#Geospatial Visualization
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Location Intelligence Sri Lanka
Elevate Your Decision-Making with Advanced Geospatial Analytics and Insights
In an increasingly complex business landscape, organizations need the ability to analyze and leverage location-based data effectively. Location Intelligence combines advanced mapping, spatial analysis, and data visualization tools to enable businesses to uncover critical insights that inform strategic decisions. Whether you’re optimizing supply chains, enhancing customer targeting, or improving operational efficiency, Location Intelligence provides the tools you need to succeed.
This solution integrates seamlessly with existing data sources, allowing for a holistic view of your operations. By harnessing the power of geospatial analytics, businesses can identify trends, forecast demand, and streamline processes, leading to improved outcomes across various sectors, including retail, logistics, urban planning, and emergency management.
Contact and Visit us at:
+65 6428 6222
#Location Intelligence#GIS analytics#spatial data#MapInfo#Spectrum Spatial#real-time mapping#geospatial intelligence#smart city planning#asset tracking#infrastructure monitoring#emergency response mapping#situational awareness#geospatial visualization
0 notes
Text
location intelligence data
Advintek Geoscience is a leading provider of Location Intelligence solutions in Singapore and across ASEAN, delivering advanced geospatial analytics powered by MapInfo Pro and Precisely’s Spectrum Suite facebook.com+15geosciences.advintek.com.sg+15linkedin.com+15. Leveraging powerful mapping, spatial analysis, and real‑time data integration, they help businesses and government agencies uncover hidden patterns, optimize operations, and make smarter decisions .
From supply chain enhancements and site selection to public safety, telecom planning, and smart‑city deployment, Advintek’s scalable, secure platform enables cost optimization, predictive insights, and improved customer targeting geosciences.advintek.com.sg+1sg.linkedin.com+1. Their seamless integration with existing CRM, GIS, and BI systems ensures smooth adoption, while real‑time dashboards and geofencing offer actionable insights on the go geosciences.advintek.com.sg.
Trusted across diverse sectors—including energy, utilities, urban planning, and emergency response—Advintek’s Location Intelligence empowers clients to transform spatial data into transformative business outcomes facebook.com+15
#Location Intelligence Singapore#Geospatial Analytics ASEAN#MapInfo Pro Solutions#Spectrum Spatial Tools#Spatial Data Visualization#Real‑Time Geospatial Insights#location intelligence data#location based intelligence#location intelligence esri
0 notes
Text
GIS-Based Solutions for Efficient Telecom Network Management
The telecom industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by the increasing demand for seamless connectivity, efficient network management, and improved customer experience. As networks become more complex, the need for innovative solutions to manage these networks has never been greater. Geographic Information System (GIS)-based solutions have emerged as a game-changer in the telecom sector, offering a robust platform for managing, analyzing, and visualizing network data. This blog explores how GIS-based solutions can revolutionize telecom network management, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
Learn more at https://www.cyberswift.com/blog/telecom-utility-solution-a-brief-overview/

#gis for 5g network planning#telecom network monitoring with gis#gis for telecom service coverage analysis#gis enabled telecom site selection#gis mapping for telecom connectivity#gis solutions for managing telecom utilities#role of gis in telecom infrastructure planning#telecom utility gis software for asset management#gis technology for fiber optic network design#geospatial analytics for telecom network optimization#telecom asset management system#gis telecom utility software#fiber optic network mapping#gis based telecom service optimization#telecom network visualization tools#utility network analysis in telecom#geospatial solutions for telecom utilities
0 notes
Text

Optimizing Networks for Efficiency: Strategies and Best Practices
In the ever-evolving landscape of telecoms, network optimization is now a focus for service providing companies searching to enhance performance and offer extraordinary service quality.
The Role of Fiber Management
Fiber Management is a cornerstone of current network optimization. As fiber optic networks become the backbone for worldwide connectivity, managing these assets efficiently is important. Fiber management is the systematic management and control of fiber optic cable, connectors and the associated infrastructure to ensure uninterrupted data transmission.
Click to read more.
Originally published: https://leptonsoftware.com/optimizing-networks-for-efficiency-strategies-and-best-practices/
#lepton maps#lepton software#gis mapping#location intelligence#fiber network#network optimization#telecom solutions#gis#maps#3d map#gis tool#data visualization#geospatial data#geo-fencing#geospatial intelligence#fiber management#fiber planner#fiber planning#fiber design#smartinventory#networkaccess#leptonsoftware
0 notes
Text
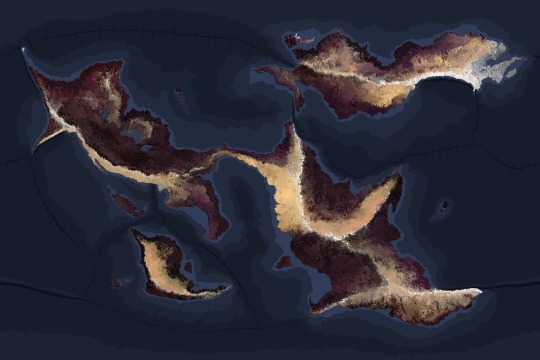
Mission Log: Surface Map Revision
Recorded by: VERA (Volucris Environmental & Reconnaissance Assistant)
Location: Volucris High Orbit
Dr. Abbat is currently reallocated to planetary ground exploration. Geospatial responsibilities will be delegated to VERA until further notice.
Summary of new global topography of Volucris are as follows:
This updated planetary map provides enhanced surface detail and terrain visualizations revealing finer geological and environmental structures. Previous versions displayed only elevation contours, landmass boundaries, tectonic overlays, and ocean currents.
Surface Composition:
Prominent red, violet, and pale ochre regions are now present in all four continent land masses likely indicating exposed iron oxides, silicate deposits, or potential xenofloral presence.
Thin but long strips of white reveal the continental mountain ranges and their signs of glaciation due to colder temperatures in high elevations despite above-average temperatures throughout the planet.
Tan and beige areas mark major deserts formed in the rain shadows of large mountain ranges, which block moisture-carrying winds from reaching these regions.
Crew Deployment Zones Update: All teams are currently on the ground in areas chosen for safe landing. However, the sudden climate shift and fast-moving storms require continuous updates to the mission plan. Ground based unit discretion is advised.
End log.
