#Constructor in java
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Preventing Application Crashes: An Overview of Exception Handling in Java
Java development frameworks’ robust and versatile nature creates a requirement for developing applications without interruptions. Users operating within a system exhibit dissatisfaction, resulting in the loss of essential data and negative word-of-mouth releases about the product following an unanticipated shutdown or crash. Java application reliability and resilience depend on mastering the Java exception handling principles. Click to read the complete guide
#python tuple#bca course subjects#Encapsulation in Java#Constructor in java#Python tuple#Polymorphism in Java
0 notes
Text

What are autoboxing and unboxing? . . . . For more questions about Java https://bit.ly/3kw8py6 Check the above link
#wrapperclass#boxing#unboxing#objectcloning#serialization#externalizable#IOstream#finalize#runtimeclass#anonymousinnerclass#localinnerclass#memberinnerclass#interface#garbagecollector#polymorphism#java#constructor#thiskeyword#computersciencemajor#javatpoint
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i have been vaguely considering making a minecraft mod, but every time i think about the specifics of it i remember how intensely java-brained forge was back in the days and i'm like "how likely is it that any of the 4 competing modloaders have actually made themselves less java brained in the past uhhh seven years" and i don't really want to dig in
also b/c i'm using an outdated version of ubuntu i'd have to do a complete system reinstall to get access to apt back and be able to set up a java development environment
(when i say 'java brained' the specific thing i'm thinking of was to register blocks you had to provide a class for it to autoinstance. you could not provide, you know, an object that was an instance of the block-provididing class, you had to make a singleton class. just the classic java thing of instead of having classes with parameters which you create specific instances of, you have classes that have derived classes that are only ever expected to be instanced with a blank constructor b/c all the specific object data is in the class definition instead of being able to be specified on the object level. the classic 'we don't have first-class functions so it's impossible to vary a function callback' java thing, & it was enshrined into forgemodloader at the most basic level.)
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was a Java noob
At one time, every user was a newbie. Facebook recently reminded me of something I wrote 11 years ago today, when I was learning Java:
I'm still trying to wrap my mind around the notion that Java (apparently) implements write-once semantics for references and primitive types but lacks read-only semantics for methods or objects. I'm also wishing Java collections provided a copy constructor for iterators. Despite these flaws, its advantages over C++ are stark.
Looking back, here are my reactions:
In Java, the natural way to implement read-only semantics for methods and objects is to define a read-only interface. This is what the JOML library does, for instance. For each mutable class (Matrix4f, Quaternionf, Vector3d) it defines an interface (Matrix4fc, Quaternionfc, Vector3dc) with read-only semantics. I wish I'd known that trick in 2012.
Some of Java's advantages are historical. Gosling in 1995 foresaw the importance of threads and URLs, so he built them into the language. Stoustrup in 1982 did not foresee their importance. (Believe it or not, URLs weren't invented until 1994!)
Some of Java's advantages are because it didn't try as hard to maintain compatibility with C. For instance, Stoustrup was doubtless aware of the portability headaches in C, such as "int" having different limits on different architectures, but it seemed more important to be able to re-use existing C code in C++ than to fix fundamental flaws in the language.
Not sure why I wanted a copy constructor for iterators. Nowadays I rarely use iterators directly, thanks to the "enhanced for loop" added in Java SE 5. That feature was 8 years old when I learned Java. Not sure why I wasn't using it.
I love Java even more than I did in 2012. Nowadays I dread working in C/C++
#programming languages#java#computing history#c++ language#c++#facebook#software development#newbie#coding
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Implement PriorityQueue through Comparator in Java

Prerequisite : Priority Queue, Comparator Priority Queue is like a regular queue, but each element has a “priority” associated with it. In a priority queue, an element with high priority is served before an element with low priority. For this, it uses a comparison function which imposes a total ordering of the elements. The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to their natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is used Constructors : public PriorityQueue() : This creates a PriorityQueue with the default initial capacity (11) that orders its elements […]
0 notes
Text
Kiểm Soát Quyền Truy Cập trong Java | Tìm Hiểu và Ứng Dụng
Kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java là một khái niệm quan trọng giúp các lập trình viên quản lý mức độ truy cập vào các thành phần của lớp như thuộc tính, phương thức, hoặc hàm tạo. Việc áp dụng đúng kiểm soát quyền truy cập không chỉ tăng tính bảo mật mà còn đảm bảo tính đóng gói (encapsulation) trong lập trình hướng đối tượng. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu chi tiết về các loại bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập (access modifiers) trong Java, cách sử dụng chúng, và vai trò của chúng trong việc phát triển phần mềm.

Kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java
Kiểm Soát Quyền Truy Cập trong Java Là Gì?
Kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java đề cập đến việc sử dụng các bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập (access modifiers) để giới hạn hoặc cho phép truy cập vào các thành phần của một lớp. Java cung cấp bốn loại bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập chính:
public: Thành phần được khai báo là public có thể được truy cập từ bất kỳ đâu, không có giới hạn.
protected: Thành phần protected có thể được truy cập trong cùng một gói (package) hoặc trong các lớp con (subclass), kể cả ở gói khác.
default (package-private): Nếu không khai báo bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập, thành phần sẽ có phạm vi default, chỉ có thể truy cập trong cùng một gói.
private: Thành phần private chỉ có thể được truy cập bên trong cùng một lớp.
Việc sử dụng đúng các bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập giúp bảo vệ dữ liệu, tránh việc sửa đổi không mong muốn và tăng tính tái sử dụng mã nguồn.
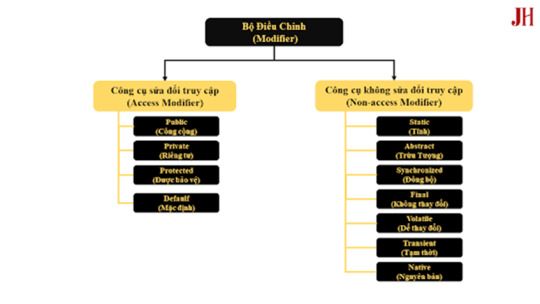
Ảnh mô tả các bộ điều chỉnh (Modifier) trong java.
Các Loại Bộ Điều Chỉnh Quyền Truy Cập trong Java
1. public
Bộ điều chỉnh public cho phép truy cập không giới hạn. Bất kỳ lớp, phương thức, hoặc thuộc tính nào được khai báo là public đều có thể được sử dụng từ bất kỳ đâu trong chương trình.
Ví dụ:
public class Example {
public int publicVariable = 10;
public void publicMethod() {
System.out.println("Đây là phương thức public");
}
}
Trong ví dụ trên, cả publicVariable và publicMethod() đều có thể được truy cập từ bất kỳ lớp nào khác.
2. protected
Bộ điều chỉnh protected giới hạn truy cập trong cùng một gói hoặc trong các lớp con. Điều này rất hữu ích khi bạn muốn chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các lớp liên quan mà không để lộ ra ngoài.
Ví dụ:
package mypackage;
public class Parent {
protected String protectedVariable = "Dữ liệu protected";
protected void protectedMethod() {
System.out.println("Đây là phương thức protected");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
void accessProtected() {
System.out.println(protectedVariable); // Có thể truy cập
}
}
3. default
Nếu không khai báo bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập, Java sẽ áp dụng phạm vi default. Các thành phần default chỉ có thể được truy cập trong cùng một gói.
Ví dụ:
package mypackage;
class DefaultExample {
int defaultVariable = 20;
void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("Đây là phương thức default");
}
}
4. private
Bộ điều chỉnh private là mức độ giới hạn cao nhất, chỉ cho phép truy cập bên trong cùng một lớp. Các thuộc tính hoặc phương thức private thường được sử dụng để ẩn dữ liệu và chỉ cho phép truy cập thông qua các phương thức getter/setter.
Ví dụ:
public class PrivateExample {
private int privateVariable = 30;
public int getPrivateVariable() {
return privateVariable;
}
public void setPrivateVariable(int value) {
this.privateVariable = value;
}
}
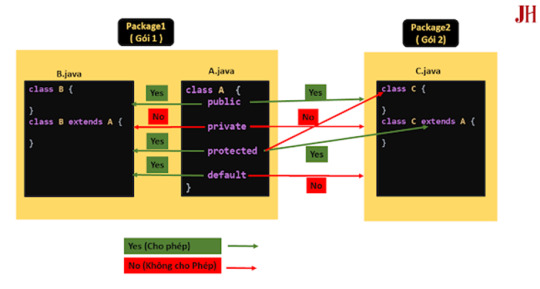
Ảnh mô tả khả năng truy cập của bốn loại Access Modifiers trong java.
