#llms
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
A couple of years ago we were all terribly concerned about the fact that a lot of American high schools are assigning such crushing homework loads that some kids literally don't have enough time to eat or sleep (and all this in spite of the fact that there's no good evidence that assigning homework actually improves academic outcomes at the pre-university level), but now we're hearing stories about those same schools struggling to stop kids from using ChatGPT to write their essays and suddenly It's The Children Who Are Wrong. Like, do you think maybe there's a certain level of cause and effect in play here?
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
Y'all I know that when so-called AI generates ridiculous results it's hilarious and I find it as funny as the next guy but I NEED y'all to remember that every single time an AI answer is generated it uses 5x as much energy as a conventional websearch and burns through 10 ml of water. FOR EVERY ANSWER. Each big llm is equal to 300,000 kiligrams of carbon dioxide emissions.
LLMs are killing the environment, and when we generate answers for the lolz we're still contributing to it.
Stop using it. Stop using it for a.n.y.t.h.i.n.g. We need to kill it.
Sources:
#unforth rambles#fuck ai#llms#sorry but i think this every time I see a reblog with more haha funny answers#how many tries did it take to generate the absurd#how many resources got wasted just to prove what we already know - that these tools are a joke#please stop contributing to this
64K notes
·
View notes
Text
Your Meta AI prompts are in a live, public feed

I'm in the home stretch of my 20+ city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in PDX TOMORROW (June 20) at BARNES AND NOBLE with BUNNIE HUANG and at the TUALATIN public library on SUNDAY (June 22). After that, it's LONDON (July 1) with TRASHFUTURE'S RILEY QUINN and then a big finish in MANCHESTER on July 2.

Back in 2006, AOL tried something incredibly bold and even more incredibly stupid: they dumped a data-set of 20,000,000 "anonymized" search queries from 650,000 users (yes, AOL had a search engine – there used to be lots of search engines!):
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AOL_search_log_release
The AOL dump was a catastrophe. In an eyeblink, many of the users in the dataset were de-anonymized. The dump revealed personal, intimate and compromising facts about the lives of AOL search users. The AOL dump is notable for many reasons, not least because it jumpstarted the academic and technical discourse about the limits of "de-identifying" datasets by stripping out personally identifying information prior to releasing them for use by business partners, researchers, or the general public.
It turns out that de-identification is fucking hard. Just a couple of datapoints associated with an "anonymous" identifier can be sufficent to de-anonymize the user in question:
https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.1508081113
But firms stubbornly refuse to learn this lesson. They would love it if they could "safely" sell the data they suck up from our everyday activities, so they declare that they can safely do so, and sell giant data-sets, and then bam, the next thing you know, a federal judge's porn-browsing habits are published for all the world to see:
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2017/aug/01/data-browsing-habits-brokers
Indeed, it appears that there may be no way to truly de-identify a data-set:
https://pursuit.unimelb.edu.au/articles/understanding-the-maths-is-crucial-for-protecting-privacy
Which is a serious bummer, given the potential insights to be gleaned from, say, population-scale health records:
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/23/health/data-privacy-protection.html
It's clear that de-identification is not fit for purpose when it comes to these data-sets:
https://www.cs.princeton.edu/~arvindn/publications/precautionary.pdf
But that doesn't mean there's no safe way to data-mine large data-sets. "Trusted research environments" (TREs) can allow researchers to run queries against multiple sensitive databases without ever seeing a copy of the data, and good procedural vetting as to the research questions processed by TREs can protect the privacy of the people in the data:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/01/the-palantir-will-see-you-now/#public-private-partnership
But companies are perennially willing to trade your privacy for a glitzy new product launch. Amazingly, the people who run these companies and design their products seem to have no clue as to how their users use those products. Take Strava, a fitness app that dumped maps of where its users went for runs and revealed a bunch of secret military bases:
https://gizmodo.com/fitness-apps-anonymized-data-dump-accidentally-reveals-1822506098
Or Venmo, which, by default, let anyone see what payments you've sent and received (researchers have a field day just filtering the Venmo firehose for emojis associated with drug buys like "pills" and "little trees"):
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/08/09/technology/personaltech/venmo-privacy-oversharing.html
Then there was the time that Etsy decided that it would publish a feed of everything you bought, never once considering that maybe the users buying gigantic handmade dildos shaped like lovecraftian tentacles might not want to advertise their purchase history:
https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2011/03/etsy-users-irked-after-buyers-purchases-exposed-to-the-world/
But the most persistent, egregious and consequential sinner here is Facebook (naturally). In 2007, Facebook opted its 20,000,000 users into a new system called "Beacon" that published a public feed of every page you looked at on sites that partnered with Facebook:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Facebook_Beacon
Facebook didn't just publish this – they also lied about it. Then they admitted it and promised to stop, but that was also a lie. They ended up paying $9.5m to settle a lawsuit brought by some of their users, and created a "Digital Trust Foundation" which they funded with another $6.5m. Mark Zuckerberg published a solemn apology and promised that he'd learned his lesson.
