#Active RFID Reader
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Active RFID Reader For Long Range People Tracking
Active RFID Reader is an effective era used for monitoring and identifying belongings, people, or cars over lengthy distances. At the coronary coronary coronary coronary heart of any active RFID tool is the RFID reader, a device that detects and communicates with lively RFID tags, which can be powered with the useful resource of an internal battery. This setup allows dependable, extended-variety, real-time location monitoring and information trade in dynamic environments.
What Is an Active RFID Reader?
An energetic RFID reader is a specialized device designed to accumulate signals transmitted with the useful resource of active RFID tags. Unlike passive RFID readers, which supply out electricity to "awaken" passive tags, energetic RFID readers pay interest for indicators broadcasted by way of the use of battery-powered tags. These tags can transmit indicators periodically, at set durations, or in reaction to particular activities like motion or temperature adjustments.
Because the tags are powered, lively RFID structures can be characterized over significantly longer stages—normally 30 to a hundred meters, or at the same time as a good buy as three hundred meters in outstanding conditions. Active RFID Reader & RFID People Tracking may additionally embody antennas, wi-fi network interfaces, and connection ports to transmit information to number one systems for processing and show.
Applications of Active RFID Readers
Active RFID Reader Supplier in Canada are widely applied in environments wherein actual-time monitoring over huge regions is wanted:
Supply Chain and Logistics: For tracking pallets, packing containers, and vehicles in large warehouses or shipping yards.
Healthcare: Monitoring the real-time vicinity of important devices, frames of personnel, and patients' internal hospitals.
Manufacturing: Tracking equipment, system, and artwork-in-development gadgets in the course of manufacturing flooring.
Security and Access Control: Monitoring employees motion in excessive-protection regions like labs, military bases, or statistics centers.
Mining and Oil Industries: Locating employees in far off or unstable regions to decorate safety and reaction instances.
Benefits of Active RFID Readers
Longer Range: Can stumble upon tags from tens to hundreds of meters away.
Real-Time Tracking: Provides non-stop updates on the vicinity and status of property.
High Data Capacity: Active tags can supply greater information and beneficial resource sensors for temperature, humidity, and masses of others.
Durability: Suitable for rugged environments collectively with introduction of net web web sites or industrial organization company plant life.
Automation: Reduces the need for manual monitoring, enhancing common standard overall performance and accuracy.
Challenges and Considerations
While powerful, Active RFID Reader do encompass some drawbacks:
Higher Cost: Both the readers and energetic tags are greater steeply-priced than passive structures.
Battery Maintenance: Active tags require battery opportunity or charging, which include operational obligations.
Complex Installation: Requires cautious planning for reader placement to make certain complete insurance.
Conclusion
Active RFID Reader in Canada are critical machines for massive-scale, real-time monitoring systems. Their capability to expose assets and people over prolonged distances makes them best for excessive-fee, protection-essential packages. While greater steeply-priced than passive systems, the overall overall performance and flexibility they offer can deliver massive returns in productivity, visibility, and control.
#Active RFID Reader#Active RFID Reader in Canada#RFID People Tracking#RFID People Tracking in Canada#Active RFID Readers
0 notes
Text
As businesses continue to innovate, efficiency, automation, and streamlined operations are key priorities. One of the standout technologies in this space is RFID (Radio Frequency Identification). Whether you're managing inventory, tracking assets, or boosting security, RFID technology has become a vital tool across industries like retail, logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing.
However, understanding the different types of RFID—tags, inlays, and labels—is essential to choosing the right solution for your business. Each option has unique strengths and selecting the most suitable type can help you maximize your operations.
#rfid technology#rfid solutions#rfid tags#rfid reader#rfid tags manufacturers#active rfid tags#rfid inlays#rfid labels#rfid antenna#business
0 notes
Text
RFID Tags: The Future of Smart Inventory Management
An RFID tag, at its core, consists of two components – an antenna for transmitting and receiving signals, and an RFID chip (or integrated circuit, IC) storing the tag’s ID and other data. These tags are attached to items, facilitating their tracking using an RFID reader and antenna. Efficiency is paramount in inventory management. Saving time with increased accuracy poses an ongoing challenge for inventory managers across industries. Utilizing RFID Technology in inventory management, where each item is equipped with an RFID Tag and strategically placed readers or handheld RFID readers are used for rapid inventory, is rapidly gaining traction. This trend is driven by complexities arising from the sheer volume of inventory items, the rapid technological advancements, and the ever-expanding retail sector.
Moreover, current inventory management methods rely on manual counting processes or manual barcode scanning, both of which are time-consuming and not always accurate, resulting in potential sales losses or poor customer experiences.

Selecting the right RFID Tag for your inventory management system is crucial for its success. Below are some key considerations when choosing the appropriate RFID Tag:
Size & Form Factor: The size of the tag directly impacts its read range. Choosing the size based on the form factor of the RFID tags, such as wet inlays, labels, hard tags, or high-temperature tags, is essential.
Read Range: The appropriate read range, determined by the chip and RFID reader, should align with the application requirements, typically ranging from 3 feet to 12 feet.
Attachment Method: Various attachment options, including adhesive, magnet, screw, riveting, stitching, or hot stamping, are available and can also be customized.
Mounting Surface: Selecting the right tag for the existing mounting surface is crucial for optimal RFID performance. Metal surfaces, for instance, require specific Mount on metal tags rather than standard labels or tags.
Hundreds of RFID tags are available in diverse shapes and sizes, offering options tailored to specific environments, surface materials, and applications. Choosing the ideal tag for the application, environment, and item material is vital for optimal performance.
A successful inventory management system provides a clear, accurate view of inventory always. It offers item-level visibility and maintains historical records, enabling a chain of custody for each product. Users can track a specific product's journey from arrival to sale, allowing for detailed reports on product trends, replenishment information, and product visibility and display success.
#RFID tags#RFID tag manufacturers#RFID laundry tags#RFID clothing tags#RFID technology#RFID solutions#Active RFID tags#RFID readers#RFID chips
0 notes
Text
RFID Tags: Revolutionizing Identification and Tracking

In today's fast-paced world, efficiency and accuracy are paramount. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags have emerged as a game-changing technology, offering a streamlined and reliable solution for identification and tracking across a wide range of industries. These tiny tags, embedded with microchips and antennas, can store and transmit data wirelessly, enabling seamless tracking of assets, inventory, and personnel.
The Significance of RFID Tags
RFID tags have revolutionized various sectors due to their unique advantages:
Enhanced Efficiency: RFID tags eliminate the need for manual scanning or barcode reading, significantly reducing time and labor costs.
Improved Accuracy: RFID tags provide error-free identification, eliminating the potential for human error often associated with manual data entry.
Real-time Tracking: RFID tags allow for real-time tracking of assets, enabling businesses to monitor their inventory and optimize their supply chain.
Versatility: RFID tags can be attached to a wide range of objects, from clothing and electronics to livestock and vehicles, making them a versatile solution for various applications.
A World of Applications
RFID tags have permeated various industries, transforming operations and enhancing efficiency. Here are some notable examples:
Supply Chain Management: RFID tags streamline inventory management, enabling real-time tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution.
Access Control: RFID tags enable secure access control systems, granting authorized personnel access to restricted areas or buildings.
Asset Tracking: RFID tags are widely used to track valuable assets, such as medical equipment, library books, and industrial tools, preventing theft and loss.
Animal Tracking: RFID tags are employed for animal identification and tracking, providing valuable insights into livestock management, wildlife conservation, and research.
Retail: RFID tags enhance retail operations, enabling efficient inventory management, loss prevention, and personalized customer experiences.
