#robots.txt allow google
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Hey!
Do you have a website? A personal one or perhaps something more serious?
Whatever the case, if you don't want AI companies training on your website's contents, add the following to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
User-agent: anthropic-ai
Disallow: /
User-agent: Claude-Web
Disallow: /
User-agent: CCbot
Disallow: /
User-agent: FacebookBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Google-Extended
Disallow: /
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: PiplBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ByteSpider
Disallow: /
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: cohere-ai
Disallow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Disallow: /
User-agent: Omgilibot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Omgili
Disallow: /
There are of course more and even if you added them they may not cooperate, but this should get the biggest AI companies to leave your site alone.
Important note: The first two lines declare that anything not on the list is allowed to access everything on the site. If you don't want this, add "Disallow:" lines after them and write the relative paths of the stuff you don't want any bots, including google search to access. For example:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: /super-secret-pages/secret.html
If that was in the robots.txt of example.com, it would tell all bots to not access
https://example.com/super-secret-pages/secret.html
And I'm sure you already know what to do if you already have a robots txt, sitemap.xml/sitemap.txt etc.
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
Less than three months after Apple quietly debuted a tool for publishers to opt out of its AI training, a number of prominent news outlets and social platforms have taken the company up on it.
WIRED can confirm that Facebook, Instagram, Craigslist, Tumblr, The New York Times, The Financial Times, The Atlantic, Vox Media, the USA Today network, and WIRED’s parent company, Condé Nast, are among the many organizations opting to exclude their data from Apple’s AI training. The cold reception reflects a significant shift in both the perception and use of the robotic crawlers that have trawled the web for decades. Now that these bots play a key role in collecting AI training data, they’ve become a conflict zone over intellectual property and the future of the web.
This new tool, Applebot-Extended, is an extension to Apple’s web-crawling bot that specifically lets website owners tell Apple not to use their data for AI training. (Apple calls this “controlling data usage” in a blog post explaining how it works.) The original Applebot, announced in 2015, initially crawled the internet to power Apple’s search products like Siri and Spotlight. Recently, though, Applebot’s purpose has expanded: The data it collects can also be used to train the foundational models Apple created for its AI efforts.
Applebot-Extended is a way to respect publishers' rights, says Apple spokesperson Nadine Haija. It doesn’t actually stop the original Applebot from crawling the website—which would then impact how that website’s content appeared in Apple search products—but instead prevents that data from being used to train Apple's large language models and other generative AI projects. It is, in essence, a bot to customize how another bot works.
Publishers can block Applebot-Extended by updating a text file on their websites known as the Robots Exclusion Protocol, or robots.txt. This file has governed how bots go about scraping the web for decades—and like the bots themselves, it is now at the center of a larger fight over how AI gets trained. Many publishers have already updated their robots.txt files to block AI bots from OpenAI, Anthropic, and other major AI players.
Robots.txt allows website owners to block or permit bots on a case-by-case basis. While there’s no legal obligation for bots to adhere to what the text file says, compliance is a long-standing norm. (A norm that is sometimes ignored: Earlier this year, a WIRED investigation revealed that the AI startup Perplexity was ignoring robots.txt and surreptitiously scraping websites.)
Applebot-Extended is so new that relatively few websites block it yet. Ontario, Canada–based AI-detection startup Originality AI analyzed a sampling of 1,000 high-traffic websites last week and found that approximately 7 percent—predominantly news and media outlets—were blocking Applebot-Extended. This week, the AI agent watchdog service Dark Visitors ran its own analysis of another sampling of 1,000 high-traffic websites, finding that approximately 6 percent had the bot blocked. Taken together, these efforts suggest that the vast majority of website owners either don’t object to Apple’s AI training practices are simply unaware of the option to block Applebot-Extended.
In a separate analysis conducted this week, data journalist Ben Welsh found that just over a quarter of the news websites he surveyed (294 of 1,167 primarily English-language, US-based publications) are blocking Applebot-Extended. In comparison, Welsh found that 53 percent of the news websites in his sample block OpenAI’s bot. Google introduced its own AI-specific bot, Google-Extended, last September; it’s blocked by nearly 43 percent of those sites, a sign that Applebot-Extended may still be under the radar. As Welsh tells WIRED, though, the number has been “gradually moving” upward since he started looking.
Welsh has an ongoing project monitoring how news outlets approach major AI agents. “A bit of a divide has emerged among news publishers about whether or not they want to block these bots,” he says. “I don't have the answer to why every news organization made its decision. Obviously, we can read about many of them making licensing deals, where they're being paid in exchange for letting the bots in—maybe that's a factor.”
Last year, The New York Times reported that Apple was attempting to strike AI deals with publishers. Since then, competitors like OpenAI and Perplexity have announced partnerships with a variety of news outlets, social platforms, and other popular websites. “A lot of the largest publishers in the world are clearly taking a strategic approach,” says Originality AI founder Jon Gillham. “I think in some cases, there's a business strategy involved—like, withholding the data until a partnership agreement is in place.”
There is some evidence supporting Gillham’s theory. For example, Condé Nast websites used to block OpenAI’s web crawlers. After the company announced a partnership with OpenAI last week, it unblocked the company’s bots. (Condé Nast declined to comment on the record for this story.) Meanwhile, Buzzfeed spokesperson Juliana Clifton told WIRED that the company, which currently blocks Applebot-Extended, puts every AI web-crawling bot it can identify on its block list unless its owner has entered into a partnership—typically paid—with the company, which also owns the Huffington Post.
Because robots.txt needs to be edited manually, and there are so many new AI agents debuting, it can be difficult to keep an up-to-date block list. “People just don’t know what to block,” says Dark Visitors founder Gavin King. Dark Visitors offers a freemium service that automatically updates a client site’s robots.txt, and King says publishers make up a big portion of his clients because of copyright concerns.
Robots.txt might seem like the arcane territory of webmasters—but given its outsize importance to digital publishers in the AI age, it is now the domain of media executives. WIRED has learned that two CEOs from major media companies directly decide which bots to block.
Some outlets have explicitly noted that they block AI scraping tools because they do not currently have partnerships with their owners. “We’re blocking Applebot-Extended across all of Vox Media’s properties, as we have done with many other AI scraping tools when we don’t have a commercial agreement with the other party,” says Lauren Starke, Vox Media’s senior vice president of communications. “We believe in protecting the value of our published work.”
Others will only describe their reasoning in vague—but blunt!—terms. “The team determined, at this point in time, there was no value in allowing Applebot-Extended access to our content,” says Gannett chief communications officer Lark-Marie Antón.
Meanwhile, The New York Times, which is suing OpenAI over copyright infringement, is critical of the opt-out nature of Applebot-Extended and its ilk. “As the law and The Times' own terms of service make clear, scraping or using our content for commercial purposes is prohibited without our prior written permission,” says NYT director of external communications Charlie Stadtlander, noting that the Times will keep adding unauthorized bots to its block list as it finds them. “Importantly, copyright law still applies whether or not technical blocking measures are in place. Theft of copyrighted material is not something content owners need to opt out of.”
