#Overfitting
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Understanding Regularization in Machine Learning: Ridge, Lasso, and Elastic Net
Struggling with overfitting in your machine learning models? Have a look at this complete guide on Ridge, Lasso, and Elastic Net regularization. Learn these regularization techniques to improve accuracy and simplify your models for better performance.
A machine learning model learns over the data it is trained and should be able to generalize well over it. When a new data sample is introduced, the model should be able to yield satisfactory results. In practice, a model sometimes performs too well on the training set, however, it fails to perform well on the validation set. This model is then said to be overfitting. Contrarily, if the model…
0 notes
Text
youtube
#Radiomics#Radiogenomics#SyntheticData#MachineLearning#DeepLearning#CancerResearch#GANs#VAEs#DataAugmentation#PersonalizedMedicine#MedicalImaging#FeatureEngineering#PredictiveModeling#Biomarkers#Overfitting#DataScarcity#TumorCharacterization#AIInHealthcare#BigDataInMedicine#HealthTech#oncology#youtube#cancer#cancerawareness#Youtube
0 notes
Text
An Introduction to Regularization in Machine Learning
Summary: Regularization in Machine Learning prevents overfitting by adding penalties to model complexity. Key techniques, such as L1, L2, and Elastic Net Regularization, help balance model accuracy and generalization, improving overall performance.

Introduction
Regularization in Machine Learning is a vital technique used to enhance model performance by preventing overfitting. It achieves this by adding a penalty to the model's complexity, ensuring it generalizes better to new, unseen data.
This article explores the concept of regularization, its importance in balancing model accuracy and complexity, and various techniques employed to achieve optimal results. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of regularization methods, their applications, and how to implement them effectively in machine learning projects.
What is Regularization?
Regularization is a technique used in machine learning to prevent a model from overfitting to the training data. By adding a penalty for large coefficients in the model, regularization discourages complexity and promotes simpler models.
This helps the model generalize better to unseen data. Regularization methods achieve this by modifying the loss function, which measures the error of the model’s predictions.
How Regularization Helps in Model Training
In machine learning, a model's goal is to accurately predict outcomes on new, unseen data. However, a model trained with too much complexity might perform exceptionally well on the training set but poorly on new data.
Regularization addresses this by introducing a penalty for excessive complexity, thus constraining the model's parameters. This penalty helps to balance the trade-off between fitting the training data and maintaining the model's ability to generalize.
Key Concepts
Understanding regularization requires grasping the concepts of overfitting and underfitting.
Overfitting occurs when a model learns the noise in the training data rather than the actual pattern. This results in high accuracy on the training set but poor performance on new data. Regularization helps to mitigate overfitting by penalizing large weights and promoting simpler models that are less likely to capture noise.
Underfitting happens when a model is too simple to capture the underlying trend in the data. This results in poor performance on both the training and test datasets. While regularization aims to prevent overfitting, it must be carefully tuned to avoid underfitting. The key is to find the right balance where the model is complex enough to learn the data's patterns but simple enough to generalize well.
Types of Regularization Techniques

Regularization techniques are crucial in machine learning for improving model performance by preventing overfitting. They achieve this by introducing additional constraints or penalties to the model, which help balance complexity and accuracy.
The primary types of regularization techniques include L1 Regularization, L2 Regularization, and Elastic Net Regularization. Each has distinct properties and applications, which can be leveraged based on the specific needs of the model and dataset.
L1 Regularization (Lasso)
L1 Regularization, also known as Lasso (Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator), adds a penalty equivalent to the absolute value of the coefficients. Mathematically, it modifies the cost function by adding a term proportional to the sum of the absolute values of the coefficients. This is expressed as:

where λ is the regularization parameter that controls the strength of the penalty.
The key advantage of L1 Regularization is its ability to perform feature selection. By shrinking some coefficients to zero, it effectively eliminates less important features from the model. This results in a simpler, more interpretable model.
However, it can be less effective when the dataset contains highly correlated features, as it tends to arbitrarily select one feature from a group of correlated features.
L2 Regularization (Ridge)
L2 Regularization, also known as Ridge Regression, adds a penalty equivalent to the square of the coefficients. It modifies the cost function by including a term proportional to the sum of the squared values of the coefficients. This is represented as:

L2 Regularization helps to prevent overfitting by shrinking the coefficients of the features, but unlike L1, it does not eliminate features entirely. Instead, it reduces the impact of less important features by distributing the penalty across all coefficients.
This technique is particularly useful when dealing with multicollinearity, where features are highly correlated. Ridge Regression tends to perform better when the model has many small, non-zero coefficients.
Elastic Net Regularization
Elastic Net Regularization combines both L1 and L2 penalties, incorporating the strengths of both techniques. The cost function for Elastic Net is given by:

where λ1 and λ2 are the regularization parameters for L1 and L2 penalties, respectively.
Elastic Net is advantageous when dealing with datasets that have a large number of features, some of which may be highly correlated. It provides a balance between feature selection and coefficient shrinkage, making it effective in scenarios where both regularization types are beneficial.
By tuning the parameters λ1 and λ2, one can adjust the degree of sparsity and shrinkage applied to the model.
Choosing the Right Regularization Technique
Selecting the appropriate regularization technique is crucial for optimizing your machine learning model. The choice largely depends on the characteristics of your dataset and the complexity of your model.
Factors to Consider
Dataset Size: If your dataset is small, L1 regularization (Lasso) can be beneficial as it tends to produce sparse models by zeroing out less important features. This helps in reducing overfitting. For larger datasets, L2 regularization (Ridge) may be more suitable, as it smoothly shrinks all coefficients, helping to control overfitting without eliminating features entirely.
Model Complexity: Complex models with many features or parameters might benefit from L2 regularization, which can handle high-dimensional data more effectively. On the other hand, simpler models or those with fewer features might see better performance with L1 regularization, which can help in feature selection.
Tuning Regularization Parameters
Adjusting regularization parameters involves selecting the right value for the regularization strength (λ). Start by using cross-validation to test different λ values and observe their impact on model performance. A higher λ value increases regularization strength, leading to more significant shrinkage of the coefficients, while a lower λ value reduces the regularization effect.
Balancing these parameters ensures that your model generalizes well to new, unseen data without being overly complex or too simple.
Benefits of Regularization
Regularization plays a crucial role in machine learning by optimizing model performance and ensuring robustness. By incorporating regularization techniques, you can achieve several key benefits that significantly enhance your models.
Improved Model Generalization: Regularization techniques help your model generalize better by adding a penalty for complexity. This encourages the model to focus on the most important features, leading to more robust predictions on new, unseen data.
Enhanced Model Performance on Unseen Data: Regularization reduces overfitting by preventing the model from becoming too tailored to the training data. This leads to improved performance on validation and test datasets, as the model learns to generalize from the underlying patterns rather than memorizing specific examples.
Reduced Risk of Overfitting: Regularization methods like L1 and L2 introduce constraints that limit the magnitude of model parameters. This effectively curbs the model's tendency to fit noise in the training data, reducing the risk of overfitting and creating a more reliable model.
Incorporating regularization into your machine learning workflow ensures that your models remain effective and efficient across different scenarios.
Challenges and Considerations
While regularization is crucial for improving model generalization, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Balancing regularization effectively requires careful attention to avoid potential downsides and ensure optimal model performance.
Potential Downsides of Regularization:
Underfitting Risk: Excessive regularization can lead to underfitting, where the model becomes too simplistic and fails to capture important patterns in the data. This reduces the model’s accuracy and predictive power.
Increased Complexity: Implementing regularization techniques can add complexity to the model tuning process. Selecting the right type and amount of regularization requires additional experimentation and validation.
Balancing Regularization with Model Accuracy:
Regularization Parameter Tuning: Finding the right balance between regularization strength and model accuracy involves tuning hyperparameters. This requires a systematic approach to adjust parameters and evaluate model performance.
Cross-Validation: Employ cross-validation techniques to test different regularization settings and identify the optimal balance that maintains accuracy while preventing overfitting.
Careful consideration and fine-tuning of regularization parameters are essential to harness its benefits without compromising model accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Regularization in Machine Learning?
Regularization in Machine Learning is a technique used to prevent overfitting by adding a penalty to the model's complexity. This penalty discourages large coefficients, promoting simpler, more generalizable models.
How does Regularization improve model performance?
Regularization enhances model performance by preventing overfitting. It does this by adding penalties for complex models, which helps in achieving better generalization on unseen data and reduces the risk of memorizing training data.
What are the main types of Regularization techniques?
The main types of Regularization techniques are L1 Regularization (Lasso), L2 Regularization (Ridge), and Elastic Net Regularization. Each technique applies different penalties to model coefficients to prevent overfitting and improve generalization.
Conclusion
Regularization in Machine Learning is essential for creating models that generalize well to new data. By adding penalties to model complexity, techniques like L1, L2, and Elastic Net Regularization balance accuracy with simplicity. Properly tuning these methods helps avoid overfitting, ensuring robust and effective models.
#Regularization in Machine Learning#Regularization#L1 Regularization#L2 Regularization#Elastic Net Regularization#Regularization Techniques#machine learning#overfitting#underfitting#lasso regression
0 notes
Text
Machine Learning in Finance: Opportunities and Challenges
(Images made by author with MS Bing Image Creator ) Machine learning (ML), a branch of artificial intelligence (AI), is reshaping the finance industry, empowering investment professionals to unlock hidden insights, improve trading processes, and optimize portfolios. While ML holds great promise for revolutionizing decision-making, it presents challenges as well. This post explores current…