SB Components: Your One-Stop Shop for RFID Tags
SB Components is a leading provider of high-quality RFID tags, catering to the diverse needs of businesses and individuals. Our extensive range of RFID tags includes a variety of frequencies, sizes, and functionalities to suit specific applications.
Whether you're looking to track inventory, manage access control, or enhance customer experiences, SB Components has the RFID tags that meet your requirements. Our expert team is always ready to assist you in selecting the right RFID tags for your unique needs.
Embrace the Future with RFID Technology
RFID tags have revolutionized identification and tracking, offering a powerful and versatile solution for businesses and individuals alike. As technology continues to advance, RFID tags are poised to play an even more significant role in streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and improving decision-making across industries.
To explore the vast potential of RFID tags, visit SB Components today and discover the innovative solutions that await you.
#rfid tags#rfid chip#rfid sticker#rfid nfc#rfid labels#rfid in iot#tag reader#rfid tag reader#rfid tag for car#rfid tag price#active rfid#rfid asset tracking#passive rfid tags#rfid tags for inventory#rfid decathlon#active rfid tag
0 notes
Text
What is the mechanism behind RFID hotel key cards?
In the modern hospitality industry, enhancing guest experience and operational efficiency is a core goal for every hotel manager. With advancements in technology, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) has become an essential tool in hotel management. Particularly in the application of hotel key cards, RFID technology has brought unprecedented transformations. RFID hotel key cards not only simplify the check-in and check-out processes but also provide enhanced security, significantly improving guest convenience and overall satisfaction. How does RFID technology make all this possible? What is its working principle? This is a common curiosity among hotel managers, and today, we will explore this topic.

1. The Working Principle of RFID Hotel Key Cards
Before delving into how RFID hotel key cards work, let’s briefly introduce what RFID technology is.
What is RFID Technology?
RFID technology facilitates the exchange of information between objects through radio waves. It employs a tag and a reader for contactless data transmission, eliminating the need for physical contact. Users can simply bring an RFID card close to the reading device, and data will automatically transfer to complete authorization, authentication, or operations.
RFID hotel key cards are a type of RFID tag that connects with the hotel lock system via an RFID reader installed on the door lock, enabling contactless identity authentication and unlocking functions. Each card contains a tiny embedded chip that can store encrypted data such as the guest's room number, validity period, and access permissions. When a guest approaches the door lock with their card, the RFID reader communicates with the card via electromagnetic waves, retrieves the stored information, and decides whether to unlock the door based on pre-set security rules.
How RFID Cards Interact with Hotel Lock Systems
The interaction between RFID cards and hotel lock systems is grounded in simple, efficient wireless communication. In this process, the embedded chip within the RFID card contains a unique ID number, which is decoded by the RFID reader upon receiving a signal. Here’s a breakdown of the specific workflow:
Signal Emission: When the RFID card nears the lock system, the RFID reader within the lock emits an electromagnetic signal, activating the chip in the card.
Data Transmission: The chip in the card transmits its stored ID information to the reader, which then compares this information against the hotel management system.
Authentication and Authorization: If the card information matches the records in the system and the access validation is successful, the door lock will unlock, granting the guest entrance to their room.
The contactless feature of RFID technology makes the hotel check-in process smoother and more convenient, as guests don’t have to insert the card or physically manipulate a key, significantly enhancing the overall fluidity and experience of entering the hotel room.
Additionally, RFID cards offer heightened security. Compared to traditional magnetic stripe cards, the data transmission of RFID cards employs more complex encryption algorithms, making it harder to copy or tamper with information, thus providing greater security for hotels.
Through this series of simple and efficient operations, RFID hotel key cards not only ensure guest convenience but also significantly enhance hotel operational efficiency and security.
2. Advantages of RFID Hotel Key Cards
The introduction of RFID hotel key cards offers significant advantages to hotels, enhancing not only security but also customer experience and operational efficiency.
Enhanced Security
RFID cards utilize encrypted data transmission and unique chip designs to prevent card information from being copied or hacked. They can also be configured with specific validity periods and access permissions, ensuring that rooms can only be accessed within authorized times, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized entry. Many five-star hotels have effectively improved room security and protected customer privacy through such solutions.
Improved Customer Experience
RFID cards streamline the check-in and check-out processes, allowing guests to simply hold the card near their room door to unlock it automatically. This contactless operation not only enhances convenience but also reduces the risk of contact transmission, increasing guests' peace of mind.
Cost Savings in Operations
RFID technology aids hotels in automating management tasks related to rooms and keys, minimizing human errors and wasted time. The system can monitor card usage in real time, alerting staff to lost or unauthorized use of cards promptly, which improves management efficiency and lowers operational costs.
Increased Management Flexibility and Scalability
RFID technology can seamlessly integrate with other management systems, enabling hotels to expand functionality on demand, such as automated climate control or lock management. This flexibility allows hotels to respond quickly to changing demands and easily upgrade their systems.
Enhanced Brand Image and Customer Loyalty
The use of RFID cards boosts the technological appeal of the hotel, enhancing its brand image. Additionally, through RFID cards, hotels can offer personalized services, which helps increase customer loyalty.
In summary, RFID hotel key cards provide a range of advantages that contribute to a safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable experience for both guests and hotel staff. This technology is not just a trend but a valuable asset in modern hotel management.
3. Future Development of RFID Hotel Key Cards
As technology continues to advance, the application of RFID technology in the hotel industry is expected to become more widespread and intelligent.
Smarter Integrated Systems
Future RFID systems will be more tightly integrated with other intelligent systems within hotels, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart room controls, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. Through this integration, hotels can offer more personalized services, such as automatically adjusting room temperature, lighting, and other amenities based on guest preferences, thereby enhancing the customer experience and reducing energy consumption.
Enhanced Security and Encryption Technologies
As security requirements continue to grow, future RFID hotel key cards will employ more advanced encryption technologies to ensure the safety of guests' personal information and room security. With dynamic encryption and multi-factor authentication mechanisms, RFID cards will effectively defend against various cyber attacks and forgery attempts, further strengthening the security of hotel management.
Data Analytics and Personalized Services
RFID systems will evolve beyond being simple door lock management tools. In the future, they will integrate with data analytics tools to help hotels analyze guest behavior and preferences, thereby enabling more personalized services. For example, hotels could automatically push tailored offers and services based on guests’ check-in history and spending habits, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
In summary, the future of RFID hotel key cards promises to be more intelligent, secure, and personalized, transforming the hospitality experience and paving the way for a new era in hotel management. As these technologies develop, they will not only improve operational efficiency but also create a more satisfying experience for guests.
4. RFID Hotel Key Cards: The Key to Enhanced Hotel Management Efficiency and Customer Experience
Through contactless, efficient, and secure solutions, RFID hotel key cards not only provide guests with a more convenient and safe check-in experience but also enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs for hotels.
As technology continues to advance, RFID systems will become increasingly intelligent and integrated, with a stronger focus on security and data analytics functions. Whether through integration with smart room control systems or the fusion of mobile devices with RFID cards, future RFID technology will bring even more innovative opportunities to the hospitality industry.
However, to ensure the successful deployment of RFID systems and maximize business value, choosing an appropriate RFID vendor is crucial. With over a decade of deep experience in RFID technology, many hotel managers have achieved intelligent upgrades and heightened management efficiency through our customized RFID solutions, providing guests with an unparalleled stay.
If you are interested in the RFID hotel key card system or want to know more about solutions for improving hotel management efficiency, please feel free to contact us. Our RFIDCard.com professional team is ready to provide you with free consultation and testing services to ensure you select the RFID products and systems that best meet your needs. Take action now, and let us help you offer your guests a safer, more convenient check-in experience while driving your hotel towards future success!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
An access control system regulates entry to a physical or virtual space, ensuring only authorized individuals gain admittance. Employing various mechanisms like key cards, biometrics, or passwords, it meticulously manages permissions, bolstering security and confidentiality.