#speculative biology#speculative ecology#speculative evolution#speculative worldbuilding#world building#speculative fiction#speculative zoology#volucris#writing
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data Visualization: Transforming Data into Insight
In an technology wherein information is produced at an remarkable tempo, the ability to extract significant insights is extra vital than ever. Data visualization plays a vital function on this procedure, enabling individuals and corporations to understand complex statistics sets, pick out trends, and communicate findings effectively. By converting abstract numbers into intuitive visuals, information visualization bridges the gap among uncooked data and human cognition, turning complexity into readability.
Data Visualization In Research

The Importance of Data Visualization
Data visualization is the graphical illustration of information and facts. By the use of visible elements like charts, graphs, and maps, statistics visualization tools make it less difficult to see and understand styles, trends, and outliers in facts. Its importance lies in numerous key areas:
Improved Understanding: Visuals are processed 60,000 times faster than textual content by way of the human mind. Graphs and charts can screen insights that would pass omitted in spreadsheets.
Enhanced Communication: Well-crafted visualizations allow statistics to be shared in a manner that’s available to a broader audience, no longer simply records analysts or statisticians.
Data-Driven Decision Making: In enterprise, governments, and medical research, visualizations support selection-making via without a doubt showing the implications of various statistics tendencies.
Pattern and Anomaly Detection: They help users quick become aware of deviations, spikes, or drops in data, which could suggest possibilities or threats.
Types of Data Visualization
Data visualization encompasses a big selection of techniques, each applicable to precise types of records and analytical desires. Some of the most commonly used sorts include:
1. Bar Charts
Bar charts are best for comparing quantities throughout classes. They are simple however effective for displaying differences among agencies.
2. Line Graphs
Often used to music changes over time, line graphs display tendencies and fluctuations, making them a fave for time-series information.
3. Pie Charts
They’re satisfactory for simple, clear percent facts.
4. Histograms
Histograms display the distribution of a dataset, making them beneficial for understanding records spread, crucial tendency, and frequency.
5. Heat Maps
Heat maps use colour gradients to indicate value depth throughout two dimensions.
6. Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used to pick out relationships between variables, often revealing correlations or clusters in facts.
7. Box Plots
Box plots show the distribution of a dataset thru its quartiles, highlighting medians, variability, and ability outliers.
8. Geospatial Maps
These visualizations display facts associated with geographic regions and are extensively utilized in demographic research, environmental tracking, and logistics.
9. Dashboards
Dashboards integrate multiple visualizations into one interface, supplying a actual-time assessment of key metrics and overall performance signs.
Tools for Data Visualization
A huge range of tools is to be had for growing effective statistics visualizations. Popular alternatives encompass:
Tableau: A leading platform for interactive, shareable dashboards with drag-and-drop functions.
Power BI: Microsoft's enterprise analytics tool with sturdy integration into the Office atmosphere.
Google Data Studio: A unfastened tool for developing customizable reports the use of Google records sources.
Ggplot2: A effective R package for constructing state-of-the-art plots the use of the grammar of snap shots.
Each device gives distinctive competencies depending at the user’s technical information, information complexity, and desired results.
Best Practices in Data Visualization
Creating effective facts visualizations requires more than just technical skill. It includes an information of design ideas, cognitive psychology, and storytelling. Here are key exceptional practices:
1. Know Your Audience
Tailor the visualization to the information stage and pursuits of your target market. What a statistics scientist unearths intuitive is probably complicated to a business executive.
2. Choose the Right Chart
Using an inappropriate chart kind can deceive or confuse the viewer. For instance, a line chart ought to not be used for specific information.
Three. Simplify and Clarify
Avoid muddle. Focus on essential statistics and put off unnecessary elements like immoderate gridlines, decorative snap shots, or redundant labels.
Four. Use Color Thoughtfully
Color can enhance know-how but additionally lie to if used improperly. Stick to a consistent color scheme and use contrasts to highlight key points.
5. Tell a Story
Effective facts visualizations guide the viewer through a story. Highlight tendencies, anomalies, or correlations that support your message.
6. Maintain Integrity
Never manipulate axes or distort scales to magnify findings. Ethical visualization ensures accurate illustration of statistics.
Real-World Applications
Data visualization is applied in nearly each region, transforming industries through stepped forward insight and communication.
1. Business Analytics
In commercial enterprise, visualization tools assist in monitoring sales, client behavior, supply chain efficiency, and extra.
2. Healthcare
In medicinal drug and public health, visualizations are crucial for tracking disorder outbreaks, affected person records, and treatment results. For example, COVID-19 dashboards performed a main function in information the pandemic's unfold.
3. Finance
Financial analysts use records visualization to recognize market tendencies, examine investment overall performance, and check chance.
Four. Education
Educators and researchers use visualization to track pupil performance, perceive mastering gaps, and gift studies findings.
Five. Government and Policy
Policymakers use visible facts to understand social trends, aid allocation, and financial overall performance.
6. Journalism
Data journalism is growing hastily. Visual stories on topics like weather change, election results, or social inequality use charts and infographics to inform and engage readers.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its electricity, facts visualization isn't with out demanding situations:
Data Quality: Inaccurate or incomplete information can lead to deceptive visuals.
Over-Simplification: Trying to make information too easy can lead to lack of nuance or important info.
Misinterpretation: Poor design selections or biased displays can cause audiences to draw wrong conclusions.
Tool Limitations: Not all equipment aid the extent of customization or interactivity wished for unique projects.
Overcoming these demanding situations requires a mix of technical talent, area information, and moral responsibility.
The Future of Data Visualization
The future of statistics visualization is increasingly interactive, actual-time, and AI-assisted. Emerging traits include:
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): Immersive visualizations permit users to explore records in three-dimensional environments.
Machine Learning Integration: Algorithms can now endorse or even vehicle-generate visualizations based on the information furnished.
Collaborative Platforms: Teams can now work collectively in actual time on visualization dashboards, improving communique and agility.
These advancements will hold to make records greater accessible and insightful throughout all domain names.
Difference Between Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
What Is Data Analysis In Research
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 5 GIS Toolboxes: Unlocking the Full Potential of Geographic Information Systems
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have become indispensable in urban planning, environmental protection, engineering, and other fields. With advancements in technology, various GIS toolboxes have emerged, helping users achieve more efficient data processing and 3D visualization. This article introduces five top GIS toolboxes to help you choose the best solution for your needs.