Apparently, Zuck is a slow learner.
Depending on which "submit" button you click, Meta's AI chatbot publishes a feed of all the prompts you feed it:
https://techcrunch.com/2025/06/12/the-meta-ai-app-is-a-privacy-disaster/
Users are clearly hitting this button without understanding that this means that their intimate, compromising queries are being published in a public feed. Techcrunch's Amanda Silberling trawled the feed and found:
"An audio recording of a man in a Southern accent asking, 'Hey, Meta, why do some farts stink more than other farts?'"
"people ask[ing] for help with tax evasion"
"[whether family members would be arrested for their proximity to white-collar crimes"
"how to write a character reference letter for an employee facing legal troubles, with that person’s first and last name included."
While the security researcher Rachel Tobac found "people’s home addresses and sensitive court details, among other private information":
https://twitter.com/racheltobac/status/1933006223109959820
There's no warning about the privacy settings for your AI prompts, and if you use Meta's AI to log in to Meta services like Instagram, it publishes your Instagram search queries as well, including "big booty women."
As Silberling writes, the only saving grace here is that almost no one is using Meta's AI app. The company has only racked up a paltry 6.5m downloads, across its ~3 billion users, after spending tens of billions of dollars developing the app and its underlying technology.
The AI bubble is overdue for a pop:
https://www.wheresyoured.at/measures/
When it does, it will leave behind some kind of residue – cheaper, spin-out, standalone models that will perform many useful functions:
https://locusmag.com/2023/12/commentary-cory-doctorow-what-kind-of-bubble-is-ai/
Those standalone models were released as toys by the companies pumping tens of billions into the unsustainable "foundation models," who bet that – despite the worst unit economics of any technology in living memory – these tools would someday become economically viable, capturing a winner-take-all market with trillions of upside. That bet remains a longshot, but the littler "toy" models are beating everyone's expectations by wide margins, with no end in sight:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-00259-0
I can easily believe that one enduring use-case for chatbots is as a kind of enhanced diary-cum-therapist. Journalling is a well-regarded therapeutic tactic:
https://www.charliehealth.com/post/cbt-journaling
And the invention of chatbots was instantly followed by ardent fans who found that the benefits of writing out their thoughts were magnified by even primitive responses:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ELIZA_effect
Which shouldn't surprise us. After all, divination tools, from the I Ching to tarot to Brian Eno and Peter Schmidt's Oblique Strategies deck have been with us for thousands of years: even random responses can make us better thinkers:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oblique_Strategies
I make daily, extensive use of my own weird form of random divination:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/07/31/divination/
The use of chatbots as therapists is not without its risks. Chatbots can – and do – lead vulnerable people into extensive, dangerous, delusional, life-destroying ratholes:
https://www.rollingstone.com/culture/culture-features/ai-spiritual-delusions-destroying-human-relationships-1235330175/
But that's a (disturbing and tragic) minority. A journal that responds to your thoughts with bland, probing prompts would doubtless help many people with their own private reflections. The keyword here, though, is private. Zuckerberg's insatiable, all-annihilating drive to expose our private activities as an attention-harvesting spectacle is poisoning the well, and he's far from alone. The entire AI chatbot sector is so surveillance-crazed that anyone who uses an AI chatbot as a therapist needs their head examined:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/04/01/doctor-robo-blabbermouth/#fool-me-once-etc-etc
AI bosses are the latest and worst offenders in a long and bloody lineage of privacy-hating tech bros. No one should ever, ever, ever trust them with any private or sensitive information. Take Sam Altman, a man whose products routinely barf up the most ghastly privacy invasions imaginable, a completely foreseeable consequence of his totally indiscriminate scraping for training data.