This system not only safeguards against unauthorized access but also provides an audit trail, logging entry attempts and granting administrators insights into user activity. Vital across industries from corporate offices to government facilities, its versatility extends to digital realms, safeguarding data integrity and privacy. With its role evolving alongside technological advancements, access control systems remain paramount in fortifying the barriers against intrusion and upholding confidentiality.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is RFID? Definitions & How RFID Makes Inventory Smarter in 2025 – AIDC India

Introduction to RFID Technology
In the fast-paced world of modern business, technologies like RFID have transformed how we manage inventory and track assets. RFID, short for Radio Frequency Identification, uses radio waves to identify and track objects without needing direct contact. In this blog, we’ll explore RFID? Definitions, why it matters, and how it helps make inventory smarter in 2025.
What is RFID? Understanding the Basics
At its core, RFID is a technology that relies on small tags and readers to exchange data. A tag attached to an object holds information, which a reader captures and sends to a database. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags don’t need to be in a direct line of sight. This makes them incredibly useful in warehouses, retail stores, and supply chains where speed and accuracy matter.
When people search for RFID? Definitions, they often want to know the simple explanation: RFID makes it easy to track products and assets using radio waves. This straightforward idea helps save time and reduce errors in day-to-day operations.
Key RFID Definitions You Should Know
To fully understand RFID, it helps to learn a few important terms often included when people ask about RFID? Definitions:
RFID Tag: A small device attached to an item that stores data.
Reader: A device that captures data from the RFID tag.
Active Tags: Tags with their own power source, used for longer ranges.
Passive Tags: Tags without batteries that draw power from the reader’s signal.
Knowing these RFID? Definitions helps businesses choose the right equipment and setup for their needs.
How RFID Makes Inventory Management Smarter in 2025
Inventory management has always been a challenge, especially for large businesses. RFID helps simplify the process by allowing items to be tracked automatically. Instead of scanning each product manually, a reader can scan multiple RFID tags at once. This saves time and reduces the risk of human error.
In 2025, businesses are expected to rely even more on RFID to improve stock visibility, reduce losses, and make data-driven decisions. The role of RFID? Definitions in this transformation is crucial, as businesses need to know exactly what each term means to use the technology effectively.
Types of RFID Systems and Their Uses
There are several types of RFID systems, and each has unique advantages:
Low Frequency (LF): Used for short-range applications like animal tracking.
High Frequency (HF): Suitable for library systems and smart cards.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF): Ideal for warehouse inventory, logistics, and retail because of its longer range.
When learning about RFID? Definitions, it’s important to understand these types so businesses can choose the best option for their industry.
Benefits of Using RFID in Modern Business
The adoption of RFID brings many benefits:
Speed: RFID readers can scan hundreds of items quickly.
Accuracy: Reduces manual errors and improves inventory data.
Security: Makes it harder to lose track of high-value items.
Real-Time Data: Provides updated inventory information instantly.
All these benefits show why knowing RFID? Definitions matters for businesses planning to use this technology.
Why Choose RFID Solutions from AIDC India
AIDC Technologies India is known for delivering high-quality RFID solutions tailored to meet different business needs. They don’t just sell equipment; they offer expert consultation, installation, and ongoing support. Their focus is on helping businesses use RFID to become more efficient and competitive.
AIDC Technologies understands the value of clear RFID? Definitions and makes it easier for clients to implement the right system without confusion. From choosing tags to setting up readers, their team provides end-to-end support.
The Future of RFID Technology Beyond 2025
RFID is evolving to meet the demands of smarter supply chains, IoT integration, and real-time analytics. In the future, RFID will work seamlessly with cloud software, making it easier for businesses to track inventory globally.
Understanding RFID? Definitions will remain important as the technology gets more advanced. Businesses that learn these basics now will be ready to adapt to new features and innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions About RFID
Q: Do RFID tags replace barcodes? Not always. RFID often complements barcodes, adding automation to processes where barcodes alone are too slow.
Q: Are RFID systems expensive? The cost has come down over the years, making it affordable for businesses of different sizes.
Q: Can RFID work outdoors? Yes, many RFID systems are built for outdoor use, even in harsh weather.
Q: Why focus on RFID? Definitions? Clear definitions help businesses choose the right tags, readers, and software for their needs.
Conclusion: Embracing RFID for Smarter Inventory with AIDC India
RFID technology makes inventory smarter, faster, and more reliable. By learning the right RFID? Definitions, businesses can unlock new possibilities and stay ahead of the competition.
Book now with AIDC Technologies India to discover how modern RFID solutions can simplify your operations and bring greater accuracy to your inventory.
0 notes
Text
RFID Clothing Tags: Revolutionizing Apparel Retail and Inventory Management

In the fast-paced world of retail and fashion, tracking inventory, preventing theft, and streamlining checkout processes are top priorities. One game-changing technology that addresses all these challenges is RFID clothing tags. These tiny yet powerful tags are reshaping how retailers manage their apparel inventory and how customers experience shopping.
In this article, we'll explore what RFID clothing tags are, how they work, their benefits, real-world examples, and answers to frequently asked questions. If you're in the apparel business or interested in retail technology, this guide is for you.
Introduction: What Are RFID Clothing Tags?
RFID clothing tags are small, embedded devices attached to garments or apparel items that use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to store and transmit data wirelessly. Each tag contains a unique identifier that can be read remotely by an RFID scanner.
Unlike traditional barcodes, which require a direct line of sight and manual scanning, RFID clothing tags can be read from a distance—even through fabric or packaging. This capability allows for faster inventory counts, real-time stock updates, theft prevention, and a more efficient retail environment.
How Do RFID Clothing Tags Work?
To understand the power of RFID clothing tags, it helps to look at the basic working mechanism:
● RFID Tag
Attached to the garment, it contains a microchip and antenna. The chip stores data like product ID, size, color, batch number, and price.
● RFID Reader
Placed at checkout counters, store entrances, or stockrooms. It emits radio waves that activate the tags within range.
● Data Transfer
Once activated, the tag sends its data back to the reader, which relays it to the retailer’s inventory or point-of-sale (POS) system.
This real-time interaction enables retailers to know where an item is, whether it's in stock, or if it's been moved, purchased, or stolen.
Benefits of Using RFID Clothing Tags
The growing adoption of RFID clothing tags is driven by a wide range of advantages for retailers, warehouse managers, and even customers. Here are some key benefits:
1. Improved Inventory Accuracy
With RFID, you can achieve up to 99% inventory accuracy. This is a significant upgrade from the typical 60–80% accuracy with manual or barcode systems.
2. Faster Stock Counting
RFID allows scanning of hundreds of items within seconds—no need to touch or even see each tag. This reduces labor costs and speeds up restocking.
3. Enhanced Loss Prevention
RFID clothing tags can trigger alerts when items leave the store without being properly checked out, acting as an anti-theft mechanism.
4. Better Customer Experience
Real-time inventory tracking ensures that customers can easily find what they’re looking for—online and in-store.
5. Reduced Out-of-Stock Situations
Accurate, real-time data ensures faster replenishment of popular sizes and styles, minimizing lost sales.
6. Streamlined Returns and Exchanges
Retailers can quickly verify returned items using RFID, ensuring authenticity and streamlining the refund process.
Real-World Applications of RFID Clothing Tags
● Fashion Retailers
Brands like Zara, H&M, and Uniqlo have adopted RFID clothing tags to enhance inventory control and customer satisfaction. Zara, in particular, uses RFID to restock items within 24 hours of a sale.
● Department Stores
Retail giants such as Macy’s and Decathlon use RFID technology to track every piece of apparel from warehouse to checkout.
