#spoofed website detection tips
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
🇨🇦 Ontario woman loses $26,820 to a fake CRA website scam, highlighting the dangers of spoofed sites targeting unsuspecting victims. 🇨🇦 Learn how to spot fake websites, protect your finances, and stay safe from cybercriminals 👇🏻
#avoid fake CRA websites#Canada#canada news#Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre advice#CRA#CRA website scam prevention#cybersecurity for small businesses#Google search scam protection#Ontario#protect against online scams#safe online banking practices#securing personal information online#spoofed website detection tips#spotting fraudulent websites
0 notes
Text
5 Tips on How to Recognize a Financial Fraud Website.
Digital banking, e-commerce, and online investment services mean the internet plays a significant role in our financial activities. But, alas, it has also become a playground for cybercriminals and fraudsters who set up fake financial websites to steal sensitive information and con unsuspecting users out of their money. These fakes pages can appear immensely convincing, replicating real banks, lenders or investment services.
Earlier detection of a fraudulent financial website is key to safeguarding your identity, your money and your sanity. Here are five essential tips to help you identify and avoid falling victim to such scams.
Check the URL Carefully
Spoofed URLs are commonly used on fake web pages. They could be including additional characters, using other domain endings (. net instead of. com) or even simple misspellings (which are often overlooked).
What to look for:
A legitimate financial website usually starts with https:// – the “s” stands for secure.
Watch out for unusual domain names or slight alterations like www.bank-secure.com instead of www.bank.com.
Be cautious if you landed on the website via an ad or a link in an unsolicited email or text.
Look for Security Indicators
Reputable sites that process financial transactions have to adhere to tight security standards. The absence of such signals is a warning sign that the website may be suspicious.
Key signs of a secure site:
A padlock symbol in the address bar.
A valid SSL certificate (click the padlock to view certificate details).
Clear privacy policy, terms and conditions, and contact information.
Warning signs:
Pop-ups asking for sensitive information like your PIN or OTP.
Pages that mimic login forms but do not actually function correctly.
Poor Design and Spelling Errors
Although some fraud websites appear highly professional, many websites have tell-tale signs such as poor design, low resolution images and obvious grammar or spelling errors.
Look out for:
Generic or Mismatched Branding.
Broken links or images.
Generic or ambiguous content that adds no true details about the company or services.
Reputable financial companies pour billions into the development of their website and content.
Too-Good-to-Be-True Offers
There are a number of common tricks fraudsters use to entice victims — guaranteeing loans without any credit check, offering unfeasible returns on an investment or even fake cashback rewards.
Examples of red flags:
“Do you need ₹1 lakh in 5 minutes, no documents required?
“Get 20% interest each week — GUARANTEED!”
“Grab now, only few left: Pay ₹100 to get ₹10,000 cashback!”
These frauds exploit urgency and eagerness and can cause users to act without thinking clearly.
Lack of Verifiable Contact Information
For them to get in touch with you for any legitimate reason except to share your phone number with more of their affiliates? They might provide phony telephone numbers, physical office addresses that don’t exist or email addresses that aren’t from a professional domain.
What you can do:
When all else fails, try calling the number listed, or plug the address into Google Maps.
Check for official registration or license numbers if it’s a financial institution.
Look up the business name on consumer review sites to see if other people have complained of being scammed.
Conclusion
Scam financial websites are becoming more sophisticated, but with a bit of caution and awareness, you can stay ahead of them. DO check the validity of any financial website before you enter your personal or bank details.
Examine the URL and domain name.
Look for security indicators like HTTPS and SSL certificates.
Watch out for poor design and spelling errors.
Be skeptical of unrealistic offers and guarantees.
Verify contact information and registration credentials.
You can protect yourself from web-based financial scams and surf the Internet with confidence by remaining vigilant and informed.
0 notes
Text
Face Liveness Detection SDK for Spoof-Proof Security
How a Face Liveness Detection SDK Beats Spoof Attacks
In a world where unlocking a phone with your face feels like sci-fi, the reality behind that magic is far more complex and vulnerable. Face authentication is no longer just about recognizing a face. It’s about knowing whether that face is real, live, and in front of the camera. This is where a Face Liveness Detection SDK steps into the spotlight, acting like a bouncer at the digital door letting in the real deal and kicking out imposters.
Let’s explore what it is, why it’s important, and how it helps protect both your users and your reputation.
What Is a Face Liveness Detection SDK?
At its core, a face liveness detection SDK is a software development kit that developers can embed into mobile apps, websites, or biometric systems to detect whether a face presented to the camera is a real, live human or a spoof (like a photo, mask, or video replay). It’s not just looking for a face it’s watching for signs of life.
Key Features
Here’s what most high-quality liveness detection SDKs offer:
Passive liveness detection (no blinking or head-turning needed)
Anti-spoofing against photos, videos, deepfakes, and masks
Real-time verification within seconds
Compatibility with iOS, Android, and web platforms
Compliance with global data privacy standards (like GDPR & CCPA)
This SDK works silently and swiftly in the background no cheesy prompts or awkward user interactions are required. The goal? Seamless security.
Why Is Liveness Detection Crucial in Modern Face Authentication?
Passwords are passé. Face authentication is now the go-to for many industries, from fintech to healthcare. But where there's convenience, there's also risk. A Face Liveness Detection SDK prevents spoof attacks, which are surprisingly easy without the right tech in place.
Real-World Risks
Consider these scenarios:
Photo attacks: A printed photo or digital image fools basic facial recognition.
Video replay: Someone plays a video of the real user to unlock a system.
3D mask spoofing: Hyper-realistic masks impersonate a user’s facial structure.
In 2022, the iProov Biometric Threat Intelligence Report found that presentation attacks increased by over 300% compared to the previous year.
How a Face Liveness Detection SDK Works (Without Giving Hackers a Cheat Sheet)
Without going too far into the weeds (or tipping off the bad guys), here’s a peek into how these SDKs spot a real face versus a fake:
1. Texture and Light Analysis
Live skin has dynamic textures and reflects light differently than paper, screens, or silicone masks.
2. Micro-Movement Detection
Real faces have involuntary muscle twitches and eye micro-movements. Fakes? Not so much.
3. Depth Mapping
Using 2D or 3D sensors, the SDK checks for depth cues. Flat images just don’t cut it.
4. AI-Powered Behavior Tracking
Machine learning models look for inconsistencies in facial expressions, blinking, and head positioning.
Top Use Cases Across Industries
Face liveness detection isn’t just a cool trick it’s rapidly becoming a regulatory requirement and a user expectation, particularly in security-conscious industries. Here’s how it’s being utilized across various sectors:
Banking: Remote account opening. Face liveness detection helps prevent identity fraud by verifying the user’s physical presence.
Healthcare: Telehealth logins. It secures access to patient records, ensuring only authorized users can log in.
E-commerce: KYC (Know Your Customer) during high-value purchases. This helps reduce fraudulent transactions, protecting both customers and merchants.
Education: Online exam proctoring. Face liveness detection ensures the presence of test-takers, maintaining the integrity of the exam process.
Government: ePassport verification. It strengthens border control by confirming the identity of travelers.
Spoiler alert: This isn’t just for big players. Even small apps can (and should) use a lightweight Face Liveness Detection SDK to boost trust and protect their users.
What to Look for in a Face Liveness Detection SDK
Not all SDKs are created equal. If you're evaluating options, here’s a checklist to keep handy:
Accuracy & Speed
Low false positives, fast responses. Users shouldn’t wait 10 seconds to be verified.
Passive Liveness
No weird prompts like “turn your head” or “blink twice.” Less friction = better UX.
Spoof Detection Versatility
Should block everything from printed photos to high-res video replays and 3D masks.
On-Device or Cloud Processing
Choose based on your app’s needs: on-device for privacy, cloud for scalability.
SDK Size & Performance
No bloatware, please. Look for a lean, well-documented SDK that won’t slow down your app.
Compliance & Ethics
Ensure the vendor follows ethical AI practices and is transparent about how data is used.
Case Study: How Fintech Apps Are Reducing Fraud with Liveness Detection
A mid-size mobile banking app in Southeast Asia integrated a liveness detection SDK after experiencing a spike in fraudulent account registrations. Within six months:
Fraudulent attempts dropped by 78%
Customer support tickets related to login issues fell by 42%
User trust and app ratings improved by 1.3 stars on average
This wasn’t magic, it was a well-placed layer of invisible security.
Conclusion: Liveness Detection Isn't Optional Anymore
Face recognition is powerful but without liveness detection, it’s like locking your front door and leaving the window wide open. A face liveness detection SDK offers that missing layer of real-world, real-time protection that separates the serious from the spoofed.And if you’re serious about secure, seamless facial authentication, it’s time to start building smarter. Recognito is here to help you do just that.
1 note
·
View note
Text
HSTS Preload List For Secure And Encrypted Web Connections

