#RPA Implementation in Accounting
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
As technology continues to reshape the accounting industry, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) have emerged as two leading solutions for enhancing efficiency and accuracy. While both technologies offer significant advantages, understanding their distinct roles is crucial for US-based CPAs, EAs, and accounting firms seeking to optimize their processes.
This blog explores AI vs. RPA in accounting, their applications, benefits, and how to determine the best fit for your firm.
#AI in Accounting#unison globus#RPA for CPAs#Accounting Automation#CPA Technology Trends#AI Benefits for Accountants#RPA Implementation in Accounting#Future of Accounting Technology#AI and RPA Integration#RPA solutions for US accounting firms#Future trends in AI and RPA for accountants
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unlocking Efficiency and Innovation: The Role of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)

In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a powerful tool that can help businesses achieve these objectives.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that allows businesses to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. It uses software robots, also known as "bots," to mimic human actions and interact with digital systems. These bots can log into applications, navigate through screens, input data, and complete tasks just like humans would.
The Role of RPA in Business:
RPA can be used to automate a wide range of tasks across various industries and departments. Here are some examples:
Finance and Accounting: Automating tasks such as accounts payable and receivable, invoice processing, and financial reporting.
Customer Service: Automating tasks such as answering FAQs, resolving customer inquiries, and processing orders.
Human Resources: Automating tasks such as onboarding new employees, processing payroll, and managing benefits.
IT: Automating tasks such as provisioning accounts, managing user access, and deploying software updates.
Impact of RPA on Businesses:
Implementing RPA can offer numerous benefits to businesses, including:
Increased efficiency and productivity: RPA can automate time-consuming and tedious tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
Reduced costs: RPA can help businesses save money on labor costs, as well as reduce errors and compliance risks.
Improved accuracy and compliance: RPA bots are programmed to follow specific rules and procedures, which can help to improve accuracy and compliance with regulations.
Enhanced process visibility and control: RPA provides businesses with a clear view of their processes, which can help them identify and address bottlenecks.
Improved customer satisfaction: RPA can help businesses improve customer satisfaction by automating tasks such as order processing and customer service interactions.
RPA Services:
Implementing RPA successfully requires a partner with expertise in the technology and a deep understanding of business processes. A comprehensive RPA solution should include the following services:
Document AS-IS Process: This involves mapping out the existing process to identify areas for automation.
Design & Development of Bots, workflows, and forms for process automation: This includes designing and developing the software robots that will automate the tasks.
Bot license (We will use the appropriate underlying technology): This provides access to the software robots and the underlying technology platform.
Infrastructure: This includes setting up the necessary infrastructure to support the Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solution.
Production Deployment of the Bots: This involves deploying the bots to production and monitoring their performance.
RPA support: This includes ongoing support for the RPA solution, such as troubleshooting and maintenance.
Test & Deploy bots to production: This involves testing the bots in a production environment and making any necessary adjustments before they are deployed to full production.
Configuration data changes: This involves making changes to the configuration data of the bots as needed.
Password updates: This involves updating the passwords of the bots as needed.
Errors in executing the Bots: This involves resolving errors that occur during the execution of the bots.
Determining the “root cause” of a recurring issue or incident & recommendations: This involves identifying the root cause of a recurring issue or incident and recommending solutions to prevent it from happening again.
Infrastructure/application related issues: This involves resolving issues with the infrastructure or applications that the bots are interacting with.
Conclusion:
RPA is a powerful technology that can have a significant impact on businesses of all sizes. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA can help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase productivity. However, it is important to choose a reputable Robotic Process Automation (RPA) companies with the expertise and experience to help you implement a successful RPA solution.
Ready to embrace the power of RPA?
Contact us today to learn more about how RPA can help your business achieve its goals.
#robotic process automation#robotic process automation rpa#rpa automation#robotic process automation software#rpa software#robotic process automation companies#robotic process automation technology#robotic process automation in healthcare#robotic process automation in banking#rpa solution#robotic process automation for finance#process automation solution#robotic process automation services#robotic process automation for insurance#rpa system#what is rpa automation#robotic process automation solution#robotic process automation benefits#robotic process automation consulting#robotic process automation consultant#rpa service provider#rpa consulting services
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Power of SAP Robotic Automation
1. Introduction
In a world where data and processes drive businesses, sap robotic automation is a technology that stands out. It promises to transform the way enterprises operate by automating repetitive tasks, enabling employees to focus on more strategic activities.
2. What is SAP Robotic Automation?
SAP Robotic Automation, often referred to as RPA (Robotic Process Automation), is a technology that uses software robots or "bots" to automate routine and rule-based tasks within an organization. These bots mimic human actions, interact with various systems and applications, and can work around the clock without rest.
3. How Does SAP Robotic Automation Work?
SAP Robotic Automation works by employing bots to execute predefined tasks. These bots are trained to follow specific workflows, interact with user interfaces, extract and input data, and make decisions based on predefined rules. They can seamlessly integrate with existing software systems, making them highly versatile.
4. Benefits of SAP Robotic Automation
Streamlined Processes
One of the primary advantages of SAP Robotic Automation is the streamlining of processes. It allows organizations to automate repetitive tasks, reducing the time and effort required to complete them.
Reduced Errors
Humans are prone to errors, but bots are not. By automating tasks, SAP Robotic Automation significantly reduces the chances of human error, leading to higher accuracy in operations.
Enhanced Productivity
With routine tasks automated, employees can focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their roles, ultimately leading to increased productivity and job satisfaction.
5. Applications of SAP Robotic Automation
Finance and Accounting
In the finance sector, SAP Robotic Automation can automate tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and reconciliation, allowing financial professionals to concentrate on financial analysis and strategy.
Human Resources
Automating HR tasks like employee onboarding, payroll processing, and attendance tracking frees HR teams to focus on employee engagement and talent development.
Supply Chain Management
SAP Robotic Automation can optimize supply chain processes by automating inventory management, order processing, and demand forecasting.
6. Implementing SAP Robotic Automation
Selecting the Right Processes
Not all processes are suitable for automation. Organizations should carefully choose which tasks to automate based on criteria like frequency, rule-based nature, and potential ROI.
Integration with Existing Systems
Smooth integration with existing software and systems is crucial for the success of SAP Robotic Automation projects.
Training and Development
Employees need to be trained to work alongside bots and understand how to manage and maintain automated processes.
7. Challenges and Solutions
Data Security Concerns
As bots interact with sensitive data, ensuring data security is a top priority. Implementing encryption and access controls can mitigate these concerns.