It’s unclear whether Apple is any closer to closing deals with publishers. If or when it does, though, the consequences of any data licensing or sharing arrangements may be visible in robots.txt files even before they are publicly announced.
“I find it fascinating that one of the most consequential technologies of our era is being developed, and the battle for its training data is playing out on this really obscure text file, in public for us all to see,” says Gillham.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tumblr Growth - Its tough trying to face the world from inside Tumblr.
I used a service called Make | Automation Software | Connect Apps & Design Workflows | Make to push my Youtube videos (All of them that I could on a free plan) to Tumblr - ive been also forming connections and commenting and being part of the community. I had issues where it would post the link to the video, well the ID and I had to manually push the you tube url video = [VideoID] but it didnt embed so I have been editing them one by one to properly embed them and tag them. Its paying off slowly, also pushing thebritbeardo.tumblr.com to the world, frustrated that tumblr is blocking bing bot and @tumblrsupport in a reddit thread said speak to Bing, Bing does not control robots.txt for my site so I kindly asked and will continue to ask tumblr support to remove the block to bingbot, I have sent screenshots from bing webmaster tools. Also, Google is not properly indexing britbeardo.tumblr.com because its not the canonical URL and no matter the tags I put in the html it seems that there is a tumblr controlled canonical url that is set to tumblr.com/accountname. All the canonical testers tell me this.
It seems they are really focusing on users using internal tumblr network and not reaching out to potentially new tumblr users. Its a shame as if you configure Tumblr correctly, follow the right people its actually a much better social environment that Facebook or X, Threads, Masterdon etc. I use them all pretty much and found Tumblr to be a breath of fresh air except for these few frustrations.
@TumblrSupport please allow users more control of blocked search engines in the robots.txt, even if its a check box for allow Yandex, Allow BingBot etc. And give us control of the canonical URL, if I put a Tag in my HTML to override please honor my request to use account.tumblr.com I considered buying a domain but in still concerned that using a domain will cause me to still blocked by bingbot and not have control of the canonical settings.

3 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'd like some people to participate in a quick LLM experiment - specifically, to get some idea as to what degree LLMs are actually ignoring things like robots.txt and using content they don't have permission to use.
Think of an OC that belongs to you, that you have created some non-professional internet-based content for - maybe you wrote a story with them in it and published it on AO3, or you talked about them on your blog, or whatever, but it has to be content that can be seen by logged-out users. Use Google to make sure they don't share a name with a real person or a well-known character belonging to someone else.
Pick an LLM of your choice and ask it "Who is <your OC's name>?" Don't provide any context. Don't give it any other information, or ask any follow-up questions. If you're worried about the ethicality of this, sending a single prompt is not going to be making anyone money, and the main energy-consumption associated with LLMs is in training them, so unless you are training your own model, you are not going to be contributing much to climate change and this request probably doesn't use much more energy than say, posting to tumblr.
Now check if what you've posted about this OC is actually searchable on Google.
Now answer:
robots.txt is a file that every website has, which tells internet bots what parts of the website they can and cannot access. It was originally established for search engine webcrawlers. It's an honor system, so there's nothing that actually prevents bots from just ignoring it. I've seen a lot of unsourced claims that LLM bots are ignoring robots.txt, but Wikipedia claims that GPTBot at least does respect robots.txt, at least at the current time. Some sites use robots.txt to forbid GPTBot and other LLM bots specifically while allowing other bots, but I think it's probably safe to say that if your content does not appear on Google, it has probably been forbidden to all bots using robots.txt.
I did this experiment myself, using an OC that I've posted a lot of content for on Dreamwidth, none of which has been indexed by Google, and the LLM did not know who they were. I'd be interested to hear about results from people posting on other sites.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Different Google Indexing Methods
Google's indexing methods are behind websites' appearance in search results and show webmasters a path to visibility. Knowing what makes every indexing method unique can take you, the site owner, further along the process toward better optimization of your site ranking. This article looks at various indexing approaches by elaborating on ideal pros and cons of automated and manual indexing tools in order to guide you in choosing an optimal option for your website. Also you can get 200 links indexing for test in indexing tool.
What is Google Indexing
Google Indexing: This is when Google's bots, known as "crawlers," go through and document all the pages of a website so they can be found on any search results. Google uses highly sophisticated algorithms to crawl, index, and rank content for relevance, quality, and freshness. These all form the backbone of the engine in facilitating quick information findings.
The use of these tools and methods for indexing depends on whom site owners consider and will be a matter of choice to facilitate Google. Most of the methods either rely on automating or manually doing something. Choices are made depending on the reached goal, which confers speed, accuracy, and the amount of indexed data. This means weighing up the pros and cons of each method.

Manual versus Automatic Indexing Techniques
Google provides both manual and automated indexing methods that have their own special advantages and disadvantages. Now, let's discuss in detail these two approaches and describe the primary characteristics of each.
Manual Indexing Tools
Manual indexing is about having direct contact with those indexing tools provided by Google, which need to be prompted for the required indexing. This can be a very tiresome process, but manual indexing gives more control and specification over which pages will be indexed and updated.
Examples of Manual Indexing Tools
Google Search Console: Probably the most-used tool for manually asking for indexing on a given page.
Fetch as Google: This is a feature within the Search Console; it allows users to request certain URLs for indexing.
Indexing API: Primarily used for job posting sites and live stream pages, the Indexing API actually manually sends URLs for faster indexing to Google.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Indexing
Pros:
More Control: This allows the webmaster to specify which pages will index, especially for high-priority or new pages.
Selective Indexing: Used for visibility control in those cases where some kind of content may be kept from being included among the results of a search.
Faster Results for Certain Key Pages: By manually requesting, the outcomes for the most important pages could be obtained quicker.
Cons:
Time-consuming: Each page requires attention; hence, this is impractical for large sites.
Limited Scale: Manual indexing is not well-suited to handle heavy indexing needs and quickly becomes impractical with large volumes of content.
Periodic Re-indexing: Because of how frequent the updates are, re-indexing requests can only be manually done, which is cumbersome.
Auto Indexing Tools
The automated indexing methods automatically enable Google crawlers to discover and index new pages of any site. Generally, the possibility of such methods depends on XML sitemaps, automated submissions, and scripts that make it easy for Google to crawl large websites.
Examples of Automated Indexing Tools
XML Sitemap: An XML file in which all the URLs contained on a site are housed to help Google properly understand the site structure, focusing on which pages are most important.
Ping Services: Notify Google and other search engines that new or updated content is on hand; this starts the indexing process.
Robots.txt: Instructs the search spiders on pages to crawl and index, and those not to crawl or index.
Pros and Cons of Automated Indexing
Pros:
Ease of Use: It indexes all the web pages of a site automatically and hence is ideal for bigger web sites.
Periodic Crawling: Google's spiders revisit pages from time to time to update their indexes with new content.
Scalability: Automation techniques can handle large volumes of content without extra effort being applied.
Cons:
Less control: All pages are indexed unselectively and therefore include those that should not be seen.
Over-Indexing: Sometimes, automated indexing indexes unnecessary pages and can be harmful for SEO.
