#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality for Learning vs Mixed Reality
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
In recent years, immersive technologies like Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) have gained massive attention, reshaping industries and changing the way we interact with the world around us. From gaming to education, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail, these technologies are driving innovation. If you’re looking to explore these technologies, Simulanis stands out as a leader in this space, offering cutting-edge solutions to businesses across various sectors. Let's dive into how Simulanis, a Virtual Reality Development Company in India, Augmented Reality Development Company in India, and Mixed Reality Development Company in India, is at the forefront of this technological revolution.
#Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality#VR vs AR vs MR#Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality for Gaming#Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality in Education#AR vs VR vs MR for Business#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality in Healthcare#Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality for Marketing#AR vs VR for Customer Engagement vs MR#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality for Training#Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality for Simulation#Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality for Retail#Mixed Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality for Industrial Use#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality for Learning vs Mixed Reality#VR vs AR vs MR for Tourism#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality in Manufacturing#Mixed Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality for Remote Collaboration#Virtual Reality vs Mixed Reality for Design vs AR#Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality for Mental Health vs MR#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality in Entertainment vs Mixed Reality#Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality for Architecture vs AR#Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality in Engineering#Virtual Reality vs Mixed Reality for 3D Visualization vs AR#Mixed Reality vs Virtual Reality for Real Estate vs AR#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality in Healthcare vs MR#Mixed Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality for Collaboration#AR vs VR vs MR in Sports Training#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality in Education#Augmented Reality vs Mixed Reality for Training Simulations vs VR#Mixed Reality vs Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality for Consumer Electronics
0 notes
Text
AR vs VR : Understanding the Core Differences
Main Difference Between AR and VR
The development of Educational Technology has transformed how students engage with learning resources. Among the most innovative breakthroughs in this sector are Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). Although these technologies produce immersive learning environments, they vary in their operation, user interaction, and learning impact. This article explores the main differences between AR and VR in EdTech, as well as their advantages, disadvantages, and potential future applications in education. What is Augmented Reality?

How AR Works
AR uses a mix of hardware and software, such as cameras, sensors, and computer vision, to identify things in the real world and superimpose digital data on top of them. This data can be presented in a number of ways, including text, audio, animations, and pictures. In order to improve user experiences, augmented reality (AR) applications frequently make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and real-time data processing.
AR in Edtech
By making traditional learning more dynamic and interesting, augmented reality, or AR, is having a significant impact on the EdTech industry. Students can investigate topics like the solar system, human anatomy, or historical landmarks in 3D with the use of augmented reality (AR)-based applications, which simplify difficult subjects. It gives studying a more practical component, which keeps students engaged and improves their memory of the material. Additionally, coding platforms and STEM instruction kits are utilizing AR to let students see their work come to life in authentic environments. Virtual field trips are made possible by programs like Google Expeditions, which bring distant locations into the classroom. Teachers can also profit from AR by using it to simulate classroom situations and provide realistic training.
What is Virtual Reality?
By isolating users from the outside world and allowing them to interact with realistic objects, spaces, and scenarios, virtual reality (VR) creates an immersive digital environment that allows users to fully immerse themselves in a simulated world. VR is particularly useful for simulations, skill-based training, and interactive lessons, which help students understand complex concepts through hands-on experience rather than just theory. VR improves engagement and gives a deeper understanding of subjects in a way that traditional methods cannot give generally.
How VR Works
As it provides completely immersive, hands-on experiences, virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing the way students learn. Through the use of controllers, motion sensors, and headsets, virtual reality (VR) produces a 360-degree virtual world in which students can walk around and engage with their surroundings. Students may experience teachings in a far more engaging way, whether they are completing a science experiment, seeing a historical landmark, or investigating the human body. Virtual reality (VR) makes learning seem thrilling and real by stimulating sight, sound, and occasionally even touch. It’s a fantastic method to keep children engaged in their study and simplify difficult subjects.
VR in Edtech

Core Differences between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality With their own distinct advantages, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are revolutionizing education. AR is frequently utilized in interactive textbooks and digital learning tools, providing students to explore 3D models and animations superimposed on the real world using a phone or tablet; it improves classroom experiences by providing additional information during field trips it aids in visualizing scientific experiments; and it makes literature come to life through augmented storytelling, in medical studies, AR supports learning by allowing students to examine anatomical structures in a more visual and interactive manner for language learners, AR can instantly translate words in real contexts, making it easier to naturally understand new languages, and it is useful in blended learning. Virtual reality main characteristics represented in imaginary space, immersion in virtual space, sensory feedback and interactivity while augmented reality includes contextuality, which means combination of virtual and actual world simultaneously, interactivity at the same time and spatiality in the 3D world.
While Augmented Reality (AR) enhances learning by imposing digital elements into physical surroundings, Virtual Reality (VR) on the other hand offers a fully immersive experience, making it an excellent choice for self and, in-depth learning that requires complete focus and engagement. VR transports students out of their physical surroundings and places them into a completely digital environment, making it ideal for virtual classrooms, lab experiments, and training. In contrast to simply viewing content on a screen, VR immerses students in a 3D world where they can interact with objects just as they would in real life. This makes VR especially useful for virtual field trips, allowing students to explore historical landmarks, remote locations, or even fictional worlds that would otherwise be impossible to visit.
Which One is Better?
The question is not which one is better, but rather which one is more suitable for a specific purpose. Augmented Reality enhances real-world experiences, while Virtual Reality is ideally used for fully immersive experiences. For example, students might use AR to explore the human body through AR-enabled textbooks. On the other hand, VR offers fully immersive environments that allow students to work in a virtual lab without physical limitations or risks. In every field both AR and VR offers unique benefits tailored to different learning needs.
Conclusion
In our quest for more immersive digital experiences, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) offer two different but complimentary avenues. While VR provides total immersion into virtual worlds, AR adds digital overlays to the real world. Both technologies have amazing promise in a variety of fields, including business, entertainment, healthcare, and education. We can better appreciate each of their unique capabilities and see how they can influence our digital future when we are aware of their fundamental differences. Regardless of whether you like AR’s improved realism or VR’s complete immersion, one thing is certain: these technologies constitute the cornerstone of a new era of interaction.
0 notes
Text
VR Software: Stepping Into New Realities
Imagine exploring distant planets, training for a job in a simulated factory, or unwinding in a virtual beach paradise—all without leaving your room. Virtual reality (VR) software makes this possible, creating fully immersive digital worlds that captivate and empower users. These tools build environments you can step into, offering experiences that entertain, educate, and innovate. What makes VR software a portal to the future, and how can it redefine your reality? Let’s dive in.

What is VR Software?
VR software is a collection of digital tools that design, develop, and power virtual reality experiences. It’s the tech that constructs 3D environments you can explore through VR headsets, controllers, or even gloves, shutting out the physical world for a total dive into the digital. Unlike augmented reality, which overlays content onto reality, VR replaces it entirely with a crafted universe.
Today, these platforms tap into artificial intelligence (AI), high-fidelity graphics, and motion tracking to serve gamers, educators, businesses, and creators, blending realism with limitless possibility.
Why VR Software Matters
VR isn’t just a toy it’s a revolution in how we experience and interact. From entertainment to professional training, it’s rewriting the rules of engagement. VR software matters because it:
Immerses Fully: Engage all senses for unforgettable experiences.
Transform learning: Practice skills in safe, simulated settings.
Boosts Creativity: Build or explore worlds without physical limits.
Connects Globally: Share virtual spaces with others, anywhere.
X posts often buzz about tools like Unreal Engine for VR brilliance, showing its growing footprint across industries.
Key Features of VR Software
The best VR software offers a dynamic toolkit:
3D Environment Design: Craft detailed worlds with textures and physics.
Motion Tracking: Sync headsets and controllers for natural movement.
Audio Integration: Add spatial sound for a 360-degree feel.
Interactivity: Program objects to react to user actions.
Multi-Platform Support: Run on Oculus, Vive, or PSVR seamlessly.
AI Enhancements: Add smart NPCs or adaptive scenarios.
These features turn VR into a living, breathing alternate reality.
Top Benefits for Users
VR software delivers standout perks:
Realism: Feel present in a world that looks and sounds authentic.
Safety: Train for risky tasks—like surgery—without real-world stakes.
Efficiency: Prototype products or rehearse presentations virtually.
Fun Factor: Escape into games or adventures with total immersion.
A student using VRoxy might ace a virtual lab, while a gamer on SteamVR loses hours to epic quests.
Popular VR Software
The VR space shines with top options:
Unreal Engine: High-end tool for stunning VR games and apps.
Unity: Versatile engine with strong VR support for all levels.
Oculus Software: Native platform for Oculus headsets and experiences.
SteamVR: Hub for VR games and tools across hardware.
VRoxy: Open-source pick for accessible VR development.
How to Choose the Right VR Software
Picking your VR tool takes a plan:
Purpose: Gaming (SteamVR) or training (Unity)?
Skill Level: Beginners might pick Oculus; pros go Unreal.
Hardware: Match your headset—Oculus, Vive, or mixed?
Features: Need simple scenes or complex physics?
Cost: Free (VRoxy) vs. paid tiers (Unreal subscriptions at $99/month)?
The Future of VR Software
The future of VR software is mind-blowing. AI will craft dynamic worlds that evolve with you—think NPCs that learn your habits. Lightweight headsets will ditch cords, powered by 5G for instant load times. Social VR will explode, letting friends hang out in virtual spaces, while haptic tech—like gloves or suits—will add touch to the mix. The horizon is about deeper, more connected immersion.
Challenges to Watch For
There are hurdles. High-end tools like Unreal demand serious computing power—your rig better be beefy. Costs vary; premium VR setups aren’t cheap. Motion sickness can hit newbies, so ease in. Development complexity might slow solo creators, and battery life on wireless headsets limits long sessions. Security-wise, encrypt data to keep virtual worlds private.
Real-World Impact
Gamers: A player uses SteamVR to battle in a sci-fi epic.
Professionals: A pilot trains on Unity-made flight sims risk-free.
Socializers: Friends meet in Oculus Horizon for a virtual movie night.
Conclusion
VR software is your ticket to worlds beyond the ordinary. It’s not just about escape—it’s about learning, creating, and connecting in ways the physical world can’t match. Whether you’re gaming, training, or dreaming up the next big thing, the right VR tool can transport you there. Explore the options, strap in, and redefine what’s possible.
Frequently asked questions
What is VR software?
It’s a set of tools that builds fully immersive 3D digital worlds you explore via VR headsets.
Who uses VR software?
Gamers, educators, businesses, and developers crafting virtual experiences for fun or function.
How does it enhance experiences?
It surrounds you in a digital reality, boosting engagement, training, or creativity.
Is it secure?
Most platforms secure data within VR—check for encryption, especially in social apps.
What’s the difference between VR and AR software?
VR immerses you in a new world; AR overlays digital bits onto the real one.
How much does VR software cost?
Ranges from free (SteamVR, VRoxy) to $25-$100/month (Unity Pro, Unreal subscriptions).
Can it integrate with other tools?
Many syncs with game engines, motion trackers, or cloud platforms confirm compatibility.
How long until I see benefits?
Basic immersion hits instantly; mastery or creation takes time with practice.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Ideal Immersive Learning Approach Hassle-Free
In this modern day and age, you can access almost everything you need online without the hassle. Businesses in Singapore are taking note of this with most of them now running their training programs online. And there’s nothing wrong with that as it is the perfect way to ensure your employees keep pace with the latest changes in your industry.
For employees to get the most from theses online training programs, it pays off to choose the best immersive learning approach to leverage. But with so many options at your disposal, how do you make an informed decision? Actually, it is quite difficult to determine the best between augmented reality vs virtual reality in Singapore. In this simple guide, we will help ensure you make an informed decision.
Determine Key Performance Behaviors
It pays off to get an insight into your key performance behaviors, challenges, and gaps you aim to fix before moving on to the next step. You want to be sure that you’re leveraging an immersive learning approach that perfectly fits your business. Do you want to gauge your employees’ product knowledge?
If so, there is nothing wrong with trying your hand at Augmented Reality training. After all, it has the potential to help you determine how much your staff knows about the tasks at hands. In short, always ensure you determine the changes you want your employees to take up after which you can choose the best mixed reality solution to leverage.
