#ERP Integration with TPM
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Makes Agrius IT's V-ERP a Powerful Tool for Businesses in September 2024?
Agrius IT's V-ERP system enhances business operations by integrating with Third Party Maintenance (TPM) services. This integration allows businesses to manage their IT infrastructure more efficiently, combining the benefits of TPM with a comprehensive ERP solution. V-ERP supports a wide range of functions, from managing inventory to tracking performance, providing a unified platform for operational management.

Comprehensive Business Management
V-ERP is a robust tool designed to handle various aspects of business management. It offers features such as financial accounting, human resources, inventory management, and customer relationship management (CRM). By consolidating these functions into one system, V-ERP helps businesses operate more cohesively and efficiently, reducing the need for multiple disparate systems.
Advanced Data Connectivity
One of the key strengths of V-ERP is its ability to connect and analyze data from different business processes. This feature allows for better decision-making by providing a comprehensive view of operations. Businesses can monitor real-time data, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and generate detailed reports, all of which contribute to informed strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Customization and Scalability
Agrius IT’s V-ERP system is highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs. Whether a business requires additional modules, customized workflows, or unique reporting features, V-ERP can be adapted to meet these requirements. Additionally, V-ERP is scalable, meaning it can grow alongside a business and support increased operations as needed.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
By integrating with TPM services and offering a comprehensive suite of management tools, V-ERP enhances overall efficiency and productivity. The system reduces manual data entry, automates routine tasks, and ensures that all business processes are aligned. This leads to quicker responses, fewer errors, and a more streamlined workflow.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Agrius IT’s V-ERP ensures that business data is secure and compliant with industry regulations. The system includes advanced security features such as data encryption, user access controls, and regular security updates. This focus on security helps protect sensitive information and ensures that businesses meet regulatory requirements.
Agrius IT’s V-ERP stands out as a powerful tool for businesses by integrating Third Party Maintenance services with a comprehensive ERP system. With its capabilities for comprehensive management, data connectivity, customization, efficiency, and security, V-ERP offers a robust solution for businesses looking to optimize their operations and achieve greater success.
#V-ERP System Features#Business Management Software#ERP Integration with TPM#Data Connectivity and Analysis#Customizable ERP Solutions
1 note
·
View note
Text
Building Operational Excellence: Lean Manufacturing Consulting by Seicho Consulting
In today’s competitive manufacturing world, doing more with less isn’t just an option — it’s a necessity. Lean Manufacturing empowers organizations to maximize productivity, minimize waste, and deliver consistent quality — all while improving worker satisfaction and reducing costs.
At Seicho Consulting, our Lean Manufacturing Consulting Services are designed to implement operational excellence at every level of your factory floor. From layout design to daily improvement systems, we help manufacturers transform operations through Lean principles.
🔧 Key Offerings:
Process Flow Optimization: Eliminate bottlenecks and improve production speed.
5S & Visual Workplace Setup: Create clean, organized, and efficient workspaces.
Value Stream Mapping (VSM): Understand where value is added—and where it’s lost.
Kaizen Programs: Cultivate a culture of continuous improvement through employee engagement.
Standard Work & Error Proofing (Poka-Yoke): Minimize variation and human error.
Lean Layout Redesign: Enhance space utilization and material flow.
📈 Benefits of Lean Implementation:
Higher productivity and throughput
Reduced inventory and faster delivery
Better product quality and fewer defects
Improved worker safety and morale
Significant cost savings
🏭 Who We Serve:
Automotive & Ancillary Units
FMCG & Packaging Plants
Chemical & Pharma Manufacturers
Textile & Engineering Setups
SMEs & Export-Oriented Units
With over 50+ successful Lean projects, our team understands the ground reality of factories and production units. We don’t just teach Lean tools — we help your people adopt Lean culture. Plus, our approach integrates smoothly with TPM, Six Sigma, TQM, and ERP systems, making your business more agile and scalable.
💡 Ready to make your factory future-ready with Lean? Reach out to Seicho Consulting — let’s build sustainable excellence together.
