#microenvironment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Dual targeting of tumoral cells and immune microenvironment by blocking the IL-33/IL1RL1 pathway - New Study
Dual targeting of tumoral cells and immune microenvironment by blocking the IL-33/IL1RL1 pathway Summary Blocking the IL-33/IL1RL1 pathway presents a promising dual approach for cancer therapy. IL-33, released by stressed or damaged cancer cells, interacts with its receptor IL1RL1 on both tumor cells and immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. On tumor cells, this interaction can promote…
#Blocking#Cells#Dual#Haematological cancer#Humanities and Social Sciences#IL33IL1RL1#Immune#immunotherapy#microenvironment#multidisciplinary#pathway#science#Study#targeting#tumoral
0 notes
Text
Oxygen deficiency in the colon cancer microenvironment can promote tumor growth
To effectively battle cancer, scientists must study the battlefield. Now, in a recent study published in Nature Communications, a multi-institutional research team including The University of Osaka has discovered some crucial intel: localized oxygen deficiency in the colon cancer microenvironment can promote tumor growth. Until recently, oxygen deprivation, i.e., hypoxia, was thought to suppress…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Welcome to the Global Webinar on Oncology! This scientific event is designed for researchers, scientists, doctors, practitioners, students, and anyone interested in the latest advancements in the field of oncology. The Displaycia webinar will cover a wide range of topics, including carcinogenesis, cancer stages and grades, tumor pathology, tumor microenvironment, precision oncology, interventional oncology, hematologic malignancies, cancer genomics, cancer metabolism, and many more. The event will provide an excellent opportunity to learn about cutting-edge treatments, indications, and management strategies, as well as recent discoveries, current developments, technology advancements, ongoing research, updates, and the future of the oncology field. Register now to be part of this dynamic platform for cross-sectoral collaboration and drive holistic growth and innovative progress in the field of oncology!
Learn more about us or feel free to contact us at [email protected] for additional details.
#events#research scientist#scholars#science#webinar#oncology#prevention#health#causes#doctors#pharmacy#carcinogenesis#pathology#medicine#hematologic#technology#microenvironment#tumor#practitioners#scientists#scientific research#scientific method
0 notes
Text

Spread on Chips
A micropatterned chip that mimics the natural conditions of tumour spread into surrounding tissue in 3D. Invasive (metastatic) potential of cancer cells can be measured, and therapeutics screened
Read the published research article here
Still from a video from work by Smiti Bhattacharya and colleagues
Barbara T. Murphy Division of Nephrology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York; Department of Mechanical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Video originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Published in Science Advances, August 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#biology#cancer#lab-on-a-chip#microfluidics#oncology#metastasis#tumours#tumour microenvironment
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Tumor biology#cancer progression#tumor microenvironment#metastasis#oncogenes#tumor suppressor genes#angiogenesis#apoptosis#cell proliferation#cancer biomarkers#tumor heterogeneity#cancer stem cells#immuno-oncology#molecular oncology#cancer metabolism#genomic instability#drug resistance#tumor invasion#epigenetic alterations#cancer immunotherapy.#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Author Correction: Collagenolysis-dependent DDR1 signalling dictates pancreatic cancer outcome
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party…
#Cancer metabolism#Cancer microenvironment#Humanities and Social Sciences#multidisciplinary#Nutrient signalling#Science
0 notes
Text
A recent review published in Cancers highlights the significant role of progranulin in cancer development. The growth factor has been found to promote tumor growth by enhancing cancer cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to chemotherapy. It also influences the tumor microenvironment and immune surveillance. Despite these findings, the molecular mechanisms behind progranulin’s oncogenic role are not yet fully understood. Researchers from the Sbarro Health Research Organization and Temple University suggest that further exploration of progranulin could lead to novel therapeutic strategies, including its potential as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for cancer.
#Progranulin#Cancer research#Tumor growth#Cancer development#Oncology#Tumor microenvironment#Chemotherapy resistance#Cancer cell proliferation#Molecular mechanisms#Cancer biomarkers#Cancer treatment#Immunotherapy#Cancer diagnostics#Prognostic markers#Cancer therapy#Sbarro Health Research Organization
1 note
·
View note
Text
working in an archaeology lab/center is so fun. all i do is make sure someone along the way didn't fuck up recording information for 4 hours and try not to scream because they always do fuck it up.