Change Management
Introducing automation can lead to resistance among employees. Effective change management strategies are essential to ensure a smooth transition.
Maintenance and Support
Regular maintenance and timely support are necessary to keep the automation ecosystem running smoothly.
8. Future Trends in SAP Robotic Automation
The future of SAP Robotic Automation holds exciting possibilities, including enhanced AI capabilities, greater integration with IoT devices, and advanced analytics for smarter decision-making.
9. Real-Life Success Stories
Explore how leading organizations have harnessed the power of SAP Robotic Automation to achieve remarkable results.
SAP Robotic Automation is a game-changer for businesses looking to boost efficiency, reduce errors, and empower their workforce. By harnessing the power of automation, organizations can stay competitive in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Read More : https://www.beezlabs.com/tulip
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rightpath Global Services: Driving Financial Transformation
In the previous part of our blog series, we looked at how tactical automation, RPA, and AI can enhance the efficiency of Accounts Payable (AP) operations. But what if technology isn’t the only answer? Sometimes, the real transformation lies in how we approach process improvement itself. In Part 6 of our AP Transformation series, we turn to time-tested methodologies – Six Sigma and Lean – to explore non-technical ways of driving efficiency and reducing waste in the AP lifecycle.
Why Methodology Matters in Process Transformation
While automation offers significant advantages, many AP challenges stem from deeply embedded inefficiencies – such as unclear workflows, inconsistent task ownership, or redundant steps. Methodological approaches offer a structured way to analyse, question, and ultimately redesign processes. These techniques help organizations lay a strong foundation of operational discipline, making future automation efforts even more impactful.
Six Sigma: Reducing Defects, One Process at a Time
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on eliminating defects and minimizing variability in business processes. In the context of AP, this could mean fewer invoice mismatches, reduced payment delays, or more consistent posting accuracy.
For existing processes, the DMAIC framework – Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control – offers a clear roadmap. You begin by defining the problem or inefficiency, then measuring current performance and analysing the root causes. Once identified, targeted improvements are made, followed by ongoing control mechanisms to ensure the changes stick.
For processes being designed from scratch or undergoing a complete overhaul, the DMADV framework – Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, and Verify – comes into play. This helps ensure the new process is robust, scalable, and aligned with organizational goals before it’s rolled out.
Lean Thinking: Eliminating What Doesn’t Add Value
Lean methodology takes a different but complementary approach. It focuses on eliminating non-value-adding activities, commonly referred to as “waste.” In AP processes, this might include unnecessary approvals, manual hand-offs, duplicate entries, or waiting for data from other teams.
Lean categorizes waste into three broad forms: Muda, Mura, and Muri. Muda refers to activities that don’t add value. Mura represents inconsistencies that create bottlenecks or errors. Muri reflects overburdening employees due to inefficiencies in the workflow.
To make these actionable, Lean practitioners use the acronym TIMWOODS to identify eight specific types of waste: Transport, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Overproduction,
Overprocessing, Defects, and Skills. Recognizing these waste types in your AP cycle – say, too many approval layers (waiting), manual keying of already available digital data (overprocessing), or underutilized staff expertise (skills) – can open the door to meaningful improvements.
Process Discipline is the Bedrock of Smart Transformation
Both Six Sigma and Lean encourage a culture of continuous improvement. They aren’t just toolkits but mindsets that enable organizations to be proactive rather than reactive. When AP teams embrace these principles, they move from firefighting individual errors to systematically eliminating the root causes of inefficiency.
At Right Path, we help businesses not only automate but also optimize. Our Free Procure-to Pay (P2P) Assessment looks beyond technology to uncover where process redesign can deliver lasting value. Whether you’re ready to implement Lean, launch a Six Sigma initiative, or simply looking for smarter ways to streamline AP, we’re here to guide your transformation journey.
Explore our website to learn more and claim your free assessment today. Let’s build processes that are not just faster, but fundamentally better.
For more information click here: - https://rightpathgs.com/blogs/
0 notes
Text
How Task Mining Enhances Productivity and Fuels Automation Success

Task Mining is a technique that captures and analyzes user interactions with software applications to understand how tasks are executed. Unlike Process Mining, which relies on system logs to analyze end-to-end processes, Task Mining delves deeper into the specific actions taken at the desktop level. This includes mouse movements, keystrokes, and application usage patterns to reconstruct and analyze workflows at the task level.
By collecting this detailed interaction data, organizations can gain a clear understanding of how work is actually done, as opposed to how it is documented or assumed. This helps identify bottlenecks, variations in task execution, and areas where automation or standardization can bring measurable improvements.
Key Benefits of Task Mining
1. Enhanced Process Understanding: Task Mining provides a granular view of task-level workflows that often go unnoticed in traditional process maps. This visibility helps companies understand how tasks vary across users, departments, or regions.
2. Data-Driven Automation: Identifying repetitive, time-consuming tasks is a prerequisite for successful automation. Task Mining highlights high-volume activities that are suitable candidates for Robotic Process Automation (RPA) or other automation technologies.
3. Productivity Improvements: By analyzing how employees perform their daily tasks, businesses can uncover inefficiencies such as excessive switching between applications or redundant data entry. These insights support workflow optimization and time savings.
4. Employee Training and Support: Task Mining can reveal skill gaps or non-compliant practices in task execution. Organizations can use this data to provide targeted training, coaching, and real-time guidance to improve employee performance and adherence to best practices.
5. Compliance and Standardization: Monitoring task execution also helps enforce standardized procedures and ensures compliance with regulatory and internal policies. This is especially important in industries like finance, healthcare, and insurance where adherence to guidelines is critical.
How Task Mining Works
The Task Mining process typically involves the following steps:
Data Collection: Lightweight agents are installed on user desktops to record interactions such as clicks, copy-paste actions, form filling, and software navigation. These agents anonymize and securely transmit the data for analysis.
Data Processing: Collected data is cleansed and transformed into structured formats. Advanced technologies such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are often used to interpret screen content and user actions.
Workflow Reconstruction: The system reconstructs workflows by grouping related activities into tasks. These tasks are then visualized in task maps, highlighting variations and inefficiencies.
Insight Generation: AI and machine learning algorithms analyze the workflows to identify patterns, bottlenecks, and automation opportunities. Dashboards and reports provide actionable insights to stakeholders.
Implementation: Insights from Task Mining are used to redesign workflows, develop automation scripts, or provide training interventions that improve overall efficiency and compliance.