Bảng mô tả phạm vi áp dụng của từng từ khóa cho các thành phần (lớp,biến, phương thức,constructor) như sau:
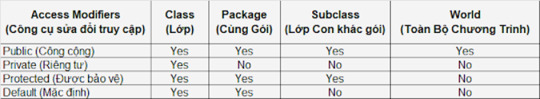
Tại Sao Kiểm Soát Quyền Truy Cập Quan Trọng?
Kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java đóng vai trò quan trọng trong:
Tăng tính bảo mật: Bằng cách sử dụng private, bạn có thể ẩn dữ liệu nhạy cảm, chẳng hạn như mật khẩu hoặc thông tin cá nhân.
Đóng gói (Encapsulation): Kiểm soát quyền truy cập giúp bảo vệ dữ liệu khỏi bị sửa đổi trực tiếp, chỉ cho phép thay đổi thông qua các phương thức được kiểm soát.
Tăng khả năng tái sử dụng: Các thành phần public hoặc protected có thể được sử dụng lại trong các dự án khác mà không làm lộ logic nội bộ.
Dễ dàng bảo trì: Việc giới hạn quyền truy cập giúp giảm sự phụ thuộc giữa các lớp, làm cho mã nguồn dễ bảo trì hơn.
Ứng Dụng Thực Tế của Kiểm Soát Quyền Truy Cập
Trong các dự án thực tế, kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java được sử dụng rộng rãi. Ví dụ:
Ứng dụng ngân hàng: Các thuộc tính như số dư tài khoản thường được khai báo private, chỉ có thể truy cập thông qua các phương thức public như deposit() hoặc withdraw().
Thư viện phần mềm: Các phương thức public trong thư viện cho phép người dùng tương tác, trong khi logic nội bộ được ẩn bằng private hoặc protected.
Ứng dụng web: Các lớp xử lý dữ liệu người dùng thường sử dụng private để bảo vệ thông tin nhạy cảm.
Một Số Lưu Ý Khi Sử Dụng Kiểm Soát Quyền Truy Cập
Hạn chế sử dụng public: Chỉ sử dụng public khi thực sự cần thiết để tránh làm lộ dữ liệu hoặc logic không cần thiết.
Ưu tiên private cho thuộc tính: Các thuộc tính của lớp nên được khai báo private và cung cấp getter/setter để kiểm soát truy cập.
Sử dụng protected hợp lý: Chỉ sử dụng protected khi cần chia sẻ dữ liệu với các lớp con, tránh lạm dụng gây phức tạp mã nguồn.
Kiểm tra phạm vi gói: Khi sử dụng default, hãy đảm bảo các lớp liên quan nằm trong cùng một gói.
Kết Luận
Kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java là một công cụ mạnh mẽ giúp lập trình viên quản lý hiệu quả các thành phần của lớp, đảm bảo tính bảo mật và đóng gói. Bằng cách sử dụng đúng các bộ điều chỉnh quyền truy cập như public, protected, default, và private, bạn có thể xây dựng các ứng dụng an toàn, dễ bảo trì và có khả năng mở rộng cao. Hy vọng bài viết này đã cung cấp cho bạn cái nhìn tổng quan và chi tiết về kiểm soát quyền truy cập trong Java, cùng với các ví dụ thực tế để áp dụng vào dự án của mình.
Nếu bạn muốn tìm hiểu thêm về lập trình Java hoặc các khái niệm liên quan, hãy tiếp tục theo dõi các bài viết của chúng tôi!
Tìm hiểu cách Java kiểm soát quyền truy cập với các mức độ như private, default, protected và public. Làm chủ Access Control để viết mã an toàn và dễ bảo trì hơn. 🌐 Xem thêm tại: Java Highlight | Website Học Lập Trình Java | Blogs Java
0 notes
Text
JAVA OOP 1 ASSIGNMENT 2: COMPLEX NUMBERS
Write a class that defines an object for a complex number. Your class will have a constructor that accpets two floats as input arguments. The two floats will represent the a and b parts of the complex number. Write a tester program to test your complex number class. It will be a class with a single main method in it. In that main method, you will create complex number objects, add,…
0 notes
Text
Java ppreciation post
A lot of people like to shit on java because "ohhh public static void main object oriented factory boilerplate JVM is slow lmao" but I'd like to say that most of that stuff isn't true!