Dependence on Google Schedule: The automatic indexing depends upon Google's schedule, which may delay the indexing of new or updated web pages.
Comparison of Indexing Methods
Which indexing tool a website employs, manual or automated, depends largely on its size, content frequency, and SEO objectives. A comparison that evidences some of the key differences follows: Feature Hand Indexing Automated Indexing Control High – select only specific pages for selection Low – allow all pages to be indexed Time Requirement Higher time investment Minimal time investment Scalability Limited scalability Highly scalable Crawl Frequency On-demand per page Set by Google's crawling schedule Content Visibility Selective, managed visibility Automatically visible Ideal For Small sites or high-priority pages Large sites or frequent updates
Issues to Consider when Choosing an Indexing Technique
Which indexing method a website owner chooses to use—manual or automated—is a matter which depends, among other things, on the size of the website, its frequency of updating, and the goals of visibility. The following are some key factors which will help an individual make an informed choice:
Website size: Large-sized websites that frequently update their content require automated indexing, whereas smaller sites with a couple of web pages can manage with manual indexing.
Content Type: Websites with very time-sensitive content, such as news sites or blogs, may want to use automated methods of continuous indexing.
Indexing Frequency: Sites which update their content often are indexed automatically so that the latest versions show in the search results.
SEO Objectives: Sometimes targeted keywords or even specific search intent drive manual indexing to give more control over what gets indexed and in what order.
How to Ensure Effective Google Indexing-Best Practices
Regardless of the indexing method, there are some best practices that raise the indexing process to a whole new level.
XML Sitemap submission: Make sure Google will have added access to an updated XML sitemap which contains all the URLs.
Use Google Search Console: Monitor regularly and request indexing for new or important pages.
URL Structure: Optimise the structure of URLs in terms of brevity and clarity to help Google understand the hierarchy and relevance of different pages.
Duplicate Content: Lessen duplicate pages to improve indexing efficiency and reduce potential penalties.
Use /robots.txt files judiciously: Keep the crawlers away from pages that need not be indexed; conserve resources on what is important.
FAQs
What is Google Indexing?
Google Indexing is where the big search engine crawlers study and cache data from your website for display in results. Proper indexing makes a website show up in results when it's relevant.
Manual Indexing vs Automated Indexing: Which Should I Use?
It all depends on how big your site is, how frequently it's updated, and what you need for SEO. Larger sites and/or rapidly updated sites would most definitely benefit from automation, although you might do smaller sites manually or at least priority pages.
Are the automated indexing tools faster than the manual ones?
Generally speaking, yes; an automated tool covers more ground faster, though the timing is up to Google. In the case of some more important, high-priority pages, this might be faster with manual means.
Is indexing of all pages necessary?
Not exactly, say the authors. Only those pages need to be indexed that have some relevance for search visibility; otherwise, too much indexing simply dilutes the SEO effort.
What does Google Search Console play a role in indexing?
Google Search Console is one of the important tools for requesting indexing, site performance monitoring, and visibility management in search results.
Conclusion
Various methods to do indexing will be mentioned in the case of Google indexing, each having certain advantages and disadvantages. While manual indexing tools give very detailed control for smaller sites or individual pages, automated indexing can provide an order for bigger sites. Site owners should ensure that the right approach is taken along with practicing the best ways to index in order to ensure that the ranking and targeted audiences are met with the content being indexed by Google. Get free 200 links indexing in SpeedyIndex.
1 note
·
View note
Text
14+ cách dùng Chat GPT tối ưu SEO mà Marketers không thể bỏ qua
Chat GPT, được phát triển bởi OpenAI, là một mô hình ngôn ngữ AI mạnh mẽ có khả năng tạo ra văn bản tự nhiên giống con người. Việc ứng dụng Chat GPT vào SEO đang trở thành xu hướng mới, đầy triển vọng trong việc tối ưu hóa nội dung trang web và cải thiện thứ hạng trên công cụ tìm kiếm. Hãy cùng khám phá 14 cách sử dụng Chat GPT cho SEO trong bài viết này nhé!
Cách dùng Chat GPT cho Technical SEO
Tạo FAQ Schema
Tạo schema HowTo
Create Robots.txt Rules
Tạo htaccess Redirect Rules
Kết nối với API và mã hóa
Tạo FAQ schema
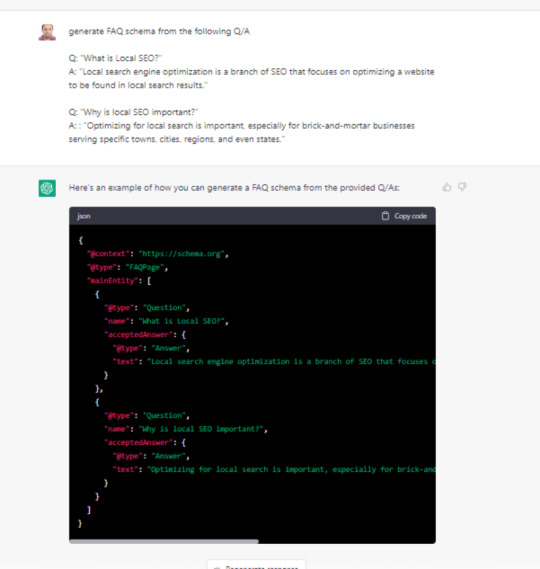
Bạn có thể sử dụng ChatGPT để tạo FAQ schema từ nội dung bạn cung cấp. Mặc dù bạn có thể sử dụng plugin CMS cho việc này, nhưng nếu bạn sử dụng nền tảng như Wix không hỗ trợ plugin, ChatGPT trở thành một trợ thủ đắc lực. Bạn chỉ cần cung cấp văn bản câu hỏi và câu trả lời, ChatGPT sẽ tạo ra mã schema phù hợp để bạn dán vào trình chỉnh sửa của mình. Bạn có thể yêu cầu ChatGPT tạo bất kỳ loại schema nào bằng cách sử dụng các ví dụ tương tự.
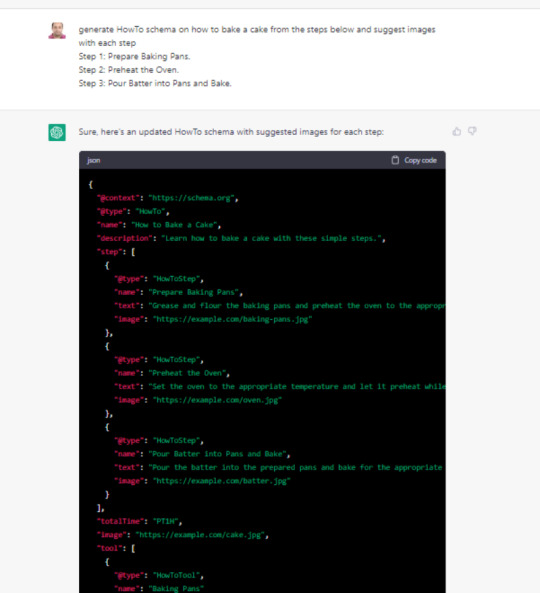
Tạo schema HowTo
Để tạo schema HowTo, bạn có thể sử dụng ChatGPT theo cách tương tự như khi tạo FAQ schema. Bạn chỉ cần cung cấp các bước chi tiết cho một quy trình cụ thể và yêu cầu ChatGPT tạo mã schema HowTo. Ví dụ: "Generate HowTo schema on how to bake a cake from the steps below and suggest images with each step."