Use Cases Across Industries
Finance: In banking and financial services, Task Mining is used to streamline back-office operations like loan processing, account reconciliation, and compliance reporting.
Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics use Task Mining to improve administrative processes such as patient data entry, billing, and appointment scheduling, allowing medical professionals to focus more on patient care.
Retail: Retailers deploy Task Mining to optimize inventory management, point-of-sale operations, and customer service workflows, resulting in better customer experiences and reduced operational costs.
Telecommunications: Service providers leverage Task Mining to enhance customer onboarding, technical support, and billing processes by identifying inefficiencies and training needs.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, Task Mining does raise some concerns. Privacy is a primary issue—organizations must ensure that employee data is anonymized and collected with clear consent. Additionally, over-reliance on Task Mining insights without involving human judgment may lead to misguided decisions.
Another challenge is the complexity of analyzing unstructured data from multiple applications and formats. Ensuring data quality and integrating insights with broader digital transformation strategies require skilled teams and robust platforms.
The Future of Task Mining
Task Mining is evolving rapidly with advances in AI, machine learning, and user behavior analytics. Future innovations may include real-time task guidance, predictive process optimization, and deeper integration with process mining platforms. As organizations increasingly embrace hybrid work models and digital workflows, Task Mining will play a pivotal role in driving operational agility and excellence.
Conclusion
Task Mining is transforming the way organizations understand and improve their operations. By capturing detailed user interactions, it provides unparalleled visibility into task execution, enabling smarter decisions around automation, training, and workflow optimization. As businesses strive for greater efficiency and resilience, Task Mining will be an indispensable tool in their digital transformation toolkit.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Efficiency: How RPA and Automation Solutions are Transforming Business Operations
In today's digital-first landscape, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and automation solutions are not just optional—they're essential for businesses aiming to remain competitive, agile, and scalable. These technologies are redefining how operations teams tackle repetitive tasks, reduce costs, and unlock new levels of efficiency.
What is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to software bots that mimic human actions to perform rule-based tasks across various applications and systems. Think data entry, invoice processing, and customer onboarding—all handled without manual input.
Why Businesses are Investing in Automation Solutions
Operational Efficiency – Automation eliminates repetitive tasks, freeing up teams for high-value work.
Cost Savings – Companies reduce labor costs and minimize error-related losses.
Scalability – Easily scale operations without hiring additional staff.
Compliance and Accuracy – RPA ensures audit trails and precise execution of tasks.
Speed and Agility – Respond to market changes faster by automating critical workflows.
Top Use Cases for RPA in Operations
Invoice Processing and Accounts Payable
HR Onboarding and Offboarding
IT Helpdesk Automation
Customer Service Ticketing
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
These use cases show how business process automation is a key driver of digital transformation.
The Role of Intelligent Automation
While traditional RPA focuses on rule-based automation, the future lies in intelligent automation—a combination of RPA with AI and machine learning. This enables bots to handle unstructured data, make decisions, and continuously learn from outcomes.
Choosing the Right Automation Strategy
Success with automation depends on:
Assessing current workflows to identify automation potential
Choosing tools that integrate well with your tech stack
Starting with quick-win use cases and scaling across departments
Engaging operations teams in change management and training
Real Impact: A Sample Case Study
A mid-size bank implemented RPA for document verification and achieved:
70% faster processing times
90% reduction in manual errors
$500,000+ in annual cost savings
Conclusion
For operations leaders, embracing RPA and automation solutions is no longer a question of "if" but "how soon." Whether you're just getting started or expanding enterprise-wide, automation is a proven pathway to workflow optimization, cost reduction, and sustained competitive advantage.
Ready to explore scalable automation for your organization? Let’s discuss how Spearhead Technology can help you design, deploy, and scale your RPA journey.
0 notes
Text
Business Accounting Software Market Size, Trends, Drivers & Market Dynamics 2032
Global Business Accounting Software Market Overview The global business accounting software market is experiencing steady growth, with an estimated market size of USD 14.2 billion in 2024. It is projected to reach USD 26.5 billion by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8.1% over the forecast period. The market growth is fueled by the rising adoption of cloud-based financial solutions, digital transformation across industries, and the need for automation in financial operations. SMEs and large enterprises alike are increasingly turning to business accounting software to streamline operations, ensure regulatory compliance, and gain real-time visibility into financial data. Enhanced demand for integrated financial systems and scalable platforms is driving vendors to offer customizable, feature-rich accounting software tailored for diverse industries. Global Business Accounting Software Market Dynamics Market Drivers: Key drivers include the rapid adoption of cloud computing, increased need for real-time data access, and regulatory mandates promoting transparency in financial reporting. Companies are focusing on cost optimization and operational efficiency, leading to a surge in demand for intelligent financial software. Market Restraints: High implementation costs, data security concerns, and limited technical expertise among SMEs remain significant hurdles. Additionally, transitioning from legacy systems to modern platforms poses integration challenges for traditional enterprises. Market Opportunities: Emerging markets present significant growth potential, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where digital infrastructure and enterprise software penetration are on the rise. Furthermore, integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and artificial intelligence (AI) creates new revenue streams for vendors. Technological and Regulatory Influence: Regulatory compliance standards such as IFRS, SOX, and GAAP are encouraging enterprises to adopt compliant accounting systems. Meanwhile, the growing emphasis on sustainability reporting is influencing the inclusion of ESG metrics in accounting platforms, reshaping market offerings. Download Full PDF Sample Copy of Global Business Accounting Software Market Report @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/download-sample?rid=33759&utm_source=PR-News&utm_medium=366 Global Business Accounting Software Market Trends and Innovations The market is witnessing significant innovation, driven by AI and machine learning integration into accounting workflows. Predictive analytics, robotic process automation (RPA), and natural language processing (NLP) are being leveraged to automate repetitive tasks, identify anomalies, and enhance decision-making. The proliferation of mobile accounting applications enables on-the-go financial management, particularly useful for freelancers and micro-businesses. Product enhancements now include multi-currency support, real-time dashboards, and embedded compliance tools. Strategic collaborations between fintech firms and traditional software vendors are fostering hybrid accounting ecosystems. Additionally, open API-based architecture is empowering businesses to customize modules and integrate third-party solutions seamlessly. Global Business Accounting Software Market Challenges and Solutions Key Challenges: The market faces challenges such as data privacy regulations, cybersecurity threats, and vendor lock-in. Pricing pressures, particularly in price-sensitive markets, create barriers to entry for premium software providers. Integration complexity with existing systems often deters smaller firms from migrating to modern platforms. Solutions: To overcome these hurdles, vendors are offering tiered pricing models, pay-as-you-go subscriptions, and modular solutions. Enhanced encryption, compliance-ready architecture, and dedicated onboarding support are also being provided to ensure secure and smooth transitions.