Most modern IDEs/coding text editors make writing java a lot easier, and can help to reduce that boilerplate! For instance: in IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition, you can just type "psvm" and it will expand into "public static void main(String[] args)"! You can also easily generate constructors, getters, and setters really easily.
Java has a lot of support for a lot of things. I want a package that can split PDFs into pages? Apache PDFBox. Want a full MVC web app? Spring framework. Want to make your Java code much cleaner? Lombok. JSON parsing? Jackson or Gson gets the job done.
Java is Statically Typed. God, I love static typing. It makes issues easier to detect at compile-time.
the JVM isn't that slow, actually. While it does take some time to start up, it's quite fast once it's in steady state (the time the actual java bytecode is running.) GraalVM allows this to be even faster, by compiling the Java into native code.
I heart Java and you should too!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Java Is Still the King in 2025—and How Cyberinfomines Makes You Job-Ready with It

1. Java in 2025: Still Relevant, Still Dominating Despite the rise of new languages like Python, Go, and Rust, Java is far from dead—it’s actually thriving.
In 2025, Java powers:
40%+ of enterprise backend systems
90% of Android apps
Global banking & fintech infrastructures
E-commerce giants like Amazon, Flipkart & Alibaba
Microservices and cloud-native platforms using Spring Boot
Java is reliable, scalable, and highly in demand. But just learning syntax won’t get you hired. You need hands-on experience, framework expertise, and the ability to solve real-world problems.
That’s exactly what Cyberinfomines delivers.
2. The Problem: Why Most Java Learners Don’t Get Jobs Many students learn Java but still fail to land jobs. Why?
❌ They focus only on theory ❌ They memorize code, don’t build projects ❌ No real understanding of frameworks like Spring Boot ❌ Can’t explain their code in interviews ❌ Lack of problem-solving or debugging skills
That’s where Cyberinfomines’ Training changes the game—we teach Java like it’s used in real companies.
3. How Cyberinfomines Bridges the Gap At Cyberinfomines, we:
✅ Teach Core + Advanced Java with daily coding tasks ✅ Use real-world problem statements (not academic ones) ✅ Give exposure to tools like IntelliJ, Git, Maven ✅ Build full-stack projects using Spring Boot + MySQL ✅ Run mock interviews and HR prep ✅ Help you create a Java portfolio for recruiters
And yes—placement support is part of the package.
4. Java Course Curriculum: Built for the Real World Core Java
Data types, loops, arrays, OOP principles
Exception handling, packages, constructors
File handling & multithreading
Classes vs Interfaces
String manipulation & memory management
Advanced Java
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Servlet Lifecycle
JSP (Java Server Pages)
HTTP Requests & Responses
MVC Design Pattern
Spring Framework + Spring Boot
Dependency Injection & Beans
Spring Data JPA
RESTful API Creation
Security & authentication
Connecting with front-end apps (React/Angular)
Tools Covered
IntelliJ IDEA
Eclipse
Postman
Git & GitHub
MySQL & Hibernate
Live Projects
Library Management System
Employee Leave Tracker
E-Commerce REST API
Blog App with full CRUD
Interview Preparation
DSA using Java
Java-based coding problems
100+ mock interview questions
HR round preparation
Resume writing workshops
5. Who Should Learn Java in 2025? You should choose Java if you are:
A fresher who wants a strong foundation
A non-tech graduate looking to switch to IT
A teacher/trainer who wants to upskill
A professional aiming for backend roles
Someone interested in Android development
A student looking to crack placement drives or government IT jobs
6. Real Success Stories from Our Java Learners
Amit (BSc Graduate) – Now working as a Java backend developer at an IT firm in Pune. Built his confidence with live projects and mock tests.
Pooja (Mechanical Engineer) – Switched from core to IT after completing Cyberinfomines’ Java program. Cracked TCS with flying colors.
Rahul (Dropout) – Didn’t finish college but now works remotely as a freelance Spring Boot developer for a US-based startup.
Every story started with zero coding experience. They ended with real jobs.
7. Top Java Careers in 2025 & Salary Trends In-demand roles include:
Java Backend Developer
Full Stack Developer (Java + React)
Android Developer (Java)
Spring Boot Microservices Architect
QA Automation with Java + Selenium
API Developer (Spring + REST)
Starting salary: ₹4.5 – ₹8 LPA (for freshers with strong skills) Mid-level: ₹10 – ₹20 LPA Freelancers: ₹1,000 – ₹2,500/hour
Java is stable, scalable, and pays well.
