#10G CWDM/DWDM SFP+
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Оптические трансиверы (модули) X2
Оптические трансиверы (модули) X2
Оптические модули типа X2 это приемо-передатчики, поддерживающие скорость передачи до 10 Gbit/s (10Гбит/с). Формат X2 далеко не новый форм-фактор 10G приемопередатчиков, и на данный момент он уже не является популярным как раньше, поскольку новое оборудование производят с более дешевыми и компактными 10G портами: SFP+ или XFP. Однако эти модули можно использовать с не новым оборудованием, использующим 10GEthernet(10GE), STM-64/OC-192, Fibre Channel и другие типы передачи данных.
Купить Оптический трансивер (модуль) DWDM X2, дальность 40 км и 80 км Оптический трансивер (модуль) X2 10G, TX 1550 нм, SC, 40 км и 80 км Оптический трансивер (модуль) X2 CWDM, дальность 10 км, 40 км и 80 км Оптический трансивер (модуль) X2 10G, 300 м, TX 850 нм, SC Оптический трансивер (модуль) X2 10G, 10 км, TX 1310 нм, SC
0 notes
Text
Sky Optics is a leading Optical Transceiver manufacturing and selling company in China. It is used to convert electrical signals to optical signals and vice versa. It combines a transmitter and receiver into a single package, enabling high-speed data communication in networks by utilizing light for data transmission and reception. For more details call us @ +8675533967196
1 note
·
View note
Text
Company Profile
https://www.optical-sintai.com/company-profile.html

Guangzhou Sintai Communication Co., Ltd, which was founded in early 2013, is specialized in the optical transmission field with R&D, production, sales and customer service. And shortly after that our OTNS8600 optical transmission network system was brought to the market. Especially, we were the one of the first companies to provide 100G wavelength division products with professional solutions in the industry in 2015. We’ve been dedicated to providing optical transmission network systems and optical transmission optimization solutions and have become one of the top optical communication products manufacturers and service providers in China.
We are committed to providing integrated optical transport network systems and optical transport optimization solutions, and our products mainly contain the WDM/ OTN systems (10G/ 25G/ 40G/ 100G/ 200G WDM system, 5G fronthaul transmission WDM systems), optical amplifier system (OEO/ EDFA/ SOA), optical protection system (OLP/ OBP/ FMS), passive optical device (AWG/ CWDM/ DWDM MUX&DEMUX/ DCM/ Splitter) and optical transceivers (SFP/ SFP+/ SFP28/ QSFP+/ QSFP28/ CFP/ CFP2). They are widely used by telecom operators and private network industry customers, including ISP, electric power, IDC, education, transport, radio and television, network security, big data and cloud services, etc.
Our products have its patented technology through our independent R&D and won the authorized certification, such as the design patent certificate, software copyright register certificates and series of quality management and test certificates.
After years of development, our products and services have extended to various industries at home and abroad. Our company base is at Guangzhou with branches at North, Northwest and East China. And the establishment of brand advantage has promoted the construction of our international marketing network. The awareness of Sintai is continuously increasing in the key markets. Our overseas business has extended to Europe, Middle East, Southeast Asia, North America, South America, Africa and so on.
In order to support our increasing domestic and overseas markets, we have built professional production team, sales team, service team and R&D team to provide the industry-leading and comprehensive products. With many years’ experience of optical communication technology, we are focusing on optical transmission and optical device technology to continuously provide a forward-looking technology development strategy and products with core market competitiveness. And we are dedicated to provide every customer the perfect pre-sales, sales and after-sales service. Customers’ concerns will be always taken good care of by our professional service teams.
Over the years, Sintai has been centering on offering customer oriented service, high quality products and optimized optical transport solutions in the optical transmission field. Creating value for customers, achieving common development with customers and making contributions to the society will always be the fundamental and mission of the company's long-term work.
0 notes
Text
White Paper: CWDM + DWDM = Increased Capacity
One way of increasing capacity in fiber optic links is to add DWDM over existing CWDM
April 2023
by Robert Isaac
Ghostwritten by Scott Mortenson

For years, service providers have been using Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) to increase the capacity of fiber optic links. CWDM filters offer up to 18 ITU (International Telecommunication Union) defined wavelengths and has been an ideal way to transport 1Gbps and 10Gbps circuits over a single fiber span.
What we are seeing now seems to be an uphill climb for CWDM applications. There appears to be a bandwidth growth requirement, and decreased support for CWDM from some equipment manufacturers.
With CWDM support from manufacturers dwindling and the need for capacity increasing at an exponential rate, the question becomes “How do we increase the capacity without forklifting the existing CWDM?”
One answer can be using DWDM over the existing CWDM.