Investment in localized language support and regional data centers can improve adoption in emerging regions. Global Business Accounting Software Market Future Outlook Looking ahead, the global business accounting software market is poised for robust expansion. Accelerated digitization, evolving regulatory frameworks, and the increasing convergence of finance with AI and big data analytics will continue to drive growth. By 2032, automation and intelligent forecasting will become standard features in accounting platforms. Cloud-native, AI-enabled solutions will dominate the market, with vertical-specific offerings gaining traction. Market evolution will also be driven by the shift toward subscription-based revenue models and the integration of sustainability metrics. Enterprises will increasingly seek end-to-end financial management suites capable of aligning business strategy with real-time financial insights. Overall, the market’s trajectory will be shaped by a blend of technological innovation, regulatory adherence, and user-centric design. Key Players in the Global Business Accounting Software Market Global Business Accounting Software Market are renowned for their innovative approach, blending advanced technology with traditional expertise. Major players focus on high-quality production standards, often emphasizing sustainability and energy efficiency. These companies dominate both domestic and international markets through continuous product development, strategic partnerships, and cutting-edge research. Leading manufacturers prioritize consumer demands and evolving trends, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Their competitive edge is often maintained through robust R&D investments and a strong focus on exporting premium products globally. Microsoft FreshBooks Acclivity Intacct Intuit Oracle Red Wing Software Sage Group Zoho Xero Expensify. Get Discount On The Purchase Of This Report @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ask-for-discount?rid=33759&utm_source=PR-News&utm_medium=366 Global Business Accounting Software Market Segments Analysis and Regional Economic Significance The Global Business Accounting Software Market is segmented based on key parameters such as product type, application, end-user, and geography. Product segmentation highlights diverse offerings catering to specific industry needs, while application-based segmentation emphasizes varied usage across sectors. End-user segmentation identifies target industries driving demand, including healthcare, manufacturing, and consumer goods. These segments collectively offer valuable insights into market dynamics, enabling businesses to tailor strategies, enhance market positioning, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. The Global Business Accounting Software Market showcases significant regional diversity, with key markets spread across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Each region contributes uniquely, driven by factors such as technological advancements, resource availability, regulatory frameworks, and consumer demand. Business Accounting Software Market, By Deployment • Cloud• On-premise Business Accounting Software Market, By Type • Commercial Accounting Software• Enterprise Accounting Software• Custom Accounting Software Business Accounting Software Market, By Organization Size • Small• Medium• Large Business Accounting Software Market By Geography • North America• Europe• Asia Pacific• Latin America• Middle East and Africa For More Information or Query, Visit @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/business-accounting-software-market/ About Us: Verified Market Research Verified Market Research is a leading Global Research and Consulting firm servicing over 5000+ global clients. We provide advanced analytical research solutions while offering information-enriched research studies. We also offer insights into strategic and growth analyses and data necessary to achieve corporate goals and critical revenue decisions.
Our 250 Analysts and SMEs offer a high level of expertise in data collection and governance using industrial techniques to collect and analyze data on more than 25,000 high-impact and niche markets. Our analysts are trained to combine modern data collection techniques, superior research methodology, expertise, and years of collective experience to produce informative and accurate research. Contact us: Mr. Edwyne Fernandes US: +1 (650)-781-4080 US Toll-Free: +1 (800)-782-1768 Website: https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ Top Trending Reports https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/refinish-paint-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/zinc-chemicals-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/impact-resistant-glass-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/flock-adhesives-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/marine-adhesives-market/
0 notes
Text
Robotic Process Automation: Streamlining Business Through Intelligent Automation

In today's fast-paced digital economy, organizations are constantly seeking innovative ways to increase efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer experiences. One transformative technology leading this charge is Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Far from the sci-fi idea of humanoid robots, RPA involves the use of software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks—freeing up human employees to focus on higher-value work.
What Is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation refers to the deployment of software “robots” that emulate human interactions with digital systems. These bots can log into applications, enter data, perform calculations, complete routine transactions, and even respond to simple queries. Unlike traditional automation, RPA doesn't require deep integration with existing systems, making it faster and more cost-effective to implement.
The Business Case for RPA
Implementing RPA offers a range of tangible benefits that make it attractive across industries:
Increased Efficiency: Bots operate 24/7 without fatigue, reducing turnaround times from hours to minutes.
Cost Savings: By automating routine processes, companies can lower labor costs and reallocate human resources to more strategic initiatives.
Improved Accuracy: Bots eliminate human error in data entry and compliance-heavy tasks, ensuring consistent quality and reducing rework.
Scalability: RPA can quickly scale up to handle peak workloads or be redeployed as business needs evolve.
Enhanced Compliance: With proper programming, bots follow rules to the letter, generating audit trails that help in regulatory reporting.
Key Use Cases Across Industries
RPA has proven valuable across sectors, from banking to healthcare. Here are a few standout examples:
Finance & Accounting: Automating invoice processing, financial reporting, and reconciliations.
Healthcare: Speeding up patient onboarding, billing, and data entry for insurance claims.
Retail: Streamlining supply chain operations, inventory management, and order processing.
Human Resources: Simplifying employee onboarding, payroll management, and leave processing.
Integrating Intelligence: The Rise of Intelligent Automation
While RPA handles structured, rule-based tasks, pairing it with Artificial Intelligence (AI) opens the door to more complex, cognitive workflows. This fusion—often called Intelligent Automation (IA)—enables bots to read unstructured data (like emails or scanned documents), interpret intent, and make decisions.
For example, an intelligent bot could:
Read and categorize customer service emails
Extract data from handwritten forms using OCR
Flag anomalies in financial reports using machine learning
This evolution significantly broadens the scope of automation, enabling smarter, context-aware systems.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, RPA isn’t a silver bullet. Organizations must carefully assess:
Process Suitability: Not all processes are ripe for automation—those with inconsistent inputs or frequent changes may not yield desired ROI.
Governance: Without clear oversight, bots can create operational risks if they malfunction or aren't updated regularly.
Change Management: Employees may fear job loss, so transparent communication and reskilling initiatives are critical to gain buy-in.