View On WordPress
#clustering#Finance#financial data analysis#kkn#machine learning#ml algorithms#nlp#overfitting#pca#portfolio optimization#random forests#svm
0 notes
Text
機器學習筆記(三)-偏誤從何而來?
Photo by Element5 Digital on Pexels.com 在做機器學習的三個步驟中,第一步就是定義一個function set(也就是model),而不同的model所對應的error是不同的。那麼,這些error是從何而來的呢? 了解error的來源其實相當重要,因為我們可以藉此對他挑選較適當的方式來增強自己model的performance。 Continue reading Untitled

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Floornight and Almost Nowhere are "diurnal," The Northern Caves and The Apocalypse of Herschel Schoen are "nocturnal."
My next work of fiction, whenever it does arrive (I am going to take a good long break first), will definitely be "diurnal." The "nocturnal" ones are painful to write in a way the "diurnal" ones aren't, and I don't want to go through that again for a long time, if ever.
[With only the slightest hint of irony] You take my meaning, of course.
#floornight#the northern caves#almost nowhere#the apocalypse of herschel schoen#is this overfitting to a few data points? possibly.#but there you have it.
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
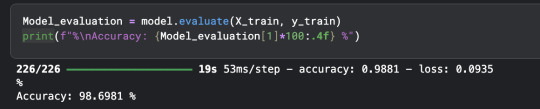
shoutout to free gpu resources by my bff kaggle

#best part is. i can probably even improve this even further! just have to work on avoiding overfitting#i am talking#coding#ml#kaggle
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
A neat image diffusion tool that generates a redlined undersketch of any illustrated girl. Tested with one of my OCs as illustrated by @fipindustries.
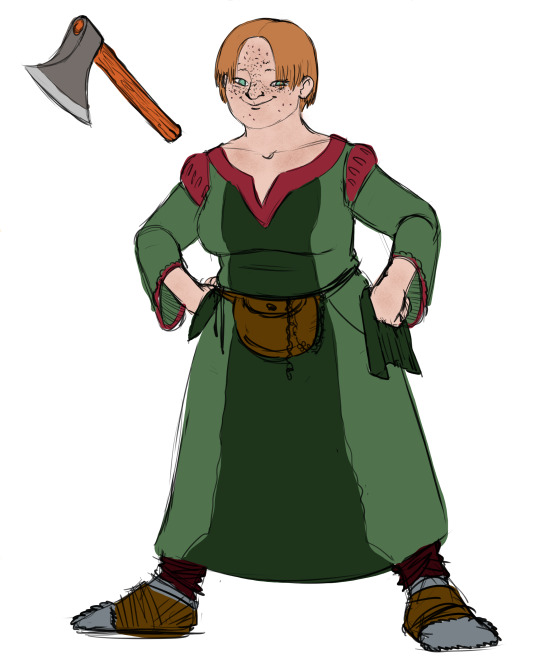
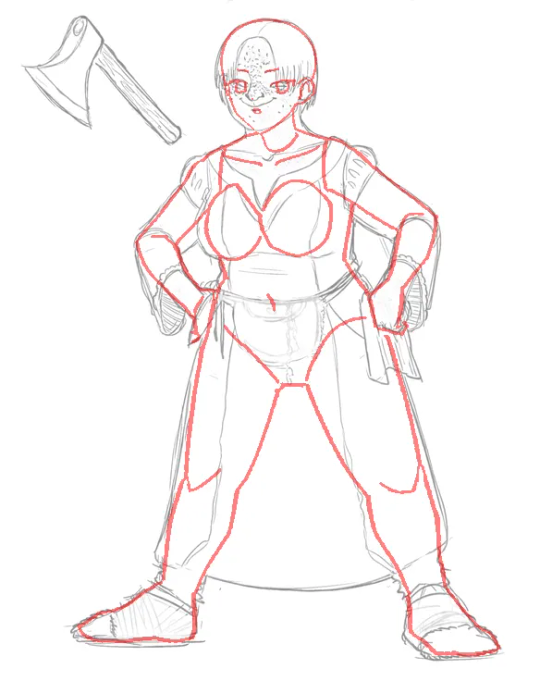