Define Your AR/VR Training Budget
You don’t have to take a toll on your finances merely because you want to invest in AR/VR training. And the only way to go about this is by defining your AR/VR training budget before moving on to the next step. Always remember the cost for VR resources tends to be higher compared to that of AR training content. The good news is you can never run out of options when in dire need of an AR/VR company in Singapore than will work within your budget.
Wrapping Up
You don’t want to go overboard merely because you want to choose the best immersive learning approach for your company in Singapore. The catch is in employing the correct measures from start to finish, and you’re good to go. It is then that you can easily find an immersive learning approach that can help you improve employee productivity.
0 notes
Text
Decoding Apple’s Vision Pro: Navigating the Confusing Realm of “Spatial Computing”

The Enigma of Spatial Computing
Apple’s latest venture into augmented reality, the $3,500 Vision Pro ski goggles, has ignited a debate over terminology within the tech community. While Apple insists it’s not virtual reality but rather “spatial computing,” the lack of a clear definition for these terms has left many scratching their heads. The confusion is not limited to consumers; even industry experts find it challenging to pinpoint the precise meanings of terms like “mixed reality,” “augmented reality,” “holographic computing,” “the metaverse,” or “XR.”
Spatial Computing vs. XR: A Linguistic Quagmire
The term “spatial computing” has been thrown around, but its definition remains elusive. Some consider it synonymous with XR (extended reality), while others argue it aligns more with mixed reality or augmented reality. The lack of consensus on these terms contributes to a linguistic quagmire, making it difficult for consumers to understand the technology and its applications.
Unraveling the Vision Pro: Mostly VR with a Dash of Augmented Reality
Despite Apple’s insistence on “spatial computing,” experts lean towards defining the Vision Pro as primarily a virtual reality (VR) device. When wearing the Vision Pro, users can experience an immersive video feed of the physical world combined with internet elements. It allows for activities such as watching movies with a virtual overlay and accessing recipe apps with cooking timers superimposed on the real-world environment. However, the nuances of these terms add an extra layer of confusion for consumers trying to comprehend the technology they’re investing in.
Immersive 3D: A Common Ground?
To simplify the complex terminology, some propose embracing the concept of “immersive 3D” experiences. This umbrella term covers a range of technologies, including virtual reality and augmented reality, and envisions a future where digital interactions seamlessly blend with the physical world. Apple’s vision for unobtrusive glasses offering immersive experiences aligns with this concept, promising a future where technology bridges the gap between reality and digital augmentation.
As Apple navigates the intricate landscape of augmented reality, the industry grapples with terminology debates, leaving consumers in a state of confusion. While the Vision Pro may be a step towards a more immersive digital future, the ambiguity surrounding these terms emphasizes the need for clearer language in describing the evolving realm of spatial computing and its various iterations.
Curious to learn more? Explore our articles on Enterprise Wired
#spatialcomputing#augmentedreality#virtualrealitygames#NewsUpdate#immersivetechnology#applevisionpro#TechDebate#futuretech
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence vs Mixed Reality: Shaping the Future, But Not in the Same Way

The future of reality is brimming with possibilities, and two transformative technologies stand at the forefront: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Mixed Reality (MR). While both hold immense potential, they paint vastly different pictures of how we might interact with the world around us.
AI
Imagine a world where machines seamlessly understand our needs and anticipate our actions. AI aspires to be the invisible hand, subtly shaping our experiences. It will power intelligent assistants that manage our homes, personalize our newsfeeds, and even optimize our health.
AI's dominance will lie in its ability to crunch vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. It will automate tedious tasks, freeing us to focus on creativity and innovation. From self-driving cars to medical diagnosis, AI will permeate every facet of our lives, making them smoother and more efficient.
MR
Mixed Reality, on the other hand, promises to blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds. Imagine overlaying digital information onto your surroundings, interacting with virtual objects as if they were real, or even teleporting to distant locations in real-time.
MR's strength lies in its ability to augment our perception, enriching our experiences and opening up new possibilities for learning, entertainment, and collaboration. Imagine surgeons training on virtual patients, architects visualizing 3D models in real-time, or students exploring historical events through interactive simulations.
So, who will be the dominant force in shaping the future reality?
The answer is: both, but in different ways. AI will be the invisible engine driving efficiency and automation, while MR will be the transformative lens through which we experience the world. They are not competitors, but rather complementary forces that will work together to redefine our relationship with reality.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Virtual Reality Vs Augmented Reality VS Artificial Intelligence

Virtual Reality Vs Augmented Reality VS Artificial Intelligence
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a system-generated simulation of the imaginary world. It is utilized in 3D motion pictures and computer games. Aside from games and diversion, Virtual Reality is likewise utilized for preparing, instruction, and science. Virtual reality takes these equivalent parts to one more level by delivering an altogether system-generated recreation of a substitute world. These vivid recreations can make practically any visual or place possible for the player utilizing hardware devices. It assists with making arrangements resembling the real world and "submerge" the watcher utilizing PCs and tangible gadgets like headsets and gloves.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) is an ideal mix of the computerized world and the actual components to establish a fake climate. Applications that are created involve AR innovation for mobile apps or desktops to combine digital components for real-world experience. More or less every individual with smartphones will be experiencing the effect of augmented reality, by making it more proficient than VR in the gaming field. AR transforms the actual world into a vivid visual one by projecting virtual pictures and characters through a mobile camera or video capturer. AR is nothing but merely the user's real-life experience.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence completely differs from VR and AR, as it does not consider the user’s experience of the real world, rather it is merely a technology that is specially designed based on the user experience. AI collects the information and processes it based on the gathered information to enhance the user experience the better way. In simpler words, Artificial Intelligence is about technology structured to solve user issues by gathering user experience by technology on its own.
The noticeable difference between VR, AR & AI
AR is visualizing things in the real world while VR is a virtual world but AI uses algorithms from the user experience.
AR clients can handle their presence in reality; VR clients are constrained by the control system; AI is completely technologied.
VR requires a headset gadget, however, AR can be retrieved using smartphones; AI does not require any gadgets.
AR improves both the virtual and real-world while VR just upgrades an imaginary reality; AI solves the user's problems.
AR, VR & AI applications are developed using completely different platforms.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
Offers individualized learning
Cultivating the learning system
Wide assortment of fields
Offers advancement and constant improvement
Expanded reality can be utilized to increase client information and data.
Individuals can share encounters over significant distances.
Benefits of Virtual Reality (VR)
Vivid learning
Establish an intuitive climate
Increase the work capacities
One of the main benefits of VR is that it assists you with making a reasonable world so the client can investigate the world.
In the educational industry, Virtual reality comforts it by making it simpler and more agreeable.
Virtual reality permits clients to try different things with a counterfeit climate.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Less human error
Available all time
Plays a major role in the repeated task
Complete digital assistance
Make quick decisions
Innovative new decisions
Future for AR, VR & AI
Developers must be aware of these advancements to sustain themselves in the game industry. It's not to say that we've dominated conventional UX (and I mean route, availability, intelligibility, shading hypothesis, versatility, saw execution, etc), yet these ideas positively aren't new and we should begin to feel intimately acquainted with what clients look for now. Augmented reality, virtual reality, artificial intelligence and wearables are the new dominators and creators need to figure out how to beat them up. Furthermore, regardless of whether the mechanics of the VR and AR probably won't mean normal UX, the tests could present to you a few novel thoughts. Concerning AI - it is it withstands the industry and rules over for years long.
0 notes
Text
The Difference Between AR and VR
These two sounds similar and come together almost every time, but they are totally different technologies. Both of them have their unique and crucial place in the tech industry and are preparing to be in future technologies. These two are already part of many different technologies in various industries, including gaming, electronics and IT, hospitality, automobile, leisure. Some recent advancements in these technologies like oculus rift, PlayStation VR and hololens attracted huge attention from users, researchers, and industries. You should have already used one of these technologies in a way or another.
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality or VR can be described as a simulated visual experience that can be similar or different from your surrounding environment. VR is being used in various industries, including entertainment, event, business, and education.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality presents an interactive mixed experience of a real world environment with computer generated virtual objects or environment. In simple words, AR is a system that consolidates three features: a combination of virtual and real-world, real-time interactions, and precise 3D visual of a virtual object.
Difference between Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality
Virtual environment, Completely Different from Real World
Visuals & other sensations are virtual
The user gets totally immersed into a virtual environment
Requires less bandwidth than AR, about 50MBPS
Users need to use additional equipment with the host device
The main purpose of VR is to take into another virtual world that is totally different from the real world
Virtual reality doesn’t affect the real world, takes users into a virtual world with sensations.
75% to 100% Virtual and 0% to 25% real
Augmented Reality
Augmented Real-world with virtual objects
Presente World with virtual objects and sensations
Users partially get into the Augmented world
Needs more bandwidth than VR, around 100MBPS
Users only need one device like a mobile phone or iPad
AR keeps user experience in the real world with virtual objects and experience.
Augmented reality is used to enhance real-world and provide users better experience
100% real world with 0% to 50% virtual world.
Advantages of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Augmented reality and Virtual reality technologies are different yet relatable; they are potentially useful in their own ways. Here are some of their advantages.
Virtual Reality
An immersive visual experience that can be used in numerous ways
With advanced equipment; can create an interactive environment
Increased work capabilities
Offer convenience
With Virtual reality, we can create a virtual environment that can be enjoyed from anywhere
Virtual reality has the potential to take education to a whole different level
With additional devices, users can interact with an artificial environment.
Augmented Reality
Offers individualized experience learning
Help visualize an object in a real environment
Wide variety of potential fields
innovation and continuous improvement
Accuracy and better results
Help increase user knowledge and information.
People can share experiences over long distances.
Helps developers to build games that offer a “real” experience to the user.
Augmented Reality & Virtual Reality Uses
Both of these have such potential to get involved in more and more uses and various departments. Here are some of the fields that we are using or planning to use AR and VR technologies.
Virtual Reality
VR technology is widely used to build a fictional reality for the gaming world.
VR is being used by the military for flight, battlefield, and other simulations, etc.
VR can help measure any activity in a simulation of a real situation.
A primary method for treating post-traumatic stress.
VR can help people overcome their fear
In the medical field, VR to practice and procedures, surgeons to pre-plan surgeries
Augmented reality
AR is mostly used via an application
The printing and advertising industries are using AR technology apps to display digital content on top of real-world magazines.
AR technology allows you to interact with your surroundings and gives you the required information like a translation app
With advanced 3D technologies, we can create 3D games like Pokemon GO
In manufacturing industries, AR help engineers to solve the problem and same can be applied in the education field
It might be wrong to say that AR & VR are different and intended to work separately. Instead, They can work together and generate an improved immersive experience and take users to a whole different level. There is a huge potential for both AR and VR in many ways; experts are trying to figure out how they can utilize them.
0 notes
Text
The metaverse will not look the way Facebook imagines it
A new GamesBeat event is around the corner! Learn more about what comes next.
Much has been said about the metaverse recently, thanks to Mark Zuckerberg’s announcement that Facebook would be evolving into a “metaverse” company. The ensuing commentaries have been numerous, with many imagining a world parallel to the real world, existing with one identity and shape, one set of rules.
That’s akin to suggesting that AOL is the internet. In reality, the internet has myriad places, identities, and purposes, appearing on an equally wide range of interfaces. It is a backbone technology, and the experiences it enables are infinite and chaotic. The only consistency is you, the human traversing it.
Therefore many of the current portrayals of the metaverse are too narrow. Zuckerberg’s description of the metaverse as “people meeting in digital spaces” is close to that of Neal Stephenson’s 1992 novel Snow Crash, where the term was first coined. But the term has since grown to mean something far more expansive.
The meta in metaverse refers to a universe built out of pure data. In 1992, it was natural to think that a virtual reality was the only way such a thing could exist, so in Snow Crash characters walked around with optical media. The idea of 5G carrying 20 gigabytes per second over the air wasn’t even comprehended yet.
Likewise, the idea that the data pool is entirely Facebook’s property and something that you must immerse in as a lifestyle choice is a natural world view for Facebook.