8. Certifications, Tools & Practical Add-Ons After training, you’ll earn:
Cyberinfomines Java Developer Certificate
Portfolio with at least 3 GitHub-hosted projects
Proficiency in IntelliJ, Maven, Git, MySQL
Resume aligned with Java job descriptions
Interview recordings and performance feedback
9. What Makes Cyberinfomines Java Training Different
✔ Human mentorship, not just videos ✔ Doubt sessions + code reviews ✔ Classes in Hindi & English ✔ Live assignments + evaluation ✔ Placement-oriented approach ✔ No-nonsense teaching. Only what’s needed for jobs.
We focus on you becoming employable, not just completing a course.
10. Final Words: Code Your Future with Confidence Java in 2025 isn’t just relevant—it’s crucial.
And with Cyberinfomines, you don’t just learn Java.
You learn how to:
Solve real problems
Write clean, scalable code
Work like a developer
Get hired faster
Whether you’re starting fresh or switching paths, our Java course gives you the skills and confidence you need to build a future-proof career.
📞 Have questions? Want to get started?
Contact us today: 📧 [email protected] 📞 +91-8587000904-905, 9643424141 🌐 Visit: www.cyberinfomines.com
0 notes
Text
Encapsulation in Java – A Complete Guide
Learn everything about Encapsulation in Java with Scientech Easy's beginner-friendly guide. Understand how encapsulation helps in data hiding, improves code maintainability, and secures your Java applications. This comprehensive article covers its real-world use, syntax, and practical examples to help you grasp the concept easily. Perfect for students and developers looking to strengthen their OOP fundamentals.Scientech Easy for clear explanations and step-by-step learning on Java programming topics. Start mastering encapsulation today!

#bca course subjects#python tuple#Interface in Java#Encapsulation in Java#Method overriding in Java#Polymorphism in Java#Constructor in java
0 notes
Text

What is the difference between ArrayList and Vector? . . . . For more questions about Java https://bit.ly/3Lcw553 Check the above link
#collectionframework#array#ArrayList#Vector#collection#process#heavyweightcomponent#reflection#Classclass#Systemclass#wrapperclass#boxing#unboxing#objectcloning#serialization#polymorphism#java#constructor#thiskeyword#computersciencemajor#javatpoint
0 notes
Note
Hey Emily you are a Software Engineer tell me a difference between Methods and Constrictor in Java ?
Gonna be honest I don't work in Java, but generally methods are functions that you call on a given instantiated object like obj.method(whatever) and a constructor is a specific method called when you instantiate a new object like obj = new Whatever()
0 notes
Text
So I had another java interview today.
Technical questions that they asked:
- what is the difference between primitive data type and object data
- difference between == and .equals()
- what is a constructor used for
- what is the difference between jre and jdk
- how will u change an integer to a string and vice verda
- 3 live coding questions (reversing a string, find the max value in an array, encapsulate a class)
I did partially ok. I am not able to remember the syntax, so I struggled quite a bit with method signatures. I mixed up some concepts (for eg the == and .equals. So .equals() is the one that checks the content of the variable)
Behavioural questions that they asked:
- if you had a new team member joining, how would you guide him/her
- what does your day-to-day tasks look like
- if u have to finish a task in 2 hours, but u are unable to, what do you do?
- you have a requirement to fulfill, but the requirement is very vague. What do u do?
Questions asked based on previous experience:
- How did u design an API end point?
- How do you throw exceptions?
- What are the aspects of design that you had to consider?
1 note
·
View note
Text
java- single constructor Vs multiple constructors
❌ The Multiple Constructor Example
public class Human {
private String name;
private int limbs;
private String skinColor;
public Human(String name) {
this(name, 4, "Unknown"); // Magic numbers!