● Laundry and Uniform Services
Industrial laundries use RFID clothing tags to track uniforms, hospital scrubs, and hotel linens for efficient cleaning and delivery cycles.
● Rental Services
Businesses renting out costumes, tuxedos, or sportswear use RFID to track usage, returns, and cleaning cycles.
Types of RFID Clothing Tags
Not all RFID clothing tags are the same. They can be categorized based on form factor and application:
● Sewn-in Fabric Tags
These are durable and washable, sewn directly into garments for long-term use—perfect for uniforms and rental clothing.
● Adhesive Tags
Applied temporarily to the inside label of a garment. These are commonly used in retail environments.
● Hang Tags
These paper or plastic tags include RFID chips and can be removed after purchase. Ideal for high-end retail or promotional items.
Integration With Retail Systems
To maximize the power of RFID clothing tags, integration with backend systems is key:
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Enables seamless inventory and supply chain management.
POS (Point of Sale): Facilitates real-time updates on stock levels and customer preferences.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Helps personalize marketing and shopping experiences based on data collected via RFID.
Retailers who leverage these systems enjoy smoother operations, reduced overhead, and increased profitability.
FAQs About RFID Clothing Tags
Q1. What is an RFID clothing tag?
An RFID clothing tag is a label attached to apparel that contains a microchip and antenna, allowing it to transmit product information wirelessly to an RFID reader.
Q2. Are RFID clothing tags reusable?
Yes, some RFID tags—especially those sewn into uniforms or rental clothing—are designed for reuse and can withstand multiple washes.
Q3. Do RFID tags replace barcodes?
In many modern retail environments, yes. RFID tags offer greater efficiency and functionality, although some businesses use both for redundancy.
Q4. Are RFID clothing tags safe?
Yes, RFID clothing tags are safe. They do not contain any personal information and emit extremely low radio waves that are not harmful to humans.
Q5. Can customers remove RFID tags after purchase?
Most retail RFID tags are designed to be removed after purchase. However, sewn-in or permanent tags (used in rentals or uniforms) are meant to remain with the garment.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive retail landscape, staying ahead means embracing smarter technologies—and RFID clothing tags are at the forefront of this revolution. From improving inventory accuracy to enhancing customer experience, RFID tags offer unmatched value across the apparel supply chain.
Whether you're a retailer, a logistics partner, or a laundry service provider, integrating RFID clothing tags into your workflow can boost efficiency, reduce shrinkage, and drive customer satisfaction. As RFID technology becomes more affordable and accessible, there's never been a better time to adopt it.
0 notes
Text
RFID Market Trends, Active Key Players, and Growth Projection Up to 2031
Allied Market Research, titled, “RFID Market by Product Type, Frequency, End Use, and Region: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2022–2031," The rfid market was valued at $11.8 billion in 2021, and is estimated to reach $31.5 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2022 to 2031.
Radio frequency identification refers to a wireless system that uses radio waves technology to passively identify a tagged object, people or animal. The RFID is comprised of two components: tags and readers. The reader is an electronic gadget with one or more antennas that transmit radio waves and take in signals from RFID tags. Tags can be passive or active, using radio waves to transmit their identity and other information to adjacent readers. Moreover, the RFID has various advantages over other identification technologies such as the ability to track many things at once, the ability to identify objects without line of sight, and the capacity to store and retrieve vast amounts of data on the tag. Passive and active RFID tags are the two primary varieties. In order to transmit information, passive tags must be in close proximity to the reader, which provides all of their power. Active tags can broadcast data over greater distances and have their own power source.
The growth of RFID is majorly driven by the surge in government initiatives to boost RFID-based solutions across various industries, coupled with the growing demand for RFID products in retail sectors. Moreover, the rise in demand for RFID solutions in banking and healthcare sectors is expected to drive market growth. However, the high rise associated with data security and privacy is acting as prime restraint of the global market. On the contrary, the surge in adoption of RFID tags for industry 4.0, Internet of Things and smart manufacturing is anticipated to provide lucrative opportunities for the RFID industry during the forecast period.

According to RFID market analysis, the retail segment was the highest contributor to the market in 2021. The security & access control and retail segments collectively accounted for around 46.8% market share in 2021. Surge in prime players initiatives to develop and deploy next generation smart infrastructure solution has led the growth of the RFID market. Further, the high frequency segment is expected to emerge as the fastest growing segment of the market during the forecast period of 2022-2031.
The outbreak of COVID-19 has significantly impacted the growth of electronics solutions. The decline in growth in manufacturing solutions has significantly impacted the demand for RFID chips and tags during the pandemic. Further, the lack of availability of a professional workforce due to the partial and complete lockdown implemented by governments across the globe has restrained the growth of the RFID market during the pandemic. However, the rise in demand for industry 4.0 and Internet of Things solutions has led to the growth of power adapter solutions and is expected to drive the growth of the RFID market post-pandemic.
Region-wise, the RFID market trends are analyzed across North America (the U.S., Canada, and Mexico), Europe (UK, Germany, France, Italy, Russia, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Rest of Asia-Pacific), and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Asia-Pacific holds a significant share of the global RFID market, owing to presence of prime players in this region. Further, China holds a dominating position in RFID market, owing to rise in investment by prime players and government agencies to develop next generation portable devices solution to offer better user experience to end users which led the RFID market growth.
KEY FINDINGS OF THE STUDY
In 2021, the retail segment accounted for maximum revenue and is projected to grow at a notable CAGR of 9.1% during the forecast period.
The high frequency segment was the highest revenue contributor to the market by frequency in 2021.
The retail and security &access control segments collectively accounted for around 47.0% market share in 2021.
North America acquired a major RFID market share with an industry share of 35.5% in 2021.
The key players profiled in the Alien Technology, LLC, Avery Dennison Corporation, Bar Code India Limited, Bartech Data Systems PVT. LTD., Bartronics India Limited, Honeywell International. Inc., IDENTIV, Inc., Infotek Software & Systems Ltd. (I-TEK), NXP Semiconductor N.V., and Zebra Technologies Corporation. Market players have adopted various strategies such as product launch, collaboration, partnership, joint venture, and acquisition to expand their foothold in the RFID market size. For instance, in October 2022, Avery Dennison Smartrac launched a AD Minidose U9 RAIN RFID inlay for pharmaceutical applications, unlocking critical RFID value for healthcare, pharmacies, and laboratory asset management. AD Minidose U9 is one of the smallest products on the market to receive ARC certification (Spec S) from Auburn University’s RFID Lab, and to be approved for use by the DoseID industry consortium.
0 notes
Text
SERMAN BRANDS RFID Blocking Slim Bifold Genuine Leather Minimalist Front Pocket Wallets for Men with Money Clip Thin Mens
Price: (as of – Details) SERMAN BRANDS Genuine Leather Wallets RFID Blocking – Theft Proof Wallet- Protect Your Identity The Secret to Keeping Your Data Safe! Identity Theft is at All Time High! Unless properly shielded, your card-based data is readily available when any active reader is in range! The Best Way to Protect Your Smart Cards from unwanted capture of data from contact less cards…
#000#Adjustable dumbbells#Air fryer under $100#Air fryer under 5000#Baby stroller combo#Best mixer grinder#Best protein powder for women#Best whey protein#Bluetooth speaker#books#Budget smartwatch#Coffee maker with grinder#DSLR camera bundle#DSLR camera under 50000#Electric kettle 1.5L#Ergonomic office chair#Gaming laptop under $1#Geyser 15L BEE 5 star#Home gym equipment#Laptop for students#Luxury skincare set#Men’s leather wallet#Neckband under 2000#Robot vacuum cleaner#Skin care kit for men#Smart thermostat#Study table for home#Tactical flashlight#TWS earbuds under 1500#Waterproof Bluetooth speaker
0 notes
Text
Active RFID Reader For Fleet And Vehicle Tracking
Active RFID Reader uses powered tags that actively transmit alerts to enhance monitoring range and accuracy. Ideal for real-time asset tracking, they paintings in big regions like warehouses, hospitals, and transportation. These readers provide dependable records series, allowing green stock control, enhanced safety, and seamless operational workflows throughout industries.