Figure 1
The Concept
Because CWDM is built with channels that are spaced 20nm apart and often have a 10-13nm passband per wavelength (see Figure 1 above), DWDM makes a lot of sense. DWDM filters are built with much smaller channel spacing (.4nm/.8nm/1.6nm), so these wavelengths can be combined and will pass through the ~13nm passband of CWDM channel. For this example, we will focus on standard DWDM filter channels that are in the C-Band (1525nm-1565nm) spectrum and 100Ghz-spaced as this is the most common and supported DWDM application.
If it is warranted this same principle can be applied using DWDM channels in the L-Band (1570nm-1610nm) as well as using channels that are only 50Ghz-spaced to increase channel count and density, and be easily supported with tunable SFP+ optics.

Figure 2
Figure 2 shows how cascading DWDM filters over an existing CWDM span would connect. In this example we use a standard, off the shelf, DWDM filter that is equipped with 8 channels (ITU Ch 52-59).

Figure 3

Figure 4
Figures 3 and 4 show how 20 DWDM channels could be added across the 1530nm CWDM port and 30 DWDM channels can be added using the 1550nm CWDM port using C-band channels. We could apply this same philosophy to the 1570nm, 1590, and 1610nm ports as well but would require L-Band DWDM channels which aren’t widely supported today.
The Challenge
Now that we know a standard 8 Channel CWDM can be expanded to include another 50 channels you may be thinking “What are the potential downsides to using DWDM over CWDM?” and that would be a very good question to ask.
This concept has been available for many years and hasn’t become part of the mainstream deployment strategy for many network operators. Why not? The only limitation to using this concept from a performance standpoint is the added insertion loss of having both the CWDM and DWDM filters between the transceivers.

Figure 5
Figure 5 shows the logical end-to-end for 8 channels of DWDM over an existing CWDM connecting two sites 30km apart. To keep losses lower, we will limit the new channels being added to 8 DWDM channels. Understanding that 10G DWDM optics have an overall power budget of 23db, we can see that adding the DWDM filters brings the overall link loss to 21.5db which falls just inside the power budget.
Because DWDM optics are built for longer reaches with higher power budgets — and CWDM is often used on shorter fiber spans, say under 30km — the insertion loss should be a non-issue. And if the loss is an issue, DWDM channels can be amplified (unlike CWDM), so placing a low-cost EDFA between the CWDM and DWDM filters could help extend the reach well beyond even 30km.
Reluctance to this concept also seems to come from not fully understanding the simplicity of passive WDM or even how to manage the engineering, installation, records, and inventory for having both technologies within the same span. If those challenges can be overcome, overlaying DWDM onto your existing CWDM can be a very efficient and cost-effective way to respond to the exponential need for bandwidth we are facing in today’s technology.
For network operators and service providers who have made a significant investment in CWDM and facing the need for bandwidth growth, this concept should be considered. Passive DWDM filters can be deployed quickly without impacting existing traffic, are a very low-cost alternative to complex active systems, and can equip your network for the future in very short order. Add the operational efficiency of 10G tunable DWDM optics, and this could be a home run for your network.
Demystifying DWDM for the DCI
If it is so easy and inexpensive, why aren’t all the data centers defaulting to using this on every fiber end? Well, that’s where things get a little tricky.
Whenever you say “DWDM” to a Data Networking person (and even some Service Provider engineers), their default reaction tends to go straight for large, complex, and expensive DWDM systems. Like Reconfigurable Optical Add Drop Multiplexing (ROADM) arrangements that are completely automated and perform optical switching, sub-signal aggregation, and even some L2 functions.
The truth is, DWDM is simply the combination and separation of circuits by wavelength — and only a small part of those larger systems. It is the basic technology that allows users to put 40+ distinct circuits on a given fiber, then separate them at the far end to connect to the individual switch ports.
As stated in the previously, this is often done passively, requiring no electrical power, software, annual maintenance agreement, etc. — and at a fraction of the cost of those more complex active systems.
So again, I ask: “Why aren’t more data center interconnects using this technology?”