But the metaverse won’t be realized in a closed-garden VR space. Instead it will emerge as our digital lifestyles begin to join us in the physical world. As one-time Magic Leaper and metaverse philosopher Brian Schwab wrote on LinkedIn earlier this week, “The ‘Metaverse’ is not a place, some escapist fantasy land like in movies. It’s not a dystopian landscape of people locked in their houses. In many ways it’s the opposite of that.” It is the opposite partly because it is expressing itself as a series of backbone technologies that accessorize the internet, like a URL or IP address, rather than a proprietary immersive experience. From a designer’s point of view, the resulting outcome of this new backbone is not a killer app or singular experience but the next pattern of computing.
Placefulness as a computing metaphor
There will come a time soon where you will tell someone “The presentation is on my desk” and that will mean two things. First, through mixed or augmented reality technologies, the presentation can literally be on your desk — not trapped in a screen but literally floating on your desk. This enables an ease of locating the file, object, image or link, providing an organizing metaphor that matches the geographic nature of the human mind. The mental pathway to finding you and then your office and then your desk is a natural and shorter path than locating you on Google Drive and following arbitrary breadcrumbs of folder names.
In the same way Windows helped users understand computers by using the metaphor of the office place (desktops, files, folders), the metaverse will allow use physical spaces (landscapes, objects, layers, prisms) as a metaphor. This new metaphor will make it easier for users to communicate about and understand computing with ubiquity and with reduced friction.
Presence vs. immersion
The vision of this pattern is not one of immersion but one in which computing will merge into our environment and exist around us with a kind of human-amplifying ubiquity. Interfaces will be worn (wearable mobile computers) not carried (handheld mobile computers) and will be spoken to or manipulated with motion and gestures. And they will increasingly appear on surfaces rather than behind screens, either by mixed reality, augmented reality, or projected onto surfaces using Interactive Light.
This pattern of computing removes the final frictions that remain in our current methods of immersive handheld and laptop computing. It will celebrate the hands-free mobility of the user rather than the inward distraction of a device. It will offer shared interfaces that mark up physical spaces and make us more heads-up and present. This is in stark contrast to the immersive VR view of the metaverse. We already feel like our devices capture too much attention. Why double down?
Yes, we will still be able to access more immersive experiences through the metaverse, in the same way we now access Facebook and the wonderful world of online gaming through the internet and handheld devices. But there will be so much more than that. Unlike the original metaverse vision, we don’t have to swim in the data pool — the data will break free and swim in the air around us.
The emergence of a meta me
The popular metaverse thinking often portrays a common interface, assuming we will all enter as Player One ready to play the same game by the same rules. But what we will see is a myriad of different business models, content types, and classes of experiences. Individuals will orchestrate the interfaces for these into workflows that bring productivity, entertainment, or socialization in the manner they want. The common thread is that all of these applications will amplify the capabilities of the individual users.
If you were to watch the data flow in the modern internet, you would see some of it flowing into a pool like Facebook. But you would see far more flowing in many different directions, creating unique patterns of activity that begin to approximate us as individuals. This kind of hyper-personalization is extending into all parts of our digital lifestyles. The tools are becoming us. In the data is a meta me that is becoming every bit as real as us.
This is a positive for humanity itself. The very devices we use will share our disposition on sensing the environment around us, amplifying us.
The metaverse has dystopian connotations because we live in an age where technology doesn’t always promote a betterment of the human condition. We are sensing a competition here and rightfully so. We don’t want to enter the machine. We want it to meet us on our terms.
We want technology in service of humanity. Privacy as a virtue. Amplification not emulation. Presence not escapism. And authenticity over influence.
Perhaps that is why there is such a strong reaction to Zuckerberg’s co-opting of the term metaverse. Because Facebook hasn’t lived up to these goals. And many of us want more out of the future interface between humans and technology.
Jared Ficklin is Chief Creative Technologist of product design company Argodesign, with two decades of experience creating products and visions for major companies. For his previous work integrating technology into the design process at Frog Design, Jared was named one of 4 Frog fellows. He has contributed to the visions, strategy, intellectual property, and products of clients including HP, Microsoft, AT&T, LG, SanDisk, Motorola, CognitiveScale, and Magic Leap.
Mark Rolston is Founder and Chief Creative Officer of Argodesign. He was previously Chief Creative Officer of Frog Design and one of the earliest design pioneers in software, helping forge the disciplines around user interface design and mobile platforms. He has worked with the world’s leading companies — Disney, Magic Leap, Dreamworks, Salesforce, GE, Microsoft, and AT&T. He currently serves as advisor to the Responsible AI Institute (RAI), working to define responsible AI with practical tools and expert guidance.
VentureBeat
VentureBeat's mission is to be a digital town square for technical decision-makers to gain knowledge about transformative technology and transact. Our site delivers essential information on data technologies and strategies to guide you as you lead your organizations. We invite you to become a member of our community, to access:
up-to-date information on the subjects of interest to you
our newsletters
gated thought-leader content and discounted access to our prized events, such as Transform 2021: Learn More
networking features, and more
Become a member
0 notes
Text
22 Examples of Augmented Reality to Inspire Small Business Owners
The year 2016 witnessed the launch of Pokémon GO, a path-breaking innovation in the world of mobile video games, and the game earned tremendous acceptance globally with 100 million downloads on Google Play in one month. It is one of the top augmented reality examples among many more that have emerged in the past two years. Apple CEO Tim Cook said in 2016 that the augmented reality technology will become so essential that it will be as much a part of a user’s day as eating three meals a day. In the FIFA World Cup 2018, football fans got an engaging opportunity to extend their support for their favorite team by adding 3D face masks to photos and videos. This became the first international sporting event to implement Facebook’s augmented reality masks. Over the past couple of years, we have come across numerous augmented reality examples, either in the news or experienced ourselves. The world of augmented reality has finally become as real as peanut butter. Its capabilities which we have seen in sci-fi fictions movies like HER are now a science-backed reality in life. It offers an enriched experience by introducing elements of the virtual world into the real world using technology. From education to entertainment, healthcare to medical science, sports to tourism, product marketing to retail shopping, construction to telecommunication, engineering to manufacturing, environment to energy, AR has marked its presence everywhere. AR is here to stay and all set to become an indispensable part of our daily lives.
Augmented Reality and its types
Augment means ‘to add’ or ‘to enhance something’. Augmented reality is an enhanced version of the real environment by superimposing graphics, sounds, touch and effects for better user experience. The primary objective of AR is to ensure a superior audiovisual experience for the user. The implementation models and applications of AR are wide-ranging and unlimited. It can be applied to simple things like text notifications for better user experience as well as to prepare medical professionals to perform complicated surgeries. AR vs VR Both virtual reality and augmented reality are changing the way we perceive reality and set to have remarkable growth in the coming years. Although they sound similar, they are two different concepts. Augmented reality adds digital elements to an existing natural environment for enhanced user experience, whereas in Virtual Reality an imagined or real-world environment is recreated. AR aficionados classify Augmented Reality majorly into five categories, although the differences between each are not quite obvious. The different types of augmented reality are: Projection-based AR It projects digital images on physical objects in real space. Recognition-based AR You scan an image and it comes to life. Location-based AR It makes use of the location-detecting feature of the smart devices. Outlining AR It is similar to projection-based AR but uses object recognition to work. Superimposition-based AR It provides an ‘alternate’ view of a particular object. Therefore, it is used widely in healthcare and military AR applications.
The current “Reality” of “Augmented Reality”
The augmented reality ecosystem has evolved very quickly over the past few years and continues to grow at a rapid rate. The International Data Corporation (IDC) expects a five-year compound annual growth rate of 98.8% for AR and VR products and services during the period 2017-2021. Major industries have started exploring augmented reality for improving customer experience and interaction, workforce enablement, brand advertising, etc. The home furnishing market has already put AR technology into action to enhance brand experience for their customers. Siemens, the engineering company, has recently used AR to showcase the new range of magnetic valves. Major brands like Coca-Cola, Spotify etc., are using augmented reality applications to advertise their products. How tech giants are defining this new reality? Google and ARCore ARCore is the platform from Google for augmented reality apps. It enables developers to integrate virtual content with the real world and thereby offer numerous AR experiences for the users. The Expeditions AR, which was introduced to provide an augmented learning experience for students, is now free for all. Google Glass, the wearable augmented reality eyeglass launched in 2012, is often reviewed as a product far ahead of its time. Apple and ARKit The ARKit2, with an impressive list of additional features, was unveiled by Apple in 2018 at the Worldwide Developer Conference. It enables developers to build AR apps that ensure a deeper level of immersion for the users. Facebook and AR Studio Facebook introduced AR Studio, the augmented reality tool, for third-party developers in 2017. While Netflix used the AR Studio tools to launch its comic book series, Nike experimented with the Camera Effects Platform to employ AR with Messenger bots for its new line of sneakers. Amazon Sumerian and Amazon AR View Amazon has also stepped into the AR world with Amazon Sumerian and AR View. Amazon Sumerian lets anyone create AR apps quickly and easily using its tools. AR View is another amazing feature from the online retail giant which lets you view the products in your home before you buy it. Microsoft Hololens Microsoft launched Hololens in 2016 to mark its presence in the world of Mixed Reality. The release of the second version of Hololens is a much-awaited event in the tech world. It is expected to be launched this year with a custom AI chip for better performance. Magic Leap This highly funded Florida-based startup has come up with its futuristic pair of augmented reality glasses named as Magic Leap One. It is designed to enhance the real world with digital objects while you can interact with everything real that is going around you. Samsung Samsung Electronics has included augmented reality features in Galaxy 9, its recently launched smartphone model. The company has also used augmented reality tech features in Bixby Vision, the smart assistant in Galaxy Note 8, for better user experience. Well, the list is not complete as there are many other AR startups and tech companies working on AR-based products and services. AR is expected to revolutionize the way businesses operate in the near future. The global spending on AR and virtual reality technology will reach $215 billion in 2021. In the next couple of years, Apple and Google together will have 4.25 billion AR-capable devices. The AR industry is expected to generate revenue of $90 billion by 2020.
Major applications categories of Augmented Reality
Social Marketing and Retail Gaming Utility Education and Training
22 of the most interesting, inspiring and innovative examples of Augmented Reality
The history of augmented reality can be traced back to the beginning of the 21st Century when Lyman Frank Baum published the illustrated novel ‘The Master Key.’ The first augmented reality device, named ‘The Sword of Damocles,’ was invented by Ivan Sutherland. Fast forward to 1990, Tom Caudell coined the term ‘Augmented Reality.’ And in the same decade, AR tech has taken its baby steps as a commercial commodity. Acknowledge it or not, AR is slowly becoming a part of our everyday life now. With numerous applications, AR is all set to transform our lives for the better. Check out below a curated list of the best AR examples put into action. 1. IKEA Mobile App – Put furniture on the streets The Swedish home furnishing company IKEA is a pioneer in taking advantage of augmented reality technology to enhance customer experience. It launched IKEA Place, the AR-based app, in the autumn of 2017. This app enables shoppers to see exactly how furniture items in the product catalog would look and fit in their homes before they buy it. It makes use of Apple’s ARKit augmented reality platform to take shopping experience to the next level. 2. Project Color App From Home Depot – Which shade for your wall?