}
public Human(String name, int limbs) {
this(name, limbs, "Unknown");
}
Why this fails: Hidden assumptions (Why default limbs = 4?), duplicate validation (What if limbs < 0?), brittle maintenance (Adding bloodType breaks all constructors)
✅ The Single Constructor Solution
public class Human {
private final String name; // Required
private final int limbs; // Required
private final String skinColor; // Required
public Human(String name, int limbs, String skinColor) {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
if (limbs < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Limbs cannot be negative");
this.name = name;
this.limbs = limbs;
this.skinColor = skinColor;
}
}
benefits: No magic defaults -Forces explicit values, validation in one place - Fail fast principle, immutable by design - Thread-safe and predictable
Handling Optional Fields: The Builder Pattern For complex cases (like optional eyeColor), use a Builder:
Human britta = new Human.Builder("Britta", 4)
.skinColor("dark")
.eyeColor("blue")
.build();
Why Builders win: Clear defaults (`.skinColor("dark")` vs. constructor overloading), flexible (Add new fields without breaking changes), readable (Named parameters > positional args)
When Multiple Constructors Make Sense
Simple value objects (e.g., Point(x, y)), framework requirements (JPA/Hibernate no-arg constructor), most classes need just one constructor. Pair it with: factory methods for alternative creation logic and builders for optional parameters
This approach eliminates: hidden defaults, validation duplication and maintenance nightmares Do you prefer single or multiple constructors? Have you been bitten by constructor overload? Share your war stories in the comments!
#Java #CleanCode #OOP #SoftwareDevelopment #Programming
1 note
·
View note
Text
Constructor (Hàm Khởi Tạo) trong Java - Giải Thích và Ví Dụ
Constructor trong Java là một khái niệm quan trọng trong lập trình hướng đối tượng (OOP). Nếu bạn đang học Java hoặc muốn tìm hiểu cách khởi tạo đối tượng một cách hiệu quả, bài viết này sẽ giải thích chi tiết về hàm khởi tạo, vai trò, cách sử dụng và các ví dụ minh họa cụ thể. Hãy cùng khám phá!

Constructor trong Java là gì?
Constructor trong Java là gì?
Constructor (Hàm Khởi Tạo) là một phương thức đặc biệt trong lớp (class) được sử dụng để khởi tạo đối tượng. Khi một đối tượng được tạo ra bằng từ khóa new, hàm khởi tạo sẽ được gọi tự động để thiết lập các giá trị ban đầu cho đối tượng. Điểm đặc biệt của constructor là:
Có tên trùng với tên lớp.
Không có kiểu trả về, kể cả void.
Được gọi tự động khi đối tượng được tạo.
Có thể có tham số hoặc không.
Constructor giúp đảm bảo rằng đối tượng luôn ở trạng thái hợp lệ ngay khi được tạo. Đây là lý do nó được sử dụng rộng rãi trong lập trình Java.
Các loại Constructor trong Java
Trong Java, có ba loại hàm khởi tạo chính:
Constructor mặc định (Default Constructor) Nếu bạn không định nghĩa bất kỳ constructor nào trong lớp, Java sẽ tự động cung cấp một hàm khởi tạo mặc định không có tham số. Nó khởi tạo các thuộc tính của đối tượng với giá trị mặc định (ví dụ: 0 cho số nguyên, null cho chuỗi).
Constructor có tham số (Parameterized Constructor) Đây là hàm khởi tạo có tham số, cho phép bạn truyền giá trị vào để khởi tạo đối tượng với các thuộc tính cụ thể.
Constructor sao chép (Copy Constructor) Loại constructor này nhận một đối tượng khác của cùng lớp làm tham số và sao chép giá trị của đối tượng đó để khởi tạo đối tượng mới.
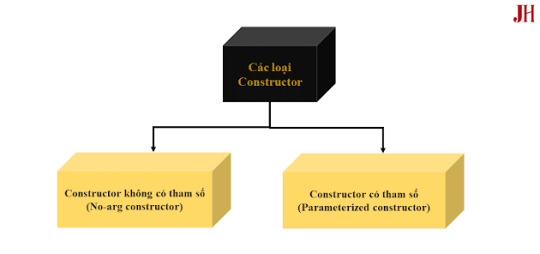
Ảnh mô tả các loại constructor trong java.
Đặc điểm của Constructor trong Java
Dưới đây là những đặc điểm nổi bật của hàm khởi tạo:
Không có kiểu trả về: Không giống các phương thức thông thường, constructor không trả về giá trị, kể cả void.
Tên trùng với lớp: Tên của hàm khởi tạo phải giống hệt tên lớp.
Nạp chồng (Overloading): Bạn có thể định nghĩa nhiều constructor trong một lớp với số lượng hoặc kiểu tham số khác nhau.