Well, DWDM system design — or transport engineering — is usually not taught during Data Networking education courses. DWDM or transport are often thought of as completing ways of architecting a network, which means there are usually two camps: You are either a Data Network Engineer, or a Transport Engineer. Either way, one typically needs the other at some point in their network.
This is not to say you don’t need complex, software-controlled transport devices in your network. The truth is you likely do. What we are singling out here are a few applications where you can get what you need: Fiber capacity between two places quickly, inexpensively, and without sending anyone to school to get certified.
These applications can be:
• Point-to-Point Data Center Interconnects (DCI) on leased, or owned fiber. • Connections between campus facilities. • Network facilities between rooms or floors.
Using Passive DWDM can:
• Reduce or eliminate leased or new fiber builds. • Maximize the data rate per-fiber of installed fiber plants. • Drastically reduce Capex cost of high-capacity switches, complex DWDM systems, and reliance on service providers to maintain the connections. • Increase capacity of DCI connections in days not months.
How can we do this in a way we can understand?
It really comes down to Optical Link Engineering.
If you take the physical map of your network and zoom in on one span where there is a capacity bottleneck, it becomes a lot easier. For simplicity’s sake, we will focus on connecting 10G switch ports, across a single span between 2km and 50km long, making the math fairly simple.
For these locations, we just need to focus on two primary factors: Link Budget vs Link Loss, and Dispersion.
Link Budget vs. Link Loss
Every optic or transceiver has a minimum transmit power, and a minimum receiver sensitivity. By subtracting these two values, you are left with the link budget — or the total amount of power loss the signal can experience and still be legible by the receiver.
In a standard connection, you would calculate (or measure) the total loss of the fiber, patch panels, cassettes, and splices between the two optics. And if that is less than the link budget, then it should work . . . right?
Passive DWDM only adds a little more math to the Link Engineering. The optics at each end would need to be specific DWDM optics, and the filters will add more insertion loss at each end — but it is still, pretty much the same math.
For 10G DWDM optics, the link budget is typically in the 23db range. If a fiber span, with DWDM filters, has less than 23db of loss, the link should work. It’s simple math.
Or is it?
Dispersion
Another important factor we account for is Chromatic Dispersion (CD). This is a characteristic of single-mode fiber where, as a signal travels along a fiber route, it spreads out and can arrive at the far end slightly ahead or slightly behind schedule, making it difficult to be deciphered by the receiver.
The optics we are using will also establish how much dispersion it can tolerate before the signal becomes undetectable. This value is typically measured in picoseconds per kilometer per nanometer (ps/km/nm) or even simply by the optic’s distance rating. For instance, a DWDM optic-rated for 80km is often limited to 1360 ps/nm/km of dispersion. This is calculated based on traveling 80km on SMF28 type fiber with a CD rating of approximately 17 ps/nm/km.
So, there you have it. If your link falls inside the specifications defined by the optics on each end, you can deploy passive DWDM to maximize the capacity of your fiber plant, and save loads of time and money.
But what if the span exceeds the link budget or dispersion rating? No problem! The addition of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) — to boost the signal power and/or passive Dispersion Compensation Modules (DCM) to account for excess dispersion between the DWDM filters — can help extend the reach and ensure the optics on each end perform to expectation to years to come.
Often when Transport Engineers speak to Data Network Engineers, it can seem like they are speaking different languages. That is to be expected. Specialized jargon or terminology, approaches to problems, and education can be vastly different.
If what your network truly needs is fiber capacity, lower cost of fiber infrastructure, and flexibility of lightning-fast circuit turn-up, passive and even amplified DWDM networks could be the perfect solution.
The 40-channel, two-fiber DWDM solution using 10g SFP+ optics is a great way to get 400G of capacity for links up to about 60km without the need for amplification or dispersion compensation. But what if you want higher data rates on the link? This is where things get a little tricky.
If we remove coherent optics from consideration due to the expense and complexity of deploying them, we see a pattern emerge. Here is a quick snapshot of the specifications of DWDM optics (non-coherent) we could consider:

Figure 6
That table attempts to remove a bunch of “noise” or complexity in determining if a simple point-to-point two-fiber solution will work. What we see when we review those specs is that as data rate increases, the unmodified reach and power budget both decrease.

Figure 7
Given these values, we can use the optical reach and power budget — along with the logical diagram shown in Figure 7 — to determine how long of a cross-connect we can achieve.
If we assume the 40-channel filter has a high-performance loss of 3db each, the patch panels have a loss of 0.5db each and the fiber loss is 0.25db per km (ITU-T G.657.A1 and G.652.D or better), then we can work backwards to see what the total span distance is per optic/data rate.

Figure 8
Reviewing the numbers in Figure 8, we can see that once you go beyond the 10G data rate, the unmodified reach becomes the limiting factor. For this illustration, we can expect to be able to establish some versatile, yet high-capacity, cross-connects.
We had already reviewed the capacity of a passive 40-channel system using 10Gbps optics and know that it can support 400Ghz worth of capacity. Using the same methodology, we can create links with a total line capacity of 1Tbps @ 25Gbps per channel up to ~15km, 1.6Tbps @ 40Gbps per channel up to ~8.8km, and a 4Tbps total capacity up to ~1.5km in fiber length. Knowing this can help reduce the total number cross-connects needed between any two points.
Also, worth noting: Not all channels need to be the same data rate. If the link distance is designed to work with 100Gbps links (or approximately 1.7km), that same link will be able to support 10G, 25G and 40G channels as well.
Summary
Earlier we mentioned we were “removing a lot of noise” — and then continued to make a great deal of assumptions to come up with these numbers. For instance, Forward Error Correction (FEC) is required and must be available on the host device for the links 25Gbps and higher. We made assumptions about fiber type, used calculated losses for the fiber spans, and assumed the total SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, and QSFP28 ports were available at each end.
What this proved is that by combining passive filters and DWDM optics, we can increase the capacity as much as 40x per cross-connect pair. All this needs no power (except the switches), can be turned up very quickly, requires only 1RU of rack space (not counting the switches or patch panels), and adds zero latency.
As should be clear by now, this is not meant to be taken as gospel, and every effort should be made to know the optic specifications you are considering, the fiber type of the cross-connect, and have measured fiber loss and dispersion values before deploying.
When planned correctly, your CWDM plus DWDM can mean increased capacity without a big financial outlay. And your network can perform better as well.
0 notes
Text
10G SFP SR vs 10G SFP Cable televisions
10G SFP SR vs 10G SFP Cable televisions
There are 2 sorts of 10G SFP+ Cable televisions, 10G SFP+ DAC and 10G SFP+ AOC, both which, together with SFP 10G SR, prevail optical components for information facility top-of-rack (ToR) cabling to attach tiny accessibility buttons and web servers. Of these, the 10G SFP+ DAC is made use of for short-range links within the shelf, while the 10G SFP+ AOC appropriates for rack-to-rack links for ToR and EoR buttons.
Conventional cabling designs usually take on centralized cabling, such as EOR and MOR, while TOR cabling frameworks take on point-to-point cabling, which decreases the variety of cabling and conserves expenses to a particular level. In the create of TOR style, a minimum of one button is positioned in each shelf, and the web servers in the shelfs are typically linked to the buttons using copper cable televisions, with the high-level buttons in each shelf linked per various other.
10G SFP Cable televisions vs 10G SFP SR vs 10GBASE-T:what's the distinction? Cisco SFP 10G SR 10GBASE-T RJ45 components are commonly wired utilizing Cat6a or Cat7 network cable televisions with an optimum transmission range of 100m at Gigabit prices and approximately 30-80m at 10G prices. In information facilities, where thousands of cable televisions are commonly called for, utilizing low-cost network cable televisions can lead to considerable set you back cost financial savings. On top of that, 10GBASE-T components can optimize making use of current copper cabling frameworks, which additionally conserves a great deal of costs. 10G SFP SR calls for making use of multimode fiber optic spot cable televisions for transmission, with an optimum range of 300m. 10G SFP+ DAC cable television is the the very least pricey of these 3 items, the just downside is that the transmission range is extremely restricted, approximately 10m, better for cabling links within and in between shelfs. If transmission range is not an aspect that need to be thought about, 10G SFP+ DAC high-speed cable television has decrease power usage and decrease latency compared to that of 10G SFP SR, production it an extra suitable cabling option for information facility cabling.
10G SFP+ optical components: web server to button link or storage space gadget to button link? Because of the high needs of web server or storage space tools linked to the button, high efficiency 10G SFP+ optical components with high integrity and scalability are required. As all of us understand, 10G SFP+ optical components consist of 10G SFP SR, LR, ER, ZR, BIDI, CWDM, DWDM and 10GBASE-T electric port components, and they can supply high-speed interconnection for networks, which are extensively made use of in next-generation mobile networks, set accessibility networks, city networks, and information facilities.
To accomplish the link in between web servers and buttons, you can utilize 10G SFP SR, LR, ER, ZR, BIDI, CWDM, DWDM optical components with LC-LC single-mode fiber spot cables or LC-LC multimode fiber spot cables with each other. To understand the link in between storage space tools and buttons, you can utilize 10GBASE-T electric port components along with Extremely Group 6 network cable television or Group 7 network cable television.
0 notes
Text
What is the difference between gigabit and gigabit modules?
The main difference between a gigabit light module and a gigabit light module is the transmission rate. The transmission rate of a gigabit light module is 1000Mbps, while the transmission rate of a gigabit light module is 10Gbps.Aside from the differences in transmission rates, what are the more specific differences between gigabit and gigabit modules?

Gigabit light module
As can be known from the name, a gigabit light module is a light module with a transmission rate of 1000Mbps, usually expressed as FE.Moreover, there are two kinds of gigabit light modules, namely gigabit SFP light module and GBIC light module, and the transmission distance can reach between 80m and 160km.Generally speaking, gigabit optical modules can be distinguished from the specification details of the product itself and the naming rules of optical modules provided by different companies.
In terms of packaging form, gigabit light modules include 1000Base SFP light module, BIDI SFP light module, CWDM SFP light module, DWDM SFP light module, SONET/SDH SFP light module, and GBIC light module.

Gigabit light module
A gigabit light module is a light module with a transmission rate of 10G, also known as a 10G light module, which is usually packaged in the form of SFP+ or XFP.The standard of 10 gigabit optical modules is IEEE 802.3ae, IEEE 802.3ak and IEEE 802.3an. When choosing 10 gigabit optical modules, we can consider the price, power consumption, space occupation and other factors.
In terms of packaging form, ten gigabit optical modules include 10G SFP+ optical module, BIDI SFP+ optical module, CWDM SFP+ optical module, DWDM SFP+ optical module, 10G XFP optical module, BIDI XFP optical module, CWDM XFP optical module, DWDM XFP optical module and 10G X2 optical module.
The gigabit optical module is used for gigabit Ethernet, dual-channel and bidirectional synchronous optical network (SONET), while the gigabit optical module is used for gigabit Ethernet, stm-64 and oc-192 rate standard synchronous optical network (SONET) and 10G optical channel.
In the application should choose gigabit light module or gigabit light module, this mainly depends on the type of network, for example, your network is gigabit Ethernet will use gigabit light module, gigabit Ethernet will use gigabit light module.
Article provided by 10Gtek, thanks for your time. If you interested in more infos about intereconnect solutions, welcome to check on our site: www.sfpcables.com, which is a fiber store runs 10 years.
recommendation:SFP28 Electrical Passive Loopback, 3.5dB It provides an economical and efficient method for SFP28 port test with low loss.