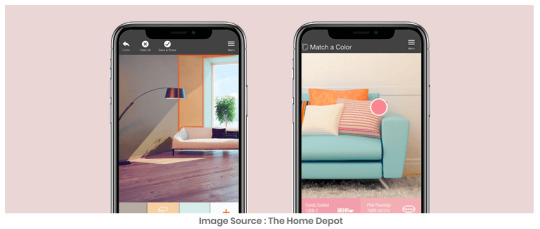
Will the wall paint make the bedroom look dull? Does the shortlisted bedroom furniture make the space jam-packed? Is the coffee table too small for the living room? These kinds of common shopping queries can become a thing of the past when home furnishing companies put AR into action. Decorating your home becomes a lot easier with the Project Color App from Home Depot. It shows the user how a particular paint looks in the wall before you actually finalize the shade. Similar to IKEA, the company has launched its dedicated AR app for home furnishing products as well. 3. Timberland – Say goodbye to fitting rooms Not many of us want to go to the fitting room repeatedly while we shop for outfits. Hence Timberland launched its virtual fitting room in a shopping center in Warsaw to offer a better retail experience. Launched in 2014, it uses Kinect Motion Sensing Technology to enable shoppers to try on different outfits virtually. You can see your face and similar-sized figure in various outfits before you buy it. 4. Sephora Virtual Artist – Virtual makeup anywhere, anytime Sephora Virtual Artist is an innovative and exciting AR feature available in Sephora’s app. It allows the prospective customers to try on thousands of Sephora’s makeup products to find the best-suited one. 5. MakeupGenius App – Unique virtual makeup experience The MakeupGenius App from L’Oreal Paris, one of the world’s top cosmetics manufacturers, gives you instant makeovers using real products and a real inspiration. By using the camera of your phone, it recognizes your facial features to offer a seamless virtual makeup experience. If you aren’t sure about which shade of lipstick or eyeliner suits you well, this app is what you need. 6. Pepsi Max, AR and the bus shelter in London A prowling tiger, a crashing meteor and an alien tentacle grabbing people in a bus stop! Well, this is not a scene from a sci-fi movie, but an astounding advertisement using augmented reality tech by PepsiCo. The company named the video campaign as “Unbelievable Bus Shelter.” 7. AccuVein for easier and safer IV insertion AccuVein is a leading example of how augmented reality application can be used to solve a real-world problem in healthcare. It uses projection-based AR to take away the guesswork involved in finding a vein. 8. AMC Theatres provides optimal convenience with AR The entertainment industry has already put AR into action in innovative ways. A perfect example is AMC Theatres which incorporates AR technology in their app to deliver the brand message at the right moment. Users can scan a film poster and receive relevant information about the movie using the app. They can go ahead and purchase the movie tickets as well. 9. Weather Channel’s AR entry to warn against winter driving hazards Weather Channel used AR technology to explain the hazards of winter driving innovatively and it garnered much attention in April 2018. The broadcast company used a virtual car through the studio to describe the hazards of driving on snowy roads. It had earlier used augmented reality technology to display a tornado in the studio. 10. AR Poser – Take a selfie with digital avatars Disney Research has recently started to use augmented reality technology to enable users to pose with, or as, a digital avatar for enhanced user experience. The app named as AR Poser takes only 2 seconds to interpret an image and project the digital avatar. The team at Disney Research had earlier developed technology using AR to project colored images from a book into 3D renderings using a smartphone. 11. Pokémon GO – The game that made AR a household name Pokémon GO does not need any explanation. Niantic surprised the whole world with its augmented reality video game Pokémon GO. The game enjoyed overwhelming success leading to the massive popularity of AR technology among consumers. The company will soon launch its next game themed on Harry Potter series and is named as ‘Harry Potter: Wizards Unite’. 12. Google’s Measure – Forget the measuring tapes Don’t have a measuring tape handy? Here’s the virtual measuring app from Google that is available on any device that runs ARCore. It lets you measure smaller dimensions quickly by just using your smartphone camera. 13. Find Your Car With AR – In case you forget Do you often forget where you parked the car and waste time over searching for it? Here’s the right solution. ‘Find Your Car With AR’ lets you see where you have parked the car, the street address, date and time of parking and much more. This AR-based app is most helpful when you park the car in crowded areas like stadiums, malls, convention centers, etc. 14. Taco Bell – Product packaging with an AR twist

When Taco Bell released its new Doritos Locos Tacos, it placed an AR feature in its app. Users can scan the product box using the app to see product-related content in Twitter and Facebook. This way, the restaurant chain employed AR technology to create a sense of community. 15. Acura – “What a Race” in Augmented Reality Acura, the luxury vehicle marque of Honda, embraced augmented reality last year by hosting the world’s first-of-its-kind live augmented reality driving experience. Named as “What a Race,” it was broadcasted on Facebook Live as part of the marketing campaign of the new 2018 TLX from the Japanese automaker. 16. Volkswagen’s AR system for workforce assistance

The German automaker, Volkswagen has introduced an AR system to guide its workers in navigating through a factory. This AR system helps the worker move anywhere in their massive factories to find a specific machine and then overlay the information they need for the task, on the spot. The company plans to use AR technology for autonomous indoor driving and guide visitors inside the factory in the near future. 17. StubHub’s AR feature for Super Bowl fans StubHub wanted to help football fans who are uncertain about the location of their seats in the stadium for the Super Bowl matches. They came up with an AR-based feature in their iPhone app to improve the overall Super Bowl experience of ticket-buyers. They can actually visualize the location of their seats, parking garages and pre-game events in the surrounding area. 18. Wikitude – The AR browser app Wikitude app is appreciated by travelers as it provides location-based augmented reality experiences and geographically relevant information. You can also get information regarding accommodation, hotel deals etc. using the app. It includes many amazing features like 3D model rendering, image recognition, tracking, and video rendering to name a few. 19. Tactical Augmented Reality for the military force Augmented Reality has been intelligently put into action by the United States Army. The technology called ‘Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR)’ is majorly used to improve situational awareness of soldiers. TAR uses goggles with night-vision which are wirelessly connected to a tablet that soldiers carry on their waists. The exciting part of TAR is that when a soldier points a weapon, the image of the target along with their details can be seen through the eyepiece. 20. Wiring worries of Boeing solved with AR Boeing, the aircraft manufacturer, uses an AR solution to speed up the wire repair process and eliminate wiring errors in the plane. This hands-free device, similar to a Google Glass, lets technicians see the wiring in the plane and gives step-by-step directions using voice commands. Additionally, workers can get expert advice from remote engineers as well, using a special feature in this AR-based solution known as Skylight. 21. Aecomis uses Mixed Reality for complex projects Architects and engineers at Aecomis work in collaboration from its Hong Kong, Denver and London offices using Mixed Reality. The company uses Microsoft Hololens Technology that projects 3D engineering models as holograms at multiple locations. The team members can walk through the visualized models of complex projects from their respective locations and thereby avoid architectural errors in the projects before construction. 22. SAVED – An oxygen mask with smart glasses Inflight smoke, fume or fire is the leading cause of emergency landing and delays. To solve this problem, FedEx Express cargo will soon introduce an oxygen mask that will include smart glass. The pilot will get the display of flight controls quickly in the mask and thus ensure safe landing of the plane immediately. ODG has come up with this AR-based technology and it is named as Smoke Assured Vision Enhanced Display (SAVED).
AR is the reality of our future
Augmented Reality is a technology in its infancy. The biggest benefits of augmented reality technology are yet to come. It has opened up tremendous possibilities. Your imagination is the only limit when it comes to AR technology. The above-mentioned examples will probably inspire you to use this new technology innovatively to grow your business. The power of AR tech is undeniable. If you are reluctant to embrace it now, your brand may be left behind in the race. Brands that acknowledge this and take necessary action will be well-positioned to capitalize on this transformation. Adding AR into your business strategy is slowly becoming a need of the hour. It can be cleverly put into action to improve the business processes, enhance customer experience and boost customer engagement, to name a few. The above-listed examples are just a tip of the iceberg. The imaginative concepts you have seen in science fiction movies can now be transformed into reality with the right AR technology. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Man vs Machine, Why we have to Join the Same Team
James Thornton @00518800
For this post I will be looking at the future of technology and digital media and attempting to create I visual of what this future could be. The main point I will be focusing on in this future is artificial intelligence and its relationship with humans.
The Integration of AI into Human Life
“I think we should be very careful about artificial intelligence. If I were to guess like what our biggest existential threat is, it’s probably that.” - Elon Musk (2014)1
The use of artificial intelligence has been commercially available for quite a while with various voice activated toys and chatbots being developed since the late 20th century. This technology really picked up when Apple introduced the world to Siri in 2011. Apples virtual assistant was not the most optimized piece of AI when it originally launched but it was the first name of many that people could call to get assistance from the machines around them. Coming into 2020 and homes around the globe now function with the help of Amazon created Alexa and Googles home assistants. These three personal assistants have increased the symbiosis between humans and machines having access to homes and cars as well as users giving permission for them to communicate with their friends and peers. This common example of AI into our lives maybe a very simple look into the future of our relationship with media and technology.
“…today, if you don’t bring your phone along, its like you have missing limb syndrome. We are already partly a cyborg” - Elon Musk (2020)2
The convenience of having everything all in one place has conditioned us into placing a huge importance on our phones and computers, such that when we are without them, we can feel lost and unproductive. Instead of having to think for ourselves and go out of our way to do simple tasks such as shopping, we find it so much easier and in some cases more enjoyable to pull out our phones and search the web or load up Amazon and eBay and then wait a few days for the fruits of our machines labour to arrive. This has evolved further with virtual and augmented reality. Originally a novelty allowing people to pretend to ride rollercoasters it can now be used to replace experiences like live events and concerts, as well as help develop medicine and other vital products easier and cheaper than ever before. Augmented reality has evolved from catching Pokémon and creating Snapchat filters to enhancing education and learning across all ages. Museums are looking into mixed reality exhibits to help demonstrate what the past and future can look like in a much more engaging form that static exhibits.
youtube
An AR Museum Exhibit ^4
The third reason I feel a merge between human and machine is inevitable in the future is down to countless attempts to enhance and further our abilities with new technologies. The most obvious examples are in the medical field and prosthetics. People have undergone surgery to replace amputations and new mechanical prosthetics have been more able than their biological predecessors. Even further than this robotic prosthetics have been developed that allow full use of limbs without any implants to the brain. Trying to alter the brain is another heavily invested in venture for our future. One of the most high-profile attempts is the highly anticipated Neuralink device. The first implications of this concept is to improve damaged spinal, nerve and brain injuries such as paralysis, dementia and epilepsy.
"The long-term aspiration with Neuralink would be to achieve a symbiosis with artificial intelligence." - Elon Musk (2018)3
The benefits of this according to CEO Elon Musk, would be the ability to make humans hyper smart as well as potentially alter the very basics of human communication. Predictions of implementing such a device to the brain see interaction on almost a telepathic level and the chance to interact through visual images and thoughts instead of spoken word. Whilst this appears on the surface as a pipe dream, Musk appeared on podcast The Joe Rogan Experience in May 2020 and exclaimed that the initial stages of the chip can be implemented ‘within a year’.
youtube
Elon Musk discussing his Neuralink Technology on the Joe Rogan Experience ^5
Pairing this attempt to change the way our brains can give and receive information with mixed reality technologies could enhance experiences and industries like education to levels only seen in sci-fi films and dreams. Physical items such as pen and paper may become obsolete, the potential for keyboard and mouse to fade away is there as well depending on how this could allow us to communicate with machines. Thanks to the COVID-19 pandemic and the sudden rise of online conferences, lectures and entertainment experiences could also join this almost scary ensemble of unfathomable potential to give a future that seems more Matrix than everyday reality.
In conclusion I feel the future of digital media and technology involves a union between humans and the devices we use, reshaping the way we live, communicate and consume information. With that said, the extent to which this happens, staying forever a concept and basic prototype or achieving its unthinkable potential, only remains to be seen.
1M. McFarland, 2014, Elon Musk: ‘With artificial intelligence we are summoning the demon.’ The Washington Post, viewed 20/5/20 <https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/innovations/wp/2014/10/24/elon-musk-with-artificial-intelligence-we-are-summoning-the-demon/>
2E. Arevalo, 2020, Elon Musk discusses Neuralink brain chip plans with Joe Rogan, Tesmanian, viewed 20/5/20 <https://www.tesmanian.com/blogs/tesmanian-blog/neuralink-musk>
3Axios, 2018, 1. Elon Musk: Humans must merge with machines, viewed 20/5/20 <https://www.axios.com/elon-musk-humans-must-merge-with-machines-1543240787-c51eee35-8cb3-4684-8bb3-7c51e1327b38.html>
4 INDE, 2015, Augmented Reality dinosaurs at Smithsonian Museum of Natural History, Washington DC by INDE, Viewed 20/5/20 <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gkLD5XkOlng&feature=emb_title>
5 JRE Clips, 2020, Elon Musk Reveals New Details About Neuralink, His Brain Implant Technology , viewed 20/5/20 <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gqdo57uky4o&feature=emb_title>
0 notes
Text
Success Secrets You Can Learn From Today’s Top Retailers
In the world of retail, every business must now market across both digital and physical channels. It doesn’t matter if you have a brick-and-mortar store, an e-commerce website or both. Cross-channel marketing is essential to success. The latest Sailthru Retail Personalization Index examines what it takes to succeed at cross-channel marketing. And it ranks the 100 retailers who are best at that game. Keep reading to find out what Sailthru measured. And see what you can learn from the top 10 retailers on the list.
