#ISRO addressing system
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
India’s Digital Addressing Revolution: DIGIPIN by India Post and ISRO
#DIGIPIN#DigitalIndia#IndiaPost#ISRO#LogisticsReform#accurate delivery India#DAC portal India Post#delivery solutions India#digital India initiative#digital pin code India#e-governance solutions#geolocation address India#get digital home address India#gps address system#GPS home code#how to get DIGIPIN#India Post DIGIPIN registration#India Post digital address#India Post innovation#Indian logistics innovation#ISRO addressing system#postal reform India#rural logistics India
0 notes
Text



How New NASA, India Earth Satellite NISAR Will See Earth
Set to launch within a few months, NISAR will use a technique called synthetic aperture radar to produce incredibly detailed maps of surface change on our planet.
When NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization’s (ISRO) new Earth satellite NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) launches in coming months, it will capture images of Earth’s surface so detailed they will show how much small plots of land and ice are moving, down to fractions of an inch. Imaging nearly all of Earth’s solid surfaces twice every 12 days, it will see the flex of Earth’s crust before and after natural disasters such as earthquakes; it will monitor the motion of glaciers and ice sheets; and it will track ecosystem changes, including forest growth and deforestation.
The mission’s extraordinary capabilities come from the technique noted in its name: synthetic aperture radar, or SAR. Pioneered by NASA for use in space, SAR combines multiple measurements, taken as a radar flies overhead, to sharpen the scene below. It works like conventional radar, which uses microwaves to detect distant surfaces and objects, but steps up the data processing to reveal properties and characteristics at high resolution.
To get such detail without SAR, radar satellites would need antennas too enormous to launch, much less operate. At 39 feet (12 meters) wide when deployed, NISAR’s radar antenna reflector is as wide as a city bus is long. Yet it would have to be 12 miles (19 kilometers) in diameter for the mission’s L-band instrument, using traditional radar techniques, to image pixels of Earth down to 30 feet (10 meters) across.
Synthetic aperture radar “allows us to refine things very accurately,” said Charles Elachi, who led NASA spaceborne SAR missions before serving as director of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California from 2001 to 2016. “The NISAR mission will open a whole new realm to learn about our planet as a dynamic system.”
How SAR Works
Elachi arrived at JPL in 1971 after graduating from Caltech, joining a group of engineers developing a radar to study Venus’ surface. Then, as now, radar’s allure was simple: It could collect measurements day and night and see through clouds. The team’s work led to the Magellan mission to Venus in 1989 and several NASA space shuttle radar missions.
An orbiting radar operates on the same principles as one tracking planes at an airport. The spaceborne antenna emits microwave pulses toward Earth. When the pulses hit something — a volcanic cone, for example — they scatter. The antenna receives those signals that echo back to the instrument, which measures their strength, change in frequency, how long they took to return, and if they bounced off of multiple surfaces, such as buildings.
This information can help detect the presence of an object or surface, its distance away, and its speed, but the resolution is too low to generate a clear picture. First conceived at Goodyear Aircraft Corp. in 1952, SAR addresses that issue.
“It’s a technique to create high-resolution images from a low-resolution system,” said Paul Rosen, NISAR’s project scientist at JPL.
As the radar travels, its antenna continuously transmits microwaves and receives echoes from the surface. Because the instrument is moving relative to Earth, there are slight changes in frequency in the return signals. Called the Doppler shift, it’s the same effect that causes a siren’s pitch to rise as a fire engine approaches then fall as it departs.
Computer processing of those signals is like a camera lens redirecting and focusing light to produce a sharp photograph. With SAR, the spacecraft’s path forms the “lens,” and the processing adjusts for the Doppler shifts, allowing the echoes to be aggregated into a single, focused image.
Using SAR
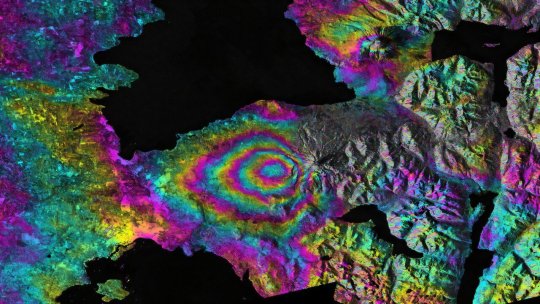
One type of SAR-based visualization is an interferogram, a composite of two images taken at separate times that reveals the differences by measuring the change in the delay of echoes. Though they may look like modern art to the untrained eye, the multicolor concentric bands of interferograms show how far land surfaces have moved: The closer the bands, the greater the motion. Seismologists use these visualizations to measure land deformation from earthquakes.
Another type of SAR analysis, called polarimetry, measures the vertical or horizontal orientation of return waves relative to that of transmitted signals. Waves bouncing off linear structures like buildings tend to return in the same orientation, while those bouncing off irregular features, like tree canopies, return in another orientation. By mapping the differences and the strength of the return signals, researchers can identify an area’s land cover, which is useful for studying deforestation and flooding.
Such analyses are examples of ways NISAR will help researchers better understand processes that affect billions of lives.
“This mission packs in a wide range of science toward a common goal of studying our changing planet and the impacts of natural hazards,” said Deepak Putrevu, co-lead of the ISRO science team at the Space Applications Centre in Ahmedabad, India.
TOP IMAGE: NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory used radar data taken by ESA’s Sentinel-1A satellite before and after the 2015 eruption of the Calbuco volcano in Chile to create this interferogram showing land deformation. The color bands west of the volcano indicat… Credit: ESA/NASA/JPL-Caltech
CENTRE IMAGE: A SAR image — like ones NISAR will produce — shows land cover on Mount Okmok on Alaska’s Umnak Island. Created with data taken in August 2011 by NASA’s UAVSAR instrument, it is an example of polarimetry, which measures return waves’ orientation relati… Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
LOWER IMAGE: A collaboration between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation, NISAR will use synthetic aperture radar to offer insights into change in Earth’s solid surfaces, including the Antarctic ice sheet. The spacecraft, depicted here in an artist’s concept, will launch from India. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Space Tech: Private Ventures and Mars Exploration

Space Tech
Beyond intrepid exploration, space technology has advanced to address pressing issues on Earth. It is becoming more and more essential to the effective operation of contemporary societies and their economic growth. Space has the potential to directly affect billions of people’s lives and open up large-scale, highly impactful solutions.
A broad term for satellites, space stations, ground stations, tracking and monitoring centers, downstream analytics and artificial intelligence, software, and other technologies, SpaceTech offers innovative ways to solve global concerns. Satellites increase communication, navigation, and earth observation capacity at low cost even in remote locations. Satellite-based earth observation data is vital, accurate, and reliable for data-driven decision-making by businesses and governments.