0 notes
Text
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has emerged as a game-changer in industries where tracking, identification, and real-time data play pivotal roles. RFID tags have simplified and optimized processes from retail stores to hospitals by enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Today, we will discuss the world of RFID tags, their functioning, various types, and how industries across sectors leverage this technology to streamline operations.
What is RFID Technology?
RFID is Radio Frequency Identification, a wireless system for identifying and tracking objects. It works through electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and capture data from RFID tags attached to objects. These tags communicate with an RFID reader, which converts the data into usable information.
RFID technology eliminates the need for direct contact or line-of-sight scanning, which is vastly superior to traditional tracking methods like barcodes. RFID technology is most commonly used in supply chain management, inventory tracking, and identification. Whether for retail, asset management, or campus security, RFID technology is indispensable in modern business processes.
What are RFID Tags
RFID tags are small devices that contain a microchip and antenna, allowing them to communicate with an RFID reader via radio waves. The RFID reader sends out electromagnetic signals that activate the tag. Once activated, the tag transmits the stored data, which the reader captures and processes. Depending on the application, this data can include product information, location, or even security details.
How Do They Work?
There exist two primary categories of RFID tags: passive and active. Passive RFID tags do not have an internal power source and depend on the reader's electromagnetic energy to power them. They are often used for low-cost, high-volume applications like retail inventory management. Active RFID tags, on the other hand, are powered by an internal battery, allowing them to transmit data over longer distances and store more information. These are commonly used in logistics and industrial settings where higher data capacities and longer ranges are essential.
#rfid technology#rfid solutions#rfid tags#rfid reader#retail solutions#inventory management#rfid tags manufacturers#handheld scanner#active rfid tags#passive rfid tags
0 notes
Text
Active and Passive RFID Tags Market : Industry Analysis, By Key Players, Segmentation, Application, and Global Forecast to 2032
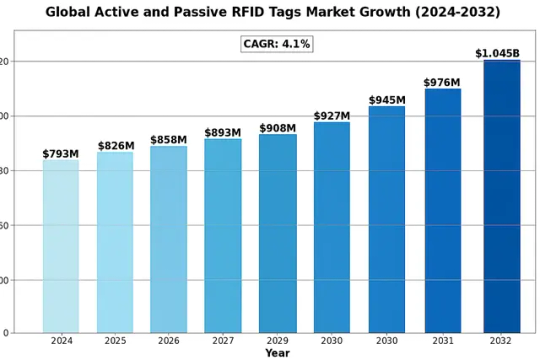
The global Active and Passive RFID Tags Market was valued at 793 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 1045 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period.
Active and passive RFID tags are key components in radio frequency identification systems. Active RFID tags are battery-powered devices that continuously transmit signals, enabling real-time tracking with extended read ranges – ideal for logistics and asset management. Passive RFID tags, which are more cost-effective and lightweight, operate by harvesting energy from reader signals, making them suitable for inventory management and access control applications. While active tags offer superior range and data transmission capabilities, their higher costs and maintenance requirements create adoption barriers in price-sensitive markets.
The market growth is driven by increasing adoption across retail, logistics, and manufacturing sectors, with passive tags dominating unit shipments due to their affordability. However, active tags are gaining traction in specialized applications requiring real-time visibility, such as healthcare equipment tracking. Recent technological advancements in battery life for active tags and improved read ranges for passive solutions are expanding potential use cases, while IoT integration is creating new growth opportunities across both segments.
Get Full Report with trend analysis, growth forecasts, and Future strategies : https://semiconductorinsight.com/report/active-and-passive-rfid-tags-market/
Segment Analysis:
By Type
Passive RFID Tags Dominate the Market Due to Cost-Effectiveness and Wide Application Flexibility
The market is segmented based on type into:
Active RFID Tags
Subtypes: Beacon tags, Transponder tags, and others
Passive RFID Tags
Subtypes: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), Ultra-High Frequency (UHF), and others
By Application
Warehousing and Logistics Segment Leads Owing to Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility Needs
The market is segmented based on application into:
Retail and Wholesale
Warehousing and Logistics
Industrial Manufacturing
Healthcare
Others
By Frequency
UHF Segment Gains Traction Due to Improved Read Range and Data Processing Capabilities
The market is segmented based on frequency into:
Low Frequency (LF)
High Frequency (HF)
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF)
By Material
Plastic Substrates Remain Preferred Choice for Most Industrial Applications
The market is segmented based on material into:
Paper
Plastic
Glass
Metal
Others
Regional Analysis: Active and Passive RFID Tags Market
North America The North American RFID market is characterized by high adoption rates across retail, healthcare, and logistics sectors, driven by advanced technological infrastructure and stringent regulatory frameworks for asset tracking. The U.S. leads the region, accounting for over 65% of regional revenue, with companies like Zebra Technologies and Honeywell dominating the competitive landscape. Demand for active RFID tags is particularly strong in supply chain management due to real-time tracking requirements. However, the higher cost of active tags compared to passive alternatives limits broader adoption in price-sensitive applications. Recent investments in Industry 4.0 and warehouse automation are accelerating market growth, with a projected CAGR of 3.9% through 2032.
Europe Europe’s market is shaped by EU-wide standardization and sustainability initiatives favoring RFID-enabled circular economy models. Germany and the U.K. are key markets, with passive tags widely used in retail inventory systems to comply with anti-counterfeiting regulations. The region shows increasing preference for UHF RFID solutions, particularly in textile tracking under the EU’s Digital Product Passport initiative. While industrial manufacturing accounts for 38% of regional RFID usage, growth faces headwinds from data privacy concerns under GDPR. Collaborative R&D projects between universities and corporations are advancing hybrid (active-passive) tag innovations for specialized applications like pharmaceuticals.
Asia-Pacific As the fastest-growing region (CAGR 5.2%), APAC’s expansion is propelled by China’s Belt & Road infrastructure projects and India’s smart city initiatives. Passive tags dominate (>70% market share) due to cost advantages in high-volume manufacturing applications. Japan leads in RFID-integrated retail, while Southeast Asian nations show surging demand for logistics tracking. Local players like Invengo challenge global brands through competitive pricing, though technology gaps persist in long-range active RFID systems. The region’s lack of unified frequency standards across countries complicates cross-border implementations despite booming intra-Asia trade.
South America Market penetration remains low but exhibits strong growth potential as Brazil and Argentina modernize supply chains. Active RFID adoption is primarily limited to mining and oil/gas asset monitoring, while passive tags see increasing use in agricultural export tracking. Economic instability has delayed large-scale RFID projects, but foreign investment in Brazilian automotive and pharmaceutical sectors is creating pockets of opportunity. The absence of localized manufacturing forces reliance on imports, inflating costs by 15-20% compared to other regions.
Middle East & Africa The MEA market is bifurcated: Gulf nations leverage active RFID for high-value asset management in aviation and construction, while African countries predominantly use low-frequency passive tags in livestock and rudimentary inventory systems. UAE’s smart city projects and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 are driving government-led RFID implementations. However, low technology awareness and fragmented distribution channels constrain growth outside urban hubs. The region shows untapped potential in RFID-based halal food traceability systems, with pilot programs underway in Malaysia and Indonesia.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Emerging Applications in Healthcare Create New Growth Avenues
The healthcare sector presents significant untapped potential for RFID solutions. Hospital asset tracking represents a $5 billion opportunity, with systems reducing equipment search times by up to 60%. Recent innovations include disposable passive RFID tags for surgical instrument tracking and active temperature monitoring for sensitive pharmaceuticals. Regulatory pressures to improve patient safety and inventory control continue to drive adoption. Successful pilot programs demonstrate 30% reductions in medication errors through RFID-enabled verification systems, showcasing the technology’s potential to transform healthcare operations.