How the Top Retailers Are Chosen
Sailthru’s process begins with a list of 250 retailers. The team members review these in a process called “experiencing the brand.” The testers evaluate the retailer’s site. They also review their app, email, product purchase experiences and so on. The reviews are done from the perspective of a customer. Sailthru then ranks retailers on 78 criteria in seven categories. These include site, email, mobile, offline, privacy, other digital and bonus. It then combines its review scores with data from 1,500 customer surveys. From this a final ranking emerges. (Read more about the Sailthru survey methodology.)
What the Best Retailers Do Right
“Customers are highly engaged on mobile and email, not just on site and in store,” said Jason Grunberg, VP of Marketing at Sailthru, when announcing the results. “The brands that performed best in the Retail Personalization Index do two things right: They deliver deep personalization on individual channels and they deliver experiences between channels that keep customers coming back.”
What do top brands have in common? In comparing the top 25 to those that did not make the top 100, Sailthru found:
Through their websites, 88% of the top 25 brands had personalized recommendations vs. only 21% of brands that didn’t rank.
Via email, 96% of the top 25 brands provided personalized product recommendations compared to 23% of unranked brands.
On mobile, 84% of the top 25 brands use push notifications vs. 10% of unranked brands.
Lessons from the Top 10 Retailers of 2019
Here’s a closer look at the top 10 cross-channel retailers for 2019 and what you can learn from each one.
Sephora
Number one for the third year running, Sephora consistently delivers a unified experience across all channels and “pushes the envelope” with innovative events and customer service. Delivering excellence both in brick-and-mortar and online, it stands out for its generous rewards/loyalty program and triggered emails that engage customers with deep personalization.
What you can do: Use triggered emails such as abandoned cart notifications or discount offers to encourage purchasing and keep customers coming back. Build a community around your loyal customers by engaging with them on all channels, celebrating user-generated content and holding special events.
Nordstrom
Nordstrom has long been known for its in-store customer service and this year it rose to number two by providing that same outstanding service online. The website stands out for personalized product recommendations, using customers’ shopping and browsing history to display personalized offers such as new markdowns on products they’ve viewed or new items from brands they love.
What you can do: Offer white-glove service such as curbside pickup, free alterations and personal shopping services. Take advantage of tools that can recommend products customers will like, both online and off. For example, loyalty program software can deliver the info you need to suggest purchases to shoppers in store based on past purchases.
Rent the Runway
This formerly online-only clothing rental business is now opening brick-and-mortar locations. User-generated content — product reviews and photos of customers wearing clothing they’ve rented—are key in creating a customer experience and building trust and loyalty. The company gathers oodles of details on members and uses them to provide spot-on recommendations of everything from style to what size to order.
What you can do: Customer reviews can be gold if you know how to use them. If your e-commerce website includes product reviews, try offering incentives to get customers to review items, and provide guidance about what types of details to include (the more, the better). Keep in mind that when you use customer data to deliver real value, customers will be more likely to share with you.
Home Depot
Home Depot’s website and mobile app excel at providing product recommendations, including suggesting add-on or related products that shoppers might need for their home improvement projects. Location-based services are also key for this retailer; shoppers can see what’s available at their local store and locate products within the store as well. The company’s website and blog share useful how-to information and ideas to inspire shopping.
What you can do: If you have more than one retail location, help customers differentiate them and find in-stock products at the store they want to visit. Use robust recommendation engines on your website that can suggest complementary products, too. Almost every business can benefit from offering “how-to” content; a clothing boutique can share how to put an outfit together for a clothing boutique or a housewares store can show how to make stir-fry.
Best Buy
With so much to sort through in the electronics world and so much riding on those decisions, Best Buy succeeds by providing thousands of product reviews and access to real-life product experts both in-store and online. Like Home Depot, their website is highly localized. Best Buy’s customer loyalty program also offers lots of value, including dedicated support and discounts.
What you can do: If you sell products that are pricey, very similar, and difficult to compare, offer all the tools you can to help shoppers sort them out. Product reviews, detailed product specs and product comparison tools on your website will help. However, there’s no substitute for the knowledge of a real-life person who can make suggestions and offer recommendations.
DSW
The discount shoe retailer stands out for its loyalty program which has increased sales by 6% year-over-year. An extensive personalization quiz tailors loyalty program offers to the specific shopper. Loyalty members get deep discounts, exclusive perks, members-only event invitations and rewards points that never expire.
What you can do: A loyalty program can be so much more than a punch-card. Implement loyalty program software that gathers detailed data on your best customers; then use that information to design rewards that will really motivate them. Don’t forget to treat your loyalty program members as VIPs and combine in-store and digital engagement opportunities.
Ulta
Customization and personalization are key for this beauty retailer. Ulta’s mobile app has tons of quizzes, allows users to try on products virtually, and lets them set detailed preferences that help the app make recommendations. Rewards are tailored to individual customers’ preferences, while in-store events help to build relationships.
What you can do: Capture as much data as you can on your shoppers’ preferences. Listen to their feedback and use it to create the perfect product mix. Make your store a desirable destination with in-store events that drive engagement.
Urban Outfitters
Given its youthful target market, it’s no surprise this retailer scored points for its excellent mobile app. Product recommendations become more robust the more users engage with the website or app. Urban Outfitters also makes good use of user-generated content and provides detailed filters that let consumers shop based on brand, style, price and more.
What you can do: Particularly if you have a young customer base, your mobile experience is key. Use text message marketing, push notifications and geolocation to interact with shoppers both inside and outside your store.
Adidas
The legendary activewear brand makes a splash with advertising that makes a statement. For example, campaigns that use celebrities and spotlight women athletes. The customer relationship starts with an extensive quiz that gathers information on customer preferences and then uses what is learned to generate highly personalized content. The loyalty program, Creators Club, is highly gamified, allowing customers to unlock new levels and discounts every time they interact with the retailer.
What you can do: Don’t be afraid to take a stand in your marketing message. Use your store to inspire your customers, not just sell to them. Treat your customers as equals in generating ideas for both digital content and store inventory.
Wayfair
Once online-only, this home furnishings retailer recently opened its first stores. Wayfair carries “zillions” of items in stock online. The site sorts, filters and gets accurate product recommendations. This keeps shoppers from getting overwhelmed. Wayfair offers free shipping among its many perks for loyalty program members. The company sells furniture. As a result, free shipping alone proves enough to make the loyalty program fee worth it. There’s also an augmented reality tool that lets shoppers see what furniture looks like in their homes.
What you can do: The more products you sell online, the better your search, filtering and recommendation functions need to be. Live chat helps keep customers on-site. It talks them through their options. Offer something worthwhile in your loyalty program. And try to get customers to pay to join.
Image: Depositphotos.com
This article, “Success Secrets You Can Learn From Today’s Top Retailers” was first published on Small Business Trends
https://smallbiztrends.com/
The post Success Secrets You Can Learn From Today’s Top Retailers appeared first on Unix Commerce.
from WordPress https://ift.tt/36EOEcu via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
DEFENSE AND INFRINGEMENT BY CHRISTINE ANN MCCALLA
SEE LINK https://drive.google.com/open?id=1ne-0II6CBwouBdbtfJznLjTUqnWEJuF41ADUgBAKzRY
DEFENSE AND INFRINGEMENT BY CHRISTINE ANN MCCALLA
This is the sole conception, design, and research of Christine Ann McCalla and all variations thereof. It was created as a continuation of the basis of probable military relationships, their incentives and consequences, (carrot and the stick), and the opportunity for collaboration with substantial assets for, and in lieu of, trade, exchange, commerce, bartering, and skills / knowledge transference, etc. and vice versa.. This also covers the extension of credit for collaboration, armed forces and their required industries, sectors, and vulnerabilities as a legitimate, certified, cohesive unit, paramilitary force, or as militia An additional element considered and evaluated here is infringement, the incentives and opportunities to do so, as well as the possible rewards thereof, both legitimately and other, temporarily and on a permanent basis.This work did not require and as a result does not include collaborative, team, or hybrid group efforts of any form, manner, or content. Given the separation of my discipline and competence (business oriented) and the defense industry, there are no conflict of interests or conflicted interests involved. No funding was received in the conception, design, and research processes, conceptual, developmental or completion. DISCLOSURE The following are excerpted from Munich Security Report 2017EU role in world affairs and vote in referendum Defense expenditure in Western, Eastern Europe, and in comparison Increased defense spending survey, and combination forces European defense institutions, proposals, and plans Russian airstrikes and other factors in Syria Humanitarian crisis in Syria and funding requirements with gap US disposition in Western Pacific Naval capacities of select countries five years ago and todayDecline of freedom around the world Development of global trade volume since 1980 and stagnating and declining in select advanced economies The following are excerpted from World Air Forces 2015Global military fleet Worldwide active fleet per region Worldwide active fleet per region (cont’d) Fleet size for leading countries by role Industry sectors most targeted by nations-state IT security incidents in 2014 The following are excerpted from Microsoft Security Intelligence Report Volume 18Number of computers reporting CVE-2014-6332 exploit attempts daily Number of computers detected being attacked each day in the campaign against government and aerospace websites Industrywide vulnerability disclosures Industrywide vulnerability disclosures by severity Industrywide vulnerability disclosures by access complexity Industrywide operating system, browser, and application vulnerabilities Vulnerability disclosures for Microsoft and non-Microsoft products Encounter rates for different types of exploit attempts in 2014 The following are excerpted from Transatlantic Trends 2012EU-US Relations and World Affairs Leadership Favorable opinions of the EU and the US Most important region to and for national interests Does China represent economic opportunity or threat? Personally affected by recent economic crisis Perception of fairness of economic system and decision regarding government spending Effect on the economy: EU members vs. using the Euro Approval of more EU economic oversight of national finances EU desire for strong US leadership in world affairs vs approval of US president Decrease government spending vs. decrease defense spending What to do about defense spending in light of the US Pivot to Asia? Support for measures against Iran’s nuclear program War is sometimes necessary to obtain justice The following are excerpted from Conflict Barometer 2014Conflict intensity Conflict - weaponry Assessing the intensities of violent conflicts Conflict - personnel and casualties Conflict - means and destruction Global conflict panorama Global conflict panorama (cont’d) Global conflicts w/ varied intensity and dates and distribution of conflicts Overview: current UN Missions led / supported by DPKO Conflicts in Europe in 2014 Conflicts in Europe in 2014 (cont’d)Conflicts in Europe in 2014 (cont’d) Conflicts in Europe in 2014 (cont’d) Virtual reality software and hardware market size worldwide from 2016 to 2020 In which fields of application do you think virtual reality headsets are likely to be used?Forecast user base of the augmented and virtual reality (VR) software market worldwide in 2020 and 2025 ln which fields of application-virtual reality headsets likely to be used? Forecast size of the augmented and virtual reality (VR) market worldwide in 2020 and 2025 Industries targeted by machine learning application developers, as of 2016 Forecast distribution of the augmented and mixed reality market worldwide in 2022Robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide market size estimates Excerpted from Artificial intelligence and life 2030 (cars) Threat intelligence security services expenditure worldwide from 2009 to 2018 How automated are your security analytics and intelligence processes? Market revenue of top 10 cases / segments of artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide Revenue from the artificial intelligence for enterprise applications market in the Middle East and Africa How automated are your security analytics and intelligence processes? References
Artificial Intelligence and Life in 2030. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/study/38608/artificial-intelligence-study-2016/
Bank of America. (n.d.). Robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide market size estimates, based on 2018 to 2030 forecasts, by segment (in billion U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/621656/worldwide-artificial-intelligence-robotics-segment-estimates/.
Conflict Barometer 2014. Retrieved May 13, 2017 from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/study/26792/report-on-global-conflicts-2014/
Forbes. (n.d.). Industries targeted by machine learning application developers, as of 2016. In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/602784/worldwide-machine-learning-industry-focus/.
Goldman Sachs. (n.d.). Forecast user base of the augmented and virtual reality (VR) software market worldwide in 2020 and 2025, by segment (in millions). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/610126/worldwide-forecast-augmented-and-mixed-reality-software-users-by-segment/.
Goldman Sachs. (n.d.). Forecast size of the augmented and virtual reality (VR) market worldwide in 2020 and 2025, by segment (in billion U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/610112/worldwide-forecast-augmented-and-mixed-reality-software-market-by-segment/.