The underserved and otherwise unprofitable regions can benefit from high-speed connectivity thanks to the satellites. The application of action plans for intelligent agriculture, resource management (land and water), infrastructure development (urban and rural), climate and weather monitoring, environmental protection (including reducing the risk of disaster), and other purposes can all benefit from the use of satellite data.
Aerospace Innovation
The space industry is predicted to increase in value from USD 360 billion in 2018 to USD 558 billion by 2026 and roughly USD 1 trillion by 2040. Even though the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is one of the world’s top space agencies and is working on projects like the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (NavIC) and the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), India currently only makes up 2%, or USD 7 Bn, of this market value.
One reason could be that the private sector’s contribution to the Indian space industry has primarily consisted of ISRO subcontracting, with ISRO historically handling the crucial value addition activities internally. Because of this, Indian private companies have lagged behind other world leaders in SpaceTech in terms of end-to-end capabilities.
The publication of SpaceCom Policy 2020, Space RS Policy 2020, Geospatial Policy 2021, and other policies, along with the creation of organizations like NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL) and the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN–SPACe), have created a national push to expedite the private sector’s involvement in the Indian space area. The Department of Space is also working on a comprehensive Space Act and other policies, including launch vehicle and space exploration policies.
Because of our natural curiosity and desire to understand the universe, space travel has long fascinated people.
Recently, private enterprise and international cooperation have transformed space exploration.
This article will explore the changing face of space exploration and emphasize the importance of international collaboration and private industry.
New Space Technologies
Pioneers of Personal Space Travel
NASA, Roscosmos, and ESA were the only government space agencies allowed to explore space. However, private companies leading space innovation changed everything:
SpaceX since 2002 has resupplied the ISS, developed reusable rocket technology, and prepared to colonize Mars.
Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin offers professional and recreational suborbital and orbital spaceflight.
Rick Branson’s suborbital space tourism company, Virgin Galactic.
Innovating, competing, and seeking commercial opportunities beyond Earth are redefining space exploration in private space ventures.
Space Exploration Companies
International Space Cooperation
Space exploration requires international cooperation even as private businesses grow:
The Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS) is a global collaboration marvel. European, Japanese, Canadian, Russian, and US space agencies participate.
Mars exploration: NASA, ESA, and others work on Curiosity and Mars Sample Return.
The Artemis Accords outlines global cooperation on the Moon and beyond, inviting international partners to lunar exploration.
Global Collaboration and Private Enterprises Benefits
Space exploration benefits from private sector involvement and international cooperation in a number of ways.
Innovation: By bringing in competition and innovation, private endeavors lower costs and advance technology.
Commercialization: Businesses worldwide can take advantage of commercial endeavors to expand their satellite deployment, space tourism, and resource exploitation capabilities.
Shared Resources: Working together, nations can pool resources, exchange knowledge, and take on challenging projects.
Scientific Discovery: Across national boundaries, international cooperation increases the possibility of scientific discovery and exploration.
Difficulties and Things to Think About
Although private and international partnerships present notable benefits, they also present certain challenges.
Regulation: To address new challenges, the framework governing international cooperation and private space endeavors needs to change.
Resource Management: A complex ethical and legal challenge is the responsible use of space resources, such as lunar mining.
Space Debris: Coordinated actions ought to tackle the expanding problem of space debris and environmentally friendly space operations.
Space Travel Prospects
Future space exploration could lead to asteroid mining, planet colonization, and scientific breakthroughs.
Space exploration is entering a new era as private companies and multinational partnerships change the space environment.
Space exploration is more accessible, sustainable, and transformative than ever thanks to private innovation and international collaboration. It shows our willingness to push the limits and our enduring spirit of exploration.
Mars Rover
What is Mars Rover?
A robotic vehicle that investigates the surface of Mars is called a rover. Rovers are long-range, remotely controlled vehicles that gather data and take images while traveling great distances. They have found evidence of water, ancient life, and possible resources on Mars, among many other significant discoveries.
Six Mars rovers have been successful so far:
In 1997, Sojourner became the first rover to set foot on Mars. During 83 days, it investigated the Ares Vallis region. The twin rovers Spirit (2004) and Opportunity (2004) touched down on Mars in 2004. For many years, they investigated the Gusev Crater and Meridiani Planum, respectively. Opportunity stopped operating in 2018 and Spirit became stuck in 2010.
Gale Crater is presently being explored by Curiosity (2012). It has found evidence of ancient lakes and rivers, among many other significant discoveries.
The Jezero Crater region is being explored in Perseverance (2021). In addition to gathering samples of rock and regolith broken rock and soil for potential return to Earth, it is searching for indications of prehistoric life.
The first Chinese rover to set foot on Mars is Zhurong (2021). It is investigating the area of Utopia Planitia.
An essential component of our Mars exploration are the Mars rovers. They have made significant contributions to our understanding of the Red Planet’s potential for habitability.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Space Tech#MarsExploration#Ventures#SpaceTech#satellites#AI#Aerospace#NASA#technews#technology#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Indian Addresses! 🇮🇳📬 Say hello to DIGIPIN, the game-changing technology from India Post!
Tired of inaccurate addresses and delivery hassles? India Post has launched DIGIPIN (Digital Postal Index Number), a 10-character alphanumeric code that provides a precise digital address for every 4x4 meter square! 🗺️
This innovative system, developed in collaboration with IIT Hyderabad, ISRO, and NRSC, ensures accurate location identification, transforming e-commerce, emergency services, and more. 🚀
Key features:
Precise Addressing: Eliminates ambiguity with a unique code for every location.
Easy to Use: Find your DIGIPIN on the official India Post website.
Revolutionary Technology: Set to transform logistics, delivery, and various sectors.
Learn more about this groundbreaking initiative and how it will impact India's future!
Watch the video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SV-P9elW84Y
#DIGIPIN #IndiaPost #DigitalIndia #Innovation #Technology #Logistics #ECommerce #AddressRevolution #ISRO #IITHyderabad #NRSC #NitishVerma
YouTube
youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Latest Government Tenders in Kerala
During the last financial year, government agencies in Kerala actively engaged in extensive procurement and maintenance works across various sectors. Over 50,000 tenders were issued for road development, including relaying, repairs, and new constructions such as WBM, BT, tar, and cement concrete roads, primarily driven by the Local Self Government Department (LSGD) and Kerala PWD. In the social infrastructure domain, more than 5,000 tenders were floated for the construction and maintenance of Anganwadi centres, while over 3,000 tenders focused on strengthening and desilting Kerala's extensive canal network. Manpower hiring saw over 650 tenders for roles like computer operators, drivers, security personnel, and specialized staff. Painting works across hundreds of government offices led to around 300 tenders, with specialized jobs issued by BPCL, Indian Army, and Airports Authority of India. Kerala also prioritized green infrastructure with 275 tenders for park development and landscape maintenance. On the goods procurement front, over 2,000 tenders were issued for construction materials, while 898 tenders covered the purchase of computers, including high-end systems. More than 600 tenders were floated for laboratory equipment by institutions like Kerala University and ISRO. Additionally, 500 tenders were published for vehicle spares, largely by KSRTC and the Indian Army, and 307 tenders addressed the procurement of essential medicines under healthcare missions such as Aardram and Karunya, led by the Directorate of Medical Education and supported by PSUs like Southern Railways.