Advancements in Chipless RFID Open New Application Possibilities
Breakthroughs in chipless RFID technology create opportunities in previously inaccessible markets. These innovative tags eliminate silicon chips, reducing costs below traditional passive solutions while maintaining adequate functionality for certain applications. Potential uses include anti-counterfeiting measures for luxury goods and mass-market retail items where conventional RFID proves cost-prohibitive. Early implementations demonstrate 40% cost reductions compared to conventional passive tags, making item-level tagging economically viable for additional product categories. This technological evolution promises to expand RFID’s addressable market substantially.
Integration with AI and Blockchain Enhances Value Proposition
Synergies between RFID and complementary technologies create significant growth opportunities. Artificial intelligence algorithms leverage RFID-generated data streams to optimize inventory management and predictive maintenance. Blockchain integration provides immutable records for supply chain provenance applications, particularly valuable in anti-counterfeiting and quality assurance initiatives. Recent partnerships between RFID providers and technology firms demonstrate the commercial viability of these combined solutions. Such integrations enable premium pricing models while addressing previously unserved market needs across multiple industries.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Technical Limitations Constrain Performance in Certain Environments
RFID systems face inherent technical constraints that challenge specific applications. Metal and liquid environments significantly degrade performance, with signal absorption and reflection causing read reliability issues. These material interactions particularly impact manufacturing and healthcare settings where metal equipment prevails. While recent advancements in antenna design and frequency selection mitigate some limitations, fundamental physics constraints persist. Developing robust solutions for challenging environments remains an ongoing engineering challenge that limits adoption in certain industrial applications.
Shortage of Skilled Implementation Specialists Slows Market Growth
The rapid expansion of RFID applications outpaces the availability of qualified implementation specialists. System deployment requires expertise spanning RF engineering, software integration, and business process redesign. This skills gap leads to implementation delays and suboptimal system configurations that undermine ROI. Training programs struggle to keep pace with technological advancements, while competition for qualified personnel increases labor costs. These human resource challenges particularly affect small and mid-sized enterprises that lack internal technical staff to oversee complex RFID deployments.
Competition from Alternative Technologies Impacts Market Share
Emerging tracking technologies present increasing competition for certain RFID applications. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and ultra-wideband (UWB) solutions offer comparable functionality in asset tracking scenarios, often with lower infrastructure requirements. While RFID maintains advantages in bulk reading and cost-per-tag metrics, intensifying competition pressures pricing and necessitates continuous innovation. Technology selection increasingly depends on specific use case requirements, requiring suppliers to clearly articulate their solutions’ differentiated value across diverse application scenarios.
ACTIVE AND PASSIVE RFID TAGS MARKET TRENDS
Rising Demand for Supply Chain Optimization Fuels RFID Adoption
The global Active and Passive RFID Tags market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient supply chain management across retail, logistics, and manufacturing sectors. With the market valued at 793 million in 2024 and projected to reach 1,045 million by 2032, organizations are leveraging RFID technology to enhance inventory accuracy and operational visibility. Passive RFID tags dominate 65-70% of the current market share due to their cost-effectiveness in large-scale deployments like item-level tagging. Meanwhile, active RFID solutions are gaining traction in asset tracking applications, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%, outpacing the overall market growth. Recent advancements in hybrid RFID systems that combine both technologies are creating new opportunities for real-time monitoring in complex logistics environments.
Other Trends
Integration with IoT and AI Platforms
The convergence of RFID with IoT ecosystems is transforming traditional tracking systems into intelligent networks. Nearly 40% of new RFID deployments now incorporate cloud-based analytics, enabling predictive maintenance and automated replenishment. AI-powered RFID readers can now process tag data 50% faster while reducing false reads by 30%, significantly improving inventory accuracy in retail environments. Major retailers have reported 15-20% reduction in out-of-stock instances through AI-enhanced RFID systems.
Sustainability and Miniaturization Drive Product Innovation
Environmental considerations are reshaping RFID tag production, with manufacturers introducing biodegradable substrate materials that maintain performance while reducing e-waste. The latest passive tags now weigh under 0.5 grams and can be embedded directly into products during manufacturing. Meanwhile, active tag batteries have seen 35% improvements in lifespan, addressing a key pain point for industrial users. This miniaturization trend is particularly impactful in healthcare, where RFID-enabled smart labels track pharmaceuticals and medical devices throughout the cold chain without compromising sterility or adding bulk. The healthcare RFID segment is projected to grow at 6.2% CAGR through 2030, supported by stringent regulatory requirements for asset visibility.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Key Industry Players
Market Leaders Drive Innovation Amid Growing RFID Adoption
The competitive landscape of the global Active and Passive RFID Tags market remains fragmented, with established technology providers competing alongside specialized RFID solution developers. Zebra Technologies has emerged as a dominant force, capturing approximately 18% market share in 2024 due to its comprehensive portfolio of enterprise-grade RFID solutions and strategic acquisitions. The company’s recent partnership with Microsoft to integrate RFID tracking into Azure IoT platforms exemplifies its innovation strategy.
Honeywell and Avery Dennison collectively account for nearly 25% of the market, leveraging their expertise in industrial automation and labeling solutions respectively. Honeywell’s acquisition of RFID middleware provider Movilizer in 2023 significantly strengthened its position in logistics automation, while Avery Dennison’s Smartrac division continues to dominate the retail RFID sector with its breakthrough dual-frequency tags.
Mid-tier players are gaining traction through specialized offerings – Alien Technology leads in high-memory passive tags for supply chain applications, whereas HID Global maintains stronghold in secure access control solutions. Meanwhile, Asian manufacturers like Invengo and Tatwah Smartech are disrupting the market with cost-competitive offerings, particularly in the passive RFID segment where price sensitivity remains high.
The competitive intensity is further heightened by continuous technological advancements. Recent developments include Zebra’s launch of ultra-wideband (UWB) active tags with 10-year battery life and Alien Technology’s introduction of environmentally-resistant passive tags for harsh industrial environments. Such innovations are reshaping competitive dynamics as companies strive to differentiate their offerings beyond basic tracking capabilities.
List of Key Active and Passive RFID Tags Companies Profiled
Zebra Technologies Corporation (U.S.)
Honeywell International Inc. (U.S.)
SATO Holdings Corporation (Japan)
TSC Printronix Auto ID (Taiwan)
Avery Dennison Corporation (U.S.)
Beontag (Brazil)
Metalcraft (U.S.)
Alien Technology, LLC (U.S.)
MPI Label Systems (U.S.)
Invengo Technology (China)
HID Global Corporation (U.S.)
GAO RFID (Canada)
The Tag Factory (U.K.)
Xindeco IOT (China)
Tatwah Smartech (China)
Learn more about Competitive Analysis, and Forecast of Global Active and Passive RFID Tags Market : https://semiconductorinsight.com/download-sample-report/?product_id=103579
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
What is the current market size of Global Active and Passive RFID Tags Market?
-> Active and Passive RFID Tags Market was valued at 793 million in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 1045 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period.
Which key companies operate in this market?
-> Major players include Zebra Technologies, Honeywell, Avery Dennison, Alien Technology, HID Global, and Invengo, collectively holding over 45% market share.
What are the key growth drivers?
