#Together with Class 12 CBSE sample paper
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top-notch advice by the experts for students to ace the CBSE board 2024 exams

CBSE board exams are a dreaded term for class 12 students as so much is dependent on the board results. Practicing previous year’s papers ensures best results in 2025 CBSE board exams. Together with Class 12 CBSE sample paper is one of the most sought books in terms of quality sample papers so it can be a great help for you during your exams.
Read More : https://rachnasagarblog.livejournal.com/2415.html?newpost=1
0 notes
Text
Quick Tips For Students Appearing In CBSE Boards 2023
Your Bigger Goals need to be pushed by the smaller objectives you decide for yourself, and the making of each objective should be followed by proper planning to it. The key to your study goals is not different. Here also you’ll have to plan vividly, before you dream of being inside your dream institution.
For CBSE students, the planning is even easier as CBSE has been releasing a marking scheme for students to decide the amount of attention they should pay to a particular topic. Added to that, CBSE issues the latest sample papers for students to be prepared with the type of questions they will get from each category. Not just that, the level of questions can be seen in the sample papers.
Marking scheme and question levels, together help you make the planning and time division. If you’re short of time, you can also take the help of sample papers to judge which topic can be skipped. The topics of great importance can be picked over the other ones.
CBSE sample papers are now available at cheap rates. MBD books is one such publisher who has recently launched a book comprising sample papers. It’s popular amongst students as MBD Rocket Sample papers. The solved solution to sample papers gives an insight into the best answer tricks that you can learn and re-learn to be able to use them. What makes those answers significant is the fact that the techniques used are time-saving. You will have considerable time to spend on other questions if you will use the time wisely.
The book also has a collection of chapter-wise important questions that helps you in last-minute reading as well. Questions are as per CBSE guidelines and have reached you after being filtered multiple times by the academicians. The questions are provided readily available for you to overview, skim, and make an analysis, as your time allows.
One another feature of the MBD Rocket sample paper books is the 5+ unsolved CBSE sample paper in it. Unsolved sample papers give a gush of a challenge to you, and these are the challenges that not only excite you, but they are also shaping you. The competitive spirit in you will be always trying to better your performance against the previous sample paper you solved. So it’s a 4-time opportunity to fight from your previous performance. Only when you better yourself, do you become the best among the rest.
This one book is your exam planner. Class 10 and 12 students must not miss the opportunity to be immune to the difficulty levels of board exams.
As the dates for CBSE Board Exams are near, students are in dire need of some quick tips that can help them achieve their desired grades. We understand that every student has a unique way of studying. Some of us study the subjects in rotation, and other study continuously the same subject for days. Some students are better to study in isolation, while some need the presence of a tutor.
Despite all the variations in the pattern of a student, some quick tips have helped most students to perform better. These tips are better recommended for students who are at the last phase of their preparation.
It is often emphasized to practice questions from multiple sources as it tells whether it’s the concept that is clear or the answers learned. The quick tips to get hold of your performance goes as:
Prioritize : High Weightage chapters should be given priority. CBSE marking scheme tells you the updated weightage given to the chapters. Check the marking scheme and make a priority list of the chapters you will revise first.
Questions : Go for the different question types. Do not stick to one subjective or objective type; rather aim at having a pool of questions that hits the same concept differently. This would be your way to check how much of the concept you hold.
Do the Questions : Some students often read the questions in the book, and think that they’d be able to do them, which is why they don’t use the pen to solve. Doing the answers on paper contributes to speed, speed being the key to excelling in exams. Even after you have the answer tricks in mind, without speed, you won’t be able to produce them in answer sheets. At least, 2-3 CBSE sample papers should be solved thoroughly by you, before you appear for your actual board exam. Replicate the exam-time scenario as it is, to judge your performance.
MBD Rocket CBSE Sample papers would be your perfect companion to follow these quick tips. Class 10 and 12 students can cheaply order their sample paper books online or buy them at the store.
The highlights of the sample paper books are:
Latest Sample Question Paper was issued by CBSE on 16th September 2022, with Marking Scheme
All types of questions:
Both Objective and Subjective types; MCQs, Very Short, Short, Long Answer
Assertion and Reason: Statement Based questions
Case-Based/ Situation Based/ Source Based/Picture-Based Questions
5 Unsolved Sample Papers For Practice
0 notes
Text
Get Latest CBSE Sample Paper (MCQ) Accountancy for 2021 Term 1 Board Exams- Rachna Sagar