Future Outlook
The RPA market is expected to continue growing exponentially, with platforms increasingly integrating AI, analytics, and low-code development features. As businesses become more digitally mature, RPA will no longer be a differentiator—it will be a baseline expectation.
Organizations that embrace RPA now, while investing in intelligent automation strategies, will position themselves at the forefront of innovation and efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Robotic Process Automation is more than just a tech trend—it's a strategic tool for transforming operations and unlocking new levels of productivity. When combined with AI and thoughtful change management, RPA can help organizations not just keep up with the competition, but leap ahead.
#financial services#investment#finance#financial advisor#financial planning#financial wellness#financial freedom#investment planning#Robotic Process Automation
0 notes
Text
AP transformation metrics that CFOs should watch
Accounts Payable transformation is no longer optional—it's a necessity for businesses aiming to stay competitive and efficient. As manual processes become bottlenecks for finance teams, AP transformation offers a way to boost productivity, accuracy, and visibility into cash flow. Companies like Rightpath understand this shift and have designed robust AP transformation frameworks to help organizations transition smoothly from traditional models to digitized operations.
The first step in transforming AP is assessing current workflows. Manual invoice entry, paper-based approvals, and poor vendor communication are common issues. Rightpath begins with a thorough diagnostic phase, identifying gaps and inefficiencies across the procure-to-pay (P2P) cycle. Once assessed, they deploy tailored solutions like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) for invoice scanning, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for invoice matching, and AI for fraud detection.
AP transformation isn't just about automation—it's about reimagining the process from end to end. That means designing new approval hierarchies, integrating AP systems with ERP platforms, and establishing real-time dashboards for decision-makers. Rightpath ensures every transformation is anchored in measurable KPIs, such as Days Payable Outstanding (DPO), invoice processing time, and payment accuracy.
The benefits extend beyond the finance department. Vendors experience quicker payment cycles, fewer disputes, and better communication. Internal teams spend less time on manual reconciliation and more on strategic analysis. Audit readiness improves, as does overall process transparency.
Moreover, AP transformation enhances compliance. With strict governance protocols and standardized processes, businesses are better prepared for tax audits and financial scrutiny. Rightpath helps implement these controls without compromising agility or speed.
As businesses scale, an outdated AP process can slow growth. But a transformed AP function becomes a competitive advantage—improving supplier relationships, cash flow predictability, and internal efficiency. Partnering with an expert like Rightpath ensures that transformation isn’t just technical—it’s strategic.
Whether you're looking to reduce costs, improve control, or simply modernize your finance operations, AP transformation is a powerful lever—and the time to act is now.
0 notes
Text
AI in Action: Intelligent Solutions for the Document Management System Market
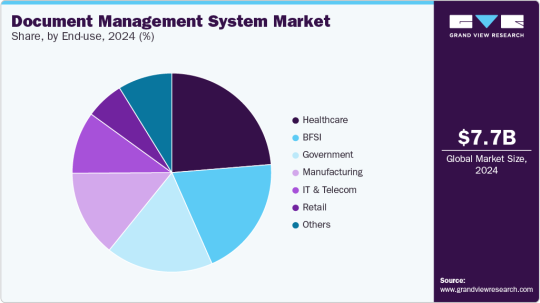
The global document management system market was valued at USD 7.68 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 18.17 billion by 2030, demonstrating a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.9% from 2025 to 2030. This expansion is primarily fueled by organizations' increasing need to securely manage and store vast volumes of digital information.
As businesses worldwide embrace digital transformation and move towards paperless operations, the demand for effective solutions for document storage, retrieval, and management has escalated. The accelerated adoption of cloud-based DMS solutions has further spurred this trend, offering businesses scalable, cost-effective, and readily accessible options. Moreover, the heightened focus on compliance and regulatory mandates is significantly contributing to the growth of the DMS industry. Enterprises operating in heavily regulated sectors like healthcare, finance, and legal are increasingly implementing DMS to ensure strict adherence to data security, privacy, and record-keeping regulations. These systems facilitate streamlined audits, maintain secure document trails, and mitigate the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Key Market Trends & Insights:
Regional Leadership: The North American document management system market commanded a substantial revenue share of almost 40.0% in 2024, driven by the escalating demand for digital transformation across various industries.
Component Dominance: The software segment held the largest market share, exceeding 67.0% of the revenue in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the growing demand for cloud-based, AI-driven, and compliance-ready solutions.
Deployment Preference: The cloud segment led the market with a revenue share of over 67.0% in 2024. This is propelled by the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) into cloud DMS platforms.
Enterprise Size Leadership: Large enterprises accounted for nearly 67.0% of the market's revenue share in 2024. This is due to the immense volume of enterprise-grade documents they manage and their critical need for scalable, secure, and intelligent document workflows.
End-Use Sector Dominance: The healthcare segment generated over 23.0% of the market's revenue share in 2024. A significant driver here is the accelerating shift towards Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and paperless systems within the healthcare industry.
Order a free sample PDF of the Document Management System Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
Market Size & Forecast
2024 Market Size: USD 7.68 billion
2030 Projected Market Size: USD 18.17 billion
CAGR (2025-2030): 15.9%
North America: Largest market in 2024
Asia Pacific: Fastest growing market
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
Leading companies in the document management system (DMS) industry, including Microsoft, IBM Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Open Text Corporation, and Hyland Software, Inc., are actively engaged in strategic initiatives to enhance their competitive edge. These strategies largely involve new product development, forging partnerships and collaborations, and entering into agreements.
Illustrative of these efforts, in April 2025, Hyland Software, Inc. significantly expanded its product offerings by integrating advanced AI capabilities. Through substantial updates to Hyland Automate, Hyland Knowledge Discovery, and key improvements to Hyland OnBase and Hyland Alfresco, the company aims to provide organizations with sophisticated tools for optimizing content, processes, and application intelligence. Their Hyland Content Intelligence product line is designed to empower businesses with actionable insights derived from simple natural language queries, thereby streamlining complex searches and delivering precise information from vast enterprise content.
Similarly, in March 2025, IBM Corporation launched IBM Storage Ceph as a Service, broadening its suite of flexible on-premises infrastructure solutions. This new service complements IBM Power delivered as a service, offering a distributed compute platform with diverse form factors and adaptable consumption models. The IBM Storage Ceph service facilitates the integration of cloud-based solutions with on-premises environments, providing a unified software-defined storage solution that encompasses block, file, and object data. Its goal is to help organizations eliminate data silos and modernize their data lakes and virtual machine storage, delivering a seamless cloud storage experience within their own data centers.