Mặc dù ChatGPT sẽ hoàn thành phần lớn công việc, bạn vẫn cần thay thế các URL hình ảnh mẫu bằng các URL hình ảnh thực tế của mình. Sau khi mã schema được tạo, bạn chỉ cần tải hình ảnh lên CMS và cập nhật đường dẫn hình ảnh trong schema theo đề xuất của ChatGPT.
Create Robots.txt Rules
Các chuyên gia SEO thường phải xử lý nhiều với tệp robots.txt. Với ChatGPT, bạn có thể dễ dàng tạo bất kỳ quy tắc nào cho robots.txt.
Ví dụ về Quy Tắc Robots.txt
Giả sử bạn muốn ngăn Google thu thập dữ liệu các trang đích của chiến dịch PPC nằm trong thư mục /landing, nhưng vẫn cho phép bot của Google Ads truy cập. Bạn có thể sử dụng lời nhắc sau: "Robots.txt rule which blocks Google's access to directory /landing/ but allows Google ads bot."
Sau khi tạo quy tắc, bạn cần kiểm tra kỹ tệp robots.txt của mình để đảm bảo rằng nó hoạt động như mong muốn.
Tạo htaccess Redirect Rules
Các chuyên gia SEO thường phải thực hiện việc chuyển hướng trang, và điều này có thể phụ thuộc vào loại máy chủ mà họ sử dụng. Với ChatGPT, bạn có thể dễ dàng tạo quy tắc chuyển hướng cho htaccess hoặc Nginx.
Ví dụ về Quy Tắc Chuyển Hướng htaccess
Giả sử bạn muốn chuyển hướng từ folder1 sang folder2, bạn có thể sử dụng lời nhắc sau: "For redirecting folder1 to folder2 generate nginx and htaccess redirect rules."
ChatGPT sẽ cung cấp các quy tắc cần thiết cho cả htaccess và Nginx. Sau khi tạo, bạn chỉ cần sao chép và dán các quy tắc này vào tệp cấu hình máy chủ của mình.

Xem thêm về Chat GPT cho SEO tại đây.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
🛠️ 4 Technical SEO Essentials You Shouldn’t Ignore! If you want your website to rank better, you need more than just keywords. You need structure, clarity, and control. Here’s how: 🔹 1. Schema Basics Schema markup is code that helps search engines understand what your content is about — whether it’s a blog, product, review, recipe, or FAQ. ✅ It enables Rich Snippets (like ⭐ ratings, event dates, prices, etc.) ✅ More clarity = better visibility on Google 🔹 2. JSON-LD This is the preferred format for implementing schema. ✅ Clean, easy to implement in the <head> tag ✅ Doesn’t interfere with your main HTML ✅ Recommended by Google Example: Use BlogPosting, Product, FAQ, or HowTo schema 🔹 3. Sitemap.xml Think of it as a map that tells Google which pages exist and should be crawled. ✅ Helps with faster indexing ✅ Essential for large or dynamic websites ✅ Submit it in Google Search Console for better tracking 🔹 4. Robots.txt This file gives bots directions — which pages they’re allowed to crawl and which they should skip. ✅ Prevents crawl budget waste ✅ Useful for blocking admin, cart, or duplicate pages ✅ Should be tested before publishing 🔎 Why It Matters Together, these tools tell Google: ✅ What’s important ✅ What’s allowed ✅ What’s valuable So, if you want your content to be found faster and perform better, get these four basics right. 💬 Want help implementing them on your site? Let’s talk. hashtag#TechnicalSEO hashtag#SchemaMarkup hashtag#JSONLD hashtag#Sitemaps hashtag#RobotsTxt hashtag#SEOStrategy hashtag#DigitalMarketingTips hashtag#SEOForBeginners hashtag#GoogleRanking hashtag#WebsiteOptimization hashtag#SEOexpert

#TechnicalSEO#SchemaMarkup#JSONLD#Sitemaps#RobotsTxt#SEOStrategy#DigitalMarketingTips#SEOForBeginners#GoogleRanking#WebsiteOptimization#SEOexpert
0 notes
Text

What Are the Key Features offered by a Professional SEO Agency? A Professional Seo Agency is involved in the following steps 1.Comprehensive SEO Audit This audit allows for Site performance and technical health check. This involves On-page and off-page SEO evaluation, Keyword ranking and competitor gap analysis 2.Keyword Research & Strategy This is for Identifying high-traffic, low-competition keywords. There is Keyword intent mapping where Long-tail keyword targeting is emphasized 3.On-Page SEO Optimization Under this Meta tags (title, description) and header is optimized. This allows for Content structuring and internal linking,URL structure and keyword placement, Image optimization like alt text, compression 4.Technical SEO Website speed optimization that involves Core Web Vitals, Mobile-friendliness and responsive design, Crawlability and indexation improvements (robots.txt, sitemap) Canonicalization and structured data/schema markup etc is taken care of. 5.Link Building & Off-Page SEO Here White-hat backlink acquisition is give importance. Guest posting and outreach campaigns are emphasized along with importance on Business listings and local citations 6.Local SEO Services Google Business Profile optimization is of key significance now with Local keyword targeting and Citation building for local directories not to forget Review and rating strategy 7.Content Strategy & Development SEO-friendly blog writing is o significance. Topic cluster and pillar content development makes a lot of impact AI-assisted content optimization and Updating old content for relevance is a step in content strategy 8.Analytics, Reporting & KPIs A Professional Seo Agency in Dubai looks at Google Analytics & Search Console setup along with Monthly SEO performance dashboards that help identify the performance based on metrics. Keyword ranking reports, Conversion tracking and ROI reporting is important. 9.AI & Automation Tools With use of AI tools like Surfer SEO, Clearscope, and ChatGPT for optimization, the AI tools use Automated technical audits and alerts, Predictive SEO and trend monitoring 10.Consultation & Communication A Dedicated SEO strategist or account manager is a plus for any account held. With Regular review meetings and reporting there is chance for Transparent action plans and deliverables
0 notes
Text
Staging on a VPS: Safely Preview Changes Before Going Live
🧪 How to Build a Staging Environment Using Your VPS
Safely test changes before going live — the smart way.
If you're running a website, web app, or SaaS project, you know the pain of broken layouts, buggy features, or downtime after updates. That’s where a staging environment comes in — a replica of your live website where you can test everything before going public.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to set up a reliable staging environment using your VPS hosting (ideal if you're hosted with VCCLHOSTING).
🧠 What Is a Staging Environment?
A staging environment is a testing ground — separate from your production (live) server — that simulates the real-world environment of your website or app. You can use it to:
Test design updates, new features, or plugin installs
Preview major code or content changes
Troubleshoot performance and security
Collaborate with your dev or QA team
Avoid downtime or user experience issues
🛠️ Why Use a VPS for Staging?