#LeanManufacturing#SeichoConsulting#OperationalExcellence#ManufacturingConsulting#5S#Kaizen#PokaYoke#LeanProduction#FactoryEfficiency#IndustrialConsulting#ValueStreamMapping#ProcessImprovement#ContinuousImprovement#TPM#SixSigma#EngineeringConsulting#TextileManufacturing#FMCGManufacturing#AutomotiveIndustry#LeanTransformation#SMEConsulting
0 notes
Photo

Lenovo IP1i Gen 7 Intel Celeron N4020 Celeron® Notebook Roam wherever life takes you while connecting and exploring with the remarkably thin and lightweight IdeaPad 1i Gen 7 (15″ Intel) laptop. It boots up in seconds with Flip to Start, which only requires you to open the lid to power up and is driven by up to Intel® Celeron® processors that let you multitask with ease. Maximized experiences & unlimited uses The IdeaPad 1i Gen 7 (15" Intel) is exactly what you need in an everyday use laptop. Watch shows on an expansive up to 15.6" FHD display with a razor-thin frame. Listen to rich and clear audio from two Dolby Audio™ speakers. And with a battery that lasts all day and charges super-fast, you can work from anywhere while enjoying clear video calls with Smart Noise Cancelling. Key Specifications Processor: Intel Celeron N4020 (2C / 2T, 1.1 / 2.8GHz, 4MB) Memory: 8GB SO-DIMM DDR4-2400 Storage: 256GB SSD M.2 2242 PCIe 3.0x4 NVMe Screen size: 15.6" FHD (1920x1080) TN 220nits Anti-glare Operating system: Windows 11 Home Single Language PERFORMANCE Processor: Intel Celeron N4020 (2C / 2T, 1.1 / 2.8GHz, 4MB) Graphics: Integrated Intel UHD Graphics 600 Chipset: Intel SoC Platform Memory: 8GB SO-DIMM DDR4-2400 Memory Slots: One DDR4 SO-DIMM slot Max Memory: Up to 8GB (8GB SO-DIMM) DDR4-2400 offering (8GB module need to be purchased separately in order to upgrade) Storage: 256GB SSD M.2 2242 PCIe 3.0x4 NVMe Storage Support: One drive, up to 256GB M.2 2242 SSD or 512GB M.2 2280 SSD (512GB SSD need to be purchased separately in order to upgrade) Storage Slot: Non-eMMC models: one M.2 slot One M.2 2280 PCIe 2.0 slot Card Reader: SD Card Reader Optical: None Audio Chip: High Definition (HD) Audio AUDIO Stereo speakers, 1.5W x2, Dolby Audio Camera: HD 720p with Privacy Shutter Microphone: 2x, Array Battery: Integrated 42Wh Max Battery Life: Local video (1080p) playback@150nits: 11 hr Power Adapter: 45W Round Tip (3-pin) DESIGN Display: 15.6" FHD (1920x1080) TN 220nits Anti-glare Touchscreen: None Keyboard: Non-backlit, English Case Color: Cloud Grey Surface Treatment: IMR (In-Mold Decoration by Roller) Case Material: PC-ABS (Top), PC-ABS (Bottom) Dimensions (WxDxH): 360.2 x 236 x 17.9 mm (14.18 x 9.29 x 0.70 inches) Weight: Starting at 1.54 kg (3.4 lbs) SOFTWARE Operating System: Windows 11 Home Single Language, English CONNECTIVITY Ethernet: No Onboard Ethernet WLAN + Bluetooth Wi-Fi 6, 11ax 2x2 + BT5.1 Standard Ports 1x USB 2.0 1x USB 3.2 Gen 1 1x USB-C 3.2 Gen 1 (support data transfer only) 1x HDMI 1.4b 1x Card reader 1x Headphone / microphone combo jack (3.5mm) 1x Power connector SECURITY & PRIVACY Security Chip: Firmware TPM 2.0 Fingerprint Reader: None Other Security Camera privacy shutter CERTIFICATIONS Green Certifications ENERGY STAR 8.0 ErP Lot 3 RoHS compliant INSIDE OF THE BOX 1 x Notebook 1 x AC Adapter
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] This affordable notebook supports smooth multi-tasking of web-based apps and basic productivity software. The 15.6” screen has a narrow frame, helping to reduce the overall footprint ofthe device while maximizing screen space. The simple design, with minimal buttons and lines, projects a modern premium image, and there is a choice of a metallic or patterned textured finish. Several design features make working outdoors easier – the anti-glare display, spill-resistant keyboard, up to 7.5hrs of battery life, and a large touchpad for easier scrolling, zooming and navigation. Display: 15.6" (39.62 cm) FHD 250 nits, Antiglare, Contrast Ratio: 500:1, 90° Viewing Angle | Graphics: Integrated AMD Radeon graphics | High Definition Audio, Realtek ALC3287 codec, Stereo speakers, 1.5W x2, Dolby Audio;Ports : 1x USB 2.0, 1x USB 3.2 Gen 1, 1x USB-C 3.2 Gen 1 (support data transfer only), 1x HDMI 1.4b, 1x Ethernet(RJ-45), 1x headphone / microphone combo jack (3.5mm), 1x power connector Camera: 1MP with Privacy Shutter | Microphone: Dual array microphone | Keyboard:6-row, spill-resistant, multimedia Fn keys, numeric keypad | Touchpad: Buttonless Mylar surface multi-touch touchpad, supports Precision TouchPad;Connectivity: 802.11ac 2x2 Wi-Fi + Bluetooth 5.0 | Security: TPM 2.0 | Physical Locks: Kensington Nano Security Slot Battery Life: Upto 7.5 hours as per MobileMark | Integrated Li-Polymer 38Wh battery, supports Rapid Charge (charge up to 80% in 1hr) with 65W AC adapter | ENERGY STAR 8.0 Rated| Design: Thin & Light Laptop, 180 Degree Hinge;Reliable and Durable laptop | Tests passed: Shock test, Vibration test, Hinge life test, Operating temperature test, Keyboard in-system test, Fan Reliability test, Panel scuff testand Pressure test to withstand extreme conditions; Additional Certifications: ErP Lot 3, RoHS compliant, TÜV Rheinland Low Blue Light | This genuine Lenovo Laptop comes with 1 Year Onsite Warranty;Inside the box: Laptop with battery, Charger, User manual Human Interface Input: Buttonsnumeric Keypadmicrophonekeyboard; Software Included: Microsoft Office 365 [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
The core differences of "Industry 4.0" between Japan, Germany, the United States and China.

This article is from (Beijing Internet of Things Intelligent Technology Association) If there is infringement, please contact us and we will delete.