Tendering processes play a crucial role in ensuring fairness and accountability in public procurement, and with the high volume of tenders in Kerala, platforms like TenderSniper are essential tools for efficiently tracking and responding to these opportunities.Here’s a detailed look at how TenderSniper can assist in accessing and managing kerala tenders.

0 notes
Text
AI and robotics professionals can shape India’s future..

India is rapidly emerging as a global hub for robotics and artificial intelligence (AI), transforming sectors like healthcare, agriculture, finance, manufacturing, and e-commerce. With the Indian government pushing initiatives like Make in India, Digital India, and AI for All, there is an increasing demand for professionals skilled in robotics and AI. If you are interested in this exciting field, here are some promising career opportunities:
1. Robotics Engineer
Robotics engineers design and build robots for industries like automobile manufacturing, healthcare, and even space exploration (think ISRO and DRDO!). From industrial automation to robotic surgery, this role is crucial for India's tech-driven future.
2. AI Research Scientist
AI research scientists work in leading research labs, universities, and companies to develop new AI models and improve machine learning systems. With institutions like IITs, IISc, and private tech giants investing in AI research, opportunities in this field are expanding.
3. Machine Learning Engineer
Machine learning engineers create AI-powered solutions used in industries like fintech (UPI fraud detection), edtech (personalized learning apps), and healthcare (AI-driven diagnostics). India’s growing startup ecosystem is creating numerous opportunities in this field.
4. Autonomous Systems Engineer
Self-driving cars, delivery drones, and AI-powered robots in logistics and warehousing are becoming more common in India. Engineers in this field design and develop these smart systems, ensuring safety and efficiency.
5. Data Scientist
With data being the backbone of AI, data scientists play a crucial role in analyzing large datasets, optimizing AI algorithms, and driving business decisions. Companies like TCS, Infosys, and startups rely heavily on data science to improve their AI models.
6. AI Ethics Specialist
As AI adoption grows, ethical concerns around privacy, bias, and fairness need attention. AI ethics specialists ensure AI systems are transparent and unbiased, addressing regulatory and ethical challenges in AI implementation.
Learn more about the career opportunities for students in educationist, Kavita Kerawalla's latest LinkedIn blog.
0 notes
Text
India’s SpaceTech Revolution: The Rise of Private Sector Innovators
Introduction

However, before diving into the industry’s rapid transformation, let’s understand the primary segments of the space market:
Upstream Market: Involves satellite manufacturing, launch vehicles, and ground systems — essentially everything required to get assets into space.
Downstream Market: Focuses on data utilization from satellites, such as communication, navigation, and Earth observation services.
Additionally, enablers such as contract manufacturers, component suppliers, and testing facilities play a crucial role in supporting the ecosystem’s growth.
With the upstream market projected to grow from $4.7 billion in 2023 to over $25 billion by 2030 and the downstream segment expanding from $10 billion to over $52 billion, the opportunities in India’s space sector are limitless.
The Downstream segment accounts for two-thirds of the total industry revenue, driven by applications in communication, navigation, and Earth observation.
Let’s Explore the Expanding Role of the Private Sector in Space
The privatisation of the space industry is proving to be a game-changer. Once dominated by government agencies, the sector witnessed more than 150 private players emerging in the last decade, attracting $280 million in funding, with over 66% directed towards the upstream segment. The involvement of key stakeholders, strategic partnerships, and technological/material advancements are creating a collaborative yet competitive ecosystem capable of catapulting India into the next leg of space prominence.
Creation of nodal bodies such as IN-SPACe and NSIL are playing a critical role in this growth. The government through various financial incentives — such as GST exemption, a new spacetech focused fund — and regulatory support — 100% FDI through automatic route — are giving a strong boost to the ecosystem.
Recent collaborations, such as Microsoft’s partnership with ISRO in 2023, underscore the growing global interest in India’s space ecosystem. The addition of over 100 new space-tech startups in 2023, further echoes the potential of a thriving market poised for exponential growth.
Startups are seen innovating across various aspects of the ecosystem, including launching satellites, developing launch vehicles, building ground stations, in-space research, providing critical downstream services such as Earth observation and communication systems.
While there is a strong potential, several hurdles must be overcome to ensure sustainable growth and wider accessibility. These challenges are being converted into opportunities by private players to drive progress in the space sector.
Key Challenges in the SpaceTech Industry
Despite this rapid progress, several challenges hinder the full-scale commercialization and accessibility of space technology:
High Development Costs: The prohibitive cost of launch vehicles and satellite manufacturing remains a barrier.
Launch Dependency: Infrastructure limitations and delays in launch schedules restrict operational efficiency.
Limited Talent Pool: Access to skilled professionals remains a challenge.
Underdeveloped Satellite Services Market: The commercial utilization of satellite-based applications is still in its infancy.
Short Satellite Lifespan: Many satellites have a limited operational period, requiring frequent replacements.
Data Usability Issues: Delays in processing space data hinder real-time applications.
Data Privacy & Security Concerns: Ensuring the protection of sensitive satellite data is paramount.
Innovations Transforming the Industry
To address these hurdles, private companies in India are pioneering innovative solutions aimed at reducing costs, improving efficiency, and enhancing satellite usability.
1. Cost Reduction Through Technological Advancements
Reusable Launch Vehicles: Lowering costs by making rockets recoverable and reusable.
Nano Satellites & Clusters: Small, low-cost satellites improving accessibility.
Use of Cost-Effective Materials: Leveraging standardized, off-the-shelf components that are 10x–100x cheaper.
Edge Computing (Compute on Board): Preprocessing data before transmission to reduce bandwidth usage.
2. Overcoming Launch Dependency
Collaborations with Multiple Launch Providers: Reducing reliance on single entities by collaborating with global companies.
New entrants in launch companies: Innovations in low-cost fuels, high-performance engineering components and subsystems for higher output.
Enhanced testing capabilities: Advanced simulators and testing facilities are being developed to minimize failures in space and increase the overall success rate of the launch
3. Enhancing the Use of Satellite Data
Advanced Imaging Technologies: Implementing SAR, multispectral, and hyperspectral sensors for improved data capture.
Onboard AI & Machine Learning: Enhancing real-time analysis capabilities.
Big Data & Cloud Computing Integration: Improving accessibility and enabling deeper insights of data captured from satellites.
4. Extending Satellite Lifespan
Sustainable Spacecraft Technologies: Innovations in materials and engineering to increase durability.