Using a VPS (Virtual Private Server) gives you:
Root access for full control
Dedicated resources (RAM, CPU)
Ability to isolate staging from live environment
Freedom to run multiple domains/subdomains or even container-based staging setups
💡 Tip: If you're using VCCLHOSTING, you can easily configure multiple environments on a single VPS or request an additional one at discounted rates for dev/testing purposes.
🧰 Tools You’ll Need
A VPS with Linux (Ubuntu/Debian/CentOS)
Web server: Apache or NGINX
PHP, MySQL/MariaDB stack (or your app’s language/runtime)
Optional: Git, Docker, cPanel, or phpMyAdmin
Domain/subdomain for staging (e.g., staging.yoursite.com)
🔧 Steps to Build a Staging Environment
1. Create a Subdomain or Separate Directory
Subdomain method: Set up staging.yourdomain.com in your DNS settings Point it to a new virtual host directory on your VPS
Folder method: Use a separate folder like /var/www/html/staging
✅ If you use cPanel or DirectAdmin (available on VCCLHOSTING), this can be done with a few clicks.
2. Clone Your Production Site
Manually copy your website files (via SFTP, rsync, or Git)
Export your live database and import it to a new one (e.g., staging_db)
Update configuration files:
Database credentials
Site URL paths (e.g., in WordPress: update wp-config.php and wp_options table)
3. Add Security
You don’t want Google indexing your staging site or hackers testing exploits.
Use .htpasswd to password-protect the staging directory
Block indexing via robots.txt
Restrict IP addresses if needed
Use HTTPS (let's Encrypt SSL or clone your live certificate)
4. Use Version Control (Recommended)
Set up Git to manage your staging deployments:
bashCopy
Edit
git clone https://github.com/yourrepo/project.git
This allows your devs to push to staging for testing before merging to live.
5. Test Your Changes in Staging First
Always use staging to:
Apply plugin/theme updates
Run database migrations
Test performance under simulated load
QA user flows, logins, carts, or contact forms
Once everything works in staging, deploy to live using:
Git-based CI/CD
Manual sync
Hosting control panel tools (e.g., Softaculous staging)
🤖 Bonus: Automate Staging with Docker or Containers
If you manage multiple apps, use Docker Compose or Kubernetes to quickly spin up isolated environments on your VPS.
Example with Docker Compose:
yamlCopy
Edit
version: '3' services: app: image: php:8.1-apache volumes: - ./code:/var/www/html ports: - "8081:80"
🛡️ Staging Environments with VCCLHOSTING
With VCCLHOSTING VPS, you get:
Full root access to configure staging as needed
Support for Linux or Windows environments
Optional cPanel/DirectAdmin for GUI-based staging
Local data center in Kolhapur for low-latency testing
Backup & restore tools to sync between live and staging
🧠 Final Thoughts
A staging environment isn’t just for big companies — it’s for anyone who cares about uptime, stability, and professionalism. Whether you're running a SaaS project or an eCommerce store, setting up staging on your VPS saves time, avoids downtime, and helps you launch with confidence.
🚀 Need Help Setting It Up?
Talk to the team at VCCLHOSTING — we’ll help you set up a staging-ready VPS with backup, SSH, and everything pre-configured.
🔗 www.vcclhosting.com 📞 Call us: 9096664246
0 notes
Text
Robots.txt Và Sitemap.xml: Khai Báo Thế Nào Là Đúng Chuẩn?
Khi nói đến SEO kỹ thuật, nhiều người tập trung vào thẻ meta, tốc độ tải trang hay mobile responsive mà quên mất rằng việc hướng dẫn bot tìm kiếm “đi đúng đường” cũng quan trọng không kém. Trong đó, robots.txt và sitemap.xml là hai công cụ thiết yếu giúp bot hiểu và thu thập thông tin website một cách hiệu quả. Vậy robots.txt là gì và cần khai báo cùng sitemap ra sao để đúng chuẩn SEO?
Robots.txt Là Gì Và Vì Sao Cần Đi Kèm Sitemap.xml?
Robots.txt là gì? Đây là một tệp văn bản đặt tại thư mục gốc của website (ví dụ: yourdomain.com/robots.txt) có nhiệm vụ hướng dẫn bot tìm kiếm (như Googlebot) những khu vực nào được phép hoặc không được phép crawl (thu thập dữ liệu).

Còn sitemap.xml là bản đồ website chứa danh sách URL mà bạn muốn bot lập chỉ mục. Khi hai công cụ này phối hợp hiệu quả, bạn có thể kiểm soát chính xác luồng truy cập của bot, đồng thời đảm bảo những nội dung quan trọng được index nhanh chóng.
Robots.txt Và Sitemap: Cách Khai Báo Đúng
Để khai báo sitemap đúng trong file robots.txt, bạn cần đặt đường dẫn sitemap ở cuối file, sử dụng cú pháp:
arduino
CopyEdit
Sitemap: https://www.tenmiencuaban.com/sitemap.xml
Ngoài ra, bạn có thể sử dụng nhiều dòng Sitemap: nếu có nhiều s�� đồ website khác nhau cho các phần như bài viết, sản phẩm, hình ảnh… Tuy nhiên, cần tránh những lỗi cơ bản như:
Chặn toàn bộ thư mục chứa sitemap bằng Disallow.
Viết sai đường dẫn sitemap (có dấu cách, thiếu https://...).
Không khai báo sitemap khi dùng CMS như WordPress hoặc Magento có sitemap động.
Sự phối hợp giữa robots.txt và sitemap sẽ giúp Google xác định nội dung nào nên crawl trước, nội dung nào cần bỏ qua, từ đó tối ưu hóa tài nguyên lập chỉ mục và tăng hiệu quả SEO.
Cách Kiểm Tra File Robots.txt Của Website
Để đảm bảo file robots.txt hoạt động đúng, bạn có thể:
Truy cập trực tiếp yourdomain.com/robots.txt để xem nội dung.
Sử dụng công cụ “Kiểm tra robots.txt” của Google Search Console.
Đảm bảo các chỉ thị (lệnh) như User-agent, Disallow, Allow, Sitemap được viết đúng cú pháp và không mâu thuẫn.
Việc kiểm tra file robots.txt của website định kỳ giúp tránh các lỗi không mong muốn như chặn nhầm URL cần index, gây ảnh hưởng đến khả năng hiển thị trên Google.

Dịch Vụ SEO Kỹ Thuật Từ TCC & Partners
Nếu bạn chưa rành về robots.txt, sitemap hoặc các cấu hình SEO kỹ thuật khác, TCC & Partners Agency có thể đồng hành cùng bạn. Dịch vụ SEO tại đây bao gồm:
Tư vấn, phân tích & tối ưu website tổng thể
Thiết lập và kiểm tra robots.txt, sitemap.xml đúng chuẩn
Duy trì thứ hạng từ khóa bền vững, tối ưu trải nghiệm người dùng
Tăng trưởng traffic tự nhiên, giảm phụ thuộc vào quảng cáo trả phí
TCC & Partners không chỉ đưa từ khóa của bạn lên top Google, mà còn xây dựng nền tảng SEO vững chắc từ gốc kỹ thuật đến nội dung.