Summary: In the meantime, the German concept of "Industry 4.0" is often mentioned together with "Made in China 2025".Are these two the same concept? What is the difference between these two under the great industrial foundation of China and Germany?
The relationship between big data and manufacturing
The relationship between big data and manufacturing can use the following figure, there are three important elements:

1, the problem: linear or hidden problems in manufacturing system , such as quality defects, lack of accuracy, equipment failure, processing failure, performance degradation, high cost, low efficiency and so on.
2, data, data from the five elements of the manufacturing system that reflect the course and the cause of the problem. Data access should be problem-oriented in order to understand, resolve and avoid problems.
3, knowledge: the core of manufacturing system, that is Know-how, including process, technology, design, process and diagnosis. Knowledge comes from the process of solving manufacturing system problems, and big data analysis can be understood as a means of quickly acquiring and accumulating knowledge.
The relationship between big data and intelligent manufacturing can be summed up as follows: A large amount of data will be generated in the process of the occurrence and solution of the problem in the manufacturing system. Through the analysis and excavation of the data, the process of the problem, the impact and the solution When these information is abstracted and modeled into knowledge, and then use knowledge to understand, solve and avoid problems. When this process can spontaneously and automatically cycle, which we call intelligent manufacturing.
Problems and knowledge are the ends, and data is the means. In the above elements,change the data to people, is the "craftsman spirit", replaced by "automated production lines and equipment" ,is "Industry 4.0", when replaced by the Internet it has become "Internet +."
Differences in understanding, accumulation and inheritance of knowledge determine the different manufacturing cultures in different countries
Japan: Continuous Improvement through Organizational Culture and Human Training, Very Dependent on the Bearing and Inheritance of Knowledge
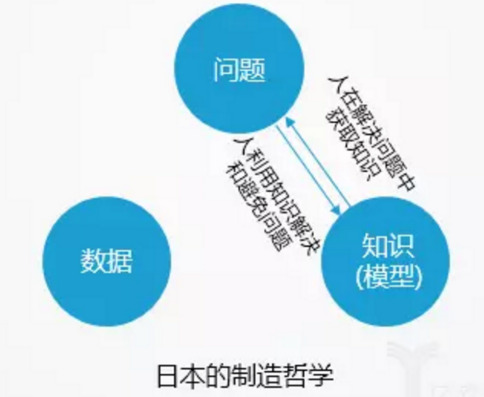
The most important feature of the Japanese manufacturing culture is ,Ihrough continuous optimization of the organization, cultural construction and human training to solve the problems in the production system.In the 1970s, Japan put forward the "production management system TPM" as the core of the production management system, the core ideas: full efficiency, system-wide and full participation, the improvement was mainly in three aspects: : improve work skills, improve the team Spirit and working environment. After the 1990s, Japan chose "lean manufacturing" as its transformation direction.
Japanese enterprises often solve problems in the following ways: Problems occur - personnel arrive at the scene, confirm the scene, explore the realities and solve the problems - analyze the causes of the problems, and avoid the problems through improvement. In the end, knowledge falls on people, and the ability to solve and avoid problems increases when people's skills are improved.
For Japanese companies, employees are the most important value. They trust people more than their trust in equipment, data and systems. All automation and informatization are built around helping people to work. Therefore, Japanese companies Will never talk robots substitutions or unmanned factory. However, such a culture has encountered enormous challenges in recent years. Japan's aging has led to a large shortage of manufacturing talent in the younger generation and no one can smriti knowledge. Japan is aware of its own lack of data and information. In Japan's industrial value chain industry alliance architecture and goals, of the 19 projects, 7 are directly related to big data.
Japan's transformation strategy is a helpless move to tackle its demographic structure and social contradictions. It faces many challenges in the process of transformation. The first is the lack of data accumulation, followed by the lack of software and IT professionals in the conservative culture of Japanese industrial enterprises.
Germany: Curing knowledge on equipment with continuous upgrading of equipment and production systems
Germany's advanced equipment and automated production lines are world-famous.At the same time, German rigorous style and unique "apprenticeship" higher education model, making the German manufacturing style is very pragmatic. However, Germany faced the problem of labor shortage very early and Germany had to make up for the deficiencies by developing more advanced equipment and highly automated production lines.
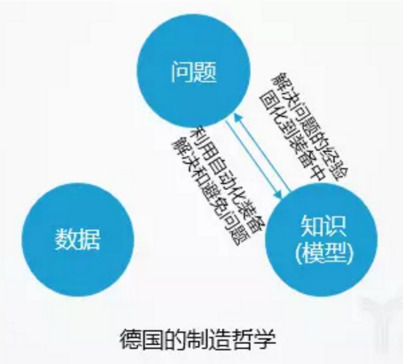
The logic in Germany to solve problems is that problems occur - people solve problems - solidify problem-solving knowledge and processes into equipment and production lines - and automatically resolve or avoid similar problems. In addition to the automatic resolution of the pursuit of production lines, Germany also minimizes the human factors in business management. The best software vendors such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Production Execution System (EMS), Automated Scheduling System (APS) are from Germany. A great deal of information entry and planning are generated and tracked through software to minimize the uncertainty associated with human factors.