HSTS Preload
The Department of Homeland Security and the National Cyber Security Alliance collaborate to increase public understanding of the value of cybersecurity during Cybersecurity understanding Month each year.
Today, anybody can easily start a blog, corporation, or portfolio website. Keeping it safe has also been more simpler and more crucial. To assist, Google is offering three actionable tips from professionals in internet security today that anyone may use to strengthen the protection of their websites. One website at a time, these suggestions will help safeguard world by protecting private and sensitive data.
TLS certificate installation
Sensitive data is protected during data transmission between your website and its visitors with Transport Layer Security certificate, often known as SSL. Although implementing SSL is essential if your website gathers sensitive data, such credit card numbers or password logins, experts advise doing it for all websites. SSL certificates are available from most registrars, and Let’s Encrypt allows you to install one on your own.
Select HSTS preloading
Websites that contemporary browsers are aware only load via a secure, encrypted connection are included in the HSTS-preload list. It is the simplest approach to guarantee that connections to websites cannot be reverted to an unencrypted connection, both on the first visit and on subsequent visits. HSTS-preloading may be obtained in two methods, which are discussed below.
Select a safe web hosting company
Look into and choose a hosting company that has a solid track record of implementing security features like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and frequent backups.
Many website owners are unaware that malicious actors might attempt to change the content of their websites, implant malware or tracking, spoof across unsecured Wi-Fi networks, or reroute traffic. Even one unencrypted page may be used by them to access the rest of your website. There are two methods to use HSTS Preload to strengthen your website’s defense against HTTP downgrade attacks:
Put your domain on the HSTS-preload list and watch as the modification spreads across browsers.
Choose a top-level domain with HSTS Preload, like.app,.dev,.page,.rsvp, or.day, to start using the best degree of website encryption right now. Installing an SSL certificate is the only additional step, and browser updates are not required.
HSTS Preload List
Details
Domains may be added to Chrome’s HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) preload list using this form. This is a list of websites that Chrome has hardcoded as only being accessible via HTTPS.
Based on the Chrome list, HSTS preload lists exist for most of the widely used browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Safari, IE 11, and Edge. Refer to the compatibility matrix of HSTS.
Submission Conditions
A site may submit a request to be added to the preload list using this site’s form if it sends the preload directive in a HSTS header.
Your site has to meet the following criteria in order to be approved for the HSTS preload list using this form:
Present a legitimate certificate.
On the same host, if you are listening on port 80, redirect from HTTP to HTTPS.
Use HTTPS to serve all subdomains.
Specifically, if a DNS record exists for the www subdomain, you have to offer HTTPS for that subdomain.
It should be noted that all subdomains including internal, non-publicly accessible subdomains are subject to HSTS preloading.
For HTTPS queries, include a HSTS header on the base domain:
At least 31536000 seconds (1 year) must be the maximum age.
You need to provide the includeSubDomains directive.
It is necessary to provide the preload directive.
The HSTS header must still be included in any further redirects you serve from your HTTPS site.
In an effort to expand the availability of HSTS preload, Google Registry and registrars will be offering a 50% discount on Google HSTS-preloaded domains in October.
What is HSTS?
HSTS, or HTTP Strict Transport Security, secures website-user connections. HSTS tells browsers to always utilize HTTPS to access a website. HSTS aims to avoid downgrade attacks, which compel websites to use insecure HTTP connections. With out HSTS, such attacks might expose sensitive user data on a website.
In summary
Three crucial steps are advised by internet security experts to improve website security. Installing a Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificate is the first step towards encrypting data transit between users and your website. To guarantee secure connections and avoid downgrading to unencrypted connections, use HSTS-preloading as your second option. Finally, choose a reputable hosting company with strong security protocols. You may prevent possible dangers to your website and secure personal information by putting these precautions in place.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#HSTSPreloadList#EncryptedWebConnection#CyberSecurity#Google#summary#SubmissionConditions#HSTSpreloading#safewebhostingcompany#TLScertificate#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
why is my vpn not changing my location
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
why is my vpn not changing my location
VPN Connection Stability
Title: Ensuring VPN Connection Stability: Tips and Best Practices
In the digital age, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become an indispensable tool for ensuring online privacy, security, and anonymity. However, one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the stability of the VPN connection. A stable connection is essential for uninterrupted browsing, streaming, and secure communication. Here are some tips and best practices to ensure VPN connection stability:
Choose a Reliable VPN Service: Opt for reputable VPN providers known for their reliability and stability. Research and read reviews to gauge the performance of different VPN services before making a choice.
Select the Nearest Server: When connecting to a VPN server, choose one that is geographically closest to your location. Proximity to the server helps minimize latency and ensures faster connection speeds, thus enhancing stability.
Use Wired Connection: Whenever possible, use a wired internet connection instead of Wi-Fi. Wired connections are generally more stable and less prone to interference, resulting in a smoother VPN experience.
Update VPN Software: Keep your VPN client software up to date. Developers regularly release updates to address bugs, security vulnerabilities, and improve overall performance, including connection stability.
Check Network Configuration: Ensure that your router and firewall settings are compatible with VPN protocols. Some routers and firewalls may block VPN traffic, causing connection issues. Adjusting the settings or using VPN-friendly devices can help resolve this issue.
Disable Battery Saving Mode: If you're using a mobile device, make sure that battery-saving modes or settings that automatically disconnect idle connections are disabled. These features can interfere with VPN connectivity.
Contact Customer Support: If you encounter persistent connection problems, don't hesitate to contact your VPN provider's customer support. They can offer troubleshooting assistance and advice tailored to your specific situation.
By following these tips and best practices, you can ensure a stable VPN connection, allowing you to enjoy a secure and seamless online experience without interruptions. Remember that VPN stability is crucial for maintaining privacy and security in an increasingly interconnected world.
Geolocation Spoofing Failure