Situational Awareness & Collision Avoidance Systems: AI-driven monitoring to reduce the risk of orbital collisions.
In-Orbit Refueling & Maintenance: Innovations in inter satellite communication for advanced docking solutions to keep satellites operational for extended periods.
Conclusion: A Thriving Future for India’s Space Economy
Opportunities continue to emerge as private players navigate challenges and push boundaries with innovation. While high costs, infrastructure limitations, and data accessibility remain hurdles, technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and strong policy support are paving the way for a new era of space commercialization.
India is poised to become a global space-tech powerhouse, with market expansion, AI-driven satellite analytics, and reusable launch systems driving growth. Private enterprises are no longer just contributors — they are leading the transformation.
With a thriving ecosystem and an influx of investment, the Indian space industry is set to redefine global standards in affordability, efficiency, and innovation. We at Seafund are extremely excited to be a part of the ecosystem at such an exciting time and play our role in pushing the ecosystem forward with the right investments, our network and support to the spacetech startups.
#Keywords#early stage venture capital firms#invest in startups bangalore#funders in bangalore#startup investment fund#popular venture capital firms#startup seed funding india#seed investors in bangalore#deep tech investors india#venture capital firms in india#best venture capital firms in india#seed investors in delhi#semiconductor startups#semiconductor venture capital#saas venture capital#b2b venture capital#saas angel investors#saas venture capital firms#deep tech venture capital#deeptech startups in india#semiconductor companies in india#investors in semiconductors#space venture capital in india#space startups#investors in space in India#venture capital investment Bangalore#venture capital firm#venture capital firms in India#early stage venture capital firm#startup seed funding in India
1 note
·
View note
Text
[ad_1] Rangsons Aerospace (RAPL) and Oversat are set to formalize their collaboration at Aero India 2025, marking a significant step in advancing satellite communication (Satcom) technology. This partnership focuses on developing Luneberg lens-based multibeam antennas—cutting-edge solutions designed to track multiple Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites simultaneously, addressing critical connectivity gaps in Maritime, Land Mobile, and Aero applications. With the rapid deployment of LEO satellite constellations by global players such as OneWeb, SpaceX, Telesat, Rivada, and Amazon, the demand for next-generation ground-based infrastructure has surged. While LEO satellites offer cost-effectiveness, lower latency, and higher data capacity compared to traditional Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites, existing ground-based antenna systems remain outdated and inefficient. Most rely on bulky, single-satellite-tracking parabolic designs, creating a bottleneck in Satcom adoption. Recognizing this challenge, Rangsons Aerospace and Oversat are pioneering a solution with advanced multibeam antenna technology, enabling seamless connectivity across multiple satellites in real-time. This initiative is expected to revolutionize Satcom capabilities for diverse sectors, including defense, aviation, and commercial enterprises. Mr. Pavan Ranga, CEO, Rangsons Aerospace "As the satellite communication landscape evolves rapidly, the need for advanced, scalable ground infrastructure has never been greater. Our partnership with Oversat is a step toward bridging this critical gap by enabling seamless, high-speed connectivity across industries. With innovations like multi-beam antenna technology, we are not just addressing current limitations but shaping the future of SATCOM—one that is more resilient, efficient, and accessible for diverse applications across land, sea, and air. At Aero India 2025, we look forward to showcasing how Rangsons Aerospace is driving this transformation." says Pavan Ranga, Managing Director, Rangsons Aerospace. Alongside the signing of this landmark partnership, Rangsons Aerospace will showcase its state-of-the-art capabilities in Avionics, Electronic Warfare (EW) PODS, and Airborne Thermal Management. The company will also present its High-Speed Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint High-Capacity Networked Data Links, along with Ku and Ka-band SATCOM-on-the-move (SOTM) solutions tailored for defense and commercial applications. Visitors to Aero India 2025 can explore these innovations at Hall H, where Rangsons Aerospace will exhibit its latest advancements, reinforcing its commitment to shaping the future of aerospace and defense technology. About Rangsons Rangsons is a diversified business conglomerate based in Mysuru, India, and a part of the NR Group, which was founded in 1948. The group operates across multiple sectors, including Defence and Aerospace, Education, Infrastructure, Agriculture, and Healthcare. Rangsons serves a wide range of clients, both domestically and internationally, collaborating with prestigious organizations such as ISRO, Boeing, and various branches of the Indian Defence and Aerospace sector. The group is dedicated to leveraging technology to develop innovative solutions that address the critical challenges of a developing economy. Its flagship company, N. Ranga Rao & Sons, is a dominant player in the Indian incense industry, best known for its iconic brand, Cycle Pure Agarbathi. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414'); fbq('track', 'PageView');
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] Rangsons Aerospace (RAPL) and Oversat are set to formalize their collaboration at Aero India 2025, marking a significant step in advancing satellite communication (Satcom) technology. This partnership focuses on developing Luneberg lens-based multibeam antennas—cutting-edge solutions designed to track multiple Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites simultaneously, addressing critical connectivity gaps in Maritime, Land Mobile, and Aero applications. With the rapid deployment of LEO satellite constellations by global players such as OneWeb, SpaceX, Telesat, Rivada, and Amazon, the demand for next-generation ground-based infrastructure has surged. While LEO satellites offer cost-effectiveness, lower latency, and higher data capacity compared to traditional Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites, existing ground-based antenna systems remain outdated and inefficient. Most rely on bulky, single-satellite-tracking parabolic designs, creating a bottleneck in Satcom adoption. Recognizing this challenge, Rangsons Aerospace and Oversat are pioneering a solution with advanced multibeam antenna technology, enabling seamless connectivity across multiple satellites in real-time. This initiative is expected to revolutionize Satcom capabilities for diverse sectors, including defense, aviation, and commercial enterprises. Mr. Pavan Ranga, CEO, Rangsons Aerospace "As the satellite communication landscape evolves rapidly, the need for advanced, scalable ground infrastructure has never been greater. Our partnership with Oversat is a step toward bridging this critical gap by enabling seamless, high-speed connectivity across industries. With innovations like multi-beam antenna technology, we are not just addressing current limitations but shaping the future of SATCOM—one that is more resilient, efficient, and accessible for diverse applications across land, sea, and air. At Aero India 2025, we look forward to showcasing how Rangsons Aerospace is driving this transformation." says Pavan Ranga, Managing Director, Rangsons Aerospace. Alongside the signing of this landmark partnership, Rangsons Aerospace will showcase its state-of-the-art capabilities in Avionics, Electronic Warfare (EW) PODS, and Airborne Thermal Management. The company will also present its High-Speed Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint High-Capacity Networked Data Links, along with Ku and Ka-band SATCOM-on-the-move (SOTM) solutions tailored for defense and commercial applications. Visitors to Aero India 2025 can explore these innovations at Hall H, where Rangsons Aerospace will exhibit its latest advancements, reinforcing its commitment to shaping the future of aerospace and defense technology. About Rangsons Rangsons is a diversified business conglomerate based in Mysuru, India, and a part of the NR Group, which was founded in 1948. The group operates across multiple sectors, including Defence and Aerospace, Education, Infrastructure, Agriculture, and Healthcare. Rangsons serves a wide range of clients, both domestically and internationally, collaborating with prestigious organizations such as ISRO, Boeing, and various branches of the Indian Defence and Aerospace sector. The group is dedicated to leveraging technology to develop innovative solutions that address the critical challenges of a developing economy. Its flagship company, N. Ranga Rao & Sons, is a dominant player in the Indian incense industry, best known for its iconic brand, Cycle Pure Agarbathi. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414'); fbq('track', 'PageView');
0 notes
Text
India’s Space Technology to Assist Asia’s Developing Nations in Satellite Communications
India's advancements in space technology have transformed over the years making it into a key global player in space exploration, with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) leading the charge. However, India’s ambitions extend beyond self-improvement, as it is now leveraging its satellite capabilities to assist developing nations in Asia. The role of satellite communications in bridging the digital divide and empowering these countries is profound, and India’s contribution to this transformation deserves attention.