Together with CBSE Sample Paper, Accountancy has been designed as per the special scheme of assessment vide CBSE Circular No. 75/2021 for Term 1 ( For 2021 Nov-Dec Examination ) for Class 12 has been prepared as per the latest assessment pattern.
Together with EAD Accountancy Sample Paper (with answers) is a perfect step-by-step approach to ensure one’s readiness for Term 1 board examination. This Sample Paper for Class 12 assists the students with the right practice and approach to the newest MCQ pattern.
EAD—Easy, Average, Difficult
The content matter in this EAD 12+1 Accountancy Sample Paper Class 12 has been arranged as complete papers with three levels of difficulty—Easy, Average and Difficult (EAD).
Easy: The first set of papers in this CBSE Sample Paper 2021 is based on 'Easy' concept, thus contains Multiple Choice Questions of simple level, which a student can attempt at the beginning of the preparatory stage.
Average: The next set based on 'Average' concept (MCQs) is graded to a level of difficulty to test mid-level preparedness for the examination.
Difficult: The challenging papers allocated to the third set based on 'Difficult' concept are a test of complete preparedness for the examination.
The EAD sample paper is a self-test drive for the students.
Key Features
This Sample Paper includes:
CBSE (2021-2022) Term 1 Sample Paper.
3 Sample Papers each of Easy, Average & Difficult level.
2 Pre-Board Papers based on CBSE pattern.
1 Mock Paper Based On CBSE Pattern with OMR Sheet.
Includes Assertion Reasoning and Case-Based Objective Type Questions.
The 4-Step Process
Step 1 The students are advised to attempt the set of EASY Papers first and obtain at least 80% marks to move onto the next set of papers which is Average.
Step 2 If the student obtains 75% marks in the AVERAGE category of this EAD 12+1 Accountancy Sample Paper Class 12, he/she can switch to the next category, i.e., Difficult.
Step 3 If 70% marks in DIFFICULT category have been obtained, the students are expected to take the PRE-BOARD PAPERS that are exactly based on the CBSE pattern.
Step 4 Attempt the MOCK PAPER (given at the end) for a final-go for your board exam preparations.
Why EAD Latest Sample Papers?
Learning gets strengthened with practice and its evaluation uplifts the preparation. The answers of the MCQs have been given at the end of each Sample Paper for evaluation purposes. The CBSE Sample Papers for class 12 All Subjects 2021-2022 have been prepared by a panel comprising experienced teachers, tabulators and examiners, who have jointly come up with a student-friendly approach to prepare the students for the forthcoming CBSE Board Examination. Repetitive practice of CBSE Sample Papers for class 12 All Subjects 2021-2022 will surely help the students to make their mark in the CBSE Board Examination.
Good Luck!
#cbse sample paper class 12#Accountancy sample paper class 12#Term 1 Accountancy sample paper#CBSE Sample Papers Term 1#term 1 mcq sample paper#CLass 12 sample paper for term 1 exam#term 1 exam#term 1 board exam#Accountancy sample paper for class 12#term 1 Accountancy sample paper
0 notes
Text
Myabhyas - The Art of Learning Smart
youtube
Myabhyas India’s best online learning platform for KSEEB & CBSE. 24/7 Online Solution to all your doubts. Get Live Learning Experience with our Virtual Reality Classroom.
My Abhyas, online training solutions are a great resource to keep them educated. It makes your children's learning process wholesome and holistic. Launched in 2020, My Abhyas offers highly personalized and effective learning programs for classes 1 - 12 (K-12). This app is like a one-stop solution for CBSE, KSEEB students. Whether it comes to homework help, doubt clearing sessions, textbook solutions, video lessons, sample papers, mock tests, easy revision notes for class 6-12, previous year board papers as well.
This online learning platform is very interactive for both the students and tutor, as they are able to see, hear, write and interact in real-time. The app features quiz, quick tests and a facility to clarify doubts. The app provides students a learning platform where they can learn, engage and be excited about charting their own path to discover the world. The platform brings together the best teachers, technology, content, media for creating a seamless, world class learning experience. With NEP 2020 laying the foundation for a New India, preparing students for the future with the knowledge that will be needed for the 21st Century, online learning app like Myabhyas is a boon to your kid…
Our Virtual Reality Features will turn your Normal classroom into something more fantastic and help you the best possible way to boost your Overall growth.
Mission
Discover, share, and implement effective technology- enhanced learning practices that promote active, collaborative, and authentic learning. Create an immersive learning environment for students to develop foundational skills and knowledge for the 21st century workplace. Provide teachers with educational technology, professional development and classroom facilitation.
Vision
Is to take education to the remotest part of India.
Provide the best educational experience to every student.
Keep the costs affordable to everyone.
Structured Courses
Structured courses offered by Myabhyas give out a well-planned flow of content to help make it easier for the user to interact with. It reduces the complexity of concepts by breaking it down into simpler sections, also known as divide and conquer.
Live tests and quizzes:
It helps stimulate a healthy competitive side of your kid which he carries on for a lifetime. Network with the group Eliminating parents biggest fear, the online learning platform provides plenty of learning and networking opportunities.
Contact: www.myabhyas.com
Toll free: 1800 572 4455
0 notes
Text
NCERT Class 12 Macro Economics Chapter 2 National Income and Related Aggregates
NCERT Class 12 Micro Economics Solutions
Chapter-2 National Income and Related Aggregates
NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED:> Q 1. Why should the aggregate final expenditure of an economy be equal to the aggregate factor payments? Explain. [3 Marks]
Ans: The sum of final expenditures in an economy must be equal to the income received by all the factors of production taken together (final spending on final goods, it does not include spending on intermediate goods). This follows from the simple idea that the revenues earned by all the firms put together must be distributed among the factors of production as salaries, wages, profits, interests earning and rents. Q 2. What is the difference between planned and unplanned inventory accumulation? Write down the relation between change in inventories and value added of a firm. [3 Marks]
Ans: Planned Inventory. It refers to changes in the stock inventories that have occurred in a planned way. In a situation of planned inventory accumulation, firm will plan to raise its inventories. Unplanned Inventory. It refers to changes in the stock of inventories that have occurred in an unexpected way. In a situation of unplanned inventory accumulation, due to unexpected fall in sales, the firm will have unsold stock of goods.
Value added of a firm (GVA) = Gross value of output produced by the firm – Value of intermediate goods used by the firm. OR GVA = Value of sales by the firm + Value of change in inventories – Value of intermediate goods used by the firm Q 3. Write down the three identities of calculating the GDP of a country by the three methods. Also, briefly explain why each of these should give us the same value of GDP. [3 Marks]
Ans: National Income = National Product = National Expenditure. Each one will give the same result. The only difference is that with product methods, NI is calculated at production or creation level with income Method NI is measured at distribution level, and with expenditure method NI is measured at disposal level. Q 4. Define budget deficit and trade deficit. The excess of private investment over saving of a country in a particular year was Rs 2,000 crores. The amount of budget deficit was (-) Rs 1,500 crores. What was the volume of trade deficit of that country? [3-4 Marks]
Ans: Budget deficit. It measures the amount by which the government expenditure exceeds the tax revenue earned by it. Budget Deficit = G – T.
Trade deficit: It measures the amount of excess expenditure over the export revenue earned by the country.
Trade Deficit = M – X Given G – T = (-) Rs 1500 crore Investment – Saving = Rs 2000 crore Trade deficit = [I – S] + [G – T] = [2000]+ [-1500] = Rs 500 crore. Q 5. Suppose the GDP at market price of a country in a particular year was Rs 1,100 crores. Net Factor Income from Abroad was Rs 100 crores. The value of Indirect taxes – Subsidies was Rs 150 crores and National Income was Rs 850 crores. Calculate the aggregate value of depreciation. [3 Marks]
Ans: National Income (or NNPFC) = GDPmp- Depreciation + Net factor income from abroad – [Indirect Taxes-Subsides] 850 = 1100 – Depreciation +100- 150 Depreciation = 1100+ 100- 150-850 Depreciation = Rs 200 Crore Q 6. Net National Product at Factor Cost of a particular country in a year is Rs 1,900 crores. There are no interest payments made by the households to the firms / government, or by the firms / government to the households. The Personal Disposable Income of the households is Rs 1,200 crores. The personal income taxes paid by them is Rs 600 crores and the value of retained earnings of the firms and government is valued at Rs 200 crores. What is the value of transfer payments made by the government and firms to the households? [3-4 Marks]
Ans: Personal disposable income = Personal income – Personal tax – miscellaneous receipts of government 1200 = Personal Income – 600 – 0 Personal Income = 1800 Crore Private Income = Personal income + retained earnings + corporate tax = 1800 + 200 + 0 = 2000 Crore Private income = NNPFC (National income) – NDPFC of government sector + Value of transfer payment 2000 = 1900 – 0 + Value of transfer payment Value of transfer payment =100 Crore Q 7. From the following data, calculate Personal Income and Personal Disposable Income. [6 Marks]