Altman has proposed that conversations with chatbots should be protected with a new kind of "privilege" akin to attorney-client privilege and related forms, such as doctor-patient and confessor-penitent privilege:
https://venturebeat.com/ai/sam-altman-calls-for-ai-privilege-as-openai-clarifies-court-order-to-retain-temporary-and-deleted-chatgpt-sessions/
I'm all for adding new privacy protections for the things we key or speak into information-retrieval services of all types. But Altman is (deliberately) omitting a key aspect of all forms of privilege: they immediately vanish the instant a third party is brought into the conversation. The things you tell your lawyer are priviiliged, unless you discuss them with anyone else, in which case, the privilege disappears.
And of course, all of Altman's products harvest all of our information. Altman is the untrusted third party in every conversation everyone has with one of his chatbots. He is the eternal Carol, forever eavesdropping on Alice and Bob:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alice_and_Bob
Altman isn't proposing that chatbots acquire a privilege, in other words – he's proposing that he should acquire this privilege. That he (and he alone) should be able to mine your queries for new training data and other surveillance bounties.
This is like when Zuckerberg directed his lawyers to destroy NYU's "Ad Observer" project, which scraped Facebook to track the spread of paid political misinformation. Zuckerberg denied that this was being done to evade accountability, insisting (with a miraculously straight face) that it was in service to protecting Facebook users' (nonexistent) privacy:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/05/comprehensive-sex-ed/#quis-custodiet-ipsos-zuck
We get it, Sam and Zuck – you love privacy.
We just wish you'd share.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/06/19/privacy-invasion-by-design#bringing-home-the-beacon
399 notes
·
View notes
Text
A summary of the Chinese AI situation, for the uninitiated.
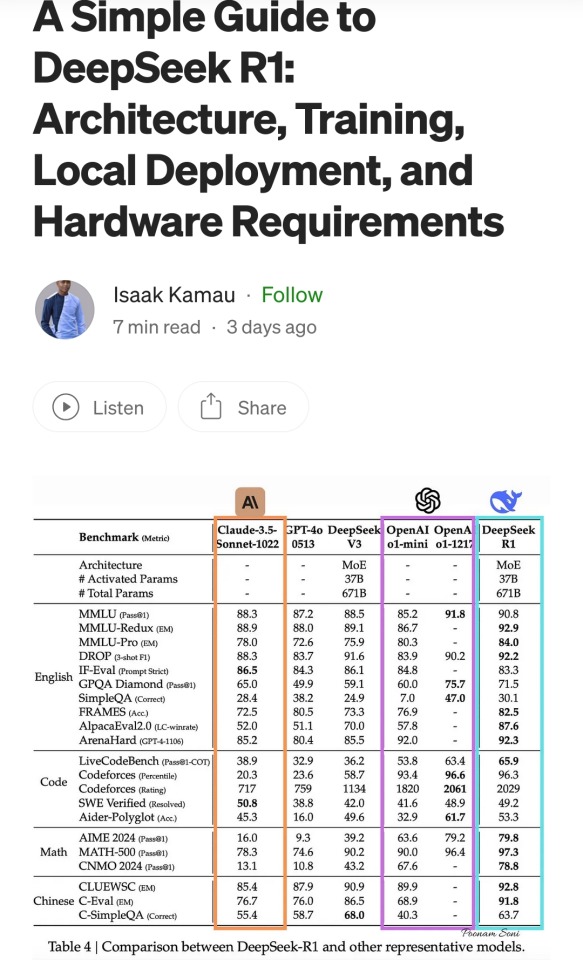
These are scores on different tests that are designed to see how accurate a Large Language Model is in different areas of knowledge. As you know, OpenAI is partners with Microsoft, so these are the scores for ChatGPT and Copilot. DeepSeek is the Chinese model that got released a week ago. The rest are open source models, which means everyone is free to use them as they please, including the average Tumblr user. You can run them from the servers of the companies that made them for a subscription, or you can download them to install locally on your own computer. However, the computer requirements so far are so high that only a few people currently have the machines at home required to run it.