0 notes
Text
Common Types of 10G and 100G fiber optic transceiver
With the development of Internet, the demand for higher bandwidth is rising rapidly. As an important part of optical network equipment, fiber optic transceiver is becoming more and more popular. There are many types of fiber transceivers given different transmission rates from 0.5 Mbps to 200 Gbps. This article will cover the two most commonly used fiber optic transceiver types, 10G transceiver and 100G transceiver, and introduce their sub-classifications respectively.
What is Fiber Optic Transceiver?
A fiber optic transceiver is a device that uses fiber optical technology to transmit and receive data. It has a transmitter and a receiver that are combined and share common circuitry or a single housing. Moreover, it also has electronic components for adjusting and encoding the data into light pulses as an electrical signal. When transmitting data, transceivers always make use of light sources like VSCEL, FP and DFB lasers, and when receiving light sources, they will make use of photodiode semiconductors.
Overview of 10G Fiber Optic Transceiver
Definition of 10G Fiber Optic Transceiver
10G fiber optic transceiver is designed for 10G or 10Gbps data transmission applications including 10 Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gbps Fibre Channel, and Synchronous optical networking (SONET).
Classification of 10G Fiber 0ptic Transceiver
10G fiber optic transceiver mainly includes 10G XENPAK, 10G X2, 10G XFP, and 10G SFP+. The following part will introduce them in turn.
10G XENPAK Transceiver
10G XENPAK fiber optic transceiver was the very first MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) for 10GE coupled with the biggest form factor. It allows all optical ports defined in IEEE 802.3ae, supporting speeds of 10.3 Gbps, 9.95 Gbps or 3.125 Gbps.

10G X2 Transceiver
0G X2 fiber optic transceiver defines a smaller 10Gbps pluggable fiber optic transceiver optimized for 802.3ae Ethernet, ANSI 10GFC (10 Gigabit Fibre Channel) and other 10 Gigabit applications. Originally centered on a 10km fiber link, the X2 transceiver is very suitable for telecom switches, standard PCI (peripheral component interconnect) server, and storage connectivity.

10G XFP Transceiver
10G XFP fiber optical transceiver is actually a standard for transceivers that are used in high-speed computer networks and telecommunication links. It can work at a single wavelength or use dense wavelength division multiplexing and mainly apply for 10 synchronous optical networking at OC-192 rates, and parallel optics links.

10G SFP+ Transceiver
10GbE SFP+ transceiver is a versatile optical module for 10Gbps data transmission applications at 850nm, 1310nm, 1550nm, CWDM and DWDM wavelengths. It is ideally suited for storage space network applications based on the IEEE 802.3ae and Fibre Channel standards. And SFP+ has become the most popular socket on 10GE systems.

Overview of 100G Fiber Transceiver
Definition of 100G Fiber 0ptic Transceiver
100G fiber transceiver is designed for 100G or 100Gbps data transmission applications. Nowadays, the market for 100G data center optics such as client-side 100G optical transceiver is accelerating. It is becoming more and more popular in Cloud computing, mobile broadband, and IPTV.
Classification of 100G Fiber Optic Transceiver
At present, the 100G optical transceivers on the market mainly include CFP/CFP2/CFP4 optical transceiver, CXP optical transceiver, and QSFP28 optical transceiver.
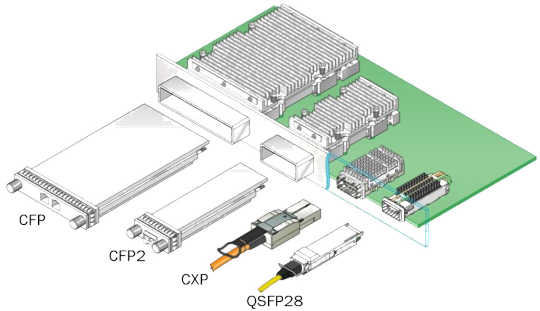
CFP Series (CFP/CFP2/CFP4) Transceivers
CFP series transceivers are the form factor pluggable optical transceiver. The volume of them is very large. From CFP to CFP4, their size becomes smaller and smaller. The size of CFP4 transceiver is only one-quarter of CFP transceiver. Nowadays, CFP4 transceiver’s bandwidth and power consumption have been greatly improved, making it more suitable for high-density 100G Ethernet.