Ans: Private Income = NDPFC – NDPFC of government sector + NFIA + Transfer Income + net interest receive from household (Interest Received by Households – Interest Paid by Households) = (i) – 0 + (ii) + (vii) + [(v) – (vi)] = 8000 + 200 + 300 + (1500 – 1200) = 8800 Crore
Personal Income = Private income – Undistributed profit – Corporation tax = 8800 – (iii) – (ii) = 8800 – 1000 – 500 = 7300 Crore Personal Disposable Income = Personal income – Personal tax = 7300 – (viii) = 7300 – 500 = 6800 Crore Q 8. In a single day Raju, the barber, collects Rs 500 from haircuts; over this day, his equipment depreciates in value by Rs 50. Of the remaining Rs 450, Raju pays sales tax worth Rs 30, takes home Rs 200 and retains Rs 220 for improvement and buying of new equipment. He further pays Rs 20 as income tax from his income. Based on this information, complete Raju’s contribution to the following measures of income Gross Domestic Product NNP at market price NNP at factor cost Personal income Personal disposable income. [3-4 Marks] Ans: GDP contribution by Raju = Rs 500 NNPMP (Raju’s contribution) = GDP – Depreciation = 500 – 50 = Rs 450. NNPrr (Raju’s contribution) = NNPMP -Indirect tax =450-30 = Rs 420 Personal Income = NNPFC-Retained Earnings = 420 – 220 = Rs 200 Personal Disposable Income = Personal Income – Income Tax = 200 – 20 = Rs 180 Crore Q 9. The value of the nominal GNP of an economy was Rs 2,500 crores in aparticular year. The value of GNP of that countiy during the same year evaluated at the prices of the same base year was Rs 3,000 crores. Calculate the value of the GNP deflator of the year in percentage terms. Did the price level rise between the base year and the year under consideration? [3-4 Marks]
Ans: GNP deflator = Nominal GNP/Real GNP x 100 = 83.3% No, the price level did not rise between the base year and the year under consideration. In fact, it fell. Q 10. Write down some of the limitations of using GDP as an index of welfare of a : countiy. [6 Marks] OR Explain how distribution of gross domestic product is its limitation as a measure of economic welfare. [CBSE Delhi 2010] OR Explain how ‘distribution of gross domestic product’ is a limitation in taking domestic product as an index of welfare. [CBSE Delhi 2011]OR Can gross domestic product be used as an index of welfare of the people? Give two reasons. [CBSE Foreign 2010] OR Explain Per Capita Real GDP as Indicator of Economic Welfare. OR Explain any four limitations of using GDP as a measure/index of welfare of a country. [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Ans: Per Capita Real GDP can be taken as indicator for economy. But by itself is not an adequate indicator. There are many reasons behind this. These are: Many goods and services contributing economic welfare are not included in GDP Or Non-Monetary exchanges.
(a) There are many goods and services which are left out of estimation of national income on account of practical estimation difficulties e.g., services of housewives and other members, own account production, etc.
(b) These are left on account of non availability of data and problem in valuation.
(c) It is generally agreed that these items contribute to economic welfare.
(d) So, if we depend only on GDP, we would be underestimating economic welfare.
Though externalities are not taken into account in GDP, they affect welfare.
(a) When the activities of somebody result in benefits or harms to others with no payment received for the benefit and no payment made for the harm done, such benefits and harms are called externalities.
(b) Activities resulting in benefits to others are positive externalities and increase welfare; and those resulting in harm to others are called negative externalities, and thus decrease welfare.
(c) GDP does not take into account these externalities.
(d) For example, construction of a flyover or a highway reduces transport cost and journey time of its users who have not contributed anything towards its cost. Expenditure on construction is included in GDP but not the positive externalities flowing from it. GDP and positive externalities both increase welfare. Therefore, taking only GDP as an index of welfare understates welfare. It means that welfare is much more than it is indicated by GDP.
(e) Similarly, GDP also does not take into account negative externalities. For examples, factories produce goods but at the same time create pollution of water and air. River Yamuna, now a drain, is a living example. The pollution harms people. The factories are not required to pay anything for harming people. Producing goods increases welfare but creating pollution reduces welfare. Therefore, taking only GDP as an index of welfare overstates welfare In this case, welfare is much less than indicated by GDP.
Change in the distribution of income (GDP) may affect welfare. (a) All people do not earn the same amount of income. Some earn more and some earn less. In other words, there is unequal distribution of income.
(b) At the same time, it is also true that in the event of rise in ‘per capita real income’ all are not better off equally. ‘Per capita’ is only an average. Income of some may rise by less and of some by more than the national average. In case of some it may even fall.
(c) It means that the inequality in the distribution of income may increase or decrease.
(d) If it increase it implies that rich become more rich and the poor become more poor.
(e) Utility of a rupee of income to the poor is more than to the rich. Suppose, the income of the poor declines by one rupee and that of the rich increases by one rupee. In such a case, the decline in welfare of the poor will be more than the increase in welfare of the rich.
(f) Therefore, if the rise in per capita real income inequality increases, it may lead to a decline in welfare (in the macro sense).
All products may not contribute equally to economic welfare. (a) GDP includes different types of products, like food articles, houses, clothes, police services, military services, etc. (b) Some of these products contribute more to the welfare of the people, like food, clothes, houses, etc. Other products like police services, military services etc. may comparatively contribute less and may not directly affect the standard of living of the people. (c) Therefore, how much is the economic welfare would depend more on. the types of goods and services produced, and not simply how much is produced. (d) It means that if GDP rises, the increase in welfare may not be in the same proportion.
Contribution of some products may be negative (a) GDP includes all final products whether it is milk or liquor. (b) Milk may provide both immediate and ultimate satisfaction to consumers On the other hand, liquor may provide some immediate satisfaction, but because of its harmful effects on health it may lead to decline in welfare. (c) GDP include only the monetary values of the products and not their contribution to welfare. (d) Therefore, economic welfare depends not only on the volume of consumption but also on the type or goods and services consumed.
I. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
Q 1. Define ‘depreciation’. [CBSE (Al) 2011]
Ans: Depreciation is an expected decrease in the value of fixed capital assets due to its general use. Q 2. When is the net domestic product at market price less than the net domestic product at factor cost?
Ans: When net indirect taxes are negative i.e., subsidies are more than indirect taxes. Q 3. Why is gross domestic product at factor cost more than the net domestic product at factor cost?
Ans: Gross domestic product at factor cost includes depreciation while net domestic product at factor cost does not include depreciation. Q 4. When will GDP of an economy be equal to GNP?
Ans: GDP and GNP will be equal when the ‘net factor income from abroad’ is zero. Q 5. When will the domestic income exceed the national income?
Ans: When the net factor income from abroad is negative. Q 6. If NDPFC is Rs 1,0000 crores and NFIA is (-) Rs 500 crores, how much will be the national income?
Ans: National Income = 10000 + (-500) = Rs 9500 Crore Q 7. If the domestic factor income is Rs 50,000 crores and the national income is Rs 45,000 crores, how much will be the net factor income from abroad?
Ans: Net factor income from abroad = 45,000 – 50,000 = (-) Rs 5000 Crore Q 8. Mention the three methods of measuring national income.
Ans: Value added method Income method Expenditure method. Q 9. Calculate the disposable income, if personal income is Rs 30,000 and the rate of income tax is 10%.
Ans: Disposable Income = 30,000 – (10% of 30,000) = ?27,000 Q 10. In which type of economy, domestic income will be equal to national income?
Ans: Closed economy. Q 11. What is the value added method of measuring national income?
Ans: Value added method is the method that measures the national income by estimating the value added by each producing enterprises within the domestic territory of the country in an accounting year. Q 12. When is value of output equal to value added?
Ans: Value of output is equal to value added if there are no intermediate costs. Q 13. What aggregate do we get when we add up the gross value added of all the producing sectors of an economy?
Ans: Gross domestic product at market price. Q 14. What is the rationale for not taking into account the value of intermediate goods in the measure of GDP?
Ans: To avoid the problem of double counting. Q 15. If compensation of employees in a firm constitutes 65% of net value added at factor cost of a firm, find the proportion of operating surplus.
Ans: 100% – 65% = 35% (assuming mixed income is zero). Q 16. What is nominal gross domestic product? [CBSE Delhi 2011]
Ans: When gross domestic product (GDP) of a given year is estimated on the basis of price of the same year, it is called nominal GDP. Q 17. Define primary sector.[CBSE AI2013,]
Ans: It is the sector that produces goods by exploiting natural resources like land, water, forests, mines, etc. This sector includes agricultural and allied activities, fishing, mining and quarrying. Q 18. Define secondary sector.
Ans: It is called manufacturing sector also. Enterprises in this sector transform one type of commodity into another type of commodity. For example: leather goods from leather, flour from wheat, sugar from sugarcane, etc. Q 19. Define tertiary sector.
Ans: It is known as service sector also. Enterprises in this sector produce services only. Examples are banking, transport, communications etc. II.MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
Q 1. Which one of the following statements is incorrect? (a) GDP at market price = GDP at factor cost plus net indirect taxes. (b) NNP at factor cost = NNP at market price minus indirect taxes. (c) GNP at market price = GDP at market price plus net factor income from abroad. (d) None of them.
Ans: (a) Q 2. National income differs from net national product at market price by the amount———–. (a) current transfers from the rest of the world (b) net indirect taxes (c) national debt interest (d) it does not differ
Ans: (b) Q 3. Net national product at factor cost is————-. (a) equal to national income (b) less than national income (c) more than national income (d) sometimes less than national income and sometimes more than it
Ans: (a) Q 4. The net values added method of measuring national income is also known as—————-. (a) net output method (b) production method (c) industry of origin method (d) all of the above
Ans: (d) Q 5. Identify the item which is not a factor payment: (a) Free uniforms to defense personnel (b) Salaries to the members of Parliament (c) Imputed rent of an owner occupied a building . (d) Scholarships given to the students of scheduled caste
Ans: (d) Q 6. Mixed income of the self-employed means (a) gross profits received by proprietors (b) rent, interest and profit of an enterprise (c) combined factor payments which are not distinguishable (d) wages due to family workers
Ans: (c) Q 7. Demand for final consumption arises in ——————-. (a) household sector only (b) government sector only (c) both household and government sectors (d) neither in households nor in government sector
Ans: (c) Q 8. Demand for intermediate consumption arises in—————— . (a) consumer households (b) government enterprises only (c) corporate enterprises only (d) all producing sectors of an economy
Ans: (d) Q 9. Which one of the following options is an economic activity? (a) Listening to music on the radio. (b) Teaching one’s own son at home. (c) Medical facilities rendered by a charitable dispensary. (d) A housewife doing household duties.
Ans: (c) Q 10. Net value added is equal to—————– . (a) payments accruing to factors of production (b) compensation to employees (c) wages plus rents (d) value of output minus depreciation
Ans: (a) Q 11. Per capita national income means: (a) NNP/population (b) Total capital population (c) Population NNP (d) None of them
Ans: (a) Q 12. Which one of the following statements is correct? (a) If national income rises, per capita income must also rise (b) If population rises, per capita income must fall. (c) If national income rises, welfare of the people must rise. (d) None of them
Ans: (d) III. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (3-4 Marks)
1. Distinguish between domestic product and national product. When can domestic product be more than national product? [CBSE (Al) 2009] OR Differentiate between Domestic Income (NDPFC) Vs National Income (NNPFC).
Ans:
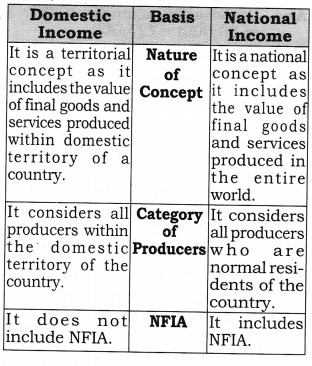
Domestic product will be greater than national product when net factor income from abroad is negative. Q 2. Differentiate between Gross Domestic Product at Market Price Vs National Income.
Ans:

Q 3. Differentiate between National Income at constant price and national income at current price?
Ans:

Q 4. Distinguish between real and nominal gross domestic product.[CBSE(AI) 2010] Or Discuss any two differences between GDP at constant prices and GDP at current Prices.[CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Ans:

Q 5. Explain how ‘externalities’ are a limitation of taking gross domestic product as an index of welfare. [CBSE Foreign 2011]
Ans: When the activities of somebody result in benefits or harms to others with no payment received for the benefit and no payment made for the harm done, such benefits and harms are called externalities.
Activities resulting in benefits to others are positive externalities and increase welfare; and those resulting in harm to others are called negative externalities, and thus decrease welfare.
GDP does not take into account these externalities.
For example, construction of a flyover or a highway reduces transport cost and journey time of its users who have not contributed anything towards its cost. Expenditure on construction is included in GDP but not the positive externalities flowing from it. GDP and positive externalities both increase welfare.
Therefore, taking only GDP as an index of welfare understates welfare. It means that welfare is much more than it is indicated by GDP.
Similarly, GDP also does not take into account negative externalities. For examples, factories produce goods but at the same time create pollution of water and air. River Yamuna, now a drain, is a living example. The pollution harms people. The factories are not required to pay anything for harming people. Producing goods increases welfare but creating pollution reduces welfare. Therefore, taking only GDP as an index of welfare overstates welfare. In this case, welfare is much less than indicated by GDP. Q 6. Explain how “Non-Monetaiy exchanges’ are a limitation in taking gross domestic product as an index of welfare.[CBSE(AI) 2011]
Ans: There are many goods and services which are left out of estimation of national income on account of practical estimation difficulties e.g., services of housewives and other members, own account production, etc. These are left on account of non¬’ availability of data and problem in valuation. It is generally agreed that these items contribute to economic welfare. So, if we depend only on GDP, we would be underestimating economic welfare. Q 7. Explain how distribution of ‘Gross Domestic Product’ is a limitation in taking gross domestic product as an index of welfare.[CBSE Delhi 2010, 2011]
Ans: All people do not earn the same amount of income. Some earn more and some earn less. In other words, there is unequal distribution of income.
At the same time, it is also true that in the event of rise in ‘per capita real income’ all are not better off equally. ‘Per capita’ is only an average. Income of some may rise by less and of some by more than the national average. In case of some it may even fall.
It means that the inequality in the distribution of income may increase or decrease.
If it increase it implies that rich become more rich and the poor become more poor.
Utility of a rupee of income to the poor is more than to the rich. Suppose, the income of the poor declines by one rupee and that of the rich increases by one rupee. In such a case, the decline in welfare of the poor will be more than the increase in welfare of the rich.
Therefore, if the rise in per capita real income inequality increases, it may lead to a decline in welfare (in the macro sense). Q 8. State the various components of the income method that are used to calculate national income.[CBSE Sample Paper 2014]
Ans: Compensation of employees: The amount earned by employees from their employer, whether in cash or in kind or through any other social security scheme is known as compensation of employees. Operating Surplus: It is the sum of income from property and income from entrepreneurship. Mixed Income: Income of own account workers (like farmers, doctors, barbers, etc.) and unincorporated enterprises (like small shopkeepers, repair shops) is known as mixed income.
Note: (i) To estimate amount of factor payments made by each producing unit. (ii) To add all factor incomes/payments within domestic territory to get domestic income, i.e., NDPFC. NDPFC = Compensation of employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income Net factor income from Abroad(NFIA): NFIA is the difference between income earned by normal residents from rest of the world and similar payments made to Non residents within the domestic territory. Addition of NFIA to NDPFC to get NY, i.e., NNPpc. NNPFC = NDPFC + NFIA Q 9. Define double counting. How can the problem of double counting be avoided?
Ans: If a single transaction is recorded twice or more than twice in the calculation of national income, then it is known as double counting.
The problem of double counting is solved by value added method. Theoretically to avoid double counting there may be two alternative ways:
Final Product Approach (Value Added Approach)
Final Product Approach: According to this, value of only final products, i.e. which go for final consumption or capital formation should be included. But in practical application of this approach double counting still creeps in as every producer treats the product he sells as final whereas the same might have been used as intermediate product by the buyer.
Value Added Approach: Value added method is most effective in avoiding double counting. According to this, instead of taking value of final goods, only value added at each stage of production by a producing unit is taken. Value added of a firm by subtracting intermediate consumption from value of output. IV. TRUE OR FALSE Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false.
Q 1. In a closed economy, gross national product is always equal to gross domestic product.
Ans: True: When net factor income from abroad is zero i.e., income from abroad is equal to income to abroad. Q 2. Gross investment can be equal to net investment.
Ans: True: It is possible when depreciation is zero. Q 3. Domestic Income of a country can be more than its National income.
Ans: True: It can happen when NFIA is negative i.e., factor income paid to abroad is more than factor income received from abroad. Q 4. Market price is always more than factor cost.
Ans: False: Market price can be less than factor cost if net indirect taxes (NIT) are negative. Market price can also be equal to factor cost if NIT is zero. Q 5. Measurement of national income at current prices provides a reliable base of comparison.
Ans: False: National Income at ‘Constant Prices’ provides a reliable base of comparison. Q 6. Nominal GDP can never be less than Real GDP.[CBSE Sample Paper 2010]
Ans: False: Nominal GDP can be less than real GDP, if prices in the current year are less than the prices in the base year. Q 7. Net capital gains from the sale of property is a part of domestic factor income.
Ans: False: It is not a part of domestic factor income. It is. a sale of property and not of factors. Q 8. Change in stock is not a part of Capital formation.
Ans: False: Change in stock is a part of domestic capital formation. Q 9. Brokerage paid on sale of shares and income from shares purchased is not a part of national income.
Ans: False: Brokerage paid on sale of shares or any other item is a part of national income. Q 10. Salary of Pakistan worker, working in Indian Embassy is not a national income of India.
Ans: True: It is an expenditure made by- Indian Embassy. It is a part of Indian domestic income. Q 11. Income tax paid is not a part of national income.
Ans: False: Income tax paid is part of national income. It is included in profit and individual income. Q 12. Income from imputed rent of self- occupied houses is a part of national income.
Ans: True: It is an estimated amount of . rent. If rented to any other person, he would receive the amount of rent. Q 13. Net profit of any Bank of India’s branch in USA will not be included in Indian National income.
Ans: False: Net profit of any Bank of India at USA branch is a part of national income of India. Q 14. Exports do not form a part of domestic factor income.
Ans: False: Exports are made from domestic production. It is a part of domestic factor income. Q 15. Gross domestic product at market price includes net factor income from abroad and net indirect taxes.
Ans: False: GDPMP does not include net factor income from abroad but includes net indirect taxes. Q 16. Gross National Product is always less than Gross National expenditure.
Ans: False: Gross national product is always equal to gross national expenditure. Q 17. Exports are a part of net factor income from abroad.
Ans: False: Exports are a part of domestic income. Exports are sent from home production. Q 18. Real GDP includes domestic income at current prices.
Ans: False: Real GDP is taken at some constant prices. It does not have the influence of price fluctuations. Q 19. National disposable income includes current transfers income of government.
Ans: False: National income includes income of government sector in the form of receiving of taxes. Q 20. Private income does not include net factor income from abroad.
Ans: False: Private income is a national concept. It also includes net factor income from abroad. Q 21. Personal income does not include income from personal taxes.