IDC. (n.d.). Threat intelligence security services* expenditure worldwide from 2009 to 2018 (in million U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/417588/threat-intelligence-security-severices-spending-worldwide/.
Microsoft Security Intelligence Report Volume 18. Retrieved May 13, 2017 from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/study/28084/microsoft-s-worldwide-and-regional-cyberthreat-assessment-2014/
Munich Security Report 2017. Retrieved May 13, 2017 from, https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/study/44205/munich-security-conference-report-2017/
PwC. (n.d.). Industry sectors most targeted by nations-state IT security incidents in 2014. In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 13, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/387974/cyber-crime-nation-state-incidents-industries/.
SANS Institute. (n.d.). How automated are your security analytics and intelligence processes?*. In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/499710/survey-information-security-automation-levels/.
SuperData Research. (n.d.). Virtual reality software and hardware market size worldwide from 2016 to 2020 (in billion U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/528779/virtual-reality-market-size-worldwide/.
Statista. (n.d.). In which fields of application do you think virtual reality headsets are likely to be used?*. In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/457056/virtual-reality-headset-applications-in-the-united-states-by-age-group/.
Statista. (n.d.). In which fields of application do you think virtual reality headsets are likely to be used?*. In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/457059/virtual-reality-headset-applications-in-the-united-states/.
Tractica. (n.d.). Revenues from the artificial intelligence for enterprise applications market worldwide, from 2016 to 2025 (in million U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/607612/worldwide-artificial-intelligence-for-enterprise-applications/.
Tractica. (n.d.). Market revenue of top 10 use cases/segments of artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide, from 2016 to 2025 (in million U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/607835/worldwide-artificial-intelligence-market-leading-use-cases/.
Tractica. (n.d.). Revenue from the artificial intelligence for enterprise applications market in the Middle East and Africa, from 2016 to 2025 (in million U.S. dollars). In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/607677/middle-east-africa-artificial-intelligence-for-enterprise-applications/.
Transatlantic Trends 2012. Retrieved May 13, 2017 from, https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/study/11714/transatlantic-trends-2011/
World Air Forces 2015. Retrieved May 13, 2017 from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/study/25683/report-about-combat-fleets-worldwide-2015/
Woodside Capital Partners. (n.d.). Forecast distribution of the augmented and mixed reality market worldwide in 2022. In Statista - The Statistics Portal. Retrieved June 14, 2017, from https://www-statista-com.proxy1.ncu.edu/statistics/610066/worldwide-forecast-augmented-and-mixed-reality-software-assumptions/.
0 notes
Text
Without these high-performing components working in sync, you could have a pretty miserable experience. A powerful system will ensure that you’ll have fun as you lean in, stand up, or walk around. VR that lags makes it impossible for the virtual world to respond as you expect, which can lead to more than just disappointment; it increases the risk of motion sickness.A high-end processor assists in positional tracking and controls how real and immersive your virtual environment will be, so you'll enjoy a deeper experience in a higher-fidelity environment. For a great VR experience, consider the latest generation Intel Core™ i7 processor.A discrete graphics processing unit (GPU) is recommended, or in the case of Oculus Rift*, HTC Vive*, and Windows Mixed Reality Ultra*, it is required. The GPU is responsible for rendering the high resolution, immersive images needed for VR. Oculus, HTC, and Microsoft all have profiler tools that you can download from their websites, and you can use to run on your PC to determine if it meets the minimum requirements for their VR headsets.Choose Your Experience New VR and AR technologies and products continue to come to market, making new environments accessible to the masses. Virtual, Augmented, Mixed—the choice for a new reality is up to you. Let your imagination, and your readiness to try new gear, enhance your experience!Key VR Terms to Know Use this chart to learn more VR terms and definitions.Using Virtual Reality Technologies From gaming, to movies, to medicine, the uses for Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality are expanding.Healthcare—For training, such as for surgical simulationsFilm and TV—For movies and shows to create unique experiencesVirtual travel—For virtual trips to an art museum—or another planet—all from homeProfessional sports—For training programs like STRIVR to help pro and amateur athletesGaming—For over 1,000 games already available, from first-person shooters to strategy games to role-playing adventuresDemystifying the Virtual Reality Landscape
The differences between Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality, and how you can get ready to experience a new reality for yourself.
Learn more about this landscape and the requirements for a computing system that can handle the demands of these new, immersive experiences.
The border between the virtual and real world continues to break down, providing breathtaking experiences that, a short time ago, could only be found in the imagination of sci-fi writers.
Virtual Reality (VR) has been the “next big thing” for several years, but its time has finally come as a way to generate realistic images, sounds, and other sensations that put you smack in the middle of a spectacular imaginary world. Augmented Reality (AR), which adds virtual stuff to your real world environment, is contributing to the buzz, and both technologies should become a big part of our future. With Mixed Reality (MR), you can play a virtual video game, grab your real world water bottle, and smack an imaginary character from the game with the bottle. Imagination and reality have never been so intermingled.
So much is happening so fast that the differences between VR, AR, and MR can seem a little puzzling at first. Each of these spellbinding technologies are accessible to almost everyone, but before you throw down your hard-earned money for the latest head-mounted display, let’s take a closer look at what you’ll need for an amazing VR, AR, or MR experience.
The History and Future of Virtual Reality We’ve been trying to capture “Virtual Reality” for much longer than just the past five to ten years. There were popular peer-through toys in the 1950s and enclosed flight simulators debuted in the 1960s, but the idea of VR goes back even further.
As early as the 1930s, science fiction writers, inventors, and tinkerers dreamt of an environment where you could escape from reality via art and machines. We were weighing questions about Virtual Reality vs. Augmented Reality vs. Mixed Reality long before we had the technology to make them possible.
Technology has caught up to fiction, and market researchers predict rapid growth for the VR industry.
VR and AR Meet MR First things first, let’s define the terminology. Virtual Reality can be used as an umbrella term to describe other technologies similar to, but different from, an actual Virtual Reality experience. But what's the difference between Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality? Here are some more details:
Virtual Reality VR is the most widely known of these technologies. It is fully immersive, which tricks your senses into thinking you’re in a different environment or world apart from the real world. Using a head-mounted display (HMD) or headset, you’ll experience a computer-generated world of imagery and sounds in which you can manipulate objects and move around using haptic controllers while tethered to a console or PC.
Augmented Reality AR overlays digital information on real-world elements. Pokémon GO* is among the best-known examples. Augmented reality keeps the real world central but enhances it with other digital details, layering new strata of perception, and supplementing your reality or environment.
Mixed Reality MR brings together real world and digital elements. In mixed reality, you interact with and manipulate both physical and virtual items and environments, using next-generation sensing and imaging technologies. Mixed Reality allows you to see and immerse yourself in the world around you even as you interact with a virtual environment using your own hands—all without ever removing your headset. It provides the ability to have one foot (or hand) in the real world, and the other in an imaginary place, breaking down basic concepts between real and imaginary, offering an experience that can change the way you game and work today.
Using Virtual Reality Technologies From gaming, to movies, to medicine, the uses for Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality are expanding.
Healthcare—For training, such as for surgical simulations
Film and TV—For movies and shows to create unique experiences
Virtual travel—For virtual trips to an art museum—or another planet—all from home
Professional sports—For training programs like STRIVR to help pro and amateur athletes
Gaming—For over 1,000 games already available, from first-person shooters to strategy games to role-playing adventures
What You’ll Need: Headsets There are many, many VR headsets available, all with varying performance levels and prices. Entry-level gear, such as Google Cardboard*, uses your mobile phone as the screen, whereas PC-operated devices, like the HTC Vive* or Oculus Rift*, are immersive—providing a premium VR environment. Microsoft has recently announced their Windows* 10 Mixed Reality platform that initially uses fully immersive headsets offered by Acer, Asus, Dell, HP, Lenovo and Samsung.
Some AR headsets are available on the market today, with more rumored to be coming in the future. The Microsoft Hololens*, Google Glass*, and the Meta 2* headset are great examples.
Every PC-connected HMD will have different system requirements, so if you’re buying a new Virtual Reality headset, make sure you check with the HMD vendor for their recommended and minimum system requirements.
What You’ll Need: Computers If you are looking for a new computer and you’re interested in VR, you’ll need something that can handle heavy loads. When it comes to high-end desktops or laptops for Virtual Reality (and other advanced tasks like gaming or video editing), the CPU, GPU, and memory are the most critical components.
Without these high-performing components working in sync, you could have a pretty miserable experience. A powerful system will ensure that you’ll have fun as you lean in, stand up, or walk around. VR that lags makes it impossible for the virtual world to respond as you expect, which can lead to more than just disappointment; it increases the risk of motion sickness.
A high-end processor assists in positional tracking and controls how real and immersive your virtual environment will be, so you'll enjoy a deeper experience in a higher-fidelity environment. For a great VR experience, consider the latest generation Intel Core™ i7 processor.
A discrete graphics processing unit (GPU) is recommended, or in the case of Oculus Rift*, HTC Vive*, and Windows Mixed Reality Ultra*, it is required. The GPU is responsible for rendering the high resolution, immersive images needed for VR. Oculus, HTC, and Microsoft all have profiler tools that you can download from their websites, and you can use to run on your PC to determine if it meets the minimum requirements for their VR headsets.
Choose Your Experience New VR and AR technologies and products continue to come to market, making new environments accessible to the masses. Virtual, Augmented, Mixed—the choice for a new reality is up to you. Let your imagination, and your readiness to try new gear, enhance your experience!
Key VR Terms to Know Use this chart to learn more VR terms and definitions.
Term
Description
Why It Matters
Frames per second (FPS)
Frequency at which a system can display consecutive images, or frames
Without a high and constant frame rate (greater than 60 FPS), the motion won’t look right, and you could even feel sick
Field of view
The angle of the observable world that can be seen
If the window of view is too narrow, you could end up making unnatural head rotations
Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
The number of directions that an object can move or rotate. The six degrees of freedom are pitch, roll, yaw, left and right, forward and backward, up and down
More DoFs allow you to move more naturally in VR
Latency
The amount of time it takes a system to react/respond to movements or commands
Latency is critical when it comes to the presence inside Virtual Reality—if the system doesn’t respond instantly, it doesn’t feel real.
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/tech-tips-and-tricks/virtual-reality-vs-augmented-reality.html
0 notes
Text
Qt AR: Why and How to Add Augmented Reality to Your Mobile App
Improved AR capabilities for mobile platforms are one of the biggest trends of 2018. Apps with AR features like Yelp, Google Translate or Pokémon GO are only the beginning. Augmented reality allows to create innovative user experiences that support your brand.
Mobile AR is on the Rise! Why?
Differences between VR and AR
Advantages of Immersive Experiences in Mobile Apps and Games
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
Why use Wikitude instead of ARKit or ARCore?
Advantages of the Wikitude SDK Architecture
How to Use the Wikitude AR Plugin in Qt Apps
How to Use the Wikitude AR Plugin in Native iOS & Android Apps
Why to use Qt & V-Play for Mobile App Development
How to Use Image Recognition and 3D Tracking in Your Mobile App
Wikitude Makes Image Tracking Easy
The Power of Instant Tracking and 3D Rendering
More AR Examples
What’s the Future for AR?
Mobile AR is on the Rise! Why?
Since the release of Apple’s ARKit and Google’s ARCore, augmented reality made its way into the mobile market. For example, to make it possible to:
Catch virtual monsters in your neighborhood. (Pokemon GO)
See restaurant descriptions while you’re walking the street. (Yelp)
Translate texts while you view a sign. (Google Translate)
Those apps mix the real world with computer-generated content. They thus show the user a different reality. In that sense, augmented reality (AR) is quite similar to virtual reality (VR), which is why they are often confused.
Differences between VR and AR
Both technologies can change the way you look at the world. However, they aim towards a different goal. Virtual reality tries to build a simulated environment around the user. It can take you to places you’ve never seen and allows you to enter a new world. When VR does its job right, you will believe that you are actually there. For example, when driving in a virtual reality racing simulator:
In contrast to VR, augmented reality does not take you to a different place. It enhances the world around you with digital information. For example, to see the route of your navigation system mixed into the real street image while driving in your car.
The world’s first pedestrian and car navigation system that integrates AR was the Wikitude Navigation app. The app was a revolutionary step forward in the navigation and guidance field and eliminates the need for a map.