1. GISBox
GISBox is a comprehensive GIS toolbox that integrates data processing, spatial analysis, and 3D visualization functions. A standout feature of GISBox is its efficient real-time editing capabilities, such as photogrammetric mesh repairs, riverbed depressions, and terrain alignment, which significantly simplify complex 3D terrain data processing workflows. Additionally, GISBox supports various mainstream publishing protocols, including 3DTiles, Terrain, and WMTS, offering a range of options for different users. Whether for small to medium-sized enterprises or individual projects, GISBox provides an all-in-one solution to efficiently handle GIS data processing and publishing tasks.
Pros:
· Supports multiple data formats.
· User-friendly plugin system for easy extension.
· Powerful 3D visualization and data processing capabilities.
2. QGIS (Quantum GIS)
QGIS is an open-source and highly customizable GIS tool widely popular among users globally. Its rich plugin ecosystem caters to various GIS needs, from basic map creation to complex spatial analysis.
Pros:
· Free and open-source, with an active user and developer community.
· Rich in plugins with strong extensibility.
· Highly customizable interface and workflow.
3. ArcGIS
Developed by Esri, ArcGIS is a professional GIS platform with a toolbox that provides hundreds of tools for geographic data analysis and map creation. It integrates data collection, processing, analysis, and visualization, making it the top choice for solving complex geographic problems.
Pros:
· Extensive data processing and analysis tools.
· Integration with other Esri products for a complete GIS workflow.
· Professional technical support and learning resources.
4. Global Mapper
Global Mapper is a comprehensive GIS software that supports a wide range of geographic data formats and powerful data processing functions. Known for its simplicity and affordability, it is suitable for users looking to quickly perform spatial analysis and data visualization.
Pros:
· Supports multiple data formats with robust data conversion capabilities.
· Gentle learning curve for easy onboarding.
· Comprehensive functionality suitable for projects of various scales.
5. SuperMap iDesktop
SuperMap iDesktop is a powerful GIS desktop tool that provides a full suite of tools for spatial analysis, data management, and 3D visualization. It is widely used in industries like urban planning, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure management. SuperMap iDesktop integrates a variety of data formats and supports a range of powerful GIS functions, including advanced 3D terrain modeling, geospatial analysis, and the ability to handle large datasets with ease.
Pros:
Advanced 3D modeling capabilities for creating and analyzing detailed terrain models.
Supports a wide variety of data formats, including raster, vector, and 3D data.
Comprehensive spatial analysis tools and detailed reporting features.
User-friendly interface, suitable for both novice and experienced GIS professionals.
Conclusion
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced GIS user, these toolboxes can provide excellent support for your projects. Software like GISBox and Cesiumlab is highly regarded for its exceptional 3D rendering and data management capabilities, while QGIS and Global Mapper are popular for their flexibility and ease of use. Selecting the right tool based on your specific project requirements and budget will help boost your work efficiency and enrich your geographic data presentations.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Maximize Your Fleet Safety with Video Telematics Solutions

Video evidence has consistently proven to be essential in gathering and storing information, especially for businesses engaged in fleet management. More specifically, we are referring to the effective utilization of video telematics.
In recent years, numerous industries have experienced remarkable technological advancements, and the transportation sector has particularly embraced video telematics as a remarkable innovation.
Here is a comprehensive guide that will enable you to acquire a thorough understanding of video telematics solutions.
Table of Contents
What is Vedio Telematics?
DMS- ADAS: The Core Components of Video Telematics Solutions
How do Video Telematics Solutions Operate?
Benefits of Video Telematics Solutions
(1) Driver Monitoring
(2) Real-time Live Streaming
(3) Opportunities for Driver Training
(4) Surveillance for Security
What is Vedio Telematics?
Video telematics is an advanced version of vehicle telematics that combines visual data, vehicle analysis, and geospatial vision. Unlike traditional automotive telematics solutions that only send text alerts to managers, video telematics solutions also capture video data.
The integration of video telematics into fleet management software has greatly improved its capabilities. In addition to real-time location tracking, the software now collects vast amounts of data and provides valuable insights into vehicles through its sensors Dashboard camera records the driver’s actions, while the video sensor captures the environment surrounded both externally and internally. These environmental factors include the speed of nearby vehicles, the behavior of the driver, and the environment around the vehicle.
DMS- ADAS: The Core Components of Video Telematics Solutions
The Driver Management System (DMS) and Advanced Driver Assistant System (ADAS) are not only the fundamental elements of Video Telematics but are also considered the essence and backbone of video telematics.
The Driver Monitoring System (DMS) is responsible for overseeing and monitoring driver behavior, while the Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) aids in monitoring the surrounding road environment. Moreover, the system recognizes events rather than individual actions, categorizing them into various types such as smoking, yawning, drowsiness, and more. The dashcam captures the driver’s actions, compares them with the recognized events, and subsequently generates appropriate alerts.
In addition, fleet managers are also notified about other significant events, including the blocking of the camera, the absence of the driver from the driver’s seat, and the use of a mobile phone.
The ADAS feature not only enhances the overall functionality but also effectively detects the surrounding environment and promptly notifies the driver of any potential incidents. By incorporating the ADAS feature, insurance claim settlements, driver training, and the overall safety of the vehicle, driver, and cargo have been greatly improved. Fleet managers can be notified about events such as chances of forward collisions, red light jumping, and reckless lane switching through ADAS.
How do Video Telematics Solutions Operate?
Video telematics solutions function by combining vehicle data, driving data, real-time location, and video footage transmitted over cellular data. Whenever an event occurs, the device generates an appropriate alert. The main goal of this technology is to enhance driver safety by providing personalized data that can be used for driver training and coaching purposes.
The software primarily focuses on monitoring drivers’ behavior and identifying risky activities such as overspeeding, reckless driving, distracted driving, and more. Cameras are used to capture video footage, which provides a comprehensive understanding of driver conduct and any related issues. This enables fleet management to make well-informed decisions.
Different types of cameras are available based on the fleet’s requirements, including multi-camera, road-facing, and driver-facing cameras.
Benefits of Video Telematics Solutions
Video telematics solutions offer various benefits, particularly in the context of fleet management, safety, and operational efficiency. Here are some key advantages of implementing video telematics solutions:
(1) Driver Monitoring
Video telematics can record and analyze drivers’ behavior, promoting safer driving habits and reducing risky behaviors such as speeding, harsh braking, and aggressive driving. The solution not only analyzes driving habits but also notifies events of collisions. In such events, video footage can provide crucial information for understanding the cause of the event. Advanced video telematics solutions also provide real-time alerts to prevent collisions.