Ans: False: Personal income includes personal taxes, but not corporate taxes. Q 22. Personal disposable income is equal to aggregate consumption and savings.
Ans: True: Personal disposable income can be disposed upon consumption and savings both. Q 23. Private income includes earned incomes of private sector from all sources.
Ans: False: Private income includes both earned income (factor income) as well as unearned income (transfer income) of private sector from all sources. Q 24. National disposable income is the disposable income of private sector.
Ans: False: It is the disposable income of the whole country (public sector and private sector). Q 25. Travelling allowance paid by employer is a part of national income.
Ans: False: Travelling allowances are paid by an employee and then recovered from employer. It is not a part of national income Q 26. Consumption of food grains by farmer himself is not a part of national output.
Ans: False: It is a part of domestic output. It is a part of national income. Q 27. Sale of second hand car is not included in national income.
Ans: True: It’s original sale has already been included in national income of previous year. If done it will be case of double counting. Q 28. Rent received by an American from Reliance Industries with respect to building located in India will neither be included in national income nor in domestic income of India.
Ans: False: Such rent will be included in domestic income of India as building is located within the domestic territory of India Q 29. Purchase of car by a consumer is a part of gross domestic capital formation.
Ans: False: It is a part of private final consumption expenditure. Q 30. Goods produced for self-consumption will be included in national income.
Ans: True: Such goods contribute to the current output and their imputed value will be included in national income. Q 31. Gross domestic capital formation is always greater than gross fixed capital formation. [CBSE Sample Paper 2010]
Ans: False: Gross domestic capital formation can be less than gross fixed capital formation if change in stock is negative. Note: As per CBSE guidelines, no marks will be given if reason to the answer is not explained. V. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS(6 Marks)
Q 1. Calculate GNP at FC from the following data by income method, and expenditure method. [CBSE 2002]
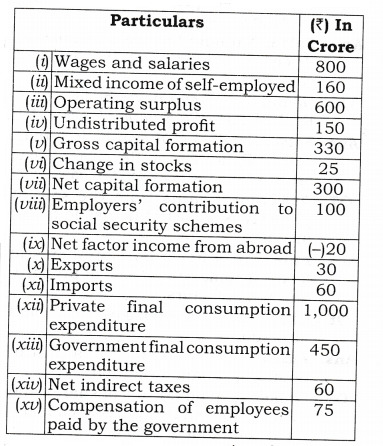
Ans: NDPFC = Compensation of employees (Wages and salaries + Employer’s contribution towards social security scheme) + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income = [(i) + (viii)] + (iii) + (ii) = [800 + 100] + 600 + 160 = 900 + 600 + 160 = 1660 Crore GNPFC = NDPFC + Depriciation (Gross capital formation – Net capital Formation) + Net Factor Income from abroad = 1660 + [(H) – (nil) + (6c)] = 1660 + [330-300] + (-20)] = 1660 + 30 – 20 = 1670 Crore GDPMP = Government final consumption expenditure (Public final consumption expenditure) + Private final consumption expenditure + Gross domestic Capital formation + Net export (Export – Import) = (xiii) + (xii) + (v) + [(x) – (xi)] = 450 + 1000 + 330 + [30 – 60] = 1750 Crore . GNPFC = GDPMP + Net factor income from abroad – Net Indirect Tax = 1750 + (be) – (xiv) = 1750 + (- 20) – 60 = 1750 – 20 – 60 = 1670 Crore Q 2. Calculate “Gross National Product at Factor Cost” from the following data by (a) Income method, and (b) Expenditure method:[CBSE 2009]
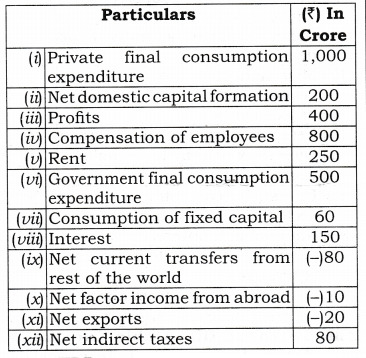
Ans: NDPFC = Compensation of Employees + Operating Surplus( profit + Rent + Interest + Mixed Income = (iv) +[(iii) + (v) + (viii)] + 0 = 800 + [400 + 250 + 150] = 800 + 800 = 1600 Crore GNPFC = NDPFC + Depreciation (Consumption of fixed Capital) + Net factor Income from abroad = 1600 + (vii) + (x) = 1600 + 60 + (-10) = 1650 Crore GDPMP = Government final consumption expenditure + Private final consumption expenditure + Gross domestic capital formation (Net domestic capital formation + consumption of fixed capital) + Net export = (x) + (i) + [(ii) + (vii)] + (xi) = 500 + 1000 + [200 + 60] + (- 20) = 500 + 1000 + 260 – 20 = 1740 Crore GNPFC = GDPMP + Net factor income from abroad – Net Indirect Tax = 1740 + (x) – (xii) = 1740 + (-10] – 80 = 1650 Crore Q 3. From the following data, calculate (a) Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost and (b) Factor Income To Abroad:[CBSE 2010]
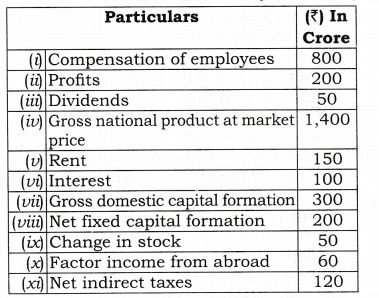
Ans: (a) NDPFC = Compensation of employees + Operating surplus (Profit + Rent + Interest) + Mixed income = (i) + P) + (v) + M] + 0 = 800 + [200 + 150 + 100] = 800 + 450 = 1250 Crore Note: Gross domestic capital formation = Net fixed capital formation + Depreciation + Change in stock (vii) = (viii) + Depreciation + (ix) 300 = 200 + Depreciation + 50 Depreciation = 300 – 250 = 50 GDPFC = NDPFC + Depriciation = 1250 + 50 = 1300 Crore (b) GNPMP = GDPFC + NFIA (Factor income from abroad – Factor income paid to abroad) + Net indirect tax (iv) = 1300 + [(x) – Factor income paid to abroad] + (xi) 1400 = 1300 + (60 – Factor income paid to abroad) + 120 1400 = 1480 – Factor income paid to abroad Factor income paid to abroad = 1480 – 1400 = 80 Crore Q 4. Calculate (a) Private Income and (b) Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost: [CBSE 2013, C, Set-I] Ans: Personal Disposable Income = Personal income – Direct taxes paid by households – Miscellaneous receipts of government (xi) = Personal Income – (iv) – (i) 200 = Personal income – 30 – 5 Personal Income = 235 Arab Private Income = Personal Income + Retained profits (Savings of private corporate sector) + Corporate Tax = 235 + (iii) + (ii) = 235 + 10 + 20 = 265 Arab „ Private income = NNPFC – Income from Domestic Product Accruing to Public Sector (Income from Property and Entrepreneurship accruing to government Administrative Departments + Saving of Non Departmental Enterprises) + National Debt interest + Current transfers from Government + Net Current transfers from rest of the world , 265 = NNPFC – [(x) + (ii)] + (viii) + (ix) + (vii) ] 265 = NNPFC – (12 + 3) + 15 + 8 + 4 NNPFC = 265 + 15 – 27 = 253 Arab GDPFC = NNPFC + Consumption of fixed capital – Net factor income from abroad = 253 + (xii) – [-(v)] = 253 + 11 + 6 = 270 Arab Q 5. Calculate (a) Private Income and (b) National Income: Ans: Personal Disposable Income =Personal Income – Direct Taxes paid by households – Miscellaneous receipts of Government (i) = Personal Income -(v)- (iii) 120 = Personal income – 15 – 4 Personal Income =139 Arab (Billion) Private Income = Personal Income + Undistributed profits of private sector + Corporate Tax = 139 + (vii) + (vi) = 139 + 3 + 6 = 148 Arab Private income = NNPFC – Income from Domestic Product Accruing to Public Sector (Income from Property and Entrepreneurship accruing to Government Administrative Departments + Saving of Non-Departmental Enterprises) + National Debt interest + Current transfers from government + Net Current transfers from rest of the world 148 = NNPFC – [(ii) + (ix)] + (viii) + (xi) + (iv) , 148 = NNPFC-(5+ 15) + 16 + 2+ 10 NNPFC = 148 + 20 – 28 = 140 Arab Q 6. Find out Gross National Product at Market price and Net National Disposable Income from the following:
Ans: GDPMP = Government final consumption expenditure+Private final consumption expenditure + Gross domestic Capital formation (Net domestic Fixed capital formation + consumption of fixed capital + Change in stocks (closing stock – opening Stock) + Net Export = (vi) + (ii) + {(ix) + (vii) + [(iv) – (i)]} + (-viii) = 300+ 1000+ {150+ 30 + [40-50]}+ (-20) = 300 + 1000 + 170 – 20 = 1450 Arab GNPMP = GDPMP + Net factor income from abroad = 1450 + (-v) = 1450 +[- (-10)] = 1460 Arab NNPFC = GNPMP – consumption of fixed capital – net indirect tax = 1460 – (vii) – 0 = 1460 – 30 = 1430 Arab NNDI = NNPFC + NIT + Net current transfer from rest of the world (abroad) = 1430 + 0 + (-iii) = 1430 + (-5) = 1425 Arab VI. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Q 1. Explain the components of NFIA.[3-4 Marks]
Ans: There are three components of NFIA. Net Compensation of Employees: The net compensation of employees receivable from the rest of the world is equal to the difference between compensation of employees received by resident workers who are living temporarily abroad or are employed abroad , and similar payments made to non- residents workers that are temporarily staying or are employed within the domestic territory of the country.
Met Income From Property and Entrepreneurship: Net income from property and entrepreneurship is equal to the difference between the income received by way of interest, rent and profits by the residents of a country and similar payments made to the rest of the world.
Net Retained Earnings of Resident Companies Abroad: Retained earnings refers to the undistributed profits of the companies. Resident companiesft.e. companies belonging to one country and working in the domestic territory of some other country) retain a part of their profits for further investment abroad. Likewise, foreign companies and their branches retain a part of their profits in the countries of their operation. The difference between the retained earnings of resident companies located abroad and retained earnings of the foreign companies located in a country is equal to the net retained earnings from abroad.
Note: It must be noted that NFIA is zero in a closed economy as such economy does not deal with the rest of the world sector. Q 2. Differentiate between National income and Private income. [3-4 Marks]
Ans:

VII. VALUE BASED QUESTIONS
Q 1. Why do non market economic activities, like Services of housewives Voluntary services and Leisure time activities help in the flow of goods and services of a country. But why are these not included in the estimation of national income? [ 1 Mark] Ans: They are not included in national income, because of non-availability of data and problem in measuring the proper monetary values of these services. Value : Implication of knowledge. Q 2. The given set of prices which is used for finding out real per capita income, should change frequently. Why? [ 1 Mark]
Ans: If the given set of prices used for assessing real per capita income changes frequently, then virtually what we get is nominal per capita income and this defeats the purpose of using or calculating the real per capita income. Value : Critical thinking Q 3. Why comparing the GDPs of various nations might not tell you which nation is better off? [ 1 Mark]
Ans: The well being of nation or standard of living of people is measured by per capita income (GDP / Total Population) and distribution pattern of income not only by GDP. Value : Critical thinking Q 4. GDP Calculation do not directly include the social costs of environmental damages, for example, global warming, acid rain. Do you think these costs should be included in GDP? Why or Why not? [ 1 Mark]
Ans:Yes, because people’s well-being is affected by these environmental damages. No, it is very difficult to assess real damages in monetary terms. Value : Awareness about social cost of GDP. Q 5. GDP growth rate in India for the last few years is more than 6% but still more than 28% of population is lying below poverty line. Explain any two factors responsible for it. [ 1 Mark]
Ans: There are two factors, Unequal distribution of GDP Rise in price level Value : Social awareness Q 6. Should we take real per capita income as an index of economic welfare? If not, why? [1 Mark]
Ans: Real per capita income cannot be taken as an index of economic welfare because there are many items and transactions relating to national income that have no connection with real GDP such as production of defence goods. Also it does not take into account any transaction related to illegal activities, black money and production of services for self-consumption. Value : Critical thinking Q 7. Rakesh pays Rs 1,000 towards premium on his full life policy with the LIC. Is this a part of compensation of employees? [1 Mark]
Ans: No, any contribution made by an employee himself to any insurance scheme is not a part of compensation to employee. Value: Analytic Q 8. How will you treat Rs 20,000 earned per month by Mr Rajesh against hiring out his bus to a neighboring school?[1 Mark]
Ans: Income earned by way of lease is rental income, and hence form part of operating surplus and is included in national income. Value: Analytic
via Blogger https://ift.tt/3kYhwU6
0 notes
Text
Over 10 Lakh Students Appear For Physical Education, Language Papers

The subsequent examination for sophistication 10 college students is on February 26 for English topic.
New Delhi:
On the fifth day of board exams, CBSE information highest participation to date. 10,51,186 college students have appeared for the examination immediately in 32 papers. A complete of seven,07,688 class 12 college students appeared for Physical Education paper and a complete of three,43,498 class 10 college students appeared for language papers.
#examtime CBSE performed examination in 32 papers for 1051186 class X&XII candidates immediately. 707688 candidates had registered for sophistication XII Physical Education examination and 343498 candidates had registered for exams in 31 languages together with Thai,Sherpa,Bahasa Melayu,Tamang,Urdu and extra.
— CBSE HQ (@cbseindia29) February 24, 2020
Class 12 college students who took Physical Education examination mentioned it to be a reasonable one by way of issue. Teachers mentioned the query paper was on the traditional line and was simple to unravel. “It was based on the sample paper .The questions were direct as well as application based which the students had intensively practiced during revision. Overall it was a well balanced paper and a good result is expected,” mentioned Suman Tomar, HOD, Physical Education, Army Public School, Delhi Cantt.
Class 12 college students who’ve opted Entrepreneurship, Office Procedure & Practices, Textile Design and Traditional Indian Textile will seem for examination on February 25.
The subsequent examination for sophistication 10 college students is on February 26 for English topic.
On the examination day, college students are being given 15 minutes time to undergo the query paper. Students are allowed to begin writing the solutions at 10.30 am.
On the fourth day a complete of 78,689 college students had appeared for the CBSE board exams. On the third day of the examination over 6 lakh college students had appeared for Painting, Graphics, Sculpture, Commercial Art, Electrical Appliances, IT, Marketing & Sales topics. On the primary day the examination was held for 36 papers through which a complete of 55364 candidates had appeared. On the subsequent day, roughly 13000 candidates appeared for 16 papers.
In complete, greater than 30 lakh college students are showing for CBSE board exams this 12 months. This is the second consecutive 12 months, the CBSE board exams have began in February as an alternative of March, with a view to expedite the analysis and outcome declaration course of. Prior to this the exams have been held in March-April.
Click right here for extra Education News
The post Over 10 Lakh Students Appear For Physical Education, Language Papers appeared first on News.
from WordPress https://ift.tt/2vWyFbR via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
CBSE Class 12 Physical Education exam tomorrow; check sample paper and marking scheme - Times of India
New Post has been published on https://apzweb.com/cbse-class-12-physical-education-exam-tomorrow-check-sample-paper-and-marking-scheme-times-of-india/
CBSE Class 12 Physical Education exam tomorrow; check sample paper and marking scheme - Times of India

Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) is going to conduct Physical Education examination tomorrow i.e. February 24, 2020. The Physical Education exam will be held from 10.30 am to 1.30 pm.
The duration of CBSE class 12 Physical Education exam is three hours and the paper is of 70 marks. The class 12 Physical Education syllabus consists of 10 units as follows — Planning in Sports, Sports & Nutrition, Yoga & Lifestyle, Physical Education & Sports for CWSN (Children With Special Needs – Divyang), Children & Women in Sports, Test & Measurement in Sports , Physiology & Injuries in Sports, Biomechanics & Sports, Psychology & Sports, and Training in Sports.
Candidates can read more to understand the Question Paper Design of CBSE Class 12 Physical Education exam 2020.
Typology of Questions
Remembering:
Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers.
Understanding:
Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas
Applying:
Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way.
Analysing and Evaluating:
Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations.
Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria.
Creating: Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions.
CBSE class 12 Physical Education Suggested Question Paper Design
Typology of Questions Objective Type/ MCQ 1 Mark Short Answer I 3 Marks Short Answer II 5 Marks Marks Remembering 5 3 2 24 Understanding 5 3 1 19 Applying 5 2 1 16 Analysing and Evaluating/ Creating 5 2 – 11 Total 20 30 20 70
Students can check CBSE class 12 Physical Education sample question paper from the link given below.
Click here to check CBSE Class 12 Physical Education Sample Question Paper
Source link
#cbse class 12 physical education class 12#class 12 physical education question paper model#physical education class 12#physical education class 12 2020#physical education class 12 notes#physical education exam 2020#sample paper of physical education class 12#Career
0 notes
Text
‘Together with’ EAD Sample Papers for Class 12 2025: An Ultimate Study Resource for CBSE Students

As the Session 2024-25 unfolds, the students of Class 12 gear up to prepare for a new phase of their academic journey- CBSE Board Exams. To assist them for the same, Rachna Sagar Pvt. Ltd. is going to release ‘Together with’ EAD Sample Papers for Class 12 2025 soon. It is a comprehensive study material prepared by the experts to ensure 100% success in 2025 board exams.
#Resource for CBSE Students#EAD Sample Papers for Class 12#‘Together with’ EAD Sample Papers for Class 12
0 notes
Text
CBSE Class 12 Guide to psychology