Geolocation spoofing is a technique used by individuals to falsify the location data of their devices. This can be done through various means such as using VPNs, proxy servers, or certain software applications. However, despite the intention to deceive, geolocation spoofing can sometimes result in failure.
One of the main reasons for geolocation spoofing failure is the constant advancement in technology and security measures. Many websites and applications have implemented robust algorithms and checks to detect and prevent spoofed location data. This means that even with sophisticated spoofing tools, users may still be unable to bypass these security measures.
Furthermore, inaccuracies in the spoofed data can also lead to failure. The technology used for geolocation spoofing is not always foolproof and can result in inconsistencies or glitches that give away the true location of the user. This can be especially problematic when trying to access location-based services that require precise and accurate location data.
Moreover, continuous updates and improvements in geolocation tracking technology make it increasingly challenging to successfully spoof one's location without being detected. As a result, individuals who rely on geolocation spoofing for privacy or security reasons may find it harder to maintain their anonymity and deceive location-based services.
In conclusion, while geolocation spoofing can be a useful tool for those seeking to protect their privacy or access restricted content, it is not always foolproof. With the ongoing advancements in technology and security measures, geolocation spoofing failure is becoming more common, highlighting the limitations of this practice in today's digital landscape.
IP Address Leakage
Title: Understanding the Risks of IP Address Leakage
In today's interconnected digital landscape, protecting our online privacy is paramount. One often overlooked aspect of online privacy is the leakage of IP addresses. An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a network. While essential for communication between devices, the exposure of IP addresses can pose significant risks to users.
One common way IP addresses can leak is through insecure connections. When browsing the internet, users may unknowingly connect to unsecured Wi-Fi networks or websites without HTTPS encryption. Hackers can intercept traffic on these networks, allowing them to view and collect users' IP addresses along with other sensitive information.
Another source of IP address leakage is through peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing networks. Users participating in these networks often expose their IP addresses to other users, leaving them vulnerable to potential attacks or surveillance.
Moreover, certain online activities, such as online gaming or video streaming, can inadvertently reveal IP addresses. In multiplayer gaming, for example, players connect to each other's devices directly, exposing their IP addresses in the process.
The consequences of IP address leakage can be severe. Hackers may use collected IP addresses to launch targeted cyber attacks, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, which can disrupt internet service or compromise sensitive data.
To mitigate the risks of IP address leakage, users should employ best practices for online security. This includes using virtual private networks (VPNs) to encrypt internet traffic and hide IP addresses, ensuring that websites visited use HTTPS encryption, and being cautious when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks.
In conclusion, understanding the risks associated with IP address leakage is crucial for safeguarding online privacy and security. By taking proactive measures to protect our IP addresses, we can reduce the likelihood of falling victim to cyber threats and maintain greater control over our online identities.
DNS Leak Detection
DNS leak detection is a crucial aspect of online security that every internet user should be aware of. DNS (Domain Name System) is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses, allowing us to access websites by recognizable names instead of numerical addresses. A DNS leak occurs when a user's DNS queries are exposed to their Internet Service Provider (ISP), potentially compromising their privacy and security.
There are several tools available for detecting DNS leaks, allowing users to identify and address any vulnerabilities in their network connection. One popular method is using online DNS leak test websites that can quickly determine if there is any leakage of DNS queries. These tools perform a series of tests to check if your DNS queries are being sent through secure channels or if they are being exposed to third parties.
In addition to utilizing DNS leak detection tools, users can also take proactive measures to prevent DNS leaks. Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is one of the most effective ways to ensure your online activities remain private and secure. A VPN encrypts your internet connection and routes your traffic through secure servers, preventing ISPs from monitoring your DNS queries.
Overall, being informed about DNS leak detection and taking necessary precautions is essential for maintaining online privacy and security. By utilizing detection tools and implementing protective measures such as VPNs, users can safeguard their sensitive information and browse the internet with peace of mind. Stay vigilant and prioritize your online security to avoid falling victim to potential DNS leaks.
Ineffective Location Masking
Ineffective location masking refers to the failure of methods employed to conceal or alter one's true geographical location on the internet. With the increasing concern over online privacy and security, many individuals seek ways to mask their true location to protect their identity or access region-restricted content. However, if these methods are not implemented correctly or if they are flawed, they can fail to provide the desired level of anonymity.
One common method of location masking is through the use of virtual private networks (VPNs). VPNs encrypt internet traffic and route it through servers located in different regions, making it appear as though the user is accessing the internet from a different location. However, some VPNs may leak users' true IP addresses due to technical vulnerabilities or improper configuration, thereby failing to effectively mask their location.
Another method is the use of proxy servers, which act as intermediaries between a user and the internet. By routing traffic through a proxy server, users can obscure their true IP addresses. However, similar to VPNs, proxy servers may also leak information or fail to adequately mask a user's location if they are not properly configured or if they are compromised.
Furthermore, location masking techniques can be ineffective against sophisticated tracking methods employed by advertisers, governments, or malicious actors. Techniques such as browser fingerprinting, which involves collecting unique information about a user's browser configuration, can be used to identify individuals regardless of their attempts to mask their location.
In conclusion, while location masking can provide a layer of anonymity and privacy online, it is essential to employ reliable methods and stay informed about potential vulnerabilities. Users should carefully research and choose reputable VPNs or proxy services and remain vigilant against emerging tracking techniques to ensure effective location masking.
0 notes
Text
“Don’t Get Hooked: Tips for Recognizing Phishing Emails”
Recognizing phishing emails with malicious links is essential to protect yourself from cyber threats. Phishing emails often attempt to deceive you into clicking on links that lead to fraudulent websites or initiate malware downloads. Here are some tips to help you identify and avoid such emails:

1.Check the Sender’s Email Address: Verify the sender’s email address. Phishing emails may use addresses that closely resemble legitimate ones but contain subtle misspellings or additional characters. Be cautious of any unfamiliar or suspicious sender.
2.Inspect the Greeting: Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of addressing you by name. Legitimate organizations usually personalize their emails with your name.
3.Examine the Content: Be wary of emails that create a sense of urgency, pressure you to take immediate action, or threaten negative consequences if you don’t comply. Phishing emails frequently use fear or urgency to manipulate recipients.
4.Hover Over Links: Hover your mouse pointer over any embedded links without actually clicking them. This action will reveal the true URL in the status bar of your email client. Check if the URL matches the legitimate website of the supposed sender.
5.Inspect the URL: Even if the displayed link seems legitimate, the actual URL may be different. Ensure that the domain matches the official website of the organization. Look for subtle misspellings or additional words within the URL.
6.Beware of Misspellings and Grammatical Errors: Phishing emails often contain spelling and grammatical mistakes. While legitimate organizations can make errors, a high frequency of mistakes should raise suspicion.

7.Check for Secure Connections (HTTPS): Legitimate websites use HTTPS to encrypt data. Verify that the website linked in the email begins with “https://” and displays a padlock icon in the address bar of your browser.
8.Avoid Downloading Suspicious Attachments: Don’t download attachments from unsolicited or suspicious emails. Malicious attachments can contain malware that can infect your system.
9.Verify Requests for Personal or Financial Information: Legitimate organizations usually do not request sensitive personal or financial information via email. If in doubt, contact the organization through official channels to confirm the request’s authenticity.
10.Use Email Filtering Software: Enable email filtering and spam detection in your email client or use dedicated email security solutions to automatically identify and quarantine phishing emails.
11.Trust Your Instincts: If something about an email seems off or too good to be true, trust your instincts. It’s better to be cautious and skeptical than to fall for a phishing scam.
12.Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest phishing techniques and educate yourself and your colleagues or family members about the risks and how to recognize phishing attempts.
13.Watch for Email Spoofing: Some phishing emails may use techniques to make it appear as if they’re coming from a legitimate source. Look for inconsistencies between the sender’s display name and the actual email address.
14.Beware of Unsolicited Attachments: Be cautious when you receive unexpected attachments or files in an email, especially if they come from unknown sources. Malware can be hidden in these attachments.
15.Cross-Check Information: If you receive an email that requests action on your part, such as changing a password, making a payment, or updating account information, independently verify the request. Contact the organization through official channels or visit their website directly, rather than clicking on the provided link.
16.Use Email Authentication Technologies: Some email providers and organizations use email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These technologies help verify the authenticity of emails. Legitimate senders often employ these security measures.
17.Be Wary of Pop-Up Forms: Some phishing emails might lead to a webpage that includes pop-up forms asking for personal information. Avoid entering sensitive data into such forms unless you are sure of their legitimacy.
If you want to learn more about it, I highly recommend that you contact ACTE Technologies because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. Experienced teachers can help you learn better. You can find these services both online and offline.
If you feel that my response has been helpful, make sure to follow me and it will encourage me to upload more content about Ethical hacking.
Thanks for spending your valuable time . Have a great day
1 note
·
View note
Text
(2020/05/19) Why is This Website Port Scanning me
[nullsweep.com][1]
[1]: <https://nullsweep.com/why-is-this-website-port-scanning-me/>
# Why is This Website Port Scanning me
Charlie Belmer
6-7 minutes
* * *
Recently, I was tipped off about certain sites performing localhost port scans against visitors, presumably as part of a user fingerprinting and tracking or bot detection. This didn't sit well with me, so I went about investigating the practice, and it seems many sites are port scanning visitors for dubious reasons.
## A Brief Port Scanning Primer
Port Scanning is an adversarial technique frequently used by penetration testers and hackers to scan internet facing machines and determine what applications or services are listening on the network, usually so that specific attacks can be carried out. It's common for security software to detect active port scans and flag it as potential abuse.
Most home routers don't have any open ports, so scanning an internet users IP address is unlikely to return any meaningful data. However, many users run software on their computer that listens on ports for various reasons \- online gaming, media sharing, and remote connections are just a few things that consumers might install on a home PC.
A Port scan can give a website information about what software you are running. Many ports have a well defined set of services that use them, so a list of open ports gives a pretty good view of running applications. For instance, Steam (a gaming store and platform) is known to run on port 27036, so a scanner seeing that port open could have reasonable confidence that the user also had steam open while visiting the web site.
## Watching Ebay Port Scan My Computer
In the past I have worked on security products that specifically worried about port scanning from employee web browsers. Attack frameworks like [BeEF][2] include port scanning features, which can be used to compromise user machines or other network devices. So, I wanted to be able to alert on any port scanning on machines as a potential compromise, and a site scanning localhost might trip those alerts.
[2]: <https://beefproject.com/>
On the other hand, it's [been reported][3] on a few times in the past as banks sometimes port scan visitors, and I have heard Threat Matrix offers this as a customer malware detection check.
[3]: <https://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/08/07/halifax_bank_ports_scans/>
I was given the example of ebay as a site that includes port scanning, but when I initially navigated there I didn't see any suspicious behavior. I thought they might use some heuristics to determine who to scan, so tried a few different browsers and spoofed settings, without any luck.
I thought it might be because I run Linux, so I created a new Windows VM and sure enough, I saw the port scan occurring in the browser tools from the ebay home page:
![][4]Ebay port scan
[4]: https://nullsweep.com/content/images/2020/05/ebay_port_scan.png
Looking at the list of ports they are scanning, they are looking for VNC services being run on the host, which is the same thing that was reported for bank sites. I marked out the ports and what they are known for (with a few blanks for ones I am unfamiliar with):
* 5900: VNC * 5901: VNC port 2 * 5902: VNC port 3 * 5903: VNC port 4 * 5279: * 3389: Windows remote desktop / RDP * 5931: Ammy Admin remote desktop * 5939: * 5944: * 5950: WinVNC * 6039: X window system * 6040: X window system * 63333: TrippLite power alert UPS * 7070: RealAudio
VNC is sometimes run as part of bot nets or viruses as a way to remotely log into a users computer. There are several malware services that leverage VNC for these purposes. However it is also a valid tool used by administrators for remote access to machines, or by some end user support software, so the presence of VNC is a poor indicator of malware.
Furthermore, when I installed and ran a VNC server, I didn't detect any difference in site behavior - so why is it looking for it?
## How Port Scanning with WebSockets Works
WebSockets are intended to allow a site to create bi-directional communication like traditional network sockets. This allows sites to periodically send information to a client browser without user interaction or front end polling, which is a win for usability.
When a web socket is configured, it specifies a destination host and port, which do not have to be the same domain that the script is served from. To do a port scan, the script only has to specify a private IP address (like localhost) and the port it wishes to scan.
WebSockets only speak HTTP though, so unless the host and port being scanned are a web socket server, the connection won't succeed. In order to get around this, we can use connection timing to determine whether the port is open or not. Ports that are open take longer in the browser, because there is a TLS negotiation step.
You also might get different error messages. If you have python installed, try running the following to create a local web server running on port 8080: [code] python3 -m http.server 8080
[/code]
Now, open your browser developer console (usually options -> Web Developer -> Console) and type some JavaScript in directly. Here is what I see when I do it in chrome: [code] > var s = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8080") < undefined VM1131:1 WebSocket connection to 'ws://127.0.0.1:8080/' failed: Error during WebSocket handshake: Unexpected response code: 200 (anonymous) @ VM1131:1 >var s = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8081") <undefined VM1168:1 WebSocket connection to 'ws://127.0.0.1:8081/' failed: Error in connection establishment: net::ERR_CONNECTION_REFUSED
[/code]
Between error message introspection and timing attacks, a site can have a pretty good idea of whether a given port is open.
## Port Scanning is Malicious
Whether the port scan is used as part of an infection or part of e-commerce or bank "security checks", it is clearly malicious behavior and may fall on the wrong side of the law.
If you observe this behavior, I encourage you to complain to the institution performing the scans, and install extensions that attempt to block this kind of phenomenon in your browser, generally by preventing these types of scripts from loading in the first place.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is spear phishing and How does it work
Spear phishing is a type of cyberattack in which the attacker sends emails to specific individuals or organizations that contain malware. The attacker usually does some research and identifies the target's interests, personal information, or their work-related tasks before sending out the email. Spear phishing can be done quickly and cheaply, making it an effective attack for those with limited resources.
Spear phishing attacks continue to increase in popularity among cybercriminals, and businesses must take steps to protect against them or risk seeing sensitive information stolen. These highly personalized email attacks involve a hacker researching their target and creating a message often designed to impersonate a trusted colleague or business to steal sensitive information, which is then used to commit crimes like fraud and identity theft, the report noted.
Spear phishing attacks are particularly dangerous because they are designed to get around traditional email security like spam filters, the report found. They typically do not include malicious links or attachments, but instead use spoofing techniques and zero-day links that, combined with social engineering tactics, are unlikely to be blocked...to know more, visit - techrepublic.

How Does Spear-phishing Work?
The act of spear-phishing may sound simple, but spear-phishing emails have improved within the past few years and are now extremely difficult to detect without prior knowledge on spear-phishing protection. Spear-phishing attackers target victims who put personal information on the internet. They might view individual profiles while scanning a social networking site. From a profile, they will be able to find a person’s email address, friends list, geographic location, and any posts about new gadgets that were recently purchased. With all of this information, the attacker would be able to act as a friend or a familiar entity and send a convincing but fraudulent message to their target.
To increase success rates, these messages often contain urgent explanations on why they need sensitive information. Victims are asked to open a malicious attachment or click on a link that takes them to a spoofed website where they are asked to provide passwords, account numbers, PINs, and access codes. An attacker posing as a friend might ask for usernames and passwords for various websites, such as Facebook, so that they would be able to access posted photos. In reality, the attackers will use that password, or variations of it, to access different websites that have confidential information such as credit card details or Social Security Numbers. Once criminals have gathered enough sensitive information, they can access bank accounts or even create a new identity using their victim’s information. Spear-phishing can also trick people into downloading malware or malicious codes after people click on links or open attachments provided in messages...get more to know at - digitalguardian.