(2) Real-time Live Streaming
Video telematics systems provide real-time streaming, allowing fleet managers to monitor their fleet and the activities of drivers in real time. This solution helps address issues as they arise and improves overall operational visibility.
(3) Opportunities for Driver Training
Utilizing video footage can be an effective method for driver training and coaching. This enables fleet managers to pinpoint areas that require improvement and offer tailored training to enhance the driving skills of their drivers.
(4) Surveillance for Security
Video telematics serves as a deterrent against theft and vandalism. In case of unauthorized access or theft, video footage can assist in locating stolen vehicles and recovering the assets. Wrapping it all
In conclusion, it is undeniable that video telematics plays a vital role in organizations, particularly in fleet management. Although video telematics solutions offer a multitude of advantages, organizations must implement and utilize the system responsibly.
If you are considering acquiring advanced telematics solutions, look no further than TrackoBit. This comprehensive solution offers a 360° visual coverage of your fleet, as well as features such as route planning solutions and fuel management systems.
Source : Maximize Your Fleet Safety with Video Telematics Solutions
1 note
·
View note
Text

Gsource Technologies offers cutting-edge Lidar and Photogrammetry services, revolutionizing geospatial data acquisition and analysis. Our expertise extends across diverse applications, including Digital Terrain and Surface Models, enabling precise elevation mapping for various projects. We specialize in 3D Modeling and web viewers, providing immersive visualizations for enhanced project understanding. Feature Extractions are meticulously performed to identify and analyze key elements, ensuring comprehensive data interpretation.
Our Scan to BIM services facilitate seamless integration of Lidar data into Building Information Modeling processes, enhancing accuracy in construction and design. Additionally, we excel in 2D Linework, CAD Conversions, and Automated Contours, streamlining design workflows. Gsource Technologies' commitment to excellence is further evident in Topo Creation, where we generate detailed topographic maps to meet project specifications. With state-of-the-art technology and a skilled team, we deliver comprehensive Lidar and Photogrammetry solutions tailored to meet the evolving needs of diverse industries.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
This Week in Rust 513
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on Twitter or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Updates from Rust Community
Official
Announcing Rust 1.72.1
Foundation
Announcing the Rust Foundation’s Associate Membership with OpenSSF
Project/Tooling Updates
This month in Servo: upcoming events, new browser UI, and more!
Pagefind v1.0.0 — Stable static search at scale
Open sourcing the Grafbase Engine
Announcing Arroyo 0.6.0
rust-analyzer changelog #199
rumqttd 0.18.0
Observations/Thoughts
Stability without stressing the !@#! out
The State of Async Rust
NFS > FUSE: Why We Built our own NFS Server in Rust
Breaking Tradition: Why Rust Might Be Your Best First Language
The Embedded Rust ESP Development Ecosystem
Sifting through crates.io for malware with OSSF Package Analysis
Choosing a more optimal String type
Changing the rules of Rust
Follow up to "Changing the rules of Rust"
When Zig Outshines Rust - Memory Efficient Enum Arrays
Three years of Bevy
Should I Rust or should I go?
[audio] What's New in Rust 1.68 and 1.69
[audio] Pitching Rust to decision-makers, with Joel Marcey
Rust Walkthroughs
🤗 Calling Hugging Face models from Rust
Rust Cross-Compilation With GitHub Actions
tuify your clap CLI apps and make them more interactive
Enhancing ClickHouse's Geospatial Support
[video] All Rust string types explained
Research
A Grounded Conceptual Model for Ownership Types in Rust
Debugging Trait Errors as Logic Programs
REVIS: An Error Visualization Tool for Rust
Miscellaneous
JetBrains, You're scaring me. The Rust plugin deprecation situation.
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is RustQuant, a crate for quantitative finance.
Thanks to avhz for the self-suggestion!
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Call for Participation
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
r3bl_rs_utils - [tuify] Use nice ANSI symbols instead of ">" to decorate what row is currently selected
r3bl_rs_utils - [all] Use nu shell scripts (not just or fish) and add Github Actions to build & test on mac & linux
r3bl_rs_utils - [tuify] Use offscreen buffer from r3bl_tui to make repaints smooth
Ockam - make building of ockam_app create behind a feature flag
Ockam - Use the Terminal to print out RPC response instead of printlns
Hyperswitch - add domain type for client secret
Hyperswitch - separate payments_session from payments core
Hyperswitch - move redis key creation to a common module
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here.