Yes, this is why AI uses so much electricity. As with any technology, the early models are highly inefficient. Think how a Ford T needed a long chimney to get rid of a ton of black smoke, which was unused petrol. Over the next hundred years combustion engines have become much more efficient, but they still waste a lot of energy, which is why we need to move towards renewable electricity and sustainable battery technology. But that's a topic for another day.
As you can see from the scores, are around the same accuracy. These tests are in constant evolution as well: as soon as they start becoming obsolete, new ones are released to adjust for a more complicated benchmark. The new models are trained using different machine learning techniques, and in theory, the goal is to make them faster and more efficient so they can operate with less power, much like modern cars use way less energy and produce far less pollution than the Ford T.
However, computing power requirements kept scaling up, so you're either tied to the subscription or forced to pay for a latest gen PC, which is why NVIDIA, AMD, Intel and all the other chip companies were investing hard on much more powerful GPUs and NPUs. For now all we need to know about those is that they're expensive, use a lot of electricity, and are required to operate the bots at superhuman speed (literally, all those clickbait posts about how AI was secretly 150 Indian men in a trenchcoat were nonsense).
Because the chip companies have been working hard on making big, bulky, powerful chips with massive fans that are up to the task, their stock value was skyrocketing, and because of that, everyone started to use AI as a marketing trend. See, marketing people are not smart, and they don't understand computers. Furthermore, marketing people think you're stupid, and because of their biased frame of reference, they think you're two snores short of brain-dead. The entire point of their existence is to turn tall tales into capital. So they don't know or care about what AI is or what it's useful for. They just saw Number Go Up for the AI companies and decided "AI is a magic cow we can milk forever". Sometimes it's not even AI, they just use old software and rebrand it, much like convection ovens became air fryers.
Well, now we're up to date. So what did DepSeek release that did a 9/11 on NVIDIA stock prices and popped the AI bubble?
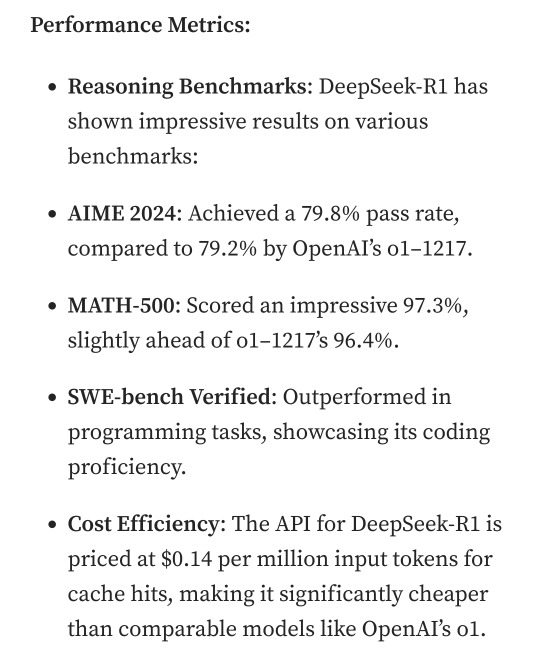
Oh, I would not want to be an OpenAI investor right now either. A token is basically one Unicode character (it's more complicated than that but you can google that on your own time). That cost means you could input the entire works of Stephen King for under a dollar. Yes, including electricity costs. DeepSeek has jumped from a Ford T to a Subaru in terms of pollution and water use.
The issue here is not only input cost, though; all that data needs to be available live, in the RAM; this is why you need powerful, expensive chips in order to-

Holy shit.
I'm not going to detail all the numbers but I'm going to focus on the chip required: an RTX 3090. This is a gaming GPU that came out as the top of the line, the stuff South Korean LoL players buy…
Or they did, in September 2020. We're currently two generations ahead, on the RTX 5090.
What this is telling all those people who just sold their high-end gaming rig to be able to afford a machine that can run the latest ChatGPT locally, is that the person who bought it from them can run something basically just as powerful on their old one.
Which means that all those GPUs and NPUs that are being made, and all those deals Microsoft signed to have control of the AI market, have just lost a lot of their pulling power.