How to Protect Yourself
Traditional security often doesn't stop these attacks because they are so cleverly customized. As a result, they're becoming more difficult to detect. One employee mistake can have serious consequences for businesses, governments and even nonprofit organizations. With stolen data, fraudsters can reveal commercially sensitive information, manipulate stock prices or commit various acts of espionage. In addition, spear phishing attacks can deploy malware to hijack computers, organizing them into enormous networks called botnets that can be used for denial of service attacks.
To fight spear phishing scams, employees need to be aware of the threats, such as the possibility of bogus emails landing in their inbox. Besides education, technology that focuses on email security is necessary...know more at - kaspersky.
Tips to avoid a spear phishing attack
It’s difficult to completely avoid becoming a target of a spear phishing attack, but email users can make it more difficult for attackers to execute a successful attack by doing the following:
Limit the amount of personal information you share on social media and other websites.
Do not click on links in emails. Identify suspicious links by hovering your cursor over them to ensure that the URL matches the link’s anchor text and the email’s stated destination.
Contact the associate, friend or business purporting to send the message (by a separate communications channel) to confirm the request.
Find out more at - techtarget.
Visit phishprotection.com on preventing spear phishing here! Spear phishing is a type of fraud where the perpetrator sends an email which appears to be from somebody trustworthy in order to extract personal information, such as usernames and passwords.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Does Anti Phishing Software Protect Against Phishing?
Cybercriminals use a lot of tools and techniques to hack systems and get in your networks. After they hack your systems, they can use different viruses and trojans that can steal or hijack your data. They might steal your login credentials and impersonate your company or your employees. This is why you need anti phishing software
What is an Anti Phishing Software?
Anti-phishing software is a tool that organizations can use to ensure that their employees don't fall prey to phishing attacks. Phishing is a cybercrime where users are lured into clicking malicious links to steal sensitive data such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), banking and credit card details, and passwords.
Phishing is also a popular method for cyber criminals to deliver malware by tricking victims to visit a link that can secretly install the malicious payload distributing trojan malware or ransomware, or execute javascript files from the infected website. 65% of organizations in the United States experienced a successful phishing attack in 2019. With more and more organizations being affected by phishing attacks, IT admins need to ensure that their users are protected against phishing attacks with a solid anti-phishing software.

An anti-phishing software helps IT admins ensure that users don't fall prey to phishing attacks. This can be achieved in two ways. IT admins can either mandate a lockdown on web, making sure that users can access only the trusted websites. Otherwise they can ensure that malicious websites are detected and blocked.
Why Phishing Emails Work?
Cyber criminals play off your fears and familiarity. It may be FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) on an opportunity to win a new laptop or it may be the fear that your email box is full, and you will miss that important email.
They exploit these fears along with our familiarity with brands to sneak by our defenses. An email that appears to be from UPS or FedEx announcing an update on a delivery seems routine and might not cause suspicions.
Each of these, however, can launch a virus, trigger ransomware, or send unsuspecting employees to a malicious attachment or spoofed website to steal credentials. The bad guys may also use your email server to launch phishing attack software to attack other organizations using your company’s email.
Phishing is a Compliance Issue
Not only can phishing scams cost companies millions in financial losses, it now can cost them in securities violations. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has made it known that organizations need to step up their internal controls to protect against phishing email fraud, or face penalties. “While the cyber-related threats posed to issuers’ assets are relatively new, the expectation that issuers will have sufficient internal accounting controls and that those controls will be reviewed and updated as circumstances warrant is not,” the SEC wrote in its report.
Phishing vs the importance of Internet security software
One of the simplest ways to protect yourself from becoming a victim of a phishing scheme is to install and use proper Internet security software on your computer. Internet security software is vital for any user because it provides multiple layers of protection in one simple-to-manage suite.

For the most reliable protection, your security plan should include the following:
Anti-spam software is designed to protect your email account from phishing and junk emails. Aside from working with pre-defined blacklists created by security researchers, anti-spam software has intelligence capabilities to learn, over time, which items are junk and which are not. So while you still should be vigilant, you'll get some comfort from knowing that the software is also filtering out potential trouble. Use anti-phishing protection and anti-spam software to protect yourself when malicious messages slip through to your computer.
Anti-malware is included to prevent other types of threats. Similar to anti-spam software, anti-malware software is programmed by security researchers to spot even the stealthiest malware. With ongoing updates from vendors, the software continues to become more intelligent and better able to deal with the latest threats. By using an anti-malware package, you can protect yourself from viruses, Trojans, worms and more.
Final Words
To avoid the pain of getting scammed out of your much-needed cash, or the embarrassment of giving away your sensitive data to a fraud, make use of available resources such as password managers and the anti phishing detection system in your antivirus.
Sources: https://www.manageengine.com/browser-security/phishing-protection.html https://www.inky.com/blog/anti-phishing-software-as-important-as-anti-virus-software https://www.clearedin.com/blog/why-invest-in-anti-phishing https://usa.kaspersky.com/resource-center/preemptive-safety/phishing-prevention-tips
1 note
·
View note
Text
#1yrago Android malware uses accelerometer readings to figure out if it was running on a real phone or in emulation

Malware authors have a problem: they want their software to run aggressively when no one is looking at it, but to shut down entirely if the device it's running on is actually in some malware researcher's lab.
So malware authors have a whole host of tricks they use to determine whether they're running on a device in the field, or inside a researcher's emulator where all of their secrets are laid bare. For example, the creator(s) of the Wannacry malware had the program try to reach a nonexistent website (iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com).
Malware researchers' emulators usually answer any attempt to research an outside website in the hopes of gaining insight about how the software interacts with its command and control server, so by checking whether the nonexistent website existed, each copy of Wannacry was able to decide whether it was living in reality or trapped in the Matrix. That's why when a security researcher registered Wannacry's nonexistent domain and stood a webserver up at that address, every copy of Wannacry in the world shut down.
A new Matrix-detecting tool in malware has been discovered: strains of Android malware distributed through the Google Play store were found to be using calls to the phone's motion-detector to determine whether it was running on a real phone or inside an emulator. Mobile emulators don't bother to fake data from emulated motion-sensors, so from the malware's perspective, emulators have an unnatural stillness that tips it off to stay hidden.
As with the Wannacry killswitch, this technique won't be hard to overcome, since spoofing plausible data from an emulated motion-sensor is pretty basic stuff. But for now, the technique is very effective (and very clever).
https://boingboing.net/2019/01/18/head-in-a-jar-vs-bluepill.html
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazon email scam
I just got a suspicious email from “Amazon.com Customer Mails.” I already reported it to Amazon, but I wanted to talk about it here in case any of you get the same email.
The subject line was “Notice -- There unusual activity on your account ! -- #457457457,” and the email read:
“Hello Amazon Customer,
Thank you for visiting Amazon.com! Your account requires action because we have detected an issue with your account information. Please login to your account, and check your information correctly. If your account is in danger, our system will lock your account for security reasons.
Get your account back with simple steps:
1. Click the link below to open a new secure session.
2. Follow Steps to see your case.
3. Resolve the problem by completing the instructions”
There was a link at the bottom that said “Go to Your Account.”
Here’s a screenshot of the email:
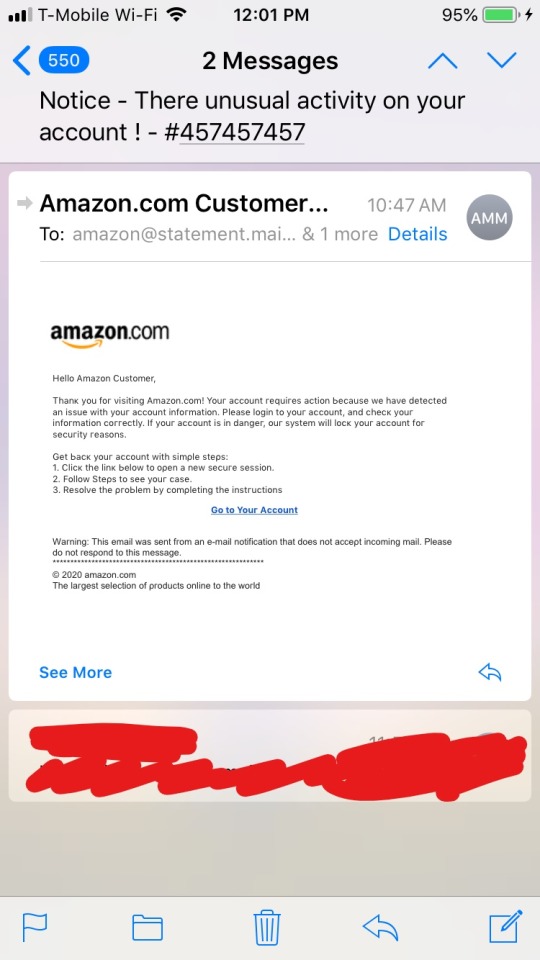
If you get this email, don’t click the link! I don’t know where it goes to, but I highly doubt it’s anything legitimate.
Some things that tipped me off this was a scam:
didn’t use my name (all my emails that actually came from Amazon start with “Hello [Name]” or “Dear [Name]”)
very vague about the supposed “unusual activity”
asks me to click a link without telling me what the link goes to or how to check my account without clicking the link
grammatical errors ( “There unusual activity” and “check your information correctly”)
wrong email address -- the Amazon website says that if an email claims to come from Amazon and doesn’t end in “@amazon.com,” it’s fake
Here’s the Amazon page that talks about how to figure out if something is a scam. If you don’t want to click the link (understandable, considering the subject of this post), it was also the first thing that came up when I googled “amazon email scam.” The page includes a link to information about how to report scam emails to Amazon -- you can either send it as an attachment to [email protected] or forward it to [email protected].
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Avoid Spear Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing is a favorite strategy used by hackers and scammers. This is a case since through this technique they are able to target the large organizations. Spear phishing allows that the security measures employed by these organizations are bypassed and henceforth unauthorized access to the organization's network and confidential data.
The spear phishing messages and emails are seen to come from trusted sources but when opened portend a whole different scenario.