The same lack of data collection in Germany is due to the fact that German manufacturing systems have zero tolerance for faults and defects, and that problems are solved once and for all through equipment-side improvements. Due to the high degree of automation and integration of the production line, the overall equipment efficiency is very stable, and the space for data optimization is relatively small.
Germany get a huge economic return relies on exports of equipment, but most industrial products can only be sold once, When sell products to one customer,it means lose a customer. In the meantime, the equipment manufacturing and industrial capacity of developing countries have risen in recent two years. The German market is constantly being squeezed. There is almost no growth in Germany's industrial exports in 2008-2012. Germany then proposed the Industry 4.0 program, Behind this is the system foundation that Germany has accumulated in manufacturing systems.at the same time, knowledge of German-made is also provided to customers in the form of software or kits as overweight service, enabling continuous profitability from customers. The core element of the German Industry 4.0 design framework is integration.
America: gaining new knowledge from data and immigration, and being good at subversives and redefining problems
In the process of solving the problem, the United States places the highest emphasis on the role of data. Customer demand analysis, customer relationship management, quality management, equipment health management, supply chain management, service management and other aspects of the data are heavily dependent on.The United States also proposed the concept of "product lifecycle management (PLM)" in the early 2000s. The core is to manage all product-related data throughout the life cycle, managing the data of the product, aiming at the value-added services of the whole life cycle and implementing the closed loop design (closed loop design).

In addition to using knowledge to solve problems, the United States is also good at using knowledge to subvert the innovation so as to redefine the problem. For example, in the field of aero-engine manufacturing, in order to reduce power consumption, most enterprises solve the problems in terms of design, materials, technology, control optimization and the like. When general Electric found that aircraft fuel consumption is closely related to pilots' driving habits and engine maintenance. So it jump from the manufacturing side and turn to the maintenance side to solve the problem, the effect is obviously better than the manufacturing side.
China: lean system is chosen and data accumulation is lacking
China's manufacturing industry mostly chose the lean system for quality and management reform after 2000. On the one hand, because of the similarities between China and Japan, the problem still exists due to the general lack of data accumulation and information basis.
The location of the value chain in manufacturing is a decisive factor in competitiveness, and the distribution of countries in the value chain is also different.
In production activities, the distribution of value elements from upstream to downstream ,it goes: ideas innovation and demand creation, raw materials and basic enabling technologies, key equipment and core components, production processes and production systems, products and services. Among the distribution of elements in the value chain, China has advantages in the production process and production system (mainly reflected in labor costs and production capacity), but it is at a disadvantage in all other aspects.Different countries have different distributions and layouts in the value chain.
The United States: firmly occupy the upper reaches of the factors of production, and try to extend to the downstream
In the distribution of elements of production activities, the United States has obvious advantages in creating ideas and creating demand, raw materials and enabling technologies, and product value-added services. The core competencies of US industrial systems come from the 6s ecosystem: space / aerospace, semiconductor, shale gas, smart ICT service, Silicon Valley spirit and sustainable talent pool.
In March 2012, the White House proposed the National Network Manufacturing Innovation Program (NNMI),establishing nine research and innovation centers in four major areas of manufacturing.With a firm grasp of the most valuable parts of the industrial value chain,even if Germany's manufacturing facilities are advanced and China's manufacturing systems are more efficient, they can ensure their core competitiveness from the source.
Germany: give full play to the technical advantages of key equipment and parts, technical advantages in production process and production system, enhance profitability and competitiveness through value-added services.
Germany has obvious technical advantages in both key equipment and key components, production processes and production systems. The invisible champion enterprises and apprenticeship dual education centered at small and medium-sized enterprises provide a solid foundation for German industry. High-skilled technical workers and engineering professionals have long been regarded as the economic pillars of Germany. However, the emerging economies represented by the BRICS have basically completed their industrialization, resulting in the stagnant demand for industrial equipment in Germany.
The core purpose of "Industry 4.0" put forward by Germany is mainly in two aspects. First, it increases the competitiveness made by Germany and opens up new markets for the export of German industrial equipment. The second is to transform the former selling equipment and the service income of the relatively small state,Focus on the product side to the server transfer, enhance the continued profitability of German industrial products.
Japan: Lost a large number of markets in the product chain, but industrial equipment competitiveness is moving upstream.
The core competitiveness that Japan made in the past mainly lies in the production process and production system, products and services. In the past two years, Japan's most powerful traditional industries, such as automobiles and consumer electronics, are constantly occupied by Korea, the United States and China. Behind the scenes is actually a shift in Japan's innovation direction, with more voice in the upstream raw materials and key equipment and key components. After losing the position of a leader in the field of consumer electronics, Sony made breakthroughs in the medical field and has occupied more than 80% of the global market share of endoscopes. In the "2015 Manufacturing White Paper," Japan has taken the field of artificial intelligence and robotics as a key development direction and will also increase its investment in materials, medical , energy and key components and parts.
China: Deep Integration of Industrialization and Informatization as the Main Line to Achieve Breakthrough Development in 10 Key Areas
In 2015, China put forward "Made in China 2025", which takes the deep integration of industrialization and informatization as the main line of development and strives to achieve breakthroughs in 10 key areas.