-> Primary drivers include rising e-commerce logistics demands, Industry 4.0 adoption, and retail inventory automation needs, with the logistics sector accounting for 32% of total RFID deployments.
Which region dominates the market?
-> North America currently leads in adoption (38% share), while Asia-Pacific exhibits the highest growth rate (6.2% CAGR) driven by manufacturing expansion in China and India.
What are the emerging trends?
-> Emerging trends include hybrid RFID solutions, blockchain integration for supply chains, and development of eco-friendly RFID tags to address sustainability concerns.
Browse Related Research Reports :
CONTACT US:
City vista, 203A, Fountain Road, Ashoka Nagar, Kharadi, Pune, Maharashtra 411014 +91 8087992013 [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Vehicle Parking Management System: Revolutionizing Urban Mobility
In the bustling environments of modern cities, managing the ever-increasing number of vehicles has become a daunting task. With limited parking space and an increasing number of vehicles on the road, the need for an efficient, intelligent, and scalable Vehicle Parking Management System (VPMS) has never been greater. This system offers a structured approach to the planning, monitoring, and execution of parking activities, reducing chaos and optimizing space usage.
This blog explores the concept, components, types, technologies, benefits, challenges, and future scope of Vehicle Parking Management Systems.
Introduction to Vehicle Parking Management Systems
A Vehicle Parking Management System is a comprehensive solution that automates and optimizes the management of parking facilities. It helps manage parking lots or garages more efficiently, enhances user convenience, reduces environmental impact, and increases revenue for facility owners.
VPMS combines hardware components such as sensors, gates, ticket dispensers, and cameras with software tools like mobile apps, analytics platforms, and control dashboards. Together, they create a smart system capable of real-time monitoring and decision-making.
Why Do We Need a Parking Management System?
The global population is urbanizing rapidly. With urbanization comes an increase in personal and commercial vehicles. However, city infrastructure, especially parking, hasn't grown at the same pace. As a result, cities are grappling with:
Traffic congestion due to vehicles searching for parking spots.
Wasted fuel and time during the search for available parking.
Increased air pollution from idling vehicles.
Security concerns in unmanaged parking areas.
Inefficiencies in revenue collection and enforcement.
A Vehicle Parking Management System addresses these issues by streamlining parking operations and making them more predictable and user-friendly.
Components of a Parking Management System
A robust VPMS includes both hardware and software components that work in synergy:
1. Hardware Components
Entrance/Exit Gates: Automated barriers controlled by software for access control.
License Plate Recognition (LPR) Cameras: Capture and recognize vehicle plates for entry/exit logging.
RFID/Bluetooth Readers: Used for automatic vehicle identification.
Ticket Dispensers or QR Code Scanners: For visitor entry, payment, and tracking.
Sensors: Ground or overhead sensors detect whether a spot is occupied.
Display Panels: Guide users to available parking spaces.
2. Software Components
User App/Web Portal: Enables users to check availability, reserve spots, make payments, and receive notifications.
Admin Dashboard: Allows facility managers to monitor usage, collect payments, and enforce rules.
Analytics Engine: Provides reports on usage, trends, and financials.
Payment Gateway Integration: Supports various payment modes, including cards, digital wallets, and UPI.
Types of Parking Management Systems
Parking management systems can be categorized based on operation mode, technology, and scale.
A. Based on Operation Mode
1. Manual Parking Systems
Rely on human staff for managing parking entries and exits.
Prone to errors and inefficiencies.
2. Semi-Automated Systems
Use ticketing machines and partial software integration.
Still requires human oversight but is more efficient than manual systems.
3. Fully Automated Systems
Uses sensors, ANPR, mobile apps, and automatic gates.
Requires minimal human intervention.
B. Based on Technology
1. Smart Parking Systems
Use IoT, AI, and cloud computing for real-time parking data and decision-making.
Suitable for smart cities and urban centers.
2. Mechanical/Automated Car Parking Systems
Multi-level or robotic systems that park cars using mechanical lifts.
Saves space but is expensive to implement.
How Does a Vehicle Parking Management System Work?
Here's a simplified flow of how a VPMS typically functions:
Entry Detection: When a vehicle approaches, ANPR or RFID systems detect the vehicle.
Availability Check: The system checks if there are available spots.
User Authentication: For registered users, the system grants access automatically. For visitors, it issues a ticket or QR code.
Parking Guidance: The user is directed to an available spot via digital signage.
Payment: Payment can be made upfront, during parking, or at the exit via mobile app or kiosks.
Exit Processing: The system checks for payment and releases the gate.
Data Logging: All activities are logged for auditing, analytics, and reporting.
Technologies Behind Modern Parking Management Systems
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT-enabled sensors help detect vehicle presence in parking slots and transmit data in real-time to the management system.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
AI algorithms optimize space allocation, predict peak hours, and suggest dynamic pricing models based on demand.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud infrastructure allows centralized control and access from anywhere, facilitating data storage, analytics, and integration with other smart city systems.
4. Mobile Apps & Web Portals
Mobile platforms enhance user experience by offering real-time updates, navigation assistance, and cashless payments.
5. Big Data Analytics
Data collected from sensors, cameras, and user interactions is analyzed to provide insights for better decision-making.
6. Blockchain (Emerging Tech)
Some systems use blockchain for secure, transparent, and decentralized parking transactions.
Benefits of Vehicle Parking Management Systems
1. Enhanced User Convenience
Real-time availability display.
Cashless, fast payments.
Reduced time to find parking.
2. Operational Efficiency
Automated logging and reporting.
Reduced dependency on human staff.
Lower operational costs.
3. Revenue Optimization
Transparent billing.
Prevention of revenue leakage.
Dynamic pricing based on demand.
4. Improved Security
ANPR and CCTV ensure proper logging of entries and exits.
Prevents theft and unauthorized parking.
5. Environmental Benefits
Reduces emissions from idling vehicles.
Encourages eco-friendly transport planning.
Challenges in Implementing Parking Management Systems
While VPMS offers numerous benefits, it comes with its share of challenges:
1. High Initial Cost
Advanced systems require a significant upfront investment in infrastructure and technology.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating VPMS with older municipal or private infrastructure can be technically challenging.
3. User Adoption
Some users may resist using digital systems due to unfamiliarity or lack of trust in technology.
4. Maintenance
Sensors and hardware need regular calibration and maintenance to ensure accurate readings.
5. Data Security
With personal and vehicle data being collected, ensuring privacy and data protection is crucial.
Use Cases and Applications
1. Shopping Malls and Commercial Complexes
Streamline visitor parking, offer VIP or reserved spots, and integrate loyalty programs.
2. Airports and Railway Stations
Manage long-term and short-term parking, support multi-level facilities, and integrate with transport schedules.
3. Residential Societies
Ensure only authorized residents and guests can park, and reduce internal disputes.
4. Hospitals
Provide quick access to emergency vehicles and ensure optimized use of limited space.
5. Smart Cities
Integrate parking management with traffic control, public transport, and urban planning systems.
The Future of Parking Management
The future of VPMS is closely tied to the evolution of smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and sustainable transport systems.
1. Integration with Autonomous Vehicles
Future parking systems will need to accommodate self-driving cars, which can self-park and communicate with VPMS directly.
2. Dynamic Pricing Models
Similar to surge pricing in ride-hailing apps, parking costs can vary based on demand, time, and location.
3. Green Parking Initiatives
VPMS will support electric vehicle (EV) charging, bicycle parking, and incentivize carpooling or low-emission vehicles.
4. Blockchain and Decentralization
For high-security environments, blockchain may provide transparent records of parking activities.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) Navigation
AR-based parking apps could guide drivers to free spots visually using smartphone cameras or car HUDs.