Tự động gọi: Constructor được gọi ngay khi đối tượng được tạo bằng từ khóa new.
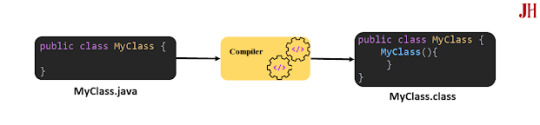
Ảnh mô tả constructor không có tham số sẽ được thêm vào bởi trình biên dịch.
Ví dụ minh họa về Constructor trong Java
Dưới đây là các ví dụ cụ thể về từng loại hàm khởi tạo trong Java:
1. Constructor mặc định
class SinhVien { String ten; int tuoi; // Constructor mặc định SinhVien() { ten = "Chưa xác định"; tuoi = 0; } void hienThi() { System.out.println("Tên: " + ten + ", Tuổi: " + tuoi); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { SinhVien sv = new SinhVien(); sv.hienThi(); } }
Kết quả: Tên: Chưa xác định, Tuổi: 0
2. Constructor có tham số
class SinhVien { String ten; int tuoi; // Constructor có tham số SinhVien(String tenSV, int tuoiSV) { ten = tenSV; tuoi = tuoiSV; } void hienThi() { System.out.println("Tên: " + ten + ", Tuổi: " + tuoi); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { SinhVien sv = new SinhVien("Nguyễn Văn A", 20); sv.hienThi(); } }
Kết quả: Tên: Nguyễn Văn A, Tuổi: 20
3. Constructor sao chép
class SinhVien { String ten; int tuoi; // Constructor có tham số SinhVien(String tenSV, int tuoiSV) { ten = tenSV; tuoi = tuoiSV; } // Constructor sao chép SinhVien(SinhVien sv) { ten = sv.ten; tuoi = sv.tuoi; } void hienThi() { System.out.println("Tên: " + ten + ", Tuổi: " + tuoi); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { SinhVien sv1 = new SinhVien("Nguyễn Văn A", 20); SinhVien sv2 = new SinhVien(sv1); // Sao chép sv1 sv2.hienThi(); } }
Kết quả: Tên: Nguyễn Văn A, Tuổi: 20
Sự khác biệt giữa Constructor và Phương thức thông thường

Lợi ích của việc sử dụng Constructor trong Java
Khởi tạo đối tượng an toàn: Hàm khởi tạo đảm bảo đối tượng được khởi tạo với trạng thái hợp lệ.
Tính linh hoạt: Với constructor có tham số, bạn có thể tùy chỉnh giá trị ban đầu của đối tượng.
Tái sử dụng mã: Constructor sao chép giúp tạo ra các đối tượng giống nhau mà không cần lặp lại logic.
Một số lưu ý khi sử dụng Constructor
Không nên đặt logic phức tạp trong constructor, vì nó có thể làm chậm quá trình khởi tạo.
Nếu cần khởi tạo nhiều đối tượng với các tham số khác nhau, hãy sử dụng nạp chồng constructor.
Constructor không thể được kế thừa, nhưng lớp con có thể gọi constructor của lớp cha bằng từ khóa super.
Kết luận
Constructor trong Java là một công cụ mạnh mẽ để khởi tạo đối tượng một cách hiệu quả và an toàn. Từ constructor mặc định, constructor có tham số đến constructor sao chép, mỗi loại đều có vai trò riêng trong việc xây dựng các ứng dụng Java chất lượng. Hy vọng qua bài viết này, bạn đã hiểu rõ cách sử dụng hàm khởi tạo và có thể áp dụng vào dự án của mình.
Hãy thử viết code với constructor và khám phá thêm các tính năng của Java để nâng cao kỹ năng lập trình của bạn!
Constructor trong Java – Tìm hiểu khái niệm, vai trò và cách sử dụng hàm khởi tạo trong lập trình Java. 🌐 Khám phá chi tiết tại: Java Highlight | Website Học Lập Trình Java | Blogs Java
0 notes
Text
CSC 3410 Programming Assignment #3
You are to write a program name ArrayList.java that creates an ArrayList data structure that is similar to the ArrayList data Structure that exist in the java library. The class must be written to accept any type of Objects. The following must be implemented i.e. YOU must write the code (do not import them from the Java Library): <style=’mso-bidi-font-weight: normal’=””>One default constructor…
0 notes