#kalec.txt#and sometimes they is ME#luckily with intake you get to be mad at other people#also theres like a 50% the people you're mad at are from the 70s/80s#for the past week ive been having to put bag tags in bags with no bag tags in a collection with 1800 items in 20 boxes#luckily its not the microenvironments with the bag tag issues but ugh. UGH.#if i never have to see a bag tag or provenience number it'll be too soon#lab is more understandable but technically we're a center now and thats above a lab!#in ur face university of georgia!
0 notes
Text
From the article:
Unlike the flat, lifeless surfaces of typical concrete seawalls, each BIOCAP tile is designed with shaded grooves, crevices and small, water-holding pockets. These textured features mimic natural shoreline conditions and create tiny homes for barnacles, oysters, sponges and other marine organisms that filter and improve water quality. The tile’s swirling surface patterns increase the overall surface area, offering more space for colonization. The shaded recesses are intended to help regulate temperature by providing cooler, more stable microenvironments. This thermal buffering can support marine life in the face of rising water temperatures and more frequent heat events driven by climate change. Another potential benefit of the tiles is reducing the impact of waves. When waves hit a natural shoreline, their energy is gradually absorbed by irregular surfaces, tide pools and vegetation. In contrast, when waves strike vertical concrete seawalls, the energy is reflected back into the water rather than absorbed. This wave reflection – the bouncing back of wave energy – can amplify wave action, increase erosion at the base of the wall and create more hazardous conditions during storms. The textured surfaces of the BIOCAP tiles are designed to help diffuse wave energy by mimicking the natural dissipation found on undisturbed shorelines.
#seawall#solarpunk#hopepunk#bioinspiration#ecology#habitat conservation#habitat restoration#wildlife#shoreline conservation#climate adaptation#climate resilience#good news#hope#climate change#global warming#innovation#ecological impact
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Targeting ribosomes reprograms the tumour microenvironment and augments cancer immunotherapy - New Study
Targeting ribosomes reprograms the tumour microenvironment and augments cancer immunotherapy Summary Targeting ribosomes, the protein synthesis machinery of cells, can significantly alter the tumor microenvironment (TME) and enhance cancer immunotherapy. Dysfunctional ribosomes in cancer cells and TME components contribute to immunosuppression. By modulating ribosome function, researchers can…
#augments#Biomedicine#Cancer#Cancer microenvironment#Cancer Research#Drug Resistance#Epidemiology#general#immunotherapy#microenvironment#Molecular medicine#Oncology#reprograms#ribosomes#Study#targeting#tumour#Tumour immunology
0 notes
Text
The Tumor Microenvironment Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Cancer Prevalence
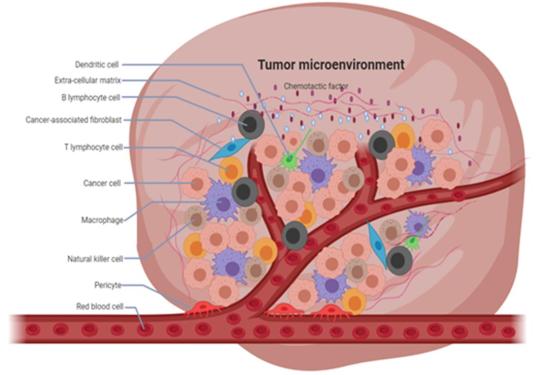
The tumor microenvironment refers to the surrounding molecules, cells, tissue and extracellular matrix that make up the microenvironment where tumors grow and develop. It plays a crucial role in tumor initiation, progression and metastasis by regulating processes such as proliferation, survival, angiogenesis and invasion. Some of the key components of the tumor microenvironment include cancer-associated fibroblasts, immune cells, blood and lymphatic vessels, signaling molecules and the extracellular matrix. The global tumor microenvironment market is estimated to be valued at US$ 1.47 Bn in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 8.5% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Market Dynamics: The tumor microenvironment market is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of various cancers worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer was the leading cause of death globally in 2021, accounting for nearly 10 million deaths. The high burden of the disease has driven increased focus on developing novel targeted therapies and treatment approaches. One such approach involves targeting and manipulating the tumor microenvironment to restrict tumor growth and spread. Another key driver for the market is the rising focus on immunotherapy. Immunotherapies work by enhancing the body's natural defenses to identify and destroy cancer cells. A better understanding of the complex interactions between immune cells and the tumor microenvironment is crucial for developing more effective immunotherapies. Several market