Advantages of Immersive Experiences in Mobile Apps and Games
Since Apple launched its app store with 20k apps in 2008, it experienced a rapid growth and now offers more than 3M apps. More than ever, businesses and developers thus thrive to provide unique app experiences that support their brand. They empower users to be creative and connect in order to boost engagement and retention rates.
Mobile AR now allows to create immersive app experiences to surprise and engage the users. Businesses have understood this potential and the International Data Corporation forecast for 2018 even expects worldwide spendings on AR and VR to increase by 95%. Let’s have a look at some innovative AR apps:
Telekom: Lenz – Gorillaz App
Telekom Electronic Beats partnered up with the Gorillaz to create a new dimension in music. The Lenz app transforms magenta surfaces into digital portals which display exclusive Gorillaz content.
youtube
Washington Post App: Unesco Heritage
The Washington Post has published another successful AR-enhanced story. This time, the Post’s article promotes all 23 of the UNESCO World Heritage sites situated in the USA. To get readers to learn about, appreciate, and visit these locations, the daily newspaper included an AR feature to get users even more involved with the story.
youtube
Augmentors: Real Monster Battles
Following in the footsteps of Pokemon GO, Augmentors is the world’s first cross-platform (iOS & Android) augmented reality game backed by the Bitcoin Blockchain. Players can trade, swop, battle, and train gaming creatures in the real world. Early stage game supporters will be rewarded with unique currency and one-of-a-kind creatures.
youtube
Augmented Cocktails: AR in Low-Light Conditions
It can be difficult to provide rich AR experiences in all kinds of situations. For example when dealing with low-light scenarios. City Social in London is known for providing great food, drinks, service and a stunning skyscraper view. With the intention of delighting their customers, even more, they paired with Mustard Design. To create an innovative app that brings their cocktails to life:
youtube
Lufthansa AR Aviation Demo
Instead of shipping and installing costly demo equipment to be displayed at trade show exhibitions, Lufthansa Technik is innovatively using augmented reality technology to show their customers detailed installation information and connectivity solutions.
youtube
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
The above showcases all rely on the mobile device camera and sensors to track images, objects and scenes of the real world:
Telekom recognizes magenta surfaces to replace it with different content.
The Washington Post app tracks reader’s surroundings and instantly layers the camera view with virtual animals like a bison.
Augmentors combines such Instant 3D Tracking with Image Recognition to bring game cards to live.
Another example app that relies on location-based AR is the Osmino app: A quick scan of your surrounding provides you with a comprehensive listing of all free Wi-Fi hotspots around you:
You can integrate some of these features in your mobile app with Apple’s ARKit and Google’s ARCore. But you also have the option to rely on cross-platform tools which go beyond ARKit and ARCore. In fact, the above showcases are all built with the Wikitude AR SDK.
Why use Wikitude instead of ARKit or ARCore?
Being in the market since 2008, Wikitude bridges the gap between different devices, platforms, and levels of AR support. With a single cross-platform API, it allows over 100,000 developers to integrate AR features across iOS, Android and Windows with a single code base, >while having a much higher market reach than ARKit and ARCore.
Advantages of the Wikitude SDK Architecture
Wikitude provides a rich AR experience across platforms. To achieve that, it relies on several abstraction layers:
The Core Components handle features like Image Recognition and Object/Scene Recognition. Wikitude built the so-called SLAM Engine to offer all AR features across devices and platforms.
In case Apple’s ARKit or Google’s ARCore are available, Wikitude can dynamically switch to these native frameworks instead of its own engine. In addition, Wikitude can also run on iOS, Android and Windows devices that do not have such native support for AR.
So compared to native development with ARKit or ARCore, Wikitude even supports AR on devices that are not able to run native AR features via ARKit or ARCore. This is a huge benefit, because your app is not bound by the market coverage of ARKit or ARCore. See this table for a comparison of ARKit and ARCore supported devices, vs the ones supported by Wikitude:
iOS ARKit Device Coverage: 81% (minimum iOS 11.0 + iPhone 6S, iPad 5 and newer models)
iOS Wikitude Device Coverage: 92% (iOS 9.0 + iPhone 4, iPad 2 and newer models) → Wikitude has + 11% iOS device coverage compared to ARKit
Android ARCore Device Coverage: 5% (minimum Android 7.0 + currently about 50 device models out of the thousands in the market)
Android Wikitude Device Coverage: 95% (minimum Android 4.4 + most existing device models), which means → Wikitude has +90% Android device coverage compared to ARCore
For detailed infos which devices are supported, see the official developer docs by Apple for ARKit supported devices, iOS version market share, and by Google for ARCore supported devices.
So if your goal is to make your app available on as many devices as possible, Wikitude is the go-to solution.
To use Wikitude, you can embed a their augmented reality view into your existing native apps. It is not required to modify other views of your iOS, Windows or Android app. Wikitude also offers several plugins to use their SDK in conjunction with cross-platform app frameworks like V-Play, via its Qt Plugin.
How to Use the Wikitude AR Plugin in Qt Apps
The Wikitude Qt AR Plugin developed by V-Play offers an API to:
Integrate Wikitude in Qt applications, and also
into existing or new native applications.
The Wikitude Qt AR plugin builds upon the native APIs of Wikitude and can run augmented reality worlds created with the Wikitude JS API.
If you have an existing or newly developed app based on Qt, you can simply load the Wikitude AR Plugin from QML-based Qt Quick applications or C++-based Qt Widgets applications.
How to Use Image Recognition and 3D Tracking in Your Mobile App
Since the release of V-Play Engine’s Wikitude Plugin you can integrate and use the Wikitude AR SDK in your Qt cross-platform app. It only takes a few lines of code. The examples below show how to run some of the Wikitude AR examples with V-Play.
Wikitude Makes Image Tracking Easy
The following demo code includes everything you need to embed a Wikitude view in your QML app. This example tracks certain images and overlays a transparent video, as if it were part of the image:
import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 import QtQuick 2.0 import VPlayApps 1.0 import VPlayPlugins 1.0 App { // name of the Wikitude example to load property string example: "11_Video_4_Bonus-TransparentVideo" readonly property bool exampleIsLoaded: samplesDl.available // NavigationStack can display Pages and adds a NavigationBar NavigationStack { id: navStack // at startup show either arPage or downloadPage, in case the example is not loaded yet Component.onCompleted: navStack.push(exampleIsLoaded ? arPage : downloadPage) } // arPage: Page with a Wikitude view property Component arPage: Page { title: "AR Example" // configure Wikitude view WikitudeArView { id: arView anchors.fill: parent arWorldSource: samplesDl.getExtractedFileUrl(example+"/index.html") running: true cameraPosition: WikitudeArView.BackCamera //license key for V-Play QML Live app licenseKey: "g0q44ri5X4TwuXQ/9MDYmZxsf2qnzTdDIyR2dWhO6IUkLSLU4IltPMLWFirdj+7kFZOdWAhRUD6fumVXLXMZe6Y1iucswe1Lfa5Q7HhQvPxEq0A7uSU8sfkHLPrJL0z5e72DLt7qs1h25RJvIOiRGDoRc/h/tCWwUdOL6ChDnyJTYWx0ZWRfX8Vh9c9kcuw4+pN/0z3srlwIHPV5zJuB1bixlulM4u1OBmX4KFn+4+2ASRCNI+bk655mIO/Pk3TjtYMrgjFR3+iYHvw1UmaYMVjsrgpcVkbzJCT6QmaW8LejnfXDNLAbZSov64pVG/b7z9IZPFLXxRSQ0MRLudoSDAh6f7wMTQXQsyqGrZeuQH1GSWtfjl/geJYOvQyDI+URF58B5rcKnrX6UZW3+7dP92Xg4npw7+iGrO1M4In/Wggs5TXrmm25v2IYOGhaxvqcPCsAvbx+mERQxISrV+018fPpL8TzR8RTZZ5h7PRfqckZ3W54U1WSiGn9bOj+FjDiIHlcvIAISpPg2Vuq88gLp0HJ5W+A+sVirqmmCyU9GKeV5Faiv62CJy6ANCZ83GGX2rWcIAh1vGOQslMr9ay4Js+rJsVN4SIhCYdw9Em9hSpoZgimnOaszI7zn9EnPwVQgNETgVm7pAZdLkH5hxFoIKOPG2e79ZKKmzlkB/IZigoHZWNDUCFnEHDNFlTZjOEwoPi8DDGfzOEOGngWE7jmp24N7GzAP7e54Y3e48KtmIJ1/U0PFKOoi2Yv0Gh+E1siU5MBf8dLO7y7GafJWJ2oCUqJG0pLb2cgTf9pjkr625BV3XxODRylgqc5/UymTY6l1J0qO43u5hH3zaejng4I9cgieA3Y553rAEafAsfhrRmWsLW/kBdu4KLfY4eQ9z4B0TweW/xsofS0bkIqxalh9YuGBUsUhrwNUY7w6jgC6fjyMhtDdEHAlXC2fW1xLHEvY9CKojLNJQUnA0d5QCa22arI8IK63Jn8Cser9Cw57wOSSY0ruoJbctGdlsr/TySUkayAJJEmHjsH73OdbAztGuMjVq7Y643bTog4P3Zoysc=" } } // downloadPage: Page for downloading the Wikitude example at runtime // this is only required to retrieve the Wikitude sources for the V-Play QML Live app, Wikitude sources can also be bundled with the app otherwise property Component downloadPage: Page { title: "AR Example - Download" Column { anchors.fill: parent anchors.margins: dp(12) spacing: dp(12) AppText { text: samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.UnAvailable ? qsTr("Wikitude example requires to be downloaded (~ 2MB)") : samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.Downloading ? qsTr("Downloading example... (%1%)").arg(samplesDl.progress) : qsTr("Extracting example... (%1%)").arg(samplesDl.progress) width: parent.width } AppButton { text: samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.UnAvailable ? qsTr("Start download") : qsTr("Cancel download") onClicked: if(samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.UnAvailable) samplesDl.download() else samplesDl.cancel() } ProgressBar { width: parent.width from: 0 to: 100 value: samplesDl.progress } } } // component to download additional app resources, like the Wikitude example DownloadableResource { id: samplesDl source: "https://v-play.net/qml-sources/wikitude-examples/"+example+".zip" extractAsPackage: true storageLocation: FileUtils.DownloadLocation storageName: example onDownloadFinished: { if(error === DownloadableResource.NoError) { navStack.clearAndPush(arPage) // open AR page after download is finished } } } }
youtube
You can test the Image Tracking AR demo with the image below. It is also found in the Wikitude Plugin documentation.
Most of the QML code above is a little overhead to let you instantly preview the example with V-Play QML Live Code Reloading.
What is V-Play QML Live Code Reloading?
It allows you to run and reload apps & games within a second on iOS, Android and Desktop platforms. You can just hit save and the app reloads instantly, without the need to build and deploy again! This is especially useful for AR, which usually requires a lot of on-device testing to tweak settings.
You can also use it to run all the examples listed here from the browser, without having to setup any native SDKs on your PC. Just download the V-Play Live Reload App, for Android or iOS to connect a mobile device.
The code above downloads the configured Wikitude example as zip, extracts the archive, and runs the demo in a Wikitude augmented reality view. Pretty amazing, actually. Go ahead and try it yourself by clicking on one of the “Run this Example” buttons.
The possibility to download assets or code at runtime is a super useful advantage of V-Play. This means that the original app can stay small while additional features are downloaded on demand. However, if the AR part is essential in your own app, you can also bundle the Wikitude code so the AR assets are available without an additional download.