CXP Transceiver
CXP fiber transceiver is 12 full-duplex channel modules with 12 x 10G transceivers. It has a smaller size than CFP transceiver and supports hot pluggable feature. And it mainly supports 100GBASE-SR10 of the short-distance transmission.
QSFP28 (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) Transceiver
The 100G QSFP28 is implemented with 4 x 25 Gbps channels and can achieve the highest possible rate of 4 x 28 Gbps. Its size is smaller than the CFP4 optical transceiver and you can switch with high port density. As the cost of the QSFP28 optical transceiver decreases, the QSFP28 optical transceiver becomes more and more popular.
Conclusion
As we can see, there are a variety of 10G and 100G fiber optic transceivers, and they are always boosting greatly. Both of them have their advantages and unique characteristics. You need to make choices based on your actual needs.
0 notes
Text
10g Copper SFP Module
We are one of the best suppliers of Copper SPF Modules in China. Worldwide delivery available. For more information visit our website.

#Fiber Optic Cable Connectors#10g Copper SFP#Cisco SFP Modules#CWDM Vs DWDM#Fiber Optic Cable Splitter
0 notes
Text
CWDM SFP+ vs DWDM SFP+ : Что Купить
С появлением технологии WDM, различные длины волны могут быть назначены для оптического модуля, таких как CWDM SFP+ и DWDM SFP+, таким образом расширяя и оптимизируя пропускную способность сети. Модули CWDM SFP+ и DWDM SFP+ используются в 10G Ethernet, и все могут достигать максимальной скорости 11.25G. Однако они различаются в таких аспектах, как длина волны, расстояние и применение. Это сообщение предназначено для руководства покупателя по выбору модуля 10G CWDM SFP+ и DWDM SFP+.
Что Такое CWDM SFP+?
CWDM SFP+ модуль часто работает на номинальной длине волны CWDM. Конкретно говоря, CWDM SFP+ модуль может поддерживать 18 длин волны от 1270nm до 1610nm, а его расстояние передачи от 20km до 80km. Это важная часть в системе CWDM.
Что Такое DWDM SFP+?
DWDM SFP+ модуль часто работает на номинальной длине волны DWDM от CH17-CH61, поддерживая расстояние передачи до 80km. Он специально предназначен для операторов и крупных предприятий, которым требуется масштабируемая, гибкая и экономичная система для мультиплексирования, транспортировки и защиты высокоскоростных данных, хранения, голоса и видео.
Модули CWDM SFP+ vs Модули DWDM SFP+
CWDM SFP+ может поддерживать до 18 каналов, а DWDM SFP+ может поддерживать более 40 каналов на одном волокне. Хотя клиенты могут получить более пропускную способность и более длиннее расстояние ссылки от DWDM SFP+, им придется платить больше, поскольку стоимость его дороже, чем CWDM SFP+. Для клиентов, которым не требуется длинное расстояние передачи, CWDM SFP+ может быть первым выбором. Но в долгосрочной перспективе DWDM SFP+ лучшее служит будущей тенденции для сети с высокой плотностью.
По сравнению с обычными SFP+ модулями, CWDM и DWDM SFP+ являются более дорогими из-за стоимости, связанной с различными режимами работы. И как уже упоминалось ранее, CWDM SFP+ дешевле, чем DWDM SFP+. И вообще, чем длиннее поддерживаемый диапазон передачи, тем дороже для модулей CWDM или DWDM. Кроме того, модули от сторонних производителей CWDM и DWDM SFP намного дешевле, чем оригинальных производителей. Поэтому покупка совместимых модулей поможет вам экономить большую сумму денег. В следующей таблице показана информация о совместимых модулей CWDM и DWDM SFP+ из FS.COM.
Руководство Модулей CWDM SFP+ и DWDM SFP+
1. Должны ли модули Cisco использоваться с оригинальным Cisco CWDM SFP+?