Developing nations across Asia face significant challenges such as poor infrastructure, limited internet access, and geographic obstacles that make traditional communication networks difficult or costly to implement. Satellite communication offers an effective solution, capable of reaching even the most remote regions which face network struggles. Countries like Nepal, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka have large rural populations that suffer from a critical digital gap, often unable to access modern communication tools due to rugged terrains and underdeveloped infrastructure. India’s satellite systems could potentially address these issues by offering high-speed internet, weather monitoring, disaster management, and broadcasting services.

With the present international relations scenario, India’s space achievements starting from its successful Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) to Chandrayaan-3, have rightfully captured global attention. However, its work in satellite technology has far-reaching implications for developing nations in Asia. ISRO operates a comprehensive satellite fleet that provides telecommunications, broadband services, and disaster management capabilities. A prime example is the South Asia Satellite (GSAT-9), launched in 2017, which was specifically designed to benefit countries within the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). This satellite, offered as a gift to the region, highlights India’s commitment to using its space expertise for the shared prosperity of its neighbors.

For countries struggling to afford their own space programs, India’s satellite services are invaluable and can be useful at the same time. Instead of relying on costly satellite services from global powers, developing nations can benefit from more affordable, regionally-sourced alternatives provided by India, making the economic chain more efficient and beneficial for developing countries. This partnership reduces their dependency on global satellite monopolies and offers a collaborative, cost-effective solution that is crucial for their development since most of the countries in South Asia products of colonization.
While India’s initiatives in space diplomacy are commendable, there is room for growth. First, India could expand its satellite programs beyond South Asia to benefit countries such as Cambodia, Laos, and Mongolia, where the need for improved communication infrastructure is equally pressing. By extending its satellite services to the broader Asian continent, India can solidify its role as a leader in space technology and development cooperation. Additionally, while India is launching satellites for its neighbors, there should be a greater emphasis on capacity building through training programs for engineers and scientists from developing nations. These initiatives would empower these countries to manage satellite systems independently, fostering a more sustainable model of growth.
Moreover, India’s private space sector, which has seen the rise of startups like Skyroot and Pixxel, could play a crucial role in these collaborative efforts. Leveraging private players for regional satellite missions could increase efficiency and introduce innovative solutions tailored to the needs of developing countries.
India’s space diplomacy also positions it as a significant diplomatic leader in Asia as well as countries in Africa. With its non-intrusive, cooperative approach, India provides an attractive alternative to the dominance of Western space powers and the expanding influence of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in the region. For smaller nations, India’s offering of satellite support allows them to develop communication infrastructure without becoming overly reliant on external powers. This approach aligns with India’s broader vision of “Atmanirbhar Bharat,” or self-reliant India, which advocates for India not only achieving self-sufficiency but also acting as a provider of solutions for other developing nations.

Looking ahead in my opinion, the applications of satellite communications in Asia’s developing nations are vast. From telemedicine services (as discussed before) that can reach remote communities to satellite-assisted agricultural monitoring and distance education, the potential for transformative impact is enormous. India’s ongoing efforts in satellite technology are setting the stage for these advancements, but the real challenge lies in maintaining collaboration, increasing investment, and ensuring that satellite communications become a tool for regional progress.
#tech#tech and ai#collaboration#conflict#india#Asia#foreign policy#foreignaid#global venture#space#space and tech#isroindia#isro#diplomacy
1 note
·
View note
Text


How the new NASA and India Earth Satellite NISAR will see Earth
When NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization's (ISRO) new Earth satellite NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) launches in coming months, it will capture images of Earth's surface so detailed they will show how much small plots of land and ice are moving, down to fractions of an inch.
Imaging nearly all of Earth's solid surfaces twice every 12 days, it will see the flex of Earth's crust before and after natural disasters such as earthquakes; it will monitor the motion of glaciers and ice sheets; and it will track ecosystem changes, including forest growth and deforestation.
The mission's extraordinary capabilities come from the technique noted in its name: synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Pioneered by NASA for use in space, SAR combines multiple measurements, taken as a radar flies overhead, to sharpen the scene below. It works like conventional radar, which uses microwaves to detect distant surfaces and objects, but steps up the data processing to reveal properties and characteristics at high resolution.
To get such detail without SAR, radar satellites would need antennas too enormous to launch, much less operate. At 39 feet (12 meters) wide when deployed, NISAR's radar antenna reflector is as wide as a city bus is long. Yet it would have to be 12 miles (19 kilometers) in diameter for the mission's L-band instrument, using traditional radar techniques, to image pixels of Earth down to 30 feet (10 meters) across.
Synthetic aperture radar "allows us to refine things very accurately," said Charles Elachi, who led NASA spaceborne SAR missions before serving as director of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California from 2001 to 2016. "The NISAR mission will open a whole new realm to learn about our planet as a dynamic system."
How SAR works
Elachi arrived at JPL in 1971 after graduating from Caltech, joining a group of engineers developing a radar to study Venus's surface. Then, as now, radar's allure was simple: It could collect measurements day and night and see through clouds. The team's work led to the Magellan mission to Venus in 1989 and several NASA space shuttle radar missions.
An orbiting radar operates on the same principles as one tracking planes at an airport. The spaceborne antenna emits microwave pulses toward Earth. When the pulses hit something—a volcanic cone, for example—they scatter. The antenna receives those signals that echo back to the instrument, which measures their strength, change in frequency, how long they took to return, and whether they bounced off multiple surfaces, such as buildings.
This information can help detect the presence of an object or surface, its distance away, and its speed, but the resolution is too low to generate a clear picture. First conceived at Goodyear Aircraft Corp. in 1952, SAR addresses that issue.