Further demonstrating industry innovation, in December 2024, OpenText introduced Core Digital Asset Management (Core DAM). This solution is engineered to optimize the digital content supply chain by incorporating powerful features that yield tangible results. Core DAM leverages practical AI to automate tasks such as image tagging, video transcript generation, and the creation of design inspiration images using OpenText Experience Aviator, significantly boosting the efficiency and accuracy of creative workflows. It also provides global content access, enabling users to generate instant links for high-performance display worldwide.
Key Players
Agiloft, Inc.
Alfresco Software Inc.
Cflowapps
DocLogix
Hyland Software, Inc.
IBM Corporation
Integrify
Browse Horizon Databook for Global Document Management System Market Size & Outlook
Conclusion
The document management system (DMS) market is rapidly growing, driven by the need for secure digital information management and paperless transitions. Cloud-based solutions and regulatory compliance are key growth factors. North America leads the market, with software and cloud deployments dominating. Large enterprises and the healthcare sector are major adopters. Leading companies are innovating with AI and strategic collaborations to enhance their offerings.
0 notes
Text

Future-proof your accounting firm with the powerful combination of AI and RPA! These technologies enhance efficiency, accuracy, and compliance, allowing your firm to focus on strategic insights and growth. Is your firm ready to implement AI and RPA? Explore how Unison Globus can help you navigate the future of accounting automation today! Visit: https://unisonglobus.com/choosing-between-ai-and-rpa-what-us-cpas-and-accounting-firms-need-to-know/
#AI vs RPA in accounting#unison globus#Accounting automation#AI in accounting#RPA in accounting#Benefits of AI for CPAs#Benefits of RPA for accounting firms#AI and RPA integration#Accounting technology trends#RPA for invoicing
1 note
·
View note
Text
Conducting Effective Business Process Improvement

Business Process Improvement (BPI) is the systematic approach to helping an organization optimize its core processes for greater efficiency, effectiveness, and adaptability.
1. Understand the Current State ("As-Is")
Map Out Existing Processes
Use process mapping tools like:
SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers)
Flowcharts
Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
Collect Data
Key metrics: Cycle time, error rates, cost per transaction, throughput
Interview stakeholders, observe workflows, review logs and KPIs
Tip: Get cross-functional input to avoid blind spots.
2. Define Clear Goals and Metrics
Use the SMART framework:
Specific – What process needs to improve?
Measurable – What metrics define success?
Achievable – Is it realistic with current resources?
Relevant – Does it align with strategic goals?
Time-bound – When should results be achieved?
Examples:
Reduce invoice processing time by 40% in 90 days
Eliminate 80% of manual handoffs in customer onboarding
3. Analyze the Root Causes
Use proven diagnostic tools:
5 Whys Analysis
Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram
Pareto Analysis (80/20 rule)
Process mining tools for digital workflows
Look for:
Bottlenecks
Redundancies
Manual tasks that could be automated
Communication failures
4. Design the Improved Process ("To-Be")
Use Lean, Six Sigma, and Agile Principles:
Eliminate waste (Lean: TIMWOOD – Transport, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Overproduction, Overprocessing, Defects)
Reduce variation (Six Sigma)
Shorten feedback loops (Agile)
Redesign for:
Simplicity
Speed
Scalability
Automation where possible (e.g., RPA, workflow platforms)
Create To-Be maps, RACI charts, and updated SOPs.
5. Implement the New Process
Focus Areas:
Change Management – Train teams, communicate clearly, and manage resistance
Pilot Testing – Try improvements on a small scale before a full rollout
Project Management – Use agile sprints or phased rollouts to maintain momentum
Key Tools:
Communication plan
Training modules
Feedback loops (daily standups, weekly reviews)
6. Monitor, Optimize, and Sustain
Track KPIs:
Real-time dashboards
Weekly metrics reviews
Before vs. after comparisons
Continuous Improvement:
Encourage feedback from frontline users
Use Kaizen or PDCA cycles to keep iterating
Build a culture of accountability and excellence
7. Document and Standardize
Finalize new SOPs and documentation
Create playbooks or handbooks
Assign process owners for ongoing accountability
Tip: Use a centralized knowledge base or BPM tool to manage version control.
Bonus Tools & Frameworks
Tool/MethodUse CaseLean Six Sigma (DMAIC)Structured process improvementBusiness Process Model and Notation (BPMN)Process design and documentationKPI Tree / Metrics TreeLinking process improvements to business goalsVoice of the Customer (VoC)Ensure customer impact is central to changes
Summary Cheat Sheet
StepFocus1. Assess Current ProcessMap + Measure2. Define GoalsAlign with business impact3. Root Cause AnalysisFind what's broken4. Design Future StateLean + tech + feedback5. Implement ChangesTraining + testing + rollout6. Measure & ImproveMonitor, adapt, optimize7. Document & SustainSOPs, ownership, culture shift
0 notes
Text
APIs, Automation, and Entity Integrity: The Future of Legal Entity Data

In the modern data-driven economy, the availability, quality, and integrity of legal entity data are essential for effective business strategies, compliance, and operational efficiency. Organizations are dealing with more complicated global compliance requirements, intricate organization entity structures, and the need for immediate data availability. To keep up with these demands, businesses are adopting a mix of automation, APIs, and entity integrity in order to improve their data governance and management processes.
The Challenge of Managing Legal Entity Data
Legal entity data includes crucial details like entity titles, registration IDs, jurisdictions, ownership structures, and activity updates. This information supports multiple important activities, including KYC, AML (Anti Money Laundering) processes, accounting, acquisitions, and supply chain risks.
Despite its importance, legal entity data faces issues including duplication, inconsistency, outdated records, and data silos. These issues can cause compliance breaches, reputational damage, and poor business decisions. With the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the U.S. Corporate Transparency Act, and newer rules regarding AML, organizations cannot continue to depend on manual workflows or legacy systems to maintain and manage legal entity data. Automation, APIs, and entity integration help solve these matters.
APIs: Enabling Real-Time Data Integration
APIs are transforming the methods through which businesses seek, share, and integrate legal entity information. They create a safe environment for interaction between different software systems, allowing real-time communication. This allows organizations to fetch the latest legal entity information from authoritative government registries, financial institutions, or third-party data providers.
Also, APIs can enhance internal datasets by adding external data, as for example ownership structures, beneficial ownership details, or even sanctions list screening data. This helps in creating a more complete and accurate entity profile, which aids risk assessment and due diligence processes.