Нет. Существует много совместимых модулей, предоставляемых сторонним поставщиком модулей, которые вы можете использовать для замены Cisco CWDM SFP+ или даже Cisco DWDM SFP+. Если вы можете получить модули у надежного стороннего поставщика, они будут надежными, как и Cisco, но за небольшую часть цены.
2. Возможно ли преобразовать обычную длину волны, например 850nm в длину волны DWDM или CWDM?
Да. Если вам нужно преобразовать длины волны в длины волны CWDM или DWDM, вы можете использовать транспондер (OEO), чтобы реализовать его. транспондер (OEO) реализует преобразование длины волны на основе технологии преобразования O-E-O.
3. Как выбрать подходящие оптические кабели для модулей CWDM и DWDM SFP+?
Оптические кабели можно разделиться на два типа: одномодовые и многомодовые оптические кабели. Первый обычно используется для передачи на большие расстояния, а второй - для ближней передачи. Для модулей CWDM и DWDM SFP+, который может поддерживать связь до 80km, мы выбираем одномодовые оптические кабели, которые заканчиваются разъемом LC.
4. Есть ли разница между длинами волны CWDM и DWDM для качества передачи? Какие длины волны лучше?
Да. Разная длина волны может обеспечить разное качество передачи. Вообще говоря, 1470nm и 1550nm являются наиболее широко используемой длиной волны, причем 1550nm являются более популярными, поскольку затухание при 1550nm является малым и обеспечивает лучшее качество передачи в дальнем применении.
Купить FS Модули CWDM и DWDM SFP+
Как ведущий поставщик оптических продуктов, FS.COM может предоставить все необходимое оборудование для построения сети CWDM или DWDM. И все эти продукты гарантированы с гарантией и возвратом. FS.COM предоставляет заказанные услуги, включая имя поставщика SFP, тип интерфейса, расстояние, длину волны, DDM/DOM, температуру, этикетку, дизайн этикетки и упаковку. Если вам нужна заказанная услуга или вы не знаете, какой тип вам нужен, вы можете связаться с FS.COM.
0 notes
Text
10 SFP+ C/DWDM Transponder
https://www.optical-sintai.com/products/10-sfp-dwdm-transponder.html
10G OTU service card launched by Sintai Communication Co., Ltd. supports four types of service access with 42M~11.3G rates.
Its main function is to finish the 3R regeneration of any 5-channel signals under any protocol within the rate of 1.25 Gbit/s~11.3 Gbit/s to be accessed, and then convert them to optical signals of a standard DWDM wavelength or standard CWDM wavelength, so that the multiplexing unit can conduct WDM for optical signals of different wavelengths and also achieve the inverse process of the above process.
It's applicable to the wavelength division transmission solution for any access of services with the rate of 11.3G or below.
10 SFP+ C/DWDM Transponder Specification
Function
Note
Card type
10G OTU-3R
10G OTU-2R
interface
·
Client-side interface: 5 SFP+ hot-pluggable, compatible with SFP
·
·
WDM-side interface: 5 SFP+ hot-pluggable, compatible with SFP
·
Line mode
Supports transparent transmission of any type of service in four 42M~11.3G rate ranges, and converts four service optical signals into four WDM standard wavelength optical signals.
Relay mode
Support 42M~11.3G wavelength electrical relay.
Support service type
GE, 10GE
1/2/4/8/10G FC
STM-16/64
CPRI-2/3/6/7
FE, GE, 10GE
1/2/4/8/10G FC
STM-1/4/16/64, OTU1/OTU2/OTU2e
CPRI-1~8, 42M~11.3G Any
WDM technology
·
Support CWDM: 18 waves
·
·
Support DWDM: C band 50GHz 96 waves
·
Occupied slot number
Support OTNS8600 series chassis, occupy 1 slot
Network management function
Support real-time monitoring of the port working state, including transmitting optical power and receiving optical power, temperature, etc.
Power consumption
16W (max, including transceiver)
MTBF
>100000 hours