"It's a technique to create high-resolution images from a low-resolution system," said Paul Rosen, NISAR's project scientist at JPL.
As the radar travels, its antenna continuously transmits microwaves and receives echoes from the surface. Because the instrument is moving relative to Earth, there are slight changes in frequency in the return signals. Called the Doppler shift, it's the same effect that causes a siren's pitch to rise as a fire engine approaches then fall as it departs.
Computer processing of those signals is like a camera lens redirecting and focusing light to produce a sharp photograph. With SAR, the spacecraft's path forms the "lens," and the processing adjusts for the Doppler shifts, allowing the echoes to be aggregated into a single, focused image. A collaboration between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organ
Using SAR
One type of SAR-based visualization is an interferogram, a composite of two images taken at separate times that reveals the differences by measuring the change in the delay of echoes. Though they may look like modern art to the untrained eye, the multicolor concentric bands of interferograms show how far land surfaces have moved: The closer the bands, the greater the motion. Seismologists use these visualizations to measure land deformation from earthquakes.
Another type of SAR analysis, called polarimetry, measures the vertical or horizontal orientation of return waves relative to that of transmitted signals. Waves bouncing off linear structures like buildings tend to return in the same orientation, while those bouncing off irregular features, like tree canopies, return in another orientation. By mapping the differences and the strength of the return signals, researchers can identify an area's land cover, which is useful for studying deforestation and flooding.
Such analyses are examples of ways NISAR will help researchers better understand processes that affect billions of lives.
"This mission packs in a wide range of science toward a common goal of studying our changing planet and the impacts of natural hazards," said Deepak Putrevu, co-lead of the ISRO science team at the Space Applications Centre in Ahmedabad, India.
TOP IMAGE: NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory used radar data taken by ESA’s Sentinel-1A satellite before and after the 2015 eruption of the Calbuco volcano in Chile to create this interferogram showing land deformation. The color bands west of the volcano indicate land sinking. NISAR will produce similar images. Credit: ESA/NASA/JPL-Caltech
CENTRE IMAGE: A SAR image—like ones NISAR will produce—shows land cover on Mount Okmok on Alaska's Umnak Island. Created with data taken in August 2011 by NASA's UAVSAR instrument, it is an example of polarimetry, which measures return waves' orientation relative to that of transmitted signals. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
LOWER IMAGE: A collaboration between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation, NISAR will use synthetic aperture radar to offer insights into change in Earth’s solid surfaces, including the Antarctic ice sheet. The spacecraft, depicted here in an artist’s concept, will launch from India. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
0 notes
Text
NEP 2020's Impact on Integrated Learning in Schools
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 is a comprehensive framework for education in India. It was started by the Union Cabinet of India on July 29, 2020, and aims to transform India’s education system by 2030.
The policy addresses the challenges that India's education system is facing and aims to bring it up to par with global standards and eventually make India a global knowledge superpower. NEP 2020 integrated courses for schools have sought to make education more accessible, inclusive, and equitable to improve the quality of education at all levels including both schools and colleges. Further, it’ll contribute as an instrumental player in seasoning the learners with 21st-century workforce skills.
The NEP 2020 was drafted by a committee led by Dr. K. Kasturirangan, a renowned scientist and former chairman of ISRO. The committee included experts from various fields, including education, administration, and research.
Let’s discover the key highlights of the National Education Policy:
A major change brought by the policy is the introduction of a new educational structure with a 5+3+3+4 design, replacing the traditional 10+2 system.
This includes five-year foundational education (ages 3–8), three-year preparatory education (ages 8–11), which is followed by another three years of middle education (ages 11–14), and finally a four-year-long secondary education (ages 14–18).
Rather than just teaching English in schools, interestingly, a keen focus is laid on diverse language learning to prepare students for the global stage. It encourages students to learn one foreign language and choose different streams after the 8th class.
While preparation for a global stage is a prime focus, the policy also emphasises giving the students ease of learning in their more familiar regional language during their foundational education.
Over 28 languages are to be used in teaching and learning in grades 1–5 and this is recommended to facilitate the learning process and ensure a better understanding of concepts during the early years of education.
NEP also stresses how it’s extremely crucial to integrate technology-driven and STEM-integrated learning in the K-12 curriculum. Experiential learning like this equips students with the most relevant skills needed in the 21st century. The future is evolving rapidly and so will our students with the help of STEM-integrated learning in the K-12 curriculum.
The best part is that the policy allows the teachers to go beyond marks to judge the smartness of the students. They grade them on multiple levels which helps them to understand the student’s weak points better and help them in overcoming specific challenges.
While there is way more to the policy and there is a long list of reforms it brings upon, simply put, the core of NEP 2020 integrated courses for schools is to make both school and college education more holistic, flexible, and multidisciplinary, suited to 21st-century workforce skills needs.
To sum it all up, NEP 2020, has integrated learning in schools as an educational approach that combines multiple subjects into a cohesive learning paradigm, focusing on interconnecting concepts and ideas across different disciplines. This method very effectively encourages students to make connections between various areas of study, leading to a deeper understanding and retention of knowledge.
0 notes
Text
Exploring Frontiers: Breaking latest Science News in India. buzzerstory.online
a.
Introduction:
Latest science news india today Stay ahead of the curve with the latest developments in the world of science, all from the vibrant landscape of India. In the dynamic landscape of science, India stands as a hub of innovation, research, and groundbreaking discoveries. From advancements in space exploration to pioneering medical breakthroughs, the Indian scientific community continuously pushes the boundaries of knowledge. In this blog post, we delve into the latest science news emerging from India, offering a glimpse into the country's vibrant scientific endeavors.

Exploring Space:
India's space agency, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), remains at the forefront of space exploration. With recent missions like Chandrayaan-2 and Mars Orbiter Mission, ISRO has showcased its prowess in space technology. Currently, anticipation surrounds the upcoming Gaganyaan mission, which aims to send Indian astronauts to space. The successful launch of satellites, advancements in satellite navigation systems, and collaborations with international space agencies underscore India's growing significance in the global space arena.
Healthcare Innovations:
India's healthcare sector is witnessing transformative innovations aimed at improving public health outcomes. From indigenous COVID-19 vaccine development to affordable medical devices, Indian scientists and healthcare professionals are addressing pressing health challenges. Noteworthy developments include the production of mRNA vaccines, advancements in telemedicine, and initiatives to combat antimicrobial resistance. These efforts highlight India's commitment to leveraging science for the betterment of society.
Renewable Energy Initiatives:
In the wake of climate change concerns, India is accelerating its transition towards renewable energy sources. Solar power, in particular, has gained significant momentum, with ambitious targets set for solar energy generation. The country's focus on renewable energy technologies, such as wind and hydroelectric power, underscores its commitment to sustainable development. Collaborative research efforts and government policies are driving the adoption of clean energy solutions, positioning India as a leader in renewable energy innovation.