The minimum QML code required thus boils down to a few lines of code:
import VPlayApps 1.0 import VPlayPlugins 1.0 App { WikitudeArView { id: arView anchors.fill: parent arWorldSource: Qt.resolvedUrl("assets/11_Video_4_Bonus-TransparentVideo/index.html") running: true cameraPosition: WikitudeArView.BackCamera licenseKey: "" } }
How to Create Wikitude AR Worlds
The Wikitude SDK makes it easy to create such augmented reality views. It builds on web technologies (HTML, JavaScript, CSS) to create so-called ARchitect worlds. These augmented reality experiences are ordinary HTML pages. They use the ARchitect JavaScript API to create objects in augmented reality. That is why the WikitudeArView QML component in the above example has an arWorldSource property. It refers to the index.html of the ARchitect world:
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <meta content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1,maximum-scale=5,user-scalable=yes" name="viewport"> <title></title> <script src="https://www.wikitude.com/libs/architect.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="../ade.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/default.css"> </head> <body> <script src="js/transparentvideo.js"></script> </body> </html>
It is quite simple, as all the magic happens in the JavaScript code for the Architect world. The above example includes transparentvideo.js, which amounts to only 80 lines of code. This is how the main part for the image tracking and video overlay looks like:
var World = { init: function initFn() { this.createOverlays(); }, // create augmented reality overlays createOverlays: function createOverlaysFn() { /* Initialize ClientTracker */ this.targetCollectionResource = new AR.TargetCollectionResource("assets/magazine.wtc", { onError: function(errorMessage) { alert(errorMessage); } }); this.tracker = new AR.ImageTracker(this.targetCollectionResource, { onError: function(errorMessage) { alert(errorMessage); } }); /* initialize video drawable */ var video = new AR.VideoDrawable("assets/transparentVideo.mp4", 0.7, { translate: { x: -0.2, y: -0.12 }, isTransparent: true }); video.play(-1); video.pause(); /* handle video playback when image is tracked */ var pageOne = new AR.ImageTrackable(this.tracker, "*", { drawables: { cam:
}, onImageRecognized: function onImageRecognizedFn() { video.resume(); }, onImageLost: function onImageLostFn() { video.pause(); }, onError: function(errorMessage) { alert(errorMessage); } }); } }; World.init();
See the Wikitude documentation for details of their JavaScript API and step-by-step tutorials.
Wikitude Studio – No Coding Required
For those who are not very comfortable with coding, Wikitude also offers a simple drag-and-drop web editor: Wikitude Studio. It is your one-stop shop for generating and managing target collections, as well as for creating and publishing AR experiences!
youtube
Wikitude Studio optimizes your projects for the Wikitude SDK. It minimizes the effort of creating image target collections (wtc files) and object target collections (wto files). The Studio Editor makes it possible to add augmentations to your targets. You can test AR experiences and make them available to clients inside the Wikitude App, or inside your own app built with the Wikitude Plugin.
The Power of Instant Tracking and 3D Rendering
Wikitude is not only simple, it is also powerful. In addition to Image Tracking, it can instantly track the camera (Instant Tracking) or real live objects (Object Tracking). The following demo uses Instant Tracking to put 3D objects into the world:
App { // changed configuration to load the instant tracking demo property string example: "05_InstantTracking_4_SceneInteraction" // ... // no other changes required, DownloadableResource automatically uses the new example as source DownloadableResource { source: "https://v-play.net/qml-sources/wikitude-examples/"+example+".zip" // ... } }
youtube
With 230 lines of JavaScript code, the ARchitect world of this example is simple and short as well.
More Augmented Reality Examples
Do you wanna play around some more? Then go ahead and try one of these examples:
Geo Tracking: POI Radar
// run this demo to get a full QML snippet that downloads and opens the chosen example property string example: "10_BrowsingPois_2_AddingRadar"
youtube
Run This Example
Can be used to:
Show Points Of Interest around you, based on the GPS position.
For example to implement Augmented Navigation or see infos of Hotels or Restaurants around you.
Gesture Image Tracking
// run this demo to get a full QML snippet that downloads and opens the chosen example property string example: "02_AdvancedImageTracking_1_Gestures"
youtube
Can be used to:
Drop images, gifs or videos onto an image.
For example to let users create and share AR experiences, similar to SnapChat / Instagram video processing with tracked objects.
Snap-To-Screen 3D Model
// run this demo to get a full QML snippet that downloads and opens the chosen example property string example: "07_3dModels_4_SnapToScreen"
youtube
Can be used to:
Show additional information or 3D scene when scanning a certain image.
For example to enhance your print advertisement in a magazine with AR features:
Wikitude SDK Examples App
The following demo app allows you to to browse all Wikitude SDK Examples from within a single app:
import QtQuick.Controls 2.0 import QtQuick 2.0 import VPlayApps 1.0 import VPlayPlugins 1.0 App { id: app DownloadableResource { id: samplesDl source: "https://v-play.net/qml-sources/wikitude-examples/WikitudeSdkSamples.zip" extractAsPackage: true storageLocation: FileUtils.AppDataLocation storageName: "WikitudeSdkSamples" } //samples.json lists all the SDK examples readonly property url samplesJsonFileUrl: samplesDl.available ? samplesDl.getExtractedFileUrl("samples.json") : "" readonly property string samplesJson: samplesDl.available ? fileUtils.readFile(samplesJsonFileUrl) : "[]" //map the JSON file to a list model for ListPage readonly property var samplesData: JSON.parse(samplesJson) readonly property var samplesModel: samplesData.map(function(category) { return [ { isHeader: true, name: category.category_name } ].concat(category.samples) }).reduce(function(a, b) { return a.concat(b) }, []) Rectangle { anchors.fill: parent color: "white" } NavigationStack { id: navStack ListPage { id: examplesListPage listView.visible: samplesDl.available title: "Wikitude AR Examples" model: samplesModel delegate: SimpleRow { enabled: !modelData.isHeader style.backgroundColor: enabled ? Theme.backgroundColor : Theme.secondaryBackgroundColor iconSource: modelData.is_highlight ? IconType.star : "" icon.color: "yellow" text: modelData.name detailText: !modelData.isHeader && modelData.path || "" onSelected: navStack.push(arPage, { sample: modelData }) } Column { visible: !samplesDl.available anchors.fill: parent anchors.margins: dp(12) spacing: dp(12) AppText { text: samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.UnAvailable ? qsTr("Wikitude SDK examples need to be downloaded (134 MB)") : samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.Downloading ? qsTr("Downloading SDK examples... (%1%)").arg(samplesDl.progress) : qsTr("Extracting SDK examples... (%1%)").arg(samplesDl.progress) width: parent.width } AppButton { text: samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.UnAvailable ? qsTr("Start download") : qsTr("Cancel download") onClicked: if(samplesDl.status === DownloadableResource.UnAvailable) samplesDl.download() else samplesDl.cancel() } ProgressBar { width: parent.width from: 0 to: 100 value: samplesDl.progress } } } } property Component arPage: Page { property var sample readonly property bool usesGeo: sample.requiredFeatures.indexOf("geo") >= 0 title: sample.name WikitudeArView { id: arView anchors.fill: parent arWorldSource: samplesDl.getExtractedFileUrl(sample.path) running: true //set this to false to use the device location service overrideLocation: !usesGeo //license key for V-Play QML Live app licenseKey: "g0q44ri5X4TwuXQ/9MDYmZxsf2qnzTdDIyR2dWhO6IUkLSLU4IltPMLWFirdj+7kFZOdWAhRUD6fumVXLXMZe6Y1iucswe1Lfa5Q7HhQvPxEq0A7uSU8sfkHLPrJL0z5e72DLt7qs1h25RJvIOiRGDoRc/h/tCWwUdOL6ChDnyJTYWx0ZWRfX8Vh9c9kcuw4+pN/0z3srlwIHPV5zJuB1bixlulM4u1OBmX4KFn+4+2ASRCNI+bk655mIO/Pk3TjtYMrgjFR3+iYHvw1UmaYMVjsrgpcVkbzJCT6QmaW8LejnfXDNLAbZSov64pVG/b7z9IZPFLXxRSQ0MRLudoSDAh6f7wMTQXQsyqGrZeuQH1GSWtfjl/geJYOvQyDI+URF58B5rcKnrX6UZW3+7dP92Xg4npw7+iGrO1M4In/Wggs5TXrmm25v2IYOGhaxvqcPCsAvbx+mERQxISrV+018fPpL8TzR8RTZZ5h7PRfqckZ3W54U1WSiGn9bOj+FjDiIHlcvIAISpPg2Vuq88gLp0HJ5W+A+sVirqmmCyU9GKeV5Faiv62CJy6ANCZ83GGX2rWcIAh1vGOQslMr9ay4Js+rJsVN4SIhCYdw9Em9hSpoZgimnOaszI7zn9EnPwVQgNETgVm7pAZdLkH5hxFoIKOPG2e79ZKKmzlkB/IZigoHZWNDUCFnEHDNFlTZjOEwoPi8DDGfzOEOGngWE7jmp24N7GzAP7e54Y3e48KtmIJ1/U0PFKOoi2Yv0Gh+E1siU5MBf8dLO7y7GafJWJ2oCUqJG0pLb2cgTf9pjkr625BV3XxODRylgqc5/UymTY6l1J0qO43u5hH3zaejng4I9cgieA3Y553rAEafAsfhrRmWsLW/kBdu4KLfY4eQ9z4B0TweW/xsofS0bkIqxalh9YuGBUsUhrwNUY7w6jgC6fjyMhtDdEHAlXC2fW1xLHEvY9CKojLNJQUnA0d5QCa22arI8IK63Jn8Cser9Cw57wOSSY0ruoJbctGdlsr/TySUkayAJJEmHjsH73OdbAztGuMjVq7Y643bTog4P3Zoysc=" cameraPosition: sample.startupConfiguration.camera_position === "back" ? WikitudeArView.BackCamera : WikitudeArView.FrontCamera cameraResolution: WikitudeArView.AutoResolution cameraFocusMode: WikitudeArView.AutoFocusContinuous } } }
What’s the Future for AR?
Augmented reality still has a lot of exciting features and functionalities in store for users, for example with Cloud AR and Multiplayer AR capabilities. Wikitude already offers a cloud-based image recognition service. The latest release, SDK 8, which is supported by the Qt Wikitude Plugin, brought many interesting features like Scene Recognition, Instant Targets or Extended Object Tracking you can now use. And in terms of shared experiences, support workers can display 3D content even though they are remote on another user’s device.
Apple recently introduced their new ARKit 2 framework, a platform that allows developers to integrate
shared AR, which allows multiplayer augmented reality experiences
persistent experiences tied to a specific location
object detection and
image tracking to make AR apps even more dynamic.
To showcase the new multiplayer feature, Apple introduced their augmented reality game ‘Swift Shot’:
youtube
The use-cases for shared augmented reality are vast, for both mobile games and apps. For example, your AR navigation system could show augmentations that other users placed. You would then also see digital warning signs along the road in addition to the route.
You can also build such multi-user experiences with V-Play Multiplayer. Together with Wikitude, a shared augmented reality experience created with QML + JavaScript is also only a few steps away. V-Play also plans to integrate Qt 3D Rendering with Wikitude’s Native APIs to boost rendering performance even more.
If you have a business request for these cutting-edge features currently in development or if you need assistance in developing an AR experience with high quality standards, don’t hesitate to drop a line at [email protected] or contact us here. The V-Play SDK is free to use, so make sure to check it out!
Download V-Play
If you enjoyed this post, please leave a comment or share it on Facebook or Twitter.
More Relevant App Development Resources
Handle Safe Area Insets, Notch & Display Cutout for iPhone X, iPad X and Android P
Wikitude and V-Play bring AR for Qt Developers – Wikitude Release Announcement
Why Mobile AR Matters
Why Mobile AR is evolving faster than you think
Wikitude Showcases
Wikitude Documentation
Wikitude SDK Examples
Wikitude Qt AR Plugin Documentation
The Best App Development Tutorials & Free App Templates
All of these tutorials come with full source code of the mobile apps! You can copy the code to make your own apps for free!
How to create a mobile app for iOS & Android with a single code base
How to support multiple languages and internationalization in your mobile app
Common Widgets & Controls in a cross-platform App
How to support multiple screen sizes & screen densities – Responsive App Guide
Guide for App Layout
Guide for App Navigation
How to add native code to your mobile App
How to easily style your App with Themes
How to add Animations to your App
How to add a Chat to your Mobile App
How to make a Weather App accessing a REST weather service
Conference App Template
Widget Gallery App Template
Twitter App Template
Messenger App Template
Property Finder App Template
App Development Video Tutorials
Make Cross-Platform Apps with Qt: V-Play Apps
youtube
How to Add In-App Chat or Gamification Features to Your Mobile App
youtube
How to Make a Mobile App with Qt Quick Designer (QML Designer) & V-Play
youtube
The post Qt AR: Why and How to Add Augmented Reality to Your Mobile App appeared first on V-Play Engine.
Qt AR: Why and How to Add Augmented Reality to Your Mobile App published first on https://medium.com/@TheTruthSpy
0 notes