Why learn in the same boring way, try Extramarks. With Extramarks, you have access to the various topics prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education which would make it feasible to crack the Board exams with the utmost ease. Students need not run anywhere to cater to their need for a thorough study guide. The kind of material and notes provided by Extramarks helps students to be well prepared for the upcoming Board Examinations. Extramarks provides detailed study material for students of ICSE as well as CBSE. It acts as a guide for students by making easy access to more than 15 different subjects available. With the kind of technique and expertise provided by our experts, the students are motivated to gain the maximum. One teacher, of course, could not be an expert in math, science, social science, and English, together. Imagine the loss of money and time resources in trying to get the best home learning help for your child, even if the tutor was coming home. This, however, is now a thing of the past. By opening its services directly to the user, Extramarks has ushered in a revolution in the digital home learning segment. Extramarks is an answer to all the questions regarding the sample papers or the study material and notes to clear out the board exams. The various subjects offered are in accordance with the latest syllabus prescribed by the council. The following link would be of help to the students pursuing and looking for a smart guide to CBSE class 12 psychology.
0 notes
Quote
08:45 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak Latest Updates Delhi, Maharashtra among five states to get first batch lot of COVID-19 drug Homegrown pharma major Hetero is et to deliver the generic version of antiviral drug Remdesivir to states across the country for the treatment of COVID-19 patients. Sold under the brand name Covifor, the drug has been priced at Rs 5,400 per vial and will be available at hospitals to treat the infection. Delhi and Maharashtra - the two worst-hit states in the country by the pandemic will be the first to receive the first batch of the antiviral medicine. The Hyderabad-based drugmaker has dispatched 20,000 vials of Covifor to five states. 08:07 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak in Uttar Pradesh Latest Updates Atmanirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan to focus on 31 districts The Atmanirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan is focused on providing jobs, promoting local entrepreneurship and creating partnerships with industrial associations and other organisations to create employment opportunities. At least 31 districts have been covered under the scheme and the state government is likely to use the occasion to showcase the work it has been doing for the welfare of the workers. 08:00 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak in Uttar Pradesh Latest Updates Modi to launch Atma Nirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan today Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Friday will launch a 125-day campaign to provide employment to migrant workers and others in Uttar Pradesh, who lost their jobs during coronavirus pandemic. Modi will launch the Atma Nirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan, being undertaken as part of the Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyan that the prime minister started on 20 June for 116 districts in six states in the country. 07:56 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak in Odisha Latest Updates Odisha's COVID-19 cases jump to 5,962; govt plans serology survey The Odisha government on Thursday decided to launch serology survey to ascertain the immune strength among people against COVID-19 as the state's coronavirus count increased to 5,962 with 210 more cases The state has planned to start the serological survey at Puri from Saturday, Additional Chief Secretary (Health and Family Welfare) PK Mohapatra told PTI. 07:52 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak in Karnataka Latest Updates 978 students from containment zones attend first day of Karnataka SSLC exams As many as 978 students residing in containment zones were allowed to attend exams on the first day of Karnataka SSLC exams in special classrooms after complete health screening, Education Minister S Suresh Kumar confirmed. Further, 201 students who had fever/cold-like symptoms were also allowed similarly, The Indian Express reported. 07:45 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak in India Latest Updates India's COVID-19 toll nears 15,000 India on Thursday recorded close to 17,000 new coronavirus infections, pushing the total to 4.73 lakh as the number of fatalities inched closer to 15,000, according to the Union Health Ministry's data. 07:34 (IST) Coronavirus Outbreak in Maharashtra Latest Updates Mumbai Police sets up three COVID-19 centres The Mumbai Police on Friday have set up three COVID-19 quarantine centres for their personnel, which are located in Kole Kalyan, Marol and Marine Drive. Each of the centres have a capacity of around 1,000 beds, said Mumbai Police PRO Pranay Ashok. Coronavirus Outbreak LATEST Updates: Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Friday will launch a 125-day campaign to provide employment to migrant workers and others in Uttar Pradesh, who lost their jobs during coronavirus pandemic. Modi will launch the Atma Nirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan, being undertaken as part of the Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyan that the prime minister started on 20 June for 116 districts in six states in the country. India on Thursday recorded close to 17,000 new coronavirus infections, pushing the overall tally to 4.73 lakh as the number of fatalities inched closer to 15,000, according to the Union Health Ministry's data. The surge in cases over the past few days also led to the cancellation of a number of exams in the country, including the pending papers of CBSE Class 10 and ICSE. COVID-19 cases spike in India, but recovery rate improves The data updated at 8 am showed the daily COVID-19 cases increased by 16,922 to reach 4,73,105, while the death-toll climbed to 14,894 with 418 new fatalities. This was the sixth consecutive day when coronavirus cases increased by more than 14,000. On 20 June, the country registered an increase of 14,516 cases. On June 21, the increase was of 15,413 cases; 14,821 cases on 22 June; 14,933 cases on 23 June; and 15,968 cases on 24 June. Consequently, India has added 92,573 cases since 20 June, and over 2.82 lakh this month since 1 June. However, the recovery rate has improved to 57.43 percent, according to the health ministry. The number of active cases stands at 1,86,514 while 2,71,696 people have recovered and one patient has migrated. A total of 13,012 COVID-19 patients were declared cured in a single day on Thursday. The total number of 4,73,105 confirmed cases included foreigners. According to ICMR, a total of 75,60,782 samples have been tested up to 24 June with 2,07,871 samples being tested on Wednesday. Of the 418 new deaths, 208 were in Maharashtra, 64 in Delhi, 33 in Tamil Nadu, 25 in Gujarat, 14 in Karnataka, 11 in West Bengal, 10 each in Rajasthan and Haryana, nine in Madhya Pradesh, eight each in Uttar Pradesh and Punjab, five each in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Uttarakhand. Bihar, Goa and Jammu and Kashmir have reported one COVID-19 fatality each. Of the total fatalities, Maharashtra tops the tally with 6,739 deaths followed by Delhi (2,365), Gujarat (1,735), Tamil Nadu (866), Uttar Pradesh (596), West Bengal (591), Madhya Pradesh (534), Rajasthan (375) and Telangana (225). The COVID-19 death toll reached 188 in Haryana, 164 in Karnataka, 124 in Andhra Pradesh, 113 in Punjab, 88 in Jammu and Kashmir, 57 in Bihar, 35 in Uttarakhand, 22 in Kerala and 17 in Odisha. Chhattisgarh has registered 12 deaths, Jharkhand 11, Assam and Puducherry nine each, Himachal Pradesh eight, Chandigarh six, Goa two and Meghalaya, Tripura and Ladakh have reported one fatality each. More than 70 percent deaths took place due to comorbidities, the health ministry said. Maharashtra has reported the highest number of cases at 1,42,900 followed by Delhi at 70,390, Tamil Nadu at 67,468, Gujarat at 28,943, Uttar Pradesh at 19,557, Rajasthan at 16,009 and West Bengal at 15,173, according to ministry data. The number of COVID-19 cases has gone up to 12,448 in Madhya Pradesh, 12,010 in Haryana, 10,444 in Telangana, 10,331 in Andhra Pradesh and 10,118 in Karnataka. It has risen to 8,209 in Bihar, 6,422 in Jammu and Kashmir, 6,198 in Assam and 5,752 in Odisha. Punjab has reported 4,627 novel coronavirus infections so far, while Kerala has 3,603 cases. A total of 2,623 people have been infected by the virus in Uttarakhand, 2,419 in Chhattisgarh, 2,207 in Jharkhand, 1,259 in Tripura, 970 in Manipur, 951 in Goa, 941 in Ladakh and 806 in Himachal Pradesh. Puducherry has recorded 461 COVID-19 cases, Chandigarh has 420, Nagaland has 347, Arunachal Pradesh 158 and Mizoram 142 cases. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu together have reported 120 COVID-19 cases. Sikkim has 84, Andaman and Nicobar Islands has registered 56 infections so far while Meghalaya has recorded 46 cases. "Our figures are being reconciled with the ICMR (Indian Council of Medical Research)," the ministry said, adding, 8,493 cases are being reassigned to states. State-wise distribution is subject to further verification and reconciliation, it added. Several exams cancelled across India due to pandemic Following opposition from parents against holding CBSE Class 10 and 12 papers, the Ministry of Human Resource Development and the board have decided to completely cancel pending papers for Class 10, which were to be held from 1 July. The exams for remaining subjects of Class 12 have been indefinitely postponed, and have also been made optional. Students who choose not to give exams will be assessed on the basis of their performance in the past three exams held at the school level. Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE Class 10) and Indian School Certificate (ISC Class 12) have also declared that they will follow CBSE's pattern in according marks to students, and holding exams. Detailed guidelines by all boards are awaited on this. Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET) examination to be conducted by CBSE on 5 July has also been postponed in view of the present circumstances. Globally, infections near 10 million Global coronavirus cases crossed 9.5 million on Thursday, a day after WHO predicted the world's tally will cross 10 million before the week ends. Worldometer reported that 48,618 people have died due to the virus so far. The Chinese mainland has recorded 83,449 COVID-19 cases. A total of 97 asymptomatic patients are under medical observation. China's death toll stands at 4,647, including six from the Hong Kong SAR and seven from the Taiwan region. Indonesia crossed 50,000 cases today and the US has recorded over 2.3 million confirmed cases, with a death toll of over 121,000, John Hopkins University, which is also tracking global coronavirus cases said. Europe has seen a resurgence of COVID-19 cases as many countries begin to ease restrictions for curbing the spread of coronavirus, the World Health Organization's (WHO) regional director for Europe Hans Kluge said on Thursday. "While the European Region is reporting a decreasing proportion of global cases than earlier in the year, the region continues to report close to 20,000 new cases and over 700 new deaths daily. Last week, Europe saw an increase in weekly cases for the first time in months," Kluge told reporters. He said 30 countries have seen increases in new cases over the past two weeks. The WHO also warned that the pandemic has not yet peaked in many countries and that it was "still intense," especially in America. France opened up the iconic Eiffel Tower after a record 104-day lockdown. Tourists who are trickling back to Paris were delighted to find the landmark open when some other attractions in the French capital remain closed. The Louvre Museum isn't reopening until 6 July. Disney, meanwhile, delayed its California theme park's reopening as cases in US continued to surge. With inputs from PTI
http://sansaartimes.blogspot.com/2020/06/coronavirus-outbreak-live-updates-pm-to.html
0 notes
Text
Get Latest CBSE Sample Paper (MCQ) Business Studies for 2021 Term 1 Board Exams- Rachna Sagar