Automation: Reducing Manual Work and Increasing Scale
The use of automation improves APIs by providing workflows that are scalable, repeatable, and less prone to human error. Now, hours spent by legal, compliance, and operations teams checking entity data or preparing reports can be done with one click. Automated processes can monitor data streams, identify errors, and take corrective action in real time.
For example, robotic process automation (RPA) tools can streamline rule-based tasks such as updating corporate registries, matching entity records, or creating audit trails. Combining automation with machine learning enables the system to improve by learning from past oversight.
Automation improves business agility, making it easier for companies to adapt to changes such as new regulations, mergers, or expansion to other regions. These changes can be implemented faster because workflows can be scaled or reconfigured without the need to redesign an entire system.
Entity Integrity: The Foundation of Trustworthy Data
To maintain entity integrity at scale, businesses are increasingly adopting entity management software that integrates and manages all legal entity data on a single, centralized system. Such tools enable businesses to standardize entity records, assign and track unique identifiers, and implement validation rules at departmental and geographic levels. When paired with automation and API capabilities, these systems guarantee that every piece of entity data, regardless of internal or external sourcing, meets the highest standards of accuracy and consistency. This level of control enhances compliance and also optimizes the legal, finance, and governance functions of the organization
By maintaining entity integrity, businesses reduce the risks that arise from poor data quality, such as financial inaccuracies, compliance breaches, and operational inefficiencies. Also, such data helps organizations enhance decision-making, improve onboarding experiences, and enable advanced analytics.
A Unified Vision for the Future
The future of legal entity data is within an ecosystem where connectivity (through APIs), efficiency (through automation), and reliability (entity integrity) exist. Together, these pillars support a data strategy that is real-time, scalable, and audit-ready. This is exactly what modern businesses and regulators demand.
Forward-thinking companies are working with partners providing product development services to custom build platforms, focusing on their entity data needs. From developing compliance systems with APIs to incorporating AI-driven entity resolution powers, these provided services allow for the creation of adaptable solutions.
Conclusion
With legal entity data becoming more essential for businessess, it is clear that companies need to update their data management strategies. APIs enable businesses to access and share data in real time, automation streamlines repetitive work, and a promise to maintain entity integrity builds a solid basis of trust.
These three parts working together will transform legal entity data management, promote innovation, improve compliance, and facilitate informed decisions. The strategic advantage goes to the organization that treats legal entity data as a critical component for intelligent decisions.
0 notes
Text
Rightpath GS: Revolutionizing Process Management
In the previous part of our blog series, we looked at how tactical automation, RPA, and AI can enhance the efficiency of Accounts Payable (AP) operations. But what if technology isn’t the only answer? Sometimes, the real transformation lies in how we approach process improvement itself. In Part 6 of our AP Transformation series, we turn to time-tested methodologies – Six Sigma and Lean – to explore non-technical ways of driving efficiency and reducing waste in the AP lifecycle.
Why Methodology Matters in Process Transformation
While automation offers significant advantages, many AP challenges stem from deeply embedded inefficiencies – such as unclear workflows, inconsistent task ownership, or redundant steps. Methodological approaches offer a structured way to analyse, question, and ultimately redesign processes. These techniques help organizations lay a strong foundation of operational discipline, making future automation efforts even more impactful.
Six Sigma: Reducing Defects, One Process at a Time
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on eliminating defects and minimizing variability in business processes. In the context of AP, this could mean fewer invoice mismatches, reduced payment delays, or more consistent posting accuracy.
For existing processes, the DMAIC framework – Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control – offers a clear roadmap. You begin by defining the problem or inefficiency, then measuring current performance and analysing the root causes. Once identified, targeted improvements are made, followed by ongoing control mechanisms to ensure the changes stick.
For processes being designed from scratch or undergoing a complete overhaul, the DMADV framework – Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, and Verify – comes into play. This helps ensure the new process is robust, scalable, and aligned with organizational goals before it’s rolled out.
Lean Thinking: Eliminating What Doesn’t Add Value
Lean methodology takes a different but complementary approach. It focuses on eliminating non-value-adding activities, commonly referred to as “waste.” In AP processes, this might include unnecessary approvals, manual hand-offs, duplicate entries, or waiting for data from other teams.
Lean categorizes waste into three broad forms: Muda, Mura, and Muri. Muda refers to activities that don’t add value. Mura represents inconsistencies that create bottlenecks or errors. Muri reflects overburdening employees due to inefficiencies in the workflow.
To make these actionable, Lean practitioners use the acronym TIMWOODS to identify eight specific types of waste: Transport, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Overproduction,
Overprocessing, Defects, and Skills. Recognizing these waste types in your AP cycle – say, too many approval layers (waiting), manual keying of already available digital data (overprocessing), or underutilized staff expertise (skills) – can open the door to meaningful improvements.
Process Discipline is the Bedrock of Smart Transformation
Both Six Sigma and Lean encourage a culture of continuous improvement. They aren’t just toolkits but mindsets that enable organizations to be proactive rather than reactive. When AP teams embrace these principles, they move from firefighting individual errors to systematically eliminating the root causes of inefficiency.
At Right Path, we help businesses not only automate but also optimize. Our Free Procure-to Pay (P2P) Assessment looks beyond technology to uncover where process redesign can deliver lasting value. Whether you’re ready to implement Lean, launch a Six Sigma initiative, or simply looking for smarter ways to streamline AP, we’re here to guide your transformation journey.
Explore our website to learn more and claim your free assessment today. Let’s build processes that are not just faster, but fundamentally better.
For more information click here: - https://rightpathgs.com/blogs/
0 notes
Text
Top 7 Reasons to Choose KanhaSoft for AI‑Powered CRM & ERP Development in 2025

1. Cutting‑Edge AI Integration: Stay Ahead of CRM & ERP Trends
In 2025, AI integration into CRM and ERP systems has moved from trend to business imperative. From predictive analytics to conversational interfaces, AI-Enabled platforms are now essential.
At KanhaSoft, we embed AI deeply into both CRM and ERP — implementing:
Predictive lead scoring and customer forecasting
AI-driven workflows and task automation
Conversational UIs and chatbots for real-time assistance
Agent‑based autonomous agents handling high-volume tasks
This creates responsive, intelligent systems that act proactively, not just reactively.
2. Tailored, Customizable Solutions That Scale
In emerging markets, one-size-fits-all no longer works. As we’ve highlighted, custom ERP/CRM platforms provide your “secret sauce” — tailoring workflows, data fields, and integrations to your business logic.