Kết luận, hiểu rõ robots.txt là gì và biết cách khai báo robots.txt và sitemap đúng chuẩn là bước quan trọng trong bất kỳ chiến lược SEO thành công nào. Hãy đảm bảo bạn thiết lập đúng – hoặc để chuyên gia hỗ trợ bạn thực hiện từ đầu một cách bài bản.
0 notes
Text
Optimizing Angular Applications for Enhanced SEO: A Comprehensive Guide

In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the visibility of your web application on search engines like Google is paramount. Angular, a robust platform for building dynamic web applications, offers great features but comes with its own set of SEO challenges due to its client-side rendering nature. This article dives into effective strategies and practices for optimizing Angular applications to improve their search engine rankings and enhance discoverability.
Understanding the SEO challenges with angular
Angular applications primarily rely on client-side rendering, which dynamically generates content on the user’s browser. While this approach significantly improves user experience by making web applications fast and responsive, it presents a challenge for search engine crawlers. Traditional crawlers may struggle to index the content properly, as they might not execute JavaScript and hence, miss the dynamically generated content. Additionally, dynamically generating metadata, ensuring fast page loads, and optimizing for mobile responsiveness can be complex with angular applications.
Proven strategies for angular SEO optimization
1. Server-side rendering (SSR) with angular universal:
Implementing SSR via angular universal enables your application to serve fully rendered pages to both the browser and search engine crawlers. This ensures that your content is immediately accessible for indexing, and enhancing SEO.
2. Pre-rendering for static pages:
For applications with static content, pre-rendering can be a highly effective technique. Tools like Scully can generate static pages at build time, ensuring that crawlers have full access to the content, and improving SEO with minimal impact on performance.
3. Dynamic rendering for different user agents:
Serving different content to users and search engine crawlers can temporarily address SEO challenges. This involves detecting the user agent and serving a static page to crawlers while users receive the dynamic client-side rendered application.
4. Optimizing meta tags and titles dynamically:
Utilizing angular’s meta and title services allows for dynamic modification of HTML meta tags and titles based on the current route or content. This ensures that search engine crawlers receive relevant information, improving content indexing.
5. Structured data and schema markup:
Injecting structured data into your angular application enhances SEO by providing search engines with explicit information about your page content, potentially leading to better visibility and rich snippets in search results.
6. Efficient routing and clean URL structure:
Leveraging the angular router for managing navigation and ensuring URLs are SEO-friendly (avoiding hash-based URLs) is crucial. Using HTML5 pushstate creates clean, crawlable URLs.
7. Web performance optimization:
Search engines favor fast-loading pages. Techniques such as lazy loading, efficient bundling, and compression can significantly improve your angular application’s load times.
8. Utilizing sitemaps and robots.txt:
Ensuring your application includes a sitemap.xml and a properly configured robots.txt file can guide search engines in crawling and indexing your content more effectively.
9. Regular monitoring and testing:
Tools like Google Search Console are invaluable for monitoring your site’s SEO performance, identifying crawl errors, and optimizing your visibility in search results.
10. Stay updated:
SEO practices and search engine algorithms are continually evolving. Staying informed about the latest trends and updates in both angular and SEO communities is crucial for maintaining and enhancing your application’s visibility.
Optimizing angular applications for search engines is a multifaceted process that involves technical adjustments, strategic planning, and ongoing monitoring. By embracing server-side rendering, optimizing meta tags, leveraging structured data, and focusing on performance and mobile responsiveness, developers can significantly improve their Angular applications’ SEO performance. As online visibility becomes increasingly crucial for success, investing time and resources into SEO optimization will yield substantial benefits in terms of traffic, user engagement, and overall business outcomes.
Explore Centizen Inc’scomprehensive staffing solutions custom software development and innovative software offerings, including ZenBasket and Zenyo, to elevate your business operations and growth.
0 notes
Text
As media companies haggle licensing deals with artificial intelligence powerhouses like OpenAI that are hungry for training data, they’re also throwing up a digital blockade. New data shows that over 88 percent of top-ranked news outlets in the US now block web crawlers used by artificial intelligence companies to collect training data for chatbots and other AI projects. One sector of the news business is a glaring outlier, though: Right-wing media lags far behind their liberal counterparts when it comes to bot-blocking.
Data collected in mid-January on 44 top news sites by Ontario-based AI detection startup Originality AI shows that almost all of them block AI web crawlers, including newspapers like The New York Times, The Washington Post, and The Guardian, general-interest magazines like The Atlantic, and special-interest sites like Bleacher Report. OpenAI’s GPTBot is the most widely-blocked crawler. But none of the top right-wing news outlets surveyed, including Fox News, the Daily Caller, and Breitbart, block any of the most prominent AI web scrapers, which also include Google’s AI data collection bot. Pundit Bari Weiss’ new website The Free Press also does not block AI scraping bots.
Most of the right-wing sites didn’t respond to requests for comment on their AI crawler strategy, but researchers contacted by WIRED had a few different guesses to explain the discrepancy. The most intriguing: Could this be a strategy to combat perceived political bias? “AI models reflect the biases of their training data,” says Originality AI founder and CEO Jon Gillham. “If the entire left-leaning side is blocking, you could say, come on over here and eat up all of our right-leaning content.”
Originality tallied which sites block GPTbot and other AI scrapers by surveying the robots.txt files that websites use to inform automated web crawlers which pages they are welcome to visit or barred from. The startup used Internet Archive data to establish when each website started blocking AI crawlers; many did so soon after OpenAI announced its crawler would respect robots.txt flags in August 2023. Originality’s initial analysis focused on the top news sites in the US, according to estimated web traffic. Only one of those sites had a significantly right-wing perspective, so Originality also looked at nine of the most well-known right-leaning outlets. Out of the nine right-wing sites, none were blocking GPTBot.
Bot Biases
Conservative leaders in the US (and also Elon Musk) have expressed concern that ChatGPT and other leading AI tools exhibit liberal or left-leaning political biases. At a recent hearing on AI, Senator Marsha Blackburn recited an AI-generated poem praising President Biden as evidence, claiming that generating a similar ode to Trump was impossible with ChatGPT. Right-leaning outlets might see their ideological foes’ decisions to block AI web crawlers as a unique opportunity to redress the balance.
David Rozado, a data scientist based in New Zealand who developed an AI model called RightWingGPT to explore bias he perceived in ChatGPT, says that’s a plausible-sounding strategy. “From a technical point of view, yes, a media company allowing its content to be included in AI training data should have some impact on the model parameters,” he says.
However, Jeremy Baum, an AI ethics researcher at UCLA, says he’s skeptical that right-wing sites declining to block AI scraping would have a measurable effect on the outputs of finished AI systems such as chatbots. That’s in part because of the sheer volume of older material AI companies have already collected from mainstream news outlets before they started blocking AI crawlers, and also because AI companies tend to hire liberal-leaning employees.