Emerging Technologies:
India's tech landscape is witnessing rapid advancements across various domains, including artificial intelligence (AI), biotechnology, and nanotechnology. Startups and research institutions are spearheading projects aimed at harnessing the potential of emerging technologies to address societal challenges. From AI-driven healthcare diagnostics to biodegradable packaging solutions, Indian innovators are at the forefront of technological innovation, driving economic growth and societal progress.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While India's scientific progress is commendable, challenges persist, including funding constraints, infrastructure gaps, and the need for greater collaboration between academia, industry, and government. Addressing these challenges requires sustained investment in research and development, fostering a culture of innovation, and nurturing interdisciplinary collaborations. Despite the hurdles, India's scientific community remains resilient, leveraging its collective expertise to overcome obstacles and seize opportunities for growth and advancement.
Conclusion:
The latest science news from India underscores the country's remarkable journey of scientific discovery and innovation. From space exploration to healthcare breakthroughs, renewable energy initiatives to emerging technologies, India continues to make significant strides on the global stage. By fostering a conducive environment for scientific research and innovation, India is poised to tackle the challenges of the future and emerge as a powerhouse of scientific excellence.
0 notes
Text
Cross-Domain Collaboration

(Presentation Round /Background)
India's prowess in scientific and technological advancements has garnered global acclaim, particularly through the remarkable contributions of institutions like ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation).
ISRO stands as a beacon of success in space exploration, achieving significant milestones with missions like Chandrayaan and Mangalyaan. These endeavours underscore India's capabilities and efficiency in executing complex space missions. The organization's commitment to indigenous technology development and its cost-effective satellite launches have not only propelled the country's space capabilities but have also positioned ISRO as a preferred partner for satellite launches globally.
Contrastingly, DRDO, tasked with spearheading defence technology development, has encountered notable challenges that have impeded its path towards self-reliance. Delayed projects and a tendency towards overreliance on foreign imports have posed significant hurdles. The organization's struggle with testing and validation issues has further exacerbated development cycles, casting doubt on the overall effectiveness of the systems being developed.
While ISRO's successes have showcased India's ability to compete on a global scale in space exploration, DRDO's underperformance in defence technology development has raised concerns about the country's pursuit of self-sufficiency in the defence sector. The overemphasis on importing technology rather than fostering indigenous innovation has not only led to delays but has also diminished the potential for building a robust and self-reliant defence ecosystem.
Recognizing the need for cross-domain collaboration, the Indian government announces a groundbreaking initiative that brings together the strengths of ISRO and DRDO in an unprecedented partnership addressing DRDO's challenges and to promote synergy between space and defense technology
Task-in-hand
You are leading this partnership.
How can this collaborative and innovative partnership between ISRO and DRDO be strategically forged to synergize space exploration and defence technology, addressing challenges, optimizing resources, and fostering self-reliance in both sectors for the benefit of national security and technological advancement.
Also provide strategic roadmap on the objectives of the collaboration, key milestones and timelines for achieving specific outcomes and detailed plan for integrating the strengths of ISRO and DRDO.
Deliverables
PPT of 10 slides
A report of minimum 10 pages
Submit at - [email protected]
Deadline - 1:30 pm
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Advice On Job Recruitment

Job recruitment is actually a critical process for organizations trying to entice, choose, as well as hire the most ideal skill for their crews. In today's competitive job market, recruitment has actually advanced in to a complex method that demands mindful preparation as well as completion. This thorough manual offers an outline of crucial recruitment measures and also best methods to aid companies make educated working with choices.
Determine Your Needs
Begin by accurately determining the job position and its needs. Think about the vital abilities, qualifications, and expertise essential for the role. This action establishes the foundation for a productive upsc nda recruitment method.
Make a Job Definition
Cultivate an in-depth job description that properly mirrors the opening's obligations and also desires. The job summary need to be actually very clear, succinct, as well as eye-catching to prospective prospects.
Take Advantage Of Multiple Channels
To connect with a more comprehensive applicant pool, make use of several recruitment networks, such as online job boards, social networking sites, business websites, and staff member referrals. Transform your sourcing methods to access a greater talent swimming pool.
Candidate Tracking System (ATS)
Apply an ATS to manage as well as enhance the treatment process. ATS software aids in tracking, managing, and also analyzing applicant treatments efficiently.
Display screen Resumes
Assessment prospect resumes to evaluate their credentials and knowledge. Shortlist candidates who match the isro recruitment as well as consider their possible fit within the company.
Perform Interviews
Job interviews are actually a vital phase of the recruitment method. Perform structured meetings to review candidates' capabilities, expertises, and cultural match. Utilize a mix of behavior and situational inquiries to acquire insights into their capacities.
Abilities Assessment
Besides job interviews, look at making use of skills assessments or even examinations to assess specialized abilities as well as job-related capabilities. This action can help you help make more educated hiring choices.
Background Checks
Execute comprehensive history checks to confirm a prospect's employment past history, references, and any sort of appropriate licenses or even credentials. This is actually crucial for making sure the accuracy of relevant information supplied through candidates.
Evaluate Cultural Fit
Review candidates' positioning along with the company's worths, culture, and workplace. A strong social match can easily cause better job complete satisfaction and worker retention.
Evaluate Compensation
Establish a competitive fringe benefit that associates with sector standards as well as the applicant's adventure. A decent and pleasing promotion can substantially impact an applicant's selection to allow the job.
Make the Offer
Expand a professional job deal to the selected prospect. Be clear regarding the conditions of employment, consisting of salary, advantages, and some other relevant details.
Onboarding
The moment the provide is allowed, begin the onboarding method to combine the brand-new employee into the association flawlessly. Give training as well as positioning to make sure a hassle-free transition.
Observe Up
Consistently communicate along with new hires to ensure their requirements are met and also they are actually conforming properly to their roles. Address any type of problems or even concerns immediately to advertise job complete satisfaction.
Continuous Improvement
Assess your upsc nda recruitment procedure regularly to determine regions for renovation. Seek responses from hiring supervisors and candidates to make essential changes.
Lawful Compliance
Make certain that your recruitment method abides by all appropriate delivery rules as well as rules. This features non-discrimination, level playing field, as well as records defense rules.
Recognition Strategies
Execute employee loyalty approaches to always keep accomplished people within your institution. Offering options for career development and also recognition can aid maintain leading ability.
Lastly, job recruitment is actually a complex as well as compelling process that demands careful preparation as well as implementation. By complying with these vital actions as well as ideal practices, associations may boost their recruitment attempts and attract the best-fit candidates for their crews. A well-executed recruitment method can easily support a booming as well as successful workforce, making certain the continuing effectiveness of the institution.