KanhaSoft offers:
Low-code/no-code modules supported with AI‑assistance
Rapid customization to match unique industry processes
Scalable architecture that grows with your business
Our approach ensures your system matches your brand, not the other way around.
3. AI-Driven Automation: Efficiency Meets Accuracy
Manual tasks like invoice processing, lead nurturing, and reporting are now AI‑driven. KanhaSoft equips your CRM & ERP with AI
Robotic process automation (RPA) + AI for complex workflows
Automated email/SMS marketing, follow-ups, and segmentation
Enhanced accuracy — AI reduces human error and ensures compliance
This enables your teams to focus on strategic growth rather than repetitive admin tasks.
4. Predictive & Prescriptive Analytics for Informed Decisions
Modern enterprises count on intelligence that goes beyond analytics — to predictions and prescriptions. AI‑powered ERP / AI‑powered CRM provides:
Demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and supply chain
Customer intent prediction, churn prevention, and revenue opportunity insights
Our dashboards offer actionable insights that turn data into growth.
5. Enterprise-Grade Scalability & Integration
Whether you’re operating in a cloud-first or hybrid setup, KanhaSoft delivers:
Cloud or on‑prem deployments, optimized for performance
Open-API & micro-services architecture — easy integration with e-commerce, ERP, BI tools, and more
Modular, microservices-based builds ensuring scalability and adaptability
Your CRM/ERP grows with your business — not constraining it.
6. Robust Security, Compliance & Governance
Security is non-negotiable in 2025. Our systems include:
Encryption, RBAC & MFA for sensitive data
Audit trails and compliance-ready features (GDPR, CCPA, SOC2, etc.)
Governance frameworks for ethical and transparent AI
7. Trusted Partnership & Support Backed by Domain Expertise
KanhaSoft brings over a decade of experience across industries — logistics, real estate, healthcare, manufacturing, and more. Our strengths include:
Domain-specific templates — like Shopify integration, real-estate portals, etc.
Full-cycle services — from architecture and AI training to deployment and support
Transparent SLAs and 24/7 support with dedicated account managers
Conclusion & Call‑to‑Action
In 2025, AI‑powered CRM & ERP systems are no longer optional — they’re essential. By partnering with KanhaSoft, you gain:
AI‑filled intelligence at every level
Scalable, customized platforms tailored to your business
Efficiency through automation
Strategic benefit from analytics
Enterprise-grade integration
Security-first practices
Ongoing support from domain experts
If your business aims to future-proof operations with intelligent, scalable, and secure software, let’s connect. Discover how KanhaSoft can build the next-gen AI‑CRM & ERP solution built for your success.
0 notes
Text
AI in Banking Market Future Trends Shaping Digital Transformation and Customer-Centric Innovations
The AI in banking market is witnessing a remarkable transformation, revolutionizing traditional operations and setting new standards for innovation. As financial institutions increasingly embrace artificial intelligence to remain competitive, the market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. From automating routine tasks to enhancing customer interactions, AI is reshaping the banking landscape by making services faster, smarter, and more personalized.

Evolving Customer Expectations Driving AI Adoption
Modern customers demand seamless, real-time, and personalized experiences, similar to what they receive from leading digital platforms. This shift in expectations is compelling banks to adopt AI-powered technologies to remain relevant and competitive. AI-enabled chatbots, for instance, are now widely used to handle customer queries, offering instant responses with minimal human intervention. These tools not only improve response times but also enhance customer satisfaction by providing 24/7 support.
Predictive analytics is another major area where AI is making a significant impact. By analyzing customer data, banks can anticipate individual needs and offer tailored financial products and services. This level of personalization helps build stronger customer relationships and drives higher engagement.
Automation and Operational Efficiency
AI is streamlining internal banking processes, reducing manual errors, and enhancing efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is being used for repetitive tasks such as data entry, compliance reporting, and account reconciliation. By automating these operations, banks can significantly reduce costs and reallocate human resources to more strategic roles.
Moreover, AI algorithms assist in credit risk assessment by analyzing a broader set of data points than traditional models. This enables more accurate decision-making and faster loan approvals, benefiting both banks and their customers.
Advanced Fraud Detection and Cybersecurity
With the increasing digitalization of financial services, the risk of fraud and cyber threats has grown. AI is playing a crucial role in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities in real time. Machine learning algorithms analyze transaction patterns and flag anomalies that may indicate fraud, often before they cause any significant damage.
Biometric authentication, powered by AI, adds another layer of security, reducing reliance on passwords and PINs. Facial recognition, voice analysis, and fingerprint scanning are now commonly integrated into mobile banking apps, offering both convenience and security to users.
AI in Investment and Wealth Management
The use of AI in investment and wealth management is also on the rise. Robo-advisors, driven by machine learning algorithms, offer personalized investment advice based on individual goals and risk appetite. These platforms make financial planning accessible to a broader audience, including those who may not have the resources to hire a human advisor.
Portfolio management, trade execution, and risk assessment are all being optimized through AI, enabling faster and more data-driven decisions. As a result, investors benefit from increased transparency, reduced costs, and better performance tracking.
Regulatory Compliance and AI Ethics
Compliance with regulatory frameworks remains a critical concern for the banking sector. AI is helping institutions stay compliant by automating the monitoring and reporting of regulatory requirements. Natural language processing tools can scan legal documents and flag potential issues, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
However, the growing reliance on AI also raises ethical and transparency concerns. It is essential for banks to implement fair and explainable AI models, especially when it comes to sensitive decisions such as credit scoring and loan approvals. Transparent AI not only fosters trust among customers but also satisfies regulatory expectations.
Future Outlook: Collaborative and Human-Centric AI
Looking ahead, the future of AI in banking will be shaped by a collaborative approach where humans and machines work in harmony. AI will not replace bankers but will empower them with insights and tools to make more informed decisions. Human-centric AI will focus on enhancing the capabilities of banking professionals while delivering superior customer experiences.
The integration of AI with other emerging technologies, such as blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT), will further redefine the financial ecosystem. For example, combining AI with blockchain can enhance transaction transparency and security, while IoT data can provide real-time insights into customer behavior.
As banks continue to invest in AI-driven innovations, those that prioritize ethical practices, customer needs, and strategic implementation will be best positioned to lead the market. The journey toward a fully intelligent banking experience has already begun, and the pace of transformation will only accelerate in the years to come.
0 notes