0 notes
Link
Flypro Provide the Broad range of Fiber Optic Transceivers With high-bandwidth data communications applications. Fiber Optical Transceiver Modules/Cables(SFP, 10G SFP+, 40G QSFP+, 100G QSFP28 & CFP, CWDM & DWDM optics, DAC, AOC cable), MSA compliant Manufacturer, High Quality, Best Price .
0 notes
Link
BLIY 10G Media Converter is equipped with one 10G/5G/2.5G/1G/100BASE-T auto-negotiation port and one 10GBASE-X SFP+ slot. By using Optical - Electrical - Electrical wavelength conversion, realize the optical signal equilibrium amplification, clock extraction, and optical regeneration, and with WDM (DWDM/CWDM) technology, can achieve optical signals transmit in a single fiber by single or multiple ways over a long distance.

0 notes
Text
normal SFP BiDi can also be deployed with multimode fibres
normal SFP BiDi can also be deployed with multimode fibres
fiber-mart.com produce and stock for your full-range of optical transceivers.They are really including about SFP (SFP Plus), X2, XENPAK, XFP, SFP (Mini GBIC)and GBIC, CWDM, DWDM, PON.As an example,fiber-mart.com supply types of SFP module 100% appropriate Cisco, HP, Juniper, Netgear, SFP , SFP BIDI from 10KM up to 120KM and 10G SFP.Many optical transceivers you are able to located in here.Sopto’s…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
normal SFP BiDi can also be deployed with multimode fibres
normal SFP BiDi can also be deployed with multimode fibres
fiber-mart.com produce and stock for your full-range of optical transceivers.They are really including about SFP (SFP Plus), X2, XENPAK, XFP, SFP (Mini GBIC)and GBIC, CWDM, DWDM, PON.As an example,fiber-mart.com supply types of SFP module 100% appropriate Cisco, HP, Juniper, Netgear, SFP , SFP BIDI from 10KM up to 120KM and 10G SFP.Many optical transceivers you are able to located in here.Sopto’s…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Как Выбрать 10G SFP Модули для Коммутаторов Cisco?
Оптическая сеть 10G широко распространяется в современной телекоммуникационной сети. В настоящее время используется много волоконно-оптических устройств 10G, таких как коммутаторы, среди которых Cisco устройства чаще всего используются в соответствии со статистикой. Если вы выберете коммутатор Cisco, оригинальный бренд Cisco или совместимые модули Cisco, как SFP/SFP 10G могут быть необходимы для передачи между оптическими сигналами и электрическими сигналами. В данной статье будет предлагать подробную информацию о том, как выбрать подходящий модуль 10G SFP+ для коммутаторов Cisco.
Понимание Стандартов 10G IEEE и Как Cisco Назначение Имён Его Модулей
Теперь 10G оптическая сеть уже созрела, и существует широкий выбор стандартов 10G IEEE для различных сетевых приложений 10G и сред. Прежде чем покупать 10G SFP модули для ваших Cisco коммутаторов, в первую очередь, вы должны ознакомиться с этими стандартами 10G.
Стандарты 10G IEEE
IEEE определил стандарты 10G для разных расстояний передачи данных и сред передачи. Таких как, 10GBASE-SR для короткого расстояния макс.до 300 метров по многомодовому оптическому волокну OM3 и 10GBASE-LR для далекого расстояния макс.до 10 километров по одномодовому волокну. Существуют также стандарты для 10G передачи данных по медным кабелям, Например 10GBASE-CR и 10GBASE-T. В следующей таблице перечислены подробные информации о наиболее часто используемых стандартах 10G.
Название Продукции Cisco 10G SFP Модулей
Система назначения имён Cisco модулей 10G SFP тесно связывается со стандартами IEEE. Здесь я привел несколько примеров для Cisco модулей 10G SFP, чтобы лучше пояснять, как Cisco называется свои модули 10G SFP.
Для обычных модулей 10G SFP, Cisco использует стандарные ключевые слова для обозначения отвечающих модулей. Для особых модулей, Cisco построила другую систему назначения имён.
Для пары модулей BiDi SFP 10G, буквы «D» и «U» вместе используются для двух модулей на каждом конце оптической линии связи. Например, SFP-10G-BXD-I & SFP-10G-BXU-I представляет собой пару модулей BiDi, что может поддерживать расстояние передачи данных макс.до 10 км. Дополнительные номера добавляются для отметки расстояния передачи данных модулей BiDi. SFP-10G-BX40D-I & SFP-10G-BX40U-I представляет собой пару модулей BiDi SFP 10G, которая может поддерживать расстояние передачи данных макс.до 40 км.
Для CWDM 10G SFP и DWDM 10G SFP, длина волны добавляется в артикуле. Например, CWDM-SFP10G-1470 является артикулом CWDM SFP 10G, который работает на длине волны 1470 нм. Если вы хотите CWDM SFP 10G работать на 1550 нм, то серийный номер изделия этого CWDM модуля должен быть CWDM-SFP10G-1550. Поскольку все модули DWDM SFP 10G работают на длинах волн около 1500 нм, в серийном номере изделия модулей SFP 10G Cisco DWDM, первые два номера 1 и 5 устраняются. Например, DWDM-SFP10G-61.41 обозначает модуль DWDM SFP 10G с рабочей длиной волны 1561,41 нм.
Для таких модулей, как SFP 10G кабель прямого подключения (SFP 10G DAC) и активный оптический кабель SFP 10G (SFP 10G AOC), который содержит длину кабелей, Cisco объединяет характеристики стандарта IEEEи номера назначения имён его модулей. Cisco SFP-H10GB-CU1M представляет собой 1-метровый 10G SFP+ медный кабель прямого подключения. Cisco SFP-10G-AOC2M - это 2-метровый 10G SFP+ активный оптический кабель.
Вам Действительно Нужно Cisco Оригиальная Марка SFP 10G Модулей?
Кроме стандарта IEEE и расстояния передачи данных, выбор подходящих модулей 10G SFP следует также учитывать несколько других факторов, таких как совместимость и затраты.
Хотя Cisco имеет широкий выбор коммутаторов и модулей 10G SFP, не каждые модули SFP 10G могут хорошо работать на каждом порте коммутаторов Cisco SFP 10G. Перед выбором модулей SFP 10G для вашего Cisco коммутатора, вы должны убедиться, что этот SFP 10G совместим с вашим коммутатором.
Второй важный фактор представляет собой затраты на модули SFP 10G. Зачем? Модуль SFP 10G является лишь небольшой частью всей оптической сети, но объем использования модуля SFP 10G очень велик. Cisco оригиальная марка SFP 10G модулей обычно стоит дорого. Таким образом, необходимо выбрать экономические модули. На самом деле, Cisco оригиальная марка SFP 10G модулей не является единственным выбором. Существует также много третьесторонних модулей, что совместимы с коммутаторами Cisco. Как правило, цены на третьесторонние оптические модули намного ниже, чем оригинальные марки.
Как Купить Модули Cisco 10G SFP?
Если у вас много денег, вы можете напрямую заказать модули от Cisco. Однако, если вы собираетесь выбратьтретьесторонние модули для экономичного решения, то качество и совместимость становятся очень важными.
0 notes