1 note
·
View note
Link
6 min read NASA-ISRO Radar Mission to Provide Dynamic View of Forests, Wetlands NISAR will use radar to study changes in ecosystems around the world, such as this forest in Tikal National Park in northern Guatemala, to understand how these areas are affected by climate change and human activity, and the role they play in the global carbon cycle.Credit: USAID NISAR will help researchers explore how changes in Earth’s forest and wetland ecosystems are affecting the global carbon cycle and influencing climate change. Once it launches in early 2024, the NISAR radar satellite mission will offer detailed insights into two types of ecosystems – forests and wetlands – vital to naturally regulating the greenhouses gases in the atmosphere that are driving global climate change. NISAR is a joint mission by NASA and ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), and when in orbit, its sophisticated radar systems will scan nearly all of Earth’s land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days. The data it collects will help researchers understand two key functions of both ecosystem types: the capture and the release of carbon. Pictured in this artist’s concept, NISAR, short for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar, marks the first time the U.S. and Indian space agencies have cooperated on hardware development for an Earth-observing mission. Its two radar systems will monitor change in nearly all of Earth’s land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days.Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech Forests hold carbon in the wood of their trees; wetlands store it in their layers of organic soil. Disruption of either system, whether gradual or sudden, can accelerate the release of carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. Tracking these land-cover changes on a global scale will help researchers study the impacts on the carbon cycle – the processes by which carbon moves between the atmosphere, land, ocean, and living things. “The radar technology on NISAR will allow us to get a sweeping perspective of the planet in space and time,” said Paul Rosen, the NISAR project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “It can give us a really reliable view of exactly how Earth’s land and ice are changing.” Tracking Deforestation Forestry and other land-use changes account for about 11% of net human-caused greenhouse gas emissions. NISAR’s data will improve our understanding of how the loss of forests around the world influences the carbon cycle and contributes to global warming. “Globally, we do not understand well the carbon sources and sinks from terrestrial ecosystems, particularly from forests,” said Anup Das, an ecosystems scientist and co-lead of the ISRO NISAR science team. “So we expect that NISAR will greatly help address that, especially in less dense forests, which are more vulnerable to deforestation and degradation.” To show the kind of imagery NISAR will produce, researchers pointed to this composite that uses data from two Japanese L-band SAR missions to reveal land-cover change in Brazil’s Xingu River basin between 1996 and 2007. Black shows forest areas converted to farmland before 1996, and red shows additional areas cleared by 2007.Credit: Woodwell Climate Research Center/Earth Big Data LLC. Data courtesy of METI and JAXA. The signal from NISAR’s L-band radar will penetrate the leaves and branches of forest canopies, bouncing off the tree trunks and the ground below. By analyzing the signal that reflects back, researchers will be able to estimate the density of forest cover in an area as small as a soccer field. With successive orbital passes, it will be able to track whether a section of forest has been thinned or cleared over time. The data – which will be collected in early morning and evening and in any weather – could also offer clues as to what caused the change, such as disease, human activity, or fire. It’s an important set of capabilities for studying vast, often cloud-covered rainforests such as those in the Congo and Amazon basins, which lose millions of wooded acres every year. Fire releases carbon into the air directly, while the deterioration of forests reduces the absorption of atmospheric carbon dioxide. The data could also help improve accounting of deforestation and forest degradation – as well as forest growth – as countries that rely on logging try to shift toward more sustainable practices, said Josef Kellndorfer, a member of the NISAR science team and founder of Earth Big Data LLC, a provider of large data sets and analytic tools for research and decisions support. “Reducing deforestation and degradation is low-hanging fruit to address a substantial part of the global carbon emission problem,” he added. Monitoring Wetland Flooding Wetlands present another carbon puzzle: Swamps, bogs, peatlands, inundated forests, marshes, and other wetlands hold 20 to 30% of the carbon in Earth’s soil, despite constituting only 5 to 8% of the land surface. When wetlands flood, bacteria go to work digesting organic matter (mostly dead plants) in the soil. Through this natural process, wetlands are the planet’s largest natural source of the potent greenhouse gas methane, which bubbles to the water’s surface and travels into the atmosphere. Meanwhile, when wetlands dry out, the carbon they store is exposed to oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide. NISAR will track wetland flooding to study how these carbon-rich ecosystems are reacting to climate change. It will generate images like this one from an airborne radar that flew over Peru in 2013. Black indicates water, gray is rainforest, green is low vegetation, and red and pink are flooded plants.Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech “These are huge reservoirs of carbon that can be released in a relatively short time frame,” said Erika Podest, a NISAR science team member and a carbon cycle and ecosystems researcher at JPL. Less well understood is how changing temperature and precipitation patterns due to climate change – along with human activities such as development and agriculture – are affecting the extent, frequency, and duration of flooding in wetlands. NISAR will be able to monitor flooding, and with repeated passes, researchers will be able to track seasonal and annual variations in wetlands inundation, as well as long-term trends. By coupling NISAR’s wetlands observations with separate data on the release of greenhouse gases, researchers should gain insights that inform the management of wetland ecosystems, said Bruce Chapman, a NISAR science team member and JPL wetlands researcher. “We have to be careful to reduce our impact on wetland areas so that we don’t worsen the situation with the climate,” he added. NISAR is set to launch in early 2024 from southern India. In addition to tracking ecosystem changes, it will collect information on the motion of the land, helping researchers understand the dynamics of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and subsidence and uplift (when the surface sinks and rises). It will also track the movements and melting of both glaciers and sea ice. More About the Mission NISAR is an equal collaboration between NASA and ISRO and marks the first time the two agencies have cooperated on hardware development for an Earth-observing mission. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of the project and is providing the mission’s L-band SAR. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO’s U R Rao Satellite Centre in Bengaluru, which is leading the ISRO component of the mission, is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR electronics, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. To learn more about NISAR, visit:https://nisar.jpl.nasa.gov/ See the NISAR spacecraft in 3D in NASA's interactive Eyes on the Earth News Media Contacts Andrew Wang / Jane J. LeeJet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.626-379-6874 / [email protected] / [email protected] 2023-151 Share Details Last Updated Oct 27, 2023 Related Terms EarthEarth ScienceEarth Science DivisionEarth System Observatory (ESO)NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) Explore More 5 min read NASA, Pacific Disaster Center Increase Landslide Hazard Awareness Article 23 hours ago 5 min read AWE Launching to Space Station to Study Atmospheric Waves via Airglow NASA’s Atmospheric Waves Experiment, or AWE, mission is scheduled to launch to the International Space… Article 2 days ago 4 min read New Software Enables Atmospheric Modeling with Greater Resolution Next-generation software is making it easier for researchers, policy makers, and citizen scientists to model… Article 3 days ago Keep Exploring Discover Related Topics Missions Humans in Space Climate Change Solar System
0 notes