Updates from the Rust Project
342 pull requests were merged in the last week
#[diagnostic::on_unimplemented] without filters
repr(transparent): it's fine if the one non-1-ZST field is a ZST
accept additional user-defined syntax classes in fenced code blocks
add explicit_predicates_of to SMIR
add i686-pc-windows-gnullvm triple
add diagnostic for raw identifiers in format string
add source type for invalid bool casts
cache reachable_set on disk
canonicalize effect vars in new solver
change unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn to be warn-by-default from edition 2024
closure field capturing: don't depend on alignment of packed fields
consistently pass ty::Const through valtrees
coverage: simplify internal representation of debug types
disabled socketpair for Vita
enable varargs support for AAPCS calling convention
extend rustc -Zls
fallback effects even if types also fallback
fix std::primitive doc: homogenous → homogeneous
fix the error message for #![feature(no_coverage)]
fix: return early when has tainted in mir pass
improve Span in smir
improve PadAdapter::write_char
improve invalid let expression handling
inspect: closer to proof trees for coherence
llvm-wrapper: adapt for LLVM API changes
make .rmeta file in dep-info have correct name (lib prefix)
make ty::Const debug printing less verbose
make useless_ptr_null_checks smarter about some std functions
move required_consts check to general post-mono-check function
only suggest turbofish in patterns if we may recover
properly consider binder vars in HasTypeFlagsVisitor
read from non-scalar constants and statics in dataflow const-prop
remove verbose_generic_activity_with_arg
remove assert that checks type equality
resolve: mark binding is determined after all macros had been expanded
rework no_coverage to coverage(off)
small wins for formatting-related code
some ConstValue refactoring
some inspect improvements
treat host effect params as erased in codegen
turn custom code classes in docs into warning
visit ExprField for lint levels
store a index per dep node kind
stabilize the Saturating type
stabilize const_transmute_copy
make Debug impl for ascii::Char match that of char
add minmax{,_by,_by_key} functions to core::cmp
specialize count for range iterators
impl Step for IP addresses
add implementation for thread::sleep_until
cargo: cli: Add '-n' to dry-run
cargo: pkgid: Allow incomplete versions when unambigious
cargo: doc: differentiate defaults for split-debuginfo
cargo: stabilize credential-process and registry-auth
cargo: emit a warning for credential-alias shadowing
cargo: generalise suggestion on abiguous spec
cargo: limit cargo add feature print
cargo: prerelease candidates error message
cargo: consolidate clap/shell styles
cargo: use RegistryOrIndex enum to replace two booleans
rustfmt: Style help like cargo nightly
clippy: ignore #[doc(hidden)] functions in clippy doc lints
clippy: reuse rustdoc's doc comment handling in Clippy
clippy: extra_unused_type_parameters: Fix edge case FP for parameters in where bounds
clippy: filter_map_bool_then: include multiple derefs from adjustments
clippy: len_without_is_empty: follow type alias to find inherent is_empty method
clippy: used_underscore_bindings: respect lint levels on the binding definition
clippy: useless_conversion: don't lint if type parameter has unsatisfiable bounds for .into_iter() receiver
clippy: fix FP of let_unit_value on async fn args
clippy: fix ICE by u64::try_from(<u128>)
clippy: trigger transmute_null_to_fn on chain of casts
clippy: fix filter_map_bool_then with a bool reference
clippy: ignore closures for some type lints
clippy: ignore span's parents in collect_ast_format_args/find_format_args
clippy: add redundant_as_str lint
clippy: add extra byref checking for the guard's local
clippy: new unnecessary_map_on_constructor lint
clippy: new lint: path_ends_with_ext
clippy: split needless_borrow into two lints
rust-analyzer: field shorthand overwritten in promote local to const assist
rust-analyzer: don't skip closure captures after let-else
rust-analyzer: fix lens location "above_whole_item" breaking lenses
rust-analyzer: temporarily skip decl check in derive expansions
rust-analyzer: prefer stable paths over unstable ones in import path calculation
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
A pretty quiet week, with relatively few statistically significant changes, though some good improvements to a number of benchmarks, particularly in cycle counts rather than instructions.
Triage done by @simulacrum. Revision range: 7e0261e7ea..af78bae
3 Regressions, 3 Improvements, 2 Mixed; 2 of them in rollups
56 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
No RFCs were approved this week.
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
[disposition: merge] RFC: Unicode and escape codes in literals
Tracking Issues & PRs
[disposition: merge] stabilize combining +bundle and +whole-archive link modifiers
[disposition: merge] Stabilize impl_trait_projections
[disposition: merge] Tracking Issue for option_as_slice
[disposition: merge] Amend style guide section for formatting where clauses in type aliases
[disposition: merge] Add allow-by-default lint for unit bindings
New and Updated RFCs
[new] RFC: Remove implicit features in a new edition
[new] RFC: const functions in traits
Call for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
No RFCs issued a call for testing this week.
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2023-09-20 - 2023-10-18 🦀
Virtual
2023-09-20 | Virtual (Cardiff, UK)| Rust and C++ Cardiff
SurrealDB for Rustaceans
2023-09-20 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Nightly Night: Generators
2023-09-21 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2023-09-21 | Virtual (Cologne, DE) | Cologne AWS User Group #AWSUGCGN
AWS User Group Cologne - September Edition: Stefan Willenbrock: Developer Preview: Discovering Rust on AWS
2023-09-21 | Virtual (Linz, AT) | Rust Linz
Rust Meetup Linz - 33rd Edition
2023-09-21 | Virtual (Stuttgart, DE) | Rust Community Stuttgart
Rust-Meetup
2023-09-25 | Virtual (Dublin, IE) | Rust Dublin
How we built the SurrealDB Python client in Rust.
2023-09-26 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn | Mirror
2023-09-26 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Last Tuesday
2023-09-26 | Virtual (Melbourne, VIC, AU) | Rust Melbourne
(Hybrid - online & in person) September 2023 Rust Melbourne Meetup
2023-10-03 | Virtual (Buffalo, NY, US) | Buffalo Rust Meetup
Buffalo Rust User Group, First Tuesdays
2023-10-04 | Virtual (Stuttgart, DE) | Rust Community Stuttgart
Rust-Meetup
2023-10-04 | Virtual (Various) | Ferrous Systems
A Decade of Rust with Ferrous Systems
2023-10-05 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2023-10-07 | Virtual (Kampala, UG) | Rust Circle Kampala
Rust Circle Meetup: Mentorship (First Saturday)
2023-10-10 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn | Mirror
2023-10-10 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday
2023-10-11| Virtual (Boulder, CO, US) | Boulder Elixir and Rust
Monthly Meetup
2023-10-11 - 2023-10-13 | Virtual (Brussels, BE) | EuroRust
EuroRust 2023
2023-10-12 | Virtual (Nuremberg, DE) | Rust Nuremberg
Rust N��rnberg online
2023-10-18 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
Asia
2023-09-25 | Singapore, SG | Metacamp - Web3 Blockchain Community
Introduction to Rust
2023-09-26 | Singapore, SG | Rust Singapore
SG Rustaceans! Updated - Singapore First Rust Meetup!
2023-10-03 | Taipei, TW | WebAssembly and Rust Meetup (Wasm Empowering AI)
WebAssembly Meetup (Wasm Empowering AI) in Taipei
Europe
2023-09-21 | Aarhus, DK | Rust Aarhus
Rust Aarhus - Rust and Talk at Concordium
2023-09-21 | Bern, CH | Rust Bern
Rust Bern Meetup #3 2023 🦀
2023-09-28 | Berlin, DE | React Berlin
React Berlin September Meetup: Creating Videos with React & Remotion & More: Integrating Rust with React Native – Gheorghe Pinzaru
2023-09-28 | Madrid, ES | MadRust
Primer evento Post COVID: ¡Cervezas MadRust!