According to the previous analysis, the author made recommendations to the Chinese manufacturers that they should focus on filling the gaps in China's industrial basic technologies, changing the status of over-reliance on imports of core components and advanced materials, making efforts to increase production efficiency and shifting from a crude production model to a lean model. Emphasis on technology and manufacturing process research and production process management,Constantly improve product quality; efforts to research and development of core production equipment and intelligent devices, and refine and information the management of the use of equipment.At the same time, we should pay attention to the innovation of the original ideas, enhance the product's service capability and continuous profitability, create new market opportunities with the customer-end value gap and use value-added services to enhance the core competitiveness of China's industrial products.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
State some use cases where Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia is helpful?

BI#1 Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia is a proactive approach, whereby retailers can use data from the past to predict expected sales growth, due to a change in consumer behaviours and/or market trends. This can help retailers stay ahead of the curve, compete effectively and gain considerable market share.
BI#1 Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia

Behaviour
A portion of the key difficulties for retail firms are – improving client change rates, customizing, showcasing efforts to build income, foreseeing and maintaining a strategic distance from client beat, and bringing down client obtaining costs. These can be handled with more profoundly by Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia. Today , there are a few distinctive association focuses for customers to collaborate with their organizations, portable, internet based life, stores, online business locales and the sky's the limit from there. This causes a considerable increment in the multifaceted nature and decent variety of information you may need to amass and break down. At the point when this information is ordered and broke down, it can give bits of knowledge that you may have never considered
Personalized experience
Because of the absence of a secure and powerful approach to gauge the particular effect of promoting choices, marketing has consistently been viewed as a fine art previously, related with feel and very little else. With Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia the considerable increment in online deals, another shopping position has risen whereby the shopper physically inquire about the ideal items coming up and afterward feel free to buy it on the web.These bits of knowledge can help increment limited time viability, drive strategically pitching, and substantially more.
Customer engagement
Today it is simple for clients to get to any sort of data utilizing channels like portable, online life and web based business. This settles on choice of purchasing and buys advantageous for the clients.Simultaneously, clients have begun anticipating considerably more from organizations, such as giving reliable data, consistent encounters crosswise over channels that reflect history, inclinations and interests. Advertisers need to persistently adjust with comprehension and interfacing with their clients. This is conceivable when retailers have Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia which assist you with seeing every client's profile and history crosswise over channels.
Supply chain
Quicker item life cycles and ever-complex activities will in general make retailers utilize large information investigation to comprehend supply chains and item conveyance to diminish costs. It is significant for retailers to have Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia to increase an aggressive edge so as to drive business execution and returns. Retailers are very much aware of the gigantic strain to enhance resource usage, spending plans, exhibitions and administration quality.To increment operational effectiveness, the key is to use them to open experiences covered up in log, sensor and machine information. Such experiences which incorporate data about patterns, examples and anomalies, improve choices, activities execution and lessen costs.
Promotions optimization
A report expresses that a noteworthy bit of the retailers lose more than one-third of the cash put resources into exchange advancements. This is principally because of the failure of leaders to gauge exchange advancement adequacy and ROI and gainfully upgrade spend by utilizing information.Most CPG organizations are as yet dependent on spreadsheets or ERP or TPM frameworks to upgrade exchange advancements. Any strong Trade advancement improvement programming ought to be outfitted with cutting edge investigation. Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia can tackle huge measure of continuous unstructured and organized information from a few market and shopper contact focuses and change it into noteworthy suggestions to help run the correct exchange advancements.
Characteristics of Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia
Data Rationalization
Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia| Makkah | Madinah | Riyadh
Customer Management
Analytics of Sales
Self-service Kiosk
Inventory Tracking
Fast Checkout
Automatic Purchasing of Inventory
Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia | Makkah | Madinah | Riyadh
Mobile Ordering
Data Security
Mobile Payments
E-commerce integration
PCI compliance
Brick-and-mortar stores
Retail Analytics Solutions in Saudi Arabia | Makkah | Madinah | Riyadh
Click to Start Whatsapp Chat with Sales

Mobile: +966547315697
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Photo

Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) has been benchmarked as the most reliable practices metric for measuring the productivity of a manufacturing plant.
OEE was initially developed as part of Lean manufacturing, particularly under Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), which is one of the most holistic and powerful improvement processes. Measuring OEE is undoubtedly the best practice in manufacturing plants as it can help the manufacturer gain insights on how to orderly upgrade their production process.
Setting the baseline and gold standards for measuring manufacturing productivity, OEE has gained a lot of popularity among manufacturers who seek to quantify their production monitoring system, machine-level performance, and manufacturing line.
An OEE score of 100% for any manufacturing plant indicates that only the right parts are being manufactured in it with no stop time. In short, the plant produces 100% quality products, with 100% availability at 100% performance.
How to improve OEE?
According to industry experts, the only way to improve your overall equipment efficiency is integration, integration, and integration. Nevertheless, here are a few tips that can be leveraged to improve the OEE of any plant:
Analyze & Understand what to measure
First things first, plan the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) carefully before you begin measuring the OEE. Selecting the wrong KPIs may affect the results.
Integrate & Automate
Availability is one of the critical factors in OEE. It's impossible to avoid machinery breakdowns. Consequently, it's advised to have a strategy for mitigating its impact. An integrated and automated production monitoring system can recover automatically, by utilizing alternative production resources and using unmanned production hours to compensate unevenness caused by sudden availability issues.
Result: It helps in improving the reliability of delivery.