Conclusion
In an era where every inch of urban space is precious, Vehicle Parking Management Systems are not just a luxury—they are a necessity. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, VPMS can transform how we think about urban mobility, reduce traffic congestion, increase safety, and promote sustainable development.
For city planners, business owners, and technology providers, investing in an intelligent parking management solution is a step toward smarter and more efficient cities. As we look ahead, the evolution of parking systems will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation and urban living.
0 notes
Text
Poxo RFID Tag Solutions: Making Automation Smarter
In a digitally driven, connected world, automation is a necessity, not an option. Businesses, organizations, and agencies are rapidly transitioning to smarter, more efficient systems to provide the most important factors of accuracy, speed, and security. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is driving this revolution, and there is a company that is enabling organizations to transform without difficulty — Poxo.
Poxo RFID tag technology is helping organizations in multiple industries reimagine how assets are tracked, managed, and monitored. For instance, whether it be a library with thousands of books, a distribution center capturing the movements of high-value items, or a healthcare organization assessing the availability of devices, RFID technology has made automation not only smarter but much more accurate and dependable. And it all starts with one very powerful tool: the RFID tag.
RFID tags are small electronic chips with unique identification data embedded in them. Unlike typical barcodes that require line-of-site scanning, RFID tags can be scanned without contact, and at some distance and barriers, which is helpful in dynamic environments when an advantage is needed and immediacy is important.. Poxo has two types of RFID tags: passive tags, active tags, and semi-passive tags, depending on the needs of the clients.
One of the strongest demonstrations of the impact of Poxo is in library management systems. Libraries that employ Poxo’s RFID solutions eliminate the need for manual check-in and barcode scanning. RFID-integrated books simply get scanned automatically, with self-service kiosks and book drops. The database is updated instantaneously, resulting in faster circulation, less staff workload, and ease and simplicity for the user. The intelligent gates at the entrance guarantee that nothing unchecked goes out of the library, drastically minimizing losses and overall security enhancement.
In logistics and warehousing, Poxo’s RFID tags provide immediate visibility of assets. That translates to inventory audits that used to take days now being accomplished within hours or minutes. RFID tags on every item talk to fixed or mobile readers to deliver accurate location and status reports. Companies can monitor stock levels, movement patterns, and even possible bottlenecks, helping them make informed decisions and lower operational costs.
Healthcare is also one sector that highly benefits from RFID automation. Poxo’s RFID tags are applicable for tracking hospital equipment, drug inventories, as well as tracking patient records with very little manual intervention. Not only does this enhance efficiency, but it also enhances patient safety and minimizes the possibility of human error.
What distinguishes Poxo is its focus on delivering turnkey RFID automation solutions. In addition to offering the tags themselves, Poxo provides complete support in the form of RFID readers, antennas, system integration, and real-time dashboard monitoring. The solutions are scalable — be it a small community library or a multi-site industrial warehouse — and they provide for smooth implementation with ongoing technical support.
Security is one more field in which Poxo’s RFID technology excels. RFID tags can be encrypted and programmed to sound an alarm if touched, modified, or accessed inappropriately. This makes them perfect for organizations that have high need for confidentiality and asset protection.
Essentially, RFID tags are the cornerstones of a larger automation ecosystem. By capturing data and sending it wirelessly and precisely, they create quicker transactions, smarter insights, and effortless control. Poxo’s smart deployment of this technology makes it possible for any organization, small or large, to become future-ready.
Automation need not be complicated. With Poxo’s RFID tag solutions, it can become intuitive, smart, and highly efficient. As the world keeps accepting digital transformation, Poxo is poised to enable businesses to achieve their objectives in today’s world.
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI-Powered Solutions for School Bus Safety and Monitoring
youtube
Advancements in CCTV technology have transformed school buses from simple transportation vehicles into highly secure systems equipped with advanced safety features like MDVR and camera monitoring systems. Key requirements for school bus safety include location-based tracking, attendance verification, and real-time video surveillance of both the interior and exterior of the vehicle, addressing risks related to driver and student behavior during transit. To enhance safety, educational institutions are increasingly integrating cutting-edge technologies, such as AI, into school buses to protect both drivers and students.

ICARVISIONS, a leading Chinese manufacturer of vehicle surveillance solutions like Mobile DVR, MNVR, and telematics platforms, has over a decade of expertise in the industry. Understanding the critical importance of school bus safety for parents and stakeholders, we’ve introduced the JH4AN-HD, an advanced “all-in-one” product integrating AI technology to significantly enhance driving safety.

1. The functions of the mobile DVR surveillance solution for school bus:
The comprehensive system includes an MDVR with integrated AI for video analysis, streaming, and storage, paired with an ADAS camera for road monitoring, a DSM camera for driver behavior tracking, a rearview camera for the school bus’s rear, an interior camera for cabin surveillance, an in-cab camera for driver area monitoring, a panic button, and an RFID reader for student attendance tracking. This next-generation product, still in development, will include additional features in the future.

2. The main features of the mobile DVR surveillance solution for school bus:
AI:
DSM ( JA-MC921 ):
Yawning Detection
Eyes Closing Detection
Smoking Detection
Making Phone Calls Detection
Distraction Detection
Driver Absence Detection
Camera Covered Detection
Wearing Glasses Detection
ADAS ( JA-MC920 ):
Lane Departure Warning
Safe Distance Warning
Forward Collision Warning
Pedestrian Collision Warning
BSD (Optional):
Support 2 channels Blind Spot Detection cameras (front / right / left)
360° Panoramic Viewing System (Optional):
Install with 4 specific cameras (front, back, left, right)
Video-Input: support 2 channels 1080P AHD (DSM & ADAS) + 2 channels 1080P AHD /960P AHD /720P AHD /960H /D1 /CIF + 1 channel IPC (720P /1080P) Video input
Video Output: 3 Channels (Front Panel 3.5mm Jack, Rear Panel on 24pin I/O Port & VGA 1080P)
Audio Input: 4 Channels
Audio Output: 2 Channels (Front Panel 3.5mm Jack, Rear Panel on 24pin I/O Port)
Alarm Input: 8 Channels, Select Trigger for either less than 1VDC or greater than 5VDC
Alarm Output: 1 Channel, 12V output
Storage: Up to 2TB HDD/SSD and 1 SD card for backup(at 3G/4G/WIFI model option)
Internal G-Sensor + Gyroscope, with GPS, 4G FDD and Wi-Fi (5.8 GHz)
Anti-Vibration and Anti-Shock under acceleration of 40G (MIL-STD-810G standard)
Hard drive automatic heating start-up in cold weather
On-board UPS 8 seconds delay power-off for data protection
Operating temperature -40℃~80℃
8V-36V wide voltage power supply
3. The working theory of the mobile DVR surveillance solution for school bus:
The ADAS camera proactively warns the driver of potential collisions, significantly reducing the risk of severe traffic accidents. The DSM camera monitors the driver’s fatigue and distraction in real-time by analyzing facial expressions, issuing timely alerts to maintain focus. Powered by our independently developed, world-class visual recognition algorithm, the system ensures precise and dependable performance.
When the ADAS camera detects risks like imminent collisions, close vehicle proximity, or unintended lane departure, it alerts the driver with a warning tone to take immediate action. Similarly, the DSM camera identifies behaviors such as fatigue, distraction, smoking, or phone use, prompting corrective measures.
Upon activation of ADAS or DSM alerts, the system sends data to the Intelligent Vehicle Monitoring Management Platform (IVMS). By analyzing driver behavior data, it helps lower accident rates, boosts school bus operational efficiency, and reduces the workload of educational oversight bodies.
Our mission: ensure the SAFETY of school children and provide PEACE OF MIND for parents and schools.
Sourse:
ICARVISIONS WEB
1 note
·
View note