Together with CBSE Sample Paper, Business Studies has been designed as per the special scheme of assessment vide CBSE Circular No. 75/2021 for Term 1 ( For 2021 Nov-Dec Examination ) for Class 12 has been prepared as per the latest assessment pattern.
Together with EAD Business Studies Sample Paper (with answers) is a perfect step-by-step approach to ensure one’s readiness for Term 1 board examination. This Sample Paper for Class 12 assists the students with the right practice and approach to the newest MCQ pattern.
EAD—Easy, Average, Difficult
The content matter in this EAD 12+1 Business Studies Sample Paper Class 12 has been arranged as complete papers with three levels of difficulty—Easy, Average and Difficult (EAD).
Easy: The first set of papers in this CBSE Sample Paper 2021 is based on 'Easy' concept, thus contains Multiple Choice Questions of simple level, which a student can attempt at the beginning of the preparatory stage.
Average: The next set based on 'Average' concept (MCQs) is graded to a level of difficulty to test mid-level preparedness for the examination.
Difficult: The challenging papers allocated to the third set based on 'Difficult' concept are a test of complete preparedness for the examination.
The EAD sample paper is a self-test drive for the students.
Key Features
This Sample Paper includes:
CBSE (2021-2022) Term 1 Sample Paper.
3 Sample Papers each of Easy, Average & Difficult level.
2 Pre-Board Papers based on CBSE pattern.
1 Mock Paper Based On CBSE Pattern with OMR Sheet.
Includes Assertion Reasoning and Case-Based Objective Type Questions.
The 4-Step Process
Step 1 The students are advised to attempt the set of EASY Papers first and obtain at least 80% marks to move onto the next set of papers which is Average.
Step 2 If the student obtains 75% marks in the AVERAGE category of this EAD 12+1 Business Studies Sample Paper Class 12, he/she can switch to the next category, i.e., Difficult.
Step 3 If 70% marks in DIFFICULT category have been obtained, the students are expected to take the PRE-BOARD PAPERS that are exactly based on the CBSE pattern.
Step 4 Attempt the MOCK PAPER (given at the end) for a final-go for your board exam preparations.
Why EAD Latest Sample Papers?
Learning gets strengthened with practice and its evaluation uplifts the preparation. The answers of the MCQs have been given at the end of each Sample Paper for evaluation purposes. The CBSE Sample Papers for class 12 All Subjects 2021-2022 have been prepared by a panel comprising experienced teachers, tabulators and examiners, who have jointly come up with a student-friendly approach to prepare the students for the forthcoming CBSE Board Examination. Repetitive practice of CBSE Sample Papers for class 12 All Subjects 2021-2022 will surely help the students to make their mark in the CBSE Board Examination.
Good Luck!
#CBSE Sample Paper term 1#Term 1 sample paper for class 12#BST sample paper class 12#term 1 sample paper#class 12 sample paper for term 1#Business Studies sample paper for class 12#term 1 sample paper Business Studies#class 12 sample paper#CBSE sample paper#calss 12 term sample paper#board exam#Business Studies sample paper#class 12 Business Studies#MCQ question Business Studies for class 12
0 notes
Text
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Class 12 Exam Preparation
CBSE Class 12 examinations are the pinnacle of school-level examinations. There is a lot of hype around class 12 exams which indirectly makes it more difficult for the students. Every student has a strategy to maximize their class 12 score. However, sometimes students unknowingly commit mistakes that reduce their chances of walking down the path of glory.

#CBSE class 12 exams#CBSE Class 12 exam preparation#During Class 12 Exam Preparation#Together With CBSE Sample Paper#CBSE Together with CBSE sample papers
0 notes
Text
Practice EAD Sample Papers Class 12 CBSE 2025 for Strategic Preparatio

To succeed in cbse board exams you must practice 'Together with' EAD Class 12 Sample Paper 2025 for all subjects. EAD sample paper is that it comes in both digital and physical formats, helping you keep preparing for the exams whenever and wherever you want. By practicing exam questions with our Class 12 EAD Sample Paper 2025 you can strategize your study plan and get a rewarding learning experience. Grab your sample paper copies today to venture into a new way of learning.
#EAD sample paper 2025#EAD Sample Papers Class 12#Class 12 EAD Sample Paper 2025#Sample Papers Class 12 CBSE 2025
0 notes
Text
Top-notch advice by the experts for students to ace the CBSE board 2024 exams

CBSE board exams are a dreaded term for class 12 students as so much is dependent on the board results. There have been instances where students have been caught off guard during board exams due to unplanned preparation which becomes the cause of not scoring the marks which is expected by the student. Well here is some advice from our academic experts for the students which can boost your chances of scoring good marks.
Before beginning your preparation ensure you formulate a study plan and stick by it. Allocate time for different subjects and create a deadline for every unit, and revision so that you are not behind your schedule. After completing your preparations you need to solve the previous year’s question paper that will help you recognize your weaknesses as well as strengths. It will also help you to get an idea of the exam pattern and check your speed of attempting it.
Therefore practicing the previous year’s papers will ensure you are not behind the time when it comes to CBSE board exams. Together with the CBSE sample paper is one of the most sought books in terms of quality sample papers so it can be a great help for you during your exams.Prioritize your health and sleep: In the pursuit of achieving brilliance, some students compromise their health and sleep which won’t be their cause. Getting proper sleep improves memory, strengthens concentration, and calms down your mind. Make sure you do enough physical exercise and eat healthily.
Read More : https://rachnasagarin.wordpress.com/2024/07/29/top-notch-advice-by-the-experts-for-students-to-ace-the-cbse-board-2024-exams/
0 notes
Text
Mock Booklets for board exams | Pariksha pre-board preparation book class 12 Mathematics

Together with’ CBSE Mathematics Pariksha pre-board sample paper class 12 2025 includes set of 3 question papers and an answer booklet with OMR Sheet. The answer sheet is the replica of the original one you will get in 2026 board exam. Pariksha Pre-board sample paper class 12 2025 Mathematics help the students to get prepared for final exams confidently and get excellent results.
0 notes
Text
0 notes