Reveal Bottlenecks
Performance is the second essential factor, which signifies the speed of production. A smart manufacturing management software will simulate production even days ahead, revealing all the possible bottlenecks and resource shortages in advance. It continually tracks the modifications in orders, identifies missing tools and materials, and executes production automatically, completing all the orders in time.
Result: It will help in shortening delivery times and speeding up production.
Collaborate
Quality is considered as the third-factor for effective OEE. In the past few years, there's been a trend of working with smaller and smaller batch sizes. Manufacturing management software may horizontally combine with ERP-, CAM-, PDM- and - TDM-software, and vertically with production machines, ultimately enhancing the quality. An integrated system can automatically utilize the product documents, production order statuses, valid NC-programs, and correct tool measurement.
Result: It results in improved quality and information sharing from shop floor to top floor in real-time.
Measure other KPIs Also
By only optimizing OEE, you can get high spindle utilization but may end up producing parts to stock and delayed ordered items. Remember, by combining OEE with JIT (Just in Time) principle; you can come up with one of the best formulae for a successful business. Modern manufacturing aims to complete customer orders on time, not only run spindles.
Digital transformation in manufacturing is instrumental in improving any manufacturing plants' OEE because it can drastically reduce downtime and improve your efficiency.
0 notes
Text
Implementing Lean Maintenance System to Improve Factory Performance

Need for 100% uptime of machines from the production department has never gone out of demand. Day to day production needs are always to be met to meet delivery performance and revenue of the organisation. One may ask if zero maintenance time is really possible. Imagining a condition when a flight is already in the air and it needs maintenance in mid air.
Can we send a maintenance engineer to repair things in mid air?
Any maintenance needs are to be performed when there is break time or when production is not scheduled. Preventive maintenance time allocation in such cases becomes essential so that the machine performs to its fullest potential during its intended working hours.
Lean maintenance system works in combination of Total Productive maintenance, Reliability centred maintenance, Lean methods and TQM as integrated system. The ultimate goal is to eliminate the need for maintenance during production or Zero maintenance time.
We can call maintenance strategies into three broad categories:
Maintenance done only upon a breakdown
Periodic or preventive maintenance
Condition based corrective maintenance
Related Article– How to improve Office performance through Lean thinking and Lean management
In a lean maintenance system, maintenance planning is done based on the priority categories.
Priority category : 1
This can be classified into a critical category of maintenance. In this category, if the machine gets into a minor stoppage or breakdown, it can disrupt the production resulting in serious implication to customers.
Solutions to handle the machines in this category are:
Identify critical components of the machine
Do regular monitoring of the critical components for its effective functionality.
Where applicable, replace the critical component before it gets into failure. For this, MTBF and past records will help.
Have clear procedures and training to the designated people in handling these types of failures.
Keep critical spares always in stock with Kanban systems or through ERP with min-max triggers. No stock situation due to customer lead time, internal approvals, logistics issues and supplier issues should be considered in planning and FMEA.
Have a back-up maintenance plan with designated people availability during production operations too.
Ensure MTTR is well within the accepted time.
Have a redundancy plan or back up items to take over.
Related Article– Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) – How To Improve Customer Service With Supply Chain Management?
Priority Category : 2
The criticality of components in this case is relatively lesser compared to Category -1.
Remaining solutions are still applicable as category 1 in this case too.
Priority Category : 3
In this, the machine is still critical for operations and it can disrupt the production. However, the implication of machine failure is less on the customer and hence it can still be managed. Solutions are to be customised to the machines under this category.
Other machines are considered not very critical and hence moderate levels of maintenance planning can be recommended to optimise the costs and strike the right balance between performance and downtime implications.
There are two main strategic approaches for ensuring zero down time.
Maintenance during scheduled non-production time
Reducing maintenance time
For help in deciding right strategies in the maintenance system, Seven Steps Business Transformation systems can be consulted.
Our consultants have vast experience in the field of Operational excellence and business excellence with specialisation in
Lean manufacturing consulting
Lean Six Sigma Consulting
Total Productive Maintenance consulting
Design for Six Sigma
Lean product development consulting
5S and visual management consulting
Total Quality Management consulting
Lean consulting
Lean Hospital consulting
Lean warehousing consulting
Lean restaurants consulting
Lean services consulting
Through our group vertical Seven Steps Academy of Excellence, we conduct training programmes on the following key topics
Lean simulation training
5s and visual management training
Kanban and supermarket implementation training
Kaizen training
Lean Six Sigma Greenbelt training
Lean Six Sigma blackbelt training
Lean Six Sigma Master Blackbelt training
Lean Six sigma Yellow Belt training
Certified reliability engineer training
Certified 5S auditor training
Related Article– How to get Certified Reliability Engineer Certification
Our customer base is from multiple sectors which includes
Automotive and ancillaries
Forgings
Foundries
Pharmaceuticals
Interior decor
Food processing
Restaurants
Hospitals
Farming products
Central kitchen
Fabrication and assembly
Equipment manufacturing
Spring manufacturing
Cookware manufacturing
Banking
Telecom
Research
Software Development
Printing and packaging
Paper plants
FIBC bags manufacturing
Tool manufacturing
Education
Financial services
Furniture manufacturing
Government services
Construction
We do both onsite consulting and offsite consulting across the world with bases in India.