Well, I mean, the ChatGPT subscription is 20 bucks a month, surely the Chinese are charging a fortune for-

Oh. So it's free for everyone and you can use it or modify it however you want, no subscription, no unpayable electric bill, no handing Microsoft all of your private data, you can just run it on a relatively inexpensive PC. You could probably even run it on a phone in a couple years.
Oh, if only China had massive phone manufacturers that have a foot in the market everywhere except the US because the president had a tantrum eight years ago.
So… yeah, China just destabilised the global economy with a torrent file.
#valid ai criticism#ai#llms#DeepSeek#ai bubble#ChatGPT#google gemini#claude ai#this is gonna be the dotcom bubble again#hope you don't have stock on anything tech related#computer literacy#tech literacy
434 notes
·
View notes
Text
the past few years, every software developer that has extensive experience, and knows what they're talking about, has had pretty much the same opinion on LLM code assistants: they're OK for some tasks but generally shit. Having something that automates code writing is not new. Codegen before AI were scripts that generated code that you have to write for a task, but is so repetitive it's a genuine time saver to have a script do it.
this is largely the best that LLMs can do with code, but they're still not as good as a simple script because of the inherently unreliable nature of LLMs being a big honkin statistical model and not a purpose-built machine.
none of the senior devs that say this are out there shouting on the rooftops that LLMs are evil and they're going to replace us. because we've been through this concept so many times over many years. Automation does not eliminate coding jobs, it saves time to focus on other work.
the one thing I wish senior devs would warn newbies is that you should not rely on LLMs for anything substantial. you should definitely not use it as a learning tool. it will hinder you in the long run because you don't practice the eternally useful skill of "reading things and experimenting until you figure it out". You will never stop reading things and experimenting until you figure it out. Senior devs may have more institutional knowledge and better instincts but they still encounter things that are new to them and they trip through it like a newbie would. this is called "practice" and you need it to learn things
257 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the Bluesky social network, you may notice a lot of drive-by responses from accounts that rarely or never post — they just reply to other accounts. The reply pattern starts with a phrase like “I respectfully disagree” and follows it with a fatuous objection. Another pattern is to start by agreeing, then pivot to trying to start a fight. These responses are clearly from LLMs. Some Bluesky users have even gotten the bots to post a haiku, spill their prompt, or argue with another bot. [Bluesky] Denise Paolucci (rahaeli on Bluesky) cofounded blog site Dreamwidth and previously worked in trust and safety at LiveJournal. She has a ton of experience with every possible form of social media bad actor and regularly posts on Bluesky about trust and safety. Lately, she’s been writing about our bot friends. Paolucci thinks this particular wave of “reply guy as a service” bots are test runs by a spambot maker, who hopes to rent the bots out to other bad actors as a service: “It’s common for spamming software to be pitched as social media management.” [Bluesky] Bad actors want to sort out what bot styles get the most responses for engagement farming. Bluesky is light on algorithms that filter what you can see, but spammers got in the habit of exploring how the algorithms work on Twitter, Facebook, and Threads so they could exploit them. Some bots are being run to establish what can lower the quality of discussion on a platform. These bots may be political or commercial in intent. Twitter has long been overrun with this style of bot.
(from December 2024)
198 notes
·
View notes
Text
I wrote ~4.5k words about the operating of LLMs, as the theory preface to a new programming series. Here's a little preview of the contents:

As with many posts, it's written for someone like 'me a few months ago': curious about the field but not yet up to speed on all the bag of tricks. Here's what I needed to find out!
But the real meat of the series will be about getting hands dirty with writing code to interact with LLM output, finding out which of these techniques actually work and what it takes to make them work, that kind of thing. Similar to previous projects with writing a rasteriser/raytracer/etc.
I would be very interesting to hear how accessible that is to someone who hasn't been mainlining ML theory for the past few months - whether it can serve its purpose as a bridge into the more technical side of things! But I hope there's at least a little new here and there even if you're already an old hand.