“A process called reinforcement learning from human feedback is used right now in every state-of-the-art model,” to fine-tune its responses, Baum says. Most AI companies aim to create systems that appear neutral. If the humans steering the AI see an uptick of right-wing content but judge it to be unsafe or wrong, they could undo any attempt to feed the machine a certain perspective.
OpenAI spokesperson Kayla Wood says that in pursuit of AI models that “deeply represent all cultures, industries, ideologies, and languages” the company uses broad collections of training data. “Any one sector—including news—and any single news site is a tiny slice of the overall training data, and does not have a measurable effect on the model’s intended learning and output,” she says.
Rights Fights
The disconnect in which news sites block AI crawlers could also reflect an ideological divide on copyright. The New York Times is currently suing OpenAI for copyright infringement, arguing that the AI upstart’s data collection is illegal. Other leaders in mainstream media also view this scraping as theft. Condé Nast CEO Roger Lynch recently said at a Senate hearing that many AI tools have been built with “stolen goods.” (WIRED is owned by Condé Nast.) Right-wing media bosses have been largely absent from the debate. Perhaps they quietly allow data scraping because they endorse the argument that data scraping to build AI tools is protected by the fair use doctrine?
For a couple of the nine right-wing outlets contacted by WIRED to ask why they permitted AI scrapers, their responses pointed to a different, less ideological reason. The Washington Examiner did not respond to questions about its intentions but began blocking OpenAI’s GPTBot within 48 hours of WIRED’s request, suggesting that it may not have previously known about or prioritized the option to block web crawlers.
Meanwhile, the Daily Caller admitted that its permissiveness toward AI crawlers had been a simple mistake. “We do not endorse bots stealing our property. This must have been an oversight, but it's being fixed now,” says Daily Caller cofounder and publisher Neil Patel.
Right-wing media is influential, and notably savvy at leveraging social media platforms like Facebook to share articles. But outlets like the Washington Examiner and the Daily Caller are small and lean compared to establishment media behemoths like The New York Times, which have extensive technical teams.
Data journalist Ben Welsh keeps a running tally of news websites blocking AI crawlers from OpenAI, Google, and the nonprofit Common Crawl project whose data is widely used in AI. His results found that approximately 53 percent of the 1,156 media publishers surveyed block one of those three bots. His sample size is much larger than Originality AI’s and includes smaller and less popular news sites, suggesting outlets with larger staffs and higher traffic are more likely to block AI bots, perhaps because of better resourcing or technical knowledge.
At least one right-leaning news site is considering how it might leverage the way its mainstream competitors are trying to stonewall AI projects to counter perceived political biases. “Our legal terms prohibit scraping, and we are exploring new tools to protect our IP. That said, we are also exploring ways to help ensure AI doesn’t end up with all of the same biases as the establishment press,” Daily Wire spokesperson Jen Smith says. As of today, GPTBot and other AI bots were still free to scrape content from the Daily Wire.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
What is LLMs.txt file & how to generate it ?
The llms.txt file is a new emerging standard in the SEO and AI landscape that allows website owners to control how their website content is accessed, crawled, or used by Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Claude, etc. It's similar in concept to robots.txt, but specifically designed for AI crawlers.
🔍 What is llms.txt?
It’s a plain text file placed at the root of a website (like https://example.com/llms.txt).
It tells AI companies whether they are allowed or disallowed to use your website content for training or referencing their models.
✅ Step 1: Create the File
Open any text editor (like Notepad or VS Code).
Add directives like this:
Block all LLMs
User-Agent: * Disallow: /
Or allow specific LLMs and block others
User-Agent: OpenAI Disallow: /
User-Agent: Google-Extended Allow: /
User-Agent: Anthropic Disallow: /
0 notes
Text
Kuwait Chrisans SEO Agency
With an in-depth understanding of Kuwait’s online search behavior, we help your business reach the right audience at the right time. Our SEO campaigns are data-driven, transparent, and results-focused. We continuously track performance and make adjustments to maximize your ROI.
When you choose Chrisans Solutions, you're choosing a Kuwait SEO agency that blends technical excellence with local insight.
Our SEO Services in Kuwait Include
1. SEO Audit and Website Analysis
We begin with a comprehensive audit of your website structure, speed, content, and technical performance. This allows us to identify SEO bottlenecks and develop a roadmap for improvements.
2. Keyword Research and Strategy
Using advanced tools, we target high-traffic, low-competition keywords that are relevant to your business. Our goal is to align your website with how people in Kuwait search for your products or services.
3. On-Page SEO Optimization
We optimize meta titles, descriptions, headings (H1-H6), images (ALT tags), URLs, and internal linking to improve your site’s crawlability and relevance.
4. Local SEO in Kuwait
We optimize your Google Business Profile, ensure accurate NAP citations, and submit your site to top Kuwait business directories to improve local search visibility.
5. Technical SEO
We take care of the backend – schema markup, XML sitemaps, robots.txt, HTTPS, mobile usability, and page speed – to ensure your website meets Google’s technical standards.
6. Content Optimization & Blog SEO
From landing pages to regular blog posts, we create high-quality, keyword-optimized content that drives traffic and builds authority.
7. Link Building and Backlink Outreach
We focus on acquiring high-quality, relevant backlinks from authoritative websites to improve domain authority and off-page SEO.
0 notes
Text
Boost Your Site Performance: AEM SEO Best Practices & Page Speed Tips

In 2025, speed, structure, and seamless experiences define digital success. If your business relies on Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) for web content and digital assets, understanding how to optimize your AEM site for SEO and performance is critical.
As a powerful enterprise-grade CMS, AEM provides robust capabilities—but those capabilities need fine-tuning to meet modern search engine requirements. This blog dives deep into the top AEM SEO best practices, page speed optimization techniques, and technical configurations to improve your search rankings and user experience.
Why SEO and Performance Matter in AEM
Search engines like Google prioritize user experience. That means your AEM-powered website needs to:
Load quickly (especially on mobile)
Be easy to crawl and index
Provide structured, high-quality content
Follow Core Web Vitals benchmarks
Without the right AEM SEO strategy, even beautifully designed websites can struggle to rank.
AEM SEO Best Practices for 2025
1. Optimize Page Load Times
Slow websites kill conversions and rankings. AEM developers should:
Enable browser caching and GZIP compression
Minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML
Use lazy loading for images and videos
Optimize asset delivery through Adobe's built-in CDN or third-party solutions
AEM’s Dynamic Media capabilities also help serve responsive images, reducing file size while maintaining quality.
2. Improve Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are Google’s performance metrics, including:
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) – should load within 2.5s
FID (First Input Delay) – less than 100ms
CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) – under 0.1
AEM developers should prioritize asynchronous script loading, server response time improvements, and proper image sizing to meet these metrics.
3. Use Clean, Semantic URLs
Make sure your URLs:
Reflect the page content and keywords
Use hyphens instead of underscores
Avoid dynamic parameters where possible
AEM’s URL mapping features can be customized to ensure SEO-friendly structure.