Our reach at the moment are at the following locations in India
Bangalore
Mumbai,
Calcutta,
Chennai,
Hosur,
Mysore
Coimbatore
Tiruchirapalli,
Pondicherry
Salem,
Madurai,
Nagercoil
Nasik
Jamshedpur
Gurugram
Pantnagar
Lucknow
Neemrana
Ludhiana
Chandigarh
Visakhapatnam
Vizianagaram
Nellore,
Tirupati,
Vijayawada
Bhubaneshwar
Patna
We also serve global locations of UAE, Srilanka, United Kingdom, USA, Russia, Iran, Israil, Singapore, Vietnam, Japan, Nepal, Bhutan, Canada,Italy, Turkey, Ireland. Africa
Some of the flagship training programmes conducted at Seven Steps Academy of Excellence are:
Six sigma Green Belt
Six Sigma Black Belt
Six Sigma Yellow Belt
Skill development programme – Campus to Corporate – Precision Engineering
Applied 5S
TPM
Lean Experimental Learning Programme
0 notes
Text
Lean Management Consulting: Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
In today’s volatile and complex business environment, organizations must be agile, efficient, and relentlessly focused on customer value. That’s where Lean Management comes into play—not just as a toolkit, but as a transformational management system.
At Seicho Consulting, we don’t just implement Lean—we help you build a culture of continuous improvement that drives strategic outcomes, enhances operational performance, and engages people at every level.
🚀 What is Lean Management?
Lean Management is more than reducing waste—it's a mindset.
It’s about:
Aligning strategy with execution
Empowering people to solve problems at the source
Structuring operations to flow smoothly
Delivering consistent value with minimal effort and resources
Whether you’re a manufacturer, service provider, or administrative organization, Lean helps you transform how your teams think, act, and grow.
🔧 Our Lean Management Services
At Seicho Consulting, we offer a full suite of Lean Management Consulting solutions tailored to your industry, scale, and growth stage:
✅ Lean Transformation Strategy & Roadmap
We co-create a structured rollout plan for Lean adoption, fully aligned with your long-term business objectives.
✅ Leadership Coaching & Change Management
We guide your leadership team in becoming Lean change agents, ensuring transformation is not just top-down but sustainable.
✅ Gemba Walks & Visual Management Systems
We improve transparency and accountability with on-site observation and visual systems that expose process gaps and flow inefficiencies.
✅ Team Engagement & Problem Solving Skills
Empowered teams drive improvement. We help your staff build the capability to identify and eliminate problems at the root.
✅ KPI Development & Performance Tracking
We design clear, actionable KPIs that reflect true business performance and guide real-time decision-making.
✅ Layered Audits & Sustainment Plans
Lean doesn’t end with implementation. We install a structured audit and sustainment system to protect and evolve your Lean culture.
🏭 Industries We Serve
Our Lean Management approach has helped transform:
Manufacturing & Process Industries
Healthcare & Service-based Organizations
Administrative & Office Functions
SMEs and Corporates seeking cultural change
Whether you’re improving shop floor operations or streamlining service workflows, Lean principles are universally applicable.
📈 The Impact of Lean Management
By applying Lean thinking across your value stream, you unlock:
🔄 Reduced operational waste
⚡ Faster and more consistent output
🧠 Increased employee ownership and problem-solving
📊 Data-driven agility and continuous learning
💰 Higher value at lower operating costs
🌟 Why Choose Seicho Consulting?
What sets us apart is our depth and discipline:
✔ Hands-on experience across 50+ organizations
✔ Custom strategies for your industry, size, and structure
✔ Integration with TPM, 5S, VSM, TQM, and ERP systems
✔ Focus on culture transformation, not just tool implementation
✔ Tactical and strategic approach—ground-level change backed by C-suite alignment
💬 Let’s Build Your Lean Culture
Lean isn’t a one-off initiative. It’s a way of thinking, managing, and leading. If you're looking to make your organization more efficient, more engaged, and more aligned with customer value—we’re ready to help.
📞 Contact Seicho Consulting today to schedule a consultation and start your journey toward continuous improvement.
#LeanManagement#LeanManagementConsulting#ContinuousImprovement#OperationalExcellence#BusinessTransformation#LeanThinking#ProcessImprovement#Kaizen#GembaWalk#VisualManagement#LeanCulture#LeadershipDevelopment#SeichoConsulting#WasteReduction#LeanStrategy#BusinessConsulting#ChangeManagement#ProductivityImprovement#ManufacturingConsulting#ServiceExcellence
0 notes
Text
64 siglas de gestão industrial que todo gestor precisa saber
New Post has been published on https://www.avantts.com.br/sistema/64-siglas-de-gestao-industrial-que-todo-gestor-precisa-saber
64 siglas de gestão industrial que todo gestor precisa saber

Veja o significado da sigla:
1. ABC – Activity Based Costing (Custeio Baseado em Atividades).
2. ABC Classification – Classificação de produtos em três categorias a partir da curva de Pareto (A: pouca quantidade e grande valor; B: quantidades e valores intermediários; C: muita quantidade e pouco valor).
3. AIS – Automated Information System (Sistema de Informações Automatizado).
4. APS – Advanced Plannig Scheduling (Planejamento da Demanda de Suprimentos).
5. APS – Advanced Planning Systems (Sistemas Avançados de Planejamento), software multi-modular que auxilia na gestão empresarial.