players are investing in research analyzing these interactions to identify potential targets for immunotherapy. SWOT ANALYSIS Strength: The tumor microenvironment market has been witnessing high investments in R&D from top players. Key players are investing significantly in developing novel tumor microenvironment targeting therapies and diagnostics. In addition, growing prevalence of cancer and rising need for early diagnosis and treatment are fueling the demand for tumor microenvironment analysis solutions. Weakness: High costs associated with development of tumor microenvironment analysis tools and therapies pose a major challenge to growth of players in this market. Lengthy approval timelines for new tumor microenvironment targeting therapies can impede the commercialization process. Interpretation of complex tumor microenvironment interactions and heterogeneity also makes analysis challenging. Opportunity: Emerging economies offer lucrative growth opportunities for players. Favorable regulatory environment and initiatives to improve access to advanced cancer care in developing nations will create new avenues. Moreover, integration of AI and big data analytics can help gain deeper insights into tumor-stroma interactions and aid discovery of new targets. Threats: Presence of local and generic competitors especially in emerging markets poses pricing pressure on established brands. Stringent quality standards and regulations surrounding clinical trials also increase costs. KEY TAKEAWAYS The global Tumor Microenvironment Market share is expected to witness high growth over the forecast period. Owing to advancements in microenvironment analysis tools, molecular characterization of the TME is gaining traction. The global Tumor Microenvironment Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 1.47 Bn in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 8.5% over the forecast period 2023 to 2030.
North America currently dominates the market and is expected to maintain its lead due to presence of major players and growing adoption of tumor microenvironment profiling tests. The Asia Pacific tumor microenvironment market is anticipated grow at a rapid pace mainly driven by rising healthcare expenditure, large patient pool, and increasing focus of international players on emerging economies. Countries like China, India, South Korea, and Japan are projected to witness highest growth. Favorable government support in the form of funding for cancer research as well as availability of low-cost alternatives are supporting regional market growth. Key players related content comprises Key players operating in the tumor microenvironment market are RCSpeeds, Stalker Radar, Geolux d.o.o, Escort Ltd, Mangal security products, Decatur Electronics Inc., Gvtel Communication System, M R Communications, Shenzhen Lutu Technology Co., LTD, rockymountainradar, and Ultra Mind Technologies India Pvt. Ltd. Key players are focused on developing and commercializing novel tumor microenvironment profiling platforms and assays for improved diagnosis and monitoring of cancer progression.
Get more insights on this topic: https://www.newsstatix.com/tumor-microenvironment-market-industry-insights-trends-tumor-microenvironment-market/
Explore more information on this topic, Please visit: https://wotpost.com/office-furniture-the-foundation-for-productivity-and-collaboration-in-workplaces/
#Tumor Microenvironment#Tumor Microenvironment Market#Tumor Microenvironment Market size#Tumor Microenvironment Market share#Tumor Microenvironment Market analysis#Tumor Microenvironment Market growth
0 notes
Text
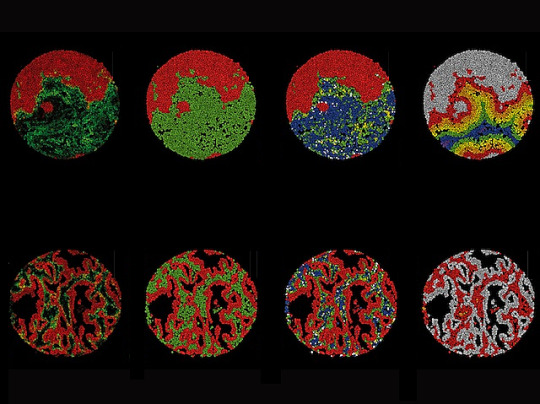
Signs in Surroundings
Single-cell mapping of lung cancer samples reveals presence of a distinct subset of connective tissue cells called fibroblasts in the tumour surroundings (microenvironment) is associated with different outcomes for the patient – tumour-like fibroblasts with poor prognosis and inflammatory type with longer survival
Read the published research article here
Image from work by Lena Cords and colleagues
Department of Quantitative Biomedicine, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution – NonCommercial – NoDerivs (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
Published in Cancer Cell, January 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#oncology#cancer#cancerawareness#cancerresearch#immunotherapy#precision medicine#tumor microenvironment#cancer research#radonc
1 note
·
View note
Text
"Morningside Park, a beloved neighborhood park in Miami with sweeping views of Biscayne Bay, will soon pilot an innovative approach to coastal resilience.