It does a good job capturing the bottom-heavy figure of the character, and breaks down the anatomy satisfyingly.
#ai tools#yes I am aware this could be used to fake the sketch layers of an AI generated image#But this specific tool is so overfitted to its purpose that I doubt you could pull that off for long
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
can't tell you how alarming the sopranos is to me. my brain keeps flagging them as cousins i don't quite remember
#aren't a lot of real wops where i live and i think i overfit somewhat#like in my childhood if i saw a white guy with a cigar and a guido chain there's like >50% it was at palm sunday
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
🤡 <- me
#im thinking about every time i saw a post and thought about tagging funnier-as-a-system but was like#well im not so would it be weird if i tagged? better not. but i am laughing at this in a plural way.#even tho im not i am looking at this in that context. clown behavior#okayokayokay i should wait. till monday. before i start just saying i am#bc maybe i am overfitting my prior experiences and she's gonna be like lol nope i was wrong you're not#but. some part of me is very much like ooohhh this. makes sense#sams ramblings
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things I could say but probably shouldn't: "Sorry I'm late to this directed feedback Zoom meeting; I do have thoughts about our RLHF approach to this turn, but I had to reverse a vent prolapse in a pullet."
Part-time farming is weird.
#oh#the disturbing cyanotic tint in the fingers of my gesticulating hand?#don't worry it's just blukote stain#anyway about the data overfitting issue ...#tmi#chickens#poultry farming
0 notes
Text
tumblr will interrupt your dashboard to show you a post that you reblogged 2 days ago and say "you seem interested 😏" yes i am interested and in fact i reblogged that because i was interested
0 notes
Text
Good news: tkinter program where you can click a button and a camera filter is applied OR you can do a hand sign and the camera filter is applied... works.
Bad news: it won't predict hand signs well... I'm not sure yet whether it is overfitting, bad quality photos, illumination... I have no idea and my classmates seem to be in the same boat as me. I'll try retraining again tomorrow. :'(
#training it again is a bit of a pain because i have to choose the right photos again#if it is blurry or something like that i just delete it...#last resort: to include the hand points lines again just in case#and i have to record several hand signs myself XD#bt maybe it is just overfitting because it wont even detect my bfs hand at all
0 notes
Text
Trying to convince myself this is a good major by giving in and heading to the ✨ coding aesthetics ✨ aisle. Wish me luck.

#yah u might wanna disregard bc more posts coming up#fr tho when u take lagorithms and u grt prnalized for dp misuse but ml says u know what go cross validate. overfit those models. more params
153 notes
·
View notes
Note
So wait, let me just ask for clarity because I want to understand. Do you support AI art?
i support art made with spontaneous and hands-off processes, i support the creation of art tools that are more art than tool & allow people to "participate" in someone else's creation vicariously a-la picrew, i don't support the institution of "AI" as a consumer grade technology industry that promises impossible things and prioritizes appearances and marketability over usability, i believe that if "AI" allowed people to siphon images directly from their brain with no effort required then it would be a good thing but I believe this is fundamentally impossible until we figure out how to read minds and the focus on arguing for or against accessibility is missing the point, i believe AI art can only ever be a pale imitation of the process of commissioning an artist who can't ever ask questions and cannot be trusted with object permanence, I believe copyright law is a head on the hydra of capitalism and doesn't serve artists, i believe that AI art isn't necessarily art theft but it CAN overfit to its data and create illegal works without telling you, which constitutes criminal levels of negligence, I believe all art is derivative in some way and some of the most seminal art made in this era of history has been far more dubiously infringing than AI art ever can be because AI art does not steal in the way a human does, I think the focus on energy consumption is transparently just a post-hoc justification for hating the thing you all already hated under the guise of environmentalism because it is a problem far from unique to AI, I think the focus on environmentalism was a distraction at best during the NFT craze too, i don't think AI art takes artists out of a job any more than stock photos or clipart does, but the proliferation of consumer-grade tools DOES run the risk of engendering bad client practices similar to the rise of machine translation and asking translators to simply "fix" a machine translated run of text at a marked down price, but this is not the fault of the technology itself and is instead a result of the ideological push being made by the biggest actors in the industry, i think AI art is ugly as sin and carries the pervasive quality of looking normal at a glance but getting worse and worse the longer you look at it, which can be interesting but often isn't, i think ai art is shit google images and the controversy is overblown but I think machine learning is here to stay and it will inevitably decentralize again after the immense costs catch up to all the corpos relying on it to win the future.
so like, yes and no.
3K notes
·
View notes