6. ATO – Assembly to Order (Montagem sob Encomenda).
7. BI – Business Inteligence (Inteligência Empresarial).
8. BOM – Bill of Material (Lista de Materiais), produto do MRP que consolida itens comuns a vários produtos.
9. BSC – Balanced Scorecard, metodologia de medição e gestão de desempenho.
10. B2B ou BTB – Business-to-Business.
11. CEO – Chief Executive Officer, Chefe Executivo da Empresa.
12. CEP – Controle Estatístico de Processos.
13. CIM – Computer Integrated Manufacturing (Manufatura Integrada com Computadores.
14. CPM – Critical Path Method (Método do Caminho Crítico).
15. CRP – Continuous Replenishment Process (Programa de Reabastecimento Contínuo).
16. DFM – Design for Manufecturing (Projeto por Manumatura).
17. EAV – Engenharia e Análise do Valor.
18. EDI – Eletronic Data Interchange (Intercâmbio Eletrônico de Dados).
19. ERP – Enterprise Resourse Plannig (Planejamento de Recursos Empresariais), são softwares complexos para controle de vários departamentos.
20. ETO – Engineering to Order (Projeto sob Encomenda).
21. EVA – Economic Value Added (Valor Econômico Agregado).
22. FCS – Finite Capacity Scheduling (Sequenciamento com Capacidade Finita), método de sequenciamento que considera as limitações de capacidade reais.
23. FEFO – First-Expire, First-Out (Primeiro que Vence é o Primeiro que Sai), gestão de estoques de acordo com a validade do produto.
24. FIFO, ou PEPS – First-In, First-Out (Primeiro que Entra é o Primeiro que Sai).
25. FOFA ou FFOA – Siglas em português para a análise SWOT.
26. GED – Gerenciamento Eletrônico de Documentos.
27. ICO – Inventory Chain Optimization (Otimização da Cadeia de Estoques).
28. JIT – Just in Time.
29. LEC – Lote Econômico de Compra.
30. LEP – Lote Econômico de Produção.
31. LT – Lead Time, ou tempo de atravessamento.
32. MES – Manufacturing Execution Systems (Sistemas Integrados de Controle da Produção).
33. MPS – Master Production Schedule, ou Plano Mestre de Produção.
34. MRP – Material Requiriment Plannig (Planejamento das Necessidades de Materiais), sistema informatizado para a elaboração de um plano de suprimentos de materiais.
35. MRP II – Manufacturing Resources Plannig (Planejamento dos Recursos de Manufatura), uma evolução do MRP que fornece uma quantidade maior de dados sobre o produto.
36. MTO – Make to Order (Produção sob Encomenda).
37. MTS – Make to Stock (Produção para estoque).
38. OEE – Overall Equipament Efectiveness, medida da utilização efetiva da capacidade dos equipamentos.
39. OPT – Optimezed Production Tecnology (Tecnologia de Gestão Otimizada), método de gestão da produção a partir de gargalos.
40. PCM – Planejamento e Controle de Materiais.
41. PCP – Planejamento e Controle da Produção.
42. PE – Planejamento Estratégico.
43. PEPS – Primeiro que Entra é o Primeiro que Sai.
44. PERT – Project Evaluation and Review Technique (Técnica de Avaliação e Revisão de Projetos).
45. PPCP – Planejamento, Programação e Controle da Produção.
46. QR – Quick Response (Resposta Rápida).
47. QRTS – Quick Response to Stock (Produção para Estoque com Base numa Resposta Rápida).
48. RTO – Resources to Order (Recursos por Encomenda).
49. S&OP – Sales and Operations Planing (Planejamento de Vendas e Operações).
50. SAP – Systeme, Anwendungen und Produke in der Datenverarbeitung (Sistemas, Aplicativos e Produtos para Processamento de Dados), nome de empresa de software alemã líder mundial no seguimento de ERP.
51. SCOR – Supply Chain Operation Model (Modelo de Referência das Operações na Cadeia de Suprimentos).
52. SKU – Stock Keeping Unit (Unidade de Manutenção de Estoque).
53. SLA – Service Level Agreement (Acordo sobre o Nível de Serviço).
54. SLM – Service Level Management (Gerenciamento do Nível de Serviço).
55. SWOT – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (Forças, Fraquesas, Oportunidades e Ameaças). A análise SWOT é uma ferramenta utilizada para fazer análise de cenários como base para a gestão e o planejamento estratégico.
56. TOC – Theory of Constraints (Teoria das Restrições).
57. TPM – Total Productive Maintence (Manutenção Produtiva Total).
58. TQM – Total Quality Management (Gestão da Qualidade Total).
59. UM – Unidade de Medida.
60. UPC – Universal Product Code (Código Universal do Produto).
61. VMI – Vendor Managed Inventory (Estoque Gerenciado pelo Fornecedor).
62. WCM – World Class Manufacturing (Melhores Práticas Mundiais em Ação).
63. WCS – Warehouse Control Systems (Sistemas de Controle de Armazém).
64. WMS – Warehouse Management Systems (Sistemas de Gerenciamento de Armazém).
Sistema de Gestão para Indústria AVANTTS
Garante aperfeiçoamento nos controles operacionais e de gestão para apoio na tomada de decisões estratégicas, melhoria na relação com os clientes e automatização da cadeia de suprimentos.
0 notes