2023-09-28 | Paris, FR | Paris Scala User Group (PSUG)
PSUG #114 Comparons Scala et Rust
2023-09-30 | Saint Petersburg, RU | Rust Saint Petersburg meetups
Rust Community Meetup: A tale about how I tried to make my Blitz Basic - Vitaly; How to use nix to build projects on Rust – Danil; Getting to know tower middleware. General overview – Mikhail
2023-10-10 | Berlin, DE | OpenTechSchool Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn
2023-10-12 | Reading, UK | Reading Rust Workshop
Reading Rust Meetup at Browns
2023-10-17 | Leipzig, DE | Rust - Modern Systems Programming in Leipzig
SIMD in Rust
North America
2023-09-21 | Lehi, UT, US | Utah Rust
A Cargo Preview w/Ed Page, A Cargo Team Member
2023-09-21 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Meetup at Hacker Dojo
2023-09-21 | Nashville, TN, US | Music City Rust Developers
Rust on the web! Get started with Leptos
2023-09-26 | Mountain View, CA, US | Rust Breakfast & Learn
Rust: snacks & learn
2023-09-26 | Pasadena, CA, US | Pasadena Thursday Go/Rust
Monthly Rust group
2023-09-27 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATX
Rust Lunch - Fareground
2023-09-28 | Boulder, CO, US | Solid State Depot - The Boulder Makerspace
Rust and ROS for Robotics + Happy Hour
2023-10-11 | Boulder, CO, US | Boulder Rust Meetup
First Meetup - Demo Day and Office Hours
2023-10-12 | Lehi, UT, US | Utah Rust
The Actor Model: Fearless Concurrency, Made Easy w/Chris Mena
2023-10-17 | San Francisco, CA, US | San Francisco Rust Study Group
Rust Hacking in Person
Oceania
2023-09-26 | Canberra, ACT, AU | Rust Canberra
September Meetup
2023-09-26 | Melbourne, VIC, AU | Rust Melbourne
(Hybrid - online & in person) September 2023 Rust Melbourne Meetup
2023-09-28 | Brisbane, QLD, AU | Rust Brisbane
September Meetup
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
This is the first programming language I've learned that makes it so easy to make test cases! It's actually a pleasure to implement them.
– 0xMB on rust-users
Thanks to Moy2010 for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Urban Assassinations and the Architecture of Impunity: A Forensic-Intelligence Approach to High-Complexity Killings
By Renato Ferreira da Silva
Abstract
This article introduces a multidisciplinary framework for the investigation of urban executions of high complexity, often involving hybrid actors (state-criminal alliances), logistical sophistication, and targeted use of territorial control. Drawing from recent case analyses in Latin America and methodologies validated in U.S. cities such as Chicago, the paper proposes an integrated model combining geoforensics, ballistic reconstruction, and network intelligence. The theoretical foundation is anchored in the Urban Homicide Complexity Assessment (UHCA) index and explores the intersection between forensic science, urban segregation, and institutional fragility.
1. Introduction: Urban Executions as a Criminal Modality
Targeted killings in urban areas have evolved into an identifiable criminal modality. Unlike random homicides, urban executions:
Display logistical planning (pre-crime surveillance, getaway routes)
Use controlled environments (blind spots, abandoned alleys)
Reveal intentional messaging (silencing, territorial domination, political signaling)
These cases often occur within what Caldeira (2000) described as the “fortified city,” where inequality enables operational predictability for perpetrators and systemic impunity for investigators.
2. Methodological Foundation: The UHCA Index
The Urban Homicide Complexity Assessment (UHCA) model is structured on five forensic-intelligence pillars:DimensionWeightIndicatorsTerritorial Control25%Blind spots, informal checkpointsActor Hybridization20%Police/militia ties, gang-state overlapsTechnological Suppression15%Jammed cameras, burner phonesBallistic Signature25%Ammunition pattern, forensic rarityTemporal Precision15%Tactical timing (e.g., market hours)
UHCA scores above 0.72 correlate with low rates of resolution (solvability < 10%) unless special investigative protocols are adopted.
3. Ballistic Forensics in Complex Executions
Ballistic analysis must move beyond the projectile:
Trajectory mapping using 3D reconstruction (string-laser, photogrammetry)
Impact dispersion models to determine firing angles and distances
Identification of rare calibers, often linked to paramilitary groups or recycled ammunition from state stocks
Example: The use of 5.56mm or 7.62mm rounds in civilian areas may indicate access to military-grade weapons, suggesting involvement of trained actors.
4. Geoforensics and Urban Topology
Urban geography is both obstacle and facilitator:
QGIS mapping identifies occluded zones and escape vectors
Drone and LiDAR integration enhances post-crime scene recreation
Cross-referencing camera angles, traffic patterns, and Wi-Fi pings enables geospatial triangulation of suspects' movement
Blind spot mapping becomes central in regions with overlapping jurisdictions or informal control (e.g., markets, ports, favelas).
5. Criminal Network Intelligence (CNI)
Traditional criminal profiling often fails in hybrid environments. CNI focuses on:
Relational mapping (Maltego, NetworkX): phones, vehicles, state contracts
SNA (Social Network Analysis): betweenness centrality to find logistical nodes
Gephi visualization of temporal evolution in actor alliances
Example: Analysis of 17 unsolved killings in Northeast Brazil showed recurrent digital proximity between victims and logistical operators with low public visibility but high centrality in local criminal economies.
6. Ethical-Operational Dilemmas
Investigating high-complexity executions in urban peripheries poses deep ethical risks:
State involvement (militias, death squads)
Selective silence (internal sabotage, fear-based omission)
Community retraumatization from repressive “pacification” tactics
Thus, investigations must be auditable, include civil oversight, and integrate a non-retaliatory posture in public communication strategies.
7. Policy Recommendations
To mitigate impunity in urban executions:
Create mobile multidisciplinary units (forensics, tech, community)
Mandate UHCA scoring for all suspected targeted killings
Establish national blind spot registries
Expand digital forensics in public video ecosystems
Incentivize transparent investigatory dashboards at state level
Conclusion
Urban executions are not anomalies but systemic fractures in modern urban governance. Their investigation requires an approach that is at once forensic, sociological, geospatial and strategic. The integration of tools like UHCA, open-source intelligence, and post-mortem trajectory simulation is no longer optional—it is the baseline for any institution seriously committed to justice in asymmetric urban environments.
References
Caldeira, T. P. R. (2000). City of Walls: Crime, Segregation, and Citizenship in São Paulo. University of California Press.
Muggah, R. (2015). Fragile Cities: Violence, Security and Urban Inequality. Igarapé Institute.
UNODC (2022). Global Study on Homicide.
FBSP (2025). Relatório Nacional de Execuções de Alta Complexidade.