4. Configure Metadata and Open Graph Tags
Use AEM’s page properties to:
Define unique title and meta descriptions per page
Implement canonical tags to avoid duplicate content
Include Open Graph and Twitter Card tags for social sharing
5. Enable XML Sitemap and Robots.txt Management
Ensure search engines can easily crawl your site:
Generate dynamic XML sitemaps through AEM workflows
Maintain a clean, purposeful robots.txt
Use Google Search Console to test coverage and indexing
6. Add Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Use JSON-LD or microdata to provide context to search engines. AEM allows embedding of schema for:
Articles and blog posts
FAQs and How-To sections
Product listings and reviews
This can boost your chances of appearing in rich results/snippets.
7. Leverage Headless AEM for Speed and Flexibility
AEM’s headless CMS model (using GraphQL or APIs) allows decoupled content delivery. When paired with frameworks like React, it:
Enhances frontend speed
Reduces backend load
Improves time-to-interactive and FID
Use AEM as a headless CMS to build blazing-fast SPAs and PWAs while maintaining SEO integrity.
8. Implement Multilingual SEO
If you're using AEM Sites for global content:
Use hreflang tags for language targeting
Ensure URLs reflect regional paths (/us/, /de/, /fr/)
Manage translations through AEM’s Language Copy feature
Page Speed Tips Specific to AEM
Use Content Fragments & Experience Fragments: Reuse content without heavy duplication or rendering overhead.
Bundle and Minify ClientLibs: AEM’s Client Library System allows combining CSS/JS files for fewer requests.
Preload Key Requests: Use AEM’s dispatcher and Apache configs to prioritize loading fonts and hero images.
Monitor Performance with Cloud Manager: Adobe Cloud Manager offers real-time insights and testing tools.
How Xerago Can Help
At Xerago, we specialize in optimizing Adobe Experience Manager platforms for performance, scalability, and search rankings. Our services include:
SEO audits tailored to AEM implementations
Page speed optimization using native and custom tools
Schema and metadata integration strategies
Headless CMS development with React, Next.js, or Vue
Personalized content delivery using Adobe Sensei
Whether you're starting with AEM or looking to enhance an existing site, Xerago ensures your digital experience meets both technical performance and marketing objectives.
Final Thoughts
Adobe Experience Manager offers unparalleled control and customization, but SEO and performance tuning are essential to realize its full value. By implementing these best practices, your brand can:
Improve rankings
Boost user satisfaction
Increase conversions
Need expert help optimizing your AEM SEO and speed strategy? Contact Xerago today to get started on building a high-performing, search-optimized digital experience in 2025 and beyond.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Fixing 'Crawled - Currently Not Indexed' Errors in Google Search Console
Dealing with pages that Google crawls but doesn't add to search results? This comprehensive guide from RapidURLIndexer explains how to diagnose and fix the 'Crawled - Currently Not Indexed' error in Google Search Console.
What Is This Error?
The 'Crawled - Currently Not Indexed' status appears in Google Search Console when Google has visited your page but decided against including it in search results. Unlike the 'Discovered - Currently Not Indexed' status (where Google has only found links to your page), this error indicates that Google has evaluated your content and found it lacking in some way.
This decision is based on various factors including content quality, uniqueness, site structure, and technical aspects of your website. When Google encounters this error, it's essentially saying, "We've seen this page, but don't think it adds enough value to include in our search index."
Why Is Google Not Indexing Your Pages?
Several common issues can trigger this indexing problem:
Content that's thin, low-quality, or doesn't provide unique value
Duplicate or highly similar content that exists elsewhere
Poor site structure that fails to signal page importance
Technical issues like improper use of noindex tags or robots.txt directives
Slow loading times that create a poor user experience
Low authority or trust signals for your website
Content that's too similar to existing indexed pages
How to Diagnose the Problem
Start your diagnosis in Google Search Console:
Navigate to the Coverage report under the Index section
Look for the 'Crawled - Currently Not Indexed' status
Examine the affected URLs to identify patterns
Use the URL Inspection Tool to check individual pages
Supplementary tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider, Ahrefs Site Audit, or SEMrush can provide deeper insights into potential issues with these pages.
Content Quality Improvements
Content quality is often the primary factor in indexing decisions. To improve your chances of getting indexed:
Expand thin content with more comprehensive information
Add unique insights, data, or perspectives not found elsewhere
Improve readability with better formatting and structure
Include relevant multimedia elements like images, videos, or infographics
Update outdated information with current facts and statistics
Ensure proper grammar and spelling throughout
Google prioritizes content that delivers genuine value to users, so focus on creating resources that solve problems or answer questions better than existing pages.
Site Structure and Internal Linking
Your site's architecture and internal linking strategy play crucial roles in indexing:
Create a logical hierarchy that shows page relationships
Implement breadcrumb navigation for better user experience
Link to important pages from your homepage and main navigation
Use descriptive anchor text that includes relevant keywords
Create contextual links within content where appropriate
Consider implementing a 'related posts' section for blog content
A well-structured site with strategic internal linking helps Google understand which pages are most important and worthy of indexing.
Technical SEO Fixes
Technical issues can prevent indexing even when content quality is high:
Improve page speed by optimizing images and reducing script bloat
Check your robots.txt file to ensure it's not blocking important pages
Review meta robots tags to confirm they allow indexing
Optimize your XML sitemap to prioritize important content
Fix any mobile usability issues that could affect crawling
Ensure proper use of canonical tags to address duplicate content
Advanced Strategies
For persistent indexing issues, consider these advanced approaches:
Content pruning: Remove or consolidate low-quality pages that might be diluting your site's overall quality
Strategic use of the 'Request Indexing' feature for high-priority pages
Improve page authority through quality backlinks from relevant sites
Enhance user engagement metrics like time on page and bounce rate
Consider updating publication dates for refreshed content (but only when making substantial changes)
Expected Timeline for Results
After implementing fixes, be patient. Google typically takes anywhere from a few days to several weeks to recrawl and reassess pages. Higher-authority sites often see faster results than newer websites.
Monitor progress in Google Search Console by regularly checking the Coverage report and using the URL Inspection tool to track changes in status.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Don't fall into these common traps when addressing indexing issues:
Relying solely on automated indexing tools without fixing underlying problems
Over-optimizing content with keyword stuffing or unnatural phrasing
Using black hat techniques that could result in penalties
Making isolated changes without a comprehensive approach
Expecting immediate results without allowing sufficient time for Google to reassess
How RapidURLIndexer Can Help
While addressing the root causes is essential, tools like RapidURLIndexer can complement your efforts by expediting the indexing process. Our service helps signal to Google that your content deserves reconsideration through a specialized submission network.
Unlike manual methods, RapidURLIndexer offers faster indexing, bulk submission capabilities, and detailed reporting on indexing status. With our pay-as-you-go model and credit refunds for unindexed URLs, it's a cost-effective solution for websites of all sizes.
Remember that while no tool can guarantee 100% indexing (as the final decision always rests with Google), combining on-site improvements with strategic use of indexing tools gives you the best chance of success.
https://rapidurlindexer.com/fixing-crawled-currently-not-indexed-errors/
0 notes