updated & Continue Your Coding Brushup
Technology evolves rapidly. A coding brushup for Java programming should be a recurring part of your development cycle. Here’s how to stay sharp:
Follow Java-related GitHub repositories and blogs.
Contribute to open-source Java projects.
Take part in coding challenges on platforms like HackerRank or LeetCode.
Subscribe to newsletters like JavaWorld, InfoQ, or Baeldung.
By doing so, you’ll stay in sync with the latest in the Java full stack developer world.
Conclusion
Web development is a constantly evolving field that offers tremendous career opportunities. Whether you're looking to enter the tech industry or grow as a seasoned developer, following a structured roadmap can make your journey smoother and more impactful. Java remains a cornerstone in backend development, and by following Java coding best practices, engaging in regular coding brushup for Java programming, and mastering both frontend and backend skills, you can carve your path as a successful Java full stack developer.
Start today. Keep coding. Stay curious.
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Software Design Patterns for Java Developers' discusses the fundamentals of software design as well as well-established design patterns that simplify and outperform the entire software development cycle. To begin with, the book covers the various types of software design patterns and how they differ from one another. Using numerous examples, you can investigate the implementation of various design patterns such as singleton, object pool, adapter, abstract factory, and proxy. Other design patterns include simplifying complex systems, changing the algorithm behavior in runtime, securing broadcasting messages, and many more. Additionally, a chapter is dedicated to understanding some of the most effective design principles and anti-patterns available today. Throughout the book, you will implement the design patterns and understand their purpose, benefits, potential drawbacks, and challenges for each of these design patterns. Publisher : BPB Publications (29 November 2021); BPB Online Language : English Paperback : 282 pages ISBN-10 : 9391392474 ISBN-13 : 978-9391392475 Reading age : 5 years and up Item Weight : 490 g Dimensions : 19.05 x 1.63 x 23.5 cm Packer : BPB Online [ad_2]
0 notes