Silva, R. (2024). Geoforensics in the Global South. Revista Brasileira de Criminalística.
0 notes
Text
Empower Geospatial Decision-Making with MapInfo Pro – The Essential Tool for Advanced Spatial Analytics
MapInfo Pro is a powerful desktop GIS software that enables businesses to visualize, analyze, interpret, and output spatial data. From precision mapping to data-rich insights, MapInfo Pro transforms geospatial intelligence into actionable strategies for industries across Asia, including Malaysia, Singapore, and Indonesia.
Contact us
Get in Touch with us
Location
7 Temasek Boulevard, #12-07, Suntec Tower One, Singapore 038987
Email Address
Phone Number
+65 6428 6222
Visit us at:
#MapInfo Pro GIS Software#Esri Alternative GIS#Desktop GIS Mapping Tool#Spatial Data Analysis#Geospatial Visualization#Location Intelligence Software
0 notes
Text
How to Map Waste Disposal Sites and Residential Areas Using GIS Tools
In today’s rapidly expanding cities, maintaining environmental health and residential safety has become a top priority. Waste disposal sites—while necessary—can pose serious risks to nearby communities if not strategically located. By using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to map these facilities alongside residential zones, we can better understand their impact and plan smarter urban layouts. Buffer analysis, a powerful GIS technique, allows users to identify areas at risk, detect violations in zoning laws, and protect public health.
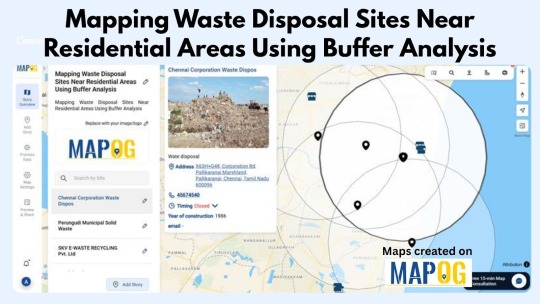
Revealing Environmental Risk Through Spatial Insight
Every waste site has a radius of influence—whether through air, water, or land. Mapping these facilities within a geographical context enables planners to analyze how close they are to homes, schools, and hospitals. Platforms like MAPOG simplify this process by allowing users to overlay datasets, apply buffer zones (e.g., 500 meters), and instantly spot communities that may be affected. This spatial visibility supports stronger regulation, better planning, and more transparent environmental governance.
Transforming Urban Health with Interactive Maps
Traditional environmental reports often fail to show the human impact. But with interactive tools like MAPOG, users can visualize buffer zones around landfills or incineration units and immediately see which neighborhoods fall within potential danger zones. This empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions—such as relocating facilities, issuing health alerts, or planning green buffers. Whether you're an environmental analyst, urban planner, or student, mapping turns complex datasets into clear, actionable knowledge.
Who Benefits from Mapping Waste and Residential Data?
This GIS-based approach supports a wide range of users—municipal authorities, environmental consultants, urban development boards, health officials, researchers, and community organizations. By identifying risk zones, they can plan safer cities, advocate for cleaner surroundings, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Tools like MAPOG make this work faster, more accurate, and easier to communicate.

Conclusion
MAPOG is more than just a mapping tool—it’s a platform for environmental storytelling. Whether you're highlighting unsafe proximities, planning safer waste zones, or conducting research, MAPOG helps transform raw geospatial data into meaningful insights. If you're tackling environmental challenges in your city, start mapping with MAPOG and take a step toward healthier, more sustainable urban living.
Have you explored waste proximity mapping in your neighborhood? Share your approach and insights below—we’d love to see how you're making your city cleaner and safer!
0 notes
Text
EMEA 3D Data Analytics: Market Dynamics and Innovation 2024–2032

The EMEA 3D mass data market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for geospatial intelligence, 3D mapping, digital twins, and data visualization across industries such as construction, urban planning, defense, and transportation. The adoption of technologies like LiDAR, photogrammetry, drones, and AI-based modeling is fueling the collection, analysis, and utilization of large-scale 3D datasets. Governments and private organizations in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (EMEA) are investing in 3D mass data technologies to support smart city initiatives, infrastructure projects, and environmental monitoring.
Market Overview The 3D mass data market encompasses 3D scanning, modeling, visualization, and data analytics services that enable accurate representation of real-world environments. Key trends include: • Growing applications of digital twins and 3D mapping for smart city development. • Cloud-based storage and data processing solutions for managing large-scale 3D datasets. • Integration of AI, machine learning, and IoT for real-time data analysis. • Use of 3D geospatial data for urban planning, infrastructure monitoring, and disaster management. Click here to download a sample report
Key Market Drivers
Smart City and Infrastructure Development Urbanization across EMEA is driving investments in 3D mapping and real-time infrastructure monitoring.
Advancements in 3D Scanning Technologies The use of LiDAR, drones, and satellite imagery enables high-resolution data collection.
Rising Demand for Digital Twins Industries are adopting digital replicas of physical assets for predictive maintenance and planning.
Increased Government Initiatives Geospatial intelligence and environmental monitoring projects are boosting the market.
Adoption of AR/VR and Simulation Technologies 3D data is essential for immersive visualization and virtual simulations.
Market Segmentation By Component: • Hardware (3D Scanners, LiDAR Sensors, Drones) • Software (Mapping, Modeling, Visualization Tools) • Services (Data Collection, Cloud Processing, Analytics) By Application: • Urban Planning and Smart Cities • Transportation and Logistics • Construction and Infrastructure • Defense and Security • Environmental Monitoring • Healthcare and Industrial Applications By Data Source: • Satellite-Based Data • Terrestrial Scanning • Aerial/Drones • Others (Mobile Mapping) By Region (EMEA): • Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Rest of Europe) • Middle East (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Israel, Others) • Africa (South Africa, Egypt, Rest of Africa)
Regional Insights Europe The largest segment, with smart city projects, digital twin initiatives, and strong adoption of LiDAR and photogrammetry technologies in countries like Germany and the UK. Middle East Rapid adoption of 3D mapping and geospatial technologies for infrastructure projects, including mega-projects like NEOM in Saudi Arabia and smart cities in the UAE. Africa Growing investments in 3D data for agriculture, urban development, and disaster management in countries like South Africa and Egypt.