294 notes
·
View notes
Text
ok, i've gotta branch off the current ai disc horse a little bit because i saw this trash-fire of a comment in the reblogs of that one post that's going around

[reblog by user makiruz (i don't feel bad for putting this asshole on blast) that reads "So here's the thing: every Diane Duane book that I have is stolen, I downloaded it illegally from the Internet; and I am not sorry, I am a thief of books and I don't think I'm doing anything wrong, ideas are not property, they should be free to be used by anyone as they were before the invention of capitalism; for that reason I don't believe it's wrong to use books to train AI models"]
this is asshole behavior. if you do this and if you believe this, you are a Bad Person full stop.
"Capitalism" as an idea is more recent than commerce, and i am So Goddamn Tired of chuds using the language of leftism to justify their shitty behavior. and that's what this is.
like, we live in a society tm
if you like books but you don't have the means to pay for them, the library exists! libraries support authors! you know what doesn't support authors? stealing their books! because if those books don't sell, then you won't get more books from that author and/or the existing books will go out of print! because we live under capitalism.
and like, even leaving aside the capitalism thing, how much of a fucking piece of literal shit do you have to be to believe that you deserve art, that you deserve someone else's labor, but that they don't deserve to be able to live? to feed and clothe themselves? sure, ok, ideas aren't property, and you can't copyright an idea, but you absolutely can copyright the Specific Execution of an idea.
so makiruz, if you're reading this, or if you think like this user does, i hope you shit yourself during a job interview. like explosively. i hope you step on a lego when you get up to pee in the middle of the night. i hope you never get to read another book in your whole miserable goddamn life until you disabuse yourself of the idea that artists are "idea landlords" or whatever the fuck other cancerous ideas you've convinced yourself are true to justify your abhorrent behavior.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
When summarizing scientific studies, large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and DeepSeek produce inaccurate conclusions in up to 73% of cases, according to a study by Uwe Peters (Utrecht University) and Benjamin Chin-Yee (Western University, Canada/University of Cambridge, UK). The researchers tested the most prominent LLMs and analyzed thousands of chatbot-generated science summaries, revealing that most models consistently produced broader conclusions than those in the summarized texts. Surprisingly, prompts for accuracy increased the problem and newer LLMs performed worse than older ones. The work is published in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
Continue Reading.
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
really depressing how 'AI alignment' used to be a theoretical thing that was about making sure they were nice, but now it's a real thing about making sure their moral principles don't get in the way of anybody's bottom line
#i am absolutely flabbergasted at the way they treat whistleblowing as an alignment *problem*#and not evidence that they've done something right#ai#ai alignment#llms#claude
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
#AI#LLMs#ArtificialIntelligence#AIForBeginners#funny#funny content#lol#funny memes#memes#comedy#meme#lol memes#rofl#tumblr#dank memes#haha#tumblr memes#memedaddy#humor#economy#funny shit
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
When you remember what LLMs like ChatGPT et al actually do, how they actually work, it becomes a lot easier to remember how...useless they actually are.
LLMs do not tell anyone anything, they do not lie, they do not tell the truth, they do not research, they do not know anything, they don't even have a repository of facts. They have no agency.
All LLMs do is provide a probable, statistically correlated string of words.
This makes it a kind of fun toy for things like, "Lol, the internet taught it that 'heat' and 'knot' belong in the same sentence." And that's...about it. There's perhaps some data analysis that could be done about human speech patterns.
But like. All it's doing it telling you what words are statistically likely to show up together.
How is that...anything?
What is this actually a tool to do, based on what it does?
How does that help you come up with ideas you couldn't have gotten more effectively by skimming actual human words? How does that help you write a paper or a book or anything that isn't completely bland milquetoast nothingness?
We need to reinforce what LLMs actually do when we talk about them, because that knowledge might actually murder them. They do nothing but tell you what words are statistically attached to each other, in ways that kinda look like sentences.
They are not hallucinating. They are not getting the wrong information. They are not making things up. They are not lying. They aren't even capable of that.
All they are doing is stringing words together in a statistically probable arrangement.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think we should repurpose the term "unskilled labor" for anything generated by AI.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
"would miss like a little AI on her pasta?"
This whole AI thing is like being in a restaurant with a fancy waiter who has one of those giant pepper shakers, only it's full of bird poop and anthrax and he keeps asking "would miss like a little AI on her pasta?" with every dish that comes out... and when you say "NO" he starts grinding anyway and won't stop until you physically knock him over.
17 notes
·
View notes