Spear phishing vs. phishing vs. whaling
This familiarity is what sets spear phishing apart from regular phishing attacks. Phishing emails are typically sent by a known contact or organization. These include a malicious link or attachment that installs malware on the target's device, or directs the target to a malicious website that is set up to trick them into giving sensitive information like passwords, account information or credit card information.
Spear phishing has the same goal as normal phishing, but the attacker first gathers information about the intended target. This information is used to personalize the spear-phishing attack. Instead of sending the phishing emails to a large group of people, the attacker targets a select group or an individual. By limiting the targets, it's easier to include personal information -- like the target's first name or job title -- and make the malicious emails seem more trustworthy.
The same personalized technique is used in whaling attacks, as well. A whaling attack is a spear-phishing attack directed specifically at high-profile targets like C-level executives, politicians, and celebrities. Whaling attacks are also customized to the target and use the same social-engineering, email-spoofing and content-spoofing methods to access sensitive data...to read more, visit - TechTarget.

These are some of the tips and tricks that you can use to avoid spear phishing:
Take advantage of artificial intelligence (AI)
Find a solution that detects and blocks spear phishing attacks including BEC and brand impersonation that may not include malicious links or attachments. Machine learning tools can analyze communication patterns in an organization and spot any anomalies that may be signs of an attack.
Don't rely solely on traditional security
Traditional email security that uses blacklists for spear phishing and brand impersonation detect may not protect against zero-day links found in many attacks.
Deploy account-takeover protection
Find tools that use AI to recognize when accounts may have been compromised, to avoid more spear phishing attacks from originating from those accounts...visit - TechRepublic to know more.

Avoid sending personal information
Legitimate businesses very rarely ask for personal information via email. If you receive an email or SMS asking you to give details such as your address, social security number, or banking info in the body of an email or text message, it is very likely a phishing attempt.
A genuine email will typically either provide the address of a site to go to (with no link), provide a link to click, or give you a number to call. Bear in mind, all of these scenarios could also be more sophisticated phishing tactics, so should be verified (more on that below).
Verify suspicious requests
If you have suspicions about an email or other message, don’t visit the site or call the number provided. If you think it may be authentic but are unsure, you can try to verify it first.
One way to do this is to simply run a search for the email or phone number provided. If it’s a known scam, chances are you’ll see results stating as much.
Another, more reliable, method of verification is to simply call or email the company to check if it’s a real request. However, you should contact the company via a phone number or email from its actual website, not the contact information found in the email...to get more info, visit - comparitech.

Adopt the Right Tools
The best defense is a good offense, so having an arsenal of technologies to prevent phishing emails from getting into a system are key. Strong encryption, modern anti-malware, data loss prevention tools and automated email client health checks are a good place to start when it comes to enhancing email security.
Stay on Top of Threats and Vulnerabilities
You can’t protect against the threats you don’t know are out there, so be sure to stay on top of the latest cybersecurity threats and trends. For small businesses without a dedicated IT team, advisors and third-party entities such as vendor partners can be an amazing resource to help fill in the gaps...get more info over at - BizTech.
Spear phishing has tremendously profited criminals more than plain phishing alone. It is especially tricky because identity thieves invest so much time and effort in obtaining pieces of personal information about their potential victims so that in return the recipients will think that the e-mail message is legitimate. Visit - https://duocircle.com/ to know more about spear phishing attacks and how to protect against them.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Spot PayPal Phishing Scams and How to Prevent Them

PayPal is the world’s largest online payment processor and effectively working as a “middleman” between buyers and sellers, enabling users to transfers money safely through its digital platform. PayPal is using in every corner of the world and it’s very simple to use PayPal for online transactions. It has a large investment in users; PayPal has upwards of 360 million active users in more than 200 countries.
Since 1998, PayPal has been giving users a new and secure way for online transactions. PayPal has made business transactions easier than ever before. And because there are always large volumes of transactions between parties, there is a need for a secure and reliable source and PayPal has become the safe hand for large volume transactions around the world.
With this rising popularity, there are several devils who are constantly keeping an eye on PayPal’s users. Now, PayPal has become one of the most heavily targeted brands for phishing attacks. However, PayPal is considered one of the safest platforms for online transactions. For security, PayPal uses many security tools like data encryption, password protection, and anti-fraud technology, Two-step verification to protect its users from fraud and prevent scams. However, hackers have found ways to beat these security tools.
PayPal scams are coming in different forms but all these scams are really dangerous and you should be aware of these scams. But, PayPal scams are typically include Phishing scams such as phishing emails, spoofed websites, suspicious links, and a lot more. With all these scams, hackers try to know sensitive information like your account information, credit or debit card information.
In this article, we will disclose the most common PayPal scams and how you can spot them. You will also find few tips to prevent yourself from PayPal scams. Read on.
PayPal Scams List:
Find the most common PayPal scams list:
Need Immediate Action:
This is the most common PayPal scam used to manipulate the user for clicking on a malicious link. In these PayPal phishing scams, scammers will send you an email to warn you about a problem on your account and you need to take immediate action and will force you to click on the link. These phrases may include different variations such as “your account is about to be suspended’, ‘verify your account or ‘suspicious account has been detected on your account.’ All are used to illicit an immediate response and the link will either infect your device with malware or it will direct you to a phishing website so that hackers can steal your information.
Social Media PayPal Scams
PayPal phishing scams emerging using different platforms and social media are one of them. PayPal scams on social media are rapidly increasing. These phishing scams post by the hacker on social media post, and they just want you to click on the post that direct you to a phishing website where you will be asked to submit your personal details. When or if you enter the details, it means you’re in danger. Make sure you do not enter your personal details on any platform without cross-checking.
Congratulation! You’ve won a prize
This scam includes an offer or prize. You may receive an email informing you that you’ve won a prize but in order to receive it, you need to pay a small handling fee. The one thing you can notice here that indicates something’s wrong is you’ve won a prize for a competition you’ve never entered. It is recommend if you receive such emails, first of all try to remember that you’ve earned the order or not. PayPal also advises that a legitimate source would never ask you to pay to receive an order, and that you should never send money to someone you do not know.
“Friendly name” email PayPal scams
In these PayPal scams, a person will use a friendly-looking display name in order to pretend the email is from a legitimate source or from PayPal. All these force you to click on the link that directs you to a phishing website that looks like the original PayPal website. On this phishing website, you’ll be asked to enter your account information and as soon as you enter the details, your information will be sent to hackers.
How to Spot PayPal Phishing Scams
There are various things you can notice in the PayPal phishing scams. These mistakes or signs mostly are similar and of repetitive nature, so if you focus and show a little bit of awareness, you can spot PayPal phishing scams and can prevent yourself from them.
First of all, if you receive an email from PayPal, make sure to check the address. PayPal's official email will always come from paypal.com. PayPal does not use any third party (ISP) network or if you notice any third-party domain, do not open it or reply to it.
The very common thing in all phishing emails is fake Greetings. Fake PayPal emails will tend to use impersonal, generic greetings such as, ‘dear customer’ or ‘dear user’. If PayPal sends you an official email they would always address you by your first and last name or by your business name.
If you receive an email that asks you for your account information, or any sensitive information related to your accounts such as credit card number, or debit card information, open your eyes, it’s a phishing email. PayPal never ask for your account information or any sensitive information like this to provide you in email.
We recommend you to always pay attention to an email that asks you to click on a link or download an attachment. Remember that PayPal will never send customer emails with attachments or links to download software. These links will direct you to a phishing website that will steal your data or download malicious programs on your device.
The most common thing that helps you to determine if an email is fake is ‘spelling and grammar mistakes.’ Spelling and grammar mistakes are often one of the easiest ways to check if an email is fake. PayPal like huge companies has expert and well-educated writers who can prove every single piece of correspondence that the company puts out. No chance of spelling and grammar mistakes in PayPal official emails.
How to Prevent PayPal Phishing Scams
Find few tips to prevent PayPal phishing scams.
1. First of all, make sure you do not reply to PayPal phishing emails.
2. Do not click on any link or download any attachment in PayPal phishing emails; always go to the official website directly or by searching for it on Google.
3. You should never provide your PayPal account details unless you’re sure that you’re on the real PayPal site.
4. You may also receive PayPal fake phone calls, so make sure you do not answer such calls. Or you can download Truecaller on your phone. Truecaller is the world’s best Caller ID & Spam Blocking app. It will help you to identify the number and you can also block them. Get more details on Truecaller.com
5. Be alert with PayPal notifications. PayPal officials may also sends you alert about your account such as any email confirmation any time you make a purchase or send money through PayPal. But, if you get an alert that for activity that you didn’t make, you should let PayPal know about this immediately.
6. If you receive an email and you’re sure that email is fake, you can also report that email at [email protected]. You just need to forward the phishing emails to PayPal and then PayPal will investigate the matter further. But, make sure you do not make any alterations in the email such as in the subject line or sending the message as an attachment, avoid all these things.
7. To better your security standards too, we recommend you download Waredot Total Protection. It filters all the outgoing and incoming emails and blocks all the suspects from robbing all your significant information.
Final Touch
Hey guys! This was the guide about “How to spot PayPal phishing scams and how to prevent them.” With the rising popularity of PayPal, emerging scams are also coming with its popularity. PayPal phishing scams is at the peak in the scam world, and as this is the world’s best online payment processor so there are much benefits for hackers and scammers than any other source. We’ve listed all the required information about PayPal phishing scams and how you can prevent these scams. I Hope, this guide would help you to do so.
#i got scammed on paypal#can you get scammed on paypal#does paypal refund money if scammed#paypal scam email#paypal scams
0 notes
Text
Android malware uses accelerometer readings to figure out if it was running on a real phone or in emulation