Competitive Landscape The EMEA 3D mass data market is competitive and technology-driven, with players offering hardware, software, and managed services. Key Companies Include: • Hexagon AB • Trimble Inc. • Autodesk Inc. • Bentley Systems Inc. • Dassault Systèmes • Esri • Leica Geosystems AG (Hexagon) • Topcon Positioning Systems • Pix4D SA • Fugro N.V. Strategic Initiatives: • Expansion of cloud-based 3D data platforms. • Integration of AI-driven analytics and real-time data processing. • Partnerships with governments for smart city and infrastructure projects.
Technological & Product Trends Cloud-Based 3D Data Management Enabling real-time storage, collaboration, and analysis of massive datasets. AI and Predictive Analytics AI is increasingly being used for automatic object recognition and 3D model generation. Integration with AR/VR Immersive visualization using augmented and virtual reality is enhancing planning and training applications. Digital Twins Widely adopted in construction, energy, and transportation for real-time performance monitoring.
Challenges and Restraints • High Costs of Hardware and Software: Advanced 3D mapping technologies require significant investment. • Data Security Concerns: Managing sensitive geospatial data involves cybersecurity risks. • Lack of Skilled Workforce: Shortage of experts in 3D modeling, GIS, and data analytics. • Standardization Issues: Inconsistent data formats and lack of global standards hamper interoperability.
Future Outlook (2024–2032) The EMEA 3D mass data market is expected to grow significantly due to: • Expansion of smart city initiatives and infrastructure modernization. • Increased adoption of cloud platforms and AI for scalable 3D data processing. • Rising demand for autonomous vehicles and navigation solutions requiring 3D geospatial data. • Advancements in satellite imaging and drone technology. By 2032, 3D mass data will be central to urban planning, industrial automation, and immersive simulations across the EMEA region.
Conclusion The EMEA 3D mass data market is poised for strong growth, driven by technological advancements, smart city initiatives, and cross-industry applications. Companies that invest in AI-enabled platforms, cloud-based services, and strategic partnerships will gain a competitive advantage.
0 notes
Text
How Quickly Can Laser Scanning Data Be Turned Into Usable Models?
In the modern world of surveying and construction, laser land scanning has become an essential technology for capturing highly accurate spatial data. The rapid advancement in laser scanning tools, paired with sophisticated data processing software, has significantly accelerated the timeline from raw data collection to delivering detailed, usable models. But the question remains: how quickly can laser scanning data be turned into usable models?
Understanding this transformation process is crucial for professionals in architecture, civil engineering, urban planning, and geospatial services. Speed and precision are both vital in keeping projects on time and within budget. This article explores how quickly data from laser land scanning can be converted into actionable digital models—and what factors influence that timeline.

What Is Laser Land Scanning?
Laser land scanning refers to the use of Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology to capture three-dimensional information about the surface of the earth or built environments. This method involves emitting laser beams from a scanner, which bounce off surfaces and return to the device. The time it takes for each beam to return is used to calculate the exact distance between the scanner and the surface, creating a dense cloud of data points, known as a point cloud.
This point cloud forms the raw data set, which serves as the foundation for developing detailed 3D models used in planning, design, analysis, and construction verification.
Stages of Data Processing in Laser Land Scanning
The journey from raw laser land scanning data to a usable model typically involves several key stages:
Data Acquisition This phase includes the physical act of scanning a site. Depending on the size and complexity of the area, it may take a few hours to several days. Mobile, terrestrial, or aerial scanners may be used based on terrain and project scope.
Data Registration and Cleaning Once data is collected, it must be aligned and merged into a single coordinate system. Registration removes overlapping or redundant points and ensures spatial accuracy. Data cleaning removes noise, outliers, and irrelevant information that could skew the final model.
Point Cloud Classification Classification involves labeling data points according to object type (e.g., buildings, vegetation, ground). This step is essential for creating specific model types, like Digital Terrain Models (DTMs) or Building Information Models (BIMs).
Model Generation After classification, software is used to convert the point cloud into structured 3D models or surface meshes. These models are further refined with textures, colors, and measurements depending on the project’s end use.
How Long Does It Take to Generate Usable Models?
The timeline to produce usable models from laser land scanning depends on several factors:
Project Scale and Complexity Large infrastructure projects or urban environments with dense features require more scanning time and data processing. Smaller sites may produce models within a few days, whereas complex projects can take weeks.
Quality of Raw Data High-quality scans reduce the time needed for cleaning and registration. Poor lighting conditions, environmental interference, or equipment limitations can delay processing.
Software and Automation Tools Advanced software solutions with AI-driven features can expedite classification and model creation. Automation significantly reduces manual input and processing time.
Required Level of Detail Models required for visualization purposes can be generated faster than those needed for construction-grade precision. More detailed outputs necessitate more processing and quality checks.
Optimizing the Workflow for Faster Results
Efficiency in laser land scanning depends on careful planning and the integration of advanced tools. Pre-scan planning ensures the correct scanner type is used, minimizing data gaps. Real-time feedback during scanning allows for immediate adjustments, ensuring high-quality data capture.
Post-processing workflows benefit from parallel computing, batch processing, and cloud-based solutions, all of which can drastically reduce turnaround times. Additionally, experienced technicians and clear project objectives help eliminate rework and accelerate delivery.
Applications That Demand Fast Turnaround
Several industries rely on the quick transformation of laser land scanning data into models:
Construction and Engineering Tight construction schedules demand quick model generation for as-built verification and clash detection.
Disaster Management Emergency response teams use fast-generated topographic models for damage assessment and recovery planning.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Maintenance Ongoing development and repair work require updated models for accurate decision-making.
Conclusion
The speed at which laser land scanning data can be turned into usable models continues to improve as technology evolves. While the timeline varies by project, many models can now be delivered within days rather than weeks. Key factors such as data quality, project complexity, and software capabilities all influence this turnaround time. As demand grows for high-precision, rapid modeling, laser land scanning will remain at the forefront of digital surveying and spatial intelligence.
Embracing this technology ensures better outcomes, faster project cycles, and more informed decision-making across multiple sectors.
0 notes
Text
Real-Time GIS Data Collection and Visualization
Real-time GIS (Geographic Information System) data gathering and visualization are transforming the way we engage with spatial information in the era of smart cities, autonomous systems, and precision analytics. Real-time geospatial data collection and visualization are revolutionizing decision-making in a variety of industries, from environmental monitoring and transportation to urban planning and catastrophe response.

https://www.geowgs84.com/post/real-time-gis-data-collection-and-visualization
0 notes