BIOCAP tiles, a 3D-printed modular system designed to support marine life and reduce wave impact along urban seawalls, will be installed on the existing seawall there in spring 2025. BIOCAP stands for Biodiversity Improvement by Optimizing Coastal Adaptation and Performance.
Developed by our team of architects and marine biologists at Florida International University, the uniquely textured prototype tiles are designed to test a new approach for helping cities such as Miami adapt to rising sea levels while simultaneously restoring ecological balance along their shorelines...
Ecological costs of traditional seawalls
Seawalls have long served as a primary defense against coastal erosion and storm surges. Typically constructed of concrete and ranging from 6 to 10 feet in height, they are built along shorelines to block waves from eroding the land and flooding nearby urban areas.
However, they often come at an ecological cost. Seawalls disrupt natural shoreline dynamics and can wipe out the complex habitat zones that marine life relies on.
Marine organisms are crucial in maintaining coastal water quality by filtering excess nutrients, pollutants and suspended particles. A single adult oyster can filter 20-50 gallons of water daily, removing nitrogen, phosphorus and solids that would otherwise fuel harmful algal blooms. These blooms deplete oxygen levels and damage marine ecosystems.
Filter-feeding organisms also reduce turbidity, which is the cloudiness of water caused by suspended sediment and particles. Less water turbidity means more light can penetrate, which benefits seagrasses that require sunlight for photosynthesis. These seagrasses convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and energy-rich sugars while providing essential food and habitat for diverse marine species.
Swirling shapes, shaded grooves

Unlike the flat, lifeless surfaces of typical concrete seawalls, each BIOCAP tile is designed with shaded grooves, crevices and small, water-holding pockets. These textured features mimic natural shoreline conditions and create tiny homes for barnacles, oysters, sponges and other marine organisms that filter and improve water quality.
The tile’s swirling surface patterns increase the overall surface area, offering more space for colonization. The shaded recesses are intended to help regulate temperature by providing cooler, more stable microenvironments. This thermal buffering can support marine life in the face of rising water temperatures and more frequent heat events driven by climate change.
Another potential benefit of the tiles is reducing the impact of waves.
When waves hit a natural shoreline, their energy is gradually absorbed by irregular surfaces, tide pools and vegetation. In contrast, when waves strike vertical concrete seawalls, the energy is reflected back into the water rather than absorbed. This wave reflection – the bouncing back of wave energy – can amplify wave action, increase erosion at the base of the wall and create more hazardous conditions during storms.
The textured surfaces of the BIOCAP tiles are designed to help diffuse wave energy by mimicking the natural dissipation found on undisturbed shorelines.
The design of BIOCAP takes cues from nature. The tile shapes are based on how water interacts with different surfaces at high tide and low tide. Concave tiles, which curve inward, and convex tiles, which curve outward, are installed at different levels along the seawall. The goal is to deflect waves away from the seawall, reduce direct impact and help minimize erosion and turbulence around the wall’s foundation.A
How we will measure success
After the BIOCAP tiles are installed, we plan to assess how the seawall redesign enhances biodiversity, improves water quality and reduces wave energy. This two-year pilot phase will help assess the long-term value of ecologically designed infrastructure.
To evaluate biodiversity, we will use underwater cameras to capture time-lapse imagery of the marine life that colonizes the tile surfaces. These observations will aid in documenting species diversity and habitat use over time...
In the coming year, we’ll be watching with hope as the new BIOCAP tiles begin to welcome marine life, offering a glimpse into how nature might reclaim and thrive along our urban shorelines.
#ocean#seawall#florida#miami#climate adaptation#coastline#united states#north america#biodiversity#waves#ocean waves#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

A cancer that progresses without input from cells is a terrifying concept. What could cause it to grow and spread? Some dark force, some alien influence? The answer is surprisingly mundane- chromosomal instability. This is a flaw in the genetic material that can cause tumors to develop and grow on their own. It's a frightening prospect, cancer that doesn't need cells to survive. But at least we know what causes it, and we can work to find a cure.
#Cancer microenvironment#Chromosomes#Chronic inflammation#Metastasis#Tumour immunology#Science#Humanities and Social Sciences#multidisciplinary#fault#Chromosomal instability#cancer#dark force#alien influence#cure.
0 notes