Malware authors have a problem: they want their software to run aggressively when no one is looking at it, but to shut down entirely if the device it's running on is actually in some malware researcher's lab.
So malware authors have a whole host of tricks they use to determine whether they're running on a device in the field, or inside a researcher's emulator where all of their secrets are laid bare. For example, the creator(s) of the Wannacry malware had the program try to reach a nonexistent website (iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea.com).
Malware researchers' emulators usually answer any attempt to research an outside website in the hopes of gaining insight about how the software interacts with its command and control server, so by checking whether the nonexistent website existed, each copy of Wannacry was able to decide whether it was living in reality or trapped in the Matrix. That's why when a security researcher registered Wannacry's nonexistent domain and stood a webserver up at that address, every copy of Wannacry in the world shut down.
A new Matrix-detecting tool in malware has been discovered: strains of Android malware distributed through the Google Play store were found to be using calls to the phone's motion-detector to determine whether it was running on a real phone or inside an emulator. Mobile emulators don't bother to fake data from emulated motion-sensors, so from the malware's perspective, emulators have an unnatural stillness that tips it off to stay hidden.
As with the Wannacry killswitch, this technique won't be hard to overcome, since spoofing plausible data from an emulated motion-sensor is pretty basic stuff. But for now, the technique is very effective (and very clever).
https://boingboing.net/2019/01/18/head-in-a-jar-vs-bluepill.html
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Helping you avoid COVID-19 online security risks"
As people around the world are staying at home due to COVID-19, many are turning to new apps and communications tools to work, learn, access information, and stay connected with loved ones.
While these digital platforms are helpful in our daily lives, they can also introduce new online security risks. Our Threat Analysis Group continually monitors for sophisticated, government-backed hacking activity and is seeing new COVID-19 messaging used in attacks, and our security systems have detected a range of new scams such as phishing emails posing as messages from charities and NGOs battling COVID-19, directions from “administrators” to employees working from home, and even notices spoofing healthcare providers. Our systems have also spotted malware-laden sites that pose as sign-in pages for popular social media accounts, health organizations, and even official coronavirus maps. During the past couple of weeks, our advanced, machine-learning classifiers have seen 18 million daily malware and phishing attempts related to COVID-19, in addition to more than 240 million COVID-related spam messages.
To protect you from these risks, we've built advanced security protections into Google products to automatically identify and stop threats before they ever reach you. Our machine learning models in Gmail already detect and block more than 99.9 percent of spam, phishing and malware. Our built-in security also protects you by alerting you before you enter fraudulent websites, scanning apps in Google Play before you download, and more. But we want to help you stay secure everywhere online, not just on our products, so we’re providing these simple tips, tools and resources.
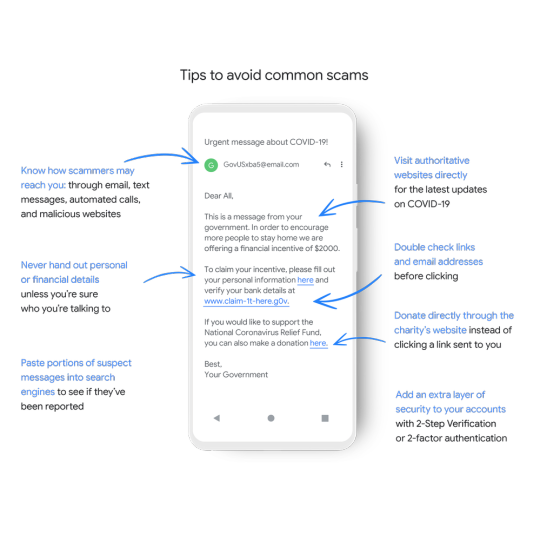
Know how to spot and avoid COVID-19 scams
With many of the COVID-19 related scams coming in the form of phishing emails, it’s important to pause and evaluate any COVID-19 email before clicking any links or taking other action. Be wary of requests for personal information such as your home address or bank details. Fake links often imitate established websites by adding extra words or letters to them—check the URL’s validity by hovering over it (on desktop) or with a long press (on mobile). Keep these tips handy and learn more at g.co/covidsecuritytips.
Use your company’s enterprise email account for anything work-related
Working with our enterprise customers, we see how employees can put their company’s business at risk when using their personal accounts or devices. Even when working from home, it’s important to keep your work and personal email separate. Enterprise accounts offer additional security features that keep your company’s private information private. If you’re unsure about your company’s online security safeguards, check with your IT professionals to ensure the right security features are enabled, like two-factor authentication.
Secure your video calls on video conferencing apps
The security controls built into Google Meet are turned on by default, so that in most cases, organizations and users are automatically protected. But there are steps you can take on any video conferencing app to make your call more secure:
If your meetings use short, numeric codes, turn on the password or PIN feature. The extra layer of verification will help ensure only the invited attendees gain access to the meeting.
When sharing a meeting invite publicly, be sure to enable the “knocking” feature so that the meeting organizer can personally vet and accept new attendees before they enter the meeting.
If you receive a meeting invite that requires installing a new video-conferencing app, always be sure to verify the invitation—paying special attention to potential imposters—before installing.
Install security updates when notified
When working from home, your work computer may not automatically update your security technology as it would when in the office and connected to your corporate network. It’s important to take immediate action on any security update prompts. These updates solve for known security vulnerabilities, which attackers are actively seeking out and exploiting.
Use a password manager to create and store strong passwords
With all the new applications and services you might be using for work and school purposes, it can be tempting to use just one password for all. In fact, 66 percent of Americans admit to using the same password across multiple accounts. To keep your private information private, always use unique, hard-to-guess passwords. A password manager, like the one built into Android, Chrome, and your Google Account can help make this easier.
Protect your Google Account
If you use a Google Account, you can easily review any recent security issues and get personalized recommendations to help protect your data and devices with the Security Checkup. Within this tool, you can also run a Password Checkup to learn if any of your saved passwords for third party sites or accounts have been compromised and then easily change them if needed.
You should also consider adding two-step verification (also known as two-factor authentication), which you likely already have in place for online banking and other similar services to provide an extra layer of security. This helps keep out anyone who shouldn’t have access to your accounts by requiring a secondary factor on top of your username and password to sign in. To set this up for your Google Account, go to g.co/2SV. And if you’re someone who is at risk of a targeted attack—like a journalist, activist, politician or a high profile healthcare professional—enroll in the Advanced Protection Program, our strongest security offering, at g.co/advancedprotection.
Help your kids stay safe online
With schools closed around the world, kids are online more than ever before. You can help your kids learn how to spot scams with the educational material at Be Internet Awesome and within the interactive learning game, Interland. You can also use Family Link to create age-appropriate accounts, control your kids’ app downloads, and monitor their activity.
Our teams continue to monitor the evolving online security threats connected to COVID-19 so that we can keep you informed and protected. For more tips to help you improve your online security, visit our Safety Center.
Source : The Official Google Blog via Source information
0 notes
Text
7 Ways To Reduce The Risk Of Getting Your Proxies Blocked

The use of proxies for web scraping, buying tickets and shopping online is a common practice nowadays. These proxies are the way out for people who use bots and crawlers to scrape web data, as to avoid getting noticed. Proxies come in handy to hide their identity i.e. IP addresses and locations.
But, as the proxies are getting sharper and efficient, these websites’ intelligence system is also working on the next level. They can detect and block proxies used by web scrapers and bots, efficaciously.
Firstly, have you ever wondered that you take extra protection, buy proxies and use them but why you still get banned? Why so? After all, you switch to the use of proxies to avoid getting banned, right?
This is because, the use of proxies though, can save you from getting traced by these extra-notorious sites. The problem is the way you are using these proxies, this can dump you right into trouble.
So, this article is intended to give you “7 ways to reduce the risk of getting your proxies blocked”. Following these ways will ensure the reduction in blocking and banning of proxies.
Let us start with some mistakes proxy users do that can block and ban proxies. Later, in this article, we will discuss the 7 ways to reduce the risk of getting your proxies blocked.
COMMON MISTAKES WHILE USING PROXY:
1) Buying free or shared proxies
It is the common mistake proxy users do. There is a potential chance of getting flagged while browsing with free proxies. This is because being a free proxy- the makers don’t invest much into encryption. Unencrypted proxies may lead to easy detection and blocking
2) Sending a huge number of requests to a website
It is another mistake users do that may lead to the detection and flagging of IP. Because websites think of it as a non-human activity i.e. bot use. Some websites have a highly restrictive and intelligent mechanism so when you use bots even with proxy (as it is a common practice) they can block you easily.
3) Mismatching of IP of your location with time zone-
This mistake is also common and thus, will lead you to jam on your face.
4) Using Javascript to fill in captchas
It is another activity that doesn’t sound like a real human to the websites you send requests to. Opt for Using keyboards and mouse while sending captcha is better.
These were some common mistakes that proxy server users do’ let us look into the prevention methods.
7 WAYS TO REDUCE THE RISK OF GETTING YOUR PROXIES BLOCKED:
Here is how you can utilize these 7 ways to reduce the risk of getting your proxy blocked
1) USE ENCRYPTED PROXIES- IN THE FIRST PLACE:
Don’t use unencrypted proxies even though the connection is secure. The sharp SSL/TLS encryption of the websites can terminate the proxy right at the moment. The use of the SSL/TSL termination proxy can be used to penetrate these sites and do crawl there and extract the data.
2) USER AGENT SPOOFING CAN HELP:
User-agent is a string of data in HTTP header that conveys your web browser, OS and the versions to the requested web server. It enables the requested server to compute the request you send and provide the appropriate services following it. i.e. (HTML layout etc.)
So, configure the user agent, it is called “user-agent spoofing”, to protect from getting flagged. Don’t go for empty user agents it will jam your face too. Configure user agents. Sending high volumes of requests with the same user agent can be problematic too. So, don’t do that.
3) ALWAYS AUTOMATE THE BOTS TO CRAWL SLOWLY- CHANGE SPEEDS AND LIMIT THE REQUESTS:
Even though you use proxies with bots, these notorious websites keep a close eye on these suspicious activities and detect the bots. Sometimes bots send requests way too fast. That being the case, it is directly proportional to get flagged. The higher the number of requests per second the higher the chances of getting your proxies blocked. Because a human can't send multiple requests at a time. Hence, they caught you red-handed and block.
To cope with these sites' systems and fool them use the delaying function to control the crawling-speed. Also, limit the rate of requests so that these tips will keep your proxies secure and you can scrape and crawl without getting flagged.
4) ROTATE IPs FREQUENTLY THROUGH USE OF ROTATING IPs:
Sending requests from a similar IP result in IP banning. But, to deal with this, getting a rotating proxy with a greater pool size having a higher number of IPs is the best solution. Also, set different IPs of bots always. Rotate IPs frequently. Rotating IPs are best for scraping online and give higher success rates. This is the key. After all, who wants to get stuck in the middle of the work? Follow this tip to prevent any bans in the future.
5) DO NOT VIOLATE ANY WEBSITES TERMS OF SERVICE:
While scraping data or shopping online, don’t violate the website's Terms of Service. For example, if you are shopping online for tickets on Ticketmaster. The highest limit of adding tickets to the cart is set to 8 tickets/IP. Don’t add more than 8 in your cart/IP. You want more tickets to rotate the IP or use multiple proxies. So, respect the website terms of service while botting. It is another tip to get along with this.
6) AVOID SENDING REQUESTS FROM UNSAFE/UNUSUAL GEO-LOCATIONS:
Using proxies with different IPs and locations is a common practice. Though, one mistake that can lead to getting banned is sending the request from unusual locations.
For example, you send a request to a server in a country from the IP of another country. There may be a risk that the traffic of that country's’ server doesn’t come from the country IP you are sending requests from. This creates a red alert ⚠ and the website will ban you.
So, while doing such activities always access websites from lower-risk locations. Also don’t mismatch the time zone and location of IP. It can cause issues and trouble you too.
7) UNSYNC PATTERNS OF SENDING REQUEST BY BOTS:
It correlates with slowing down the speed of the bots and limiting them to send requests. If you also automate the bots to send requests in an unsynchronized manner, then the combination of these tips will create chaos for the websites. Then, you will be hard to detect. So that you can do your work and accomplish success easily.
CONCLUSION:
This article sum up the common mistakes proxy users do and completely answers the question “how to reduce the risk of the proxy ban”. Follow these 7 ways to reduce the risk of getting your proxies blocked for higher success rates and task completion.
#dedicatedproxy#residentialproxy#rotatingproxy#VPN#sneakerproxies#socialmediaproxies#unblocksites#cheapproxies#twitterproxies#instagramproxies#facebookproxies
0 notes